The manifestation of candidiasis in the oral cavity is a fairly common fungal infection known to many firsthand. It may also be called oral thrush or oral candidiasis. It appears as a result of an imbalance of microflora on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and oropharynx, provoking active uncontrolled growth of pathogenic yeast fungi of the genus Candida on the mucous tissue of the tonsils, pharynx, cheeks, tongue or lips.
The main risk group susceptible to the disease are infants and older children, the elderly and heavy smokers. For example, in infants and mature postmenopausal women, the disease can manifest itself as candidiasis of the tongue and fungal stomatitis, in older children (3-10 years old) – candidiasis. In addition to infection by your own fungus, infection can also come from outside.
What is oral candidiasis
Symptoms of a fungal infection of the oral cavity begin to develop when candida multiplies intensively. These microorganisms are considered opportunistic and are present in small quantities on human mucous membranes. Under the influence of certain factors, the infection begins to intensify, affecting not only the oral cavity and pharynx, but also the genitals and skin.
Thrush occurs more often in young children and older people.
Stomatitis and glossitis are diagnosed in newborns and the fairer sex during menopause.
What does it look like
Oral candidiasis manifests itself in the form of a light coating, redness of the mucous membrane of the palate, tongue, and larynx. When trying to remove cheesy formations, eroded bleeding areas appear. A fungal infection can affect the red border of the lips, and marks appear on the corners of the mouth.
In the chronic form of hyperplastic thrush, light gray plaques can be seen on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and tongue. They have a red rim and can be scraped off. When the lips are affected by candidiasis, signs of cheilitis appear in the form of severe peeling, bleeding cracks and erosions with films and crusts.
Diet for candidiasis
In case of inflammation of the oral mucosa, it is necessary to follow a special gentle diet that would not provoke a relapse, but, on the contrary, would accelerate treatment.
Doctors have developed a special diet for candidiasis, which prohibits the intake of certain foods:
- sugar-containing;
- white bread, wheat pastries;
- fatty parts of meat, fish;
- coffee Tea;
- sweet fruits;
- juices;
- seasonings and spices;
- sausages;
- carbonated drinks.
Bad habits such as drinking alcohol and smoking are also strictly prohibited. They help reduce the effectiveness of drugs and make treatment impossible.
At the diet stage, herbal tinctures, berries, cereals, seeds, walnuts, vegetables, and herbs are recommended. Lean meat, steamed or boiled.
How is oral candidiasis transmitted?
The oral form of candidiasis develops under the influence of endogenous factors. Normally, Candida is present in the oral cavity in small quantities. With normal immune system function, thrush does not occur. Signs of the disease begin to develop when candida is activated and exceeds normal levels.
In the body of a healthy person, the proliferation of fungi is restrained by the immune system and beneficial bacteria located on the mucous membranes of the entire gastrointestinal tract. With the weakening of protective forces, a decrease in the number of lactobacilli and the development of dysbiosis, candida begins its active division. The reasons for this change are:
- Age factor. Young children under 3 years of age and older people are most susceptible to developing candidiasis. In a newborn baby, the formation of immunity continues for several months. During this period, the development of dysbacteriosis and candidiasis is possible. Elderly people are susceptible to fungal infections due to the presence of chronic pathologies that have a significant impact on the immune system.
- Taking antibacterial drugs. Dysbacteriosis is caused by a change in the balance of microflora towards pathogenic microorganisms, which is a factor that provokes the growth of candida.
- Long-term course of cytostatic drugs and immunosuppressants. The drugs are prescribed for autoimmune diseases and oncology. Side effects of drugs manifest themselves in the form of a weakening of the body's defenses.
- Pathologies associated with dysfunction of the immune system. Patients with lymphocytic leukemia, HIV, as well as people with humoral and congenital T-cell deficiency are more likely to develop oral candidiasis.
- Sluggish chronic infections and acute inflammatory processes. Patients suffering from purulent laryngitis, pneumonia, and pyelonephritis are prone to the occurrence of a fungal disease.
- Vitamin deficiency. A deficiency of important elements leads to a decrease in the body's resistance to pathogenic bacteria and fungi.
Oral thrush: causes
There are many subspecies of Candida fungi, but in about 50% of cases, oral candidiasis is caused by Candida albicans (C. albicans). Less commonly, in descending order of frequency, oral thrush can be caused by C.tropicalis, C.glabrata, C.krusei, C.pseudotropicalis and others.
Most often, oral candidiasis occurs in 2 groups of patients. Firstly, in patients with poor oral hygiene and untreated carious teeth. This is due to the fact that such patients have a large number of pathogenic bacteria in their mouths, which weaken the defenses of the oral mucosa (which is why Candida fungi begin to invade the mucous membrane).
The second most common cause is weakened immunity, and therefore the main risk group is patients with weakened immunity due to various diseases (for example, against the background of HIV/AIDS, diabetes, malnutrition, as well as patients with active oncological diseases, or after undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy).
Other causes of oral thrush:
- After taking antibiotics, the oral cavity normally contains many types of microorganisms that not only coexist, but also inhibit each other’s growth. Taking broad-spectrum antibiotics eliminates some types of bacteria in the oral cavity, which disrupts the balanced composition of the microflora. The disappearance or reduction of certain types of bacteria can lead to the growth of Candida fungi.
- While taking corticosteroids - in patients with bronchial asthma while taking inhaled steroids, oral candidiasis can occur in approximately 5-10% of adults and 1% of children. In cases where inhaled steroids are the cause, candidal lesions usually have the appearance of erythema. Candidiasis appears precisely in those areas where the steroid came into contact with the mucous membrane (usually the back of the tongue, sometimes on the palate).
- Diet – malnutrition can lead to a lack of iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid in the body, which is a predisposing factor to oral candidiasis. There is also evidence that a high carbohydrate diet also predisposes to oral candidiasis. Therefore, it is very important in such patients to avoid the consumption of sweets, including sugar-sweetened drinks. Research shows that the growth of Candida and its adhesion to the mucosa are enhanced in the presence of sugars (glucose, galactose, sucrose).
- Smoking and other factors – Other factors may include smoking, endocrine disorders (such as diabetes), and the presence of certain diseases of the oral mucosa such as lichen planus and leukoplakia. Often oral candidiasis occurs in patients with a folded tongue or after tongue piercing.
- In patients with removable dentures – most often in patients with removable dentures, candidiasis occurs due to insufficient hygiene of the denture.
In this case, the prosthesis is covered with a biofilm containing a large number of fungi of the genus Candida. For this reason, denture disinfection is a very important part of the treatment of oral candidiasis in individuals with removable dentures. A predisposing factor may be if the patient does not remove his prosthesis while sleeping. In this case, the mucous membrane is constantly deprived of oxygen and washed with saliva, which creates the preconditions for the development of anaerobes and fungi. Another reason may be that the prosthesis does not fit well with the tissues of the prosthetic bed and therefore it injures the mucous membrane. Such microtraumas to the mucous membrane also contribute to the onset of the development of oral candidiasis (24stoma.ru).
- Chronic dry mouth - a decrease in the amount of saliva and the content of various enzymes and antibodies in it is an important predisposing factor in the development of oral candidiasis. Dentists call constant dryness in the mouth the term “xerostomia.” Its treatment is a big problem in dentistry.
- Oral candidiasis in an infant - at a very young age, the immune system has not yet fully developed. Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis occurs in approximately 5% of newborns. Candida species are acquired from the mother's vaginal canal during childbirth. At an early age, the immune system has not yet fully developed and therefore infants do not have an individual immune response to Candida fungi (infant antibodies to fungi are usually supplied in the mother's breast milk).
Stages of inflammation
At the initial stage, when fungi are just multiplying, it is not possible to identify the disease. Swelling and hyperemia occur due to the influence of enzymes secreted by candida. The body's response is manifested by an increase in temperature. During the acute stage, the patient develops problems with eating and a feeling of a lump in the throat. As a result of the activity of candida, intoxication appears.
Temperature rarely rises during chronic oral infection. With the development of atrophic candidiasis, signs of mucosal hyperemia and dryness first appear. Later, patients note the appearance of a burning sensation and the release of viscous saliva.
Forms of flow
Oral candidiasis is classified by type, stage of development and form of pathology.
Stages:
- initial - the appearance of small reddish or burgundy patches on the inside of the cheek;
- medium - plaques increase in size, gradually merge, forming a plaque that can be easily removed with a scraper;
- severe - the inflammatory process covers the entire pharynx, the ulcers bleed, the functions of swallowing and eating are difficult.
By location:
- gingival - appears in newborns or when using removable dentures;
- oropharyngeal - penetrates the throat, more common after antibiotics;
- in the corners of the mouth - jams are formed due to increased salivation, injury, anatomical features (deep folds).
According to the flow form:
- acute - pseudomembranous, atrophic;
- chronic - hyperplastic, atrophic.
According to the international code classification according to ICD-10, the disease is regulated in the section “Some infectious and parasitic diseases”. Code B37.0 - oral thrush or candidal stomatitis.
Acute
There are general symptoms of acute oral candidiasis:
- the internal surfaces of the oral cavity are covered with plaques and a light gray coating;
- when removing the curdled film, bleeding ulcers are observed;
- bad breath;
- reaction to sour, spicy, salty;
- the appearance of pain, tingling;
- sensation of a lump and squeezing in the throat with deep spread (to the tonsils).
The acute pseudomembranous form is distinguished by the following characteristics:
- discomfort when eating, loss of appetite, especially in children;
- sleep disorder;
- an increase in low-grade fever is possible.
Acute atrophic candidiasis must be differentiated from an allergy to removable acrylic devices (or spraying on dental replacement metal structures).
What does the patient complain about:
- severe hyperemia of the mucous membranes, signs of xerostomia;
- scrotal tongue, covered with folds (furrows) with a coating;
- the breath smells disgusting;
- atrophy of the filiform papillae of the tongue;
- fungal colonies penetrate deep folds, forming a single whole, which prevents the tongue from being cleared of plaque.
Chronic
Chronic oral candidiasis must be differentiated from lichen planus or leukoplakia.
Distinctive features of the hyperplastic form of thrush:
- thick, firmly fixed coating of the palate and tongue with a yellowish coating;
- mucosal surfaces itch, burn, tingle;
- the appearance of spontaneous pain;
- attempts to remove plaque are practically ineffective and cause bleeding.
The atrophic form of candidiasis is more common in older people when using removable plastic plate devices.
Patient complaints:
- the coating is thin, but it is almost impossible to remove it;
- burning sensation and dry mouth;
- erosions and papillomas form on the mucous membrane, usually in areas under dentures;
- the corners of the mouth crack;
- the papillae of the tongue atrophy.
READ The most effective remedies for treating periodontal disease at home
This type of thrush can be easily distinguished by the characteristic bumps in the corners of the mouth.
Symptoms and signs of candidiasis in the mouth
The symptoms of oral candidiasis are varied and manifest not only in the form of yeast stomatitis, but also glossitis, cheilitis, and angulitis.
In acute pseudomembranous disease, which occurs more often in children under one year of age and people of mature age, swelling and redness of the tongue, palate, and a cheesy coating develops. The mucous membranes of the lips and cheeks may also become covered with white spots, which, when removed, cause ulcers. Patients complain of loss of appetite and difficulty eating. The pharynx is also affected by Candida. When a fungal infection develops, young children refuse to eat, begin to be capricious, and have problems falling asleep. Acute atrophic candidiasis is accompanied by severe swelling and redness of the oral mucosa. The larynx becomes painful, the nasopharynx becomes dry. The tongue takes on a bright red hue with a shine.
The penetration of candida into the mucous membrane of the lips contributes to the development of peeling, bleeding wounds, and gray films. The corners of the mouth may be affected, manifesting as cracks. They may also bleed and be painful.
Forms of candidiasis
Oral thrush occurs when a person’s body is severely weakened, and it is simultaneously affected by several factors that contribute to the appearance of fungi. Symptoms of oral candidiasis depend on the patient's condition and the stage of the disease. The largest number of cases occurs among the elderly and infants. The disease can be chronic or acute. There are several forms of thrush:
- Acute pseudomembranous. Symptoms: pain in the mouth and an easily removable white coating.
- Candidal cheilitis. A rare form that manifests itself as damage to the inner side of the lower lip.
- Pseudomembranous chronic. Often found in patients with AIDS or HIV.
- Atrophic acute. Accompanied by dryness, burning, discoloration of the tongue, pain in the oral cavity, and there may be no plaque.
- Chronic hyperplastic. Often found in smokers. Signs: thick coating in the palate or on the tongue.
- Atrophic chronic. Often appears in older people who use dentures. The disease can be noticed during a design change. Atrophic candidiasis is characterized by mild symptoms.
Tests: how to prepare
In order to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a blood test and plaque from the oral mucosa. If signs of candidiasis are detected, glucose levels must be determined.
A blood test is taken on an empty stomach, early in the morning. Before visiting the laboratory, you should not eat, drink caffeine-containing drinks, or smoke. The day before, it is not recommended to eat fatty and spicy foods, foods with preservatives and dyes.
A few days before blood sampling, it is advisable to stop drinking alcohol.
To confirm candidiasis, a smear with sterile cotton is taken from the pharyngeal mucosa. Biological material is placed in special environments that promote the growth of bacteria and candida.
If fungal infection of the gastrointestinal tract is suspected, endoscopy of the esophagus is prescribed. In some cases, x-rays are required. Preparation for the procedures involves abstaining from eating black bread, vegetables, fruits, legumes, mushrooms, and nuts for three days. It is forbidden to take activated carbon and preparations with iron. Smoking before the study is not recommended.
Treatment of oral candidiasis
Only a dentist, sometimes a dermatologist, periodontist, mycologist and infectious disease specialist, can establish the correct diagnosis, prescribe systemic therapy and prevent oral thrush. The course of treatment should be prescribed after examination and confirmation of the presence of fungus in the body. Based on the tests obtained, the specialist prescribes the necessary medication, selects the dosage and duration of administration. If the effectiveness is insufficient, the drugs are combined. The complex nature of the disease requires the use of the following treatment methods:
- elimination of diseases that contribute to the development of fungus;
- taking antibiotics;
- targeted medication that suppresses the development of the pathogen;
- sanitation of dental tissues;
- taking medications that strengthen the immune system;
- maintaining oral hygiene;
- balanced diet.
General treatment
Therapy for candidiasis is based on taking antimicrobial and antiparasitic drugs that have a systemic effect on the body. Such agents are capable of killing candida both on the oral mucosa and in other organs. Vitamins B, B2, B6, C, PP are prescribed as general strengthening drugs to boost immunity. They effectively restore the body's natural defenses.
- How to treat candidiasis in women and men
- Fungus on the tongue: treatment of oral candidiasis in children and adults
- Candidiasis in women - symptoms and causes. The first signs and manifestations of thrush on the mucous membranes
For a quick recovery, preventing the spread of infection and strengthening the immune system, a candida vaccine is often prescribed. The drugs Methyluracil and Pentoxyl are used for the same purpose. They activate the work of leukocytes, which effectively fight fungi. In addition, antimycotics (antifungal drugs), which are divided into imidazoles and polyene antibiotics, are used to treat candidiasis. The disease can be treated with the following medications:
- Clotrimazole. Imidazole derivative. It has antibacterial, antiprotozoal, antifungal effects. The drug should be taken at a dosage of 100 mg per day, the course of treatment is 3 weeks. The duration of medication depends on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient. Sometimes the medicine can cause side effects: allergies, swelling, blisters.
- Levorin. An antifungal agent with a fungicidal effect. Refers to polyene antibiotics. The tablets should be dissolved 6 times a day after meals for 14 days. Already on the 5th day there is a noticeable improvement: erosions heal, plaque decreases. This product is not recommended for use in children.
Nystatin
The polyene antibiotic Nystatin is capable of destroying the cellular forms of the causative agent of candidiasis. Available in ointment and tablet form. Under the influence of Nystatin, the growth and spread of fungi is stopped. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor, individually selecting the dose for each patient. As a rule, a Nystatin tablet with a dosage of 500,000 units is placed behind the cheek and wait until it is completely dissolved. The course of therapy lasts no more than two weeks. Nystatin can be taken by young children. Treatment with the drug is not recommended for severe liver diseases and pregnancy.
Fluconazole
The powerful antifungal agent Fluconazole is available in the form of ointments, tablets, suppositories and injection solution with a dosage of 50,100,150 mg. The drug is able to block the growth and reproduction of fungi. Adult patients, based on the severity of the disease, can be prescribed 150 mg of Fluconazole once a day for a week. Children - 10 or 50 mg once for 5 days. Possible side effects: nausea, headache. Contraindications: pregnancy, arrhythmia, hepatitis.
Local treatment
The main goal of local therapy is to suppress the proliferation of fungi and prevent their further spread to other organs. For this purpose, antibiotics and antiseptics, which have antifungal properties, are often used. Such products are used in the form of rinses, applications and lubrication. Aniline dyes are used as a local treatment for oral thrush. Fucorcin solution, methylene blue, and brilliant green are considered effective.
Of great importance in the course of therapy is the treatment of all inflammatory processes that occur in the mouth and sanitation of the oral cavity (proper gum care, brushing teeth). Dental dentures should be treated with special solutions (Chlorhexidine or Hexoral). In addition, you can take the following medications:
- Lugol's solution. Antiseptic for external and local use, intended to eliminate oral infections. To treat candidiasis, the solution must be diluted with warm water in a ratio of 1:3, treatment of the affected surface should be carried out 4 times a day. Side effects: runny nose, muscle weakness, excessive drooling.
- Lysobacter. Antibacterial natural product. Contains protein enzyme – Lysozyme. The product has the ability to destroy the cell structure of pathological microorganisms. In addition, Lysobact activates defenses and strengthens local immunity, stabilizes and restores oral microflora. Adults need to take 2 tablets 4 times a day. Children over 3 years old – one tablet no more than three times a day. The drug cannot be used for lactase deficiency or glucose malabsorption syndrome.
Diet
Along with taking medications, a balanced diet plays an important role in the treatment of fungal infections. To make it easier for the body to digest and assimilate food, it is necessary to combine dishes correctly, for example, carbohydrates can only be eaten with fresh or boiled vegetables. During treatment, the following foods should be excluded from the menu and then eaten in small quantities:
- mushrooms;
- fresh milk;
- sauces, marinades with vinegar;
- sugar;
- semolina porridge;
- baked goods made with yeast;
- caffeine;
- rice;
- sweet juices;
- carbonated drinks;
- smoked meats;
- dried fruits;
- sweets;
- chips;
- muesli;
- salty foods.
It is worth limiting the consumption of potatoes, corn, beans, boiled beets, and carrots. At the same time, the diet should contain fermented milk - natural yogurt without additives, kefir. Recommended Products:
- eggs;
- lean meat (chicken, beef, rabbit);
- fruits with low carbohydrate content;
- lean fish;
- vegetables (cabbage, green peppers, cucumbers);
- greenery;
- berries;
- buckwheat grain;
- linseed, olive oil.
An integrated approach to treatment
Therapy for oral candidiasis is based on the use of systemic drugs. They destroy infection on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, esophagus and other organs. As part of complex treatment, topical medications and diet are used.
Drug treatment
To eliminate candida infection, patients are prescribed:
- polyene antibacterial medications;
- imidazoles.
Anti-candidiasis medications are taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor. The course of treatment depends on the group of drugs:
- Polyene medicines. Most often, patients are prescribed nystatin or levorin. It is necessary to take tablets for candidiasis up to 6 times a day after meals for 2 weeks. To enhance effectiveness and quickly relieve unpleasant symptoms, it is better to dissolve them. A few days after the start of therapy, the plaque becomes less noticeable and the ulcers disappear. If a woman or man continues to complain of pain in the larynx and lack of effectiveness from taking medications, amphotericin is prescribed as an intravenous injection.
- Imidazoles. The medications clotrimazole and miconazole have high antifungal properties. The dosage is 0.05-0.1 g per day. The duration of treatment for candidiasis is up to 3 weeks. The regimen may vary depending on the course of the disease and the age of the patient.
Pregnancy is a contraindication for taking oral forms of drugs containing imidazole.
Patients can be prescribed fluconazole, diflucan, nizoral. If there is severe swelling of the mucous membranes, it is possible to use suprastin or fenkarol. It is recommended to rinse your mouth for candidiasis with alkaline and disinfectant solutions containing the following substances:
- borax;
- sodium bicarbonate;
- iodine;
- boric acid.
Treatment for thrush in the mouth
Treatment of candidiasis of the oral cavity and pharynx is complex. It depends on the localization of the pathological process, the form and severity of the disease. The main principle of therapy is a quick and effective effect on pathogens, which is achieved through the use of antifungal drugs of general and local action.
- In most cases, treatment of thrush begins with the use of local therapy. If it is ineffective, a transition to drugs of general (systemic) action is made.
- For widespread candidiasis, treatment begins with local and general antifungal drugs simultaneously.
The drug of choice for systemic candidiasis is taking Fluconazole (a group of azole compounds) in tablets. If the fungi are resistant to this drug, its dose increases. Intraconazole and Ketoconazole (imidazole derivatives) have a good effect. In the event of the development of fungal resistance to the drugs described above and the persistent course of systemic candidiasis, Amphotericin-B (a group of polyene antibiotics) is prescribed. When treating thrush of the mucous membranes and skin, antiseptics are additionally used.
Rice. 24. Under the influence of antifungal drugs, the shell of pathogens becomes porous, “leaky.” On the left you can see how the contents of the cell flow out onto the surface of the mycelium.
Treatment of oral candidiasis with topical antifungal drugs
Thrush in the mouth is well treated with antimiotics and topical antiseptics.
Forms and methods of use of topical antifungal drugs
Local antifungal drugs are available in the form of solutions, ointments, gels, suspensions, drops, lozenges, aerosols and lozenges.
- The gel is placed in the mouth for 30 - 40 seconds. 4 times a day and then swallowed or spat out.
- The suspension is used in the form of applications. The bottle of suspension must be shaken before use.
- The tablets are placed behind the cheek, or applied to the gum in the area of erosion and held until completely absorbed, or chewed, and the resulting paste stays in the mouth for a long time.
- Solutions, drops and suspensions are used for local applications and irrigation. Applications are carried out using cotton-gauze swabs soaked in a solution, or applied to the affected areas using a cotton swab.
- The lozenges are placed in the mouth and held until completely absorbed.
- It is more convenient to use the ointment by soaking a cotton-gauze swab with it and placing it behind the cheek.
List of topical antifungal drugs
For candidal stomatitis the following are used:
- Solutions Candide and Katrizol.
- Water suspension for mouth irrigation Levorin.
- Suspension Pimafucin 2.5% and Nystatin.
- Oral gel Daktarin and Miconazole.
- Tablets for resorption in the mouth Miconazole nitrate and Levorin.
- Powder for the preparation of Natamycin suspension.
- It is better to chew Nystatin tablets and keep the pulp in your mouth for as long as possible. The bitter taste of the medicine can be weakened by adding 50% sucrose
- Nystatin lozenges.
A good effect for candidiasis is obtained by using creams containing, in addition to an antifungal agent, a corticosteroid and an antibiotic: Candide-B, Triderm, Lorinden S, Lotriderm, Pimafukort, Mikozolon, Travocord.
Treatment of thrush in the mouth with antifungal drugs lasts about one month, but possibly longer - until the clinical manifestations of the disease completely disappear, and beyond that for about 7 days. In the chronic form of thrush, in addition to local treatment, systemic antifungal drugs of the triazole, imidazole or polyene antibiotics are used, as well as pathogenetic therapy.
Rice. 25. Nystatin ointment is used for lesions of the corners of the mouth (candidal cheilitis). When treating thrush, it is better to chew Nystatin tablets and keep the pulp in the mouth for as long as possible. The bitter taste of the medicine can be weakened by adding 50% sucrose.
Treatment of oral candidiasis with antiseptics
Antiseptics for the treatment of thrush are available in the form of solutions, aerosols, tablets and powder. The duration of treatment of candidal stomatitis with antiseptics is more than 2 - 3 weeks - until the clinical symptoms of the disease completely disappear, and beyond that another about 7 days. Medicines in this group should be alternated every week.
For local treatment of candidal stomatitis, the following are used:
- For the purpose of irrigating the pharynx, solutions of Resorcinol aqueous, copper sulfate, Chlorhexidine digluconate 0.12%, 0.1% solution of Hexetidine, Hexoral, Miramistin, Lugol, Sodium tetraborate in glycerin (Borax), 1% solution of boric acid. Rinsing should be done for 30-60 seconds after meals, 2 times a day.
- The drug Hexoral is used in the form of an aerosol. The oral cavity is treated for 1 - 2 seconds.
- Dequalinium chloride, Fluomizin, Laripront and Decamine are used in the form of lozenges. The tablets are placed behind the cheek, or applied to the gum in the area of erosion and held until completely absorbed, or chewed, and the resulting paste stays in the mouth for a long time.
- Potassium permanganate is used in powder form to prepare a rinsing solution.
Sodium Bicarbonate solution 2% is used to neutralize the acidic environment of the oral cavity.
Rice. 26. Antiseptics used to treat thrush.
The antifungal solution can be swallowed after treating the oral cavity, but the antiseptic solution cannot.
What is not recommended for candidal stomatitis
For common forms of candidal stomatitis and pharyngitis, it is not recommended:
- perform surgical interventions on the tonsils,
- wash out the lacunae,
- carry out steam inhalations,
- use compresses on the neck,
- use physiotherapy (UHF and microwave therapy),
- use tetracycline and penicillin antibiotics.
How to treat a chronic form of the disease
For chronic oral thrush, both oral forms of fungicidal drugs and topical agents are used. Patients are prescribed courses of ketoconazole, amphotericin, and levorin. If necessary, the drugs are alternated. The oral cavity is treated with Lugol's solution or fucorcin. You can lubricate the mucous membranes with candidiasis with miramistin or chlorhexidine.
If the burning sensation intensifies, the use of drugs should be discontinued.
Patients may be prescribed physiotherapy with electrophoresis and laser treatment. The prescription of complex immunotherapy is indicated for severe candidiasis. Chronic fungal infections weaken the body's defenses. Patients are recommended to take courses of vitamins and minerals to restore immunity. If dysbiosis is detected, probiotic drugs can be prescribed.
If combined infections are detected, the patient is prescribed a course of antibacterial and antifungal drugs. You should not stop taking medications immediately after the symptoms of oral candidiasis go away, since microorganisms may become resistant to the active substances.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease is manifested by a variety of symptoms. It depends on the cause, age of the patient, distribution and form of progression.
READ In what cases is Nystatin used to treat stomatitis?
What are the signs by which oral thrush can be identified:
- itching and burning sensation in the mouth;
- loss of taste, appearance of a metallic taste;
- formation of a white cheesy coating in the mouth;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- swollen soft tissues, inflamed mucous membranes;
- the appearance of shallow ulcers.
Prevention measures
The basis of prevention is strengthening the immune system and maintaining a proper diet. Reducing the consumption of simple carbohydrates and sweet foods reduces the risk of developing candidiasis. Sanitation of the oral cavity 2-3 times a day plays an important role. You should not take medications for candidiasis on your own without a doctor’s prescription.
Compliance with the rules of general hygiene also prevents the development of thrush and other fungal diseases. If there are any signs of infection, you should consult a doctor. Timely treatment helps prevent relapses and severe septic conditions.
To prevent the development of oral thrush in infants, women during pregnancy must completely eliminate the source of infection. The choice of drug is made by the doctor. Oral forms of medications are prescribed during pregnancy only in cases of severe fungal disease.
Local treatment
These are drugs that act on the mucous membrane and are not absorbed into the blood. They stop the growth and reproduction of candida, relieve unpleasant symptoms, and heal damage caused by the activity of the fungus:
- Aniline dyes are used as a local treatment for candidiasis of the oral mucosa. The most effective are methylene blue, fucorcin solution, and brilliant green.
- Nystatin or Levorin ointment. Use for cheilitis (lip damage) and yeast infections.
- Lysozyme in lozenges or Lizak have a bactericidal effect.
- Iodine preparations for applications: Yodicirin, Lugol's solution.
Sanitation of the oral cavity is of great importance, that is, the treatment of all diseases and inflammatory processes of the oral cavity. This includes healthy teeth, gums and proper care of dentures. They are treated with the same antifungal agents, except for aniline dyes.
Complications and consequences
Timely therapy prevents the development of complications of oral candidiasis. When self-medicating, the patient increases the risk of developing negative consequences, which manifest themselves in the form of fungal infection of the digestive tract, urinary tract, and kidneys.
Severe candidiasis is dangerous due to the occurrence of sepsis, which requires resuscitation measures.
Blood poisoning leads to death in half of the cases. In children, oral candidiasis can cause heart murmurs and enlargement of nearby lymph nodes. The disease increases the risk of bacterial infection of the respiratory system and the development of kidney dysfunction.
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms of thrush appear, you should not self-medicate. An unprofessional approach often harms the patient. The first basis for proving the presence of a fungal infection is a medical examination of the oral cavity with a parallel questioning of the patient about his well-being. If you have dentures, a specialist can take material from them for examination. The similarity of the external manifestations of thrush with other diseases - allergic stomatitis, syphilis, lichen planus - is the reason for prescribing the following methods of differential diagnosis:
- scraping the film from the affected areas to determine the type of pathogen;
- clinical blood test;
- endoscopy of the stomach, esophagus, duodenum;
- studying throat culture using a smear;
- X-ray of the esophagus with a contrast solution.
Therapy of candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx in a child
Treatment for oral thrush is prescribed by a pediatrician or ENT specialist. If candidiasis is detected, it is necessary to immediately disinfect all toys, pacifiers, and feeding bottles. A woman should treat her nipples with Miramistin solution.
If the child is one year old or older, it is necessary to exclude sweetened foods from the diet and introduce more vegetables and fermented milk drinks into the menu.
For candidiasis in infants, the basis of treatment is treating the oral cavity with baking soda diluted in water. The procedure is carried out 4 times a day. For older children, the mucous membranes of the mouth are treated with a solution of miramistin or chlorhexidine. Hydrogen peroxide can also be used in diluted form.
Older children can rinse their mouths with herbal infusions and soda solution. Inhalation with a decoction of chamomile or calendula helps reduce the symptoms of thrush. In case of complicated candidiasis, fluconazole or diflucan is prescribed.
Since a fungal infection provokes a violation of the absorption of iron in the body, children are prescribed drugs in the form of syrups (ferrum-lek, maltofer). To strengthen the immune system, a course of calcium gluconate, B vitamins, and ascorbic acid is prescribed. Children can take alphabet, vitrum, and complivit complexes.
If signs of candidiasis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. After receiving test results and making a diagnosis, a course of fungicidal drugs is prescribed. Self-treatment can aggravate the course of a fungal infection and lead to the development of serious conditions, the most dangerous of which is a septic complication. Full compliance with the doctor’s recommendations allows you to prevent the occurrence of consequences and quickly get rid of oral candidiasis.
What causes the disease to develop?
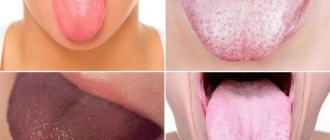
This is what a tongue affected by candidiasis looks like
The cause of candidiasis of the oral mucosa is the usual close contact with the carrier of the infectious agent (through handshakes and kisses, transmitted with saliva), through personal objects, toys contaminated with fungus. The source of infection is very often milk and drinking water.
Babies can become infected during childbirth from an infected mother or through breastfeeding.
However, this does not mean at all that mushrooms that get on the mucous lining of the mouth will immediately provoke thrush. They can easily be washed off from the surface of the mucous membrane with food or saliva in the gastrointestinal tract, and successfully removed from the body. Especially if the acidity in saliva and gastric juice is not disturbed.
Successful colonization of the pathogen and its further development must be preceded by a number of predisposing factors that weaken immune functions and impair the reactivity and stability of the body. It can be:
- Decreased immunity during pregnancy;
- In children – prematurity factor, internal or external hypotrophic processes;
- Congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies;
- Complex background pathologies - cancer or tuberculosis;
- The presence of chronic gastrointestinal pathologies, acute infections, endocrinopathies;
- Signs of hyposalivation (reduced saliva secretion), xerostomia (dry mouth) and decreased acidity in the mouth, pharynx and larynx.
The development of infections is provoked by various types of injuries to the oral mucosa caused by poor-quality fitting of denture structures, splinter scratches of damaged teeth, and burns of a chemical or thermal nature.
It has been noticed that in women, candidiasis in the mouth develops more often than in men - this is influenced by significant hormonal changes during menopause, puberty or pregnancy.
All these conditions are accompanied by immune problems that facilitate active growth and rapid reproduction of the fungal flora, manifested by the “blooming” clinical symptoms of oral thrush.
Development factors
The main age category of people most susceptible to the disease are newborns. This is due to the imperfection of their immunity. The baby can become infected with the pathogen from the mother: during the prenatal period, during childbirth or during breastfeeding.
Other reasons that contribute to the development of oral thrush in adults:
- weak immunity associated with hypothermia, chronic infections or HIV infection;
- pregnancy in women and the resulting hormonal imbalance;
- metabolic disorders due to unsatisfactory functioning of the digestive system and other internal organs, age-related changes;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics or hormonal drugs;
- injury to the mucous membranes of the mouth mechanically (wounds, cuts, rubbing from dentures) or chemically (burns);
- constant stressful situations;
- lack of vitamins B, C and PP in the body;
- oncology and radiation therapy performed during cancer;
- bad habits such as smoking, alcoholism or drug addiction.
According to statistics, every 5 children under the age of 1 year and every tenth man over 60 years old suffer from candidal stomatitis. In children, the disease develops due to the immaturity of the immune system, and in older people - due to a slow metabolism and chronic diseases acquired during life.
It is possible to become infected with candimycosis from another person by sharing utensils or personal hygiene products (toothbrush). At the time of birth, Candida fungi are transmitted to the baby from the vagina of an infected mother. People can also get a fungal infection from pets: kittens, puppies and other mammals.
Features of treatment
Treatment of oral candidiasis in adults and children is a task for an experienced doctor. Self-medication is not enough here. The sooner treatment begins, the more effective and faster it will be. It is important for the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis. The attending physician will listen to complaints, examine the condition of the oral cavity, scrape the mucous membrane, and prescribe blood tests. Therapy is quite individual. It takes into account the condition of the patient’s body and the degree of damage.
If a fungus appears on the tongue, treatment should be comprehensive. Even more effort will be required if the entire oral cavity is affected. In adults, chronic diseases must first be treated. When treating children, it is important to strengthen the immune system and restore the balance of microflora.
The dentist treats thrush.
This is often done by a dentist or periodontist. It happens that candida also affects internal organs. Then you need the help of an infectious disease specialist or mycologist. Treatment will consist of local and general therapy.
Prevention of thrush
Completely cured thrush may reappear periodically. Relapses are caused by immune disorders in the body. Therefore, the main preventative measure to prevent the development of thrush is hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, a balanced diet, and daily walks. These recommendations are especially relevant when it comes to young children.
Lotin Alexander, medical columnist
25, total, today
( 188 votes, average: 4.62 out of 5)
Alveolitis after tooth extraction: symptoms and treatment
Toothache during pregnancy: what to do?
Related Posts
What does the term “Candida” mean?
Candida fungi are an integral component of our microflora. Eight out of ten people have them. Their place of residence is the mucous membrane. You can find this ubiquitous fungus even on the skin. The development of such yeast-like fungi is inhibited by the immune system. But if it weakens, their active reproduction begins, and fungus appears in the mouth and in other areas of the mucous membrane.
Thrush in the mouth most often occurs in infants. The reason for this is that their immunity is only developing and cannot always cope. At the first signs of this disease in a child, you should consult a pediatrician.
The development of yeast-like fungi is inhibited by the immune system.
Thrush in the mouth occurs when the immune defense is reduced. It often affects the elderly, infants and those with dentures. It is very easy for fungus to grow under them.
This type of damage to the oral mucosa is more common in women and smokers. It is also very harmful to abuse medications, especially antibiotics. They disrupt the microflora, reduce immunity, and the development of fungus in the oral cavity is not restrained by anything.
Candida is a yeast-like fungus. It consists of only one cell. The number of its types is amazing. Scientists have counted about 150. However, only 20 species are dangerous. Such a fungus in the mouth leads to damage to the mucous membrane and a lot of inconvenience.
An environment with a high pH is considered favorable. It is alkaline and occurs when you abuse sweets and foods that are rich in carbohydrates.
Candida cannot form mycelium like other fungi. Therefore they are considered imperfect. But their spores are able to grow inside cells. They are easily transmitted to a healthy person from a sick person. This is facilitated by the formation of a protective shell - chlamydospores.
The most common fungus in this species is Candida albicans. It is he who is the main culprit of candidiasis. As soon as a person's immunity decreases, this fungus transforms and divides. In this case, long chains of its cells appear - pseudomycelium.
As soon as a person's immunity decreases, this fungus transforms and divides.
Candida can easily penetrate the epithelium of the pharyngeal mucosa. As soon as it develops, tissue destruction begins. This is facilitated by enzymes that it secretes in huge quantities; they are very aggressive. This is how the fungus quickly destroys the mucous membrane.
Clinical manifestations
Mucosal candidiasis is an infectious disease of fungal etiology that affects the mucous membranes of various organs. The process may involve the mucous membrane of the genital organs, intestines, oral cavity, and urethra. Most often, the disease is caused by fungi of the genus Candida albicans. The following factors contribute to the development of the disease:
- change in pH,
- dysbacteriosis,
- malnutrition,
- long-term use of antibiotics,
- HIV infection,
- tuberculosis,
- diabetes,
- drug and alcohol addiction,
- addiction to cigarettes,
- use of hormonal contraceptives,
- monotonous lifestyle,
- disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism.
Most often, fungi affect the vaginal mucosa of women. Vaginal candidiasis develops. This pathology is otherwise called thrush. The disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pathological white discharge from the genital tract,
- itching,
- burning,
- hyperemia of the labia,
- swelling of the mucous membrane,
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Many women show no signs of the disease. Thrush is detected by chance during a gynecological examination. A specific symptom of candidiasis of the vaginal mucosa is a white, curd-like discharge. They often have a sour smell. The discharge is of heterogeneous consistency and contains lumps. Their volume increases after taking a bath or shower, at night and after sexual intercourse.
In some sick women, the discharge ends with the appearance of menstruation. This is due to changes in vaginal pH. Vaginal candidiasis is often combined with diseases such as ureaplasmosis, herpes, and chlamydia. Chronic vaginal candidiasis can lead to the following complications:
- urethritis,
- cervicitis,
- infertility.
Treatment
Before treating patients, it is necessary to ensure that the diagnosis is correct. If fungal urethritis is suspected, it is necessary to conduct a general urine test and take a smear from the urethra. Additionally, a general blood test is performed. An ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the genitourinary system (prostate, bladder, kidneys). In case of damage to the oral mucosa, it is necessary to take a swab from the throat.
If vaginal candidiasis is suspected, a complete gynecological examination is necessary. Candidiasis is treated conservatively. Treatment includes the use of modern antifungal drugs, diet, and the use of local antiseptics and antibiotics. Today, 2 groups of antifungal drugs are used: polyene agents and imidazoles.
Polyene drugs include Nystatin and Levorin. For oral candidiasis, it is recommended to dissolve the tablets. If these drugs are ineffective, stronger antifungals are prescribed. These include Amphotericin B and Amphoglucamine. They should be taken after meals. The dose of the drug and duration of therapy are determined by the attending physician.
Preparations of the imidazoline group have become widespread. These include Fluconazole, Diflucan, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, Irunin. Itraconazole and its analogues (Irunin, Itrazol, Orungal) are often used. This medicine interferes with the formation of ergosterol in fungi, leading to their death. Itraconazole is used for candidiasis of the vulva, vagina and oral mucosa.
The medicine is contraindicated in case of chronic heart failure, individual intolerance to the main active ingredient, during pregnancy and lactation. It is recommended to take medications orally in the form of tablets or capsules. For candidiasis of the urethral mucosa, the following medications are most often used:
- Nystatin,
- Levorin,
- Natamycin,
- Clotrimazole,
- Amphotericin B.
Primary vaginal candidiasis is an indication for the prescription of vaginal suppositories and tablets.
Drugs such as Ginezol, Klion-D, Kanizon, Kanesten, Pimafucin are used. If local therapy is ineffective, systemic drugs are required (Diflucan, Mikosist, Diflazon). Eubiotics are used to restore vaginal microflora. Treatment of pregnant women is carried out with local remedies.
Bladder
Often the bladder is involved in the process. Candidiasis of the mucous layer of the bladder is most often a complication of fungal urethritis. Both men and women suffer from this disease. Fungal cystitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the pubic area,
- frequent urination,
- burning,
- pain when passing urine,
- general malaise,
- the appearance of blood in the urine,
- increase in body temperature.
Additional symptoms include headache, swelling of the lower extremities, white threads in the urine, and weakness. Urine is released in small portions. Fungal cystitis is often combined with intestinal and vaginal candidiasis. If not treated promptly, fungi can reach the kidneys. In this situation, there is a risk of developing pyelonephritis.
Diet
Candidiasis of the skin and mucous membranes is quite common. Often this disease affects the oral cavity. In order to get rid of the pathology much faster, doctors recommend following a special diet. Namely, try to completely give up sweets during treatment and reduce the consumption of simple carbohydrates as much as possible. Avoid eating foods that are too spicy or sour, as they will overly irritate already damaged mucous membranes. Also try not to eat unhealthy foods for a year after treatment. This will maximize the results and protect you from re-infection.
Diagnostic methods for determining the disease
In adults, before treating thrush that is localized in the mouth or on the mucous membranes of other organs, an examination is carried out. The doctor listens to the patient's complaints and examines the oral cavity. To clarify the diagnosis, he prescribes a blood test to determine glucose levels, general biochemistry, and a smear from the oral mucosa for microscopic examination.
Consultations with a dermatologist and endocrinologist help to establish the cause, how and what led to the development of the disease. It is possible to cure oral thrush in an adult only when a regimen has been developed for the treatment of current diseases: leukemia, colitis, dysbacteriosis and diabetes.
Oral candidiasis is treated by a dentist. If symptoms of general damage to the body are detected, that is, organs are affected, then an infectious disease specialist will help get rid of it.
Intestines
Fungi of the genus Candida can cause damage to the mucous membrane of the small and large intestines. There are invasive and non-invasive candidiasis. In the invasive form, fungi invade tissue. When non-invasive, they are located in the intestinal lumen. When the intestinal mucosa is damaged, the following symptoms are observed:
- abdominal pain,
- stool disorder,
- feeling of fullness,
- bloating (flatulence),
- itching in the anus,
- moderate increase in body temperature.
With this form of the disease, patients are often bothered by excessive sweating. The invasive form of candidiasis of the intestinal mucosa is the most severe. It is manifested by diarrhea or constipation, the presence of white specks in the stool, and a feeling of incomplete bowel movement. Pathological impurities are often found in the stool: mucus and blood.
Intestinal candidiasis often develops in children. This is a type of intestinal dysbiosis. In young children, the disease can cause weight loss and delays in physical development. Fungal infection of the intestinal mucosa can occur as colitis or duodenal ulcer.
conclusions
Each of us is responsible for our own health. Only we decide whether to be healthy or succumb to the weight of various diseases. Take care of yourself today, because candidiasis is not a death sentence. It is very simple to protect yourself from the development of this pathology. First of all, pay attention to your diet. Consume as many foods as possible that are responsible for strengthening your body's defenses. Doctors also recommend taking multivitamin complexes several times a year. Engage in active sports, walk more in the fresh air, accustom yourself to hardening.
It is very important to cure all chronic diseases that currently exist in your body. Go to the dentist regularly and teach your children to take care of themselves from childhood. And then you will not know what oral candidiasis is. Love yourself and be healthy!
What symptoms should you look out for?
Candidiasis develops suddenly and often becomes chronic in adults. Thrush has a common symptom - creamy-white plaque in the mouth. The symptoms are so obvious that they are difficult to miss. Loose and dense spots are located on the tongue. Cover the surface of the cheeks, palate and tonsils.
Symptoms of candidiasis in adult men include loss of strength and malaise. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. The risk group includes men with HIV infection and patients with tuberculosis.
Thrush in the mouth causes dryness. Symptoms are similar in adults and children. On examination, the oral tissues are swollen. The white clots are convex and consist of destroyed epithelial cells, keratin, fibrin and food debris.
In appearance they resemble plaques covered with a layer of cottage cheese. They are painful to the touch and bleed if you try to remove them. When brushing your teeth, there is a burning sensation and copious amounts of saliva. The activity of microbes has a detrimental effect on neighboring healthy cells. Ulcers form on the mucous membrane; with a long course of the disease, the deep layers of the mucous layer of the mouth and throat are affected.
In rare cases, the pharynx and esophagus are affected. You should be wary:
- pain;
- feeling of food stuck in the throat, sternum;
- fever if the thrush has spread beyond the esophagus.
Seizures in the corners of the lips in adults are caused by poorly made dentures. Incorrect “landing” changes a person’s facial expressions, saliva flows out and wets the corners of the mouth. The skin turns red and becomes crusty. When you open your mouth, it cracks, blood appears, and the person feels a burning sensation and pain.
Itching occurs during an allergic reaction. The burning sensation is intensified by sour, spicy and hot foods. Symptoms of oral thrush include fever, which rises in response to the irritant caused by the Candida fungus.
Urethra
Often a pathology such as fungal urethritis develops. This disease is detected only in persons with reduced immunity. If proper treatment is not carried out during acute inflammation of the urethral mucosa, the disease becomes chronic. Candidal urethritis refers to specific forms of the disease. Fungal infection of the urethral mucosa is manifested by the following symptoms:
- burning,
- pain during urination,
- whitish discharge,
- the appearance of a gray coating in the area of the glans penis.
The incubation period is up to 20 days, but the first symptoms of the disease may appear within a few hours after infection. A typical sign of fungal urethritis is a white discharge in the form of threads. Most often, patients notice them in the morning. Fungi from the urethra can penetrate the glans penis, causing posthitis.
In most cases, the disease develops in a subacute form. Only in 5% of patients urethritis occurs in an acute form. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should visit a urologist. Self-medication can cause complications (development of prostatitis, cystitis and infertility). Chronic fungal urethritis is much more difficult to cure.
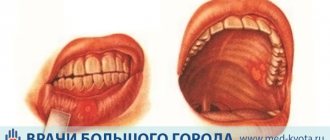
Oral thrush: symptoms of cheilitis
This is a fungal infection of the mucous membrane and skin around the lips, which has the following symptoms:
- redness of the lips, thinning of their borders;
- the appearance of a large number of cracks on them, covered with tiny white-gray scales and films, under which there is a bleeding surface;
- painful sensation of dryness, burning in the lips, discomfort when opening the mouth;
- possible jamming in the corners of the mouth;
- in severe and advanced cases - the appearance of deep, long-term non-healing cracks.
The disease is more common in countries with warm climates (Turkey, India, Brazil, etc.), therefore, when traveling or on business trips to these countries, you should immediately seek medical help at the first symptoms.
Clinical signs of the disease
At the initial stage of the disease, fungal microorganisms invade the cells of the mucous epithelium of the oral cavity. During the process of infection propagation, specific enzymes are released that irritate the epithelial membrane. A focal melting of the mucosal tissue occurs, which is accompanied by the appearance of swelling, redness, and a feeling of increased dryness. Typical symptoms of candidiasis in the mouth in women and men are pain and hypersensitivity. An increase in the number of harmful microbes further leads to the formation of pseudomycelium - threads formed by elongated Candida cells.
What does thrush in the mouth look like? Individual clusters of fungal infection form a cheesy coating that is white or slightly yellowish in color. It rises slightly above the oral mucosa. Microscopic examination reveals fibrin, destroyed epithelium, keratin, bacterial flora, and food residues in plaque.
In the early stages of this pathology, candidiasis in the mouth looks like small whitish patches located on the inside of the cheek. After some time, the number of such formations increases, they grow and can merge with each other. The appearance of the plaque also changes - it takes the form of a milky film, on the surface of which large white plaques or flakes appear. With thrush, these elements also appear on the gums, soft palate, tonsils, tongue, and skin of the lips. Initially, the plaque can be removed with a spatula quite easily. The result of such actions is the formation of a bright red erosive surface, on which small ulcers stand out noticeably. Damage to the mucous epithelium during thrush in the oral cavity occurs due to the activity of candida, which destroys nearby cells and penetrates into the deeper layers of this membrane.
Fungal microorganisms cause irritation and allergic reactions from the affected tissues, resulting in burning and itching in the oral cavity. Discomfort is more pronounced when swallowing saliva and while eating (especially when eating sour, spicy, hot foods). If the source of inflammation involves the pharynx, its swallowing function becomes difficult, and an unpleasant sensation of a foreign body (“lump in the throat”) occurs. A slight increase in temperature readings is possible.
Treatment for oral thrush
Treatment of oral thrush involves both local sanitation of the mouth and the administration of oral antifungal drugs that kill microbes inside the body in adults and children.
Treatment of fungal infection inside the body
General therapy in adults is based on antibiotics and imidazole derivatives. To eliminate the growth of fungi and get rid of infections in the mouth and other organs, Nystatin and Levorin tablets are prescribed. How to take them for thrush is prescribed by the doctor after checking the smear and blood tests.
Symptoms become less severe after a few days. Resorption of the tablet in the mouth helps to enhance the effect on the mucous membrane. In adult men, such treatment gives quick results, the pain of erosive areas decreases and the plaque on the mucous membrane gradually decreases. The doctor evaluates the result at a follow-up appointment to see how the prescribed antibiotic copes with the task. If the symptoms of the disease remain severe, thrush will be treated with Amphotericin or Amphoglucamine.
Miconazole, Clotrimazole, Econazole (imimdazoles) are used in a course. It takes at least 1 week for the symptoms to subside. The doctor will calculate the dosage and duration of use.
To reduce the activity of yeast-like fungi, the following is prescribed:
- Flucanazole. Dosage 200-400 mg per day.
- Nizoral. Dosage 200 mg. The course of therapy is 3 weeks.
- Diflucan. Daily dose 50-100 mg. Duration of treatment is from 7 to 14 days.
- Decamine caramel. Keep it in your mouth until the lozenge dissolves. Dosage: 2 pieces per day for 2 weeks.
- Suprastin, Zyrtec against allergies.
Auxiliary therapy to improve immunity includes additional intake of vitamins, calcium and iron supplements.
Local treatment of thrush
To restore microflora in the mouth and heal tissue, medications are used that disinfect the mucous membrane, remove unpleasant odors, and dissolve plaque covering inflamed areas. To remove the symptoms of the disease use:
- For cauterization, use a solution of fucorcin or brilliant green.
- For lotions - Lugol's solution.
- Lozenges for resorption and local anesthesia Lizak, Lysozyme.
- Levorin or Nystatin ointments help heal inflammation on the lips.
It will not be possible to cure thrush if there are pockets of infection in the mouth: untreated teeth, caries or lack of hygiene. In adult men who are addicted to nicotine, this likelihood is generally reduced.
Rinsing relieves symptoms of inflammation in the mouth, reduces acidity in the mouth, washes the mucous membrane, and removes dead epithelium. Solutions can be prepared either independently or using ready-made ones. After the procedure, thrush in an adult looks less noticeable, swelling decreases. Rinse your mouth with a solution of soda or borax every 2 hours. Required after meals and at night. Treatment is accompanied by the application of a gel or spray with an antimycotic effect.