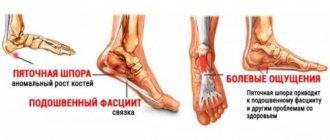
Flat feet in children and adults: symptoms and treatment.
The most common deformation of the foot structure is flat feet.
With this type of deformation, the main support of a person partially loses the usefulness of all its functions.
With a normal structure, the foot performs shock absorption and motor functions.
The foot has 2 arches: transverse and longitudinal. These parts act as shock absorbers when walking, softening shaking.
The load on the lower limbs must be balanced.
When the ligaments, muscles and joints are weak, for various reasons, the arches subsidence and the foot becomes flattened.
This leads to complete or partial loss of spring function.
In such a situation, the function of depreciation passes to other parts of the human body.
The spine, joints of the knees, ankles and pelvis begin to take on excess load.
With flat feet, the foot becomes flat, sometimes even completely flat.
It is known that the foot has a number of nerve endings. Their constant injury leads to various diseases. Aches in the legs with flat feet are just a minor thing.
- Causes of flat feet
- Degrees of flat feet
- Types of flat feet
- Symptoms of flat feet
- Pain with flat feet
- Treatment of flat feet
- Treatment of flat feet at home
Characteristics of third degree flat feet
In its normal form, the human foot has curves and anatomical irregularities. This design allows you to absorb movement and reduce the load when walking. Flat feet is a curvature of the foot that appears under the influence of various factors. Experts distinguish three forms of pathology:
- Initial. At this stage, the curvature of the sole is difficult to notice; the patient does not experience any discomfort. The pathology is latent, but develops rapidly.
- The second stage is already making itself felt. The patient notes an unpleasant sensation when walking, often pain and burning. Changes are visible on the inner surface of the foot - the instep becomes less pronounced.
- The third stage is the most difficult. Even with minimal exertion the patient experiences pain. There is a deformation of the foot, the bend is almost indistinguishable. The sole is smooth.
The third degree of flatfoot provokes the development of complications in the spine, which often leads to the formation of:
- arthritis or arthrosis of the joints;
- intervertebral hernias, various departments;
- the appearance of osteochondrosis of the spinal column.
Prevention of flat feet in children
Read more…
Prevention of flat feet in children begins from the first year of life. At this age, it will consist of the prevention and treatment of rickets and other neurological diseases that can cause flat feet. We should not forget that no shoe, even the most useful one, can replace a child’s barefoot walk on grass, sand and other natural uneven surfaces. Research by Indian doctors shows that those who spent a “barefoot” childhood are three times less likely to suffer from flat feet than those who wore shoes since childhood. However, there is one “But” in this rule. It is good for a child to walk barefoot on the grass, but walking barefoot on a completely flat and hard floor is harmful.
For older children, you can conduct special games with elements of foot gymnastics. Such gymnastics may include such simple exercises as walking on your heels, on your toes, on the outer and inner sides of the foot. Jumping in place, lifting your heels (while keeping your toes in place), crawling with your toes back and forth. It will be useful to roll gymnastic sticks with a diameter of 2-3 cm or tennis balls with your feet, lift small objects from the floor with your toes and climb gymnastic stairs. All this develops the muscles of the feet well and improves their blood supply.
Any gymnastics will show better results if it is combined with water procedures. For example, swimming is a good means of stimulating not only the tone of the body's skeletal muscles, but also hardening.
Reasons for appearance
Third degree flatfoot is the result of lack of treatment. As the pathology progresses, it reduces the elasticity of the ligaments and their tone, and depreciation decreases. Provoking factors include:
- Metabolic failure, obesity and thyroid disease. People with obesity of 2 degrees or more are at risk.
- Vitamin D deficiency.
- Presence of aggravated connective tissue diseases.
- Osteochondrosis of any part of the spine.
- Viral tissue damage, systemic infection.
What is flat feet
Flat feet is a disease that develops throughout a person’s life cycle and requires treatment. Leads to deformation changes in the arches of the feet, ankle, knee and lumbar joints (with progression of 3rd and 4th degree flat feet).
If an adult has advanced grade 3 flatfoot, when walking there is a shock load on the ankle, hip and knee joints.
Due to the impact of the articular surfaces against each other, joint injury occurs, leading to various degrees of deformation. The appearance of crunches in the knees signals that the joint tissue has begun to deteriorate, and urgent treatment is required for the disease.
With the development of progressive third degree flatfoot, the human skeleton may become distorted, making it more difficult to treat the disease.
Symptoms
It becomes possible to distinguish the presence of pathology without the help of a specialist only when the disease progresses, at stages 2 or 3 of flat feet. Symptoms of the pathology:
- Negative sensations in the feet with minimal load. A short run or walk causes unbearable pain in the feet, the patient notes a burning sensation and swelling of the tissues, and a feeling of heaviness. All these symptoms should prompt a person to think about an examination.
- The pain is not limited to the feet, it gradually moves to the hip, knee and ankle joints. The patient notes crunching and aching.
- The relief of the foot is greatly changed, the gap between the toes and the heel is not visible. The sole is flat and wide. The fingers are deformed, they lengthen and begin to squint in different directions. Negative sensations are intensified by the appearance of dry calluses and corns.
The progression of flat feet provokes poor posture; it is difficult for the patient to walk, his gait is uncertain. The back of the heel protrudes, the joint adjacent to the big toe bends to the side.
Pain is a frequent companion of flat feet in the third stage; it accompanies the patient even during the course of medical therapy.
Symptoms of flat feet
The symptoms of longitudinal and transverse flatfoot have much in common.
Only with a visual assessment by an orthopedic doctor can the type of illness be determined.
Additionally, radiography and plantography are performed.
Other signs of flat feet are the following:
- Quick fatigue of the legs when walking for a long time.
- Feeling of heaviness in the legs.
- Swelling of the feet and ankles.
- The appearance of seizures.
- Difficulty walking in heels and narrow shoes.
- Modification of the foot.
- The sole of the shoe is worn unevenly.
- Frequent headaches.
- Painful sensations in the lumbar region.
- Pain in knees and calves.
- Increased area of calluses.
- Deformation of shoes with inward slopes.
- Modification of the big toes.
- Heel spread.
- Rapid increase in the size of necessary shoes already in adulthood.
- Hammer fingers.
- "Heavy" gait.
- Change in posture.
If one of these symptoms or a combination of them appears, you should consult a doctor. Delayed treatment or lack thereof can aggravate the situation and lead to complications.
Classification
Experts divide the curvature of the feet into several types depending on the provoking factors. A congenital deviation in the formation of the foot is diagnosed already in the first year of a baby’s life; at this stage it is easy to treat. Acquired pathology is formed under the influence of other factors and often occurs latently, until visible changes appear. Static flatfoot develops as an occupational syndrome in people who spend a lot of time on their feet.
The disease is also divided into three types according to the degree of manifestation:
- Transverse flatfoot 3rd degree. One-sided curvature is noted, the arch is flat, the length of the foot decreases. The fingers become deformed and deviate to the side. The angle of deviation of the first from the second metatarsal bone is more than 20 degrees.
- Longitudinal flatfoot. There is a strong plane of the arch, minimal clearance. With longitudinal flatfoot of the 3rd degree - the heel goes back, the sole increases in size.
- Combined. A type of deformity combining transverse and longitudinal symptoms. The sole is completely deformed, it is wide, the toes are crooked.
Flat feet in children - symptoms and causes
At first glance, a child’s foot is the same as an adult’s foot, only in a smaller form. However, upon closer examination, it turns out that this is not the case. A child's foot is flat, but this does not mean that all children are flat-footed. During the “child-adult” period, the foot goes through a series of metamorphoses, forming into a full-fledged functional organ of the human skeleton.
From birth, a child's arches are filled with subcutaneous fat, so the child's imprint will always be flat. The correct formation of the foot begins with the baby's first steps. And by the age of three or four years, the bones, muscles and appearance itself acquire the outlines of an adult foot, which allows the baby to be on his feet longer. The older the child, the better the clearance of the arch of the foot is visible. In some cases, the foot is formed incorrectly and flat feet occur. However, if the foot was formed correctly in childhood, a person is still not immune from this disease in the future.
Complications
The human foot is designed to extend the life of large joints and the spine, and to absorb all parts of the musculoskeletal system. Without treatment, flat feet provoke various forms of curvature:
Longitudinal deformation provokes an inward rotation of the ankle joint, and clubfoot develops. First of all, posture suffers; a person feels unbearable pain in the legs and spine, even with minimal physical exertion.
The transverse shape provokes the appearance of growths on the fingers. Permanent trauma to the bursae causes bursitis. Lack of treatment can result in disability or even amputation.
If a patient has a combined type of flatfoot, complications provoke dysfunction of the entire musculoskeletal system. Inflammation of articular cartilage appears in different bone parts, they quickly wear out, and there is no shock absorption. The result of such a complication is complete disability, the appearance of intervertebral tumors, and paralysis.
Not only the severe form of flatfoot leads to the development of complications, but also progression at stage 2 of the disease. There is unbearable aching pain in the joints. Incorrect posture and negative symptoms cause distortion of posture, which leads to changes in gait. With severe deformities of the feet, it is difficult for the patient to maintain balance and perform basic physical activity.
One of the unpleasant consequences of finger deformation is ingrown nails. In these areas, pathogenic microflora develops and purulent foci form. Entry thresholds open for the penetration of various fungal infections.
Consequences of flat feet
Flat feet lead to a loss of shock-absorbing ability of the foot. As a result, the entire bone apparatus begins to experience harsh shocks when walking. The concussion is transmitted up the skeleton and reaches the brain. With severe flat feet, these excess loads affect various places, causing:
- changes in gait and posture. The gait becomes heavy, “clubfooted”;
- foot diseases and foot pain;
- diseases of the knee joints (arthrosis deformans, inflammation of the menisci, knee joint laxity) and knee pain;
- diseases of the hip joint (coxarthrosis);
- diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, scoliosis, herniated discs, radiculitis) and back pain;
- headache.
Diagnostics
You can notice changes in your feet even with the initial symptoms on your own if you care about your health. A clear symptom of flat feet is heaviness in the legs, rapid wear of the heels and soles of shoes.
To confirm the diagnosis, specialists use various methods, including even visual inspection of the patient’s shoes:
- Plantography is the most effective way to visually confirm the presence of flat feet. A non-greasy cream is applied to the sole, after which the patient is asked to leave a footprint on a clean sheet of paper. Sometimes products use a coloring composition instead. The orthopedist carefully examines the footprint, then makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
- Radiography, unlike plantography, is an accurate diagnostic method that helps to see the structure of the bone apparatus. The orthopedist takes photographs of frontal and lateral projections, as well as under load. The image is then measured to determine the degree of curvature and determine further treatment options.
Determining the degree of flat feet
If you are worried about the condition of your legs, you can conduct rapid testing using the Friedland method at home. To do this you will need a compass. It is used to measure the height of the foot - the distance from the surface on which a person stands to the highest point of the instep of the bend. The length of the sole in millimeters is also required. The height is multiplied by 100 and divided by the length, compared with methodological values:
- the resulting value is in the range from 31 to 29 mm - no flat feet;
- value ranging from 28 to 27 - the arch of the foot is underestimated, changes are present;
- if the readings are 26 or lower, consult a doctor to prevent the progression of flat feet.
Specialists rarely use the Friedland method, because it is less informative and much more effective in determining anthropometric indicators. Indications and goals of surgical treatment of flat feet.
Methods for diagnosing flat feet
Diagnosis of flat feet is carried out by an orthopedic traumatologist. The degree of flatfoot is determined using instrumental research methods.
Plantography
Plantography is the determination of flat feet based on the imprint of the plantar surface of the foot obtained using special equipment (plantograph).
Radiography
To diagnose flat feet, radiography of the foot is used. This research method makes it possible to establish a diagnosis and determine the degree of flat feet.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Surgery for flat feet 3rd degree
The task of surgical intervention is to give the correct degree of bending, and how to treat grade 3 flat feet quickly is determined by a specialist after diagnosis.
Surgical interventions for longitudinal flat feet
Pathology has several varieties - longitudinal, transverse, combined. To eliminate the first type of foot curvature, specialists most often perform plastic surgery of the ligaments and tendons. The degree of deformation determines whether surgeons will work with tendons or move on to the tarsal bones.
Experts distinguish several types of surgical interventions:
- Plastic surgery of tendons and ligaments.
- Subtalar arthrodesis.
- Arthrodesis.
- Osteotomy of the calcaneus.
Experts have experimentally found that the most effective method of treating longitudinal type 3 flatfoot is medializing osteotomy of the calcaneus with subtalar arthrodesis. The technique works well and does not cause complications. Repeated surgery is also not necessary.
Video treatment for flat feet
Operations for transverse flatfoot
In this type of flatfoot, an osteotomy of the metatarsal bone is performed, complementing the treatment with plastic surgery of the ligaments and tendons. Surgical intervention is indicated for hallux valgus.
What are flat feet like?
Deformation of the foot can lead to flattening of the longitudinal arch, in this case they speak of longitudinal flatfoot
.
Flatness of the forefoot is called transverse flatfoot
. If the deformity affects both arches of the foot, combined flatfoot is diagnosed.
Flat feet can be congenital
.
In this case, improper development of the foot occurs due to intrauterine defects. This is a fairly rare occurrence. Much more common is acquired flatfoot
, which can develop at any age.
Treatment of flat feet 3rd degree
If pathology is detected in an adult, it cannot be completely eliminated. You can only slow down the progression and prevent premature wear of the joints.
For the treatment of third-degree flatfoot, the following are used: drug therapy; orthopedic instep supports and a set of exercise therapy exercises.
If all these methods do not give positive dynamics, patients are indicated for surgical intervention, which consists of shortening the tendons and creating a new arch of the foot using orthopedic structures.
Often flat feet are aggravated by joint inflammation and bursitis. To relieve them, non-steroidal drugs and hormonal injections are used. How to cure third-degree flatfoot with medications:
- Take chondroprotectors of natural origin regularly.
- Diversify the diet with biological supplements with collagen and elastin, hyaluronic acid.
- Vitamin complexes and mineral supplements are needed.
An important part of therapy for eliminating grade 3 flat feet is gymnastics. It helps strengthen the spine, has a beneficial effect on muscle tone and the entire body, and prevents wear and tear on joints.
The orthopedic surgeon selects the exercises individually, but there are basic techniques for daily exercise at home. These include: picking up small objects from the floor, squeezing each toe one at a time, and rolling from heel to toe.
This set of exercises must be supplemented with a foot massage, which is performed using the following technique:
- The foot is fixed with one hand, and the sole is slowly kneaded with the other from the toes to the heel. The pressure is light, more like stroking.
- Soft movements gradually turn into more intense ones; it is necessary to work the muscles of the entire foot. This forms the correct shape and improves blood circulation in the tissues.
- After working out, proceed to massage the ankle joint, gradually to the knee. At this stage, both hands are already involved.
Methods for eliminating pathology in a child
It is completely possible to cure grade 3 flat feet in children; their joints are not yet fully formed, and the ligaments are more elastic than in adults. In addition to the use of drug therapy and therapeutic exercises, children are prescribed:
- muscle stimulation using physiotherapeutic methods;
- contrast water procedures;
- manual therapy;
- wraps and baths using various nutrients.
Therapeutic massage is a mandatory addition to therapy for flat feet in children. It is carried out in a course of a maximum of 30 procedures. Massage stimulates metabolic processes at the cellular level, improves tissue metabolism and increases the degree of blood supply, and helps strengthen the leg muscles.
It is not recommended to perform manipulations on your own; it is better to call a chiropractor or purchase specialized accessories for exercises:
- massage rollers;
- small balls;
- rubber mats with different convex parts.
Causes of flat feet in children
Sometimes flat feet are congenital, but this is the exception rather than the norm. Among all cases of flat feet in childhood, these are approximately 3%.
Indian researchers found that city residents who regularly wore shoes had flat feet three times more often than those who spent their childhood in the countryside and had the opportunity to walk barefoot. Consequently, the foot is better formed in natural and primitive conditions.
Other medical studies have found that the correct formation of the foot is influenced by the amount of load on it. The less physical activity a child has, the more likely he is to develop flat feet. This is especially true for our time, in the age of high technology and universal computerization. Children increasingly prefer the computer to playing outside and going for walks. As a result, flat feet in children are increasingly occurring together with poor posture.
The development of flat feet in children is greatly influenced by the shoes the child wears. Parents should know that shoes for a child should have a small heel (half a centimeter), soft arch support and a hard heel. In this case, the arch support compensates for the absence of stones and unevenness underfoot.
A child should not wear someone else's shoes - worn-out shoes will not distribute the load on the feet correctly.
For proper foot formation, a healthy diet is important. It is important to ensure proper phosphorus-calcium metabolism and the presence of vitamin D.
The formation of the arch of the foot requires constant training; barefoot walking is good for this. It is advisable that the child at least sometimes walk on sand, grass, pebbles and other uneven surfaces. Such surfaces can be recreated at home. Instead of the same pebbles, peas will do. In this case, the child may be wearing socks, but not shoes. These simple measures will help prevent flat feet in your child.
Can you serve in the army with third degree flat feet?
The presence of this pathology negatively affects the entire body as a whole; a person with such a disease is not suitable for military service. Even the initial stage of the disease, if progressed and untreated over a year of service, will lead to disability. Therefore, the military commissariat conducts thorough research and enters all the data into the conscript’s medical record. Young men diagnosed with flat feet of the 2nd degree, burdened with arthrosis or osteochondrosis, are guaranteed exemption from military service.
Exercises to prevent flat feet
On the Internet, here and there, you can easily find not only sets of exercises for the prevention of flat feet, but also sets of exercises for the treatment of flat feet. I must say they are very similar. Many exercises for the treatment of flat feet are also used for its prevention. All of them are performed barefoot.
- Shifting the center of gravity to the forefoot. From a standing position, with your toes and heels together, your back straight, holding onto a support (the back of a chair, a wall bars), lift yourself onto your toes for 5-8 seconds and lower back down onto your foot.
- From a sitting position on a chair, try to pick up a table tennis ball or other small object from the floor using your toes.
- "Caterpillar". From a sitting position on a chair, with your legs spread wide apart, move your feet closer and further away along the floor by flexing and extending your toes, imitating the body movements of a caterpillar.
- From a sitting position on a chair, legs together, feet closed, you should spread your knees to the sides and, lifting your heels off the floor, close your soles.
- Walk for 1-2 minutes on your toes, then 30-60 seconds on your heels, on the inside and outside of the foot.
- Standing, close your feet together, and then spread your toes as wide as possible, and then, in the same position, spread your heels as wide as possible.
- Without lifting your feet off the floor, perform 5-10 squats.
- Standing on one leg, bend the other at a right angle at the knee and perform rotational movements with the shin, and then with the foot. First clockwise, then counterclockwise. After performing 4 rotations in each direction, repeat the same with the other leg.
- Walk in a goose step for 30-60 seconds, then the same amount in a half-squat.
- Grab the pencil with the toes of one foot and walk like this for 30-40 seconds.
Exercises for flat feet are a preventive measure to keep your feet healthy and reduce the risk of developing flat feet.
Prevention
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Children can easily get rid of pathology if they pay due attention to it. As a preventive measure, you must follow simple rules and then you will not face disability:
- Monitor your child's weight and control your body weight. Avoid overeating and developing obesity.
- Those who have to stand on their feet for a long time due to duty should occasionally give their feet a rest: walk for a short period of time on the outer edge of the foot or distribute the load from one leg to the other.
- Massage your feet regularly, walk barefoot on rocks more often.
- Choose comfortable shoes with orthopedic arch support.
- Consult an orthopedist regularly.
Causes of flat feet:
- poorly chosen shoes (narrow shoes with pointed toes, high heels and platforms);
- pregnancy and weight gain, both muscle and as a result of obesity;
- hereditary predisposition: genetic abnormalities in the development of ligaments, muscles and bones of the foot and congenital weakness of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus;
- injuries: foot injuries, fracture of the ankle and heel bone, bruises and cracks of cartilage, ruptured ligaments, damage to the muscles and ligaments that strengthen the arch of the foot;
- diseases: rickets and, as a result, weakened and soft bones, which are very easily deformed, complications after polio - paralysis of the muscles of the sole and lower leg;
- insufficient physical activity, and as a result, weakness of muscles and ligaments - “sedentary” work;
- excessive physical activity - “standing” work, passion for running and jumping sports.
As you can see, there are many reasons for flat feet, but the main reason, about 8 out of 10 cases, is poor development of the muscles and ligaments of the foot. Therefore, in order to properly form the arch, you need to constantly train them. Without load, the foot muscles become weak and are unable to support the foot in a normally elevated state, which is the cause of flat feet.
Therefore, it is very important that the muscles and ligaments of the feet are strong and support the foot in an elevated state, removing the load from the joints of the legs and spine.
Interestingly, flat feet occur both in people with sedentary professions and those who spend their entire working day on their feet. This is due to the fact that in the first case, the muscles and ligaments become weak due to lack of loads, and in the second case, the loads are too large and the ligaments and muscles simply cannot cope with them.
Video about flat feet
We have collected several educational materials that will help you independently diagnose the presence of changes and begin timely treatment.
Read also:
- Occipital neuralgia
- Shants collar: how to wear it correctly and how much, types and sizes
- Symptoms and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
- Treatment of neuralgia and neuritis with herbal medicine
- Intercostal neuralgia
- Pinched nerve in the lower back - understand and treat
←Return
Forecast
So, is it possible to cure grade 3 flat feet? Unfortunately, this is a rather complex and unpleasant disease. It won't go away in a couple of months. It is necessary to prepare for long and difficult work to correct those changes that have also taken a long time to form.
In addition, it is almost impossible to cure grade 3 flatfoot completely, especially if pronounced impairments are observed. The patient’s condition can be corrected, his movement can be facilitated, his quality of life can be improved, but one should not count on a full recovery.
Treatment for this disease should become a way of life. After all, as long as the patient meticulously follows all the doctor’s recommendations, he will feel an improvement in his condition. As soon as the patient decides to give up classes, the disease will immediately make itself felt.
Manifestations of transverse flatfoot
Transverse flatfoot is characterized by flattening of the transverse arch of the foot. Its anterior section rests on the heads of all metatarsal bones. The thumb is deviated outward, and the middle finger has a “hammer” deformity. The overall length of the foot in such a patient decreases due to the fact that the metatarsal bones fan out from each other. This type of pathology is more typical for patients aged 35-50 years, especially women.
Please note: among the signs of pathology are the so-called. “bone” and “corns”.
Flat feet: complications
Flat feet, as can be generally understood from the characteristics of the course and progression of this disease, can provoke a number of specific complications, among which we highlight the following:
- a gradual increase in pain, its nonspecific manifestation (that is, pain not only in the feet, but in the hips, knees, back, headache);
- clubfoot;
- unnatural posture, curvature of the spine, development of scoliosis and other diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, hernia, etc.);
- ingrown nails;
- dystrophic changes developing in the muscles of the back and legs;
- the development of diseases directly related to damage to the feet (deformations, calluses, curvature of the fingers, neuritis, spurs, etc.).
Consequences of flat feet
As for such an issue as the prevention of flat feet, it consists, first of all, in the selection of appropriate shoes. High heels are excluded; the optimal option is considered to be a height not exceeding 4 centimeters. It is systematically important to visit a doctor to monitor the general condition of the legs; if there are any kind of problems associated with the legs, an examination by a specialist is carried out more often. As an additional measure to prevent flat feet, the need for physical exercise and gymnastics is considered. To relax muscles and relieve general leg tension accumulated during the day, baths are recommended. If you have problems with excess weight, you should take care to solve this problem, because overweight and obesity are among the main problems that contribute to the development of flat feet, as well as placing additional stress on the legs and spine.
If symptoms appear that indicate the possible relevance of flat feet, it is necessary to visit an orthopedic doctor.
Corrective therapy
Only 25% of people with flat feet require medication. They are prescribed painkillers, and then, when the pain threshold decreases, massage and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Attention! You need to start fighting to correct flat legs with strengthening exercises for the ligaments and muscles of the foot. Most often, doctors prescribe massage and physiotherapy.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy treatments include:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- UHF;
- paraffin-ozokerite application.
The sessions will help not only normalize metabolism, increase blood flow, but also reduce pain, strengthen the legs, ligaments and muscles in them.
Massages
In addition to traditional treatment, massage has a good effect on restoring the body. It is better to entrust treatment sessions to a professional, but some exercises can be done at home. To do this, it is advisable to purchase a massage mat and exercise equipment for flat feet. An excellent massage option would be to walk barefoot on sand, pebbles, and stones.
Exercise relieves muscle fatigue, improves lymph circulation, blood flow, and strengthens muscles. They are carried out in the following sequence:
- massaging the calf muscles;
- rubbing the Achilles tendon;
- calf massage;
- massaging the back of the foot;
- sole massage.
It is advisable to carry out exercises in combination with physical therapy.
Gymnastics and physical education
The doctor can prescribe physical therapy sessions, which are useful for any type of flat feet. All exercise therapy exercises are aimed at correcting the ankle joint, restoring and correcting the foot.
Classes can be done independently at home. Every day in the morning you need to set aside 10-15 minutes to perform the exercises that make up the basic program of therapeutic exercises for flat feet.
Orthopedic shoes and specialized insoles
Many flat foot problems are associated with improperly selected shoes. When choosing, it is necessary to take into account any deviations in the foot.
The principle of selecting orthopedic shoes is that the inner edge of the foot in the middle and rear sections should have an elevation, as well as the outer edge in the forefoot. This is done using special pads inside the shoes.
If flat feet are not very pronounced, then you can choose shoes that will provide support to the ligaments and muscles. Shoes should be chosen with a comfortable width, with thick, low heels. A good, cushioned sole and flex toe allow for natural foot movement.
In case of severe flat feet, shoes are selected using individual orthotics.
An orthopedic insole or insole-instep support can help correct abnormal gait. Their purpose is to prevent correct foot placement and reduce the load on the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic insoles can be used at the first stage of flat feet. They can be cork, silicone, gel, or foam. They are produced in various versions:
- forefoot inserts;
- back inserts;
- insoles for the entire foot;
- insoles for half of the foot.
Special shoes and insoles help correct irregularities in the structure of the foot, preventing flat feet and the appearance of heel spurs.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is necessary in severe cases, when the ability to walk is lost and severe and constant pain is present.
The surgery involves inserting a metal implant into the back of the foot to support the arch. Surgeries are often performed to reconstruct the tendons and fuse the joints to properly rebuild the foot.
Attention! In the postoperative period, deformation of the foot sometimes occurs, especially after exposure to soft tissue. In order to get rid of this, operations are performed on the bones of the foot.
Hallux valgus
Hallux valgus is a disease that causes curvature of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the first toe. All other fingers also gradually become deformed. Due to changes in the first toe, a person cannot wear ordinary shoes and constantly suffers from aching pain. Valgus deformation of the toe leads to the fact that it deviates outward, and the “bone” on it increases. In addition to the big toe, the rest of the toe also change, becoming deformed like a hammer. The patient's legs quickly tire, and he suffers from pain in the joints.
To diagnose this disease, radiography of the feet , plantography , which allows you to see whether the sole is flat, as well as an examination by an orthopedic doctor. It is important to take into account that hallux valgus develops in both adults and children, so parents should be extremely careful. Treatment of the disease in cases where the disease is not advanced allows you to restore both the function and appearance of the feet. As a rule, massage, physical therapy, and wearing orthopedic insoles are prescribed. For more serious forms, the patient is prescribed surgery. Osteotomy is the reconstruction of several bones of the foot. After such an operation, the patient recovers from 2 to 3 months.
To prevent foot deformity from becoming a problem for adults and children, it is necessary to prevent the development of flat feet. An important preventative measure is wearing the right shoes . Deformation of the toes often occurs due to constant wearing of shoes with heels and narrow toes. In this case, the entire load falls on the forefoot, the big toe becomes deformed, and soon treatment of the disease is necessary. To prevent foot deformity in children from becoming a serious problem, parents periodically need to take their child for examination to an orthopedic doctor.
Causes
There are many reasons why the disease appears, develops and progresses in the modern world. The main reasons are considered:
Flat feet of the 3rd degree are usually a consequence of insufficient treatment in the initial stages, when the foot deformity was still subtle. As the disease progressed, the ligamentous apparatus weakened, the bones of the foot moved further away from each other, and its longitudinal and transverse arches sagged.
The foot coped with shock-absorbing functions increasingly worse, until the clinical picture reached the third stage of pathology development.
Obesity and connective tissue diseases lead to flat feet of the 3rd degree. The factor of metabolic disorders cannot be ignored, especially if the body lacks vitamin D, which contributes to bone deformation, including the foot.
Occupational chronic damaging factors, for example, working in a static position, also have an impact. Such professions include cook, salesperson, sales floor manager and others.
Flat feet can also be a consequence of fractures and other foot injuries. Moreover, pathological processes are often associated with a long stay of the foot in a cast and lack of loads, the development of muscle wasting.
The pathology can develop against the background of osteochondrosis, diseases of the ankle, knee and hip joints, and wearing incorrectly selected shoes, including high heels.
Classifications of flat feet by type and degree
Vault imprints
The first and second stages of flat feet are less noticeable in appearance than the third. But, regardless of the stage of the disease, each of them has its own characteristic signs that allow you to notice the problem in time and consult a doctor.
The first stage of the disease is practically invisible in appearance and does not cause any pain. The main symptom of the disease is general fatigue of the legs after a hard day at work. Usually no one pays attention to this, mistaking the symptom of the initial stage of deformation of the arch of the foot for ordinary fatigue. Sometimes an additional sign of a disorder is a minor cosmetic defect of the foot.
Flat feet of the second degree have more noticeable symptoms. These include severe pain in the feet and ankle joints, increased leg fatigue, and swelling. The patient regularly feels quite severe pain in the calf muscle, sometimes as a result of deformation of the bones of the arch of the foot, the gait changes. The deformation becomes quite noticeable externally and can cause not only physical, but also aesthetic discomfort.
If a patient is diagnosed with grade 3 flatfoot, treatment of the disorder in this case becomes a necessity for patients. The reason is the danger of this stage of curvature for the body - it can cause many diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Externally, the patient’s leg loses its curved arch almost completely.
Remember that health is the most important thing a person has. Take it more attentively and seriously, do not forget about the prevention of flat feet, take measures in time.
Insoles can be purchased at pharmacies or specialty stores. The cost of such products can range from 400-500 rubles to 1500. But if you decide to make to order, you will have to pay more, namely at least 2-3 thousand. But health is priceless.
Children's. The reasons for it are still unclear. The baby is already born with foot deformities. But changes can only be detected by the age of 5-7, since at an early age the foot will in any case completely touch the floor (it has not yet had time to form).
- 1) Use of special shoes and orthopedic insoles;
- . In this case, the load on the legs should be small. Intensive skiing is contraindicated.
- :
- With your legs slightly apart, clench and unclench your toes for about 2 minutes.
- Who is recommended to use massage mats
There are massage mats for flat feet
- Formation of correct gait, do not spread your toes when walking - this overloads the inner edge of the foot and its ligaments.
- If the finger deviates by more than 50 degrees, grade 4 is diagnosed.
- Flat feet is a deformation of the foot and its arch. In the vast majority of cases, this is an acquired disease that develops as a result of prolonged “standing” work, when wearing shoes with heels or narrow toes, when gaining weight, when an increasing number of kilograms begin to “press” on the bones and muscles of the foot. Among women, flat feet are 3 times more common than among men. The photographs below show how the foot is deformed. Flat feet lead to the development of other diseases, so it is important to carry out timely prevention and follow all doctor’s recommendations if you are diagnosed with this.
- Massage for flat feet is very effective. Its main objectives include improving blood supply and lymph circulation, strengthening muscles, tendons and ligaments, relieving stress from the most tense parts, and restoring some important functions of the foot. In addition, this procedure will help you relax and get rid of pain. But it is important to trust only professionals in their field!
- Rachitic. With rickets, bones become brittle due to a lack of vitamin D and calcium. As a result, a huge load is placed on the leg bones, which they cannot always withstand.
2) Performing special physical exercises that strengthen the ligamentous apparatus of the foot;
Q66.5 – congenital flat foot.
What it is?
Try to choose a rug that has not one, but several different types of relief
Longitudinal flatfoot I and II degrees
- The deformation of the foot is clearly pronounced, as a result of which the position of the bones in the lower leg and knee changes, resulting in pain in the legs, knees, lower back, and headaches. Regular shoes are not suitable for this degree of longitudinal flatfoot.
- You need to lead an active lifestyle, but avoid putting too much stress on your feet.
- Unfortunately, the deformations have already occurred and it is not possible to eliminate them. In this case, all measures should be aimed at stopping the changes and maintaining the structure of the foot that already exists. The person will be forced to change his lifestyle and some habits. Thus, it is necessary to wear orthopedic shoes with special insoles, perform special therapeutic exercises for flat feet, avoid increased stress and periodically undergo certain procedures. This will avoid even more serious problems.
- Depending on which arch of the foot is subject to changes, there are two types:
- An orthopedist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of transverse flatfoot. At the initial visit, an examination is carried out and the patient’s complaints are taken into account. Additional research methods that clarify the degree of flatfoot include:
- is a congenital disorder, the causes of which have not yet been fully established. In this case, the foot is most often turned down and inward.
- The exercise is similar to the previous one, only this time you need to lift your socks off the floor.
Types, forms
Gymnastics for flat feet is selected individually, depending on the type and severity of flat feet. Start exercising only after you have consulted with your doctor and found out what exercises are recommended in your case.
. This will provide different types of impact on the sole. For example, in addition to “stones”, there may be fibers on the surface for a soft massage of the soles.
- impact on the reflexogenic points of the foot;
- Transverse flatfoot of the first degree, in the absence of arthrosis in the joints of the foot (middle section), exostoses (spike-shaped osteochondral growths) and contractures (limited joint mobility).
This type of flatfoot is characterized by a decrease in the length of the foot due to the divergence of the bones of the foot, as a result of which the big toe deviates to the side and the middle toe is significantly deformed. Often a “bump” appears on the thumb - a painful thickening.
Wear comfortable shoes.
- Treatment of grade 1 or 2 flat feet in children is quite possible both in a hospital and at home. The child’s bones, ligaments and joints are just forming, so until adolescence, measures to eliminate the problem will be quite effective. The chances of completely getting rid of the disease increase if it is identified at the earliest stages. Then special gymnastics, the right shoes and massage will be enough. In more complex cases, procedures, massage, and special devices are indicated. But the treatment of grade 3 flat feet is complicated, since the deformities in this case will be serious. But still, efforts, an integrated approach and continuity will allow us to achieve success. And in some cases, surgical treatment is indicated. And now about everything in more detail.
- Transverse. With this type, it is the transverse arch of the foot that lowers. The load falls on the metatarsal bones of the fingers. Because of this, the length of the foot decreases, and the toes may diverge in different directions. In a third or even half of patients, along with this disease, other foot deformities occur.
- 1) Plantography is a method that allows you to get a foot print on paper. A similar method for determining flat feet can be done at home. To do this, you need to lubricate the sole with any dye and stand with your feet on a sheet of paper, taking your normal body position. Based on the resulting print, one can indirectly judge the presence and stage of flat feet;
- The following sports are recommended for flat feet:
- 4.
Some exercises you can do for flat feet
- Inspect the rug before purchasing
- improves blood circulation and lymph outflow (due to this, swelling in the legs decreases);
- To be released from the army with flat feet, the following conditions must be met:
Like longitudinal, transverse flatfoot has several degrees. They differ in the level of curvature of the thumb and the appearance of corns.
The doctor may recommend a special preventive set of exercises.
- What shoes to wear if you have flat feet? Definitely orthopedic. It must have an instep support that provides the foot with the necessary physiologically correct bend. The heel should be no more than 3 (maximum 4) centimeters, otherwise the foot will be deformed. But a completely flat sole is also harmful. Boots or shoes should not be too tight, but they should not be too loose either. Pay attention to comfort and convenience when walking.
- With a longitudinal form, the longitudinal arch is deformed. The foot touches the support with almost its entire surface, its length increases.
- 2) X-ray examination is one of the reliable methods that allows you to assess the nature of changes, the degree of the disease, and monitor the dynamics of the pathological process. The x-ray is taken in two projections with the patient standing;
- :
Place various small items on the floor. Grab them with your toes and move them from one place to another.:
What to do?
. Make sure all protrusions and bumps are strong enough. Think about how convenient it will be to wash and store the selected model.strengthening muscles and ligaments;Longitudinal or transverse flatfoot of the second degree with the presence of severe pain syndrome, stage II deforming arthrosis of the joints of the midfoot, contracture of the toes;
- By time of occurrence. This pathology can be congenital, that is, caused by impaired intrauterine development, or acquired during life.
- Due to purchase. The reasons why a person acquires this pathology are the following classification of this disease:
- Statistical flat foot occurs in a genetically predisposed person due to the influence of external factors that can contribute to the development of pathology: obesity, prolonged standing, poor-quality shoes, etc. A person’s inattention to such trifles gradually leads to weakening of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the leg. It should be noted that 3/4 of the number of cases of flat feet can be attributed to this type.
- Traumatic deformity occurs as a result of various leg injuries. These may be fractures of the tarsus or calcaneus, ruptured ligaments and muscles, or post-traumatic pain that negatively affects proper walking.
- Rickets flatfoot is a deformation of the foot frame after suffering from rickets.
- Paralytic foot usually results from paralysis of the foot muscles caused by polio or other types of neuroinfections.
- Based on the degree of flatfoot, there are three main types of foot deformities:
- longitudinal;
- transverse;
- combined flatfoot.
- Based on the direction of expansion of the arches of the feet, the following types of flat feet are distinguished:
- longitudinal;
- transverse;
- longitudinal-transverse flatfoot.
Features of treatment
Each degree of flatfoot differs in its characteristic methods of correction; therapeutic therapy is aimed at developing the muscles of the foot so that they can effectively support the arch.
Types of treatment:
- Massage with mats, balls, rollers, pencils, spiked balls - indicated at all stages of the disease, used to improve blood circulation and strengthen muscle tone;
- Exercises are effective for minor curvature of the foot; at the initial stage they can stop the progression of the pathology;
- Shock wave therapy, electrophoresis, paraffin baths - at all stages of foot damage, improve tissue metabolism, restore joint mobility;
- Orthopedic insoles – for relieving foot deformities (indicated for pregnant women, athletes, people who spend a long time on their feet due to their occupation);
- Orthopedic shoes - prevents the development of flat feet, reduces the load on the joints, corrects foot deformities (for women, the heel is no higher than 3 cm). You should choose shoes with a wide toe and a solid base at the heel, for children in size no more than 1 cm “for growth”.
Attention!
To relieve pain, systemic analgesics are used - Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Paracetamol. For external use, Indomethacin ointment, Dolgit cream, Voltaren gel are indicated.
When choosing a massage mat, it is important to consult a doctor about the size and degree of hardness. It is best to take a surface with different types of relief - stones, fibers, waves.
With a diagnosis of flat feet, sports such as swimming, skiing with light loads, and horseback riding are recommended. Prohibited: intense dancing, jumping, strength exercises, hockey.
Features of treatment for flat feet
Methods for treating deformity
Correction of flat feet at different degrees of development differs in methods and their applications.
Patients consult a doctor only if they begin to experience severe pain and it becomes unbearable to walk. Therefore, they often talk about the impossibility of treating this problem. The first degree usually develops in young adulthood or childhood and responds well to treatment if detected early. For this purpose, massage is used in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures and a special gymnastic complex. All methods are aimed at ensuring the development of the muscle fibers of the foot, which are responsible for maintaining the arch in the correct anatomical position.
Additional treatments
Additional techniques include:
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- hirudotherapy;
- mud applications.
These types of treatments are aimed at normalizing the process in soft tissues and improving blood microcirculation. Before starting sessions, you must consult with your doctor.
Diet
For flat feet, there is no special nutrition system. The diet should be designed in such a way that metabolic processes in the body accelerate and excess weight gradually disappears.
Principles to follow when creating a menu:
- use products containing B vitamins;
- avoid excessive consumption of phosphorus, which leads to disruption of phosphorus-calcium metabolism and demineralization of bones;
- observe water-salt metabolism, to do this, include in the menu such products as pumpkin, zucchini, watermelons, prunes, dried apricots;
- eat more raw foods;
- eat more often wholemeal bread, cereals, vegetables and fruits containing fiber.
Vitamins
To normalize metabolic processes, the body needs minerals and vitamins, which help strengthen the skeletal system and reduce the risk of developing flat feet.
What vitamins should you pay attention to:
- B vitamins: B1 is found in citrus fruits, baked potatoes, peas, beans, B2 is found in dairy products, B6 is found in nuts, chicken, lentils, bananas;
- vitamin C;
- vitamin D as a prevention of rickets.
General characteristics of the disease
Flat feet can be longitudinal or transverse; in each individual case, the degrees of damage to the arch are distinguished:
- 1st degree flatfoot – the clinical picture is mild, does not cause pain, is corrected by following preventive measures, does not provoke complications;
- 2nd degree flatfoot – a moderate defect that can be determined visually, moderate clinical characteristics are observed, the patient may experience clubfoot and heavy walking;
- 3rd degree flatfoot – complete deformation of the foot, severe symptoms, the patient’s condition leads to disruption of the musculoskeletal system, which can cause scoliosis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis;
- 4th degree flatfoot – pathological deterioration of the condition of the foot, the sole turns inward, symptoms are accompanied by severe pain, the disorder can only be eliminated by surgery.
The type of flatfoot is determined by X-ray methods, when measurements of the foot are taken in the lateral projection. The degree of the transverse arch is diagnosed from an image in a direct projection with a load.
Degrees of flat feet
Separation by type
Types of flat feet
The most dangerous is not transverse or longitudinal flatfoot, but rather a combined variant, in which the patient has several health-threatening pathologies from the first and second groups. For their treatment, surgery is usually indicated. Conservative medical methods in case of neglect are usually ineffective.
Longitudinal flatfoot leads to changes in the size of the legs. As a rule, the patient increases along the foot. At the first stage, such deformation does not cause much trouble to the patient. Longitudinal flatfoot of the 2nd degree without treatment leads to the disappearance of the arch of the foot, pain appears in the knee joints and lower back. At the third stage, pain symptoms spread to almost the entire joint group of the legs and lower back, as well as the spine. Often there is growth of the head of the first metatarsal bone, headaches, and changes in gait.
The transverse type of flatfoot includes three stages. The result of the deformation is a shortening of the foot and an increase in its upper part. Orthopedic insoles are used to treat the initial stages, but they are effective only at the initial stage of the disease. There are three stages of transverse flatfoot:
- Initial - mild degree with a deviation of the first finger by twenty percent from the normal biological position. Additionally, there is the appearance of corns on the foot and pain when walking.
- Medium – the second degree, formed as a result of the progress of the disease. The first toe deviates even more, a noticeable one- or two-sided flatness of the foot appears, and the corns increase in size.
- Severe – the final third form of longitudinal flatfoot. The development of the disease leads to deviation of the first toe by more than 35 degrees, corns turn into persistent calluses that are difficult to remove, and the foot increases in size. Severe pain when walking and physical activity becomes the norm for the patient.
The stages of the disease separately are rarely used in medicine when making a diagnosis. Typically, flat feet are divided into three types - transverse, longitudinal or combined.
Diagnostic issues
There are a number of signs that will allow you to suspect that a patient has flattened feet of one type or another:
- Gait and posture undergo certain changes.
- It becomes difficult to squat, especially difficult to maintain balance. Full forward bend is much easier to achieve.
- The shoes that are familiar to your feet suddenly turn out to be tight.
- The heel wears unevenly. The inside wears out faster than the outside.
- The sole at the base of the toes is covered with skin seals.
Deformation characteristics
Foot deformity
Using degrees, the severity of such a definition as flat feet is classified. This makes it possible to assess the level of impairment of the shock-absorbing functions of the feet and predict the impairment of the uniform distribution of load on the musculoskeletal system.
The most difficult medical case is stage 3 flatfoot. Diagnosis of only the first stage is not a reason to relax. The disease may progress. And in the case of prolonged exposure to factors that provoke deformation of the arch of the foot, flat feet of the 1st degree quickly turns into the third. In parallel, a number of destructive processes occur with the transverse and longitudinal arches of the foot. They change the biologically normal shape and distribution of load on the joints of the entire musculoskeletal system.
The result is displacement of the vertebrae, deformation of the joints, compression and damage to the cartilage tissue in each area subjected to increased loads. Of course, the process does not happen in a single moment. This is why flatfoot of the first degree, as well as the condition preceding it, is dangerous. The destructive process goes unnoticed for a long time.
The medical term “flatfoot” is a characteristic of a flattened, deformed arch of the foot. There are three degrees of flat feet, each of which poses a serious health hazard.
Prevention in childhood
The formation of a correct arch of a child’s foot is, first of all, an even posture and spine. So from the first steps of the baby, you need to think about his good health.
- Only correct shoes with hard backs and orthopedic insoles are allowed. Choose models from trusted manufacturers who offer shoes made from quality materials.
- Give your child the opportunity to walk barefoot - this is the best prevention of flat feet.
- For older children, suggest doing simple exercises with alternating heel/toe walking and inner/outer foot walking.
- Water procedures, jumping rope and climbing the gymnastic ladder perfectly strengthen the leg muscles of teenagers.
Watch the video of Dr. Komarovsky - children's shoes and flat feet:
Risks and complications
From all of the above, we can conclude that flat feet are a progressive disease. And if left untreated, the pathology can lead to serious complications. Consequences of flat feet:
- deformation of the bones of the foot, curvature of the big toe and the appearance of a bone spur,
- change in the shape of the little finger;
- ingrown nails;
- persistent calluses;
- disproportionate development of the muscular skeleton;
- knee joint diseases;
- pathologies of the hip joint;
- diseases of the spine (scoliosis, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia);
- varicose veins;
- benign foot formations;
- formation of heel spurs.
Three main degrees
Vault imprints
The first and second stages of flat feet are less noticeable in appearance than the third. But, regardless of the stage of the disease, each of them has its own characteristic signs that allow you to notice the problem in time and consult a doctor.
The first stage of the disease is practically invisible in appearance and does not cause any pain. The main symptom of the disease is general fatigue of the legs after a hard day at work. Usually no one pays attention to this, mistaking the symptom of the initial stage of deformation of the arch of the foot for ordinary fatigue. Sometimes an additional sign of a disorder is a minor cosmetic defect of the foot.
Flat feet of the second degree have more noticeable symptoms. These include severe pain in the feet and ankle joints, increased leg fatigue, and swelling. The patient regularly feels quite severe pain in the calf muscle, sometimes as a result of deformation of the bones of the arch of the foot, the gait changes. The deformation becomes quite noticeable externally and can cause not only physical, but also aesthetic discomfort.
If a patient is diagnosed with grade 3 flatfoot, treatment of the disorder in this case becomes a necessity for patients. The reason is the danger of this stage of curvature for the body - it can cause many diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Externally, the patient’s leg loses its curved arch almost completely. A person begins to experience severe pain in the knees, lower back, and hip joint. Often the patient is diagnosed with a hernia, osteochondrosis, or curvature of the spine.
Depending on the angle of curvature of the foot, three stages of flat feet are distinguished. Each of them has its own characteristic features that are noticeable to the naked eye. The final third degree, in which the deformation of the foot is maximum and very pronounced, looks especially recognizable.
Exemption from the army of conscripts with flat feet (according to Russian Federation standards).
Until the age of 5-6 years, the arch of the foot is just forming in children, so it is important to make every effort to ensure that the foot develops correctly, to prevent the disease in time, and to begin treatment in a timely manner.
If a child complains of pain in the legs after active games, the arch of the feet does not change, and the shoes wear unevenly, then there is every reason to assume that the child has flat feet. If activity decreases and gait changes, it is recommended to consult an orthopedist.
The most common types of flat feet in children:
- Longitudinal;
- Transverse;
- Flat-valgus;
- Combined.
To diagnose the degree of development of the disease, a simple method is used: a harmless dye is applied to the sole of the foot, then the foot is pressed against a sheet of paper. The fixed footprint is compared with the degrees of flat feet in the photo.
There are several classifications of leg deformities; depending on the degree of development, the external signs of the disease may differ. Even from a photo of longitudinal and transverse flatfoot, one can determine the type of illness that has affected the patient and its neglect.
Very often, young people of military age are interested in the question of whether they are accepted into the army with flat feet. This is due to the fact that there is a widespread belief that the military registration and enlistment office recruits only healthy conscripts, and foot deformity is a very serious ailment.
In fact, this opinion is erroneous and flat feet and the army are compatible things to a certain extent. In this case, the situation is individual and depends on the stage of the disease: flat feet are taken if the conclusion of the medical commission indicates an early stage.
- Flat feet 1st degree. At this mild stage of curvature of the arches of the foot, the young man is classified as category “A”, which means that he is fully capable of military service and is accepted into the army.
- Flat feet 2nd degree. The young man belongs to the “B-3” category, that is, he is fit for service, but with restrictions: most likely, he will not be accepted into serious troops.
- Flat feet 3rd and 4th degree. The deformation of the foot is so severe that it places the conscript in category “B” - free from civic duty to the homeland in peacetime.
The following conditions are required for release from service:
- transverse or longitudinal flatfoot of the 2nd degree with the presence of severe pain;
- transverse or longitudinal flatfoot 3rd degree.
The reason why flat feet can serve as a deferment from service is that in this case the main functions of the foot are disrupted - shock absorption and distribution of the body load during movement.
High physical activity with a high degree of illness can be accompanied by unbearable pain syndromes. That is why young people should understand the seriousness of this phenomenon and not neglect the treatment of foot deformities in order to get a respite.
In any case, in order for a conscript to definitely know whether he is eligible for flat feet, he must wait for the conclusion of the medical commission at the military registration and enlistment office.
How to treat flat feet?
Physiotherapy is widely used to relieve pain.
In addition, the patient is prescribed analgesic medications. To restore the physiological shape of the foot, an orthopedic specialist selects special orthopedic insoles for the patient. Corrective inserts are placed in the front of the shoe, under the heel and (or) in the spaces between the toes. The optimal design is an insert with an instep support in the heel area and a pronator in the front. This insole reduces muscle strain by properly “twisting” the foot. In advanced cases of the disease, special orthopedic shoes with solid soles and high lacing are made to order.
Important: insoles must be selected strictly individually after taking measurements and establishing the nature and degree of flattening of the foot.
For the treatment of flat feet, massage and a complex of exercise therapy developed specifically for such patients are recommended. In severe cases, surgery may be required. During the operation, part of the bones of the foot is resected. The goal of such remodeling operations is to restore the physiological shape of the arch. Most often, surgical treatment methods have to be resorted to for the traumatic type of flatfoot. To treat congenital flat feet, plaster casts are applied to the baby’s legs from the first days of life, and subsequently orthopedic shoes are selected.
Diagnostic methods
Orthopedic doctors treat flat feet in medical institutions. In some countries, due to the significance of the problem, podiatrists have appeared.
Methods used in diagnosis:
- survey;
- inspection;
- podometry (conducting functional tests based on Friedland’s calculations);
- plantography (rapid footprint test using Lugol's cream or solution);
- radiography, which takes a picture of both feet in the lateral and frontal projections.
If severe pain is present, imaging tests may be performed to determine the underlying cause of the pain:
- CT scan, suitable for diagnosing arthritis and assessing foot angle irregularities;
- ultrasonography;
- An MRI can detect heel injuries and shows images of damaged bones.
Treatment for flat feet depends on the type of foot curvature, stage of progression and pain symptoms. Subsequent therapy is also influenced by factors such as whether it is flexible, rigid, congenital or acquired.