Giardia - what is it?
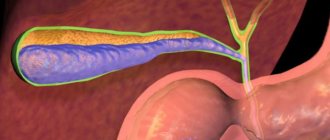
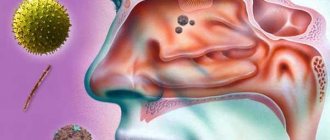
Giardia or Giardia are typical representatives of flagellated protozoa and have much in common with amoebas. These are microscopic pear-shaped parasites, their size is 10-20 microns.
Giardia is an intestinal parasite that attaches to the intestinal villi using a special disk. The parasite feeds on metabolized food, mainly carbohydrates.
Giardia forms:
- Cysts . The passive form allows Giardia to remain viable for a long time. The protective shell protects the parasite from adverse environmental conditions.
- Trophosite . Drooping into the human body, the cyst transforms into an active individual. The transformation occurs during the transition from the small intestine to the large intestine.
Giardiasis is diagnosed not only in humans, but also in many warm-blooded animals.
Giardiasis in children ranks 3rd among all parasitic infections, after ascariasis and enterobiasis.
Treatment methods
How to cure Giardia in a child? This disease is difficult to treat, so a doctor must prescribe therapy. If signs of Giardia appear in children, then independent use of folk recipes will not only not cure the pathology, but will also lead to its rapid development and deterioration of the baby’s condition.
For children under 10 years of age, only drug treatment for Giardia is indicated, prescribed by a physician based on the data obtained from the analysis. After this age, parents can try to cure their children with folk remedies, but only with the permission of a doctor.
The treatment regimen for giardiasis involves the use of toxic drugs, an overdose of which can adversely affect the functioning of the liver and kidneys. It is generally recommended to treat giardiasis in children with special antiparasitic medications. Among them, Macmiror and Metronidazole are actively used.
The dosage of any of the medications is prescribed by the doctor depending on the severity of the lesion and the stage of development of the parasites. Based on the same criteria, a treatment course is designated.
During the treatment of giardiasis in children, parents should under no circumstances change the dosage prescribed by the doctor, since lowering it may not bring a positive therapeutic effect, and increasing it can cause the development of complications and allergic reactions.
Getting rid of parasites is carried out as follows.
- A severe deterioration in the baby’s condition on the 5th day, which is caused by the absorption into the blood of a large amount of decay products remaining from dead parasites in the intestinal and liver areas. If this condition occurs, the child should take antihistamines and laxatives.
- Significant improvement on days 9-10 of therapy. At this time, the signs of lamblia in children begin to actively subside. Rashes on the epidermis, shortness of breath, paroxysmal cough disappear, lymph nodes become normal in size, stool returns to normal.
How to remove lamblia from a child after treatment? When parasites begin to die en masse in the body, the baby should be fed liquid food and fatty and high-calorie foods should be excluded from his diet. This dietary rule will allow the child to have bowel movements more often, eliminating waste products from his body.
Effective treatment consists of an integrated approach, for which the baby can be given an enema. Usually, against Giardia, in addition to medications, soda enemas are used, which can be easily prepared at home.
After completing the treatment course, parents should take the child for re-testing and make sure that all parasitic individuals and Giardia cysts are removed from the body.
How does infection occur?
The source of infection is sick people and animals who are carriers of the infection. Parasitic cysts are released into the environment along with feces.
Giardia enters the body of a new host through the oral-fecal route.
Routes of infection:
- untreated water;
- unwashed vegetables and fruits;
- food without proper heat treatment;
- dirty hands, toys, household items;
- contact with contaminated sand and soil;
- carriers of infection are flies and cockroaches;
- The habit of sucking a finger, biting a pencil, or nails contributes to the spread of pathology.
Giardia is resistant to chlorine, so you can become infected even by drinking unboiled tap water.
Giardiasis is mainly diagnosed in children aged 2-6 years. Boys get sick 2-3 times more often than girls.
What are Giardia and what do they look like?
Giardia (giardia) are single-celled flagellated formations that parasitize the intestines of mammals, some birds and humans. There are 2 stages of development of parasites: cystic and vegetative forms. The first is responsible for the distribution and entry of single-celled organisms into the host’s body, the second is responsible for the division and receipt of its nutrients.
Cysts look like immobile oval structures with a double shell. They are characterized by high resistance, allowing them to exist in the environment for a long time. If there is sufficient moisture in the summer, they can live in a reservoir for several months. Cysts are resistant to acid, so they are not destroyed in the stomach.
Adult Giardia are oval formations measuring 10-25 by 5-15 microns. In the photo you can see 4 flagella and a suction disk used for fixation on the walls of the small intestine. By attaching to the mucosa, giardia gain access to the nutritional components of the host’s body. Without experiencing the need for oxygen, they can parasitize for a long time and form new cysts.
Symptoms
Giardiasis is an intestinal disease. In addition to manifestations of damage to the gastrointestinal tract, allergic reactions and signs of intoxication occur during infection.
The severity of giardiasis in a child depends on the number of pathogens and the presence of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Signs of giardiasis:
- Malabsorption syndrome . Develops due to malabsorption of proteins, carbohydrates, microelements and vitamins.
- Disturbance of the digestive process . Parasites interfere with the normal production of enzymes.
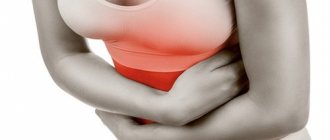
- Diarrhea . Giardia produces toxins, which leads to increased intestinal motility. Other dyspeptic disorders are also observed - abdominal pain, vomiting, flatulence, loss of appetite.
- Low-grade fever . Usually rises before bed every evening for 14 days. However, there are no other signs of a cold.
- Dysbacteriosis. Parasites absorb beneficial substances, which leads to an imbalance of intestinal microflora. Pathology manifests itself in the form of foul-smelling feces.
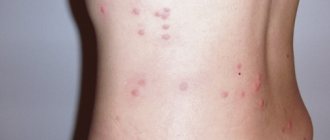
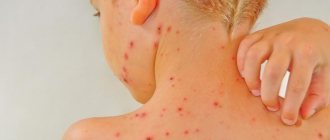
- Allergic reactions. Rash, itching, redness of the skin, rhinitis are a consequence of exposure to toxic waste products of parasites.
- Astheno-neurotic syndrome . Weakness, headache, dizziness, tearfulness, problems sleeping. Giardia is sometimes called the parasite of melancholy and sadness.
With giardiasis, intestinal manifestations are wavy in nature, and the symptoms of intoxication and allergies are constantly increasing.
In children under one year of age, infection with Giardia manifests itself in the form of bloating and severe flatulence. The feces are foamy, have a sour odor, and contain a lot of mucus and white lumps.
When infected with parasites, the synthesis of immunoglobulins is disrupted. This leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of preventive vaccinations.
Infected children often experience severe adverse reactions after vaccination.
How to treat Giardia in children?
Many doctors believe that treatment for giardiasis should be started only with prolonged diarrhea (more than 3 days). According to modern research, lamblia in the liver does not survive due to the aggressive effects of bile, so they cannot provoke the development of complications - cholangitis or hepatitis. Accordingly, asymptomatic carriage of microorganisms does not require drug therapy.
Pills
To cleanse the body of Giardia, a proven treatment regimen consisting of three stages is used:
- Preparatory. A week before taking the drugs, a special diet is prescribed. Allowed foods are lean meats and fish, boiled or stewed vegetables, kefir, cottage cheese, porridge. During this period, the child should not be given milk, sweet pastries, carbonated drinks, pasta, or chocolate. This diet helps cleanse the intestines and reduce the amount of vegetative lamblia. Additionally, sorbents are used (activated carbon, Enterosgel). The use of an enema is prohibited; it can cause additional damage to the intestinal mucosa.
- Taking antiparasitic tablets. To eliminate Giardia, drugs from the group of imidazoles or nitrofurans are used. The dosage and duration of treatment depends on the age of the child and the severity of symptoms. Usually the course of therapy does not exceed 7 days.
- Normalization of the gastrointestinal tract. During this period, enzyme preparations and probiotics are used to improve food digestion. It is recommended to continue the diet.
The effectiveness of treatment is assessed using a coprogram - there should be no parasite cysts in the stool.
Folk remedies
In alternative medicine, there are many methods to combat intestinal parasites. The most famous of them:
- Sagebrush. The herb must be dried and ground into powder. Take the resulting medicine 1 teaspoon with a large volume of water.
- Cucumber drink. To prepare it, you need to take large, ripe fruits, cut them into pieces and put them in a pan so that it fills it 25%. Then pour boiling water over it and let cool. Strain the infusion and take at least 0.5 liters per day. They can replace tea or compote.
- Use of black walnut tincture. You should take 1 tablespoon of tree leaves and brew in 1 glass of boiling water. Strain the broth and put it in the refrigerator. It is enough for a child to give 1 drop of tincture diluted in half a glass of milk or water.
- Pumpkin seeds. You need to eat 60-100 grams per day, the amount depends on the age of the patient.
Before using any of these methods, be sure to consult your pediatrician so as not to jeopardize your child's health. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing giardiasis is quite difficult; there are no tests that can confirm the presence of parasites with 100% accuracy. Doctors always prescribe a comprehensive examination.
Diagnosis of giardiasis:
- Coprogram. The presence of Giardia cysts in a child’s stool is a clear sign of the disease. But cysts are released on average after 8-14 days, so you need to donate stool several times with a week's break. Parasites can only be detected in fresh feces; within half an hour the cysts shrink, completely merge with feces, and are impossible to detect.
- FGDS . Trophozoids can be found in the duodenal contents of the duodenum. But if the parasites live in the lower parts of the small intestine, the result will be negative.
- Small intestinal biopsy . Allows you to assess the degree of damage to the mucous membranes and identify parasites.
- General blood analysis . Auxiliary diagnostic method. The presence of parasites in the body is indicated by a high level of eosinophils. With prolonged and severe course of the disease, hemoglobin decreases.
- Enzyme immunoassays - ELISA and RNIF. Promising diagnostic methods, their reliability is 90%. But tests are expensive, and they are not done everywhere.
Decoding ELISA
| Type of immunoglobulins | Meaning |
| IgM + IgG + | Appear in the blood 12-14 days after infection. After therapy, type M antibodies disappear, and G antibodies are present in the body for another 2 months after recovery. |
| IgM + IgG – | The indicators indicate acute giardiasis, no more than 3 months have passed since infection. |
| IgG + IgM – | Exacerbation of chronic giardiasis, or the initial stage of the acute form of the disease. |
To make the stool test for Giardia more reliable, you can carry out a provocation the day before. Give your child a decoction of corn silk, Cholevit, Macmiror, Metronidazole. These drugs increase the formation of cysts.
Giardiasis is becoming a fashionable diagnosis. Therefore, if your child is diagnosed with Giardia, do not be lazy to consult with another doctor.
Symptoms of the disease
It is known that this disease has several stages. When Giardia enters the child's body in large quantities, it enters the active stage and begins to multiply. If the immune system fails to cope, an acute form of the disease begins. Symptoms of giardiasis in children are very diverse. Depending on age and immunity, certain signs may appear:
- Abdominal pain, which is most often localized in the navel and hypochondrium.
- Disorders in the digestive system (prolonged diarrhea, which can be replaced by constipation, feeling of nausea, bloating). It should be noted that this is also how dysbiosis manifests itself, so another examination needs to be carried out to rule out a violation of the intestinal microflora.
- Lack of appetite, pallor, weight loss are the results of malfunctions in the child’s gastrointestinal tract as a result of Giardia infection.
- Restless sleep, grinding teeth during sleep – the toxins released by Giardia have a specific effect on the baby’s nervous system.
- Increased body temperature, most often in the evening, for more than two weeks without signs of a viral infection.
- Infants may develop skin rashes that look like diathesis or urticaria, the treatment of which does not have an effect.
- Another symptom that can be confused with other diseases is a dry, asthmatic-like cough and shortness of breath.
Please note that the disease can also be asymptomatic when the child is simply a carrier of the parasite.
All of the above can have an extremely negative impact on the child’s health, so studying the activity of Giardia in children, their symptoms and treatment is extremely important.
Features of symptoms in adolescents
In adolescent children, the presence of parasites in the body can manifest itself as symptoms such as dizziness, a feeling of nausea and motion sickness when traveling in public transport, frequent dizziness, and surges in blood pressure. Also, the course of the disease can be complicated by vasomotor rhinitis, when the vessels of the nose narrow. In the acute form of giardiasis, children may experience intestinal crises - sharp, cramp-like pain in the intestines, which can even be confused with appendicitis.
Treatment of giardiasis
In the treatment of giardiasis, broad-spectrum antiparasitic drugs are used. The duration and regimen of treatment is selected by the doctor individually, taking into account the patient’s age and weight, the severity of the disease, and the presence of chronic or concomitant pathologies.
Effective antiparasitic drugs:
- Nitrofuran derivatives . Macmiror, Furazolidone. The most effective medications to combat Giardia.
- Nitroimidazole derivatives. Metronidazole, Tinidazole.
- Benzimidazoles. Albendazole, Sanoxal.
Additionally, enterosorbents, enzymes, probiotics, and antihistamines are necessarily prescribed.
On the 2-3rd day of treatment, the child’s condition often worsens - nausea, itching, and rash bother him. These manifestations are caused by the massive death of parasites; a large amount of toxins enters the blood. To avoid severe intoxication, start giving your child Wobenzym from the second day of treatment. This drug contains enzymes that accelerate the breakdown of toxic substances.
Treatment of giardiasis is carried out in 2 stages, each of which lasts 10 days, the break between courses is 5 days.
Folk recipes
Since all antiparasitic drugs aimed at combating Giardia are toxic, many people are interested in the question: how to treat Giardia in children using traditional methods? There are several recipes for this, but traditional medicine cannot guarantee quick and complete disposal of these parasitic forms and their larvae. It is better to take these prescriptions in combination with drug therapy to alleviate the patient’s condition.
- How to get rid of Giardia using linden tree ash? To do this you will need a couple of thin branches of this tree. The branches need to be dried in the oven for half an hour, then the brushwood is crushed and burned. The resulting ash is sifted through a sieve. You should get a dessert spoon of the product. The ashes are divided into 7 parts. Every morning for a week, the child should be given one part of the ash mixed with honey. The ash is washed down with a glass of milk. This recipe increases the effectiveness of drugs in the fight against liver parasites.
- Aspen decoction. It will require buds, leaves or aspen bark. A dinner spoon of raw material is filled with a liter of water. Place the pan on the fire, bring to a boil and cook for half an hour. After preparation, the broth must be cooled and strained. How many times should you give your baby this drink? You should drink the decoction 2 times a day, half a glass. The course of treatment lasts 14 days. To find out how effective this treatment turned out to be, after a full course of traditional therapy, you should be tested for giardiasis.
- Cucumber tincture. To prepare the product you will need ripe cucumbers. 200 g of chopped cucumbers with seeds are placed in an enamel pan and filled with a liter of just boiled water. Next, they need to be left to infuse for 2 hours. During the day, the baby should drink half a liter of this cucumber infusion. The product is stored only in the refrigerator, the course of treatment takes 7 days.
Diet for giardiasis in children
Proper nutrition for giardiasis is an integral part of therapy. The diet helps improve the functioning of the digestive and immune systems, and prevents the proliferation of parasites.
Basics of a therapeutic diet for giardiasis:
- The basis of the diet is food high in fiber.
- Fast carbohydrates, which promote the growth of parasites, should be excluded from the menu.
- You need to eat food 4-6 times a day - small portions are quickly digested, nutrients are well absorbed.
- Giardia does not like foods with a sour taste.
- Dishes can be stewed, boiled, baked, steamed.
The duration of the diet is at least 12 weeks.
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
| Bran, buckwheat and oatmeal porridge in water. Baked vegetables - carrots, beets, zucchini, pumpkin. Fresh cucumbers and tomatoes. Pears, apples in any form. Citrus fruits, sour berries, natural juices, fruit drinks. Fermented milk products - kefir, yogurt without fillers, medium-fat cottage cheese. Low-fat varieties of fish and meat. Vegetable oils. | Milk. Any sweets, baked goods, baked goods. Sweet fruits and berries. Semolina. Sausages and pasta. Cabbage, legumes. Store-bought sauces. Smoked, fatty, salty, pickled foods, fast food. Radish, radish. |
Rice broth helps well with giardiasis; it should be given to the child 50-100 ml daily.
How to get tested for Giardia?
Coproscopy is a simple and painless diagnostic method. It involves detecting Giardia in a child’s stool using a microscope. For the study to be informative, it is necessary to adhere to the following rules:
- 3 days before the test, it is recommended to exclude meat products and red vegetables from the diet.
- Before collecting feces, you need to wash the child and wash the pot with soap.
- It is important to ensure that urine does not get into the stool.
- The resulting material should be placed in a sterile container and transported to the laboratory as quickly as possible.
Cysts of the pathogen are not always detected in stool the first time. In this case, you need to repeat the procedure after a couple of days.
The coprogram is necessarily performed at the stage of preparing the child for planned surgery: the doctor cannot perform the operation if Giardia is detected in the analysis.
…
Previously, the method of studying duodenal contents for the presence of Giardia was popular. This is a very unpleasant test: the child needs to insert a flexible tube through the esophagus and stomach into the duodenum to obtain a sample of bile and digested food. This method does not always help confirm the diagnosis, so doctors recommend choosing less invasive procedures, especially for children.
Modern methods for identifying lamblia have been developed:
- serological reactions (detection of antibodies to the pathogen in venous blood);
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) - it allows you to determine the DNA of the parasite in the stool, even in cases where coproscopy showed nothing.
To exclude other causes of the disease, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed.
Prevention of giardiasis
To protect your child from Giardia infection, teach him to follow a few simple rules.
Prevention methods:
- wash your hands frequently and thoroughly, especially after a walk, visiting the toilet, contact with animals, or playing in the sandbox;
- do not drink tap water, eat only washed vegetables and fruits;
- You should not bite your nails, pencils, suck your finger, or put various objects in your mouth;
- You can't eat on the street.
Parents need to wash and disinfect toys and the room several times a week. It is advisable to avoid swimming in unknown bodies of water.
Infection
Outbreaks of the disease usually occur in the spring and summer. Parasites are spread by the fecal-oral route. They pass not only from person to person. You can get infected from cats, dogs and guinea pigs. A child can easily pick up parasites simply by playing in the sandbox or after contact with an animal.
Infection can occur even during the process of caring for your beloved pets, for example, when washing the litter box. The habit of putting dirty fingers in your mouth and biting your nails can also cause the infection to spread. In order for giardiasis to develop in the body, the penetration of just one individual is sufficient.
Cysts can enter a child’s body in three ways:
- Water. When using tap water for drinking. Also, when swimming in a pond, a child may accidentally swallow water.
- Domestic. Parasites can live on toys, clothes, dishes, towels, door handles, and other household items. Pathogens can easily enter a child's body through unwashed hands. That is why, from early childhood, it is important to instill in children the rules of personal hygiene.
- Food. After eating poorly washed or insufficiently heat-treated foods. Experts recommend not only washing vegetables and fruits before eating, but also pouring boiling water over them.
Infection of a person with Giardia (shown in the photo) may not manifest itself in any way for a long time
Giardiasis is often observed in children who live in private houses with an outdoor toilet. An infected child actively spreads parasites around him. Through feces, Giardia gets onto the skin, and then onto personal items, water and food. Sources of infection are not only patients, but also carriers, as well as some mammals (dogs).
In order to become infected, it is enough to ingest a very small amount of cysts. A person with giardiasis excretes millions of parasites in their feces per day, so one can only imagine the likelihood of infection if hygiene standards are not followed.
Interesting! Experts note that if a child’s diet is dominated by a large amount of sweets and carbohydrates, parasites multiply much faster. If he eats more protein and plant foods, then the pathological process slows down.
It is not necessary that clinical symptoms appear after parasites enter the intestinal tract. A person can become an asymptomatic carrier of the disease. Several factors may influence the development of parasitic infestation:
- state of the immune system;
- presence of problems in the functioning of the biliary system. If there is not enough bile secretion in the small intestine, it will be easier for Giardia to take root;
- acidity level in the stomach. The lack of hydrochloric acid creates ideal conditions for the life of parasites.
When a carrier state develops, cleansing the intestinal tract from pathogens can occur spontaneously, without any treatment. In this case, self-infection should not occur. To do this, a person must properly observe the rules of personal hygiene. If parasites take root in the intestines and actively multiply, this causes digestive problems, inflammation and a lack of nutrients in the body.
Giardiasis can cause painful abdominal cramps. This occurs because pathogens irritate the nerve endings of the organ. Giardia metabolic products can provoke allergic reactions. In addition, these substances poison the body, causing signs of intoxication. An important aspect in the prevention of giardiasis is the fight against household insects: cockroaches, flies, bedbugs.
The risk of developing giardiasis in children increases in the following cases:
- incorrectly composed diet (insufficient consumption of protein foods);
- operations on the abdominal organs;
- weakened immune system;
- disturbances in the functioning of the bile ducts;
- reduced enzymatic activity in the gastrointestinal tract.
Why is giardiasis dangerous?
With timely detection and proper treatment, you can get rid of Giardia without serious consequences for the body.
Complications occur in severe and chronic forms of pathology:
- the liver and spleen enlarge;
- lymph nodes become enlarged and painful;
- sleep deteriorates, neurological problems appear;
- dyskinesia of the bile ducts develops;
- the duodenum becomes inflamed;
- cheilitis develops - inflammation of the mucous membrane and red border of the lips, seizures, peeling around the mouth;
- vitamin deficiency, anemia.
Severe forms of giardiasis are fraught with severe dehydration and significant loss of body weight.
Treatment regimen
It is necessary to begin treating giardiasis from the moment the pathology is identified. The basis of diagnosis is a stool test for oocytes, a complete blood count and immunological tests. Treatment of giardiasis in children consists of three main stages:
- Preparatory, aimed at reducing intoxication of the body. For this purpose, children are prescribed choleretic drugs, sorbents, and enzymes. At the same time, it may be necessary to use antispasmodics, as well as medications to strengthen the immune system. Diet plays an important role. Patients will have to give up simple carbohydrates. Sweets, flour products, and whole milk are strictly prohibited.
- Antiparasitic therapeutic therapy. At this stage, the attending physician selects medications individually. In many ways, the choice is determined by the child’s condition, as well as existing contraindications. The doctor describes in detail the dosage regimen, dosage, and duration of the treatment course. The disease in children can be cured with the help of drugs such as Metronidazole, Ornidazole, Macmiror, Furazolidone, Nemozol.
- Recovery stage. Its task is to strengthen the body's defenses and eliminate disorders caused by the pathological activity of Giardia. Children are prescribed multivitamins, as well as prebiotics to restore the gastrointestinal microflora.
A specialist will help you create a treatment menu. The basis of the diet should be vegetables, slimy porridges, dried fruits, and vegetable oils. Pumpkin and pumpkin seeds are considered a particularly valuable product for parasitic infections. To enhance peristalsis, it is recommended to eat greens, vegetable and fruit purees, and fresh fruits.
Compliance with the drinking regime is also important. A sufficient amount of fluid will help you quickly get rid of the symptoms of intoxication. Traditional treatment will help improve the child’s condition and speed up the recovery process. For giardiasis, cucumber tincture and a decoction of dandelion roots are very popular.
To prepare the infusion you will need seeds from an overripe vegetable. They should be mixed with crushed pulp and pour boiling water over it. To prepare a decoction, the crushed dry roots of the plant are poured with boiling water, boiled over a fire and consumed chilled and filtered.
So, the prevention of giardiasis lies in observing the rules of personal and general hygiene. Of course, it is impossible to ensure that a child does not put his hands in his mouth, but parents can teach him to comply with sanitary standards and strengthen the body. The prognosis of the disease is favorable with timely diagnosis. Effective treatment involves the use of antiparasitic drugs, adherence to dietary nutrition and strengthening the immune system.
How to detect Giardia?
Due to the lack of a clear clinical picture, diagnosis of invasion is difficult, which raises the question: how to identify giardiasis in adults? Currently, various types of laboratory tests are used for this. One of the simplest options is a stool test, in which cysts or a vegetative form of parasites can be detected. But since such studies are not always sufficiently accurate, doctors have recently given preference to immunological methods based on identifying specific antibodies in the blood. If Giardia is detected, it is necessary to immediately begin effective treatment.
Diet
Nutrition correction is an important part of the treatment. Doctors recommend giving up flour, baked goods, sweets, sweet fruits, milk and milk porridges, and products containing starch. It is also necessary to limit the consumption of canned food, smoked meats, fast food, spices, carbonated water, legumes and a number of vegetables (radishes, horseradish, garlic, radishes and hot peppers).
An acidic environment is considered unfavorable for Giardia, so it is necessary to include fermented milk products (not milk!) in the diet. You need to drink a lot of fruit juices, fruit drinks and compotes, but without sugar. You can eat a lot of berries, vegetables, sour fruits. The daily menu should include boiled and baked fish, meat, low-fat cheeses and unflavored yoghurts, and porridge without sweeteners. You should eat often, but in small portions.
Important! It is advisable to follow such rules for 4–5 months, then you can switch to the regular menu.
Giardia in the liver: symptoms in children
Thanks to blood circulation, it is easy for Giardia to reach the liver and settle in it.
This infection has some distinctive features and is expressed as follows::
- When examining a child, you can pay attention to his “coated” tongue. He is covered in plaque all along with the oral cavity. There are cases of no plaque. Instead, ulcers and acne are visible.
- The child may begin to vomit frequently. Vomit consists of food mixed with bile.
- When Giardia is localized in the liver, this organ enlarges, pain is observed in the right hypochondrium, spreading to the entire abdomen. Palpation reveals an enlargement of not only the liver, but also the spleen.
Giardia: methods of infection
How can you become infected with Giardia? The main routes of infection with Giardia are fecal-oral and contact-household. Parasitic cysts can be found on fruits and vegetables, or accidentally inhaled with soil particles. Giardia often affects natural fresh water reservoirs: rivers, streams, lakes.
If one person in any group is infected, then the cysts can get on household items and be transmitted by shaking hands. Therefore, outbreaks of giardiasis are often observed, especially in institutions such as hospitals, all kinds of medical institutions, kindergartens, and so on.
Drugs for treatment
For the treatment of giardiasis in children, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Antiparasitic.
- Sorbents.
- Nitroimidazoles.
- Benzimidazoles.
- Nitrofurans.
- Choleretic agents.
Typically, the following drugs fall into these categories:
- "Niridazole".
- "Furazolidone".
- "Tiberal".
- "Pyrantel".
- "Metronidazole".
- "McMirror."
The most popular drug is Macmiror for giardiasis in children. It is quickly absorbed and less toxic. Not a teratogen and not a carcinogen. It is prescribed not only to children, but also to pregnant women.
Only a doctor can prescribe medications. Do not give medications to children without consulting a doctor. With the correct selection of medications, giardiasis can be cured, but a violation of the treatment regimen and ineffectively selected medications can transform the disease into a chronic form.
Traditional treatment
The chronic course of the disease is quite difficult to cure with medications, or rather, it takes a lot of time. To speed up the healing process of children, parents use traditional methods. However, experts recommend combining folk recipes with traditional medications.
Horseradish
The horseradish-based product is prepared as follows:
- 2-3 roots must be washed well, dried, small roots removed, the top skin must not be removed;
- chop with a knife or grater, add cold boiled water so that the mixture fits into a 1 liter jar;
- after 72 hours, strain through cheesecloth, add May honey in the same amount and leave for another 72 hours;
- Stir the resulting product periodically.
Can be given to children from one year of age, but provided there is no allergic reaction to the components. Children are given 1 tsp. three times a day, older children - a dessert spoon, adults - 1 tbsp. l. You need to take the medicinal mixture for no more than 10 days; if necessary, the course is repeated every other week.
The product has received both positive and negative reviews from experts. The fact is that, according to dietary recommendations, it is better for patients to avoid all sweets, but this recipe uses honey. Therefore, before taking horseradish-based infusion, it is better to consult your doctor.
Horseradish has a bitterness that pathogens do not like
Garlic
To get rid of giardiasis, it is recommended to take an alcohol tincture based on garlic. Ingredient ratio 1:4 (by weight and volume). The slices are crushed, placed in a dark glass bottle and filled with diluted ethyl alcohol or vodka. After a week, the product can be used. Experts do not allow giving such alcohol tinctures to young children. For older patients, add 20 drops to water and should be taken before meals.
An effective recipe The recipe is as follows:
- Prepare birch tincture with cognac in advance. Wash the birch leaves, chop them, pour good quality cognac, leave for 7 days.
- After a week, strain and take 300 ml of tincture.
- Select several beets and carrots, wash, peel and squeeze out the juice so that you get a glass of each.
- Combine the juices and tincture and take a third of a glass 3 times a day.
Diagnosis of giardiasis
If a child is suspected of being infected with Giardia, a scatological examination of stool is performed. This laboratory method is not reliable enough, since often the material provided for analysis is collected incorrectly, which makes it difficult to identify the disease.
If signs of the disease are obvious and the scatological examination is negative, the doctor may order additional postgraduate testing of the upper jejunum or duodenum.
The most accurate methods for diagnosing the disease are:
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- duodenal biopsy
- immunoelectrophoresis
These research methods are indicated by the doctor as additional if there is a deterioration in the child’s condition and all the symptoms of the disease are present, and tests have not shown the presence of parasites in the biomaterial.
Containers for testing biomaterial for giardiasis
What does lamblia look like?
The simplest single-celled microorganisms are not visible to the human eye; they are detected only in laboratory tests. Giardia is a flagellated parasite, and this is how they look under a microscope with high magnification - like flagella digging into the mucous membrane. But in this form they do not live long - they need to degenerate into cysts with active vegetative abilities.
Penetrating into the large intestine, Giardia is transformed into the form of cysts, which leave the intestine with feces. Leaving the body, Giardia dies very quickly, but the cysts live in the outdoor environment for up to 70 days, especially if the environment is humid. Once in the water, cysts live up to 3 months. They have an oval shape up to 1 mm, which is 2 times the size of Giardia. But the cysts are immobile; Giardia requires them only for reproduction.
What kind of parasites are these?
Giardia are protozoan parasites from the helminth family. They rarely affect an adult organism, since a person has already developed normal immunity, which does not allow these protozoa to survive in the internal environment.
Children's immunity is not yet sufficiently developed, it has weak protection against any helminths, and Giardia easily coexists in the child's intestines. They penetrate the intestinal mucous membranes of babies. Giardia infection is common in children's institutions, where many children can be carriers and distributors of these parasites.
Treatment of Giardia in children is offered by Dr. Komarovsky, who is familiar with the symptoms of damage to the child’s body by these protozoan parasites.