Not all diseases of the gynecological tract are manifested by an immediate reaction of the body after infection.
There are dormant infections that steadily progress and lead to the most dramatic consequences.
Such diseases are often caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
It provokes not only the formation of unpleasant condylomas on the skin.
But it also directly affects the likelihood of developing cancer in women.
To eliminate the negative impact of HPV on the body, it is necessary to carry out timely diagnosis of the disease and antiviral therapy.
What is HPV
HPV (human papillomavirus) is a well-known disease among women and men. Almost 8 out of 10 women face this problem in their lives. The infection is dangerous because it may not show itself for quite a long time, and the consequences can be very distressing. This virus can become an impetus for the development of cervical cancer.
HPV usually infects the upper layers of the epithelium, which begin to multiply at a high rate, which often turns into cancer.
Who is at risk?
How is it that there are so many carriers of HPV, but not everyone suffers from unpleasant growths? In order for the mechanism of the virus’s influence on a human cell to start, a favorable condition is necessary for this. This is a decrease in the immunity of the infected person, a weakening of the body’s condition against the background of any external or internal shocks. The people most at risk are:
- addicted to smoking, alcohol, drugs;
- obese;
- patients with type 2 diabetes;
- those who suffered an illness on their feet or simply treated the symptoms without eliminating the cause;
- who is in a state of depression, moral depression, constant stress, with neuralgic disorders;
- pregnant women;
- teenagers in adolescence;
- with disrupted hormonal levels;
- with immunodeficiency;
- have recently undergone surgery;
- having promiscuous sexual relations.
As you may have noticed, the main factor in the activation of the virus in the human body remains the inability of the immune system to identify and neutralize the enemy in time. It is easy to draw logical conclusions from this - in order for the body to remain clean from unpleasant warts and dangerous papillomas, you must always monitor your health, keep it in good shape and not weaken the immune system even during periods of lack of natural vitamins.
Obesity creates preconditions for the development of the virus
Etiology of the disease
Human papillomavirus belongs to genus A of the family Papovaviridea. During the replicative cycle (penetration into a cell and influence on its DNA), the viral genome produces up to 10 proteins, of which E6 and E7 are cancer-forming. All strains of the human papillomavirus are divided into three categories according to the risk of developing cancer:
- low degree - strains 6, 11, 42, 43, 44;
- medium - types 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 58;
- high oncogenic activity - 16, 18, 45, 56.
If the first two types require only removal of the tumor from the surface of the body, followed by procedures to increase general immunity, then if any virus from the last category is detected, constant dynamic monitoring by an oncologist is necessary.
How is HPV transmitted?
It is believed that this virus is sexually transmitted and even condoms do not guarantee complete protection against HPV. Gynecologists assure that condoms still reduce the risk of catching this virus. According to research and statistical data from epidemiologists, women are often infected with the papilloma virus in the first 2 years of sexual life.
Many people know that most types of HPV are transmitted sexually. It is much less known that the risk of infection and the severity of the consequences are greater in women than in men.
Moreover, the risk of getting HPV in girls is lower with age, which cannot be said about men. At the moment, scientists have identified almost 150 types of HPV, which are divided into four classes. A number of studies have also been conducted, the result of which was the conclusion that HPV can also be transmitted through household contact. Due to this type of transmission of the virus, a person does not realize that he is already a carrier of HPV.
Prevention
It is impossible to rid yourself of the risk of getting HPV into your body.
Compliance with the following preventive measures will reduce the likelihood of activation and replication of the virus:
- Normalization of sexual life - close relationships and sexual contacts only with trusted and permanent partners;
- Providing protection against sexually transmitted diseases using barrier protection;
- Active sports and giving up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Visiting a gynecologist at least once a year and undergoing preventive tests;
- Compliance with the norms and rules of personal hygiene , as well as ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet;
- Ensuring sufficient rest , avoiding stressful situations and emotional fatigue;
- Proper education of girls from a very early age.
Symptoms of HPV in women
Gynecologists most often detect HPV in women. We figured out what it is, you should also familiarize yourself with the symptoms. The fundamental symptoms of this virus are growths on both the genitals and the body. Moreover, the symptoms of HPV are the same for both the fairer sex and men.
Doctors claim that this virus is considered more dangerous specifically for women, because infection with oncogenic viruses can lead to the development of cervical cancer. Most often, gynecologists recognize genital warts, which usually appear 2-3 months after penetration into the body.
Such condylomas most often grow in the area of the labia minora and vagina. There are often cases where a patient was found to have such growths in the anus area.
During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the following external manifestations of a viral infection (general symptoms of HPV in women):
- signs of cervical erosion (a smear is taken for cytology); signs of dysplasia;
- genital warts on the genitals;
- papillomas located in the vagina;
- sudden appearance or complete disappearance of warts during pregnancy;
- the presence of neoplasms on the cervix;
- pain in the genital area;
- burning, itching, unusual discharge, etc.
Diagnosis of the disease
If unpleasant symptoms occur that indicate a possible HPV infection, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist or dermatovenerologist as soon as possible in order to establish an accurate diagnosis, determine the strain of the virus and prescribe appropriate therapy.
A comprehensive examination for papillomatosis includes:
- Careful collection of patient complaints and medical history.
- A general examination, during which a specialist carefully examines the woman’s skin, paying special attention to the genital area, perineum and perianal area.
- Examination in speculum with mandatory taking of smears for flora and atypical cells (PAP test) from the mucous membranes of the vagina, cervix and cervical canal.
- If a malignant neoplasm of the cervix is suspected, the doctor may perform a biopsy - take a small fragment of the cervical epithelium and perform a histological examination.
- In order to determine the presence of HPV in the body and determine the type of virus, the polymerase chain reaction technique is used.
- The double hybrid trap method is a highly specific and accurate method for diagnosing HPV.
Bacteriological culture and serological reactions to other sexually transmitted diseases are used as additional research methods, since they can occur in parallel with HPV infection and mask its symptoms.
For a more accurate diagnosis, it is important to follow a number of simple measures before taking tests. Before a gynecological examination and taking smears, the external genitalia should be toileted; on the eve of the examination, vaginal suppositories and creams should not be used; 2-3 days before the examination, one should abstain from sexual intercourse. Blood for serological analysis must be taken in the morning on an empty stomach, regardless of the day of the menstrual cycle.
If cervical pathology is detected, a test for tumor markers is mandatory. To diagnose cervical cancer caused by HPV, the level of the specific E7 protein is determined.
Types of HPV
Today, almost 150 types of papillomavirus have been discovered. But they all cause growths of different characters (simple, pointed, flat, thread-like, plantar).
Simple
The simple type of HPV is also called ordinary or vulgar papillomas. They are considered the most common benign growths on the body. Simple papillomas initially manifest themselves as a small spherical papule, which will darken over time and turn into an uneven and rough surface.
They may appear in groups or in isolated cases. Simple growths usually include papillomas that occur on the hands and fingers.
Pointed
The pointed type of HPV in women is often found in the labia area. These are growths that look like papillae and usually come in a variety of colors (from light flesh-colored to reddish).
They can also be in the anus area. Since this type of HPV is classified as a moderately oncogenic type, doctors recommend treating and removing them to avoid the risk of developing cancer. Methods for removing such papillomas are very different: from a special laser to the use of liquid nitrogen.
Flat
Another popular type of HPV is flat condylomas. They, unlike pointed papillomas, no longer protrude outward, but occupy the highest position in terms of the degree of oncogenic potential. If flat condylomas are detected, gynecologists immediately send the patient for colposcopy and biopsy.
Since they are most often located on the cervix, the risk of getting cervical cancer is very high. If the test result is negative for dysplasia of the area, these growths are immediately removed.
Filiform
Threaded papillomas are formed due to HPV, which enters the body through the slightest injury to the skin.
A person who suffers from excessive sweating and oily skin has a higher chance of contracting this virus. This type of HPV has an oblong shape and occurs most often in women over 30 years of age. Almost all elderly people have this virus. Children do not get this type of HPV.
Plantar
This type of HPV, such as plantar papillomas, is not of the oncogenic type. These are rather benign formations that are most often found on the feet. People with damaged skin on their legs and those with atherosclerosis get sick faster. It is also easier for a person who suffers from diabetes and varicose veins to catch this type of virus.
In addition, the following factors can stimulate the development of the virus in the body:
- Excessive sweating of the feet, or dry skin.
- Flat feet and arthritis of the foot joints.
- Wearing uncomfortable shoes made of synthetic materials.
Disease prevention
You can prevent the occurrence of papillomas on the body by observing basic rules of personal hygiene and timely disinfection of any wounds. It is imperative to use a separate towel, comb, manicure equipment, and shoes for each family member in everyday life, and non-regular sexual contacts should always be protected with condoms. It is also important to always take a shower after sexual intercourse and treat contact areas of the skin and mucous membranes, since it takes some time for the virus to enter the human body.
Best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how to avoid buying stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to curb your sweet cravings: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
In modern medicine, there is also a vaccine against papillomavirus. It has already been tested in 72 countries and is effective against HPV subtypes 16 and 18, which cause cervical cancer in 90% of all diagnosed cases. Vaccination also successfully fights viruses of subtypes 6 and 11, which provoke the development of genital warts, which are difficult to treat. Due to the sexual route of infection with these viruses, it is recommended to vaccinate before a person becomes sexually active. Most often, experts recommend using the vaccine three times for girls aged 11-12 years. There is also a vaccine called Cervarix, which prevents infection with only two subtypes of HPV - 16 and 18. It can be administered to the body from the age of ten. The World Health Organization recommends that boys also be vaccinated to prevent the possibility of HPV circulation.
Types of HPV in women
Currently, scientists know about the existence of 150 types of human papillomavirus, and almost a third of them are considered the most dangerous for women's health.
HPV type 16
HPV type 16 belongs to the group of oncogenic viruses. It is so common that almost every second person with HPV is diagnosed. The virus reduces the level of immunity against tumors, which is the root cause of formations on the skin. This virus itself is destroyed in the body a year after infection. This is facilitated by the active action of the human immune system.
Given this information, doctors prescribe the test three times. If the body has not overcome this virus within a year, then experts recommend treatment with various drugs and antiviral tablets. They also insist on taking additional vitamins.
HPV type 18
Type 18 of HPV is considered extremely dangerous for women; when it enters the human body, it begins to actively cause the growth of tumors. It is considered dangerous because these formations can eventually turn into cancer. Only 3 out of 10 infected women can recover from this virus themselves thanks to their strong immunity.
The self-healing process also takes almost a year. Unlike other types of HPV, this virus affects the deep zone of the skin.
HPV type 31
HPV type 31 is considered dangerous, as are types 18 and 16. Due to the unique structure of DNA, this papilloma virus has a special genotype, which in most cases is dangerous for both sexes. Since women’s weak immunity cannot cope with the virus, papillomas appear on the skin and genitals.
It often happens that several months may pass from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first symptoms. During this time, a person can unknowingly infect his partner. Only at the right moment, when the body weakens and the immune system fights other viruses, will HPV begin to actively multiply and transform into neoplasms.
Due to the imperceptible incubation period, complications will appear in the body, which will not be so easy to cure.
The following accompanying factors can increase the risk of infection:
- Chaotic and unprotected communications.
- Stress and hormonal imbalance.
- Other infections in the body.
- Diseases of the intestines and stomach.
- The period of pregnancy and childbirth.
- Hypothermia and colds.
HPV type 33
A virus such as human papillomavirus type 33 is extremely dangerous for humans. This type of virus is the root cause of the formation of malignant tumors in the body. According to statistics, in the world a high level of oncogenic diseases occurs in people infected with this HPV. But this virus does not live in the human body all its life.
Unlike herpes, it can be cured with medications. Sometimes a person’s immune system can destroy the virus itself. To avoid complications, doctors also recommend various tablets and subcutaneous injections.
HPV type 35
HPV type 35 belongs to the group with an average level of oncogenic risk. Entering the body through promiscuity, they begin to penetrate deeply into the DNA of cells.
There are several options for the behavior of the virus in the human body:
- Once in the body, the virus itself is destroyed thanks to strong immunity.
- Once infected, the virus remains dormant. But at the same time, we should not forget that a person is already a carrier of HPV and can infect others.
- Penetrating into the body, the virus actively progresses and multiplies cells.
Often, type 35 of HPV manifests itself in people in the form of genital warts, which over time will occupy a fairly large area of the body.
HPV type 39
A person of any age can become infected with type 39 virus. The virus not only provokes the development of tumors, but also the appearance of various pathologies. It usually affects the genitals and also feeds on healthy cells in the body.
It mainly manifests itself in the form of flat and also genital warts that appear on the female genital organs. Experts assure that the presence of flat condylomas indicates the spread of HPV type 39.
HPV type 45
HPV type 45 is often accompanied by other diseases such as herpes and chlamydia.
This type of virus goes through several stages in the body:
- The appearance of genital warts on the internal and external genital organs.
- Devastating growth of the epithelial layer around the anus.
- Overgrowth of condylomas on the walls of the vagina.
If a virus is detected, treatment and removal of condylomas are prescribed.
HPV type 51
Virus type 51 is known for its high oncogenic risk. Girls with cervical erosion should be careful when choosing a partner, since infection with this virus can cause cancer.
HPV type 52
Papillomavirus type 52 is often found in people under 40 years of age. Frequently changing partners may increase the range of infection risk. A gynecologist can detect the presence of HPV when genital warts are detected.
HPV type 56
HPV type 56 usually affects a woman's reproductive system. This type of virus provokes cervical erosion. The first symptoms of infection are thrush or a cold, which are the result of a weakened immune system.
HPV type 59
Human papillomavirus type 59 marks itself as a skin disease with effects at the DNA level. Doctors consider the high growth of oncogenic tumors to be a negative aspect in relation to this virus.
Don't miss the most popular article in the section: Laser hair removal on the face and body - how it is done, effectiveness, before and after photos, contraindications.
Local and surgical treatment of HPV
When condylomas appear, many women attempt to get rid of them using folk remedies.
However, the mechanism of such treatment is exclusively the removal of local inflammation and an attempt to necrotize condylomas.
Folk remedies do not work on the virus!
This means that HPV will continue to multiply.
Which will lead to relapse of pointed neoplasms with a high risk of malignancy.
Therefore, attempts at uncontrolled use of herbal remedies for topical effects will lead to a direct threat to a woman’s life.
Traditional remedies for local use are mandatory.
They are used in combination with drugs prescribed orally.
The following medications are recommended for topical use:
- Miramistin
- chlorhexidine
- Panavir
- epigene
- geneferon
- verrucacid
- solcoderm
Topical medications are usually prescribed in suppositories.
In rectal or vaginal, depending on the location of the papillomavirus process.
The classic therapeutic regimen in gynecology for the elimination of HPV includes:
- ferrovir 10 ml per day intramuscularly in 2 injections for 10 days
- lykopid 6 capsules per day sublingually, divided into 3 doses
- chlorhexidine - irrigation or suppositories 4 times a day
- genferon - vaginal or rectal suppositories 2 times a day at different times with antiseptics
The full course of treatment is individual.
A clear deadline is set only for the administration of injections.
But according to the doctor’s decision, the duration of the course may increase or decrease.
The effectiveness of therapeutic measures for lesions of the cervix is very high.
And genital warts often have to be removed surgically.
Numerous reviews indicate that minimally invasive interventions significantly improve the rate of recovery from a viral infection.
Among the surgical techniques widely used are:
- electrocoagulation of condylomas
- laser vaporization
- mechanical removal with a scalpel
- cryodestruction using liquid nitrogen
- exposure to chemically active acids and alkalis
The above methods are highly effective.
But only with conservative support with antiviral drugs and immunomodulators.
If there is dysplasia in the cervix, extended surgical intervention is possible - laser or mechanical conization.
The procedure is also usually performed on an outpatient basis.
Since it is a small operation.
Thus, human papillomavirus is extremely common in the population.
When the gynecological tract is affected, HPV can bring a woman a lot of serious suffering.
Sometimes it provokes deadly diseases.
Modern medicine has a lot of possibilities to completely eradicate a microorganism.
Even in the absence of a clinical picture, and even more so after the appearance of genital warts, it is necessary to immediately contact a dermatovenerological clinic.
At the VDC, an accurate diagnosis of the type of virus is carried out, and all types of specialized treatment are prescribed.
Only a timely visit to a doctor will allow you to prevent in advance the dangerous effects of papillomavirus on a woman’s body.
Classification of HPV according to oncogenic risk
Scientists have compiled a list of all types of HPV and classified them by oncogenic risk.
Non-oncogenic
Experts call those HPV types of zero oncogenic risk that never provoke the development of cancer. Doctors include types 1 to 5, as well as types 10, 28 and 49, in this group.
Low level of oncogenic risk
Tumors caused by low-oncogenic risk types rarely progress to the cancer stage. Experts classified these types as types 6, 11, 13, 32 and 34. Also included in this group are types from 40 to 44 inclusive. Types 51 and 72 are also considered to be low-oncogenic risk types.
Medium risk level
Doctors consider a group of different types of the virus to be medium-risk types: 26, 30, 35 and 52, as well as 53, 56, 58 and 65.
High oncogenic risk
High oncogenic risk prevails in such types of HPV as: 16, 18, 31, 33, and 39. This group includes types 45, 50, 59, and 61 to 62. HPV types 64, 68, 70 and 73 are considered to have a high oncogenic risk.
Stages of development of PVI
It is customary to distinguish 3 stages of development of PVI:
- Initial stage (hidden) . There are no external manifestations. At this stage, it is impossible to determine the presence of the virus using diagnostic methods. There is no change in the tissue structure: the virus has already entered the cell, but the structure of the DNA remains the same. The pathogen is dormant and its numbers are minimal.
- Stage of subclinical manifestations . At this stage, small tissue changes that are invisible to the eye are detected. They can be recorded during diagnosis - colposcopy and histology. At this time, the virus has already entered the gene of a healthy cell, but does not yet make itself felt.
- Stage of clinical manifestations . Viral cells begin to multiply rapidly, resulting in warts and condylomas.
Treatment of HPV in women in gynecology
Treatment of HPV in women involves interrelated therapy, which consists of medications and surgery. This is such a situation that without modern diagnostics it is impossible to be completely cured.
PCR diagnostics, which only require a smear, are considered effective in their field. At the moment, there are a number of medications and folk remedies for the treatment of HPV.
Medication
Medications are aimed at radically curing the body of the virus.
After HPV is detected, doctors prescribe a whole range of drugs, which includes:
- Interferon-based drugs. Interferon can be sold in the form of tablets, various creams and ointments. You can also find solutions. Analogues of interferon are: “Viferon”, “Intron A”, “Genferon” and “Wellferon”.
- Immune function stimulants. Thanks to the enhanced production of antibodies to HPV, treatment time is accelerated. Well-known immunostimulants are Isoprinosine, Kemantan, Gepon and Immunomax.
- Cytotoxic agents that destroy tumors. These drugs include: Podophyllin and Podophyllotoxin.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods involve the use of recipes based on rare forest herbs:
- The most famous method is compresses with a decoction of celandine. It is believed that a month is enough for treatment. It is worth considering that the number of procedures should be about 4-5 times per day.
- You can also apply ice cubes frozen in a decoction of string and chaga. This method should be used 3 times a day.
- A decoction based on dandelion, plantain, lemon balm and horsetail also has a positive effect on the treatment process.
- Experts also advise paying attention to garlic. You can use garlic to prepare an anti-HPV ointment. To do this, you just need to add chopped garlic to the thick baby cream.
- Grandmothers recommend regular laundry soap, because soap has a drying effect, after which the condyloma is removed.
Before using folk methods of struggle, you should be careful, since folk remedies act locally, while the virus lies dormant deep in the body.
What is papilloma, locations of localization in men and women
Papilloma is a growth on the skin or mucous membrane. The only cause of its occurrence is the human papillomavirus (HPV). It penetrates the DNA of a healthy cell and causes it to rapidly divide, forming characteristic growths. The virus is able to penetrate deep layers of tissue, but it multiplies on the surface.
Each age is characterized by certain types of papillomas. The pathogen is also characterized by tissue specificity, when each strain of the virus infects certain tissues in certain areas of the body.
Papillomas are found in all sorts of places on the body; below we will look at the most common of them.
On the face
They usually occur in adolescents during puberty and are called flat warts. Such rashes do not exceed 1–2 mm in height and have an oval or round shape. They may go away over time without treatment. If they do not go away, you should consult a dermatologist.
On fingers and toes, palms, soles
They occur mainly in children and are called common (simple or vulgar) warts. They reach a height of 2–3 mm and have a dome-shaped shape and a rough surface. They like to be located near the nail plates, between the fingers.
Unlike simple warts, prickles occur primarily on the feet and palms. They are denser and larger in size. The pain when pressed resembles the prick of a sharp thorn and interferes with walking. The spines are also removed by a dermatologist.
On the neck, eyelids, armpits, in the fold under the breasts in women
This type is typical for middle-aged and elderly people, 35 years and older. They are distinguished by their small size and thread-like shape on a thin stalk. Formed in areas with thin skin. With age, the number of such warts may increase, they form clusters and darken in color. Such growths can be easily and quickly removed by a dermatologist.
On the genitals of women and men
These growths resemble cauliflower or cockscomb in appearance. They are called genital warts. They are located in the vagina in women, on the penis in men, in the urethra, in the anus, in the mouth.
This virus is transmitted sexually. The likelihood of infection is highest at the age of 18–35 years; the percentage of infected people during this period can reach 50%. Moreover, men are more likely to suffer from the disease, and women are more likely to get sick.
Important!
This type of virus can cause cervical cancer in women and penile skin cancer in men. He definitely needs to be treated. For treatment, women need to see a gynecologist, and men need to see a venereologist and dermatologist.
In the larynx, trachea
Papillomas in the form of multiple papillae form on the mucous membrane of the larynx and trachea. They grow and gradually reduce the lumen of the airways, making it difficult to breathe and speak.
Such formations are especially dangerous in infants due to the risk of suffocation. A child is infected with the virus during childbirth from a mother with genital warts. Such formations are removed by an ENT doctor.
Methods for removing papillomas
The most common method of treating HPV is the removal of papillomas followed by the use of medications. At the same time, the methods for removing papillomas are very different.
Laser removal
Removal of papillomas with a laser is the most effective and safest removal of HPV condylomas in women . This is a type of removal that completely eliminates the possibility of bleeding and scarring. This procedure is absolutely safe and does not lead to inflammatory processes.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is considered a completely radical method of removal. Using a scalpel, surgeons simply cut off the condylomas.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves the use of liquid nitrogen during the removal of papillomas. This procedure has a huge drawback - due to the uncontrolled depth of nitrogen exposure on condyloma, relapses are common.
Also a feature of this method are scars.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is based on the use of high-frequency current against HPV in women, which burns out condylomas. This burning process involves the coagulation of protein tissue, which is an excellent fight against tumors. This procedure is usually controlled visually.
The human papillomavirus aggressively affects women's health. All girls need to be careful and get tested on time, since the virus can be asymptomatic, and the consequences are very dire. HPV often manifests itself and develops during times of weakened immunity.
If a virus is detected, treatment must be started immediately, as this can lead to the development of malignant tumors.
Treatment for HPV should consist of medications and local removal of tumors. As an addition, the use of traditional methods of combating the virus is encouraged.
Treatment of pathology
When the DNA of a highly oncogenic papillomavirus is detected in a woman’s body and the symptoms of papillomatosis, the gynecologist selects a comprehensive effective treatment. Measures in the presence of HPV infection should be aimed at reducing the activity of the dangerous virus, eliminating the manifestations of the disease, and preventing the occurrence of malignant neoplasms.
When described, pathologists use:
- local therapy aimed at destroying warts and condylomas;
- systemic antiviral drugs leading to the elimination of the virus from the body;
- surgical intervention;
- immunomodulatory drugs and multivitamins to increase the body's defenses;
- symptomatic therapy (drugs that eliminate itching, detoxification).
The most effective is the combination of surgery to remove condylomas with specific antiviral treatment.
When treating papillomatosis, an integrated approach and careful adherence to all medical recommendations are very important. It is also mandatory to examine the sexual partner and prescribe special therapy for him if HPV is detected. This is necessary to avoid reinfection and complications.
Surgical treatment of papillomatosis
Surgical treatment is used for active growth of condylomas and warts, which creates an obstacle to childbirth and normal sexual life. As treatment, a woman is offered:
- Laser removal of skin lesions is the most effective and safe method that can be used even for young, nulliparous girls and during pregnancy. The only drawback of this method is the relatively long recovery period (from 6 months to 1 year).
- Surgical intervention - excision of warts and condylomas. Indications for this are large sizes of papillomas. Scars may form after the intervention, so this method is not indicated for nulliparous women planning a pregnancy in the near future.
- Cryodestruction - used to remove external papillomas localized on the skin of the perineum of the labia. During the intervention, pathological lesions are exposed to liquid nitrogen. The advantages of the method include its speed, painlessness, short recovery period and the absence of postoperative scars. The disadvantage is the high risk of relapse of the disease some time after treatment.
- The radio wave method is the most effective modern method. Recovery after this intervention averages 2-3 weeks, and the risk of recurrence of the disease is minimal.
- Electrocoagulation is the removal of condylomas with electric current under local anesthesia. The method is contraindicated during pregnancy.
The choice of surgical treatment technique is made by the attending physician, based on data on the localization and extent of the pathological process, as well as taking into account associated factors (the woman’s health status, pregnancy).
After removal of condylomas, the patient must be prescribed a course of etiological and restorative treatment. These measures are the prevention of relapse of HPV infection and papillomatosis.
Conservative therapy
Drug treatment of HPV infection consists of local and systemic therapy.
Local medications are designed to destroy condylomas chemically. Drugs such as Podophyllin and Foresol cauterize and lead to mummification of the affected tissue. Solcoderm destroys warts at the cellular level.
The following are also used as conservative therapy:
- Groprinosin - tablets with antiviral and immunomodulatory activity. Most often, the drug is prescribed in combination with burning local agents or surgery.
- Vaginal suppositories Panavir are an antiviral drug of plant origin that have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. The medicine has virtually no side effects; the only contraindication to its use is an allergy to the components of the product.
- Creams and ointments based on Acyclovir (Zovirax, Acigerpin). The products have a delicate effect on the skin and mucous membranes of the affected area, without leaving burns or scars. The drugs are approved for use in the treatment of pregnant women.
- Viferon suppositories are an antiviral, immunomodulatory drug that prevents the proliferation of oncogenic viruses.
- Likopid is an effective tablet drug prescribed for cervical papillomatosis. The use of this drug in combination with antiviral therapy significantly increases its effectiveness.
- Cytostatics (5-fluorouracil, Bleomycin) are prescribed for diagnosed cervical precancer.
In order to increase the body's defenses, doctors often prescribe multivitamin preparations. It is especially important that they contain vitamins A, B, C and E. During treatment, you should try to avoid stress, overwork and follow a specialized diet. The diet of patients must be balanced, sufficient in calories and contain all the necessary nutrients. During the treatment period, it is important to give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol), and exclude hot, smoked and spicy foods.
Antibiotics are ineffective against the human papillomavirus, but can be part of complex conservative treatment if a woman has a concomitant bacterial infection of the genital tract.
Treatment of the disease at home
When starting treatment, you should remember that HPV cannot be effectively gotten rid of using folk remedies. However, by using home remedies, you can increase the body's defenses and immunity, which will speed up recovery.
Traditional methods for fighting papillomavirus include:
- Herbal decoction prepared from dried lemon balm, plantain, horsetail and dandelion. Dry herbs should be taken in equal quantities and mixed, then 3 tbsp. l. Pour 1 liter of clean water into the resulting mixture, let it boil and cook for 10 minutes. The resulting drink must be filtered and taken 2 tbsp. l. three times a day half an hour before meals.
- Cranberry is a berry that has the ability to increase the body's defenses. It has long been used for colds, infections of the genitourinary system and papillomatosis. To prepare cranberry broth at home, 0.5 kg of fresh berries should be rubbed through a sieve or twisted in a meat grinder. Add 2 finely chopped apples and a handful of chopped walnuts to the resulting mass. Then add 0.5 kg of sugar and a glass of water to the mixture and boil over low heat until thickened. You need to take 2 tbsp of the medicine. l. twice a day. For greater effectiveness, it is recommended to drink the product with strong black tea.
- Potato juice recipe is widely used to treat HPV. To prepare the product, it is better to choose pink varieties of potatoes. The course of this therapy is 2 months, during which you need to drink 0.5 glasses of juice 30 minutes before meals.
- A mixture of dried fruits is an effective means for stabilizing the immune system. Chopped dried fruits (dried apricots, raisins), nuts and honey are mixed and transferred to a sterile jar. You need to take this vitamin mixture 1 tbsp. three times a day.
Treatment with home remedies can be used for papillomavirus. However, when highly oncogenic strains of microorganisms are detected in the body, it is important not to hope for a complete cure with their help, but to undergo medical and surgical treatment prescribed by a doctor.
Before using any traditional methods for the treatment of HPV, you should definitely consult with your doctor to identify possible contraindications.
The most characteristic symptoms
The papillomavirus has a long incubation period and a hidden nature of the disease. The incubation period refers to the period of time from the moment a pathogenic microorganism enters the body until the first signs appear.
For HPV, it takes on average from a month to several years. At this time, the patient does not experience any discomfort or symptoms. The virus lies dormant until favorable conditions for development occur.
The appearance of papillomas and condylomas on the skin and mucous membranes is almost the only obvious sign of the disease. It means that the disease is in an active stage and requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Often HPV symptoms in men show the following:
- pain during urination, defecation and intimacy;
- bleeding of papillomas, resulting in the formation of ulcers;
- in rare cases, itching occurs;
- psychological discomfort;
- development of Bowen's disease.
Typically, such signs of HPV in men indicate that the formations have been damaged.
What are papillomas and what do they look like?
HPV in men is an infection that is characterized by the appearance of single or multiple warts or genital warts on the penis, foreskin, skin of the scrotum, as well as in the anus and perineum.
In some cases, the pathology affects the urethra. Warts are soft, flesh-colored bumps that are painless to the touch. This virus can provoke the development of oncology, but today medicine has developed a sufficient number of methods for its treatment. In men, this pathology often occurs between the ages of eighteen and twenty-five.
The carrier of the infection poses a danger to his sexual partner, as he can become infected during sexual intercourse. Other family members can become infected through household contact, for example, through bed linen or a towel.
The HPV virus does not appear immediately in men; the incubation period can range from one month to one year. The virus begins to activate when immunity is significantly reduced.
Genital warts are a common manifestation of a viral disease that develops as a result of damage to the skin and mucous membranes by the human papillomavirus. Against the background of damage to the epithelium by the papilloma virus, its pathological growth and the formation of characteristic warts are observed.
Genital warts in men and women are soft to the touch and quite fleshy formations, which, as a rule, do not differ from the surrounding healthy tissue in any specific shade. Most often, this type of condylomatosis affects the mucous membrane in the corners of the mouth, genitals and the skin of the perianal area.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the development of genital warts
Genital warts in men and women often appear against the background of reduced immunity, as this predisposes to uncontrolled proliferation of the human papillomavirus in the epithelial layers of the mucous membranes.
Among all types of HPV, types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31 most often provoke the development of genital warts in men and women. It is worth noting that types 16, 18 and 31 of HPV are potentially dangerous, since genital warts in women and men can subsequently degenerate into malignant tumors.
In the vast majority of cases, infection of a healthy person occurs through contact. Infection often occurs:
- when sharing personal hygiene items;
- wearing someone else's clothes;
- sexual intercourse;
- ignoring the rules of personal hygiene.
- Transmission routes
- Human papillomavirus: types
- Types of papillomas
From this article you will learn what papillomas are, where they are most often formed in men and women, and what is the reason for their formation. Papillomas are benign neoplasms localized on the skin and mucous membranes. The reason for their formation is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is transmitted in various ways. The appearance of the formations depends on the type of virus that caused them.
Transmission routes
Routes of transmission of HPV
The main “condition” for infection is the presence of microdamages (wounds, cracks, scratches) of the skin or mucous membranes. They serve as the “gateway” for HPV.
Most often, transmission of the virus occurs when the skin or mucous membranes of two people come into contact. Therefore, the main route of papillomaviruses is sexual contact. Moreover, the use of condoms does not exclude the possibility of infection. The virus can be transmitted through oral sex, during which contraception is not always used. In addition, the condom does not cover the entire surface of the penis, and is often put on already in the middle of sexual intercourse. HPV can also be transmitted through kissing.
HPV can also be transmitted:
- From mother to child as the baby passes through the birth canal.
- In everyday life: when using other people's hygiene products (towels, toothbrushes, shaving accessories).
- In public places: baths, gyms, swimming pools.
Reference! The survival period of papillomaviruses in the external environment is short. Therefore, although the risk of domestic infection exists, it is much lower than through sexual contact.
Self-infection is also possible: transfer of the virus from one part of the body to another during depilation, scratching the skin, biting nails.
Infection through contact with the virus does not occur in all cases. The following factors increase the risk:
- Decreased immunity.
- Bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse.
- Stress.
- Presence of sexually transmitted infections.
- Diseases of the urinary system.
- Injuries to the skin and mucous membranes.
- Immunodeficiency states.
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives.
Reference! For women, oncogenic strains of HPV are more dangerous than for men, since they become infected with them more often.
Immunomodulators
In the treatment of human papillomavirus, drugs with immunomodulatory properties occupy an important place. The fact is that a pathogenic microorganism is not capable of causing even minimal harm to a person if his immune system is actively ready to fight the infection and suppress it.
All symptoms of HPV and exacerbations of the disease are associated with a decrease in the body’s immune defense. It is precisely to increase immunity that the action of immunostimulants is aimed.
Can be used:
- human interferon;
- Cycloferon;
- Reaferon;
- Neovir;
- Immunofan et al.
Immunomodulators are generally harmless drugs, but in some patients they provoke severe allergic reactions.
If there are signs of intolerance to one drug, it is recommended to discontinue its use. And start using another medicine with similar properties.
The optimal replacement drug is selected by the doctor.
Some traditional medicines also have an immunomodulatory effect. But their use must be agreed with the doctor. It is a mistake to think that folk recipes are a panacea. In the case of HPV, they may be useless, and the woman will only waste time using them.
How does infection occur?
HPV infects stratified epithelium, which determines the affected area - the skin and mucous membranes. The DNA of the virus seeks to penetrate the nucleus of a human cell. Its goal is the reproduction of oncogenic proteins there. After this happens, they begin to rapidly replicate. If this is a benign growth, then the cells do not extend beyond the epithelium. If malignant, the spread of the pathological process triggers the occurrence of metastases. The incubation period lasts about three months.
Asymptomatic carriage of human papillomavirus (HPV)
In reality, many more people are infected with HPV than statistics show. Most of them simply do not know about it, since there are no symptoms of condyloma.
The virus may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, since the human immune system does not allow it to develop to the required extent. However, at any time, with a decrease in both general and local immunity, this can happen, and then papillomas and/or condylomas appear.
Leading clinics in Israel
Causes of the disease and how infection occurs
The virus is transmitted through contact with the skin or mucous membrane of a sick person.
Infection can happen:
- during sexual intercourse (including through anal and oral types of sexual intercourse);
- at birth. From mother to newborn baby as it passes through the birth canal during childbirth. The disease is detected in the first years, when papillomas can appear in the mouth (laryngeal papillomatosis) and on the skin;
- with autoinoculation. Infection can occur due to a simple lack of personal hygiene rules - when shaving or hair removal;
- by everyday means. Due to the fact that such a virus is extremely tenacious, and especially in a humid environment, there is a risk of catching it when using public places: saunas, swimming pools, toilets, baths, gyms. The virus penetrates through the smallest breaks in the skin.
You can get sick with some types of virus even by shaking hands. If there is someone in the family who is a carrier of the virus, then the risk that other family members are sick with it is very high. This virus is always highly contagious.
Various types of virus can cause or contribute to the development of diseases:
- cervical dysplasia – 62%;
- genital warts of the urinary tract and genital organs - in approximately 50% of cases;
- pre-invasive and invasive cervical cancer – 38%;
- Also, in 85% of patients with genital condylomas, foci of HPV infection of the vagina and cervix in various forms are detected.
This gives rise to suspicions that people with genital tract HPV belong to the cancer risk group - they may develop cervical intraepithelial carcinoma.
Factors contributing to HPV infection:
- decrease in general immunity due to the influence of various carcinogens;
- overwork, the presence of stress of various types;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pregnancy (due to changes in the body and changes in hormonal levels);
- the presence of diseases that cause metabolic and metabolic disorders.
If the virus enters a healthy body with good immunity, then the immune cells destroy it, and no infection occurs; it poses no threat to a completely healthy person.
What does the result mean?
During research, qualitative and quantitative analysis is taken into account. The first may indicate the presence or absence of a virus. The second is about the concentration of the pathogenic agent in the human body. Only an experienced specialist can decipher the information received, taking into account all the surrounding circumstances. There is no need to take a positive test result as a death sentence. Often during research, errors are made that affect the indicators and make it impossible to determine the correct data. In most cases, mistakes are made by patients while preparing for an upcoming test. Reference values must be taken into account.
False positive HPV
False-positive HPV test results are common. This happens if:
- the bio sample was contaminated;
- there was an incorrect collection of materials;
- the patient was treated before the analysis;
- the person did not comply with the standards of preparation for diagnosis.
To avoid getting distorted results, you need to take into account some rules. Within 12 hours before submitting biological material, it is prohibited to take antiviral, antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs. You should shower on the day of the smear test. Over the next 2-3 days, it is better to refuse sexual intercourse. A smear test is not required during menstruation. People often encounter false test results if they tried to treat the infection with antiviral drugs the day before. The virus itself is neutralized, but antibodies remain in the body.
Referential meaning
Reference values of an indicator (another name is reference) imply general values obtained during laboratory research on a specific category of the population. These can be young people aged 20-30 years, women during pregnancy, those who have given birth, those who have not given birth, etc. Such indicators are necessary to obtain the average total indicator of the relative norm.
This is how a quantitative HPV test is determined. The average value of 3-5 Lg, which implies a questionable result, was collected based on the assessment of a certain category of carriers of the papilloma virus. Therefore, reference values cannot be assessed as the only correct indicator. The concept of normal may differ depending on the characteristics of the body, age, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In most cases, only the qualitative result of the study is important, which indicates the presence of the virus. In cases of detection of a non-oncogenic type of HPV, its concentration is insignificant.
Signs of papilloma in men: incubation period
Signs of papilloma in men most often do not manifest themselves immediately after the virus enters the body, since HPV has a fairly long incubation period - from two weeks to more than two years. This kind of disease is characterized by a latent (hidden) course.
At the same time, you can become infected with several types of viruses at once. Activation of HPV, its development and progression is created against the background of various factors, after which the active stage of the disease occurs.
If a doctor suspects a patient has HPV, he may prescribe:
- Examination of the outside of neoplasms that have appeared on the skin.
- Biopsy of these neoplasms.
- PCR test (Polymerase chain reaction test) is a test for detecting the human papillomavirus; it is taken from the skin of the glans penis and the mucous membrane of the urethra.
- Cytological screening is the most acceptable option for detecting HPV, allowing to identify the subclinical or clinical form of the disease.
- How is a DNA test for HPV taken in men? This analysis gives the most accurate result. Using this type of diagnosis, you can detect the disease even in the initial stages and begin treatment in advance. The accuracy of this examination is about 95%. For a correct result, a man must refrain from urinating for 1.5 hours before the test.
- What are genital warts
- Types of genital warts
- Reasons for appearance
- Signs and symptoms
- Among women
- In men
- Treatment of genital warts in women and men
- Surgery
- Drug treatment
- Complications of genital warts
- Condylomatosis during pregnancy
- Diagnostics
- Prevention
It is rare, but it happens that some are faced with the problem of the appearance of genital warts or, as they are also called, anogenital warts. This problem is common among some men and women. What it is, what types there are and how to deal with them, we will consider in more detail below.
What are genital warts
Anogenital warts grow on the epithelium and mucous membranes, present as soft growths, they can mainly be seen on the genitals and around the anal area. They look similar to cauliflower.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is an extremely common disease, it is easily transmitted, but no panacea has yet been invented for it. Treatment involves the removal of papillomas, warts, condylomas formed as a result of infection and maintaining immunity.
A large number of people are carriers of this disease, almost a third of the female population, but it is not a fact that it affects a woman’s life or manifests itself in any way. The situation is similar with men, but there is one difference: in the stronger sex the incubation period lasts from three months to a year, while in women it is from 1 to 8 months.
Human papillomavirus, after infection of the body, often becomes the cause of the development of diseases of the reproductive system. Among the more than 100 varieties of HPV known to modern medicine, some pathogenic bacteria, when accompanied by favorable factors, cause changes in cellular structure.
Detection of DNA of oncogenic papillomavirus type 16 or type 18 in women is very dangerous, as it can subsequently cause cervical cancer. However, the right medical actions help you recover and live a full life.
Features of HPV types 16 and 18
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is transmitted through unprotected sex and remains latent for a long time. Sometimes the detection of a pathogen occurs directly during the diagnosis of a malignant tumor. For the female body, infection is more dangerous than for men.
Due to their high oncogenic abilities, viruses 16 and 18 cause changes in the epithelial cells of the cervix, which leads to the development of dysplasia and cancer. In addition, papillomavirus can provoke the appearance of oncology on the external genitalia, vaginal walls, and in the anus area.
The manifestation of negative consequences does not always occur; sometimes the period of transformation of benign formations takes 10-15 years after infection with a pathogenic microorganism, and with timely diagnosis, the infection can be successfully treated. However, some factors can accelerate the transition of HPV from a latent state to the active phase of reproduction.
These include:
- Weakened immunity in women;
- Diseases of an inflammatory and chronic nature;
- Diagnosed pathologies of the cervix, changes in vaginal microflora;
- Abortions and miscarriages;
- Hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- Hereditary predisposition to cancer.
Pregnant patients and women during menopause are at risk. A large percentage of papillomavirus carriers are among those who began sexual activity early and often change sexual partners.
Symptoms of body infection
In addition to the sexual route, in rare cases, HPV enters the body through airborne droplets or through skin lesions through physical contact. Under accompanying conditions, the virus multiplies in tissue cells, causing a change in structure and the appearance of the following formations in various parts of the body:
- Warts: have a bright red or dark color, stand out on the skin as small round growths. Mainly affects the area of the palms, feet, elbows;
- Papillomas: usually have a flesh-colored color and are first localized in the armpits, groin area, and fat folds. Without proper treatment, spread throughout the body;
- Condylomas: the most dangerous lesions of the skin and mucous membranes, since they can subsequently transform into a malignant tumor. New growths have a pointed shape. They appear on the genitals and near the anus, and can move to the surface of the thighs. If condylomas are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Such symptoms give rise to a diagnostic test for HPV. The peak risk of developing cervical dysplasia and subsequently cancer is reached at the age of 45 years.
Incubation period
The introduction of the virus into the chromosomal apparatus of cells takes some time, after which, with weakened immunity, the development of pathological processes begins. If the body's immune defense works without failures, women under 30 years of age have a high probability of self-elimination of HPV type 18 within 1-2 years.
With age, the chances of spontaneously getting rid of human papillomavirus infection decrease. Even with successful treatment, the virus remains in the human blood forever.
Diagnosis of HPV
According to medical data, from the moment the body is infected with a virus, transformation into a malignant tumor occurs within 12-15 years. When factors are favorable for the propagation of the pathogen, the period is reduced to 6-7 years. Therefore, it is important to diagnose papillomavirus in the female body in a timely manner.
Often, HPV is detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist, so even in the absence of unpleasant symptoms, you should visit your doctor regularly.
Diagnosis of damage to the female body is carried out using the following methods:
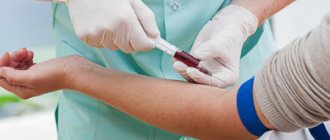
- Polymerase chain reaction analysis for human papillomavirus. The procedure is painless and involves taking a smear from the cervical mucosa. Using a biomaterial sample, it is possible to determine the presence of HPV, the genotype and number of viral bacteria. In addition, from one sample it is possible to see the types of pathogens existing in the body. The analysis detects infection at an early stage, which facilitates further treatment. Diagnosis is recommended every 3 years, since the number of dangerous strains during this period can increase significantly and lead to the degeneration of benign formations into malignant ones.
- Papillomavirus DNA analysis (Digene test). The hybrid capture method is more accurate and allows you to determine the concentration of viral cells in 1 ml of sample. Only clinically significant indicators are taken into account, when exceeding the permissible value can subsequently lead to cervical precancer. To obtain data, a tissue scraping is taken from the cervical canal.
- In some cases, the doctor takes a smear for cytological examination and performs a colposcopy. To exclude the progression of pathological changes, a biopsy of cervical tissue is performed. For preventive purposes, a smear for cytology is taken every 2 years after 25 years.
If, as a result of diagnosis, the papillomavirus is detected in a woman’s body in a latent state, it is necessary to monitor the dynamics of development every 6 months through a gynecological examination. If the answer is positive about pathological changes in tissues, the patient should not fall into despair.
If the tumor is detected at an early stage, the tumor can be cured without negative health consequences. .
Treatment methods
The main methods of treating an infection before it reaches the stage of a malignant tumor include symptomatic therapy and general strengthening of the body using medications. Removal of warts, papillomas or condylomas is necessary for subsequent preventive treatment with medications.
To do this, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, laser exposure or cauterization with chemical compounds are performed.
Papilloma virus. Diagnostics:
- Consultation with a dermatovenerologist . Only a dermatovenerologist can make a diagnosis during an initial examination, assessing the clinical picture, conducting a test with acetic acid, and, if necessary, using the dermatoscopy method.
- Laboratory diagnostics. It is necessary to conduct a HPV test using the PCR method, which will allow you to estimate the amount of the virus, as well as determine which type of HPV is present in this case (they are divided into types with high and low risk of oncogenicity). A PCR test must also be performed on all sexual partners of a patient with genital warts. A positive test result in the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease means that treatment is necessary to suppress the development of the virus in the body.
- Urethroscopy is a study of the condition of the urethral mucosa using special endourethral endoscopes. Considering the increase in recent years in the number of patients with endourethral condylomas, this study is necessary for all patients, both men and women.
- Extended colposcopy - examination of the cervix using a colposcope and performing a test with acetic acid and the Schiller test. It is necessary for all women to undergo laboratory confirmation of papillomavirus infection, since the presence of flat condylomas on the cervix is possible.
- Immunogram is a study of the state of the immune system. This will allow for the most effective HPV therapy.
Treatment of papillomavirus
HPV in the fairer sex causes the growth of vulgar and flat warts, papillomas and genital warts. However, it can also cause pathological conditions:
- dysplasia (improper tissue development);
- leukoplakia (keratinization of the mucous membrane) of the cervix;
- adenocarcinoma (cancer of the glandular epithelium) of the cervix;
- neoplasia (cellular changes) of the vulva, vagina, grade II, III;
- cervical neoplasia of the I, II and III degrees;
- cancer.
Clinical manifestations of malignancy (malignancy) of cells can develop only during the period of cessation of hormone production in the ovaries (menopause). Systematic tests, check-ups and visits to the gynecologist will help a woman prevent unwanted pathologies.
Human papillomavirus is a huge group of viruses, which includes 27 species and about 500 strains (types). Most of them do not entail pathologies in the human body, they exist unnoticed, without complications, but some types are potentially dangerous. They can cause various diseases, including oncology, reproductive dysfunction, and HIV.
In many cases, viral papilloma is asymptomatic, does not appear externally and goes away on its own after some time. The degree of severity depends on the type of virus and its characteristics. People discover a problem when papillomas appear on the body - small cone-shaped warts, which are considered symptoms of HPV.
Among women
HPV in women manifests itself in the form of condylomas - small pointed or flat bodily formations on the inside of the vagina and outer labia. Single or multiple warts can appear on different parts of the body: limbs, head, neck. They are mostly painless, small, and cause more psychological and aesthetic discomfort.
In men
In men, papillomas appear on the soles of the feet, hands, face and head. When infected with a dangerous virus, papulosis of the penis and testicles is possible: it is yellow or pink papillomas that stand out slightly above the skin. Another unpleasant symptom of HPV in men is Bowen's disease: red plaque-like formations, growths on the head of the penis.
The main question that concerns patients is whether HPV (papilloma) can be cured completely and forever? Unfortunately no. In 90% of cases, the immune system copes on its own, but there are no effective methods for eliminating it from the body. Treatment boils down to the removal of warts, condylomas and possible consequences of the disease - benign or malignant tumors, damaged epithelium. Some medications are used to help the body fight infection and speed up the process of tissue repair.
Human papillomavirus infection in women can be a harbinger of dangerous diseases, so it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist and do preventive checks if necessary. If condylomas are found on the body, there is no need to try to remove them yourself, this can cause even more serious consequences.
- surgery;
- chemical cauterization;
- laser removal (carbon dioxide, neodymium beam);
- destruction of the concentration of affected cells with liquid nitrogen;
- electrocoagulation.
Removal of condylomas and warts does not mean a cure: this is only a temporary measure that helps prevent the formation of malignant cells, and women need it because of the high likelihood of cervical cancer with HPV. After surgery, relapses or complications are possible in the form of damage to areas adjacent to those that were removed. With timely intervention, not only cancer can be avoided, but also uterine surgery can be performed without harm to reproduction and women’s health.
Treatment of papillomavirus with drugs occurs only after the medications are prescribed by a doctor, since all medications perform only an auxiliary function and are not the main means of therapy. To treat HPV in women, antiviral tablets and immunomodulatory drugs are used. How do they help fight the disease:
- Antiviral: act directly on “foreign” cells in the body, increase the production of antibodies; may interfere with reproduction or have a stimulating effect on natural immune resources.
- Immunomodulatory: have the ability to cause nonspecific resistance - resistance and increased protection of the body, regeneration of damaged tissues. There are a number of side effects, it must be used in dosage.
- Rectal and vaginal suppositories: help get rid of condylomas and warts in the anogenital area. Before use, you need to treat the area with a special disinfectant.
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) belongs to the genus A of the Papovaviridae family and is transmitted primarily through sexual contact, infecting epithelial (cover) cells - the skin, mucous membrane and urogenital area. Infection of the skin and genital organs occurs through microtraumas. The papilloma virus is contained in the urethra, Bartholin's glands and seminal fluid. The development of malignant tumors of the penis, vagina, and cervix is associated with human papillomavirus.
HPV strains, of which science knows more than 100, behave differently in the cell. Some exist separately from chromosomes, others are able to integrate into the cell genome (they most often cause complications). When the viral DNA is inserted into the nucleus of the host cell, it controls the cell's genetic material, leading the cell to malignant transformation.
The virus infects stem cells located in the basal layer, and they transmit the infection to the surface epithelial cells. Superficial dividing immature cells are especially susceptible to HPV, which explains the high risk of oncogenes affecting the vulva, lower part of the vagina and cervix.
A type of papillomavirus in women and men is genital and flat condylomas developing on the genitals. They must also be removed.
A complication of the virus is a precancerous condition - cervical dysplasia and its logical conclusion - cervical cancer. You can avoid cancer by treating dysplasia. Treatment also involves removing the affected layer of cells.
Papillomavirus enters the human body in different ways, the probability of infection is 60%. You can get an infection in the following ways:
- Sexually, regardless of the type of sexual relations - oral, genital and anal. The presence of genital warts in a partner guarantees infection by 98-100%.
- Contact household - in the case of using a shared towel, washcloths, etc. The virus can also be transmitted through saliva during a kiss.
- Through wounds - a violation of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes - an open gateway to the body.
- Infection of a child during the passage of the birth canal - children suffer from rare forms, papillomas grow in the nasopharynx and sinuses. Recent studies have shown that children born by cesarean section also become infected - this may indicate that the virus is able to penetrate the placenta.
Infection does not always guarantee the development of the disease. HPV causes disease in the body in 50% of cases, the rest are limited to carriage of the infection: a strong immune system can keep the virus in numbers that are not dangerous to the body. The incubation period ranges from a year to 20 years, with an average of 3-5 years.
It should be understood that infection of epithelial cells is a necessary but not sufficient factor for the development of oncology. According to Professor V.A. Molochkov, a well-known and respected scientist in the world of medicine, a number of other factors are necessary for the development of irreversible neoplasia:
- active expression of genes E6, E7 of highly oncogenic types hpv16 and hpv18;
- induction of estradiol metabolism to 16-OH;
- multiple damage to chromosomal DNA in an infected cell.
Fibroepithelial (skin) neoplasms with a thin stalk or a broad base. They can be single or merge, forming a growth that looks like a cauliflower head. Condylomas can become inflamed and bleed when injured, as they contain blood vessels that feed them.
Condylomas can be found on the clitoris, labia minora, urethra, vagina, cervix, around the anus and in the anus. Exophytic forms of OC are a consequence of the activity of benign types of the HPV virus - 6, 11. Endophytic condylomas (flat and inverted) grow on the cervix and initially do not give symptoms. Detected during extended colposcopy. Genital warts affecting the lips, tongue and palate are visible during routine examination.
- Anal warts. Anal warts can be found up to the dentate line of the rectum. At first they do not cause discomfort, but over time they itch, hurt, and smell unpleasant.
- Urethral warts. In women, the external urethral opening is affected in no more than 8%. Such warts are easily identified by a gynecologist. Deep damage to the urethra (urethra) cannot be determined visually, but the disease gives symptoms of sluggish urethritis. Urethral warts in men cause a split urine stream associated with a narrowing of the urethral opening.
Flat condylomas
Diagnosis
The infection is usually diagnosed in women under 30 years of age. A gynecologist may suspect the presence of papillomavirus in a patient if she finds:
- erosion;
- various growths on the body;
- metaplasia and dysplasia (changes in cell types).
There are several ways to diagnose the virus:
- a general blood test that detects the presence of papillomavirus in the body;
- PCR test that determines the strain of the virus;
- Digene (digen test), which identifies the risk of developing cancer;
- colposcopy, performed to detect pathological changes in the cervical mucosa;
- cytological examination of a smear from the cervical mucosa;
- biopsy - obtaining samples of material for further thorough examination in the laboratory.
Causes of papillomas
Doctors say that the prerequisites for HPV infection are: smoking, frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages, and a large number of sexual partners. It is transmitted:
- sexually (it is also transmitted during anal and oral sex);
- upon contact (by accidental touching, by kissing, through minor abrasions and cuts on the skin);
- through household means (through dishes, shaving accessories, toilet seat, etc.);
- from mother to child during childbirth;
- through self-infection (for example, when shaving).
The cause of papillomas can be considered the pathogenesis of infection: when it enters the body, the virus is localized in the lower layers of the epithelium; it is easiest for it to penetrate into vulnerable, soft tissues, such as the female uterus and vagina. It coexists with cells or interferes with DNA and causes changes in the body, in these cases the development of malignant tumors occurs. Warts are obtained directly from the activity of the virus at the intracellular level, its influence on the skin from the inside.
Medicines in the form of suppositories
If we are talking about a representative of the fair sex, the doctor may prescribe medications in the form of suppositories for her treatment.
Medicines in the form of vaginal suppositories can stop inflammatory processes in the cervix and reduce the likelihood of cancerous degeneration in the organ. Also, these medications do not allow condylomas and papillomas to form on the vaginal mucosa and protect the body from other infections. At the discretion of the doctor, for example, Viferon or Polyoxidonium can be used.
There are alternative options that differ in the severity of the effect and the characteristics of the active substance. On average, to prevent problems, it is recommended to insert 1-2 suppositories per day into the genital tract.
Read also Orchitis
Most doctors recommend performing the procedure in the morning and then in the evening.
The average course of using suppositories is 10 days, but at the doctor’s discretion it can be extended to two weeks, and sometimes more. Suppositories are not used in isolation from other medications. They give a pronounced effect only if they are combined with other medications that are used in the treatment of HPV.
HPV and pregnancy
HPV in a pregnant woman is not the most dangerous disease for herself and her unborn child. An expectant mother should only be wary if she is diagnosed with types 6 or 11 of HPV (causing genital or anal condylomas), which, when transmitted to a newborn, can have consequences in the form of respiratory papillomatosis.
All other forms of papilloma (non-condylomatous lesions) are harmless to the child and the course of pregnancy.
If a woman, after taking tests, discovers that she has HPV, this is not a reason to panic. The obstetrician-gynecologist will prescribe drug treatment in the second trimester, when the baby’s organs have formed. Some doctors recommend agreeing to a planned cesarean section if you have HPV.
However, there is an assumption that strains of the virus are able to penetrate the placenta. If the mother is infected, then the risk of infection of the child during natural childbirth tends to 100%.
Thus, HPV is an insidious virus that can lead to neoplasms of various types. In order to prevent infection, a woman should refuse promiscuity and should immediately treat all sexually transmitted infections. She also needs to lead a healthy lifestyle so that if she becomes infected, her body can fight off the infection. At least once a year, a woman should visit a gynecologist’s office and get tested for HPV.
Signs of papilloma in men: incubation period
Typically, symptoms of HPV in men do not appear for a long time. The main sign of pathology is the formation on the skin and mucous membranes of the groin and anus, penis and scrotum of papillomas and condylomas, warts, which do not differ in color from healthy areas of the skin.
Condyloma is a type of papilloma, attached to the skin with a stalk. Such formations can be multiple.
They often merge with each other, forming entire colonies that resemble cauliflower in appearance.
Warts look like round formations that are difficult to detect immediately. Sometimes they can be localized on the arms and soles of the legs. Papillomas often appear on the neck, chest, and oral cavity. The appearance of a round plaque with clear boundaries and a velvety surface on the skin of the penis indicates Bowen's disease, which is caused by the papillomavirus.
If there is an accumulation of a large number of warts in the anus, this may indicate that they are widespread in the rectum. These formations do not cause pain.
PCR in diagnostics
Today there are no uniform rules for the diagnosis and treatment of papillomavirus. This is due to the difference in strains and localization of the pathogen. Despite the fact that the diagnosis of PVI is carried out by doctors of different specializations, it includes the following stages:
- Visual inspection of lesions.
- Collection of biological material.
- Tests for the presence, identification of the type of HPV and the number of viral particles.
Methods for diagnosing urogenital type HPV:
- Colposcopy is an examination of the cervix with a special microscope. The examination allows you to clarify the presence, size and location of formations.
- Biopsy is the removal of tissue samples from the lesion. The procedure allows you to identify a precancerous condition and includes 2 types of studies. Cytology - taking a scraping of the affected area for examination under a microscope. Histology is the collection of a piece of tissue from the affected area for layer-by-layer examination using special compounds and examination under a microscope.
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) research. PCR is a fast and reliable way to diagnose papillomas. Due to the high level of specificity, it allows you to isolate a specific infectious agent, its type and type, regardless of the stage of the pathology. The smear test is ready in 4–5 hours.
The doctor first examines the medical history and then conducts an examination. The detection of papillomas on the genitals indicates not only the presence of a virus in the body, but also a disruption of the immune system, as well as the possible development of other STDs. The doctor examines the skin and mucous membranes, identifying any formations on them.
Diagnosis of HPV in men also involves additional research methods. Usually prescribed:
- Laboratory tests of blood and urethral discharge. This makes it possible to determine the DNA of the virus.
- Urethroscopy, which examines the urethra.
- Carrying out a biopsy of papillomas to detect cancer cells.
One of the informative diagnostic methods is PCR. It makes it possible to accurately detect the DNA of the virus in the human body. Blood, prostate secretions or a smear from the urethra are taken for analysis. If there are homosexual contacts, the laboratory technician takes a swab from the anus. An equally effective method is Digene-Test; it allows you to identify the virus, its variety and oncogenicity.
Manifestations of HPV
- Warts. Dense growths with an uneven surface and color from gray to black. Appear after infection with low-oncogenic types of the virus. They do not threaten human life and health, but cause cosmetic problems. They are most often localized in the area of the hands and feet, but can also appear on the surface of the entire skin. There are also plantar warts, which become thicker and rougher when walking. Their characteristic difference is the appearance of blood when the top is cut off.
- Genital warts. They are benign neoplasms located on the skin and genitals. There are growths that are flesh-colored, pink or brown. Their characteristic feature is rapid spread. They can occur in the cervix, but it is also possible that the urethra, rectum and anus are affected. Condylomas cause discomfort in the form of itching and burning. At an early stage, single growths most often appear. At later stages, condylomas show the ability to merge. They do not pose a risk of degeneration into malignant neoplasms.
- Flat condylomas. More dangerous in terms of the development of cancer. The likelihood of cancer increases as new growths appear. This type of condylomas is usually located on the vaginal mucosa.
- Bowenoid papulosis. A viral disease considered precancerous. A characteristic feature is a rash in the genital area. Pigmented papules also appear - smooth brown formations. Papules often appear together with condylomas and warts. The components of the rash can lead to various types of cancer that are dangerous for women.
- Cervical cancer. For every woman, there is a risk that the virus will degenerate into a chronic form, and the precancerous condition may ultimately develop into cancer. If you don't treat the virus, it will just be a matter of time. In women with good immunity, such processes occur within 15 years. For those whose bodies suffer from weakened immunity, for example, HIV-positive women, this will take only 5 years.