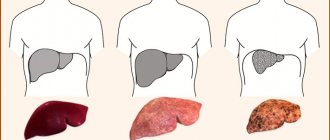
Cirrhosis is a serious chronic liver disease, as a result of which functional cells die and are replaced by connective tissue. This causes serious disturbances in the functioning of the liver and ultimately leads to its complete failure.
Timely diagnosis of liver cirrhosis in the early stages extremely important, since only at the very beginning of the disease is it possible to stop it.
Questioning and inspection
Diagnostics necessarily includes interviewing the patient. This allows the doctor to exclude possible diseases in the patient and make a preliminary diagnosis, on the basis of which further examination will continue. During the interview, the doctor clarifies the symptoms that bother the patient. As a rule, with the development of liver cirrhosis, complaints are received about:
- skin itching;
- scratching on the skin;
- drowsiness;
- fatigue;
- decreased mental and physical activity;
- bruises on the body that occur for no reason;
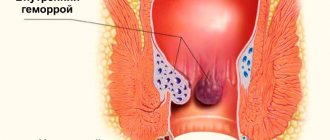
- frequent exacerbations of hemorrhoids;
- periodic vomiting with blood;
- redness of the palms and face;
- hair loss;
- problems with potency (in men);
- menstrual irregularities (in women).
Stages of development of liver cirrhosis
After the doctor has clarified the symptoms that are troubling the patient, the interview does not end. He also needs to examine the patient's medical history. To do this, he studies his medical history. This allows you to preliminarily identify the causes that could provoke the development of cirrhosis. As a rule, people suffering from this disease have previously been diagnosed with:
How to determine pancreatitis
- chronic alcohol dependence;
- hepatitis A, B and C virus;
- diseases of the biliary tract;
- hereditary metabolic disorders;
- primary biliary cirrhosis of the liver;
- ulcerative colitis;
- drug and chemical intoxication of the body;
- oncology;
- liver cysts, etc.
After the doctor has completed a complete interview with the patient and received all the necessary information about his condition, he begins the examination. First of all, he examines the sclera of the eyes, skin and mucous membranes (if the liver function is impaired, 90% of patients develop obstructive jaundice). Then the doctor asks the patient to lie down on the couch and palpates the abdominal organs. As a rule, in the presence of cirrhosis the following is noted:
- increase in liver size;
- changes in the contours of the liver (if the disease is present, they become uneven and lumpy);
- enlarged spleen.
Liver palpation
When palpating the liver, the patient does not notice any strong painful sensations. Based on the data obtained, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis. And to confirm it, he prescribes a number of diagnostic measures.
Manifestations depending on the type and stage of the disease
While the disease is just beginning, the patient may not even be aware of its presence. A latent stage or course without any symptoms is considered quite dangerous. If the first signs of liver cirrhosis are observed at a stage that is considered advanced, then serious consequences should be expected throughout the year. Indeed, in this case, the cells cannot recover.
It should be said about the main types of the disease, which are diagnosed depending on how cirrhosis of the liver manifests itself.
We are talking about cirrhosis:
The patient suffers from nosebleeds, bloating and enlargement of the abdomen (ascites), diarrhea, accompanied by bleeding from the veins of the esophagus and stomach (its lower part). The pathological process can last about two years. There is an increase in ascites and the appearance of an expanded venous network. Nausea and vomiting are more disturbing. Weight decreases to such an extent that complete exhaustion is diagnosed.
There is dryness and flabbiness of the skin. There is no jaundice. Blood pressure is usually low. Hepatic coma or acute hemorrhage leads to death.
The first signs of liver cirrhosis appear in the form of icteric discoloration of the sclera and skin, flat yellow growths on the eyelids, face and chest, as well as itching. The reason for such manifestations is stagnation of bile, while bile pigments are observed in the blood.
The disease develops over 5-8 years. Bleeding can result in death.
It is characterized by a severe course, since symptoms indicating both portal and biliary lesions are simultaneously present.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis are related to pathological changes.
Therefore, you need to know that there are stages:
- initial (signs and changes of a biochemical nature are not detected);
- subcompensatory (pronounced symptoms);
- decompensatory (accompanied by portal hypertension, swelling of the feet and legs, ascites, irreversible changes in the body).
The last stage can be recognized by certain symptoms.
Firstly, due to the fact that ammonia compounds, which are extremely toxic, accumulate in the blood, the patient is diagnosed with encephalopathy. Subsequently, hepatic coma develops. After a short period of euphoria, consciousness is depressed and orientation is completely lost. Problems arise with sleep and speech. Then a depressive state occurs and the patient loses consciousness.
Secondly, the presence of ascites, in which there is a significant accumulation of fluid, provokes bacterial peritonitis. The eyelids and legs swell.
Thirdly, it is because of heavy bleeding that patients most often die.
It is not difficult to recognize the last stage. The existing symptoms indicate the futility of any therapeutic measures.
Therefore, it is so important to detect external manifestations in order to prevent the situation from worsening.
Laboratory diagnostics
Laboratory diagnosis of liver cirrhosis involves examination of stool, urine and blood. The first step is to perform a general blood test. During this procedure, blood cells are counted, including platelets.
If a person actually develops cirrhosis of the liver, a general blood test will show a decrease in the number of liver cells. Congestion in the veins, which is characteristic of this disease, provokes hypersplenism syndrome. It is characterized by an increase in the size of the spleen and an increase in its activity. And since this organ is responsible for the composition of the blood (controls the level of hemoglobin, leukocytes and platelets), naturally, when its functionality is impaired, the development of anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia is observed.
In addition, a general blood test shows an increase in ESR, which indicates a low-grade inflammatory process in the body and a change in the ratio between blood proteins.
Complete blood count – normal values
In the absence of pathological processes in orgasm, a general blood test shows the following results:
- hemoglobin level – in men – 130–160 g/l, in women – 120–140 g/l;
- erythrocyte level – in men – 4–5 x 1012/l, in women – 3–4 x 1012/l;
- leukocyte level – 4.9 x 109/l;
- platelet level – 180–320 x 109/l;
- ESR level – 6–9 mm/h.
A decrease in these values indicates impaired functioning of the spleen and liver, which gives rise to further examination. And speaking about what other tests are performed for liver cirrhosis, we should also talk about a biochemical blood test.
During this study, various deviations from the norm were also noted. There is an increase in the level of bilirubin, which has a toxic effect on the body and contributes to the destruction of hepatocytes. Its excretion is carried out through bile. But since its outflow is also disrupted in cirrhosis, bilirubin begins to accumulate and has a negative effect on the body. Normally, this indicator should not go beyond 8.5–10.5 µmol/l.
During a biochemical blood test, doctors are most interested in the concentration of alanine aminotransferase (AlT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Normally, the ALT level is 7–40 IU/l, AST – 10–30 IU/l. An increased content of AST indicates the active destruction of hematocytes in the body. And an increase in ALT concentration indicates ongoing inflammatory processes.
Normal values of biochemical blood test
Also, special attention is paid to the level of gammaglutamyl transpeptidase. Normally, its levels in women are 6–42 U/l, in men 10–71 U/l. With the development of cirrhosis, the level of these indicators increases, which indicates the development of intrahepatic cholestasis.
In addition, when conducting a biochemical blood test, an increase in the following indicators is noted:
- alkaline phosphatase (normal 80-306 U/l);
- gamma globulins (normal 12-22%).
In this case, there is a significant decrease in the level of albumin (protein) in the blood, the synthesis of which is carried out by the liver. Normally, this indicator should vary between 35-50 g/l. If these indicators decrease, we can talk about impaired liver function.
Blood is also taken to determine antibodies to hepatitis. These tests determine the average blood clotting and the presence of markers of viral origin. If hepatitis antibodies are detected in the blood, then in some cases this even makes it possible to determine the cause of the development of cirrhosis - hepatitis.
Early diagnosis of cirrhosis also involves a blood test for hormonal changes. With the development of this disease, antibodies to mitochondria and fetoproteins are noted in the studied material. Moreover, this clinical picture is complemented by an increased concentration of insulin in the patient’s blood.
In addition to blood tests, patients also undergo a general urine test. The development of liver cirrhosis causes an increase in the level of bilirubin in the biological material being studied, which normally is not present at all. Another enzyme also appears in the urine - urobilinogen. It is also absent in the morning urine; it is present in the day, but in small quantities - no more than 10 mg.
General urine test: normal
A calogram is also performed to diagnose liver cirrhosis. When examining biological material, a change in its color is noted (stool takes on a white or clay tint) and a decrease in the level of stercobilin (its norm is 75-350 mg/day). If the patient has hemorrhoids or rectal fissures, a calogram will reveal blood in the stool.
A dangerous signal is darkening of the stool. If it takes on a blackish tint, this indicates internal bleeding. As a rule, in such situations, the calogram detects the presence of insoluble protein in the stool.
Preparing for the test
Blood biochemistry is prescribed if it is necessary to check liver function. Proper preparation for donating blood will help you get the most accurate results. Two to three days before visiting the laboratory, you need to exclude fatty, fried foods, fast food, sweets, smoked foods, cocoa, coffee, and marinades from the menu.
You should stop drinking alcohol a week before the test. Ethyl affects not only the condition of hepatocytes, but also the blood clotting rate. On the morning of blood donation, the patient should not smoke. But it is better to give up nicotine 10–12 hours before visiting the laboratory.
7 days before the test, you must stop taking any medications, including vitamin complexes. If this is not possible, then you need to stop taking the pills at least on the morning of blood donation. A woman must be sure that she is not pregnant. Due to gestation, it is possible that the permissible norms may be exceeded. And this cannot be considered as a symptom of a pathological condition.
On the morning of donating blood, you should avoid doing morning exercises, since increased physical activity can affect blood counts. The donation of biomaterial is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. The last meal should take place the night before. Dinner should be light.
Blood is drawn from the ulnar vein. The procedure is painless, but may be accompanied by slight dizziness. The interpretation of the resulting analysis should be carried out by the attending doctor, since only a qualified specialist is able to compare all the data received and determine the presence or absence of pathology.
Computer diagnostics
Speaking about how to diagnose liver cirrhosis, it should be noted that the results of examination, questioning and tests of feces, urine and blood are not the basis for making an accurate diagnosis. To diagnose it, you will need to undergo a more detailed examination, which includes various computer diagnostic methods. Among them is ultrasound.
This study allows not only to identify pathological processes in the liver, but also to detect the development of complications against them. During an ultrasound, a specialist pays special attention to the boundaries of the organ, its size and structural content.
With an ultrasound examination, the doctor can distinguish healthy functioning areas of the liver from damaged ones, determine the extent of their prevalence, identify fragmented foci of inflammation that can cause cancer, and also conduct hemodynamics of the liver. The transcript of the study and the diagnosis are described in a form, which is then given to the patient immediately after the ultrasound is completed.
Ultrasound examination of the liver for cirrhosis
FGDS is an equally informative diagnostic method. Used to diagnose diseases associated with internal bleeding processes. Carrying out FGDS allows you to determine the stage of development of the disease, the degree of dilation of the hepatic ducts, and in some cases even determine the cause of cirrhosis.
Computed tomography (CT) also provides a lot of information about the condition of the liver and the presence of a cancerous tumor in it. In the presence of pathological processes, under the influence of ultrasonic vibrations, painful areas of the organ begin to be punctured and painted a different color.
CT is probably the only diagnostic method that allows you to immediately make a correct diagnosis. But since computed tomography also makes it possible to identify recurrent diseases that occur against the background of cirrhosis, it is recommended not only for making a diagnosis, but also for monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
There is another equally informative method for diagnosing liver cirrhosis - MRI. It allows you to evaluate the parameters of the organ in accordance with established standards, determine the structural component of the liver, its location and lesions. In addition, MRI makes it possible to obtain information about the condition of the portal vein, which passes through the liver and is the main source of its blood circulation.
How to recognize complications?
Complications during cirrhotic processes most often appear in the later stages, but in hepatological practice they also occur in the initial stages of development.
The main complications are presented in the table:
| Complication | Description and symptoms |
| Hepatic coma, encephalopathy | Pathological conditions are characterized by disorders of the central nervous system. A good mood quickly gives way to causeless aggression. Symptoms such as sleep disturbance, deterioration in concentration and memory are observed. |
| Internal bleeding | The vomit contains streaks of blood, the feces have a rich black color (sometimes there are also inclusions of blood impurities). |
| Ascites | The complication is easy to diagnose visually, since the abdomen increases in size, a venous pattern clearly appears on it, and the navel protrudes. |
According to doctors, it is possible to reliably determine cirrhosis and differentiate the pathology only through a comprehensive examination of the patient. At home, it is difficult to even suspect, since symptoms do not appear in the initial stages.
Instrumental diagnostics
To identify liver cirrhosis and complications developing against its background, a biopsy is performed. This diagnostic method makes it possible to detect the development of pathological processes in organ tissues that are malignant in nature. To do this, fragments of liver tissue are collected and further histologically examined.
Despite the fact that there are many methods for diagnosing liver cirrhosis, the principles of which are based on detecting pathological processes in the organ and determining the degree of their development, laparoscopy is considered the most informative method. It allows you to thoroughly examine the affected organ, assess its physical condition, determine the level of functionality and the possible development of cirrhosis.
Laparoscopic diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
If the patient has large-nodular cirrhosis, then during a laparoscopic examination of the liver, brown nodular compounds that form on its surface will be visible. Their diameter ranges from 3 to 4 mm, their shapes are irregular, and their contours are unclear. In the case of micronodular cirrhosis, the shape of the liver remains unchanged, but there is a thickening of its capsule and expansion of the portal vein.
The role of the nurse in caring for a patient with cirrhosis of the liver
The role of the nurse in caring for a patient with cirrhosis of the liver:
- • provide a medical and protective regime;
- • control over compliance with diet;
- • consumption of any alcohol is prohibited;
- • in weakened patients - bed rest, which provides general care and a comfortable position in bed for the patient;
- • limitation of physical activity;
- • with the development of ascites, it is necessary to limit table salt to 5 g per day and liquid to 1 liter per day;
- • monitoring the patient's diuresis;
- • body weight control;
- • control over the complete and timely intake of medications prescribed by a doctor;
- • it is necessary to explain to the patient the meaning of medical procedures;
- • when a doctor prescribes tests, preparation for them;
- • skin care;
- • monitoring the patient's mental state.
Share the article on social media. networks:
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis distinguishes the nature of the pathology and its type and includes ultrasound, biopsy, histology and laparoscopy. Diff. diagnostics can give an accurate assessment of the condition of the liver and eliminate the possibility of making an incorrect diagnosis. When it is carried out, the following are revealed:
- foci of inflammation;
- degree of prevalence of pathological processes;
- degree of dysfunction of the organ;
- the presence of complications and the degree of their development;
- malignant transformation of the liver.
After making an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will be able to decide on further treatment tactics. What it will be depends on several factors - the patient’s age, the presence of concomitant diseases, the degree of liver function. First, they try to eliminate the development of pathological processes through drug treatment. But if it does not give positive results, surgical intervention is performed.
When do you need urgent help from a specialist?
Liver cirrhosis provokes a number of serious complications for the human body. Often they are the main problems that lead to deterioration of health, and sometimes even become the cause of death. In order to help a patient with liver damage in a timely manner, it is necessary to call an ambulance in the following conditions:
- vomiting coffee grounds – possible internal bleeding;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure and cold sweat, weakness - possible internal bleeding;
- fever, weakness, swelling, jaundice – hepatic coma;
- the appearance of spots similar to urticaria, symptoms of suffocation, Quincke's edema - allergic shock;
- fever, specific sounds when listening, weakness, signs of intoxication - infection of fluid in the abdominal cavity.