The activity of our body directly depends on its circulatory system. Circulatory disorders are an abnormal condition in which the supply of tissues with oxygen and essential nutrients deteriorates due to changes in the properties and volume of blood in the vessels. The result of this is the development of hypoxia and a slowdown in metabolic processes, leading to the occurrence of a large number of diseases.
How does the circulatory system work between mother and fetus?
Of course, the placenta is considered the central link in the utero-fetal blood flow, but the circulatory system between the fetus and the mother is complemented by blood vessels. Therefore, it can be argued that the uteroplacental system consists of the following components:
Placenta
Ensures the transfer of blood from mother to fetus in such a way that their blood does not mix. This is achieved as a result of the complex anatomical structure of the system. The placenta is attached to the wall of the uterus by means of villi designed for this purpose, which seem to sink into the uterine mucosa. In fact, these villi directly penetrate the walls of the uterine vessels, where all the necessary nutrients are transferred from the mother’s blood to the fetus’s blood. And decay products return from the child’s blood.
This kind of metabolic processes is carried out at the cellular level, and they are separated only by the hemoplacental barrier - several layers of cells that form a kind of barrier between the placenta and the mother’s blood. And two flows of blood: from the child to the mother and vice versa, meet precisely in the placenta.
Terminal branches of the uterine arteries
Their main feature is that, until the moment of fertilization, they include muscle cells that have the ability to contract in order to close the opening of the vessel. Thanks to this phenomenon, uterine bleeding stops during menstruation. But during pregnancy, the muscle layer disappears (this happens at 4–5 weeks), resulting in increased blood flow to the placenta. And at the end of the fourth month of pregnancy, a complete transformation of these arteries occurs.
Umbilical cord vessels
This is one vein and two arteries. The blood circulation of the fetus is carried out as follows: the arteries carry blood (and with it useful substances) towards the tissues and organs of the child, and the vein ensures the process of reverse transfer of blood towards the placenta. In situations where disruption of blood flow occurs at this level, it is called fetoplacental and there is evidence for a poor prognosis for the fetus.
Symptoms of pathology
Circulatory disorders can form in any organ, but the most significant lesions occur in the myocardium, brain and kidney tissue, as well as in the vasculature of the lower extremities.
Heart
In the heart muscle, the predominant type of microcirculation disorder is ischemia. It leads to a decrease in myocardial contractility. Clinical manifestations are angina attacks, heart attack and sudden cardiac arrest. Can lead to fatal complications or the formation of chronic failure.
The first signs of ischemia development:
- general weakness;
- the occurrence of shortness of breath and palpitations with minor exertion;
- poor tolerance to physical activity;
- minor or moderate pain, tingling in the heart area;
- decreased performance.
With severe ischemia, patients feel severe attacks of pain behind the sternum, which spread to the arm, shoulder blade, and neck.
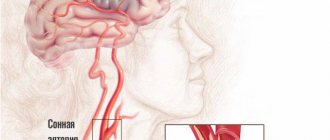
Brain
With an acute cessation of brain nutrition, a stroke is formed. Gradual blocking of arteries against the background of atherosclerosis, hypertension, osteochondrosis leads to stagnant processes and swelling of the brain tissue with foci of necrosis. This provokes the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy with the following symptoms:
- forgetfulness,
- disturbance of the emotional background,
- decreased ability to cognition,
- dizziness,
- headache,
- difficulty coordinating movements,
- unsteadiness when walking,
- weakness in the limbs.
Cerebral ischemia (impaired microcirculation)
Kidneys
Disorders of microcirculation in the renal tissue occur during acute cessation of blood flow (acute failure) or as a result of chronic progressive processes. The latter are much more common and accompany:
- hypertension,
- diabetes,
- autoimmune diseases,
- pyelo- or glomerulonephritis.
Acute renal failure
In these diseases, capillary-trophic disorders develop more slowly than in acute ones, their manifestations can be erased: general weakness, headache, increased blood pressure, frequent urination at night, swelling under the eyes and on the ankles in the morning.
Acute renal failure is accompanied by a sharp drop or cessation of urine output, poisoning of the body with nitrogenous metabolic products. Only with timely consultation with a doctor can the situation be corrected.
Lower limbs
Common causes of microcirculatory disorders in the legs are:
- smoking (arterial spasm, intermittent claudication);
- thrombosis of arterial vessels;
- phlebeurysm;
- angiopathy in diabetes.
With thrombosis, tissue nutritional disturbances can occur suddenly. Its symptoms include severe pain, swelling, pallor or cyanosis of the skin. Chronic changes are characterized by a slow increase in these manifestations and a decrease in sensitivity.
With diabetes, patients note constant chilliness of the legs, a crawling sensation, numbness, loss of reaction to cold and heat, and microtraumas . Often microcirculatory disorders contribute to the development of fungal infections on the feet, ingrown nails, cracked heels and the appearance of long-term non-healing ulcers.
Watch this video about peripheral circulatory disorders:
Causes that can lead to impaired blood flow
Experts have found that disruption of uteroplacental blood flow grade 1a can be provoked by the following factors:
- Development of anemia in pregnant women. The bottom line is that a decrease in hemoglobin levels inevitably entails an increase in blood flow in the vessels, including the uterine arteries. This is explained by the fact that in such a situation all the body’s reserves are aimed at increasing the rate of transport of oxygen volumes into the blood. This is accomplished by increasing the speed of circulating blood.
- Deviations regarding the attachment of placentas. This may be placentation or low presentation, which are caused by a decrease in the intensity of blood flow. This is possible in a situation where the placenta is attached to the area of the uterine scar left as a result of a previous birth performed by cesarean section. For this reason, it is impossible to ensure adequate blood flow, and for the normal development of the fetus, the incoming blood is usually not enough.
- Late toxicosis. With gestosis, damage to small vessels occurs, which leads to disruption of blood flow in the uteroplacental system.
- Infectious diseases. The reason is that pathogens are capable of causing various types of pathological changes in the placental tissue. As a result of this phenomenon, placental insufficiency may develop.
- High blood pressure. Increases the speed of blood movement through the vessels, which can cause disruption of blood flow.
- Multiple pregnancy. In most situations, it is characterized by a disruption of the blood supply. This occurs due to the fact that several fruits are developing. Also, in some cases, most of the blood flow passes to one of the fetuses, due to which, accordingly, it decreases in the other (or others).
- Diabetes. Its inevitable consequence is pathological changes in the internal walls of the arteries, which negatively affects blood flow.
- Uterine fibroids. During pregnancy, myomatous nodes tend to increase in size, this, in turn, entails an increase in their blood supply. Thus, the fetus receives much less blood than in a situation where there is no fibroid.
- Immune-conflicted pregnancy. In some cases, hemolytic disease of the fetus may develop, hemoglobin decreases and anemia develops in the fetus.
- Pathologies at the endometrial level. This phenomenon can be preceded by inflammatory diseases (endometritis), as well as surgical interventions (multiple abortions), and the presence of bad habits, such as smoking and alcohol abuse, contributes to this.
- Pathologies of umbilical cord vessels. In some situations, the results of diagnostic studies indicate a change in the number of vessels, which may result in impaired blood flow.
- Anomalies of uterine development. The most common pathologies include a bicornuate uterus. In such situations, the uterine cavity is divided by a kind of septum, dividing it into two parts. In this case, the process of fetal development is localized in one of these parts, which entails a disruption of its blood supply. This is due to the fact that in a bicornuate uterus there are no connections between the uterine arteries, the arterial network does not expand, as a result of which an insufficient amount of blood flows to the placenta.
All of the above reasons are grounds for examining a pregnant woman using Doppler ultrasound.
Clinical picture and symptoms of circulatory disorders
The clinical picture of the disease with different types of its manifestation has its own characteristics; let’s consider some of the symptoms of circulatory disorders:
- Hyperemia. Dilatation of the blood vessels of the body with an excessive increase in blood filling. It is manifested by a change in the color of the skin at the site of damage to the vessel as a result of filling with blood, acquiring a pink-red color. The patient feels pulsation and increased temperature in the affected area;
- Bleeding. The release of blood from a vessel, when its walls rupture, can be external or internal, arterial bleeding is pulsating, bright scarlet in color, venous bleeding is dark red, and with capillary bleeding, pinpoint bleeding from small vessels is observed;
- Ischemia. A reduced supply of arterial blood to the vessels is manifested by a feeling of pain in the affected organ due to a lack of oxygen supply and the accumulation of metabolic products;
- Thrombosis. A blood coagulation disorder, in which the lumen of the vessel is blocked by a thrombus, there may be complete or partial blockage. The consequence is a slowdown in the outflow of blood from the affected area, with swelling, cyanosis of the skin, and pain;
- Embolism. Blocking of the lumen of the vessel with foreign particles such as pieces of adipose tissue, microorganisms, air bubbles. The symptoms are the same as for thrombosis;
- Shock. A clinical condition caused by a decrease in blood supply to tissues due to impaired autoregulation of the microcirculatory system. It manifests itself as destructive changes in internal organs; if blood circulation is disrupted, it can lead to rapid death.
Also often with peripheral damage, the following symptoms of circulatory disorders are observed: pain, tingling, feeling of chilliness and numbness in the extremities, dizziness, tinnitus, memory impairment, weakened vision, sleep disturbance. The symptoms are most pronounced after physical activity, the degree of their manifestation also depends on the severity of the disease.
Main symptoms of the disease
The main method for detecting FPC and MPC during pregnancy is Dopplerography. But there are still a number of external signs that make it possible to recognize impaired blood flow in pregnant women in the early stages. The most common symptoms of this disease include:
- Unsatisfactory fetal heart rate results. Listening to heart sounds is done using a stethoscope. As a result of this type of examination, muffled tones and changes in heart rate can be observed.
- Insufficient level of growth (or its complete absence) for the main indicators based on the results of measuring the pregnant woman’s abdomen. As a rule, the specialist measures the circumference of the abdomen, as well as the height of the uterine fundus.
- Unsatisfactory results of cardiotocography. Checking the electrical activity of the fetal heart is carried out from the 30th week of pregnancy. If any negative changes are observed, there is a need to conduct an ultrasound examination of the fetus.
Disease prevention
Painful sensations in the legs are not only the fate of older people; problems in this category are increasingly observed in young people, and even in children. Many people often associate pain in the lower extremities with increased stress or simple fatigue, however, often the source of the problem has a more complex and dangerous etiology. Conventionally, the primary sources of the disease can be divided into three basic categories:
- Pathologies of peripheral segments of arteries.
- Stenosis of vascular branches in the lower extremities against the background of atherosclerotic formations in the blood vessels.
- Inflammation of the vascular membranes or spasms of the arterial tracts.
The causes of such pathological processes are often serious diseases, the most common of which are:
- Atherosclerosis of the obliterating type. The disease is characterized by the accumulation of harmful fats and cholesterol in the vessels of the legs, which provokes their fragmented or complete blockage with sclerotic formations. The disease most often manifests itself in mature people who lead an unhealthy lifestyle, regardless of gender.
- Autoimmune vascular disease, chronic, called thromboangiitis. Pathology is a common cause of deterioration in blood supply to the extremities as a result of spasm of one or more vessels of the hip region. Most often it is diagnosed in representatives of the stronger sex who abuse addictions, however, recently it is often diagnosed in women over thirty years of age.
- Diabetic vascular disease. It develops against the background of existing diabetes mellitus, dangerously rapidly progressing necrosis of the vascular membranes and tissues of the legs, which results in gangrene with the need for amputation of the limb.
- Thrombophlebitis, as a serious pathology of the veins, contributes to disruptions in the blood supply to the extremities and the outflow of fluid, which is accompanied by a decrease in the tone of the vascular walls.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6YsjJ-vfB_U
Sometimes the cause of deterioration in blood flow is problems with the spine, as well as serious impairments in the functionality of the kidneys and heart.
The problem of deteriorating blood circulation in the lower extremities is one of the ailments that can be prevented by following simple principles of healthy living:
- Through physical activity and correct eating style, maintain weight criteria within normal limits.
- Give up bad habits, try to avoid psycho-emotional stress.
- Give preference to loose-fitting clothing and comfortable shoes.
- For people who work in an office and regularly sit or stand, it is important to learn to alternate activities by systematically changing positions.
- Contrast showers and foot baths, used regularly, will help stimulate the activity of the circulatory system.,
Degrees of disturbance of uteroplacental circulation
There are three main degrees of disturbance of utero-fetal blood flow:
- The first degree implies the presence of minor violations and contains the following varieties:
- 1a - at this degree, disruption of the uteroplacental blood flow occurs in the uterine artery system, while the fetoplacental blood flow remains normal.
- Degree 1b violations - here there are no violations of the uteroplacental blood flow (this blood circulation is preserved), and pathologies affect the post-placental level, which may be evidence of a violation of the fetoplacental fetal blood flow.
- In grade 2, disruption of uteroplacental blood flow is observed at two levels at once: feto-placental and uteroplacental. At the same time, there is no critical deterioration, which suggests that there is no serious threat to the development of the fetus in the near future. The danger is that negative changes can happen at any time. Therefore, this condition requires close attention from a doctor.
- The third degree means the presence of critical changes in the feto-placental blood circulation, while the uteroplacental blood flow can be disrupted or preserved. This type of violation requires immediate medical care and constant monitoring of the expectant mother until the condition is completely stabilized.
Depending on the degree of the disorder, the tactics for managing the pregnant woman and the type of treatment measures used are selected.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment regimen primarily depends on the cause that provoked pathological changes in the peripheral circulatory system. First of all, an experienced specialist will prescribe a diagnostic test to see what indicators the blood has at the moment. Using a general blood test, it is possible to determine the number of platelets, hemoglobin, erythrocytes, and leukocytes. Depending on the data obtained, the doctor can preliminarily diagnose the disease that caused the changes. Further diagnosis will depend on the organ and cause that provoked the changes or were involved in the pathological process.
If the doctor diagnoses an acute disorder, then treatment, in most cases, is surgical. The operation allows the patient to completely remove the blocked vessel in order to restore proper blood flow.
There are extreme cases when the vessel cannot be removed, and the doctor recommends removal of the entire organ. Such an outcome is always a person’s disability.
If the pathological changes are not acute and develop slowly, then doctors first carry out drug therapy. All medications are prescribed only by a doctor, but you must remember that alcohol and smoking cause blood vessels to spasm and work incorrectly. When diagnosing pathologies of peripheral circulation, you need to completely get rid of bad habits.
Diagnostic methods
Doppler testing is considered the most effective way to diagnose uteroplacental fetal blood flow. This method is the most effective and allows us to identify the smallest changes in the process of blood circulation between the fetus and mother.
In addition, secondary methods for diagnosing pathology are widely used, which make it possible to obtain a complete picture of the condition of the fetus and prevent possible negative consequences. Of course, they can only indirectly indicate the presence of blood flow disorders, but in some situations they cannot be avoided.
Dopplerography
Dopplerography is considered as a type of ultrasound examination. It is carried out on a conventional device, but it requires special software. This type of study makes it possible to obtain an adequate assessment of the intensity of blood circulation in various vessels (most often the vessels of the umbilical cord and uterus are examined).
Modern equipment makes it possible not only to assess the degree of intensity of blood flow, but also to find out the speed of the blood, as well as its direction in all types of vessels (umbilical cord, uterine), as well as obtain all information regarding intraplacental circulation.
This method makes it possible to make the most accurate prediction of fetal development. The fact is that disturbances in the utero-fetal blood flow, as a rule, precede clinical changes (heart rhythm disturbances, weight loss). Detection of circulatory disorders allows timely measures to be taken to prevent adverse consequences.
This diagnostic method does not have a negative effect on either the pregnant woman or the baby.
At the same time, the price for Doppler ultrasound of uteroplacental blood flow differs in each medical institution. It varies from 600 rubles and can reach 5 thousand rubles. If we are talking about metropolitan clinics and medical centers, then the average cost of this diagnostic procedure is 2 thousand rubles.
Secondary diagnostic methods
Secondary methods for diagnosing disorders of the uteroplacental circulation include the following:
- Collection and analysis of the patient’s complaints - usually in the event of a blood flow disturbance, fetal hypoxia occurs, which manifests itself in the form of an increase in the intensity of its motor activity.
- Listening to the child's heartbeat with a stethoscope - oxygen starvation may be indicated by an acceleration or decrease in the rhythm, which does not correspond to normal physiological indicators.
- Cardiotocography - to diagnose fetal hypoxia, 40 minutes is enough.
In addition, there are a number of ultrasound indicators that allow us to judge the deterioration of the fetus’s condition. A biophysical profile study and premature aging of the placenta can be used here.
Traditional medicine
It is worth immediately indicating that folk remedies will be effective if leg problems are mild. In case of a more serious illness, you cannot do without a doctor.
You can try the following procedures:
- In the morning, the soles of your feet are generously lubricated with lemon. Do not put on socks or shoes until the juice is completely absorbed into the skin.
- For blood flow in the legs, it will be useful to take foot baths with the addition of a decoction of calamus root. In this case, it is also necessary that the skin absorbs the liquid as much as possible.
- Baths with chamomile, nettle, oregano, blackcurrant leaf, thyme and string help well.
- Ground red pepper brewed in hot water will help against varicose veins. You need to take this medicine 3 times a day, and the course of treatment itself is 14-20 days.
Many modern people rely more on traditional medicine recipes to improve blood circulation in their legs. In general, there is nothing wrong with this, but it is better to use complex treatment. That is, take traditional and traditional medicine. Firstly, this will allow you to achieve greater effect, and secondly, the result will come much faster.
How dangerous is NMPC for the fetus?
In practice, it has been proven that disruption of uterine blood flow during pregnancy inevitably leads to oxygen starvation of the fetus. And the consequences of this kind of violation can be the most unpredictable, including premature birth or even the death of the baby.
The most common consequences of impaired uteroplacental circulation include the following:
- A decrease in the size and weight of the fetus, which indicates the presence of intrauterine growth retardation syndrome.
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Various types of deviations in the functioning of the baby’s hormonal system.
- A significant reduction in fat depots means a decrease in the child’s body weight.
- Various heartbeat disorders - bradycardia and tachycardia are most often diagnosed, but arrhythmia may also occur, which occurs as a result of changes in the electrolyte composition of the blood.
- Violation of the acid-base balance in the baby's body.
To determine whether there is a circulatory disorder between mother and fetus, a specialist assesses the norm of blood flow in the uterine arteries and umbilical cord vessels in relation to the results obtained as a result of Doppler sonography.
Types of Circulatory Disorders
The circulatory system is conventionally divided into central and peripheral. Anomalies of the central system are caused by disturbances in the functioning of the heart and large blood vessels. Lesions in the peripheral system are caused by structural and functional disorders of these vessels. Circulatory disorders are divided into the following types: hyperemia, ischemia, bleeding, thrombosis, embolism, shock.
Chronic and acute circulatory disorders are also distinguished. Chronic pathologies develop over a long period of time with the gradual development of atherosclerotic plaques on the inner surface of the arteries, leading to their narrowing until complete obliteration. Occlusive lesions of the vessels of the lower extremities can cause the development of necrosis.
Acute lesions of the circulatory system are usually a consequence of cardiovascular failure, but also occur against the background of damage to the central nervous system, endocrine diseases and other pathologies. Acute circulatory disorders include strokes and cerebral vein thrombosis.
Treatment of uteroplacental blood flow disorders
It is worth noting that treatment of utero-fetal circulation disorders is required in all cases. Conditions with the first degree of violation are considered the most harmless. But a critical violation of fetoplacental blood flow requires immediate treatment. The faster measures are taken to eliminate critical changes affecting blood flow, the higher the chances of saving the baby’s life.
The main directions of treatment of fetoplacental circulatory disorders are as follows:
- blood pressure control;
- normalization of the lifestyle and diet of a pregnant woman;
- therapy with antibiotic and antiviral drugs in cases where intrauterine infection occurs;
- in case of Rh-conflict pregnancy, plasmapheresis is very successfully used;
- use of magnesium preparations;
- use of antispasmodic medications;
- taking vascular medications.
If acute hypoxia occurs due to blood flow disorders that can be classified as second or third degree, early delivery is used. This measure is resorted to in situations where conservative therapy does not produce any results.
Problem solving
The therapy program is determined depending on the disease. If you consulted a doctor at the initial signs of pathology, you can get by with conservative treatment methods.
If the problem is neglected, radical measures cannot be avoided.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is necessary when the blockage of arteries and veins cannot be eliminated with the help of medications . Since impaired blood circulation leads to necrosis of limbs or organs, it is necessary to quickly eliminate the cause of this disorder. The operation is reduced to removing the affected areas of the vessels, their reconstruction and replacement.
Filtration is carried out to eliminate and remove blood clots.
In difficult situations, when the blood supply to vital organs is disrupted, phlebologists and pathologists decide to add vessels to the organ.
If gangrene develops, amputation of the limb is required.
Medicines
Drug treatment is quite extensive . Depending on the pathology, it is necessary to use several medications at once.
- Achieve blood thinning.
- Eliminate narrowing or dilation of blood vessels.
- Normalize blood pressure.
- Eliminate formed blood clots and other substances.
- Improve the elasticity and strength of blood vessels.
- Get rid of vascular spasm.
also necessary to eliminate symptoms (pain, swelling or fever).
In most cases, the following drugs are used to improve peripheral circulation:
However, their use should be discussed with a doctor.
Diet
Balanced diet : avoiding some foods and taking others can significantly improve the deplorable state of peripheral circulation.
First of all, you need to give up alcohol, carbonated and sweet drinks. Infusions and teas based on lemon balm, mint and chamomile have a beneficial effect on resolving the problem.
If your blood circulation is impaired, you should avoid the following foods:
- fat;
- fried;
- flour;
- sweet;
- yeast;
- smoked;
- salty.
You should eat more liquid (soups, gravies), and increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in your diet.
Fish and chicken also contain a lot of useful substances.
Citrus fruits have a beneficial effect on the condition of blood vessels and the heart.
The daily diet should be divided into 5-6 parts and under no circumstances should you overeat.
Other methods
- Physical activity. 15 minutes of charging three times a day is enough, this will help restore blood supply to the organs. Doctors prescribe certain types of exercise therapy.
- Physiotherapy (hirudotherapy, magnetic therapy). Possible at the initial stage of the disorder.
- Phytotherapy. Traditional medicine is relevant, but self-medication is contraindicated.
Prognosis and consequences of the disease
The prognosis largely depends on the degree of disturbance of the utero-fetal circulation, the duration of such changes, as well as the timing of pregnancy. The consequences of such violations are not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. The risk that such a condition can transform into the second degree of circulatory impairment at any time is very high.
Although it is believed that disruption of the uteroplacental blood flow of grade 1a is not too dangerous, it is nevertheless recommended to begin treatment from a time when the changes have not become serious and can be eliminated with the least effort. This allows you to significantly reduce the risk of threatened miscarriage and prevent fetal death.
Possible consequences include various kinds of disorders in the child’s development that are life-threatening.
Arterial thrombosis and embolism
In this case, acute disturbances of the peripheral arterial circulation occur, which in a matter of hours can lead to the development of gangrene of the limb if timely assistance is not provided.
A thrombus in an artery can form on an atherosclerotic plaque, in the area of inflammation of the vessel wall or its damage. An embolus is a blood clot brought by a blood stream from another part of the vascular bed. As a result, the lumen of the vessel is completely blocked, blood flow stops, tissues begin to experience ischemia, and if this situation persists for a long time, they die (gangrene develops).
Prevention
Preventive measures to avoid disturbances of the placental-uterine circulation are primarily aimed at:
- elimination of extragenital pathologies;
- following a healthy lifestyle - you need to monitor your diet, which should include all the necessary nutrients, get rid of bad habits and avoid stressful situations;
- refusal of excessive physical activity;
- reducing the risk of infectious diseases - this requires avoiding sources of potential infection.
To prevent disturbances in uterine blood flow, compliance with the norm for weeks must be monitored at the first symptoms of such a pathology. If there are prerequisites for the development of disturbances in the uteroplacental circulation, it is immediately recommended to conduct Doppler measurements to determine the extent of such changes and prescribe effective treatment.
During pregnancy, it is very important to constantly monitor the condition of the mother and fetus and their performance of vital functions. One of the most significant studies is the analysis of blood flow in the arteries of the uterus, the woman’s umbilical cord, as well as in the aorta and cerebral vessels of the child.
Among the main causes of perinatal mortality and morbidity, disruption of uterine blood flow (uteroplacental and fetal placental) is not the least important.
Blood flow in the placenta
The placenta, in which the fetus is located, supplies it with nutrition and oxygen from the mother’s blood and removes metabolic products from the child’s body. It is this organ that unites two complex vascular systems - the maternal one, which connects the vessels of the uterus and the placenta, and the fetal one, which passes into the umbilical arteries and leads to the fetus.
The above-mentioned circulatory systems are separated by a membrane that does not allow the blood of the mother and child to mix. The placenta acts as a kind of barrier, resistant to many viruses and harmful substances.
In some cases, for completely different reasons, placental insufficiency may develop, which inevitably affects the performance of the trophic, metabolic, transport, endocrine and other vital functions of the placenta. In this condition, the metabolism between the body of mother and child deteriorates significantly, which is fraught with consequences.
Causes of the disease
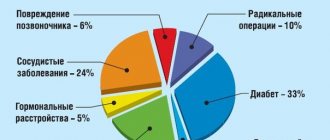
Poor circulation is one of the symptoms of a large number of diseases of the cardiovascular system. Conventionally, all the causes of pathology can be divided into five groups:
- Compression;
- Traumatic;
- Vasospastic;
- Caused by the occurrence of tumors;
- Obliterating.
Also, the cause of the anomaly may be the presence of infectious diseases, hormonal imbalances, hypertension, diabetes, and renal failure. Favorable factors for the development of circulatory disorders are burns, aneurysms, and Raynaud's phenomenon.
Causes of uterine blood flow disorders
Poor blood circulation in the uterus can be caused by increased pressure, pneumonia, intrauterine infection and insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus (hypoxia).
To diagnose the blood flow system in obstetric practice, three-dimensional ultrasound (Doppler) is used, with the help of which the vessels are visible in the so-called 3D (three-dimensional) image. With the help of this modern diagnostic method, there is a prospect of diagnosing retroplacental bleeding and assessing cardiac malformations by monitoring blood flow. This method is indispensable, since with its help you can see defects even in the smallest vessels that form the microvasculature, monitor the development and formation of intraplacental hemodynamics, and also control the amount of oxygen and nutrients that should enter the fetal body. New opportunities have opened up for the early detection of obstetric complications, and if correction or treatment is started without wasting time, then circulatory disorders and further associated pathologies can be practically avoided.
Violation of uterine blood flow during pregnancy is a serious problem that can cause various complications during the intrauterine development of the fetus. Currently, the assessment of this indicator is included in the generally accepted standards for the management of women expecting a child.
In the absence of pathologies, girls must undergo three routine ultrasound examinations, which show whether there is a violation of uteroplacental hemodynamics during pregnancy or not. If it is identified, the severity of this condition will be determined, as well as the treatment method.
How is it regulated?
The speed and volume of peripheral blood circulation is regulated by resistance to blood flow : mainly, this is a change in the lumen of blood vessels as a result of contractions of smooth muscles.
Anna Poniaeva. Graduated from the Nizhny Novgorod Medical Academy (2007-2014) and Residency in Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics (2014-2016).Ask a question>>
Regulation of peripheral blood circulation
is carried out thanks to the coordinated work of the nervous system .
When the nerve fibers that carry the signal from the brain to the organs are excited, the smooth muscles of most arteries contract, due to the function of the endocrine glands. Certain hormones (adrenaline, vasopressin) begin to be produced at double speed, narrowing the vessels of the periphery, but dilating the vessels of the brain and heart. This includes the amount of reserve oxygen necessary for the normal functioning of these organs. Due to the interconnection of all organs of the body, these hormones promote increased production of histamine, which subsequently dilates the capillaries, and the substance acetylcholine produced by some nerve endings increases the lumen of blood vessels. Several factors influence normal blood circulation :
- eating;
- exercise stress;
- fatigue;
- physical activity;
- arterial pressure;
- blood viscosity;
- heart function;
- tone, integrity of blood vessels.
For example, with a prolonged lack of nutrients or poor functioning of the heart muscle, microcirculation slows down.
And with physical exertion and physical activity, on the contrary, it accelerates.
General information
The majority of people who do not have special medical education believe that the placenta is solely responsible for the process of blood circulation between the fetus and mother. However, everything is much more complicated, since the uteroplacental blood flow system is a complex that includes the placenta and blood vessels of the fetus, as well as the mother.
Experts distinguish three levels of this system. The first are the terminal veins of the uterine arteries, through which blood flows to the placental complex. Until pregnancy occurs, the arteries are called spiral because they contain muscle cells necessary to contract and close the lumen of the vessel.
How does the uteroplacental circulation work? Source: 900igr.net
This function is needed to quickly stop bleeding during menstruation. After fertilization, at approximately 4-5 weeks, certain transformations occur during which muscle cells disappear from the walls of the artery. Thanks to this, blood constantly flows to the placenta.
The next link in this system is the placenta. This part can be called the most complex, since processes occur here in which blood is transferred from mother to fetus. There is also a hematoplacental barrier here, thanks to which the blood of the child and mother does not mix with each other.
The final level is the umbilical cord, which contains two arteries and one vein. Thanks to the first, blood flows to all organs and tissues of the fetus, and through a vein returns back to the placenta. Disruption of uterine blood flow during pregnancy, localized in this area, is called fetal-placental. In this case, the specialist diagnoses a severe degree of pathology.
Peculiarities
Peripheral circulation is blood circulation that occurs within certain organs . Various medical textbooks and other sources use different names for such blood circulation:
- organ;
- fabric;
- local;
- regional.
Blood, a source of oxygen and useful micro- and macroelements, passes through arteries and veins.
Thanks to the peripheral blood supply, the necessary volumes of blood and pressure in organs and tissues are provided . In addition, leukocytes contained in the blood actively monitor the condition of organs and the body as a whole, and platelets can quickly solve problems with vascular damage.
Blood supply occurs thanks to the heart muscle, which pumps the required amount of oxygenated blood from the lungs, and vessels and capillaries carry it to the organs. Due to the fact that the heart muscle constantly contracts and relaxes, pulsation keeps the blood vessels in good shape. In this way, the required pressure is ensured at a certain moment. Veins carry waste blood away from the organs. Microcirculation of the peripheral circulation is the link that delivers blood to the organs.
Regional blood circulation occurs in the following vessels, the size of which does not exceed 200 microns:
- Aorta and large arteries. Here, progressive blood flow occurs due to the energy of the stretching walls.
- Small arterioles and arteries. The main function is to determine the resistance value.
- Capillaries. They carry out metabolism between blood and organ tissues.
- Venach. Despite their poor elasticity, they are able to stretch, allowing blood to pass further.
Along arteriovenous anastomoses - areas connecting veins and arteries - the total blood flow from the artery to the veins is redistributed, while the capillaries are not affected.
Some concentrated amounts of blood are retained in organ tissues, such as the bone marrow, spleen, or liver. The rest of the blood, ranging from 4 to 6 liters, in percentage terms this is at least 8% of a person’s body weight, is constantly in the process of circulation: from the heart to the organ - through the arteries, from the organ to the heart - through the veins.
Causes
Poor blood flow in the uterus during pregnancy can develop in women with anemia. When the level of hemoglobin decreases, the blood circulation process accelerates so that the tissues receive the necessary amount of oxygen. This reaction is called compensatory and can occur in the uteroplacental system.
Blood flow during pregnancy is impaired, perhaps due to placenta previa and or its low attachment. In this case, the blood circulation process slows down, since the muscle layer of the lower segment of the uterus is much thinner. This condition can occur in women who have previously had a caesarean section delivery and the placenta has implanted in the area of the scar.
Standard forms
Depending on the mechanism of microcirculation disturbance, the following forms are distinguished:
- Intravascular (inside a vessel) – occurs when systemic blood flow and lymphatic drainage are disrupted, provoked by thick blood, blockage by a thrombus, embolus, plaque, or proliferation of the inner lining. Also, vasospasm under high pressure and the action of stress hormones leads to the discharge of blood from the arterial into the venous network.
- Transmural (through the wall) - an increase or decrease in permeability for the liquid part and blood cells. Occurs with hypovitaminosis, vasculitis, loss of elasticity due to age-related, atherosclerotic processes.
- Extravascular (outside the vessel) - accompanied by a change in the volume of fluid between cells, a violation of its return transition to the microvasculature. Causes: blood stagnation, swelling, allergies, neoplasms, inflammation. Leads to metabolic disorders, accumulation of biologically active substances that enhance vascular reactions.
Complications
Violation of uterine blood flow during pregnancy is a very serious pathological condition. If it is present, specialists often diagnose fetal growth retardation syndrome, which manifests itself in the insufficient weight of the child. If the electrolyte composition of the blood is disturbed, the occurrence of tachycardia, bradycardia and arrhythmia cannot be ruled out.
When the blood circulation process is disturbed, the fetus develops hypoxia. Source: beremennostnedeli.ru
The acidity level of the biological fluid may also change, the hormonal levels will not correspond to the norms, and the amount of fat depots decreases sharply. All this, in most cases, can provoke spontaneous abortion, and in a severe situation, intrauterine fetal death cannot be ruled out.
How to stabilize blood circulation in the vessels of the legs
Discomfortable symptoms in the legs, such as systematic pain, lameness during sudden movements or exertion, and limb cramps are an indicator of poor blood circulation. Such precedents force people faced with a problem to look for a question to answer: what to do when poor blood circulation in the legs interferes with normal life, what actions to take first?
The answer to these questions is clear: you need to visit a medical facility to identify the original source of the problem. The doctor, based on the patient’s complaints, studying the family history, conducting the necessary examinations of the body and standard laboratory tests, will be able to make a diagnosis, the variation of which determines the methodology of further treatment.
Methods for restoring blood circulation in the legs depend directly on the primary source of the disease and the neglect of the disease. If the disease is at an early stage, and there are no critical pathologies among the causes of the disease, it is often possible to restore blood flow without the use of drastic measures, by coordinating the patient’s lifestyle, using alternative therapy, special exercises and physiotherapeutic procedures.
In more complex situations, radical treatment will be required, with the inclusion of medications in the complex of treatment measures. Situations with advanced cases may require mandatory surgical intervention, which may consist of either removing the blockage of a vessel or expanding the stenotic segment with a special expander, or amputating a limb, at least if it is impossible to stop the process of necrosis and rotting by medicinal methods.
Making a specific diagnosis for the patient is helpful for prescribing measures for the treatment of blood circulation disorders in peripheral vessels. According to the regulations, the doctor initially prescribes drugs to the patient, the action of which is aimed at eliminating the provocateur of the disease. Often, the patient is prescribed a complex of drugs, both in tablet or injection form, and in the form of ointments or gels. The basis of complex treatment of the disease are drugs to improve blood circulation of the following drug groups:
- Antiplatelet agents, the action of which is aimed at normalizing blood circulation by stopping and preventing atherosclerotic processes.
- Anticoagulants that prevent thrombosis by inhibiting blood clotting.
For vein pathologies, vascular drugs are used to improve blood circulation in the legs from the category of phlebotropic and venotonic drugs. Frequently prescribed drugs in these categories include tablets such as Detralex, Venoruton and Antistax; ointments such as Troxevasin or Escin can be used for topical application, which, in addition to strengthening and toning the venous walls, have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect.
In complex treatment, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Indomethacin or Diclofenac, available both in injection forms and in tablets or ointments, can be used. Combinations of drugs, as well as their type, are determined by the treating doctor, depending on the diagnosis and medical indications, the complexity of the disease and disturbing symptoms.
Of no small importance in the comprehensive restoration of blood flow in the vessels of the lower extremities is given to methods of alternative medicine, time-tested and proven effective in practice. You can improve the condition of blood vessels at home by taking products prepared according to the following recipes:
- Horse chestnut flowers, weighing fifty grams, must be infused in a dark place with half a liter of vodka for fourteen days, shaking the container with the tincture every day. Take one teaspoon of the tincture three times a day before meals, first diluting it in a glass of water at room temperature. Treatment must be carried out in ten-day courses, with five-day breaks.
- Take three hundred grams of hazelnuts and prunes, five hundred grams of raisins and walnuts, grind all the ingredients in a blender or meat grinder. Fifty grams of honey are added to the finished mixture, the resulting medicine is taken one tablespoon before each meal.
- Decoctions of adonis or wild rosemary have a beneficial effect on blood circulation. To prepare the potion, you need to take a spoonful of the crushed plant, pour a glass of boiling water and simmer over low heat for half an hour, let the potion brew and strain. The resulting decoction must be stored in the refrigerator, take one spoon three times a day. The course of therapy should not exceed a month.
If blood flow in the region of the lower extremities is poor, baths are often used at home. Pine baths have the most effective effect on the vascular system; however, medicinal herbs such as oregano, calamus, chamomile, string, and nettle are also often used. The use of baths must be agreed upon with a doctor, since in case of certain cardiovascular diseases, steaming the legs is strictly prohibited.
Massage, acupuncture
Therapeutic foot massage and acupuncture procedures are characterized by effective effects on circulatory disorders of various locations. To improve blood circulation in the extremities, a light massage helps well, gradually turning, after relaxing the muscles, into rolling and rubbing the problem segments of the leg, with periodic, moderate pressure, which will help strengthen the vascular lines.
Massage problem areas for no more than fifteen minutes so that the procedure does not have the opposite effect. If you have no experience in performing massages, you can initially use the services of specialists, which will allow you to visually and tactilely feel how to correctly perform the procedure at home.
Despite the rapid development of medicine in all directions, alternatives to human physical activity as a method of combating and preventing many diseases have not been invented. Physical activity of a person, exercises, and feasible exercises are integral areas of treatment and prevention of cardiovascular problems.
- Take a lying position on your back. Perform leg movements based on the principle of simulating cycling.
- From a similar starting position, perform synchronous movements with your legs, according to the principle of crossing them, imitating “scissors”. To begin with, you can carry out movements by raising your legs at a right angle relative to the floor, gradually complicating the task by reducing the angle to a minimum.
- Lying on your back, raise your arms and legs up, vibrating them. Exercise helps to relax the limbs, helps clean vascular lines from deposits, and is an excellent prevention of thrombosis.
- Standing position: you need to perform raises on your toes, with parallel muscle tension. You must repeat at least 10 lifts at a time.
- From a standing position, keeping your feet shoulder-width apart, bend forward, trying to reach the floor with your fingertips. When bending, it is important that your legs do not bend at the knees.
- Starting position: sitting on the floor with your legs spread apart as far as stretching allows. Place your arms at chest level and bend forward, trying to reach the floor. Repeat the exercise 5 times, then take a break by repeating the bends.
The total charging time should not exceed half an hour to avoid overloading the body. In addition to specific exercises, jogging, swimming, fitness, dancing or other sports will be beneficial for health, and for people who cannot afford intense exercise, they can be replaced with easy, but regular and long walks.
Degrees
The principle of treatment for impaired uteroplacental circulation is determined based on the severity of the pathological process. Experts highlight the following:
- 1A – there is a disturbance in the process of blood outflow in one uterine artery, while other systems are functioning normally;
- 1B – specialists identify circulatory disorders at the fetal-placental level, while no abnormalities are observed in the uterine arteries;
- 2 – circulatory disturbance occurs at the level of the uterine and umbilical vessels;
- 3 – critical state of indicators, which can cause reverse blood flow in the arteries.
This principle of classifying the pathological condition of a pregnant woman is convenient for gynecologists and obstetricians, since doctors clearly understand in which part there is a violation of the circulatory process. In case of detection of 1A or 1B degree, the pregnancy is maintained; in case of the third degree, emergency delivery can be performed.
Treatment
Symptoms and treatment of blood circulation are interrelated. Until the doctor identifies which disease all the signs relate to, therapy cannot be prescribed.
The best treatment result will be for the patient in whom the pathology was diagnosed in the initial stages and therapy was started on time. To eliminate the disease, doctors resort to both medicinal and surgical methods. If the disease is detected at the initial stage, then you can recover by simply reviewing your lifestyle, balancing your diet and playing sports.
Treatment of impaired blood circulation is prescribed to the patient according to the following scheme:
- eliminating the root cause;
- increased myocardial contractility;
- regulation of intracardiac hemodynamics;
- improvement of cardiac function;
- oxygen therapy.
Oxygen therapy
Therapy methods are prescribed only after the source of the pathology has been identified. If circulatory disorders of the lower extremities occur, the patient needs to use drug therapy. The doctor prescribes medications to improve vascular tone and capillary structure. The following medications can cope with such goals:
- venotonics;
- phlebotropic;
- lymphotonics;
- angioprotectors;
- homeopathic tablets.
For additional therapy, doctors prescribe anticoagulants and anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, and also use hirudotherapy.
If necessary, the patient is provided with surgical assistance - angioplasty or open surgery. Angioplasty is performed using several punctures in the groin, and a small catheter with a balloon is inserted into the artery. When the tube reaches the site of blockage, a special balloon expands, which increases the lumen in the artery itself and blood flow is restored. A special stent is installed on the damaged area, which is a preventive measure against recurrence of narrowing. The same procedure can be carried out if other parts of the body are affected.
Diagnostics
Currently, the generally accepted method for identifying disorders of the uteroplacental circulation is to conduct a Doppler study. Thanks to it, specialists are able to determine even the slightest changes, if any. Diagnostics must be performed using modern equipment with a high level of sensitivity.
Doppler is a standard procedure that is similar to ultrasound screening, but it is enhanced by the Doppler effect. It is thanks to him that it is possible to track various changes in the frequency of ultrasonic waves that are reflected from objects in motion.
Doppler procedure. Source: beremennost.jofo.me
Also, specialists must introduce additional research methods that make it possible to confirm or refute the presence of other pathologies:
- The most thorough history taking. The woman should tell the doctor about all the sensations. In particular, if there is a state of hypoxia, that is, lack of oxygen, the child will move more often.
- Additional listening to the child's heartbeat using a stethoscope. The doctor will count the number of heartbeats and compare them with the norm; if there are more or less of them, then the state of hypoxia is once again confirmed.
- Registration of CTG. Within 40-60 minutes, specialists record cardiotocography indicators, the results of which also indicate oxygen deficiency in the fetus.
When examining a woman to identify disorders of the uterine circulation, other diagnostic methods can be performed. For example, certain ultrasound indicators can reveal premature aging of the placenta, which is considered a dangerous pathological condition for the unborn child.
Diagnosis of peripheral blood flow disorders
To identify ischemic disorders, the following methods are used (depending on the location of the pathological process):
- myocardium - ECG (including Holter monitoring, exercise tests), lipidogram, coagulogram, electrolytes and blood sugar, cardiac ultrasound, scintigraphy and coronary angiography;
- brain - the same examinations as for myocardial ischemia, as well as examination of the fundus, ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck, cerebral angiography, EEG;
- kidneys - excretory urography, ultrasound, blood test with renal samples, urine tests (general, according to Nechiporenko), determination of filtration rate;
- lower extremities - blood test for cholesterol, glucose, platelets and coagulability, ECG, ultrasound of the vessels of the extremities, aorta, angiography (arteriography and rheovasography), capillaroscopy, thermography.
Determining the causes of violations can be difficult due to many factors in their formation
What emergency situations may arise?
In case of pathology of the communicating vascular system of the uterus with the placenta of 2-3 severity, situations may arise that require the emergency initiation of therapeutic measures:
- Acute fetal hypoxia.
- The formation of heart defects or other anomalies in a child that are incompatible with life or jeopardize the life of the newborn.
- Detachment or premature aging of the placenta.
- Death of the fetus in the womb.
Each of these situations is decided in accordance with the condition of the woman and child, gestational age and the degree of threat to the fetus and mother.
What symptoms indicate blood flow problems during pregnancy?
It is very difficult to suspect problems with blood flow in the placenta without examination. But there are several symptoms, if they occur, it is better to consult a doctor:
- Pathological motor activity of the baby. If it is overly active or, conversely, practically does not move, this signals hypoxia.
- Severe toxicosis in the second half of pregnancy. Late gestosis often accompanies pathology of placental blood flow.
- Too slow increase in abdominal circumference. It is difficult to notice this on your own, so the gynecologist usually pays attention to this during a routine visit to the patient.
- Bloody vaginal discharge. This is the most dangerous symptom that indicates placental abruption.
Signs of pathology
The clinical picture of blood flow disorders is determined by their severity. Compensated disorders usually occur latently and are detected only with ultrasound diagnostics. Decompensated and acute forms of fetoplacental insufficiency are usually accompanied by changes in the motor activity of the fetus, which is either minimized or becomes excessively pronounced. Normally, the fetus should move at least ten times per day.
Sometimes such deviations are accompanied by insufficient growth of the pregnant woman’s tummy, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, severe gestosis or hyperedema, sudden weight gain or pressure surges, and the appearance of protein compounds in urine. The most dangerous manifestation of placental circulatory insufficiency is considered to be uterine bleeding, which usually occurs against the background of placental abruption. In such a situation, a woman can only receive meaningful help from specialists, so it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Prevention and treatment
At present, unfortunately, it is not possible to completely relieve a pregnant woman from placental insufficiency using any therapeutic interventions. The means of therapy used can only help to stabilize the existing pathological process and maintain compensatory and adaptive mechanisms at a level that allows for the continuation of pregnancy until the optimal date of delivery. Therefore, it is very important to carry out prevention in women who have risk factors for developing placental insufficiency.
The leading place in prevention is the treatment of the underlying disease or complication, which may lead to placental insufficiency. An important condition is for the pregnant woman to follow an appropriate regimen: adequate rest (sleeping on the left side is preferable), elimination of physical and emotional stress, staying in the fresh air for 3-4 hours a day, and a rational, balanced diet.
The course of prevention includes multivitamins, iron supplements, breathing exercises to increase oxygen delivery through the lungs, the use of amino acids, glucose, Galascorbine, potassium orotate, ATP, which serve as a direct source of energy for many biochemical and physiological processes.
With initial signs of placental insufficiency, treatment is possible in a antenatal clinic with a repeat ultrasound examination with Doppler 10-14 days after the start of treatment. With more severe placental insufficiency, especially in combination with other complications of pregnancy or general diseases of the mother, hospitalization in a hospital is required.
The duration of therapy should be at least 6 weeks (in a hospital, with continuation of therapy in a antenatal clinic). If this pathology is detected and appropriate therapy is carried out in the second trimester, to consolidate the effect of the first course, treatment should be repeated at 32-34 weeks of pregnancy.
If indicators deteriorate during treatment, signs of decompensation of placental insufficiency appear, determined by a sharp deterioration in the condition of the fetus and the possibility of its death, emergency delivery by cesarean section is indicated, regardless of the gestational age.
Summarizing
The appearance of discomfort in the legs, consisting of pain, fatigue, swelling or other unpleasant symptoms, may indicate disturbances in blood circulation in the vascular lines of the lower extremities. Such signals should serve as a reason to visit a doctor in order to identify the cause of the disease, diagnose it at the initial stages of progression, which will prevent serious consequences through the selection of optimal medications and preventive measures.
Conclusion
Study of uteroplacental blood flow using Doppler ultrasound is a mandatory study during pregnancy. Practice shows that the use of this method has had a positive effect on the prevention and treatment of many obstetric complications. However, we should not forget that in order to obtain reliable and informative results, blood flow studies must be carried out using expert-class devices by highly qualified specialists.
https://youtu.be/hOJRAd6ai48
Causes of the problem
A change in blood flow between the uterus and placenta does not happen on its own. There are always reasons for this, but most often this problem arises due to the fact that the mother’s blood pressure is constantly rising or she has had pneumonia. In addition, the development of pathology can be influenced by intrauterine infections and lack of oxygen in the fetus, that is, hypoxia.
To determine the problem, specialists prescribe an ultrasound examination in three-dimensional format, that is, Dopplerometry. Thus, the vessels become visible from all sides, which makes it possible to determine the problem quickly and efficiently.
It is worth noting that this diagnostic method is quite popular and very effective. It helps to identify any problems with blood vessels and even see the development of heart disease. Experts highly value this technology, as it allows them to see defects in small vessels and determine the amount of nutrients required for the baby
Considering the effectiveness of Doplerometry, it is possible to identify pathology at an early stage, including placental, and begin timely treatment, which is important for getting rid of many ailments
Disturbance of uterine blood flow
Other medicines
How to improve blood circulation in the legs? Other medications are also used for these purposes.
Bioflavonoids help increase the elasticity of red blood cells, which improves blood flow. Ganglion blockers dilate venules, arterioles and small veins and evenly distribute the blood volume in the lower extremities. Such drugs include “Dimecolin”, “Camphonium”, “Pahikarpin”, “Temekhin”, “Pirilene”.
Medicines such as alpha-blockers also solve this problem. They have a complex effect on the entire body, dilating blood vessels not only in the lower extremities, but also in the internal organs.
https://youtu.be/MRPdg3R_9hU
Blood flow in the umbilical cord is normal
The formation of the placenta and umbilical cord ends by the end of the 3rd month of pregnancy. This is a very important process, since it is the blood flow in the umbilical cord that provides the baby with the necessary nutrients and oxygen. How does everything happen, and are there any difficulties?
The initial length of the umbilical cord is only a few millimeters. As the baby grows, it stretches and by the time of birth reaches approximately 50 cm.
Many people ask: how many vessels does the umbilical cord have? We answer: three vessels - two arteries and one vein. All vessels are enclosed in connective tissue, which fixes them, protects them from compression and ensures the flexibility of the umbilical cord.
The blood flow system in the umbilical cord is unique. It begins at the point where the umbilical cord attaches to the placenta. Blood from the capillary network converges into the umbilical vein, through which the movement of blood enriched with oxygen and nutrients occurs.
Immediately the ultrasound said that more often the opposite happens: the umbilical cord is normal, but the uterine arteries are not, she also said that they would treat me, and then come back for a Doppler test.
Most likely these are some kind of functional disorders. Initially, a search for umbilical cord vessels is carried out in the B-mode or in the Color Doppler mode. To obtain reliable results when studying CSCs in the umbilical cord arteries, it is necessary to adhere to a number of methodological approaches.
Doppler measurement is one of the ultrasound methods, so it is carried out using a conventional device, but equipped with special software. It is based on the ability of ultrasound waves to reflect from moving objects, thereby changing their physical parameters.
The active use of Doppler ultrasound has become a real breakthrough in the diagnosis of almost all types of obstetric pathology, which is usually associated with circulatory disorders in the mother-placenta-fetus system. Through clinical observations, indicators of norms and deviations were determined for various vessels, which are used to judge a particular pathology.
Doppler testing during pregnancy makes it possible to determine the size and location of blood vessels, the speed and characteristics of blood movement through them at the moment of heart contraction and relaxation.
The doctor can not only objectively judge the pathology, but also indicate the exact location of its occurrence, which is very important when choosing treatment methods, since hypoxia can be caused by pathology of the uterine arteries, umbilical vessels, and disturbances in the development of fetal blood flow.
Doppler testing can be duplex or triplex. The latter option is very convenient because not only the speed of blood flow is visible, but also its direction. With duplex Doppler, the doctor receives a black-and-white two-dimensional image, from which the machine can calculate the speed of blood movement.
example of a triplex Doppler examination frame
Triplex examination is more modern and provides more information about blood flow. The resulting color image shows blood flow and its direction. The doctor sees red and blue streams on the monitor, but to the average person it may seem that this is arterial and venous blood moving.
No special preparation is required before Doppler ultrasound, but the woman may be advised not to eat or drink water for a couple of hours before the procedure. The examination does not cause pain or discomfort; the patient lies on her back, and the abdominal skin is treated with a special gel that improves ultrasound performance.
During pregnancy, especially in the last trimester, doctors may refer the expectant mother to a study such as Doppler ultrasound.
Fetal Doppler is a subtype of ultrasound diagnostics that allows you to evaluate the characteristics of blood flow in the vessels of the child, uterus and placenta. Based on the results of the study, it is possible to judge whether the baby suffers from a lack of oxygen (hypoxia) and, if the answer is positive, determine where exactly the blood flow disturbances occurred: in the uterus, placenta or umbilical cord.
Oxygen is the most important element, with the participation of which the metabolism in the cell occurs properly. If there is not enough oxygen, then the energy necessary for tissue growth and function is not enough. As a result, hypoxia is a reason for intensive treatment in a hospital setting.
The method is based on the so-called Doppler effect - the property of an ultrasonic wave to be reflected from moving bodies and thereby change the frequency of its oscillations. In our case, this is a change in the frequency of the reflected ultrasonic signal from an unevenly moving medium - blood in the vessels.
Changes in the frequency of the reflected signal are recorded in the form of blood flow velocity curves (BVR). The first attempt to use Doppler in obstetrics was made in 1977 to assess blood flow in the umbilical artery.
In subsequent years, the widespread use of Doppler measurements has made it possible to significantly reduce the percentage of such serious complications as severe forms of preeclampsia, placental insufficiency, intrauterine growth retardation and intrauterine fetal death. The incidence of complications during childbirth (distress syndrome, fetal asphyxia) has decreased.
The procedure does not require any preparatory measures: neither the diet nor the fullness of the bladder and stomach affect the examination results. The only recommendation is to take a break from eating for a couple of hours before the examination.
The technique of Doppler ultrasound is similar to transabdominal ultrasound. The woman lies down on the couch with her back and exposes her stomach. The doctor applies a special gel to the area under study to improve the passage of ultrasonic waves and then moves the sensor along it, while simultaneously examining the data obtained on the monitor. An interpretation of the results is given to the woman on the same day.
Doppler measurements during pregnancy can be carried out in several ways:
- Doppler ultrasound is used to assess the direction, intensity, and nature of blood flow in the vessels.
- Duplex research differs from the previous method in being more accurate and informative. Used to assess vascular blood flow and their anatomy.
- Color mapping – the condition of even the smallest vessels and their patency is color coded.
Blood flow disturbance
Source: https://bebeku.ru/krovotok-pupovine-norma/
Indications for Doppler
Adequate placental blood flow ensures normal pregnancy. Impaired blood flow can lead to intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), therefore the main reason for prescribing Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy is precisely the discrepancy between the size of the baby’s body and/or organs and the norms.
It is not necessary that if blood flow is impaired, the child will lag behind in development, but the risk of an unfavorable course of pregnancy increases significantly. Well, and vice versa, if there is a suspicion of a developmental delay in the fetus, but the blood flow is not impaired, then in most cases this indicates that the woman is carrying a low-weight but healthy child.
Doppler ultrasound is also prescribed for:
- premature maturation of the placenta;
- pronounced oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios;
- umbilical cord abnormalities;
- Rhesus conflict;
- gestosis (late toxicosis, complicated by vomiting, severe swelling and increased blood pressure in a pregnant woman);
- the expectant mother has kidney disease, hypertension, diabetes;
- suspected chromosomal pathology;
- non-immune hydrops fetalis;
- uneven development of babies during multiple pregnancies (when there is a difference in their body weights of more than 10%).
If the fetus has heart problems, Doppler is performed together with CTG, the so-called Doppler echocardiography.
In case of fetoplacental insufficiency, Doppler measurements are carried out systematically every 2-3 weeks.
Also, if complications develop during a previous pregnancy, Doppler ultrasound may be prescribed during a subsequent pregnancy.
Preparing for the study and how it is carried out
Doppler testing in pregnant women is carried out according to indications, and is not a mandatory examination during the normal course of pregnancy. But more and more often, in antenatal clinics, all women, without exception, undergo Doppler ultrasound at 30-34 weeks to assess the condition of the fetus.
This procedure is painless and harmless to both mother and fetus. The principle of Doppler testing is the same as a regular ultrasound during pregnancy: a special Doppler sensor is moved across the abdomen, which is equipped with every modern ultrasound diagnostic device. Therefore, this type of research does not require special preparation.
Doppler is a visual assessment of blood flow (when an ophthalmologist observes a color and graphic image of blood flow velocity curves from the monitor screen).
Dopplerography is the same as Doppler, only the readings are additionally recorded on a tape in order to monitor changes (improvement/deterioration) in blood flow after treatment.
Interpretation of Doppler measurements
Uterine arteries (a. uterina dextra - right and a. uterina sinistra - left uterine artery, respectively).
The uzist must determine the nature of blood flow in both the left and right uterine arteries, because with gestosis it can be disrupted in only one artery.
Thus, by assessing the blood flow in only one artery, one can give a false conclusion, which will negatively affect the health of the baby and the expectant mother.
There is a scientific theory that if blood flow is disrupted in only one (mainly the right) uterine artery, a woman has a high risk of developing late toxicosis (preeclampsia) with all the negative consequences.
With gestosis, the blood flow in the uterine artery is first disrupted, and as the situation worsens, the blood flow in the umbilical cord arteries deteriorates. Therefore, if blood flow in the uterine arteries is disrupted, it is necessary to periodically repeat Doppler to monitor the situation.
To assess blood flow in the uterine arteries, the resistance index (IR or RI) is calculated.
Often, pregnancy-induced hypertension develops due to impaired uterine blood flow. The expectant mother's body independently increases blood pressure to increase blood flow into the intervillous space. This is how the mother, without realizing it, helps the baby. Thus, it is necessary to improve blood flow and hypertension will disappear on its own.
Impaired blood flow in the uterine arteries is when the value of IR, PI or SDO is greater than normal.
The pulsation index (PI) of the uterine arteries should be within the following limits.
Indicators in the right and left uterine artery may differ slightly from each other. If both indicators are within normal limits, then this picture is not considered a negative phenomenon.
Deviation of blood flow indicators from the norm in two uterine arteries at once indicates a violation of the uteroplacental circulation. This situation requires specific treatment - move more (regularly go swimming or do gymnastics for pregnant women).
Violation of blood flow in only one uterine artery indicates an asymmetry of uteroplacental blood flow. If the pregnancy proceeds normally and the baby develops in accordance with the term, then the placenta is fulfilling its functions.
You should be aware that at 18-21 weeks there may be a temporary disruption of blood flow in the uterine arteries. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that the adaptive physiological process of cytotrophoblast invasion has not yet been completely completed. Therefore, if abnormalities are detected in the uterine arteries, a repeat Doppler ultrasound should be performed after 2-3 weeks, i.e. observe the blood flow over time.
The systole-diastolic ratio (SDR) in the uterine arteries should be:
Umbilical cord arteries (a. umbilicalis).
To obtain true results, the study should be carried out only while the baby is at rest, and only when his heart rate is between 120-160 beats per minute. After all, physiologically it is so laid down that when the heart rate increases, the IR in the umbilical cord artery decreases, and vice versa, when the heart rate decreases, the IR increases.
Measuring blood flow in the umbilical cord arteries should be done while the pregnant woman is lying on her back! Assessment of the severity of umbilical cord blood flow disturbance cannot be objective when the expectant mother is positioned “on her left side.”
The umbilical cord should have two arteries and one vein. If there is an anomaly (a single umbilical cord artery), then the fetus may suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients, which is why it lags behind in weight and growth. But it happens that the fetus adapts to such an existence and does not experience a deficiency of necessary substances.
Such babies are born with low weight, but absolutely viable. Therefore, if there is one umbilical cord artery and the blood flow in it is not impaired, then there is no cause for concern.
But if the blood flow in a single artery is impaired, inpatient treatment should be carried out to improve blood flow and, if necessary, early delivery (if the fetus is severely delayed in development).
The most widely used method for assessing the nature of blood flow in the umbilical cord arteries is the resistance index. The readings in both umbilical cord arteries should be almost the same.
Impaired blood flow in the umbilical cord is when the value of IR, PI or SDO in the umbilical cord arteries is higher than normal.
The pulsation index (PI or PI) of the umbilical cord arteries must meet the following standards:
Registration of zero and reverse values of diastolic blood flow is pathological. This means that the fetus is in critical condition.
There are only 2-3 days left from the moment permanent reverse values appear until the death of the fetus, so it is necessary to perform a caesarean section as soon as possible in order to save the baby’s life. This is only possible starting from week 28, when the baby is viable.
Systole-diastolic ratio (SDR) in the umbilical cord arteries:
If the blood flow in the umbilical cord is impaired, then, as a rule, fetal development is delayed. If there is no developmental delay now, but the blood flow in the umbilical cord is impaired, then without treatment, the fetus may experience developmental delay.
Middle cerebral artery of the fetus (a. cerebri media). When the fetus suffers, an increase in the values of PI, SDO and velocity in the MCA is observed.
Maximum velocity (aka V max) in the fetal middle cerebral artery:
Systole-diastolic ratio (SDR) for the middle cerebral artery:
Fetal aorta. It emerges from the left ventricle of the heart, runs along the spine and ends in the lower abdomen, where the aorta divides into two iliac arteries, which provide blood supply to the human legs.
Abnormalities in the blood flow of the aorta can only be detected after 22-24 weeks of pregnancy.
Impaired blood flow is an increase in the values of IR, PI and SDO. Registration of extremely low values up to their complete disappearance is considered critical (indicating the death of the fetus).
- Changes in the aorta characterize the severity of intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
- Systole-diastolic ratio (SDR) for the fetal aorta:
Ductus venosus (DV). It is studied with enhanced Doppler assessment of blood flow.
During the study, it is necessary not to take into account episodes of hiccup-like respiratory movements of the child and active movement.
Indices are not used to assess the ductus venosus.
A diagnostic criterion for the pathological condition of the fetus is the presence of negative or zero blood flow values during the phase of atrial contraction. Zero or reverse values are recorded for fetal malnutrition, congenital defects of the right heart, and non-immune hydrops fetalis.
Even with critical blood flow in the umbilical cord arteries, but with preserved blood flow in the ductus venosus during the phase of atrial contraction, it is possible to extend gestation until the optimal time for childbirth.
Description of blood flow disorders and their treatment
1 A degree - disturbance of blood flow in the uterine arteries, while in the umbilical cord blood flow remains normal.
This degree of blood flow disturbance is not dangerous for the fetus.
Drug treatment for this condition is ineffective. Doctors still prescribe therapy with Actovegin and Curantil.
Don't see each other on occasion! In fact, if blood flow in the uterine arteries is impaired, it is more advisable to simply walk more often in the fresh air (breathing deeply) + eat right + move more (hiking, special exercises for pregnant women, morning exercises, yoga, swimming). And don't sit at the computer for hours! That's all the treatment is.
Grade 1 B – disturbance of blood flow in the umbilical cord arteries, and hemodynamics in the uterine arteries are normal.
This degree of blood flow impairment requires the use of blood thinning drugs to avoid developmental delay and fetal hypoxia.
In this case, treatment is prescribed aimed at improving blood circulation (the drug Placenta compositum, Curantil or Trental). Actovegin is prescribed as an antihypoxant that improves oxygen supply to the fetus.
A blood test for clotting ability (coagulogram) is also prescribed.
In case of increased blood clotting, it is necessary to take stronger blood-thinning drugs than Curantil (for example, heparin or a product containing acetylsalicylic acid).
Degree I of the disorder does not lead to fetal death. Systematic monitoring of the nature of blood flow is carried out (every 2 weeks) “plus” monitoring of fetal CTG (after 28 weeks of pregnancy). In addition, be sure to monitor the blood pressure of a pregnant woman.
2nd degree – simultaneous disturbance of blood flow in the uterine arteries and in the umbilical cord, which does not reach critical values (when blood flow is preserved in the venous duct).
In this condition, it is mandatory to prescribe drug treatment in a hospital, where round-the-clock monitoring of the condition of the fetus is provided. It is also necessary to monitor the state of blood flow by performing Doppler + CTG every 2 days.
In grade II, hemodynamic disturbances are rare, but cases of intrauterine mortality may occur.
3rd degree – critical disturbances of blood flow in the umbilical cord with intact or impaired blood flow in the uterine arteries. A critical violation is understood as registration of reverse diastolic blood flow or its absence at all.
The third degree of violation poses a danger to the child’s health, because in half of the cases the baby’s intrauterine death occurs. Therefore, if a 3rd degree of blood flow disorder is detected, it is necessary to urgently perform a cesarean section in order to save the baby’s life, because at this stage of the disorder, treatment is not effective.
Conservative (natural) childbirth in the 3rd degree can lead to perinatal death of the child.
Source: https://zaletela.net/zdorove/dopplerometriya-pri-beremennosti-kak-i-kogda-delayut-doppler-ego-rasshifrovka-i-normy.html
What to do to prevent blood flow disorders?
Gynecologists urge women at risk to prepare themselves for pregnancy in advance and prevent unplanned conception.
Choosing the right body position while sleeping helps fetal blood flow
If you are already pregnant, it is recommended:
- avoid emotional and physical overload;
- eliminate bad habits;
- organize nutritious meals for the pregnant woman;
- monitor daily walks and stay in a ventilated room;
- do special gymnastics for pregnant women, yoga exercises;
- control body weight, carry out monthly weighing and measurement of abdominal circumference;
- It is considered more beneficial to sleep on the left side; this position reduces pressure on the inferior vena cava, which runs to the right of the uterus, but in some cases, with stagnation in the kidneys, sleeping on the right side improves the outflow from these important organs.
Modern diagnostic methods and approaches to the management of pregnant women make it possible to prevent severe disorders. However, many possibilities depend on the woman herself and her desire to have a healthy heir.
Diagnosis of placental insufficiency
To preventively detect possible problems with blood flow, all pregnant women undergo diagnostics three times, which includes Doppler testing. Recommended periods for ultrasound examination: from 11 to 14 gestational weeks, from 20 to 24, and from 32 to 34 weeks.
Obstetric examination
Pregnant women who are at risk for the formation of placental insufficiency are subject to regular clinical monitoring. Particular attention is paid to the following indicators:
- Woman's weight. Exceeding this value often indicates hidden gestosis.
- Abdominal circumference and uterine fundus height. Deviation from the norm of these indicators in 50% of cases indicates a delay in fetal development.
- Uterine tone and bleeding.
- Fetal movement and heart rate. A decrease in these indicators indicates possible fetal hypoxia.
This diagnosis is used to determine the condition of a pregnant woman in the third trimester with compensated blood flow impairment. For this purpose, monitoring of the woman’s hormonal status is carried out, provided that the fetus has no signs of malnutrition (intrauterine retardation).
Laboratory tests include the following:
- Calculation of the amount of alkaline phosphatase in venous blood.
- Determination of oxytocin levels.
- Study of estradiol concentration in urine.
This complex name belongs to a painless diagnostic procedure that allows:
- measure the speed of blood flow in the veins and arteries connecting mother and child;
- determine the direction of blood flow;
- diagnose pathological changes before the appearance of external symptoms.
Additionally, you can evaluate the following indicators:
- The degree of aging of the placenta.
- Much or little water.
- Possible developmental defects.
- Fetal hypoxia.
- Genetic abnormalities.
- Signs of intrauterine infection.
- Refinement of the placenta.
Such an examination is carried out using additionally equipped ultrasound machines or special portable devices. Thanks to sensors that measure indicators, all data is reproduced on the monitor. During the diagnosis, a Dopplerogram is compiled, which shows the systolic-diastolic ratio of blood flow.
To diagnose placental insufficiency, the following are used:
- Assessment of fetal cardiac activity. In addition to simple listening with an obstetric stethoscope, the most accessible and common method for assessing fetal cardiac activity is cardiotachography, which is based on recording changes in fetal heart rate depending on uterine contractions, the action of external stimuli or the activity of the fetus itself in the period after 28 weeks of pregnancy.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). At the same time, the size of the fetus and its correspondence to the gestational age are determined, the location and thickness of the placenta, the correspondence of the degree of maturity of the placenta to the gestational age, the volume of amniotic fluid, the structure of the umbilical cord, and possible pathological inclusions in the structure of the placenta are assessed. In addition, the anatomical structure of the fetus is studied to identify abnormalities of its development, as well as the respiratory and motor activity of the fetus.
- Doppler. This is a variant of ultrasound examination, which evaluates the speed of blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, umbilical cord and fetus. The method allows you to directly assess the state of blood flow in each of the vessels in the second half of pregnancy.
- Laboratory methods. They are based on determining the level of placental hormones (estriol, human chorionic gonadotropin, placental lactogen), as well as the activity of enzymes (oxytocinase and thermostable alkaline phosphatase) in the blood of pregnant women at any stage of pregnancy.
Based on a comprehensive examination, a conclusion is made not only about the presence or absence of placental insufficiency, but also about the severity of such a disorder. The tactics of pregnancy management for different degrees of severity of placental insufficiency are different.
DETAILS: Cardiac arrhythmia during pregnancy ⋆ Heart Treatment
Impaired blood flow during pregnancy: causes of pathology
An ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound helps to identify deformities in the fallopian tube, artery or placenta of a pregnant woman. It allows you to detect problems associated with blood vessels and calculate the rate of nutrients and oxygen supplied to the child.
Placental insufficiency in pregnant women is a common occurrence, so every expectant mother needs to learn why blood flow is disrupted and what this may be associated with.
The following reasons are known in medical practice:
- pregnancy at a very early or too late age;
- little time has passed from the last birth to the current pregnancy;
- toxicosis in the later stages of pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- kidney pathologies;
- formations in the uterus of various nature;
- an intrauterine infectious disease is diagnosed;
- there have been abortions or miscarriages in the past;
- development of more than one fetus is observed;
- lack of iron in the body of a pregnant woman;
- atypical location of the placenta;
- Rh factor incompatibility;
- blood clotting disorder.
The causes and consequences of placental insufficiency are interrelated.
Treatment of pathology
The possibility of maintaining pregnancy with the help of conservative treatment remains with the degree of impaired blood flow Ia and b. The second degree is considered borderline, the third requires urgent surgical delivery.
Treatment takes into account the pathogenesis of disorders. To achieve results it is necessary to influence all links:
- In case of mild disturbance of microcirculation, Chofitol (with a mineral-herbal composition) is prescribed, in more severe cases - Actovegin, Petoxifilin.
- If a mother’s tendency to form blood clots and disrupt the aggregation properties of blood is detected, then drugs such as Curantil, Trental are indicated. They can improve blood flow through the vessels.
- If low blood pressure is detected, Venofundin, Stabizol, ReoHES are used.
- Vasodilators - No-spa, Eufillin in injections - eliminate spastic contraction of blood vessels.
- It is recommended to reduce the tone of the uterus with the help of Magnesia, the drug Magne B6, this acts as an antihypoxic way to improve blood flow.
- A group of vitamins with antioxidant action eliminates negative consequences (vitamin E, ascorbic acid).
Medications are prescribed by a doctor. If necessary, the woman is offered hospitalization. This allows:
- provide bed rest;
- Constantly monitor the progress of pregnancy.
If there is an effect of conservative treatment, the woman independently carries to term and gives birth to a child. If there are no results, doctors may decide to perform an early cesarean section. In the third stage, only surgical delivery is indicated.
Balanced and healthy diet
One of the integral areas in the complex treatment of circulatory problems is nutritional adjustment, which allows normalizing blood flow and actively resisting cholesterol and atherosclerotic deposits. In addition, a correct, balanced and vitamin-rich menu helps strengthen the immune system, helping to improve the body’s vascular system. When preparing your diet, it is important to adhere to the following rules:
- Minimize the consumption of fat-containing animal products, which affect blood quality and quantitative cholesterol criteria.
- Try to completely avoid street snacks, in the form of fast food and processed foods, fried and smoked foods, confectionery, and minimize sugar consumption by replacing it with honey.
- Avoid caffeinated drinks, carbonated drinks, and alcohol.
- Increase consumption of juices, fruit compotes, mousses, water.
- Include fruits, vegetables and grain ingredients in your diet.
When creating a menu that helps improve blood flow, it is important to know which foods thin the blood in order to include them in the diet as much as possible. These include:
- Watermelon contains a decent amount of lycopene, which helps improve blood flow in the vascular arteries and remove toxic components from the body.
- Potatoes, legumes and lentils normalize blood circulation due to their high content of vitamin B.
- Ginger is a storehouse of natural vitamins and microelements, promotes the breakdown of harmful fats and takes an active part in hematopoiesis, stabilizes metabolic processes in the body. Can be consumed by adding to tea or as a spice to salads and other dishes.
- Mustard, garlic, horseradish, and red pepper help reduce blood viscosity.
- Carrots, beets, apples, as well as buckwheat and rice help stimulate blood cycling.
When compiling a daily menu, it is important to calculate the calorie content of dishes, which will allow you to keep weight parameters normal, analyze the component composition of dishes in order to maximally satisfy the body in all the components, vitamins and microelements necessary for its life.
Preventive measures
The best prevention of vascular disorders is a healthy lifestyle. For people at risk, doctors recommend constantly using ointments and gels to improve the condition of blood vessels and maintain them in working condition. Products for external use often contain a plant base - horse chestnut extract, red grape leaves, biolavonoids, salicylates. The most popular drugs are Troxevasin Neo, Lyoton, Troxerutin, Venoton. They enhance peripheral blood circulation and improve the condition of vascular walls.
Women at risk of developing varicose veins should give up high heels and the habit of sitting cross-legged. As a preventative measure, you can use compression stockings. Flat feet require constant attention to your feet. They will benefit from daily massage.
https://youtu.be/14amGfQ9gtg
Drug treatment
Drugs that improve blood circulation in the legs should only be prescribed by a doctor. After questioning and external examination of the patient, he is sent for examination. Based on the results obtained, the doctor prescribes the necessary medications to normalize blood circulation in the lower extremities. So how can you improve blood circulation in your legs? To do this, use the following means:
- Angioprotectors. They are necessary to improve microcirculation, as well as normalize vascular permeability, so that normal metabolic activity returns to the walls. These include “Curantil”, “Persantin”, “Trental”, “Flexital”, “Doxy-Chem”, “Pentoxifylline”, “Radomin”, “Vazonit”.
- Low molecular weight dextran drugs. Thanks to such drugs, additional blood volume flows from the intercellular space into the bloodstream. As a result, blood flow is significantly improved. The following medications belong to this category: “Reomacrodex” and “Reopoliglyukin”.
- Preparations containing prostaglandin E1 (“Vasaprostan”). Thanks to them, blood flow improves and microcirculation is normalized. These drugs also help to expand blood vessels and normalize blood pressure.
- Calcium channel blockers, which even affect the blood vessels of the brain. These include: “Kordafen”, “Kordaflex”, “Adalat”, “Stamlo”, “Norvax”, “Plendil”, “Foridon”, “Latsipil”.
- Antispasmodics of myotropic action. With the help of such medications, blood vessels dilate and blood begins to circulate freely. In addition, they relieve spasms well. Such medications are “Mydocalm”, “Cavinton”, “Eufillin”, “Halidor”.
For some patients, lifestyle changes and non-drug treatments may not eliminate or sufficiently relieve the symptoms of poor blood flow in the legs. In such cases, doctors, taking into account the cause of blood supply disorders, prescribe drug therapy.
The following drugs are used:
- Antiplatelet agents (aspirin, clopidogrel) are drugs that prevent platelets from sticking together and forming blood clots. Doctors prescribe one of these drugs for atherosclerosis of the lower extremities. Side effects of aspirin include stomach upset and increased risk of bleeding; side effects of clopidogrel are headaches, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea or constipation, abdominal pain, bleeding.
- Anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin, Xarelto) are drugs that prevent blood clotting. These drugs are often prescribed for venous thrombosis, less often for arterial insufficiency of blood supply. The main side effect of anticoagulants is increased bleeding.
- Statins (atorvastatin, rosuvastatin) are drugs that help reduce the production of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the liver. By reducing cholesterol in the blood, the risk of formation and increase in atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels of the lower extremities is reduced. Side effects of statins include stomach upset, headache, nausea, and muscle pain.
- Cilostazol is a drug used for arterial insufficiency that helps increase physical activity, that is, it helps increase the distance a person can walk without pain. Cilostazol causes the arteries to dilate and increase blood flow in the legs. Side effects include headache, diarrhea and dizziness. Cilostazol should not be used in patients with heart failure.
- Pentoxifylline is a drug that improves blood flow in the lower extremities by reducing its viscosity. It is used for disorders of the arterial blood supply to the legs.
- Medicines for diabetes. Treatment of diabetes and careful control of blood glucose levels are necessary measures for patients with deteriorating arterial blood flow in the legs.
- Diuretics are diuretics that doctors prescribe for swelling and venous congestion in the legs.
- Diosmin is a drug that increases the tone of the venous wall. Used for varicose veins and thrombophlebitis.
Drugs to improve blood circulation in the legs
Causes of circulatory disorders in the mother-fetus system
- Disorders of placentation - the formation and functioning of the placenta. Such disorders can be primary - at the stage of pregnancy - placental abruption, lack of progesterone, defective uterine mucosa. The already formed placenta may also suffer. This is caused by disturbances in the coagulation system, infections, and trauma to the placenta.
- Coagulation system disorders - spontaneous and induced thrombosis. Blood clots block large and small branches of the vessels of the uterus and placenta.
- Intrauterine infections damage the placenta and trigger the formation of blood clots.
- Complications of pregnancy - Rh conflict, gestosis, twin steal syndrome, placental abruption, premature birth.
- Lack of nutrients and vitamins - in particular, iron deficiency - anemia.
- Maternal diseases - diabetes mellitus, hypertension, thrombophilia, vascular and vascular wall defects, heart and lung diseases.
- Exposure to harmful environmental factors - harmful working conditions, the effects of medications, smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction.
- Stress and nervous tension.
Glucometer for measuring blood sugar levels. The presence of diabetes mellitus in the mother can lead to circulatory problems in the mother-fetus system
Choosing the time and method of labor
If a woman is diagnosed with 1st degree of change in blood flow, regardless of whether it is subtype A or B, the pregnancy is prolonged and childbirth is subsequently carried out through the natural birth canal.
With grade 2 pathology, the condition is considered borderline and requires constant monitoring. If possible, they try to prolong pregnancy for as long as possible so that the respiratory system of the fetus has time to form and the surfactant necessary for the breathing of the newborn is produced.
If the therapy is ineffective or the pregnant woman is diagnosed with stage 3 disorders, the choice of specialists is on urgent surgical delivery.