Category: Joints and ligaments
It is probably impossible to find a single adult who did not know what “lumbar osteochondrosis” is. On average, every third healthy, middle-aged person, and sometimes more often, has had an episode of acute lower back pain in his life, and every fifth or sixth indicates that such problems arise regularly, and are even the “source” of sick leave.
However, patients are most often unable to explain in detail exactly what kind of disorder occurred in the lower back. Most of them have never been examined, and treatment, consisting of “injections,” “ointments,” and massage sessions, usually helps for a period of several months to a year.
If you “push” such a patient and start asking him about the diagnosis, then, after suffering a little, he will declare that he is sick with “osteochondrosis.” What does this disease mean in relation to the lumbar spine?
What is osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
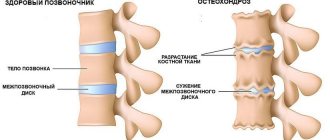
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic pathology that initially affects the intervertebral discs. Due to insufficient supply of nutrients, they lose their ability to retain moisture. Regeneration processes slow down, discs become flat and fragile. The distance between adjacent vertebrae decreases, therefore, to stabilize the lumbar segment affected by osteochondrosis, bone tissue grows. Osteophytes are formed - bone growths, when displaced, soft tissue structures, nerve roots, and blood vessels are injured.
Reasons for development
There are many factors that can cause osteochondrosis. Most often, the disease occurs due to predisposition and uneven load on the spine. In addition, the causes of dystrophic changes in cartilage tissue are:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- presence of scoliosis ;
- weak muscle tone ;
- constant stress ;
- lack of micro- and macroelements in the diet;
- professional participation in heavy sports .
The presence of the above factors in a person’s life significantly increases the likelihood of osteochondrosis even at a relatively young age.
Stages of pathology
The stage of osteochondrosis is a stage in the development of the disease, which is characterized by certain destructive changes in the discs and vertebral bodies. It is established using radiographic examination. The resulting images clearly show specific signs of destruction of vertebral structures. Each stage corresponds to the severity of osteochondrosis and a set of symptoms. The higher it is, the more difficult the disease is to treat conservatively.
| Stage of lumbar osteochondrosis | Radiographic signs and clinical manifestations |
| First (preclinical) | There are no signs of osteochondrosis on radiographs. Occasionally, discomfort occurs in the lower back after physical exertion or standing on your feet for a long time. |
| Second | Straightening of the lordosis is noted, less often - bevel of the vertebral bodies, deformation of the semilunar processes. The height of the discs has been reduced slightly. Painful sensations appear more often and their duration increases |
| Third | Subchondral sclerosis of the end plates, damage to a large number of semilunar processes, and a moderate decrease in disc height are observed. In addition to pain in the lumbar region, the clinic also presents with crunching and stiffness of movement. |
| Fourth | The semilunar processes are deviated outward and posteriorly. Compensatory growth of bone tissue and the formation of multiple osteophytes are observed. Pain occurs with movement and at rest |
How to recognize the disease?
Osteochondrosis is a chronic inflammatory process and degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs. As a result, they become less elastic and cause pinching of nerve endings, causing severe pain. Depending on which part of the spine is affected by the disease, cervical, thoracic and lumbar osteochondrosis is distinguished, but it is the latter that occurs most often - the lower back always bears the greatest load, which means that the intervertebral discs in this area wear out first.
There are many factors that provoke the development of lumbar osteochondrosis: a passive lifestyle, an excess of harmful foods in the usual diet, heavy physical labor, various spinal injuries and even extra pounds gained. We cannot discount the genetic predisposition to deformation of the spinal discs, which by nature may have a looser structure. In any case, no matter what the reasons underlie the appearance of osteochondrosis, the sooner its symptoms can be detected and complex therapy can be started, the higher the patient’s chances of feeling well and living a full life, without constant pain and discomfort.
Typical signs of lumbar osteochondrosis include:
- sharp paroxysmal pain in the lower back, aggravated by walking;
- difficulty moving;
- numbness of the extremities, especially after sitting for a long time, tingling or sensation of goosebumps crawling on the skin;
- cold feet.
In addition, there are nagging pains with osteochondrosis, radiating to the leg, especially when trying to turn, bend over or lift something heavy. And although at an early stage these manifestations of the disease may not cause a person much concern, without proper treatment they can provoke very serious consequences. Most often we are talking about the development of intervertebral hernia, radiculitis, spondyloarthrosis, prostatitis, inflammation of the adrenal glands, ovaries, weakening of potency in men and even, in especially severe cases, complete loss of the ability to move.
Causes of the disease
The reasons for the development of osteochondrosis are often increased loads on the lumbar spine. Discs are constantly micro-injured, not having time to recover in a timely manner. A significant part of them is gradually damaged, triggering deformation of the bone bodies of the vertebrae. The following pathological conditions can also provoke destruction of the lumbar segment:
- congenital or acquired anomalies - flat feet, scoliosis, kyphosis, hallux valgus, hip dysplasia;
- systemic pathologies - rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, lupus erythematosus;
- endocrine and metabolic diseases - gout, diabetes, hypo- and hyperthyroidism, obesity;
- previous injuries - vertebral subluxations and fractures, spinal cord injuries;
- circulatory disorders, including those caused by a sedentary lifestyle.
One of the main reasons for the development of osteochondrosis is the natural aging of the body. After 50 years, recovery processes slow down, collagen production decreases, and the condition of ligaments worsens.
Performing physical exercises for lumbar osteochondrosis
Physical therapy should be carried out regularly; only under this condition will the effect of the exercises be achieved. Physical activity should become the norm of life for people with spinal osteochondrosis. Not only a set of special exercises, but also walking have a positive effect on the spine.
There are certain restrictions that must be followed to reduce the risk of lower back injury during gymnastics. For example, you should not do exercises with weights. This will lead to additional stress on the vertebrae, which are in a destroyed state. It is also not recommended to twist in the lumbar region. This is especially true for patients with protrusions and hernias.
Physical therapy cannot be performed if the patient, in addition to lumbar osteochondrosis, has injuries, tumors of various origins, and hematomas. It is not recommended to engage in active sports if you have spinal diseases.
Characteristic signs and symptoms of the disease
At the initial stage of development, osteochondrosis does not manifest itself clinically. A person mistakes mild pain in the lower back for muscle strain after a working day and does not consult a doctor. But the severity of the symptoms slowly increases - soon the pain is joined by crunching when bending and turning the body, sensitivity disorders, and stiffness.
Radicular syndrome
This is the name for damage to the spinal roots, which leads to motor, autonomic and pain disorders. Radicular syndrome develops with osteochondrosis of 3-4 degrees of severity. At these stages, an intervertebral hernia is formed, compressing the spinal roots. The pathology occurs according to the type of lumbago, lumbodynia and lumboischialgia. In addition to severe pain, radicular syndrome is characterized by sensations of numbness, tingling, crawling, decreased or complete absence of sensitivity.
Ischemic syndrome
In the later stages of lumbar osteochondrosis, compression of large blood vessels by hernial protrusion is possible. The pelvic organs stop receiving enough nutrients, which leads to disruption of their functioning. The trophism of the spinal cord is also upset, a neurological deficit develops - intermittent claudication appears, temperature and pain sensitivity disappears.
Spinal syndrome
As a result of a decrease in the distance between adjacent vertebral bodies and the proliferation of bone tissue, the lumbar vertebral segments are gradually deformed. The situation is aggravated by the constant compensatory tension of the back muscles with their subsequent atrophy. A person’s gait and posture change pathologically, including due to improper redistribution of loads. The likelihood of involvement of other parts of the spine and leg joints in the destructive-degenerative process increases significantly.
Pain syndrome
In the lower back there is a large sciatic nerve formed by the sacral spinal roots. When it is pinched by a hernial protrusion, bone growths, or spasmed muscles, sciatica occurs - a typical symptom of lumbar osteochondrosis. Acute pain appears, spreading along the sciatic nerve to the hips, knees, and legs (lumboischialgia). Another specific sign of pathology is lumbago, or a “lumbago” in the lower back after a sharp bend or turn, or hypothermia.
Diagnostics
To identify the disease, hardware examinations and diagnostic tests are used. First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination and testing. It is important to exclude diseases with similar symptoms. To determine the extent of damage, use:
- MRI;
- X-ray;
- CT.
After examination and various tests, a preliminary diagnosis is made. With the help of hardware examination, it is possible to accurately determine the cause of the ailment. Osteochondrosis at the first stage can only be detected using computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
Lasègue reflex
The Lasegue reflex is a symptom that is detected only in neurological and dystrophic pathologies of the spine. The presence of the Lages reflex is determined by a neurologist. This happens as follows: a person takes a lying position; the doctor raises the straightened leg up. If a person experiences pain when raising his leg more than 30 degrees, then the test is considered positive. The test does not require special equipment, so it is carried out even during the initial examination.
Only a doctor can correctly conduct a test to identify Lasègue’s symptom. Using this test, you can almost accurately determine the affected area.
Bekhterev's reflex
This test is almost always carried out during the initial examination. The essence of the Bekhterev reflex is that if a person presses his straightened knees against a flat surface, he experiences pain. It is worth noting that this test is not always positive for dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs, but it does not require much time to perform. If the result is positive, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis of osteochondrosis.
Hardware methods
Hardware examinations are the most effective in diagnosing osteochondrosis. Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is used. An X-ray examination of the lumbar region will also help in making a diagnosis. These methods will allow you to assess the extent of the lesion and the distance between the vertebrae. In addition, they can be used to diagnose complications that often arise during illness (hernias, curvatures).
Diagnostic methods
When making a diagnosis, radiographic images taken in two projections are most informative. To study the affected lumbar segment in more detail, an MRI is performed. The study allows you to assess the condition of the spinal cord, soft tissue structures, blood vessels, and nerve roots. The degree of damage to nerve trunks can be determined using evoked potentials, electroneurography, and electromyography. Discography is used for targeted examination of affected discs.
Prevention
Compliance with prevention will help to avoid treatment for osteochondrosis. For this it is recommended:
- avoid hypothermia of the lumbosacral region;
- lifting/lowering weights should be done without jerking;
- avoid lifting heavy objects;
- regular changes in the position of the spine, which will help avoid stooping;
- performing physical exercises.
To avoid the occurrence of osteochondrosis, you should not perform heavy work without appropriate training. If you need to work at the computer for a long time, you should choose the right chair and table, and take care of the lighting.
How is the treatment carried out?
An integrated approach to the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis is practiced. Treatment is aimed at eliminating pain, restoring range of motion, and preventing the spread of pathology to healthy discs and vertebrae.
Drugs
The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen), glucocorticosteroids (Diprospan, Triamcinolone), muscle relaxants (Mydocalm, Sirdalud) allows you to get rid of lower back pain. In therapy, drugs are used to improve blood circulation (Pentoxifylline, Nicotinic acid). Patients are necessarily prescribed B vitamins (thiamine, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin), chondroprotectors (Structum, Dona, Teraflex).
Physiotherapy
This is the most effective and affordable method of treating osteochondrosis. After 1-2 months of daily physical therapy exercises, the muscles of not only the lower back, but also the entire back, are strengthened, posture is improved, and blood supply to damaged connective tissue structures is accelerated. Exercise therapy doctors recommend that patients perform slow, smooth turns and bends of the body, shallow squats and lunges.
Massage
Patients with lumbar osteochondrosis are recommended for all types of massage - vacuum, acupuncture, connective tissue, segmental. But the classic one is most in demand. During the session, the massage therapist performs basic massage movements: stroking, rubbing, kneading, vibration. The goals of the procedures are to eliminate muscle spasms, improve blood circulation in the affected segment, and strengthen skeletal muscles.
Physiotherapy
In the acute and subacute period, patients are prescribed electrophoresis or ultraphonophoresis with glucocorticosteroids, anesthetics, and B vitamins. During the remission stage, sessions of laser therapy, magnetic therapy, shock wave therapy, and UHF therapy are often performed. Ozocerite therapy, paraffin applications, hirudotherapy, mud therapy, radon and hydrogen sulfide baths are also used.
Surgical intervention
The main indication for surgical intervention is infringement of the spinal cord by a hernial protrusion. During the operation, the herniated disc is removed and the spinal canal is decompressed. The most commonly used methods of surgical intervention for lumbar osteochondrosis are microdiscectomy, puncture vaporization or laser reconstruction of the disc, installation of an implant, and stabilization of the spinal segment.
ethnoscience
After carrying out the main therapy and achieving stable remission, homemade ointments, herbal teas, compresses, oil and alcohol rubbing are used in treatment. Folk remedies do not affect the cause of osteochondrosis, therefore they are used to eliminate weak, aching pain, heaviness in the lower back after hypothermia, a sudden change in weather or increased physical activity.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, drugs
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis and its complications involves the following measures. In the acute phase (first day – two):
- In order to reduce swelling of the muscles and spine, a salt-free diet and limiting the amount of fluid consumed are indicated. You can even give a tablet of a mild diuretic drug, Veroshpiron, which conserves potassium.
- It is recommended to wear a semi-rigid orthopedic corset, which protects the muscles from excessive movement.
- From the first days, rubbing in warm ointments containing NSAIDs and applying patches, for example, “pepper” patches, are recommended. Popular ointments include Capsicam, Fastum-gel, and Apizartron with bee venom.
- During the acute phase, heating cannot be done. As inflammation increases, swelling increases. Therefore, any heating pads are prohibited. You can warm up by removing your own heat (a wool belt, warming ointments), which do not add it from the outside, but, on the contrary, remove it from the depths to the outside.
- In the acute phase of lumbar osteochondrosis, short-term treatment can be carried out with intramuscular “injections” of NSAIDs and muscle relaxants: daily, for example, with the drug “Movalis”, 1.5 ml intramuscularly for 3 days, and “Mydocalm”, 1 ml also intramuscularly for 3 days. 5 days. This will help relieve swelling of the nervous tissue, eliminate inflammation, and normalize muscle tone.
In the subacute period, after overcoming the maximum pain, “injections” should no longer be taken, and attention should be paid to restorative agents, for example, modern drugs of group “B”, for example, “Milgamma”. They effectively restore impaired sensitivity, reduce numbness and paresthesia.
Physiotherapeutic measures continue, the time has come for exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. Its task is to normalize blood circulation and muscle tone, when swelling and inflammation have already subsided, but muscle spasm has not yet completely resolved.
Exercises for lumbar osteochondrosis of the spine must be carried out after a light general warm-up, on “warmed up muscles”.
The main therapeutic factor is movement, not the degree of muscle contraction. Therefore, in order to avoid relapse, the use of weights is not allowed; a gymnastic mat and a gymnastic stick are used. With their help, you can effectively restore range of motion.
Rubbing in ointments and using the Kuznetsov implicator continue. Swimming, underwater massage, Charcot shower are shown. It is during the stage of fading exacerbation that drugs for home magnetic therapy and physiotherapy are indicated.
Usually treatment takes no more than a week, but in some cases, osteochondrosis can manifest itself with such dangerous symptoms that surgery may be necessary, and urgently.
Complications of lumbar osteochondrosis of the spine
We are talking, first of all, about a condition when a disc herniation has become an independent fragment and, having penetrated the central canal, has formed a free sequestration. There it can compress the nerves of the cauda equina, and it can suddenly (right in the gym, after an episode of acute pain) develop severe weakness, or paralysis in the legs, numbness of the perineum.
After a few minutes, severe pain in the legs appears, and then a reflex urinary retention or the appearance of incontinence is possible, and impotence develops. This arose cauda equina syndrome as a complication of a herniated disc. In this case, urgent intervention is required, removal of the sequestrum, and restoration of the function of the cauda equina nerves with their decompression.
However, more often than not, other complications arise. With age, multiple hernias and protrusions occur, osteoporosis of the vertebrae appears, and mobility simply decreases significantly and the risk of acute back pain increases. Such patients necessarily “take sick leave” a couple of times a year and are often treated in sanatoriums.
Treatment prognosis
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the symptoms and treatment of which we discussed above, as we have understood, is for the most part not a disease at all, but simply a manifestation of inevitable aging and premature “shrinkage” of the intervertebral discs.
Can humanity be completely freed from lumbar osteochondrosis? This answer can be answered in the affirmative, but then we will have to master a different style of movement: walking on all fours all our lives, or, like Ichthyander, swimming into the depths of the ocean, constantly moving in the water from childhood. It is then that the axial, static load on the intervertebral discs will disappear, and along with it the signs of “chondrosis” will disappear. But another problem will arise: in water such a powerful structure will simply become unnecessary and will begin to change until it disappears or is significantly reduced.
As for the personal, individual prognosis for osteochondrosis, it all depends on the time when the person “decided to come to his senses.” If by this time there is no pronounced destruction of the intervertebral discs, protrusions, hernias and deformations, then, subject to a healthy lifestyle and hygiene of physical activity, you may not have problems with the lower back until a very old age.
In the same case, when there is already a “hot spot” in the lumbar region, for example, in the form of a hernia, which periodically compresses a nerve root, then a person needs to especially take care of awkward turns, physical exertion, improper lifting of weights and seasonal hypothermia, which cause usually cause exacerbation of spinal osteochondrosis.
Tags: Osteochondrosis, vertebra
- Radiculitis (lumbar, thoracic, cervical) - symptoms and...
- Malaria - causative agent, symptoms and treatment, drugs
- Polyarthritis of the hands - symptoms and treatment of joints, medications
- Pericarditis - types, symptoms and treatment, drugs
- Tracheobronchitis - types, symptoms and treatment, drugs
- Sacroiliitis - degrees and symptoms, treatment, drugs
Prevention measures and prognosis
The prognosis is favorable when pathology of 1-2 severity is diagnosed. It responds well to conservative treatment, and in young patients, partial restoration of intervertebral disc tissue is even possible. If complications develop, the prognosis for full recovery is less favorable.
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine consists of controlling body weight, eliminating excess loads, and timely treatment of endocrine and metabolic diseases. Neurologists and vertebrologists recommend visiting a swimming pool, doing water aerobics, Pilates, and Nordic walking.
Treatment
Treatment of osteochondrosis should be comprehensive. During therapy, you must adhere to the following principles:
- exclusion of provoking factors;
- elimination of concomitant pathologies;
- relieving inflammation;
- stimulating the restoration of cartilage tissue.
The success of treatment depends not only on the doctor, but also on the person. You will need to follow a regimen, engage in physical therapy, and go to physical therapy. Some medications are used only during the acute period.
Throughout the entire therapy, it is necessary to exclude vertical loads on the spine, as this can aggravate the pathology.
Medication
Medicines are used in the acute period of the disease. The main goal is to get rid of pain and inflammation. For this purpose, medications can be used in the form of ointments, injections and tablets. The following classes of drugs are used :
- analgesics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- chondroprotectors;
- muscle relaxants;
- vasodilators.
The doctor selects specific medications. Injecting NSAIDs into the affected area will help relieve pain quickly. Chondroprotectors will help stop degenerative changes and start the recovery process. With the help of medications, you can effectively fight osteochondrosis only in the first and second stages; for more complex cases, more complex treatment methods are used.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy helps to get rid of minor pain and consolidate the results of drug treatment. The following procedures apply:
- phonophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- exposure to vibration;
- detensor therapy.
Most procedures can only be performed during remission. The moment when it is most appropriate to use physical therapy is determined by the doctor. To achieve a therapeutic effect, you will need to visit the physiotherapy office regularly. A minimum of 7-10 treatments are required to achieve lasting improvement.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy can help relieve stiffness, muscle spasms and pain. Direct impact on the affected area with your hands allows you to create conditions for a speedy recovery of the spine. With osteochondrosis, it is possible to relieve the load that may arise due to incorrect posture. The chiropractor works on the lumbar region and the entire back with massage movements. The effect of manual therapy is noticeable after just a few procedures.
Manual therapy should only be performed by a qualified specialist who has all the necessary certificates. Improper impact on the spine will aggravate the situation.
Physiotherapy
A person with osteochondrosis should strive to correct their posture and strengthen their muscle corset. The exercise therapy complex can be used during remission. The following exercises can be performed:
- Get on your knees and take a lying position. Raise your head and bend your lower back, then lower your head, returning to the starting position. Repeat 8-10 times.
- Lie on your back. Alternately bend your legs at the knee joint. Repeat 10-12 times.
As the muscles strengthen, the load may increase. Static exercises can be used to strengthen the lumbar muscles. The specific complex is selected based on the individual characteristics of the person and the degree of osteochondrosis. After achieving stable remission, you need to continue to exercise. This is one of the best preventions of the disease.
Folk recipes
Various natural compresses can be used to relieve pain and inflammation. Among the most effective recipes are:
- Compress of mustard and vodka . You will need 50 g of dry mustard, 100 ml of vodka and 50 ml of camphor alcohol. The components are mixed and infused for 10 hours. Soak a cloth in the resulting liquid and apply it to the affected area for 20-25 minutes, 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 7-10 days.
- Compress made from raw potatoes and honey . Peel and chop the potatoes, then mix them with honey. Apply the resulting consistency to the lumbar region, cover with polyethylene and secure. Keep the compress for 30-45 minutes.
Warming compresses will help get rid of pain. Lasting improvement is possible when combined with other treatment methods.
You can read about the need for physical therapy for synovitis of the ankle joint in this material.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is a last resort measure that is used when irreversible changes occur in tissues. With the help of surgery, the cause of pain is eliminated. The most common procedure is a discectomy, during which the intervertebral disc that is compressing the nerve is partially or completely removed. The specific type of surgical intervention is selected individually. It is worth noting that performing any surgery on the spine is quite difficult.
The therapeutic effect from a single surgical intervention is not always achieved. If a person delays treatment for a long time, several operations may be required.
Folk recipes
External means
Hot pepper infusion
- Everyone knows that pepper patch helps with osteochondrosis. But you can make your own home remedy based on hot red pepper. Thanks to additional components, its effect is enhanced. Grind five pods of hot pepper and pour half a glass of purified kerosene and unrefined sunflower oil into it. After fourteen days, remove the pepper pieces from the infusion. Once a day, before going to bed, rub the pepper infusion on your lower back, apply an insulating bandage on top, and leave it on all night.
- Or make an ointment from hops and butter. It should be noted that the oil must be fresh, natural, unsalted. Grind dry hop cones to a powder. Take a piece of softened butter approximately equal to the volume of hop powder. Combine thoroughly, rubbing the mass. Before going to bed, massage the ointment onto your lower back, rubbing until completely absorbed.
Onion peel compress
- A compress of steamed onion peels provides excellent pain relief. Collect onion peels, place them in hot water and, putting on fire, bring to a boil. Immediately remove, remove the husks with a slotted spoon and spread them in an even layer over the compress cloth. When the husk has cooled to a tolerable temperature, secure the compress to the lower back. It is recommended to carry out the procedure in the evening, leaving it overnight.
- Red elderberry rub is a very popular remedy for osteochondrosis. Pour one cup of rubbing alcohol into four cups of red elderberries. The berries, after you have measured them, should be slightly mashed. Infuse for at least ten days. After straining, rub the tincture on your lower back twice a day.
Horseradish rub
- Wash and peel fresh horseradish root. Grind it until mushy. Mix a glass of ground horseradish with a glass of high-quality forty-proof vodka. Use a lower back rub. After the procedure, apply a warming bandage. After an hour, rinse your skin with water.
- Take two tablespoons of softened butter and grind it with two tablespoons of purified kerosene, honey and vodka. Apply the ointment to the lumbar spine twice a day - morning and evening.
Acacia
- Pick a few branches of flowering acacia. Cut them finely with scissors and place two spoons of raw material in half a liter of good vodka. After a week of infusion, strain the tincture. Use for daily rubbing of a sore lower back.
- For the next anesthetic procedure you will need sawdust from any tree. Pour five hundred ml of hot water into a saucepan, add three handfuls of sawdust into the water, place on the stove and bring to a boil. Remove immediately. Prepare everything for the compress: lay out a large towel on the bed, with plastic on it. Spread hot sawdust over the polyethylene. Lie down on the sawdust with your lower back, wrap yourself in a towel, and cover yourself with a blanket on top. Lie down until you feel the warmth emanating from the sawdust. Healers promise complete relief from pain within a week of daily procedures.
Warming up with sawdust
- For rubbing and compresses, prepare a mixture of one raw chicken egg mixed with a glass of table vinegar and two glasses of purified turpentine. Mix all ingredients thoroughly. After two hours the product is ready for use. It works equally well in compresses and as rubs.
- A folk remedy, but with the addition of modern pharmaceutical ingredients. It is so effective that we simply have no right not to talk about it. Prepare one package of ten analgin tablets, two spoons of iodine tincture and camphor alcohol and three hundred ml of medical alcohol. Combine iodine and alcohols, crush the tablets and pour into the liquid. Stir until the analgin powder is completely dissolved. Rubbing the lower back with this remedy almost immediately relieves pain in the lower back.
Potato-honey compress
- Take a healthy, undamaged potato tuber, rinse it and, without peeling, grate it on a fine grater. Add about the same amount of honey to the grated potatoes. Prepare a compress cloth according to the size of your lower back, spread a mixture of honey and potatoes over it and apply it to the sore spot. Lie quietly for two hours, then remove the compress and wipe the skin.
- A rich infusion of burdock leaves is an excellent remedy for pain due to osteochondrosis. Rinse fresh leaves with water and cut them. Pour a glass of boiled water and leave until it cools completely. Strain and squeeze the plant material into an infusion. Soak the prepared piece of cloth in the infusion, place it on the lower back, secure with a waterproof bandage, and place a woolen cloth on top. Keep it for about half an hour.
Tincture of calendula
- A very effective tincture can be made from calendula. Rub fifty grams of dried flowers with your hands, place in a glass jar and pour in two hundred ml of vodka, camphor alcohol and triple cologne. Leave to infuse in a dark cabinet for fourteen days. After straining, use to rub the lumbar spine.
- Compress from a decoction of herbal tea, which includes a spoonful of burdock and dandelion roots and St. John's wort. Grind the roots and place them together with the grass in a saucepan, add a glass of hot water, heat to a boil and boil for about five minutes. Cool slightly and strain off the vegetable matter. Soak a cloth in the broth and secure it with a waterproof material on your lower back. Keep it for a quarter of an hour.
Parsley root
- It is very easy to prepare a decoction of parsley root. Pour three tablespoons of carefully crushed dry roots into half a liter of water, heat to a boil and, reducing the heat to low, simmer for one hour. Strain after cooling. Twice a day - morning and evening, drink two tablespoons of the decoction.
- Lingonberry leaf infusion is indispensable in the treatment of osteochondrosis. Infuse one hundred grams of lingonberry leaves in a liter of boiled water for two hours, covering the bowl with a thick towel. Place the infusion on the stove, pour in three hundred ml of high-quality vodka and keep on the fire after boiling for a quarter of an hour. Drink strained one hundred ml three times a day.
pumpkin juice
- Pumpkin juice is extremely useful for osteochondrosis. There is no need to buy it in the store; prepare the juice yourself at home. Pumpkin is a long-lasting and very juicy product, so storing it and extracting juice will not be much of a hassle. Start drinking juice from half a glass a quarter of an hour before breakfast and dinner. Every day, gradually increase the amount of juice you drink, eventually bringing it to one and a half glasses at a time.
- If you have the opportunity to pick or buy green walnuts, prepare an infusion from them with the addition of a spoonful of dried arnica and two spoonfuls of beech nuts. Chop four or five nuts into smaller pieces, add herbs and pour in one liter of boiling water. Leave for two hours. Take one spoon of infusion immediately before meals.
Herbal collection
- First, collect a herbal mixture from four parts each of horsetail, strawberry leaves and knotweed, two spoons of agrimony and one barberry. Mix the ingredients well and pour six tablespoons of the raw material into four glasses of vodka. After two weeks of infusion, take the strained tincture twenty-five drops four times a day.
Miscellaneous
Dog hair belt
- Traditional healers advise everyone who suffers from lumbar osteochondrosis to purchase at a pharmacy or make their own a healing belt from natural wool - sheep, but preferably dog wool. If you tie it on your lower back for several hours a day, the condition improves significantly and the pain becomes less painful.
Walking barefoot
- If you constantly live in a rural area or spend the summer at the dacha, use this circumstance for your health. Every morning, go out onto the lawn and walk for ten minutes on the grass, on which there is still dew, with your bare feet. And in general, use every moment to walk barefoot, unless, of course, you are sure that the area is clean and you will not injure your feet.
Treatment with gold
- There is another remedy for osteochondrosis, but it is perhaps suitable for the wealthy. Traditional healers recommend disassembling the gold chain into individual links and scattering them over the lower back, previously smeared with any medicinal ointment with a warming effect. Begin to gently rub the ointment, incorporating the gold grains. As soon as the ointment is completely absorbed, without removing the gold from your back, place a waterproof insulating bandage on top. Leave the golden compress on overnight. In the morning, carefully remove, collect the gold links, put them in hot water and boil for several minutes. Then rinse under the tap and dry. Only after this can they be used for the subsequent procedure. And after removing the compress, it is recommended to rinse your back with water infused with gold. It’s easy to do - in the evening, put all the gold items without stones that you have in a liter of warm boiled water. In the morning, remove the jewelry and use the water for its intended purpose.
Folk remedies for osteochondrosis can improve the condition, relieve swelling, pain and tension, and also stimulate blood circulation in the affected area. The following agents are used for therapy:
- Compresses are the easiest to use for treating the lower back, and their effect is almost immediate.
- Decoctions, ointments and infusions with a warming effect. The warming effect is achieved by adding irritating products to them: pepper, horseradish, mustard, honey, alcohol. Warm up the lower back with lightly heated salt, sand, buckwheat.
- Cocktails made from herbs - have anti-inflammatory and nutritional effects, nourish the body with vitamins.
Having become ill with osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, treatment with folk remedies will not only bring relief to the patient, but can also significantly help get rid of the pathology. The folk medicine cabinet is rich in unique ancient recipes, but before using them, consultation with a specialist is required.
You should also not use recipes that include products and components that are allergenic to humans (even food allergies are noted).
Among the most effective recipes are the following.
Recipe: grind burdock leaves, then pour a tablespoon of raw material into a glass of boiling water, leave until it cools, strain.
Diagnostic methods
During the examination, the doctor may notice the following changes:
- palpation reveals sharp pain;
- decreased skin sensitivity;
- sagging foot;
- scoliosis and kyphosis;
- displacement of the buttock – asymmetry;
- limited movement;
- asymmetry of the Michaelis rhombus;
- when walking, the patient raises his leg high.
An x-ray of the sacrolumbar region determines the height of the discs, the presence of growths and salts, and narrowing of the gaps between the vertebrae. Performed in 3 projections.
CT scan allows you to obtain more informative images than radiography; MRI provides the most accurate diagnosis.
Forecast
Pain syndrome in lumbar osteochondrosis occurs in the form of remissions and exacerbations. Lumbago lasts 10–15 days, after which the patient’s condition improves and the pain subsides. Additional secondary diseases may interfere with a favorable outcome. Often, with lumbar osteochondrosis, there is a recurrence of pain attacks, which each time become more intense and prolonged.
In the complex treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, physical therapy plays a significant role.
Patients with severe lumbar osteochondrosis, with persistent pain and other manifestations are considered temporarily disabled. If their condition does not improve within four months, the issue of establishing a disability group is decided.
Possible consequences and complications
The main complications of lumbar osteochondrosis are:
- formation of intervertebral hernia;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- spondylolysis, spondylolisthesis;
- osteophytosis;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- spinal canal stenosis, which leads to compression of the spinal cord and can cause permanent disability and decreased quality of life.
Long-term compression of the nerve roots innervating certain organs of the abdominal cavity over time leads to a deterioration in their functioning. As a result, patients experience intestinal dysfunction (constipation, diarrhea, flatulence) and pelvic organs (urinary disorders, erectile dysfunction, frigidity, infertility).
Stages of development of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine
The stages are similar when the pathology is localized in other parts:
- Chondrosis of the articular surfaces associated with disruption of the normal blood supply to bone tissue and the occurrence of local osteonecrosis.
- Prehernia. A stage that is associated with the capture of all elements of the disc (the entire articular surface is involved).
- Intervertebral hernia. Protrusion of disc elements beyond the joint (medial, lateral, paramedial).
- Fibrosis. It occurs as a natural process of repairing a damaged disk. The deformed areas are replaced by dense fibrous tissue, but it does not stretch and is not able to provide movement in the joints.
In the English-language literature, the listed stages appear as separate diseases and symptom complexes, and not as progressive phenomena of one disease.
Salt baths
This simple method helps to quickly get rid of pain and congestion in muscles and joints due to osteochondrosis. It is recommended to use sea bath salts or Epsom salts. The advantage of the latter is that the magnesium contained in the salt helps in regulating the acidity of the entire body.
As a result, muscle tension, signs of inflammation and swelling are reduced. The pain in the neck and lower back gradually goes away. All you need to do is add a pinch of salt to a warm bath, or make a paste of water and salt and rub it on the affected areas for 10-15 minutes. This procedure is contraindicated for people with high blood pressure, kidney disease and diabetes.
Sea bath salt
ethnoscience
Folk remedies for lumbar osteochondrosis should be used in addition to the main treatment, but not instead of it. Due to the fact that any intervention can cause harm to the patient, it is necessary to first coordinate all your actions and the use of traditional methods with your doctor.
Typically, various herbal products are used for this:
- To prepare a locally irritating ointment that will improve blood supply to the affected area, you will need five red peppers and 100 ml of kerosene and vegetable oil. After receiving the infusion, you need to lubricate the painful areas at night. A dry wool compress is applied on top.
- Mix butter and hop cones in equal quantities. The resulting ointment is applied to the lumbar region as needed.
- An infusion of arnica, walnuts and medicinal letter should be taken after each meal, one spoonful.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis with folk remedies can be effective in the early stages of the process. Therefore, it is necessary to begin therapy immediately after the onset of symptoms.
Complications
List of complications and their causes:
| Complication | Cause |
| Chronic or acute cerebrovascular insufficiency | Manifestation of cervical osteochondrosis |
| Pain syndrome | Neurological complication of spinal osteochondrosis |
| Cervicago | Cervical osteochondrosis |
| Cervicalgia | Cervical osteochondrosis |
| Lumbago, lumbodynia | Lumbar osteochondrosis |
| Thoracalgia | Complication of thoracic osteochondrosis |
| Discogenic radiculitis | Lumbosacral osteochondrosis |
| Cervical sciatica | Cervical osteochondrosis |
| Wartenberg's brachialgia | Cervical osteochondrosis and radiculitis |
| Vascular-radicular conflict | Ischemia, lumbar osteochondrosis, complicated hernia formation |
Related ailments
Osteochondrosis is the cause of the development of diseases such as:
- radiculitis;
- pain syndrome;
- cardiovascular disease;
- neuromuscular diseases.
Physiotherapy
Performing exercise therapy with correctly selected exercises and daily activities is an important link in the treatment of osteochondrosis. Regular physical activity helps:
- Restore the mobility of the spine.
- Regain the ability to walk without feeling pain and not expecting “shots” at any moment.
- Restore the movement of blood and lymph in the diseased area, which helps renew damaged tissues.
- Raise the patient's mood and condition.
It is necessary to choose exercises that can be performed constantly or during exacerbations. Some exercises are prohibited for lumbar osteochondrosis. They are selected by a neurologist or exercise therapy instructor. You can attend a couple of classes to properly perform gymnastics and continue doing it at home. It is important to know that during the acute course of the pathology, you cannot do elements of flexion and extension, twisting and turning of the spine in the lower back.
There are exercises that are undesirable to perform with this disease. These include:
- Exercises for lifting weights (dumbbells, kettlebells) from a sitting and standing position.
- Flexion and extension, twisting and turning, performed at an accelerated pace.
There is a group of exercises that can always be done (but it is better to consult with a specialist first):
- All exercises are in a supine position, in which there are no elements of twisting or turning in the lower back.
- Hanging on the bar.
- Gymnastics elements in a prone position, without tension in the lower back.
- Exercises while standing on all fours - soft bends, maintaining balance on all limbs.
- Swimming and doing exercises in the pool.
When a lumbago occurs and the patient experiences severe pain, it is necessary to refrain from exercise. During this period - the recovery period - you need to lie on a hard bed on your back. It is allowed to start therapeutic exercises again after eliminating the pain syndrome only with the permission of a doctor.
Types of osteochondrosis in the spine
Osteochondrosis is a serious disease that requires immediate treatment. There are several varieties of this pathology - their type depends on the method of treatment.
At the moment, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- Reflex syndromes – lumbago, lumbodynia, lumboischialgia;
- Radicular syndromes – lumbosacral radiculitis;
- Radicular-vascular syndromes – radiculoischemia.
With lumbago, a person feels severe pain in the back. Lumbodynia is a chronic disease, the pain in which is quite acute. Usually occurs when sitting in one position for a long time or due to physical activity. Lumboischialgia is a bright pain that radiates to the limbs. In this case, vegetative-vascular abnormalities may be present.
Radiculitis occurs due to pressure on two roots. Severe pain and loss of sensitivity occurs in a certain area.
Radiculoischemia occurs when the vertebral disc begins to put pressure on the radicular spinal artery.