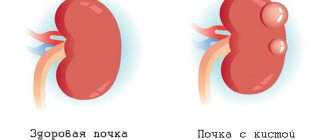
Baker's cyst (Becker, popliteal fossa) is an accumulation of joint fluid in a stretched intertendinous bursa located in the popliteal region. It is formed in various diseases of the knee joint. It is a benign neoplasm that occurs at any age, but more often in older people. In many cases it is asymptomatic. Complaints usually appear when it is significant in size and complications develop. Various treatment options for pathology are possible: conservative and surgical.
A Baker's cyst develops in the popliteal fossa, usually due to injury or overuse of the knee joint.
Size
Education is small in size. Therefore, it is almost impossible to notice. If the bubble is large, it can be easily detected visually. It is represented by a dense, elastic formation. The tumor usually has an oblong shape. On top of the neoplasm, the dermis remains unchanged. Her color is normal. There is no adhesion to the underlying tissues.
Diseases of the knee joint that are inflammatory in nature, as well as injuries, can provoke such a pathology. But in most cases, doctors cannot accurately determine the cause of the tumor.
Reasons for appearance
Often, a Baker's cyst forms for no apparent reason. However, there are a number of factors that provoke its occurrence. These include:
- old age, and as a result, worn-out joints;
- overweight;
- frequent and intense sports activities associated with stress on the legs;
- mechanical damage to the menisci and injuries to the knee joint resulting from a fall, etc.;
- rheumatoid arthrosis;
- osteoarthritis;
- chronic synovitis of the knee joint;
- osteoarthritis;
- patellofemoral arthrosis.
In addition to older people, the disease can develop in athletes and young women who often wear high-heeled shoes . Baker's cyst is rarely diagnosed in children, since, due to the anatomy of the bursa of their joints, they are not prone to inflammatory processes. However, cases have been recorded around the world in which bursitis of the knee joint formed in children aged 9-15 years.
Education pathology
A special feature of education is its ability to develop back. A person may have a Baker's cyst in the popliteal region throughout his life. It is also possible that it will only exist for a few months. Self-resorption of fluid is observed when cysts form after constant physical exercise. loads during sports.
The pathology in question was called Baker's cyst because it was William Baker (Becker) who published the first detailed reports regarding synovial cysts. This happened in the 19th century. Baker was an English surgeon.
The specialist found that Baker's bubble (popliteal fossa) is more often found in older people. To know what a popliteal fossa synovial cyst looks like, check out the pathology photo.
Complications after a cyst
The appearance of a Baker's hernia in the knee can lead to rupture of the walls and leakage of the contents into the muscles of the leg. Severe swelling causes loss of motor ability. The patient experiences itching and increased temperature in the calf.
A ruptured cyst in the knee joint causes severe pain.
At this point, the risk of infection of the musculoskeletal tissue increases. A ruptured Baker's cyst in the knee joint causes severe pain. The contents of the tumor take a long time to resolve, so the patient is forced to take a large amount of painkillers. To prevent this, you must consult a doctor immediately.
Complications of Baker's cyst include a long rehabilitation period. For some period, the patient will have to change his lifestyle, eliminating any load on the limb. Pain will persist during lifting and intense walking. Failure to follow the surgeon’s recommendations often leads to relapse of the pathology and deterioration of the joint condition.
Classification of synovial pathological cavity
Patients feel the tumor under the skin in the form of a ball. Its diameter varies from 1 to 7 cm. It is easiest to detect a tumor in a position when the leg is fully extended. At this time, the epidermis stretches, the tumor protrudes from under the knee.
Experts have developed a special classification of cysts. They identified the following types:
- Primary. It is also called an idiopathic cyst. Baker's bubble of the knee joint is formed in children and young people whose age does not exceed thirty years. Inflammation of the joint capsule begins after infection. This is possible after bruises or a fall while playing sports. With this type of cyst, concomitant diseases practically do not appear.
- Secondary. This type of neoplasm is often detected in people whose age has already passed 40 years. Doctors associate the development of this formation with the presence of a number of concomitant diseases and disruptions of the endocrine system. Pathologies such as rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis, meniscal tears, and gout provoke the production of excessive amounts of synovial fluid.
It is possible to develop a pathological Baker's cavity in the left or right knee joint.
The following knee cysts are also distinguished:
- Synovial cyst of the knee joint.
Meniscal cyst of the knee joint. There is a medial pathological cavity of the meniscus (protrusion on the inside of the meniscus) and lateral (protrusion visible on the outside of the knee).
- Baker's cyst.
Ganglion cyst of the knee joint. It is considered rare. The ganglion pathological cavity of the knee joint is formed from the tendon sheath, the joint capsule.
- Subchondral cyst.
- Parameniscal.
Surgical intervention
Sometimes surgery is performed to remove a Baker's cyst, especially if the swelling is the result of an injury. Surgery to remove the cyst is done if it is very large, painful, or other types of treatment have not worked. Sometimes the keyhole technique is used to close the connection between the leaking synovial fluid into the tissue and the knee joint.
Baker's cyst surgery is also recommended to treat an underlying knee problem, such as a torn meniscus, since it is a secondary condition in these types of injuries.
Causes
Experts have not yet fully elucidated the etiology of the pathology. A similar formation is found in people who engage in hard work (carrying heavy objects), as well as in those who engage in active sports. The main reason why the production of synovial fluid increases, protrusions of the thin walls of the membranes of the joints occur, is considered to be inflammatory, degenerative processes.
Joint
A healthy joint works smoothly due to the presence of a special fluid inside the cavity. This fluid is used when the joint operates as a lubricant and shock absorber.
The mucous tendon bursa is localized between the gastrocnemius muscle and the semimembranous muscle fibers. This structure is typical and is considered the norm for approximately 50% of people.
Prolonged inflammation
Prolonged inflammation provokes the flow of synovial fluid into the tendon bursa from the joint. Liquid passes through a slit-like hole. It accumulates inside the bag. This is how a mobile soft cyst is formed. Exudate is unable to return inside the joint cavity. A special valve prevents this.
When too much synovial fluid is produced inside the joint, some of it is directed to the popliteal bursa. There it accumulates. This creates a Baker's cyst under the knee.
The causes of hyperproduction of joint fluid may be the following:
- Osteoarthritis/osteoarthritis;
- the presence of inflammation in the knee joint, which arose due to rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory joint diseases;
- overload of knee joints. They are possible when performing the following actions: jumping, running, squats. It is also possible to overload connections due to excess weight;
- bursitis of the knee joint;
- knee ligament rupture;
- cartilage injury;
- injuries of the knee articulation , in which damage occurs, degenerative changes in the ligamentous apparatus, menisci.
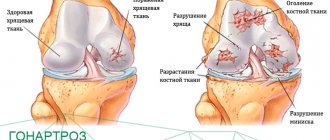
Baker's cyst of the knee - what is it?
Behind the knee are the tendons of the gastrocnemius and semimembranosus muscles. Between them, in half of healthy people there is an intertendinous bursa, which is a variant of normal development. The mechanism of Baker's cyst formation depends on the presence or absence of connection between this bursa and the knee joint.
| Relationship between the joint cavity and the interarticular tendon bursa | Formation option |
| There is a message | The occurrence of an inflammatory process in the joint, accompanied by excessive production of synovial fluid, leads to its entry into the interarticular bursa. The latter stretches and, in fact, forms a hernia of the popliteal fossa, or a cyst. This is how most liquid cavity formations in this area are formed. |
| Missing message | Some cystic formations have no connection with the articular cavity; they exist in isolation. In this case, excessive accumulation of fluid in the mucous bursa located between the muscle tendons is caused by its primary inflammation. This process is called bursitis. |
Characteristic signs
Baker's bubble (popliteal fossa) may not make itself felt for a long time. Patients do not experience any discomfort. With a constant negative impact on the knee articulation, an increase in the size of the tumor is possible. Over time, the cyst will make itself felt. The exception is a formation that resolves on its own.
The pathological Becker cavity, formed under the knee, has the following symptoms:
- Swelling, a feeling of fullness in the popliteal fossa;
- painful sensations in the area of the popliteal fossa. Their intensification is noted after a person bends his knee while walking;
- gradual atrophy of the muscle fibers of the lower leg. This sign appears due to the fact that the sick person reduces physical activity. activity, so as not to experience pain, discomfort;
- decreased sensitivity, the onset of various trophic disorders. They occur in cases where the neoplasm is large. The cyst gradually compresses blood vessels and nerves. The most advanced cases are dangerous by the development of thrombophlebitis, gangrene, and trophic ulcers on the lower limb;
- severe pain, fever, swelling of the lower leg. These signs usually indicate a cyst rupture.
The popliteal pathological Baker's cavity disappears on its own in rare cases. Usually the size of the cyst increases. As the lump grows, it begins to hurt. This tumor compresses the knee vein. This provokes blood stagnation, thrombosis, phlebitis, and varicose veins develop. In this case, the patient notices such clear signs of pathological changes:
- Swelling of the limb;
- change in leg color. It becomes initially purple. Then the color changes to brown;
- Trophic ulcers form. They are difficult to treat.
Due to the migration of detached blood clots to different organs, ischemia and thromboembolism are possible. This is dangerously fatal.
Symptoms
In appearance, Baker's cysts are dense but elastic formations, characterized by elasticity. Therefore, they are easy to detect, especially if they are located on the knee joint, because cysts are visible to the naked eye, even if they are small. If a Becker cyst is located in the popliteal fossa and is small in size, a person may not know about the presence of this pathology for a long time, since its symptoms will not be expressed.
If the Becker cyst in the popliteal region begins to increase in size, then it is not only visually visible, but you can also feel the presence of a compaction.
The symptoms caused by the pathology depend on the size of the formation. The small size of a Becker cyst does not cause them, but as soon as the formation begins to grow, compression of the tissues surrounding the joint occurs, which leads to the formation of edema in the popliteal area and causes pain in the person.
Subsequently, the symptoms progress - the pain becomes more and more pronounced, and the swelling spreads not only to the area in which the Becker cyst was localized, but also to the entire knee joint.
As a result, other symptoms of a Becker cyst develop:
- local temperature increase;
- limited mobility;
- redness;
- gait disturbance;
- decreased sensitivity of the leg and foot due to compression by the formation of nerve fibers.
Sometimes Becker cysts go away on their own over time, and sometimes they remain unchanged for a long time, worsening a person’s quality of life. In some cases, Becker cysts lead to the development of complications. Therefore, if a Baker's cyst is detected in a child or adult, treatment should be timely. In particular, due to compression of blood vessels, the blood supply to the affected limb is disrupted, which over time becomes the cause of the development of varicose veins and thrombophlebitis.
In addition, Becker cysts are scary because they can rupture. If a Becker cyst ruptures, the fluid contained in the formation cavity drains into the lower leg, and although it is sterile and does not cause a bacterial inflammatory process, serous inflammation with severe symptoms nevertheless forms. Thus, people who have ruptured a Becker cyst experience severe pain, swelling of the lower leg with redness of the skin and the appearance of unbearable itching, local and general hyperthermia. The inflammatory process can last for several weeks, causing severe suffering to a person.
Diagnostics
To determine the presence of a Becker cyst, the doctor will first need to conduct an objective examination. He examines the back of the knee joint. This is necessary to detect a round tumor. He will also be able to determine the location of pain and assess the range of motion of the joint.
When the synovial bladder of the knee joint is small, palpation will not allow it to be identified. In this case, additional diagnostic methods are used:
- Laboratory. They consist of conducting a study of synovial fluid. This is necessary to determine the nature of the inflammation. The study allows us to exclude various specific inflammations of the compound (gout, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis).
- Instrumental. From this group, ultrasound of the knee joint and popliteal fossa is used. The diagnostic method provides information about the presence of accumulations of excess fluid inside the joint cavity, the popliteal bursa. It makes it possible to determine the integrity of a number of structures (menisci of knee joints, tendons). Determines the localization of fluid accumulation inside the intermuscular spaces and the presence of cyst rupture.
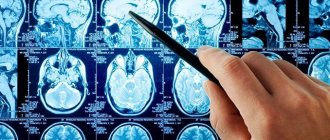
- An MRI may also be ordered. This method of examining Baker's cyst is considered more detailed. With its help, it is possible to describe the condition of the soft tissues of the following elements: tendons, joints, ligaments, synovial bursae, bone structure of the joint.
Which doctor treats Becker's cyst?
If you suspect a cyst, you should contact an orthopedist, surgeon or traumatologist. A simple test will help you detect a cyst yourself: you need to sit on a chair, put your feet on the floor, bending your knees at a right angle. Relaxing the leg muscles, feel the soft tissues under the knees. If there is a dense and soft lump, we can assume that it is a Becker cyst.
Diagnostics includes examination, laboratory and instrumental studies. To confirm the diagnosis, ultrasound, x-rays, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, as well as blood and urine tests may be prescribed.
If necessary, the patient is sent for diaphanoscopy - transillumination of the cyst with a narrow beam of light. If there is a clear liquid inside the formation, it will be red in color. Cloudy contents cannot be seen through. Thus, we can conclude about the presence/absence of pus in the tumor.
In difficult cases, arthroscopy is performed to collect a puncture and bacteriological analysis of the intra-articular fluid - synovium.
Cyst treatment
The choice of treatment method for a pathological Baker's cavity depends on a number of nuances:
- The degree of inflammation of the joint;
- the amount of accumulated liquid;
- localization of education.
Synovial cyst of the popliteal region requires an integrated approach. It is advisable to combine drug therapy with exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and traditional medicine.
Drug therapy
Conservative methods of treating Baker's cyst were ineffective. To relieve inflammation inside the joint, the doctor prescribes the following medications.
- NSAIDs, analgesics. Their use promotes an active effect on the source of inflammation. Usually prescribed:
- Aspirin.
- Etodolac.
- Celecoxib.
- Diclofenac.
- Ibuprofen.
- Ointments, gels. With their help, fluid outflow accelerates and blood circulation improves. Specialists appoint:
- Troxevasin.
- Ketoprofen.
- Rescuer.
- Meloxicam.
- Mineral, multivitamin complexes, hepatoprotectors, probiotics. These medications are aimed at protecting internal organs and strengthening the immune system when using potent drugs.
- Chondroprotectors. They are very beneficial for cartilage tissue. Medications help restore cartilage. Typically used:
- Don.
- Chondroitin.
- Alflutop.
- Structum.
Surgery
Surgical methods of therapy are used in the following situations:
- Lack of effect from conservative methods of therapy;
- the large size of the Baker's bladder of the knee joint is a prerequisite for surgery;
- deterioration in the functioning of the knee joint;
- unexpected cyst rupture;
- the presence of necrotic inclusions inside the bag;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
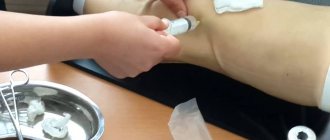
The synovial pathological cavity of the popliteal fossa is treated by puncture followed by evacuation of the contents. After this, glucocorticoids are administered:
- Diprospan.
- Flosteron.
The described procedure is performed under ultrasound guidance. During the operation, anesthesia (local, spinal) is used.
The surgeon makes an incision over the tumor. The formed neoplasm is enucleated. Then the connection of the tendon bursa to the knee joint is ligated. Then the bladder is removed, the wound is sutured, and bandaged tightly. The procedure takes about half an hour. The operation is not complicated. You need to remain under observation in the hospital for 24 hours. The patient is then discharged.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of cysts
Before using herbal medicine, consult a specialist. Basic therapy can be supplemented with folk remedies. They will help stop the growth of formation, reduce inflammation, and normalize the production of synovial fluid.
in the picture “APPLE VINEGAR AND HONEY USED IN THE TREATMENT OF BAKER CYST OF THE KNEE JOINT”
Here are the most effective recipes:
- Compress (honey + aloe).
- Dressing (bile + camphor).
- Bandage (infusion of celandine, burdock root + castor oil).
- Apple cider vinegar + honey (take orally).
- Golden mustache tincture (inside, for compresses).
in the figure "possible complications with Baker's hands"
How to treat Baker's cyst of the knee
Therapeutic tactics for popliteal fossa cysts are possible, both conservative and surgical. Small asymptomatic formations in the popliteal region can simply be observed over time. In some cases, they gradually decrease in size on their own and go away.
Treatment of Baker's cyst without surgery
The cyst is punctured with a large-diameter hollow needle, the contents are suctioned, and corticosteroid drugs (hydrocortisone, etc.) are then introduced into the cavity. Conservative tactics rarely lead to the disappearance of the pathology; recurrence often occurs.
If the cystic cavity becomes infected, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
Home methods for treating pathology can somewhat reduce swelling and relieve pain. The most famous folk recipes are compresses with golden mustache and burdock. But they are not able to radically cure the patient. You should not waste time on them, especially if complications develop; in this case, qualified medical assistance is required.
Surgery
The radical treatment method is surgery. It is necessary when:
- rapid growth;
- significant size of popliteal hernia;
- the occurrence of complications;
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy.
The doctor performs excision of the cyst under local anesthesia: the place where it connects to the articular cavity is sutured, bandaged, and the formation is removed. After surgery, wearing a tight bandage and temporarily limiting the load are indicated.
There is an endoscopic removal technique performed using an arthroscope. It allows you to reduce the trauma of surgical intervention. Performing additional coagulation of the anastomosis between the popliteal hernia and the joint cavity during surgery prevents the development of relapse and improves long-term results of therapy.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely adequate therapy, complications are possible. The most common consequences of the pathology in question are:
- Cyst rupture. After the integrity is broken, the liquid flows out of the formation. It penetrates into the interfascial spaces of the calf muscle fibers. A similar complication is recorded in every 10 sick people.
- Acute pain, swelling of the affected area. These signs appear after the cyst ruptures. Swelling is found in the back of the leg. The rupture is also accompanied by redness of the dermis of the lower leg. A local increase in temperature is possible.
- Thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the vein walls).
- Difficulty in the outflow of blood through the veins of the leg.
- Thrombosis. A blocked vein becomes blocked by a blood clot.
- Deposition of calcium salts inside the cyst. This process causes the cyst to become denser. It begins to put more pressure on the surrounding tissue.
- Varicose veins of the saphenous veins of the leg.
- Compression of the tibial nerve. In this condition, the patient feels weakness, tingling, and numbness in the lower part of the limb.
Description of the disease
Baker's cyst is a type of bursitis of the knee joint, when exudate fills the synovial bursa in the area of the popliteal fossa . From a medical point of view, this is a neoplasm that has minimal chances of malignancy - turning into a malignant form. According to WHO statistics, knee bursitis occurs mainly in people over 40 years of age. In 50% of cases, these are elderly people whose joints have age-related degenerative processes. In addition, Baker's cyst may be accompanied by pathologies such as arthritis and osteoartosis. Typically, bursitis occurs under the knee joint on one leg, but cases have been reported in which the disease affects both legs. The neoplasm can have different sizes, ranging from insignificant to several centimeters in diameter. The larger the tumor, the more pronounced the clinical signs.
Anatomical features
The neoplasm is localized exclusively in the upper corner of the popliteal fossa. With bursitis of the popliteal fossa, a characteristic protrusion occurs. It appears due to the inflammatory process in the knee, when fluid or exudate begins to actively accumulate. The neoplasm is dense, elastic and elastic in structure, has a round or semicircular shape. In the early stages, it is difficult to detect pathology; patients often attribute a small swelling to a bite or bruise. Clinical symptoms of the pathological process appear in later stages of the disease. Pain is felt on palpation.
At the first signs of the disease, you should immediately consult a specialist in order to diagnose bursitis in time and take the necessary measures.
What ointment to use to treat heel bursitis is described here.
Prevention of pathology
To prevent cyst formation, it is enough to follow preventive measures. They are represented by the following provisions:
- Prevention of injury to joints.
- Normalization of body weight.
- Elimination of bad habits.
- Proper nutrition.
- Start treatment in a timely manner when connection pathologies are detected.
- Wearing orthoses. Special knee pads are needed to reduce the stress placed on the knee joints when performing heavy exercises.
Knowing what a Baker's cyst of the knee joint is, it is important to recognize it in time and begin treatment. This way you can prevent it from breaking.
Symptoms and signs
The main symptom of a Baker's cyst is the appearance of a nodule-like mass at the back of the knee; a mass that feels hard when pressed directly.
The general picture of symptoms is as follows:
- the appearance of a nodule-like mass at the back of the knee (see photo above);
- swelling of the knee;
- knee pain that radiates to the calf muscle;
- immobility of the knee joint;
- noise (crunching, crackling) when moving the knee.
These symptoms occur to varying degrees depending on the severity of any pre-existing joint disease. Although in rare cases, some patients may not exhibit the above-mentioned symptoms. In these cases, doctors accidentally notice a Baker's cyst, for example, while performing an MRI while examining other diseases.
Folk recipes
Traditional methods can be used as part of complex therapy:
- Rinse a handful of fresh raspberry and elderberry leaves with water and pour 100 ml of boiling water over them. Leave for 30 minutes, then transfer the leaves to cling film, apply to the affected area, and secure with a bandage. After 2 hours, remove. Do these compresses every day.
- Pour boiling water over young celandine leaves and leave for 20 minutes. Transfer the resulting mixture to gauze and tape it to the tumor. It is recommended to do it twice a day.
- Collect young golden mustache grass, chop it, put it in a jar, pour 1.2 liters of boiling water. Leave covered for 3 weeks in a dark place. Then strain, and take the infusion 50 ml 2 times a day. The gruel can be used for compresses.
- Chop and add water (to cover) the leaves of the cloves. Then chop the dandelion root. Pour 50 g of raw material with water, put it on the stove, when it boils, reduce the heat and boil it for 20 minutes. Grind the dandelion roots and mix with cloves. Add 25 ml of alcohol to the mixture. Place the mixture on gauze, fix it on the affected area, and insulate it on top. Remove after 3 hours.
A compress made from the infusion of golden mustache is used as part of the complex treatment of Becker’s cyst.
You can also prepare an infusion of St. John's wort, birch buds, mint, nettle, plantain, lingonberry, and knotweed. To do this, pour 25 g of the collection into 220 ml of boiling water and leave for 60 minutes. Drink ½ glass of medicine daily.
And an ointment made from calendula flowers, goose fat, and propolis will help relieve inflammation and pain.
Folk remedies can be used only after the approval of the attending physician.
Alternative Treatment
Treatment of a Becker cyst can be based on the use of non-standard techniques. Such events are somewhat specific, so they should be carried out exclusively by specialists, paying for treatment courses consisting of several sessions. Such effective treatment options include the following:
- Su-jok therapy. This is an ideal opportunity to normalize the functioning of an inflamed joint. The essence of this method is the direct impact of the fingers on certain points of the body and on the legs.
- Becker's cyst of the popliteal joint can be easily treated through kinesiotherapy. This technique allows you to detect a certain imbalance in the muscles. To effectively eliminate it, you will need to use measures such as reflexology, effective manual therapy and even psychocorrection. This is a very useful recovery program.
- The formation can be treated through regular muscle stretching and light massage using a tennis ball.
The use of these alternative treatment methods will allow you to quickly get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
Folk remedies for cysts
Now let’s look at the basic recommendations on how to treat the neoplasm in question with folk remedies. Some traditional medicines are considered quite effective in the treatment of Baker's cyst. Popular recipes are considered especially effective at the initial stage of pathology development. In any case, before using folk remedies to treat a cyst, conduct a dialogue with doctors.
Diagnosis of Baker's cyst
If a knee joint cyst is diagnosed, treatment with traditional methods is possible after a dialogue with a doctor. Let us list the folk methods that are considered the most effective in treating the disease in question:
- Golden mustache. To prepare a remedy for Baker's cyst, first collect the following parts of the medicinal plant: leaves, tendrils. They are placed inside a large container. Then vodka is poured inside the container (3 liters is enough). Cover the vessel with a lid and let it brew for 3 to 4 weeks.
- Compresses are made with the prepared product. They are applied to the cyst area. The resulting tincture can also be used to lubricate the affected area. It is also possible to take the prepared tincture orally. 1 tbsp is enough. l. twice a day.
- Celandine (leaves). A decoction is prepared from this plant. This product copes well with inflammation. It reduces the severity of pain. Apply similar compresses to the sore area.
- Elderberry + raspberry (plant leaves are used). The raw materials are used to prepare a decoction. It is then used for compresses. These procedures should be performed daily for one month. Treatment with folk remedies is usually long-term.
- Cabbage leaves. The sheets should be doused with boiling water before use. Then they are smeared with honey. It is necessary to apply such compresses to the affected area at night.
- Sunflower oil. It is also necessary to use this product to create a compress. This oil has a strong anti-inflammatory effect.
- Propolis tincture. This substance is ideal for compresses. This procedure helps relieve pain. In addition, it relieves the feeling of tension that has arisen in the area of the affected knee.
- Healing tea. The preparation of a remedy for Baker's cyst is made from the following elements: celery seeds, cayenne pepper, cinnamon, chamomile, calendula, ginger. Drinking the infusion is 0.5 cups. Use twice a day.
- Apple vinegar. This remedy is used to remove fluid accumulated there from under the knee. To prepare the product, use vinegar (1 tbsp), honey (1 tsp), warm water (1 tbsp). You should drink the prepared product three times a day. Consume it before meals.
- Tea with pieces of ginger. This liquid helps relieve inflammation inside the joint capsule under the knee.
- Spices. Spices for Baker's cysts are considered especially useful. You can use garlic, cayenne pepper, cinnamon, ginger. These drugs reduce the intensity of inflammation. It is recommended to enrich the menu with these spices during therapy.
- Aloe juice. It is used for compresses. To prepare the product, we use aloe juice (1 tsp), lemon juice (1 tsp), streptocide (1 g). After the mixture becomes homogeneous, it is applied to the cyst. Leave the compress on overnight.
- Dandelion + cloves (infusion is being prepared). We prepare the specified raw material for Baker's cyst: grind it, place it inside the container. Then fill it with water. It should slightly cover the grass. Then simmer the mixture over low heat for about 15 minutes. Grind the dandelion root and add it to the herb. Add more purified alcohol (1 spoon). The finished mixture is placed inside gauze. It is applied to the painful area. A wool scarf is wrapped over it. Leave the bandage soaked in the medicinal solution for three hours.
Conservative treatment methods
If the tumor is small, then conservative treatment can be used; use various ointments and creams or folk remedies. It is imperative to focus on the different nature of physiotherapeutic procedures and specially selected gymnastics (physical therapy). For each person suffering from this disease, the doctor must choose an individual treatment method.
There are many painkillers that also have anti-inflammatory effects. For example, Lornoxicam, Ketarol and others. Antispasmodics are also prescribed to relieve muscle tension and pain. Hormonal drugs are well suited for relieving inflammation and local hyperemia.
Antibiotics are used less frequently. They are prescribed for cyst rupture or suppuration. In any case, the doctor prescribes treatment. Self-medication is not recommended.
The benefits of ointments
Ointments for Baker's cyst are also considered very effective. They are prepared from medicinal herbs and folk remedies.
Bee glue cream with calendula
Use a remedy to relieve inflammation and resolve formation. Treatment is carried out at home. Pound the calendula flowers thoroughly and pour in goose fat (it needs to be melted). Add propolis to the heated mixture. You need to stir everything until the propolis is completely dissolved.
The ointment is applied to the cyst after cooling.
Rub it very thoroughly. Then they wrap it in warm material (shawl, scarf) and leave it for several hours.
Hemlock ointment
It is considered a very powerful tool. The effect of the ointment is aimed at reducing the size of the cyst, eliminating pain and other unpleasant signs of the disease. This product is poisonous, so it should only be used under the supervision of a doctor.
Ointment from marigold flowers
It is advisable to use any remedy after consultation with your doctor. This approach will help prevent the development of complications and rupture of the tumor.
Causes
The formation of a Becker cyst can be caused by inflammatory and metabolic-dystrophic pathological processes in the knee joint:
osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, patellofemoral arthrosis, etc.; chronic inflammation of the membranes of the knee joint; knee injuries; damage and destruction of cartilage; degenerative changes in the menisci.
All of the above processes lead to the production of large volumes of synovial fluid. It accumulates in the tendon bursa and forms a cyst. As it grows, it puts pressure on the nerve endings and causes discomfort.
Treatment for ruptured knee cyst
Baker's knee rupture is accompanied by severe pain with swelling of the lower leg. It is caused by the gradual flow of liquid contents into the intermuscular space of the tissues. Treatment of a ruptured cyst comes down to eliminating the burning sensation and manifestations of the inflammatory reaction.
Primary actions:
- ensuring immobility, fixation;
- calling an ambulance;
- oral administration or intramuscular injection of an anesthetic in compliance with all aseptic rules;
- Ice in a heating pad or bottle is applied to the area with the greatest pain intensity.
Apply cold objects with caution; it is advisable to wrap them in a thin towel to avoid local hypothermia.
After hospitalization in a hospital setting, the patient’s management tactics are determined. For a small rupture with minor damage to surrounding tissues, NSAIDs, painkillers, chondroprotectors, and corticosteroids are prescribed. Blockades with Novocaine and drugs for resorption of hematoma are indicated.
In the case of a widespread process of Baker's knee tumor, the affected area is immediately punctured or excised under ultrasound control. A quick solution is needed to prevent a blood clot from forming in a blood vessel and then breaking off. A “free” thrombus can lead to occlusion of a blood vessel of a vital organ.
Review of therapeutic methods
1. Drug therapy.
The specialist prescribes anti-inflammatory and painkillers at the first signs. First of all, a puncture is necessary to remove excess fluid and diagnose. This is a fairly simple procedure: a puncture is made in the synovial bursa with a thick needle, through which the contents are pumped out. Only after this the doctor injects drugs into the sore spot.
- Treatment is carried out using steroid hormones. Diprospan has antishock, desensitizing and mild corticoid effects. The speed of onset of the effect is ensured by the betamazone phosphate contained in the composition. The dose and route of administration depend on the clinical picture. The injections are not painful, but for local treatment they are sometimes combined with Ledocaine or Procaine as an anesthetic. In case of infected areas, weak joints, bleeding disorders and previous arthroplasty surgery, Diprospan is contraindicated.
- Hydrocortisone is an adrenal hormone that helps improve protein and carbohydrate metabolism. Treatment is carried out by injecting the drug into the synovial bursa in the knee area. The product reduces inflammation, capillary permeability, and reduces allergic reactions. In severe forms of hypertension, psychosis, nephritis, osteoporosis, stomach ulcers, pregnancy, hydrocortisone should not be used.
- For severe pain, treatment is carried out with Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Ketaprofen, which relieve inflammation and relieve discomfort.
- If the patient complains of cramps, muscle relaxants such as Diazepam are used.
- Microcurrents, UHF, magnet and laser exposure are auxiliary methods. Such manipulations are carried out only during the period of remission, since physical effort can cause complications.
- Along with physiotherapy, the doctor prescribes gymnastics. At first, the exercises are done under the supervision of a specialist; in the future, you can continue treatment at home.
- In order to reduce pain, it is recommended to undergo SUV irradiation, low-intensity laser exposure and UHF. Hydrogen sulfide and radon baths help improve blood flow and are used as a prophylaxis to prevent the formation of clots and prevent the development of thrombophlebitis and varicose veins.
3. Traditional methods.
If the size is small, Becker cysts under the knee can be treated using herbs at home.
- The golden mustache plant infused with alcohol is used as compresses. To do this, the leaves are dipped in liquid and allowed to react for 20 days. The resulting cake is applied to the knee overnight. The solution is taken orally three times a day, after meals.
- You can treat a tumor at home using celandine and burdock. The plants are crushed into crumbs and placed in a water bath. The mixture, cooled to an acceptable temperature, is coated with a sore spot, and wrapped on top with plastic film and a cloth made of natural wool.
- It is recommended to treat the cyst with compresses of slightly warmed vegetable oil. Gauze is dipped in liquid, wrapped around the leg, and a scarf is used for insulation. The product is left overnight, washed off in the morning and wiped dry.
- The cabbage leaf is smeared with honey or propolis, placed on the knee, with polyethylene on top. It is necessary to keep the bandage on for 2 hours. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- It is good to treat a tumor with a mixture of camphor and bile in proportions of 250 to 150 g. A homogeneous mass is placed on gauze and wrapped around the knee on all sides. To prevent the liquid from evaporating, wrap it in film and leave it overnight.
Read also: Cyst in the knee joint
When is surgery required?
Indications for removal are the following:
- Large education size.
- Compression of blood vessels.
- Meniscus tear.
- Impaired mobility.
- Severe pain.
- Growing progression of pathology.
- Ineffectiveness of conservative methods.
- Systematic relapses.
Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. An incision is made over the formation, and the cyst is excised. Sutures are placed at the junction of the tendons and joints, and an arthroscope is used in the process. The operation lasts no more than half an hour, then the doctor applies a plaster cast or a tight fixing bandage. The patient is in the hospital for several hours, but he is allowed to step on his foot on the fifth day. If there is no relapse or complications, the sutures are removed after 10 days.
What reasons can provoke a Baker's cyst?
This pathology develops against the background of injuries, inflammatory processes and degenerative diseases of the joints of the lower extremities or as their complication. But there are cases when the origin of the cyst cannot be determined.
In this case, as a result of inflammation in the joint, synovial (articular) fluid is intensively formed, which fills the articular cavity and begins to flow into the intertendinous bursa under the knee. This is the basis of neoplasm.
The main causes of the disease are:
Various knee injuries; Physical overload (sports and professional); Arthrosis; Arthritis, especially of rheumatoid origin; Synovitis (inflammation of the synovium of the joint); Injuries and diseases of the meniscus of the knee joint.
According to statistics, this disease occurs more often in older people, athletes, and loaders.
Basic therapy methods
If the diagnosis confirms the presence of a pathology such as a Baker’s cyst, the specialist prescribes comprehensive treatment. For each individual special pathological case, its own therapy is selected.
In serious and advanced situations, a specialist prescribes medications, and sometimes operations are prescribed.
If the pathology was detected at the initial stage, it will be quite possible to get by with traditional methods. The most common and effective methods for eliminating pathology include the following:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen. The tablets are quite effective in reducing pain and eliminating swelling. Despite the high effectiveness of drugs of this type, they can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. The reason is their ability to cause side effects;
- If the cyst has reached a serious size and causes acute pain, the doctor prescribes aspiration;
- Sometimes patients are given Cortisone injections. A course of such injections can reduce pain and eliminate swelling. The peculiarity of this form of treatment is the relatively short-term positive result;
- Pulse therapy and bioresonance procedures;
- Therapy with traditional recipes. Experts often prescribe various types of herbs made from them, tinctures and a variety of compresses; Physical exercises aimed at strengthening the joint and its main elements, as well as muscle strength. Properly selected exercises are effective if the cause of the disease is standard arthritis.
Is treatment possible at home?
Baker's cyst is a benign lesion that can be treated. Treatment at home in the early stages of development has a greater chance of success if you add pharmaceuticals and physical therapy. Home treatment as an independent method of treating knee bursitis in an advanced form is ineffective. Compresses, lotions and various decoctions of medicinal herbs are used as folk medicine. It should be understood that treatment at home is only possible in the following cases:
- symptoms are mild;
- the formation is small in size and does not increase;
- The operation has already been performed and a course of rehabilitation has been prescribed;
- as additional measures to traditional treatment.
For medium and large cysts, treatment at home can be dangerous, since opening the tumor can lead to blood poisoning and suppuration of the wound.
You can learn about the symptoms of subcoracoid bursitis here.
Diagnosis and treatment
Having dealt with the question of what a Baker's cyst of the knee joint is, we will consider the main methods of its treatment. Treatment tactics are developed individually, depending on the volume and growth rate of the tumor, the age and health of the patient.
Note! If a Becker cyst is confirmed, you should consult a doctor even if there are no painful symptoms. The pathology is amenable to effective conservative treatment only at an early stage.
Conservative therapy
What is the name of the doctor who treats Baker's cyst? This disease is within the competence of the orthopedist, who, after a diagnostic examination of the patient, prescribes treatment. The doctor also prescribes preventive procedures for diseases of the motor elements.
The treatment program for the knee joint is selected individually, depending on the person’s age, physical condition, and the presence of concomitant diseases. The doctor finds out what his patient is complaining about, what is bothering him. Among the mandatory procedures are blockade - removal of fluid before drug treatment begins.
Medicines are prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation. Injections and injections are made - the medicine is injected directly into the joint. An elastic bandage or bandage is placed on the knee to stimulate circulation and stabilize the joint.
The ointments used are hormonal, warming, which relieve pain and soothe the joint - Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac and others. Voltaren helps well in the initial stages of the disease. You can use folk remedies. An ointment made from geranium leaves, calendula flowers and lard has a positive effect. Treatment with ointments is an addition to the main procedures.
Important! When using ointments, you must follow the dosage and apply the remedy correctly.
Leech treatment is also used. This allows you to reduce the size of the cyst. The functions of the joint improve after 7-8 sessions.
Further treatment options will be selected as the disease develops, taking into account the causes that caused it. At the initial stage, you can try to do without surgery.
It is advisable to begin treatment at home after diagnosis, research and other activities. You can use compresses, ointments, and herbal applications.
Seals are treated with ointments, compresses from decoctions of medicinal herbs - celandine, elderberry leaves, currants, raspberries.
A tincture of golden mustache shoots, spicy cloves, and dandelion root helps well. The cooking recipe is not complicated: the raw materials are crushed, placed in a container, water is poured, put on fire, brought to a boil, and cooled.
You can add a few tablespoons of alcohol. The mixture is transferred into a gauze bag and applied to the sore spot, wrapped with a towel on top, and then with a woolen scarf for insulation.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. In some situations, a Baker's cyst resolves on its own; treatment is required only when the formation is large and accompanied by severe discomfort.
A physical therapist may recommend specific exercises combined with cold compresses to speed up healing. In other cases, conservative and surgical methods of eliminating the formation are used.
The treatment strategy for Baker's cyst is usually determined by a surgeon or orthopedist.
includes puncture of the cyst, suction of excess fluid using a syringe (drainage of the cyst), as well as subsequent injection of anti-inflammatory steroids into the cyst, for example, diprospan, kenalog or hydrocortisone. The main problem with conservative treatment is that it is not always effective and often provokes relapses.
If the knee joint is inflamed, then it is necessary to first cure the underlying ailment. In this case, physiotherapy (bioresonance therapy, pulse), compresses, ointments and tablets are prescribed (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, see below).
a list of all NSAIDs in the article: injections for back pain), drug blockades using hormonal medications, as well as a set of physical exercises aimed at strengthening the knee joint.
For Baker's cyst of the knee joint, folk remedies can be used in complex therapy, these are medicinal herbs such as burdock (see burdock root - benefits and harm), celandine, golden mustache. If the patient does not have allergic reactions to these plants, then with small cysts, compresses have a fairly good effect, and you can also take infusions of these herbs orally.
- Surgery
Surgical intervention provides much greater results. Often they resort to it when the cyst reaches a large size and impedes the movement of the joint, its flexion, while squeezing the popliteal neurovascular bundle. The reason for surgery may be unsuccessful conservative treatment and recurrent synovitis.
The surgical method for removing a Baker's cyst is based on its excision. As a rule, local anesthesia is used (in children, general anesthesia), and the procedure itself lasts no more than a third of an hour. The technology of the operation is as follows: a 3-4 cm long incision is made at the site of the cyst, the surgeon isolates the formation, and the junction of the cavity of the knee joint with the cyst is bandaged and stitched, and the cyst is cut off.
Sometimes such an operation is performed using an arthroscope, which is the least traumatic, since only 3 small incisions are made with the diameter of the inserted tube. After the operation, the patient recovers in the hospital for about 3-5 hours, the stitches are removed after a week.
The patient is allowed to walk independently only 5 days after the operation. In the postoperative period, the patient wears a tight bandage or plaster.
Traditional healing has been very popular since ancient times. The traditional method is used only after examination, consultation with the attending physician, at the initial stage of the disease, if the cyst is small in size. Let's consider therapy with effective folk remedies/
Treatment with tincture of golden mustache
To treat a ruptured Baker's cyst of the knee joint (photo below), the following main pharmacological groups of medications are used to alleviate the patient's condition:
- “Prednisolone”, “Diprospan”, “Metypred” are corticosteroids. They have anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects.
- "Dona", "Arthra" - chondroprotectors, restore cartilage tissue.
- "Tramadol", "Analgin" - analgesics, relieve pain.
- "Movalis", "Voltaren", "Celecoxib", "Celebrex" - NSAIDs, remove the inflammatory process and relieve pain.
- Vitamin complex – improves metabolic processes, saturates tissues with vitamins and microelements.
In addition, drugs that enhance immunity are used to treat a ruptured Baker's cyst of the knee joint. A syringe is used to suck out the liquid, then hormonal drugs of the steroid group, for example Diprospan, which gives an anti-inflammatory effect, are injected into the cavity.
Unfortunately, drug therapy is temporary, and the undesirable consequences of cyst rupture return again. Therefore, doctors recommend surgical treatment.
There are several treatment methods that can be used to both reduce the size of the cyst and get rid of it completely. If the cyst is small in size and does not cause any inconvenience, then first of all, therapy is selected for the underlying disease.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out directly to treat the cyst, and a course of therapeutic exercises is also prescribed. During this period, doctors allow the use of folk remedies.
If the formation is large, then a puncture is recommended, as a result of which excess fluid is pumped out. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
To prevent inflammation, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial medications are injected into the knee joint. Unfortunately, the fluid can build up again.
For severe pain, ice compresses, drug therapy (analgesics, NSAIDs, hormones) and the creation of conditions for resting the sore leg are indicated. In addition, physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated: laser, magnetic and bioresonance therapy.
In the absence of timely treatment, there is a risk of Baker's cyst rupture. This occurs due to an increase in intracavitary pressure due to the filling of the cyst with fluid.
The contents of the capsule flow out and spill into the muscle tissue located nearby. Sharp pain, swelling and hyperemia appear.
In case of minor damage to the calf muscle, therapy is aimed at pain relief, relief of the inflammatory process and resorption of the hematoma, and in case of voluminous damage, surgical treatment of a ruptured Baker's cyst of the knee joint is indicated (photo above).
In the initial stages of the disease and in order to prevent the growth and rupture of Baker's cyst, it is permissible to use alternative medicine methods in treatment in consultation with the treating doctor. Compresses from:
- Burdock and celandine. Pre-plant raw materials, taken in equal parts, are crushed.
- Mix aloe and lemon juice with Streptocide tablets.
- Sunflower oil. It is better to use unrefined.
- Golden mustache tincture.
Soak a cloth or gauze in the above mentioned agents, apply it to the affected area of the knee, cover it with polyethylene, wrap it in a warm cloth and leave it overnight.
Specifics of therapy
In cases where the Baker cyst is small and does not cause any discomfort to a person, it is recommended to simply monitor its size. If the neoplasm causes discomfort and interferes with normal life, then in such cases a puncture of the capsular fluid is indicated. The procedure is carried out by taking exudate with a needle. When a puncture is taken, an anti-inflammatory drug is injected into the cavity. This method of treatment is not considered very effective, since in 50% of cases the capsule is filled with fluid again and a recurrence of knee bursitis occurs.
For recurrent forms of the disease, surgical treatment is indicated. The operation is performed with minimal disruption of soft tissue, by making a small incision in the popliteal fossa and draining the cyst and removing the capsule itself.
You can learn about the treatment of suprapatellar bursitis of the knee joint by clicking on this link.
Arthroscopy
The modern method of surgical therapy for treating Baker's cyst is arthroscopy. This method is low-traumatic; during it, local mini-punctures are made in the cyst, through which a valve is excised, which impedes the outflow of fluid from the cyst into the joint cavity. This allows the exudate to leave the cyst on its own, as a result of which it disappears on its own.
After surgery, a rehabilitation period is required. At this time, physical therapy, special massage, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are necessary. Drug treatment for Baker's cyst is less effective because it is only symptomatic . Using gels and ointments, you can only reduce swelling and relieve pain, but this does not help completely eliminate the tumor.
Special exercises
By performing special exercises selected by a doctor, you can effectively strengthen the muscle corset of the knee. Every day you need to do the following simple exercises:
- The knee must be wrapped with a special tape expander, first securing it to a vertical support. The leg is threaded into the formed loop. It is necessary to move a certain number of steps away from the installed support for the device to tighten. In this form, the leg needs to be extended, feeling the general resistance. This exercise must be repeated 10 times, performing at least three approaches;
- While sitting, you need to put special weights on the ankle of the sore leg and try to straighten your leg completely. You need to stay in this position for about one minute, then bend your leg to 45 degrees and hold for another 30 seconds. To get a positive result, you need to perform several cycles of this exercise;
- You need to sit on the floor, bend your healthy leg and pull it slightly towards your chest. The affected limb, with a weight attached to it, straightens and rises above the floor surface. It must be held in this position for at least 20 seconds. The back should be completely straight.
When performing these exercises, you need to ensure that the load is not very strong. Relatively light gymnastic exercises are quite enough, but they need to be done every day.