What is this?
Steroid hormones are synthesized in the body from bile acids. Their synthesis is a chain of chemical transformations with complex regulation. Women are probably familiar with the sex hormone progesterone. Its effect on the reproductive system is one of the mechanisms that contribute to preparation for conception and maintaining pregnancy. Progesterone is produced in the ovaries, and during pregnancy in the placenta.
Progesterone metabolism occurs in the ovaries and adrenal cortex, and during pregnancy, in the placenta. When it is hydroxylated, that is, the OH group is added to the 17th carbon atom, 17 oh progesterone, or hydroxyprogesterone (17 OP), is formed. This is a hormonal substance that, through a series of chemical reactions, is converted into cortisol, testosterone or estradiol.
Normally, an increase in the synthesis of cortisol from hydroxyprogesterone occurs in stressful situations, when a feeling of fear appears. Its role is to prepare the body to “repel an attack.”
Cortisol is a stress hormone that is formed during the metabolism of 17 OP, causing an increase in blood pressure, a rush of blood to the heart and muscles, and the release of a large amount of energy due to the saturation of the blood with glucose.
A change in the amount of hydroxyprogesterone in the follicular phase of the menstrual blood cycle indicates a disruption in the production of other hormones (progesterone, cortisol, testosterone). This indicator is used to identify hormonal imbalances and clarify the diagnosis.
To do this, the level of the substance in the blood is determined in the follicular phase in women and at any time in men. By comparing the indicators with the norm, the presence of changes in hormonal levels is determined.
An increase in the concentration of hydroxyprogesterone occurs with an increase in its production from progesterone or a decrease in the formation of cortisol. Moreover, the rate of synthesis of sex hormones (androgens) usually remains the same.
This hormonal imbalance causes infertility in women, and if conception occurs, the development of frozen pregnancy, miscarriage, or placental insufficiency is possible. In addition, this can affect the gestation process and cause pathologies in the fetus.
This is due to the fact that if 17 OH progesterone is elevated, there is a hormonal imbalance in the body, most often expressed as a violation of the ratio of sex hormones and hyperandrogenism. Hyperandrogenism is the excessive formation of androgens (male sex hormones). This condition affects the maturation of eggs in the follicular phase and the maintenance of pregnancy.
Symptoms of hormone excess
Elevated 17-progesterone is manifested by the following symptoms:
- disorder of the monthly cycle (menstruation may not occur for several months);
- breast enlargement;
- weight gain, obesity;
- disruption of intestinal function (manifested in the form of constipation or diarrhea);
- the appearance of acne on the face;
- increase or decrease in blood sugar;
- intensive growth of body hair;
- the appearance of swelling in the legs;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- increased amount of cholesterol in the blood;
- development of osteoporosis.
Norms at different periods of life
In a newborn in the first days of life, progesterone is normally elevated. This is especially evident in premature babies. Then within 5-7 days it decreases and remains low until puberty. During the formation of sexual characteristics, an increase in the level of the hormone in the blood is observed.
In men of reproductive age, the amount of 17 OP in the blood is 1.55–6.4 nmol/l, and the values may differ in different laboratories. Usually, when conducting tests, reference values (normal values) are given along with the result for comparison.
In women with the onset of menstruation, a cyclic change in hydroxyprogesterone is observed, they correspond to the level of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), responsible for the synthesis of cortisol. Normal values in nmol/l throughout the cycle are:
- follicular phase - 1.25–8.3;
- in the ovulation phase - 0.9–4.3;
- luteal phase - 0.85–8.6.
Normally, 17 OH progesterone in the follicular phase should have low values. It rises slightly before ovulation. The peak of the rise corresponds to the maximum level of luteotropic hormone in the blood. Then the indicators decrease to a certain level. They remain this way until the end of the menstrual cycle, unless conception occurs.
In the case of fertilization of the egg and implantation, due to the functioning of the corpus luteum, the amount of hydroxyprogesterone increases. Its increase occurs throughout pregnancy and ranges from 3.35 to 33.5 nmol/l. A repeated decrease in the hormonally active substance is observed before childbirth.
The table shows normal values of 17 OD in ng/ml.
That is, hydroxyprogesterone gradually increases in the follicular phase, then its level remains stable until the onset of menstruation.
The role of progesterone in a woman’s body
This is an additional substance formed in the body as a result of a complex chain of synthesis of hormones of the adrenal glands and sex glands. Even a small amount of 17 He progesterone affects a woman’s reproductive ability.
The hormone 17 OH progesterone has the following functions:
- inhibits the production of gonadotropins by the pituitary gland;
- provides secretory transformation of endometrioid tissue;
- creates favorable conditions for implantation of an embryo in the uterus;
- neutralizes the effect of oxytocin;
- helps form fetal steroid hormones;
- has a positive effect on vascular endothelial cells;
- stimulates the development of glandular tissue in the mammary glands;
- regulates glycemic index.
In the first phase of the cycle, the substance is produced by the ovaries. Its concentration begins to increase in the middle of the cycle and remains unchanged during the second phase.
During fertilization, the level of 17 opc gradually increases. In the absence of conception, the concentration of 17 opc decreases until a new cycle begins.
The article will answer what 17 op hormone is, when it is necessary to take tests for its concentration, and what standards exist.
17-OH-progesterone (hydroxyprogesterone) is a transitional product that is involved in the metabolism of hormones and is produced by the body in different quantities in men and women. Abbreviated as 17 opk. Its production occurs in the adrenal glands and gonads. The formation of 17 OPA occurs due to the interaction of progesterone and 17 - hydroxypregnenolone.
Hydroxyprogesterone can be produced in the placenta and genitals, converted to androstenedione, which is the starting point for the formation of either testosterone in men or estradiol in women.
The number of 17 opcs changes under the influence of the time of day. Its highest level is observed in the morning, and its minimum in the evening and at night. In females, it changes under the influence of the menstrual cycle.
During ovulation, 17-OH-progesterone is increased. Then its level decreases, and with the beginning of a new phase the amount of the hormone begins to increase again. There is a strong relationship in the female body between the amount of this substance and the level of progesterone and estradiol. During pregnancy, the concentration of 17 opc increases.
This product performs the following functions:
- synthesis of cortisol and androstenedione;
- participates in the regulation of puberty;
- affects the menstrual cycle;
- affects reproduction (conceiving and bearing a child);
- helps to resist stress;
- influences sexual behavior.
Age also affects the level of this product in the blood. Its maximum level is recorded during the period in the mother's womb with the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy and immediately after birth.
17 – OH – progesterone is increased in a child if he was born prematurely. With the beginning of the first week of life, the hormone level decreases and gradually becomes the lowest.
During the period when puberty occurs, it grows and is set at its maximum in adulthood.
17 opcs are affected by enzymes. Even a slight change in them entails a negative effect of the hormone.
Some people confuse the concepts of progesterone and 17-OH progesterone. What is progesterone? Progesterone in women is called the pregnancy hormone. It is considered a full-fledged hormone, while 17 opc is a transitional hormone.
When there is an interruption in the functioning of hormones or when there is a strong increase in the adrenal cortex, the patient is sent to study the level of oxyprogesterone. These failures are present:
- for infertility, when there is speculation that the cause is hormonal imbalance;
- with increased body hair. They densely cover the face, chest, back and other places not typical for their growth;
- in case of interruptions in the menstrual cycle or no period;
- with assumptions about formations in the adrenal glands;
- during a course of treatment of the adrenal glands with steroids to establish the positive effect of the drugs used;
- if there is a suspicion of congenital hyperplasia (the process of increased production of cellular structure, resulting in a disruption of the metabolic process) of the adrenal glands in children;
- hormonal imbalances in males and females;
- to establish the existence of neoplasms in the ovaries.
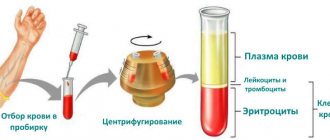
To study the hormone, blood is taken from a vein. A woman's 17-OH progesterone is examined in the follicular phase. In order for the result on 17 - OH-progesterone in the follicular phase to be the most true, you should donate blood on the fifth day after your period begins.
It makes no sense to carry out the blood donation procedure after the 20th day of the cycle, due to a decrease in hormone levels, and the obtained values will not be reliable. Children and men can donate blood any day. The analysis is taken in the morning, on an empty stomach.
You should not eat less than eight hours before your test. You are allowed to drink water in any quantity.
It is possible to determine the volume of hydroprogesterone only after testing. The specialist comprehensively studies all the results of 17 oxyprogesterone. The standards of 17 opk are given in the table below.
| Group | Norm in n mol/l | Norm ng/ml |
| Newly born | 0,7-2,3 | 0,23-0,75 |
| Child under 13 years old | 0,1-2,7 | 0,03-0,9 |
| Adolescence boys from 13 to 17 years old | 0,2-5,3 | 0,07-1,7 |
| Male | 0,9-6 | 0,3-2 |
| Teenage girls from 13 to 17 years old | 0,1-7 | 0,03-2,3 |
| Female gender during the follicular phase of the cycle | 0,2-2,4 | 0,07-0,8 |
| Female gender during the luteal phase of the cycle | 0,9-8,7 | 0,3-2,9 |
| Women during the first trimester of pregnancy | 4,1-9,5 | 1,3-3 |
| Female gender during the second trimester of pregnancy | 6,4-15,9 | 2-5 |
| Female gender during the third trimester of pregnancy | 15-,9-26,4 | 5-8,3 |
The limits of normal hormone values are wide. A slight change in its concentration is safe. Its indicators are always overestimated during pregnancy and in the second period of the cycle. Stress and nervous conditions provoke a jump in hydroxyprogesterone.
The results obtained can be attributed to one of three options:
- Option 1. 17 oxyprogesterone is contained in normal amounts. This means that the adrenal glands and ovaries are not the cause of hormonal imbalance.
- Option 2. High amount of 17 hydroxyprogesterone. 17 – OH – progesterone is increased in children who were born before the end of the pregnancy. It starts to decline after about one or two weeks. When it comes to a high concentration of this product in adulthood, the following pathologies may be present: there are tumor formations in the adrenal glands and ovaries;
- if the values are not too high, infertility and interruptions in the menstrual cycle are possible;
- 17 – OH – progesterone is increased due to an inherited defect of the adrenal cortex. The disease is transmitted genetically to a child due to a malfunction of one of the enzymes, which leads to active metabolism of hormones. Male newborns experience symptoms of virilization - enlargement of the penis and scrotum. In females, hermaphriditism manifests itself - a large clitoris and labia, which at first can be mistaken for the penis and scrotum. Children also suffer from metabolic problems that lead to deprivation of potassium and sodium salts.
- side effect from taking drugs containing progesterone.
Signs of elevated hydroprogesterone levels include excessive hairiness, oily skin, acne, and disruption of the menstrual cycle.
When treating an increased amount of 17 oxyprogesterone, therapy with hormonal agents (dexamethasone or methylprednisolone) is carried out. While using these drugs, weight gain is possible because they retain fluid in the body.
No other adverse effects are observed, since large doses are not used when used. The dosage regimen is prescribed exclusively by a specialist, taking into account the periods of the menstrual cycle and the symptoms of the disease. It is better to split the use of the product into several stages. The intervals between doses should be the same.
All medications are taken after meals. It is worth donating blood periodically to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
In the absence of proper treatment, disorders such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and heart problems can develop.
- Option 3. A low concentration of hydroxyprogesterone in the blood has a negative impact on health. Occurs when there is a lack of enzymes that take part in the synthesis of steroids in the adrenal cortex. Deficiency leads to: Addison's disease;
- pathologies of the adrenal glands that are acquired or present from birth;
- false hermaphroditism in men.
- When fertilization occurs with a low level of the hormone, the body does not receive information that it is necessary to prepare for bearing a fetus, and as a result, rejection of the fertilized egg may occur. In such a situation, spontaneous abortion occurs in the first trimester.
If a woman has problems conceiving a child, which lasts for a long time, she is referred for testing. They will show what level of hormones is in the body. If the values are too high and fertilization is planned, treatment is necessary. Typically, such women do not ovulate. When pregnancy occurs, low readings may indicate a high probability of miscarriage.
When 17-OH-progesterone is elevated in women in the follicular phase, testosterone levels increase, which interferes with fertilization.
In a situation where 17-OH-progesterone is low during pregnancy, it is necessary to conduct studies that will show whether the fetus is developing correctly. This value may indicate a non-developing pregnancy or other fetal pathologies.
The concentration of hydroprogesterone must be observed over time and then conclusions can be drawn. When 17-OH-progesterone is elevated during pregnancy, this indicates that the fetus is developing normally.
The state of the body is influenced by various combinations of hormones. An overestimated or underestimated level of 17 OPC does not always indicate pathology. According to the recommendations of doctors, it is necessary to periodically undergo hormone testing. Disruptions in the body can be avoided if the disease is detected in time.
How to get tested
17 oh progesterone is checked both when complaints or certain symptoms appear, and for preventive purposes or when certain diseases are suspected.
Indications for the purpose of analysis are as follows:
- hirsutism;
- acne;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- amenorrhea, other menstrual irregularities;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- infertility;
- miscarriage;
- suspicion of adreno-cortical syndrome, congenital dysfunction;
- tumors of the ovaries, adrenal glands.
Since the level of hydroxyprogesterone changes throughout the day - it is increased at dawn and decreases in the evening, blood is taken for analysis before 10 a.m., on an empty stomach. It is important to avoid stress, nervous and physical strain the day before and on the day of the examination, as this can lead to a false positive result.
Men can get tested any day. Women should be tested for progesterone 17 in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle on days 3–5. You can check the concentration of hydroxyprogesterone in the luteal phase, along with other hormones, since there are special tables with average data that determine the norm on any day of the cycle. But if a woman becomes pregnant and does not yet know about it, then the readings will be different, since during pregnancy 17 OP increases. Therefore, it is better to get tested in the first phase or make sure there is no pregnancy.
If hydroxyprogesterone is elevated, then you may need to check other hormones (progesterone, DHEA, testosterone) and undergo instrumental examination (ultrasound, CT, MRI).
Preparing for tests
For the study, blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach; the last meal should be in the evening .
It is allowed to drink boiled water, but you cannot consume any additives or drinks. Therefore, collection of materials most often occurs at 9–10 a.m., which is consistent with the main release of the hormone by the adrenal glands. The peak state allows you to more accurately determine the normal state of the body.
If a woman is just planning a pregnancy , or she needs examination for another reason, then you should pay attention to the norm of the menstrual cycle. The optimal time for collecting material is considered to be the period between the third and fifth day from the beginning of discharge. This corresponds to the first half of the menstrual cycle, when the hormone increases to its maximum value. It is believed that the value will be inaccurate if blood is obtained starting from day 6, and after 10 days does not provide the whole picture of changes.
If the reason for your visit is irregular menstruation , and there is no stable cycle, then when the doctor decides to donate blood for testing, it is considered the norm to do this several times. This will help doctors determine the dynamics of hormone changes and show the maximum and minimum normal values. It will also make it possible to predict the causes of disorders and select the correct treatment.
Article on the topic: Progesterone is the norm in women at different stages of life
Reasons for the increase
If 17 OH progesterone is elevated in the follicular phase, this may indicate various pathologies, so the analysis must be deciphered, taking into account not only the patient’s complaints and medical history, but also the indicators of other hormones. Most often, hydroxyprogesterone increases with the following pathologies:
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex
Occurs due to deficiency of enzymes involved in the synthesis of cortisol. Currently, cases of deficiency of 7 different enzymes have been described, but the most common are deficiencies of 21-hydroxylase and 11-beta-hydroxylase. The cause of the pathology is a genetic mutation. A deficiency of the enzyme leads to a decrease in cortisol in the blood and, through feedback, to increased production of ACTH, which stimulates the production of hydroxyprogesterone and its accumulation in the body. At the same time, androgen production continues, leading to hyperandrogenism. Signs of virilization, acne, hirsutism - hair growth, alopecia - loss, fragility, thinness of hair on the head appear. To clarify the diagnosis, hormonal levels are determined, stress tests for 17 OH progesterone, and genetic studies are performed.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
A disease associated with metabolic disorders due to instability of the endocrine system. Patients experience a change in the ratio of FSH and LH, increased secretion of testosterone and insulin. In the ovaries, ovulation does not occur; the follicles are transformed into numerous cystic formations that support the inflammatory process and cause sclerosis of the membrane. These are distinctive signs of pathology that are detected on ultrasound.
Itsenko-Cushing syndrome
A group of diseases in which there is a long-term effect of glucocorticoids on the body. The pathology is caused by increased production of AHTK, which can cause an increase in OP 17 in the blood.
Tumors
Tumors of the adrenal glands, ovaries, hormone-producing cysts. They also lead to hormonal imbalance through feedback.
Hypothalamic syndrome
It occurs as a result of injuries to the hypothalamus, psychogenic disorders, and during the restructuring of the body during pregnancy. May cause the development of Cushing's disease.
Taking progesterone medications
This is relevant for women with infertility who are indicated for IVF treatment.
There may be other causes of increased hydroxyprogesterone, so when choosing a treatment method, the patient should be carefully examined to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Reduced 17OH progesterone
The reasons for this phenomenon may be hidden in chronic diseases of the genitourinary system or taking a number of medications (eg birth control pills). Its amount is also influenced by factors such as stress, smoking, excessive drinking, and poor nutrition.
Hormonal imbalance manifests itself in nervousness, lethargy, mood swings, weight gain, headaches, soreness and swelling of the breasts, and menstrual irregularities.
Complications
When 17 OH progesterone increases, one of the main complications of this condition is infertility. Moreover, even the use of assisted reproductive technologies may turn out to be useless, since termination of pregnancy is observed in the early stages (miscarriage, fading). Often women request early miscarriages or frozen pregnancies for examination.
And when it is discovered that OP 17 in the follicular phase is increased, they begin to look for the cause of the pathology in order to carry out appropriate treatment.
High levels of this hormone can also affect other body systems. For example, it causes overstrain of the cardiovascular system, and if the problem is not corrected in time, the risk of developing myocardial infarction increases.
Due to the effect of the substance on brain tissue, in particular on the hypothalamus, patients often note memory impairment and forgetfulness. Long-term exposure can lead to disturbances in brain activity and the appearance of mental disorders, since the hormone affects the receptors responsible for taste, joy, and pleasure. Patients' mood changes and depression appears.
You need to be very careful when taking medications that contain progesterone (Utrozhestan, Proginorm, etc.). They are used in the treatment of infertility and IVF. The dosage must be strictly observed, since excess progesterone in the blood has an immunosuppressive effect. If for implantation of an embryo it is necessary to reduce the woman’s immunity so that the body does not reject the fertilized egg as a foreign agent, then the excess content of hydroxyprogesterone leads to defenselessness against infections.
When is treatment required?
Even if 17 OH progesterone is found to be elevated, treatment is not always required. If only one analysis is performed, in the follicular phase, an increased concentration of hydroxyprogesterone may be associated with the following situations:
- The reagents used in the laboratory are more sensitive, so you need to compare the indicators with reference values, and not with a table of standards, which are usually indicated next to the result.
- Before the test, the patient was nervous, and fear causes an increase in the secretion of cortisol and 17 OP.
- The subject is taking progesterone medications.
In such cases, there is no need to worry; you should take the test again, properly preparing for it. When blood is donated during the luteal phase, a high concentration may indicate that the woman is pregnant, and this should be clarified. During pregnancy, it is more difficult to determine whether 17OH progesterone is elevated, so treatment is carried out only if its values exceed the norm by 2-3 times.
If treatment was prescribed for infertility, women are often interested in whether it needs to be continued after pregnancy has occurred. In such a situation, the doctor is guided by the degree of increase in indicators and the gender of the child. Since high hydroxyprogesterone in congenital adrenal hyperplasia causes virilization, the level of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) should also be checked. And if it is high, treatment is prescribed only for high levels, for pregnant women carrying a female fetus, in order to avoid virilization and hermaphroditism.
Symptoms of hormone excess
Sometimes an increase in the hormone is observed in newborns, especially premature infants. But most often, after a week the indicators return to normal and remain until adolescence. And then the level rises to the normal level of an adult.
In addition to natural reasons for the increase in this hormone, there are also those that signal significant health problems, namely:
- dysfunction of the adrenal glands;
- formation of tumor formations in the ovaries;
- reactions to taking progesterone-based drugs.
In these cases, only treatment will help.
Some physiological reactions that were formed more than a century ago can also provoke an increase in progesterone: a stressful situation, a depressed mood, fear. If the central nervous system has received a signal about such conditions, then a large number of hormones are released into the circulatory system, including progesterone. Such a release leads to activation of the entire muscular system, and in case of prolonged stress, to muscle burning.
How to reduce
Before starting therapy, the cause of the pathological condition should be established. This may require additional clinical studies of progesterone, testosterone, and other hormone levels. They also conduct special stress tests to identify congenital adrenocortical insufficiency, ultrasound diagnostics, computer and magnetic resonance imaging. Once the final diagnosis is made, a treatment plan is developed.
Decreased progesterone in PCOS and tumors
Infertility due to PCOS requires complex therapy. For this purpose, combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are prescribed, which correct the menstrual cycle and hydroxyprogesterone levels. If pregnancy does not occur after correction, other methods of therapy are used - stimulation of ovulation or surgical treatment with dissection of the sclerotic membrane of the ovaries.
Treatment tactics for hormone-producing cysts, ovarian tumors or adrenal tumors are usually surgical. The pathological focus is removed surgically. For corpus luteum cysts, in some cases, conservative therapy with COCs is possible. Only after this do they plan to become pregnant.
Decreased hormone levels due to adrenal dysfunction
Congenital adrenal dysfunction is treated with glucocorticoids. The medicine, dosage and duration of administration are selected by the doctor.
Dexamethasone or Methylprednisolone tablets are usually prescribed. The dose of the drug is divided into 2-3 doses per day. Therapy is carried out until 17 OH progesterone decreases, then the dosage of the drug is gradually reduced and pregnancy is planned.
During gestation, the pregnant woman is under the supervision of a doctor. The decision to continue therapy during pregnancy is made individually in each case. If the level of hydroxyprogesterone remains high and exceeds the norm by 2-3 times, hormonal therapy is again prescribed, especially when the female gender of the fetus is confirmed. In severe cases, the drug may need to be taken throughout life.
Treatment for Itsenko-Cushing syndrome
It can also be treated either conservatively (hormonal therapy) or surgically. For example, for pituitary tumors, it is possible to irradiate the affected area or remove the tumor.
Since hormonal drugs are used to reduce the level of 17 OP, treatment must be prescribed and monitored by a doctor. It is impossible to correct hormonal levels by other means, but they can be used as an additional factor.
Nutrition for high progesterone
Traditional medicine uses infusions of rowan flowers, cloves (flowers, buds), carrot seeds, hogweed stem and others. But you can take them only after consulting a doctor.
Proper dietary nutrition can also speed up treatment. A diet for such a pathology should include a minimum amount of protein products and be rich in vegetables and fruits. Dishes made from carrots, potatoes, beets, onions, and legumes (peas) are healthy. It is also necessary to saturate the body with vitamin C, which is abundant in citrus fruits, fresh herbs, sea buckthorn berries, and raspberries.
An increase in hydroxyprogesterone levels indicates hormonal disorders that are associated with various pathologies that require treatment and correction. It can cause infertility and miscarriage. Treatment is selected depending on the cause that caused the hormonal changes.
How to increase 17-OH-progesterone levels
In order to restore the level of the hormone 17-OH-progesterone, drugs containing progesterone are used. These can be for oral administration (in the form of tablets) or topical application (in the form of suppositories). It is not recommended to use them on your own, since an incorrectly selected dose can cause other disorders. The drug and treatment regimen should be prescribed by a doctor after a face-to-face consultation and receipt of test results.
If the hormone level is slightly reduced, it can be adjusted by normalizing your lifestyle. First of all, you should eat right and introduce foods that contain a large amount of zinc into your diet:
- beans;
- wheat bran;
- rabbit and chicken meat;
- rice;
- citrus;
- some berries - black currants, raspberries;
- figs
Moderate physical activity can normalize hormone levels with minor disturbances
It is also necessary to give up alcohol and smoking. Moderate physical activity and healthy sleep are recommended.
https://youtu.be/SrMbLXfZQSs
Lowering the norm
In general, in women 17 hydroxyprogesterone is initially found in low concentrations. Under what conditions the hormone begins to be produced in large quantities is clear. What to do if there is a decrease in oxyprogesterone? Why is this happening? Should we panic?
Not really. But, as practice shows, quite often an increase in this hormone is observed. Its decrease may indicate diseases of the adrenal glands, for example. Both congenital and acquired. In some cases, 17 hydroxyprogesterone is found in small quantities if the body experiences a too short luteal phase. Also, low levels of the hormone indicate infertility. In fact, severe abnormalities in oxyprogesterone are a common cause of fertility problems.
Methods for increasing and decreasing hormones
So, in order to easily regulate the concentration of the studied substance in the body, it is necessary, as a rule, to take a variety of medications. By the way, if a person has been treated for a long time, then 17 hydroxyprogesterone increases. It is enough to simply stop taking pills and other medications, as soon as the hormone level drops to the expected norm.
In general, elevation is treated with various types of hormonal drugs. The most commonly prescribed medication is Dexamethasone. It should be taken carefully - excess weight gain is possible. Other hormonal medications are prescribed only by your doctor.
You can increase 17 hydroxyprogesterone either by improving your diet or by treating a particular disease. In some cases (most often this is the route recommended by doctors), a variety of hormonal drugs are also prescribed. In fact, if deviations from the norm are identified in time, then bringing oxyprogesterone to the desired level is not so difficult. Problems may arise during pregnancy. Then treatment comes down to traditional methods. Or the doctor prescribes the least dangerous hormonal drugs both to increase the hormone in the blood and to decrease it.
What are the dangers of low hormone levels?
Why should you be wary of a decrease in 17 hydroxyprogesterone when planning a pregnancy? The point is that this substance, as already mentioned, increases in an interesting situation. In fact, its sharp decrease is a pathology. A low concentration of the substance leads to the fact that the fertilized egg cannot attach to the uterus. This phenomenon either causes an ectopic pregnancy or leads to unsuccessful conception.
In the early stages of pregnancy, a reduced level of a hormone called 17 hydroxyprogesterone can lead to miscarriages, improper formation of the placenta, and fetal pathology. Fortunately, raising or lowering hormone levels is not that difficult.
Therapeutic measures
An increase in 17 he progesterone is usually eliminated with the help of hormonal agents. The most commonly prescribed synthetic glucocorticosteroid, which is a derivative of fluoroprednisolone, is Dexamethasone.
It can be found in pharmacy chains under the following trade names:
- Dexamethasone;
- Decadron;
- Dexazone;
- Dexafar et al.
In addition to specific properties, drugs of this class have anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive effects, and relieve symptomatic manifestations of allergies.
The course of taking the drugs is long and can take from 3 to 6 months. All treatment is accompanied by periodic tests to determine the concentration of the hormone in the body and the tendency towards its decrease.
Description
First you need to understand what substance 17 hydroxyprogesterone is. What is this anyway? This hormone is sometimes called “intermediate”. It plays an important role in the formation of various substances in the body. For example, progesterone. It is an intermediate steroid. Produced by the adrenal cortex.
In addition to progesterone, it promotes the formation of estrogen and androgen. Available in both men and women. But for girls 17, oxyprogesterone plays a more important role. Important for conception and pregnancy in general. Therefore, it is important to be able to determine the amount of this substance in the human body. For normal conception, both men and women must have sufficient amounts of oxyprogesterone.
What is progesterone responsible for in men?
- PG reduces the activity of aldosterone, a hormone that helps the kidneys create more concentrated urine and reduce the sodium content in it.
- The mammary glands are sensitive to PG and can change under its influence in both sexes.
- The skin also contains PG receptors. Its amount changes the skin's firmness, elasticity, and strength.
- Like other sex hormones, it affects sexual desire, sexual function, and fertility.
- In the nervous system, it participates in the creation of important proteins, neurotransmitters, and other hormones.
Drug therapy
Hormonal agents are used to lower progesterone in the blood. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Methylprednisolone and Dexamethasone. Side effects of the therapy include significant weight gain as a result of fluid retention.
When getting rid of infertility, the doctor never uses increased dosages of drugs. The treatment regimen is determined only taking into account the manifestations of the disease and necessarily the phase of the monthly cycle.
Medications must be used several times a day according to the established schedule. If there are disorders in the digestive system, taking medications after meals is allowed.
Drug treatment may include the use of combined oral contraceptives - Zhanina, Yarina, Anteovin. They improve well-being and have a beneficial effect on hormonal status.
Whatever the reasons for the decrease in the level of hormone 17 progesterone, it is necessary to take this pathology seriously. A long-term deficiency state can lead to dysfunction of the adrenal glands and their appendages, destabilizing the production of other equally important hormones - cortisol, testosterone, estradiol. Such failures can have a detrimental effect on a woman’s ability to procreate.
Treatment for insufficient levels of 17 progesterone involves taking medications whose active ingredient is progesterone. This is how the hormone deficiency in the body is replenished.
Pharmacological companies produce a number of medicines containing this hormone:
- Natural progesterone. Available in the form of injections for intramuscular or subcutaneous administration. Depending on the concentration, it may contain 10 or 25 mg of active progesterone.
- Utrozhestan. A drug in which the active ingredient is micronized natural progesterone. Can be used in 2 ways - orally and vaginally.
- Duphaston. A synthetic drug that is an analogue of the hormone progesterone. Depending on the diagnosis, the dosage is prescribed; the duration of treatment can be up to 6 months.
- Krinon-gel. Contains a high amount of progesterone and is a vaginal preparation. It is usually administered in the evening, starting from the 18th to the 21st day of the menstrual cycle. During pregnancy, it is used during the first month.
- Ingesta. Contains hydroxyprogesterone (minor progestin). It is administered intramuscularly daily.
Hormonal drugs of this class can be purchased without a prescription at the pharmacy, but this does not mean that you can take them yourself or replace them with analogue ones without consulting a doctor.
Application of hormonal properties
People appreciated the unique property of 17 he progesterone to endow a person with real superpowers in a very short time.
This hormone, or rather energy drinks and special nutrition with its addition, was used by athletes to achieve record results. The military used it in combat operations and testing equipment. The hormone and its derivatives have also found application in pharmacology. Based on them, a huge number of resuscitation drugs and drugs that promote recovery and regeneration have been developed.