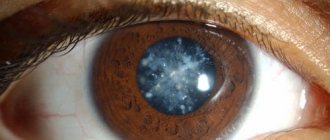
Glaucoma occurs against a background of persistently elevated intraocular pressure. This is a chronic ophthalmological disease with serious complications - narrowing of the visual field and damage to the optic nerve. Glaucoma cannot be completely cured; at best, it is only possible to maintain visual functions at a relatively acceptable level. Let's look at the causes of glaucoma, methods of prevention and reduction of intraocular pressure.
What is glaucoma?
The eye disease glaucoma is not a separately considered pathology, but a certain group of diseases that occurs with a simultaneous increase in internal pressure in the eyes, with a significant narrowing of the total field and angle of vision and complete atrophy of the nerve endings.
If the disease is not treated, the nerves in the eyes gradually die. In this case, the patient cannot be helped; irreversible blindness occurs.
Important! The main danger of this pathology is the complete absence of symptoms until the disease takes on a form that is difficult to treat.
This “asymptomatic” condition is based on the fact that the main cause of vision loss is increased eye pressure. An ordinary person does not feel such an increase; accordingly, the disease develops completely unnoticed. You cannot do without consulting a doctor during periodic preventive examinations.
If, during an examination, a doctor discovers a similar problem, it is important to urgently undergo the prescribed course of treatment and then lead a lifestyle that fully complies with the recommendations of specialists.
It is impossible to cure glaucoma, since at the moment there are no drugs invented to restore the organs of vision. The maximum that can be done is to keep the disease under control.
The earlier this problem is detected, the easier it will be to control. Based on this, we can conclude that regular examinations by an ophthalmologist are extremely necessary.
Development mechanism
In the pathological organ of vision, an increase in intraocular pressure occurs (in normal conditions, its levels should not exceed 20 mm Hg). The reason for the increase in IOP is the impaired circulation of aqueous humor, the production of which is carried out with the participation of special cells of the ciliary body. In a healthy eye, the daily volume of this fluid reaches 3–9 ml.
If the process of outflow of liquid substance is disrupted, it accumulates excessively in the chambers of the eye, which is fraught with an increase in IOP and subsequent glaucoma.
Causes of pathology
Glaucoma, a form of eye disease, occurs in all people. Social status, general level of education and gender do not matter here. Any person is susceptible to such a pathology. Despite this prevalence, there are several main causes and risk factors for the development of glaucoma:
- Age. The older the person, the higher the risk of developing this pathology;
- Race. Eye damage is less common in Caucasians. Representatives of the Mongoloid race are most often affected by the disease. Due to the structure of their eyes, in half of the cases a special closed-angle form of pathology develops;
- Genetic factor. The level of daily internal pressure and the risk of the appearance and development of pathology are directly related to genes. If relatives have been diagnosed with a similar problem, the likelihood of developing the disease increases by an additional 10%;
- Diabetes mellitus. Clinical studies have shown a connection between this disease and glaucoma;
- Reduced blood pressure every day. The lower this indicator, the higher the likelihood of pathology and a rapid decrease in the clarity and quality of vision;
- Myopia, which is often accompanied by an increased risk of glaucoma;
- Retinal diseases. If a person has suffered retinal detachment, if thrombosis has been noted in the eye vessels, the problem appears much more often.
Glaucoma is a rather unpredictable disease. It may not develop if all of the listed factors are detected and may appear in their complete absence. It is for this reason that the only option to prevent the development of pathology is to undergo an annual examination.
Types of surgical treatment
The Rascheskov Eye Surgery clinic uses several types of surgical treatment for glaucoma
Trabeculotomy ab interno
Microsurgical operation aimed at restoring the drainage system.
During the operation, through an ultra-small puncture in the cornea, drainage incisions are applied in a circle inside the canal wall using a special probe and an optical system from the inside (ab interno), which improves the outflow of the intraocular fluid.
As a result, the canal is cleared and the IOP is stabilized.
Cost – 25,000 rubles.
| Important! This operation is very effective even with organic changes in the drainage system. Can be used in combination with cataract phacoemulsification surgery |
Phacoemulsification
Cataracts and glaucoma are diseases of different nature, but very often they can coexist with each other. In many cases, the cause of increased IOP is the lens, which has disproportionately increased due to the development of cataracts and has shifted due to incompetent ligaments, which disrupts the outflow of IOP. Therefore, the first step at the stage of IOP decompensation is an operation to replace the natural lens with an intraocular lens (phacoemulsification).
This completely turns off the pathological mechanism, normalizes intraocular disproportion and improves the outflow of intraocular fluid.
At the same time, glaucoma can exist as an independent disease, and cataracts can develop later.
In any case, the situation when cataract is complicated by glaucoma requires timely surgical intervention.
The FEC operation consistently reduces the IOP level by 5 mmHg. Has high efficiency if there are no changes to the drainage system
Cost from 30,000 rub.
Stenting of Schlemm's canal with Glaucolight light guide
A microinvasive operation that is used to activate the natural outflow pathways of the intraocular fluid.
During the operation, a laser light guide is inserted into the drainage channel through a micropuncture. It removes the block inside it and helps to insert a thread, with the help of which the inner wall of the canal is expanded and the canal is held open. As a result, there is an increase in the outflow of intraocular fluid.
This surgical intervention best preserves the anatomy of the eye.
Cost 45,000 rub.
When operations that improve the natural outflow of intrauterine fluid are ineffective or in conditions that do not allow the natural outflow of intraocular fluid to be restored, technologies are used aimed at creating an alternative drainage system.
For this purpose, the Rascheskov Eye Surgery clinic uses the author’s patented technology for implanting the Ahmed GlaucomaValve drainage valve.
Ahmed valve implantation
The Ahmed valve is an intraocular pressure control device that is implanted inside the eye.
Allows you to create an additional reservoir for liquid and remove it behind the eye through a microtubule laid in the inner membranes of the eye.
Rascheskov Alexander Yurievich developed the Ahmed valve implantation technology, which can largely reduce the risk of postoperative complications.
This technology is patented (patent for the invention “Method of implanting a drainage valve to normalize intraocular pressure” No. 2434613 dated November 27, 2011.
Cost 50,000 rub.
Non-penetrating deep sclerectomy
A surgical intervention that allows you to restore the natural balance of fluid in the eye by creating alternative pathways for the outflow of intraocular fluid.
A special feature of NGSE is that to facilitate the outflow of fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye in glaucoma, through holes are not created, but surgically or with a laser, the peripheral portion of the corneal membrane, which has natural moisture permeability, is thinned.
NGSE can be combined with the implantation of special collagen drainages, which prevent tissue scarring and reduce the effect of surgery in the future.
In addition, it is NGSE that allows you to get rid of glaucoma in the early stages of the disease, when there are still no organic changes in the drainage system and optic nerve fibers.
Cost 25,000 rub.
Signs and symptoms of glaucoma
As noted above, one of the main dangers of the disease is the complete absence of symptoms at the initial stage of development. Even if a person is satisfied with his vision, even if he does not notice any pathologies, this does not mean that everything is completely fine with his eyes. To understand whether there are certain eye problems, it is worth asking yourself the following questions:
- Do both eyes see equally clearly?
- Does a network of blood vessels appear on the eye, do they often turn red;
- Are there moments of temporary complete blurring of vision;
- Is there a feeling of heaviness and pain in one or two eyeballs;
- Are there any difficulties in focusing vision at different viewing distances;
- Is there fatigue and eye pain?
- Do such unpleasant symptoms appear as nagging pain, the appearance of rainbow circles near light objects;
- Is the viewing angle being the same?
- Is there a feeling that the eyes look at the world as if through a hole;
- Has it become difficult to move around at dusk;
- Has your vision deteriorated over a one-year period?
If all of the above questions are answered in the affirmative, you must undergo an appropriate examination.
These signs are not a consequence of the development of glaucoma; they may be other diseases of the visual organs. Regardless of the cause that causes vision problems, treatment must be completed.
Prevention of glaucoma
Glaucoma cannot be completely prevented, but these steps can help detect it early, limit vision loss, slow its progression, and give you the opportunity to live a better life:
- You need to take regular eye care and see a doctor before permanent damage occurs. As a general rule, you should have comprehensive eye exams every four years starting at age 40 and every two years starting at age 65. More frequent screening may be needed if there is a high risk of glaucoma.
- You need to know your family's medical history. Glaucoma tends to occur in relatives. If a person is at increased risk, more frequent screening may be required.
- Exercises. Regular, moderate exercise can help prevent glaucoma by reducing pressure on the eyes. It is advisable to talk to your doctor about an appropriate exercise program.
- Taking prescribed eye drops regularly. Instilling eye drops can significantly reduce the risk of high pressure glaucoma. To be effective, eye drops must be used regularly, even if there are no symptoms - this rule must be remembered forever.
- Wearing eye protection. Serious eye injuries can lead to glaucoma. Safety glasses should be worn when using power tools or when engaging in hazardous sports. Preventing eye damage plays an important role in preventing glaucoma, and it is more important to protect yourself from it than to treat the consequences.
Foods you need in your diet to prevent eye disease: dark green, yellow and orange fruits and vegetables, lutein and zeaxanthin are especially important for healthy vision, fruits and vegetables rich in vitamin C, foods rich in vitamin E (eggs, fortified cereals , fruits, wheat germ, nuts, nut butters, vegetable oils, green vegetables and whole grains) and with vitamins A and , also include foods rich in zinc and omega-3 fatty acids.
It is very important to monitor the hygiene of lighting in the room, it is advisable to use table lamps, avoid too bright lighting, insufficient lighting is also undesirable, get rid of the habit of watching TV with the lights off, working on a computer, as well as sleeping in a completely dark room, normalize your routine.
An important point in secondary prevention of glaucoma is medical examination of patients by an ophthalmologist.
Types of glaucoma
Before prescribing effective treatment, a competent ophthalmologist will definitely conduct an examination. It is necessary not only to diagnose pathology, but to determine its type and form. At the moment, experienced ophthalmologists note 4 main types of glaucoma:
- The primary form of the disease occurs in people over 40 years of age. The main reasons for the development of the problem are all of the factors listed above, as well as standard age-related changes in the eyeballs;
- Secondary is a consequence of problems with the organs of vision, such as uveitis or more dangerous cataracts. Pathology can also develop after injury. As a result of these factors, the balance in the movement of a special intraocular fluid is disrupted, which automatically causes an increase in internal ocular pressure. Elimination of this form of pathology leads to complete normalization of indicators;
- Adolescent juvenile glaucoma. It makes itself felt from 3 to 35 years and is directly related to visual impairment;
- Congenital form of the disease. In this case, the pathology manifests itself in the form of congenital problems such as dropsy or buphthalmos, that is, bull's eye. A problem of this kind arises during the intrauterine development of the fetus. Among the reasons include special forms of genetic disorders, the development of intrauterine infection, injury and poisoning of the body.
The exact form of glaucoma can only be diagnosed and determined by an experienced doctor. Based on the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes quality treatment. If you strictly follow his recommendations, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing such a serious and irreversible consequence as blindness.
Causes
Considering the causes of the pathological process, the disease is divided into several varieties. Experts distinguish primary, secondary and congenital forms of the disease, each of which is characterized by its own provoking factors.
Primary
Primary glaucoma is characterized by independent development, independent of any pathologies present in the body. The process is mainly bilateral and affects both eyeballs.
The development of the primary form may be associated with the following factors:
- hereditary predisposition (if the mother or father has a defective gene, the probability of the pathology occurring in the child reaches 50%, if the disorder is present in both adults, the possibility of its transmission reaches 80–100%);
- age-related phenomena in the visual apparatus (after reaching the 40th birthday, microcirculation processes in the area of intraocular structures are often disrupted, due to which the outflow of intraocular substance weakens, IOP increases and glaucoma forms);
- dysregulation, fraught with improper functioning of the eyes, various parts of the central nervous system, improper circulation of aqueous humor and other negative phenomena;
- farsightedness, myopia, in which there is a significant susceptibility to glaucoma (despite the fact that IOP is often within normal limits).
The development of the primary type of pathology is also associated with race. Studies have confirmed that African Americans are especially prone to high intraocular pressure, which is why they are more likely to develop glaucoma.
Secondary
The development of secondary glaucoma is associated with existing damage to the visual organs. With this form of the disease, the pathology is mainly observed in the area of one eyeball, and the main symptoms tend to disappear after the provoking factor is eliminated.
Experts distinguish several types of secondary glaucoma - post-burn, traumatic, pigmentary, phacogenic, neovascular, postoperative and others.
Congenital
Pathologies that occur during pregnancy or childbirth lead to the appearance of congenital glaucoma. Such a disorder can be provoked by intrauterine anomalies, dysgenesis of the angle of the anterior ocular chamber.
The congenital form of the disease often manifests itself immediately after the baby is born. In some cases, it makes itself felt as the child develops and grows.
According to statistics, the congenital form of glaucoma is diagnosed in 80% of patients, while the primary and secondary types are detected in the remaining 20% of patients.
Main forms of pathology
The forms of the described problem directly depend on the shape and structure of the physiology of the eye.
Directly depending on the general structure of the eye, acute glaucoma, as a pathology, is divided into several types:
- Open angle is the most common form. This name is based on the fact that the area through which the fluid outflows is not blocked by anything. He has gone a little further, which automatically leads to an increase in the overall pressure in the eyes;
- Closed angle. With this form of the disease, the outflow tract is completely blocked. This form of pathology affects females approximately 4 times more often than males. Also most common in people of Asian descent;
- Mixed form. With the development of this form of pathology, a certain combination of different causes of increased pressure is noted. This form of the disease does not have severe symptoms;
- Normal pressure glaucoma is the most dangerous form of the described pathology. The reason is that it is quite difficult to detect even at a doctor’s appointment, since the main symptom is absent - increased eye pressure.
The form of the disease, as well as the type, can only be determined by a qualified specialist after conducting a competent, thorough examination. Based on the results obtained, the doctor prescribes the most appropriate therapy.
Kinds
Ophthalmologists distinguish between two forms of glaucoma: open-angle and closed-angle.
- Open-angle glaucoma is characterized by difficulties with the outflow of intraocular fluid caused by contractions of the spaces between the trabeculae of the pectineal ligament. Fluid accumulates inside, which in turn leads to increased intraocular pressure. The open-angle form is divided into pigmentary, primary and pseudoexfoliative.
- Angle-closure glaucoma in most cases occurs because the iris blocks the free flow of intraocular fluid. This form is diagnosed much less frequently than the open-angle form, and most often develops in older people.
Both forms of glaucoma do not have pronounced symptoms at an early stage, so the onset of the disease very often goes unnoticed, which delays diagnosis and treatment. There is also a division into primary and secondary glaucoma. Primary glaucoma occurs as an independent disease, secondary glaucoma develops as a result of an acute inflammatory process, mechanical trauma or an attack of diabetes.
Stages of development of glaucoma
In modern medicine, there are 4 stages of disease development. They can only be identified and installed through a thorough examination. Here are the characteristic signs of each stage of development of the pathology:
- Stage 1 - at this initial stage of development of the problem, the acuity and clarity of vision, the general boundaries of the viewing angle are slightly different from the norm;
- Stage 2 – there is a narrowing of the natural field of vision by about 10 degrees from the established norm. The level of contrast and natural twilight vision is also reduced;
- Stage 3 – the field of view is already quite significantly narrowed. The patient sees as if through a keyhole. At the same time, there is a decrease in visibility;
- Stage 4 is a special terminal glaucoma in which the eye completely loses central vision. He can only view the sides of pictures.
The transition of glaucoma from one advanced stage to another is accompanied by a deterioration in the overall health of the optic nerve, which gradually dies. Ophthalmologists record different changes in the nerve by color - from a pink healthy state it gradually becomes gray and white. This is direct evidence of the death of nerve fibers.
The development of the disease is also divided into several stages. The very first is preglaucoma, which is manifested by a rare increase in eye pressure. There is no decrease in visual indicators. The disease can also develop in a chronic form. In this case, increased intraocular pressure and fairly progressive vision loss will be noted.
There is also an acute manifestation of glaucoma. This is a serious emergency health condition that requires prompt consultation with a specialist and completion of the prescribed course of treatment. An exacerbation is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Severe, unbearable pain and pain in the eye;
- Exhausting headache in the eyeball area;
- Vomiting after nausea;
- The presence of circles before the eyes;
- Rapid loss of vision.
Important! If this condition develops, you should immediately contact the clinic. Spending three hours in this state is enough to irreversibly damage the optic nerve.
Symptoms of glaucoma
However, obvious symptoms of glaucoma appear quite late. However, they may not cause severe discomfort, but may manifest themselves in slight blurred vision or the appearance of a small rainbow halo when looking at light sources (for example, a light bulb or candle).
The truly problematic symptoms in the form of pain, redness and burning begin when the disease has reached the terminal stage and becomes incurable. The patient will not be aware of glaucoma until he notices a significant deterioration in vision. In some cases, vision declines so slowly that it goes unnoticed. Of course, this is typical only for open-angle glaucoma. Angle closure can manifest itself with an acute attack. The latter is accompanied by severe pain in the eyes, nausea, vomiting, bradycardia, headache, blurred vision or its complete absence. Taken together, the symptoms of a glaucoma attack can be mistaken for a neurological disease or severe poisoning, which makes glaucoma even more dangerous.
The open-angle form is also accompanied by attacks at advanced stages, but they are characterized by pain in the superciliary part of the head, eyes and blurred vision. Nausea and bradycardia rarely occur.
In general terms, the symptoms of glaucoma can be described as follows:
- an unpleasant feeling of “heaviness” in the eyes, accompanied by pain, stinging and narrowing of the field of vision (impaired peripheral vision);
- a feeling of moisture in the eyes, similar to increased tearfulness, as with colds;
- minor pain in the upper and lower eyelids, redness of the whites;
- stable vision deterioration at night and in the evening;
- “rainbow circles” when looking at bright light sources - lamps, lanterns, car headlights, etc.
- the appearance of a “mesh” before the eyes, loss of clarity, blurred vision.
If you notice these symptoms, you need to consult an ophthalmologist for a diagnosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
To prevent the development of glaucoma, you need to undergo a preventive examination at least once a year by an appropriate specialist. Many people neglect this rule, on the basis of which doctors are able to detect a disease that has already reached stages 3 and 4 of development.
These are periods when a person is faced with irreversible deterioration of vision, against the background of which he decided to consult an ophthalmologist.
To accurately determine the disease and to identify the stage of its development, experienced doctors use several mandatory techniques:
- Biomicroscopy is the study of the condition of the eye using a special slit lamp. All the signs of glaucoma development are very clearly visible here;
- Tonometry – measurement of intraocular pressure. The doctor measures each eye separately and compares the results;
- Study of natural visual fields. This is a mandatory element of the examination, during which the doctor can obtain the most accurate information regarding the width of the visual angle produced, characteristic of an individual eye;
- Modern gonioscopy is a check of the structure of the viewing angle of the anterior chamber of the eyeball. In this area there is a special drainage zone through which fluid naturally drains from the eye.
All of these are standard examination methods, with which you can detect obvious deviations and changes in the development of the disease. There are also more expensive examination methods. We are talking about HRT and OCT, which are special non-contact techniques of laser scanning and standard computed tomography. They can be used to measure the thickness of the fibers of the optic nerve and retina.
More modern and reliable research methods are rarely carried out in regular clinics, where regulations allow an average of 12-14 minutes for each patient. If you suspect glaucoma, you do not need to waste time and money on visiting a paid clinic. In a situation with glaucoma, it is very important to use modern medical equipment and conduct a comprehensive high-quality examination.
Diagnostic methods
How is an eye examination for glaucoma performed? Experienced ophthalmologists determine ophthalmotonus by palpation, but few doctors are capable of this. Most often, the disease is diagnosed using hardware methods - old and new. Modern clinics are equipped with the latest equipment for fundus examination.
Examination of ophthalmotonus is carried out using:
- Maklakov tonometer;
- electrotonography;
- pneumotonometry;
- pachymetry.
Maklakov tonometer is an old method for determining ophthalmotonus. First, the patient is instilled with a medicine that causes a temporary spasm of accommodation. This is necessary to stop the reaction of the lens to near/far objects. Then colored weights are placed on the cornea. Based on the condition of the weights, the ophthalmologist determines ophthalmotonus.
Electrotonography is a modern non-contact method for studying intraocular pressure and the quality of the hydrodynamics of the optical apparatus. Examination of the state of the visual organs with a pneumotonometer does not give a convincing result, so additional devices are used to clarify the diagnosis.
Pachymetry allows you to examine the thickness of the corneal layer. With thickening of the cornea, ophialmotonus is actually lower than the indicators of the devices, and with a thin cornea, it is higher than the indicators. Diagnostics is used to clarify hardware data. Patients are also examined using perimetry - identifying dark spots in the field of view. Many patients do not even know about them.
In what case are we talking about pathology of intraocular pressure? The indicators depend on the type of device used. On average, pressure up to 22 mmHg is considered normal, but there may be deviations.
Examination of the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye:
- gonioscopy;
- biometroscopy;
- tonography;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- other methods.
The functionality of the anterior chamber angle is determined by gonioscopy and biomicroscopy. The depth of the anterior chamber is examined, which allows you to determine the likelihood of developing glaucoma. Tonography examines the production and quality of circulation of intraocular fluid. Ophthalmoscopy examines the condition of the optic nerve in detail by dilating the pupil. For clarifying diagnostics, other hardware methods for examining the optical apparatus may be prescribed.
A single diagnosis of the fundus and the level of ophthalmotonus does not provide a comprehensive answer, so the diagnosis is carried out several times in a row.
Making a diagnosis is complicated by the structural features of the patient’s body. Each person has his own threshold for exceeding normal intraocular pressure, as well as the sensitivity of the optic nerve to pressure.
Main principles of glaucoma treatment
As noted above, glaucoma cannot be cured. If this disease has developed, you need to prepare for the fact that it will accompany the person throughout his life. The maximum that can be done is to keep the development of pathology under control. The overall treatment regimen is influenced not only by the effectiveness of previously prescribed therapy, but by such important factors as:
- The severity of the disease at the time of diagnosis;
- Estimated life expectancy of the patient. Relatively young patients are prescribed therapy that can lead to a maximum reduction in eye pressure.
Due to the fact that the main cause of the development of pathology is an increased level of eye pressure, therapy will be aimed at reducing pressure. With properly selected therapy, it will be possible to reduce the indicators by about 25%, which in turn will reduce the risk of rapid vision loss. To effectively reduce blood pressure, patients are prescribed a therapy regimen in the form of special drops that reduce blood pressure.
Important! These drops should be used every day throughout your life. It is unacceptable to miss a single dose of a drug prescribed by a doctor!
Unfortunately, many people neglect this rule, which automatically leads to complete loss of vision. If the patient regularly uses the prescribed eye drops for some time, and the pressure does not decrease, the doctor may prescribe a laser vision correction procedure or surgery. Each of the three glaucoma treatment options needs to be considered in more detail.
Laser correction of glaucoma
Laser treatment of glaucoma is one of the most advanced methods of getting rid of the disease. The operation is performed using local anesthesia. First you need to examine the condition of the whole body and take general blood and urine tests, and do an electrocardiogram.
The essence of the manipulation is that by controlling laser beams, the surgeon makes small holes in the cornea. Thus, aqueous humor is able to circulate freely, and the pressure is reduced.
Only the doctor can decide whether the early stage of the disease is an indication for laser treatment.
Treatment with eye drops
With the help of drops, eye pressure is influenced and effectively reduced. The effectiveness of such treatments is based on the fact that the drops tend to reduce the production of natural eye fluid. According to research, the less fluid there is in the eye, the lower the pressure will be.
The bulk of specialized eye drops work precisely on this principle. As an effective supplement for treating glaucoma, doctors prescribe eye drops aimed at improving the drainage of fluid from the eyes. If you use such drugs at the initial stage of the disease, you can quickly stabilize the pressure, thereby reducing the risk of blindness.
Early diagnosis of glaucoma is the key to fast and effective treatment.
One of the most important studies is ocular tonometry - a procedure for measuring intraocular pressure. The doctor monitors exactly how the level of pressure changes when exposed to the cornea. The procedure can be carried out contact or non-contact. For contact tonometry, preliminary anesthesia is necessary.
The doctor also conducts:
- gonioscopy – examination of the anterior chamber of the eye;
- direct ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus.
Early diagnosis of glaucoma using professional equipment allows you to begin treatment as soon as possible. In addition, other eye diseases can be detected at an early stage along the way.
Additional treatments
At the initial stage of the disease, in order to effectively stop the development of secondary pathology and eliminate unpleasant physiological symptoms, doctors often recommend light massage. Simple, not time-consuming movements will be an ideal prevention of glaucoma, as they significantly increase blood circulation in the eyeballs.
The essence of the massage procedure is quite simple. You will need to perform the following steps: Close one eye with a finger and massage it with light pressure in the direction from the apple to the temples for 30 seconds; The same is done with the second eye; The eyelids are closed and massaged for two minutes with the pads of the fingers.
Important! When performing these movements, it is strictly forbidden to press hard on the eyes.
Proper massage is an ideal prevention of the disease. You can effectively relax your muscles and promote healthy blood flow.
Symptoms of pathology
At an early stage of pathology, slight blurred vision often occurs. The first signs of the disease are mild, and pain is often absent.
Subsequent symptoms appear as:
- blurred vision;
- the appearance of various inclusions before the eyes;
- redness of the eyeballs;
- headache;
- photophobia;
- profuse lacrimation;
- soreness in the temples;
- increased eye fatigue associated with reading and computer work.
A pronounced sign of the development of glaucoma is a gradual narrowing of the field of vision - the space that a person observes around him. In the initial stages of the disease, there is a slight limitation of vision, to which the patient often does not attach due importance. As the pathology progresses, an increasing narrowing of its boundaries occurs, as a result of which a person is able to observe only a section of space located directly in front of him.
In the final stages of the disease, the signs of eye glaucoma become most pronounced. Patients develop so-called “tubular vision,” which resembles looking into a long tube, gradually turning into a state of complete blindness.
Acute attack of glaucoma
An acute attack of this pathology can be triggered by the presence of a variety of unfavorable factors:
- Severe stress, psycho-emotional experiences.
- Prolonged stay in the dark.
- Exacerbations of other ophthalmological diseases.
- Injection of mydriatics (drugs that help dilate the pupils) into the eye area.
The main signs of an acute attack of glaucoma include severe pain in the pathological eye, spreading to the temples, the corresponding part of the head, and the brow ridge. A typical symptom is the so-called “stone eye” - hardening of the eyeball caused by an increase in IOP. Other manifestations of an attack of the disease include:
- intense redness of the organs of vision;
- changes in the cornea, its acquisition of roughness, loss of normal shine;
- disturbance of visual perception;
- the appearance of halos around light sources and nebulae.
Often during an attack there is nausea, vomiting, resulting from the spread of impulses from the diseased eye to other organs and systems, pain in the heart, and bradycardia (decreased heart rate).
Chronic angle-closure glaucoma
This form of pathology is characterized by periodic exacerbations occurring with the following symptoms:
- inflammation of the eyeballs;
- sudden deterioration, blurred vision;
- the appearance of pain syndrome;
- dilation of the pupil (mydriasis);
- headache;
- general fatigue.
In especially severe cases, pain in adult patients can radiate to the abdomen and heart muscle.
Signs of the disease in children
Typical symptoms of glaucoma in children manifest themselves in the form of:
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- increased IOP;
- deterioration of visual function;
- changes in the area of the optic nerve head;
- an increase in the diameter of the cornea, its swelling;
- enlargement of the eyeball;
- slowing pupillary reactions.
If the disease is congenital, the appearance of other serious defects (heart defects, deafness, microcephaly) cannot be ruled out.
Summing up
Concluding this topic, it can be noted that glaucoma is a fairly serious disease that leads to disability. In this case, the prognosis can be quite favorable, but only if high-quality treatment is carried out.
Particular attention should be paid to certain preventive measures.
It is important to undergo regular examination by an ophthalmologist, especially in the presence of unfavorable heredity and the presence of somatic factors.
Reboots and all types of overwork are strictly prohibited. Another important preventive measure is the complete abandonment of bad habits; it is necessary to actively exercise in the gym. You need to work on a PC, read and watch TV only in very good lighting.
Classifications of glaucoma
Of course, it is extremely difficult to immerse yourself completely in the modern medical classification of glaucoma, especially without the appropriate medical education. We will present a more simplified diagram that is understandable to every person. It is customary to distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- congenital;
- primary;
- secondary.
Now we primarily pay attention to diseases that occur in people in old, middle age. Secondary glaucoma appears as a complication after injury, while congenital glaucoma accompanies a person throughout his life. It is important for us to learn how to diagnose early glaucoma based on its characteristic symptoms, so we consider in detail the primary form of this dangerous disease.
Diagram of a healthy eye and an eye with glaucoma
Here are the types of primary glaucoma known. Let's talk about the key characteristics.
| Type of primary glaucoma | Features of the disease |
| Open angle | Open-angle glaucoma is characterized by a significant increase in intraocular pressure. This occurs due to the deterioration of the outflow of fluid, which usually occurs through the drainage system of the eyes |
| Closed angle | In this case, access for intraocular fluid to a special filtering zone is blocked when the anterior chamber angle is blocked |
| Mixed form | With a mixed form of development of primary glaucoma, the outflow of intraocular fluid is simultaneously slowed down and the anterior chamber angle is blocked |
Classification of glaucoma
Angle-closure glaucoma
Experts note that the main risk is associated with the closed-angle form of glaucoma. This course of the disease is the most complex, as it is associated with great difficulties for the patient’s life. Many restrictions immediately arise that have a huge impact on everyday life:
- You can’t tilt your head too often;
- It is prohibited to work in places with elevated air temperatures;
- It is forbidden to strain your eyesight in the dark, twilight, or in poor lighting;
- It is imperative to strictly limit the amount of liquid consumed throughout the day;
- Any medications that cause pupil dilation or increased intraocular pressure are contraindicated.
The structure of the eye with angle-closure glaucoma
It is important to be extremely attentive to your health and take care of it. The thing is that any careless step, especially related to the use of medications, can easily lead to irreversible consequences and severe complications.
Risk factors
Let's outline the key points.
- You need to give up bad habits so as not to provoke an increase in blood pressure.
- You need to watch your diet and drink less liquid.
- It is extremely important to strictly monitor the use of medications. The most common cases are: doctors stop an attack, for example, of asthma or hypertension, by administering aminophylline. This is precisely what provokes an acute attack of glaucoma. In this case, the patient may completely lose vision.
The only conclusion that can be drawn is that you need to know that a person has glaucoma. Only then can measures be taken to prevent serious complications, including blindness, in time.
Stages of development of glaucoma
Symptoms of angle-closure glaucoma
Now we will briefly outline the key signs characteristic of the clinical picture of the course of angle-closure glaucoma.
- Vision begins to blur, objects become blurred.
- In the area of the brow ridges and in the eyes, pain occurs from time to time.
- The most important symptom is the appearance of bright rainbow circles around light sources and ordinary objects.
- The disease can occur cyclically. Periods of sharp exacerbation are replaced by relief, when the person begins to feel that everything is in order. In fact, the disease continues to develop at this time, and the condition of the eyes worsens.
- A detailed ophthalmological examination may reveal narrowing or even closure of the anterior chamber angle. During the period when intraocular pressure rises sharply, it is even possible visually, with a superficial examination, to determine the general redness of the eye and swelling of the cornea.
Angle-closure glaucoma
As you can see, the course of the disease can be quickly determined by the obvious symptoms of angle-closure glaucoma.
Difficulties in determining open-angle shape
When it comes to the open-angle form of the disease, the symptoms are quite hidden. And this is a serious problem. The patient may not even suspect the presence of the disease for a long time, and in the meantime glaucoma will actively develop. For example, the pressure inside the eye increases very slightly and reaches peak values slowly. And obvious symptoms appear only at the final stage, terminal, when the disease is already extremely difficult to cope with. The issue of early diagnosis of glaucoma, regardless of its type, in order to prevent the development of complications and vision loss is acute.
Open-angle glaucoma
Treatment with folk remedies
It is not necessary to refuse drug treatment, since it is quite possible to combine it with folk remedies. Is it possible to cure stage 4 glaucoma with these methods? At this stage, only surgery is suitable. But at the beginning, traditional medicine is quite suitable.
Duckweed will help in the fight against glaucoma - this is a grass that grows in water, it can be a pond or lake. It is necessary to wash several bunches of grass and grind them in a blender, after which you need to add two glasses of vodka to it. Next, the composition should sit for about a week. You should drink this infusion one teaspoon 2 times a day with any drink.
Coriander, cumin and dill, mixed in equal proportions, will also help against glaucoma. Brew one teaspoon of dried herbs and leave until completely cool, then strain. It is advisable to drink a glass a day, gradually increasing the amount. You need to take this decoction for quite a long time, but, as a rule, after it, glaucoma goes away forever. As mentioned above, dill is also useful for this disease. Just take a spoonful of seeds and pour boiling water over them, then boil for 5 minutes. At the end, you need to let the broth brew and drink half a glass a day before meals.
Who is at risk?
The main cause of blindness throughout the world is glaucoma (it becomes more active in the age group over 40). For safety reasons, it is necessary to know the main symptoms of eye disease in order to contact an ophthalmologist in time and avoid disability. It is worth noting that the absence of any symptoms is the most dangerous situation. Because only a qualified specialist can accurately determine that the disease that is plaguing you is glaucoma. Where and how can glaucoma be cured and can the secondary form be put into remission? Is therapy carried out at home or in a medical facility? It all depends on the state of vision and the age of the patient.
Dietary recommendations
A diet rich in beneficial microelements and vitamins and minimizing harmful foods that affect the health of the eyes and the body as a whole are the keys to successful prevention and treatment of glaucoma.
Skolkovo talked about the possibility of complete restoration of vision
A new drug for the treatment of vision was presented at the innovation center. The medicine is not commercial and will not be advertised...
Read completely
Prohibited products:
- alcohol;
- fatty, salty, smoked foods;
- strong tea;
- concentrated meat broths;
- pickled, soaked foods;
- baked goods, chocolate, sugar, other fast carbohydrates.
We recommend reading: Nutrition for glaucoma
It is advisable to include in the diet:
- fruits and berries, fresh vegetables (especially blueberries, blueberries, rose hips, cabbage, spinach);
- various oils (olive, sunflower, flaxseed, hemp, corn, peanut);
- fish;
- nuts;
- cereals, yeast;
- meat.
Vitamins
For eye health, preventing the progression of glaucoma and other ophthalmological diseases, it is necessary to receive beneficial microelements and vitamins:
- lutein;
- zeaxanthin;
- anthocyanins;
- selenium;
- vitamin C;
- B vitamins;
- vitamin E and A.
This can be done in two ways: enriching the diet with useful substances, taking multivitamin complexes. Pharmacy organizations offer drugs and supplements - Vitrum Vision, Blueberry forte regular and with lutein, Complivit ophthalmo, Visionace, Myrtilene and others.
Forms and stages of the disease
Home page » Main symptoms of glaucoma in the early stages. What do you need to know?
At this stage of development of ophthalmology, almost all eye diseases can be cured, it all depends on the degree of damage to the eye. It is better to treat any disease in the early stages, not to mention eye diseases. Therefore, it is important to know the symptoms of glaucoma in the early stages in order to be able to consult a doctor in time and begin treatment. Is it curable? Yes, only if you go to the doctor on time.
Glaucoma is an age-related disease. This diagnosis is mainly given to older people. Although, recently, the disease has become rapidly younger. The reason for this is poor, unhealthy diet, lifestyle, all kinds of stressful situations, injuries to the organs of vision, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Despite all the achievements of doctors in this area, glaucoma remains a serious ophthalmological disease. About 15% of patients lose their vision. The reason is the severe course and the reluctance of patients to seek help in a timely manner.
Pensioners in our country cannot afford expensive surgical treatment and adhere to a conservative method of treatment. They, in large numbers, fall into this fifteen percent.
What an ophthalmologist can offer from medications cannot stop the development of glaucoma, but only slows down the destructive processes. In the early stages, before starting serious treatment, such drugs are effective.
At first, glaucoma goes unnoticed; over time, the disease progresses and moves to other stages, and then symptoms begin to appear that are difficult to miss. By determining the stage, the condition of vision and the optic nerve can be assessed.
| Stage | Symptoms |
| initial stage | If glaucoma is detected at this stage and treated correctly, the chances of maintaining vision are very high. The disease only slightly changed the radius of the visual field and slightly deepened the optic disc |
| Developed | Field of view narrowed by more than 10 degrees on the nasal side |
| Far gone | There is a pronounced persistent narrowing of the field of view. A person may complain about the loss of some visual areas from the field of vision, and the quality of vision also deteriorates. Such changes usually take several years. |
| Terminal | Characterized by complete, irreversible loss of vision. Occasionally, a small piece of the visual field in the temporal sector is preserved |
Drugs used in therapy
Drops used to enhance the outflow of fluid inside the eye, narrowing the pupil and retracting the iris, which allows excess fluid to drain and thereby reduce pressure:
- Xalatan,
- Oftan
- Polycarpine,
- Travatan,
- Polycarpine hydrochloride.
A medicine of the same effect, which, among other things, is prescribed for corneal dystrophy, as well as for bronchial asthma, bradyarrhythmia, dry keratitis:
- Arutimol,
- Azopt,
- Niolol,
- Betoptik,
- Cusimolol,
- Timolol.
Combined drugs intended for the treatment of glaucoma, the purpose of which is to reduce the aqueous fraction of intraocular contents and improve their outflow:
- Fotil-forte,
- Fotil,
- Timpilo.
And the use of a drug such as Simax (methionyl-glutamyl-histidyl-phenylalanyl-prolyl-glycyl-proline), which is intranasal drops that quickly reach the brain tissue, which is very important for pathological changes inside the eye.
There may be metabolic failures in the tissues of the eye, which are especially typical for elderly patients, therefore, in addition to direct-acting medications, drugs are also prescribed that increase overall tone and strengthen the immune system. Such as ATP (adenosine triphosphoric acid), cocarboxylase, B vitamins and vitamin E.
Treatment of glaucoma without surgery requires compliance with certain conditions. This is a mandatory agreement with the attending physician on the list of absolutely all medications used.
If a patient has a disease of the musculoskeletal system and is prescribed chondroprotectors, then some drugs on the ophthalmologist’s list will either be contraindicated or cause side effects. The same applies to medications that help with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pachymetry and perimetry
To measure the thickness of the cornea of the eye, it is necessary to perform pachymetry. If the cornea is different in thickness, then, as a rule, the pressure inside the eye will be low. And finally, this type of diagnostics, such as perimetry, allows you to see dark spots on the patient’s eye. And the test will show their exact location; for this you need to use a bowl-shaped device called a “perimeter”. The computer, in turn, gives the person a signal that he should see the luminous point and inform the doctor every time he sees it.
Signs of illness
The deception of the disease is manifested in the fact that it does not appear until it becomes incurable. In the initial stage, it is much easier to cure. The occurrence most often occurs in middle-aged people who need to measure the pressure inside the eye for preventive purposes. The disease manifests itself in different ways. All patients are divided into 3 groups:
Symptoms of group 1:
- “flickering of flies” occurs in front of the eyes;
- severe eye fatigue during periods of eye strain.
2nd group:
- the perception of the eye becomes foggy over periods, objects are visible through a kind of veil, swelling of the cornea occurs, pressure in the pupil increases;
- Rainbow circles appear from light sources with the appearance of darkness, outlined by a “rainbow circle” of the entire spectrum of colors; in 75% of cases, glaucoma develops.
3rd group:
- the headache is similar to a migraine, pain in the temple with a pulsating character.
Onset of the disease:
- Watery eyes are a sign of early glaucoma. Its occurrence is associated with an imbalance in the replenishment and release of ocular fluid from the tissues in the eye, leading to increased pressure in the eyes. Hence the increase in fluid volume (tears).
- Sensation of wetness, filling the eye with an imaginary tear. When wiping your eyes, the handkerchief remains dry. The perceived hydration is proportional to the pressure in the eye.
When contacting an ophthalmologist, it is necessary to measure your blood pressure. Pay attention to families where there are relatives with glaucoma. There is heredity and predisposition here.
Glaucoma refers to diseases where the circulation of the eye fluid is disrupted. Accumulation of more eye fluid than removal. There is an increase in pressure. The blood vessels that supply nutrition to the retina, membrane and nerve are compressed.
The first signs are iridescent circles, a foggy field of vision, eye pain, pain in the temple, brow ridge. Peripheral perception is worse, the visual field narrows in a limited “tunnel”. The onset stage is characterized by changes in the parameters of the periphery and visual structure of the nerves. The features of the disease are weakly expressed or absent. At this stage, drug treatment is especially effective.
Treatment
It is impossible to completely cure glaucoma. You can only prevent or slow down its development. There are 2 main methods of treatment: conservative and surgical.
Treatment of glaucoma with drops
Conservative treatment mainly uses medications. Most often these are anti-glaucoma drops that improve the outflow of intraocular fluid, thereby reducing IOP. In the initial stages of disease development, they are a very effective method, but abandoning them leads to a sharp relapse. It is impossible to completely cure glaucoma with drops, and only open-angle glaucoma can be effectively treated. At this stage, characteristic changes in the structure of the visual organs have not yet occurred. The drops will have to be used throughout your life to prevent the disease from developing. Angle-closure glaucoma is practically not amenable to conservative treatment.
Surgery is more effective as a treatment method. But it does not eliminate the disease forever. Glaucoma surgery is performed on the eye if there is a risk of complete loss of vision. During the operation, new pathways are formed for the removal and movement of intraocular fluid, thereby reducing intraocular pressure. However, this effect is also temporary. Yes, after a long time, but still the disease returns due to narrowing or overgrowth of new channels.
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor, and the method depends on the form of the disease. By following all the doctor's instructions, the disease will not bother you. You should not skip routine examinations to prevent the condition from worsening, and if you experience any discomfort, you should immediately visit the clinic.
Complications
Having started the disease, the patient will almost certainly completely lose vision and it will no longer be possible to restore it. The sooner treatment begins, the fewer irreversible processes can be prevented. Also, in order not to provoke the development of the disease, it is advisable to follow a special diet prescribed by the attending physician.
Remember that the worst complication of glaucoma is complete loss of vision without the possibility of recovery!
Complications of glaucoma: damage to the iris
Prevention
To avoid the development of this disease, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist in a timely manner for routine examinations. Be sure to treat any diseases of the organs of vision. This is especially true for any injuries and cataracts. Be attentive to any changes in the lens and any pathology must be eliminated immediately.
A balanced diet rich in essential elements will also help. The diet must include protein foods. Light physical activity that stimulates proper blood circulation in the body. Including in the organs of vision, preventing oxygen starvation. But to prevent a sharp increase in intraocular pressure, you should avoid lifting heavy objects.
Symptoms of retinal detachment - everyone should know about this!
What is amblyopia and how often does it occur in adults, read this article.
Erosion of the cornea of the eye: https://eyesdocs.ru/zabolevaniya/eroziya-rogovicy-glaza/chem-opasna-boleznj.html
Therapeutic measures for angle-closure glaucoma
This type of glaucoma develops when there is an absolute impossibility of outflow of intraocular fluid through the drainage angle. The pathology can be congenital or acquired as a result of injury, while the iris or other structures of the eye block the exit to the trabecular meshwork and the intraocular fluid simply has nowhere to go. Is glaucoma treated in this case? Yes, and treatment is predominantly surgical. Medicines are used to relieve acute attacks of angle-closure glaucoma and before surgery to slightly reduce fluid production.
The main directions of intervention are the formation of another path for the outflow of moisture and the maximum reduction in its production.
Artificial channels are formed during the installation of fistulas and valves from the anterior chamber of the eye into the sub-Tennon space, where the intraocular fluid is drained.
Reducing the production of aqueous humor is achieved by transscleral cyclocoagulation. With the help of heat or cold, some of the ciliary cells are destroyed, affecting them through the layers of the conjunctiva and sclera.
Laser iridectomy (formation of outflow through a hole in the iris) is indicated if the patient has congenital acute-angle glaucoma. In this case, the operation is preventive in nature. With a closed angle, this operation allows you to quickly eliminate an acute attack of IOP growth.
Laser peripheral iridotomy is used for narrow-angle glaucoma to increase the angle between the iris and cornea to improve fluid removal
Physical unblocking of the drainage angle can be achieved using modern methods of laser gonioplasty, in which the iris is coagulated in the root zone. This stage must be followed by trabeculoplasty, otherwise the coagulation zone may grow again in the future.
After treating glaucoma with surgical methods, as well as while taking medications, regular examinations with a doctor are required. They are necessary to control IOP and take timely measures - replacing medications with stronger ones or adjusting the dose.
Causes
It is impossible to single out any one reason for the development of this disease. Optic nerve atrophy is classified as a so-called threshold disease: that is, a group of causes provoking the disease must accumulate before it manifests itself. Provoking factors can accumulate throughout life, which is why manifestation so often occurs in middle-aged and older people. The main predisposing factors include:
- Increased ocular or intracranial pressure. This is the main trigger for the development of glaucoma in children.
- Impaired circulation of intraocular fluid. Excess moisture accumulates, also causing pressure on the nerve.
- Improper or insufficient blood circulation within the visual system. Diabetes, atherosclerosis and hypotension are associated with this factor, when the capillaries either atrophy or become clogged, or the blood pressure is insufficient, the organ does not receive its norm of nutrients.
- Genetic predisposition. If a person has a family member who suffered from this disease, the risk of occurrence doubles or more.
- Any pathological changes in the eyes, ranging from ordinary myopia and astigmatism, entail the risk of developing this disease.
It is worth highlighting juvenile glaucoma and neonatal glaucoma. The latter manifests itself either due to genetic factors, or is associated with unsuccessful childbirth, and can act as a subtype of birth trauma. The juvenile form is diagnosed in persons over three and under thirty years of age, being quite rare, according to most ophthalmologists - genetically determined.
Diagnostics
Examination for glaucoma is uniform throughout the world; it consists of several stages:
- Visometry (visual acuity can reach an absolute value even in the case of tubular vision);
- Perimetry - the use of this method allows you to determine the relevance of even the slightest changes in the nature of the manifestation that are within the field of view;
- Capimetry - in this case, the study is focused on the area of the blind spot (that is, the area that is excluded from a person’s field of vision during normal vision);
- Biomacroscopy - allows you to determine the relevance of vascular dilation in the conjunctival area, emissary symptom (in which pigment is deposited along the ciliary anterior vessels), iris dystrophy, cobra symptom (in which dilation of the episcleral veins occurs in a funnel-shaped form until the sclera is perforated);
- Tonometry;
- Gonioscopy-inspection (makes it possible to determine the dimensions corresponding to the angle of the anterior chamber);
- Tonography;
- Ophthalmoscopy (the optic disc is examined to determine the relevance of excavation) in combination with examination using a Goldmann lens.
- Heidelberg retinotomography;
- Rheoophthalmography (makes it possible to determine the current degree of hypervolemia or ischemia in each eye);
- Stress tests (the method is focused on diagnosing angle-closure glaucoma, with pupil dilation and closure of the anterior chamber angle with the development of symptoms corresponding to an acute attack).
Each of these methods is highly informative, therefore, only one of them can be used in dynamic monitoring of the effectiveness of glaucoma treatment.
Principles of conservative treatment of glaucoma
Treatment begins with one of the first-choice drip medications. If therapy does not bring the expected effect, a replacement is made with the next first-choice drug, or a combination treatment is carried out with a first-choice drug and a second-choice drug, or two first-choice drugs.
If intolerance or contraindications to first-choice drugs are detected, treatment can begin with one of the second-choice drugs.
In the case of prescribing combination therapy, it is optimal to prescribe combined antiglaucoma drugs.
Drugs with an identical mechanism of action are not prescribed in combination therapy.
Long-term treatment requires periodic replacement of prescribed medications.
Antiglaucoma drops
I. Topical agents that accelerate the outflow of aqueous humor
1. Miotics
- The active ingredient pilocarpine is pilocarpine hydrochloride solutions 1%, 2%, 4% (Russia, Ukraine), Oftan Pilocarpine solution 1% (Finland), Isopto-carpine solutions 1%, 2%, 4% (USA), etc.
- The active ingredient is carbachol. Isopto-Carbachol solution 1.5 or 3% (USA).
2. Sympathomimetics
- The active substance is epinephrine. Solutions Glaucon 1% or 2% (USA), Epiphrine drops 0.5%, 1% or 2% (USA).
- Active ingredient: dipivefrin. Oftan-dipivefrin drops 0.1% (Finland).
3. Prostaglandins
- The active substance is latanoprost. Xalatan solution 0.005% (USA).
- The active ingredient is travoprost. Travatan solution 0.004% (USA).
II. Solutions that reduce the production of intraocular moisture
1. Selective sympathomimetics
- Active ingredient: clonidine. Clonidine solution 1.125%, 0.25% or 0.5% (Russia).
2. Beta blockers
- Non-selective adrenergic blockers (ß1,2). The active substance is timolol. Drops Oftan timolol (Finland), Timolol-DIA and Timolol-LENS (Russia), Timohexal (Germany), Arutimol (USA), Niolol (France), Okumol (India), Timoptic and Timoptic-depot - a form with prolongation action (Netherlands ), Cusimolol (Spain).
- Selective (ß1) adrenergic blockers. Active ingredient: betaxolol. Betoptik drops 0.5% and Betoptik C ophthalmic suspension 0.25% (Belgium).
3. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
- Active ingredient: dorzolamide. Trusopt solution 2% (USA).
- The active ingredient is brinzolamide. Azopt ophthalmic suspension 1% (USA).
III. Combination drugs
a. Active ingredients: proxodolol + clonidine, Proxofelin drops (Russia). b. Active ingredients timolol + pilocarpine, drops Fotil and Fotil forte (Finland). c. Active ingredients: pilocarpine + metypranolol, Normoglaucon drops (Germany). d. Active ingredients: dorzolamide + timolol, Cosopt drops (France).
When determining the tactics of drug treatment of glaucoma, the first choice drugs are: Timolol, Pilocarpine, Xalatan, Travatan.
Second choice drugs include: Betaxalol, Brinzolamide, Dorzolamide, Clonidine, Proxodolol, Dipivefrin, etc.
Secondary glaucoma
The manifestations of secondary glaucoma differ only in the accompanying symptoms, since it is provoked by other eye diseases. The causative factor may be inflammation, traumatic injury, circulatory disorders, pathological processes in nearby tissues, tumors and cysts.
Brain and mental disorders can also trigger the disease, but so far no single cause has been found. Based on the listed risk factors, the clinical manifestations of glaucoma can be very diverse:
- Unilateral glaucoma due to thermal, chemical, mechanical damage is accompanied by signs of pain, swelling of the eyelid, and swelling of the eye.
- Glaucoma, provoked by impaired blood circulation, is accompanied by progressive deterioration of vision. Complete blindness with inadequate treatment occurs within a year.
Glaucoma of various types and stages is a very complex disease that raises many questions among the best specialists in ophthalmology and surgery. It is almost impossible to completely prevent the disease, but every person with a predisposition to this disease or the presence of risk factors should know its first symptoms and accompanying manifestations.
Gymnastics for the eyes
Eye exercises are an unconventional way to improve the quality of vision, reduce the adverse effects of excessive visual stress on the eyes and relieve fatigue.
After each exercise, you need to blink for 50-70 seconds.
A complex of gymnastics for the eyes for glaucoma:
- slow rotation of the eyeballs clockwise, then in the opposite direction;
- initial position – completely relaxed eyes, then close your eyes tightly for 3-5 seconds, then return to the starting position and repeat 5 times;
- acupressure of closed eyes, temples, eyebrows;
- draw a bow using eyeball movements - to do this, first look at the upper right corner without turning your head, then at the lower right, upper left and complete the drawing at the lower left, slowly do 5-8 repetitions.
It is important not to make sudden movements when performing eye exercises.
Self-diagnosis
There is an opportunity to take a health test yourself and identify an eye disease, let’s get started:
How many positive answers do you have?
- Close your left and right eyes in turn and compare whether you see the same clear image (if you wear glasses, you don’t need to take them off)?
- Do you have a red vascular network in your eyes?
- Do you have a foggy haze in your eyes?
- Do you feel heaviness in your eyes?
- Is it difficult to focus your vision at different distances over time?
- Do your eyes get tired easily?
- Do you see bright circles around light sources?
- Does eye pain lead to headaches?
- Has your vision changed in the dark?
- Has your vision suddenly deteriorated?
If you have several positive answers, you should immediately run to the doctor. Since there is an obvious problem caused by an eye disease, it will be very good if it is not glaucoma, but something milder. But under no circumstances should you delay!