One of the most common diseases of the 21st century is osteochondrosis. has noticeably looked younger over the past few years. It is diagnosed not only in older people, but also in those under thirty; more and more teenagers are suffering from the disease.
The reasons for its occurrence are a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, sedentary work, and stress on an untrained back.
The disease leads to disruption of many vital functions of the body: arrhythmia, loss of sensitivity and paralysis of the limbs, often to disability.
Mechanism of disease development
The pathogenesis of osteochondrosis is based on the loss of the nucleus pulposus of its hydrophilic properties. This semi-liquid structure consists of connective tissue fibers and a gelatinous substance (chondrin). As a person grows older, the vascular bed in each intervertebral disc decreases. The supply of nutrients to it occurs diffusely, that is, according to the principle of spontaneous equalization of concentrations. This explains the impossibility of complete restoration of cartilage tissue after injury or excessive physical stress on the spinal column.
Osteochondrotic processes are aggravated by hormonal changes and an unbalanced diet. The cartilage tissues do not receive enough nutrients for their full functioning, which provokes the following violations of their structure and properties:
- strength and elasticity are lost;
- shape, consistency and configuration changes.
The intervertebral discs become flattened, and radial cracks form in the fibrous rings. This causes a decrease in the distance between adjacent vertebrae, as well as displacement of the facet joints. Gradually, the connective tissues of the fibrous rings and ligaments are involved in the pathological process. In response to tissue breakdown, the immune system begins to produce immunoglobulins, which leads to aseptic inflammation and the formation of edema in the area of the facet joints and nearby soft tissues. The joint capsules stretch, so the intervertebral discs no longer securely fix the vertebrae. And with instability of the intervertebral segments, the likelihood of pinching a nerve root or squeezing a blood vessel increases. This often occurs with cervical osteochondrosis and becomes the cause of its pronounced vertebral symptoms.
Signs of osteochondrosis in women
The structure of the female spine is somewhat different from the male one. In women, the intervertebral plates are more fragile and weaker. They do not have developed muscle mass and therefore succumb to destruction much more quickly. The symptoms of osteochondrosis in the fair half of humanity are more pronounced, the process is very noticeable. As a rule, the disease manifests itself in the early stages.
The disease is characterized by:
- headaches, migraines;
- severe spasms in the neck;
- numbness of limbs (hands), tongue;
- impaired coordination;
- nausea;
- the appearance of snoring;
- toothache;
- decreased hearing, vision;
- heaviness in the head;
- tinnitus;
- head incontinence (you even have to use a frame);
- fainting.
Read: What exercises for cervical osteochondrosis
To avoid many of the listed symptoms, it is important to consult a specialist doctor for help in a timely manner. Doctors often recommend that women do gymnastic exercises to increase the muscles that will support the spine. The main thing is that you need to do this very carefully. At the stage of exacerbation of the disease, it is best to refrain from any stress on the neck.
Causes and provoking factors
The condition of the intervertebral discs is negatively affected by the reduced tone of the skeletal muscles of the spinal column. Irrational, asymmetrical muscle functioning occurs when a person remains in a non-physiological position for a long time, for example, with his head down while working at a computer. The destruction of cartilage tissue can be provoked by constantly carrying a heavy bag on one shoulder, sleeping on a soft mattress and a high pillow.
Headaches and dizziness are symptoms of osteochondrosis.
The following external and internal negative factors also accelerate the destruction of intervertebral discs:
- endocrine and metabolic disorders;
- infectious pathologies, especially chronic ones;
- previous spinal injuries (compression fractures, bruises);
- frequent hypothermia;
- the presence of systemic or degenerative diseases - gout, psoriatic, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis.
If a person has bad habits, then he is at risk. Smoking and alcohol abuse worsen the condition of blood vessels, leading to insufficient blood circulation and nutrient deficiency in the cartilage tissue of the discs.
If you have flat feet or club feet, the risk of developing osteochondrosis of any localization increases significantly. Such congenital or acquired defects cause increased load on the spine due to the inability to provide adequate shock absorption with support. A predisposing factor to the occurrence of pathology is obesity.
Excess weight and obesity provoke the development of osteochondrosis.
When fatty tissue is deposited in various parts of the body, maintaining balance becomes more difficult, which leads to excessive stress on the intervertebral joints.
Osteochondrosis and its types
Osteochondrosis is a deformation of articular cartilage, bone tissue of the spine and intervertebral discs.
Osteochondrosis occurs:
- lumbar (lumbosacral),
- cervical,
- chest
Causes of osteochondrosis:
- upright posture,
- rachiocampsis,
- spinal injuries,
- flat feet,
- frequent lifting of weights,
- frequent changes in body position,
- staying in uncomfortable positions for a long time,
- spinal overload,
- physical inactivity and obesity,
- malnutrition,
- stressful conditions.
Clinical picture
The first clinical manifestation of cervical, thoracic or lumbar osteochondrosis is back pain. During relapses, it is piercing, radiating to nearby parts of the body. The slightest movement leads to increased severity of pain. A person’s response is to adopt a forced position in which the intensity of discomfort is minimal:
- people with cervical osteochondrosis prefer to turn to the side not their head, but their entire body;
- with chest pathology, a person is afraid to even take a full breath, as this causes acute pain in the thoracic region;
- patients with lumbar osteochondrosis have difficulty sitting down, standing up and walking due to pinched spinal nerves.
Most patients complain to a vertebrologist about dull, constant pain and a feeling of stiffness in movements in the morning. This requires additional differential diagnosis to exclude myositis (inflammatory process in the skeletal muscles of the back) and osteoarthritis. The reason for the appearance of aching, pressing pain is compensatory tension of muscle tissue to stabilize the affected spinal motion segment. Constant pain of mild or moderate severity also occurs due to significant stretching of the intervertebral disc and the development of aseptic inflammation.
Osteochondrosis of a certain localization is characterized by specific symptoms. For example, with lumbar pathology, lumboischialgia often occurs - a pain attack in the lumbar region and posterior thigh. Thoracic osteochondrosis is clinically manifested by visceral pain in the cardiac region, right hypochondrium, abdomen, numbness, skin paresthesia, crunching in the vertebrae. But the pathology affecting the cervical intervertebral discs is characterized by the most pronounced and varied symptoms.
As a result of the displacement of the vertebrae and the formation of osteophytes, the vertebral artery, which feeds the brain cells and provides them with oxygen, is compressed. A person suffers from impaired coordination of movements, tinnitus, headaches, and arterial hypertension.
Determining the diagnosis
The diagnosis is established at an appointment with a neurologist based on the patient’s complaints (pain, limited mobility, etc.). The spine is examined by him in the position of the patient standing, sitting and lying (at rest and in motion). When examining the back, attention is paid to posture, structural features of the torso, lower angles of the shoulder blades, lateral contours of the neck and waist, position of the shoulder girdles, etc. After this, the doctor, as a rule, refers the patient to an x-ray, computed tomography or MRI, with the help of which the diagnosis is clarified and specified, the extent of the lesion is determined, and hidden deviations from the norm are identified. Based on the data obtained, the neurologist prescribes appropriate treatment. As a rule, this is complex therapy, including the use of medications, massage, exercise therapy and other methods.
What can happen if left untreated?
Most complications of osteochondrosis occur due to the formation of a herniated disc. It is formed when this vertebral structure is displaced backward, which leads to rupture of the posterior longitudinal ligament. The disc becomes even more unstable and part of it protrudes into the spinal canal. A hernia is considered ruptured if, during its formation, its nucleus pulposus penetrates into the canal along with the disc.
This pathological condition of the vertebral structures predisposes to compression of the spinal cord and the development of discogenic myelopathy. Clinically, it manifests itself in numbness, weakness of some muscle groups of the legs or arms, paresis, muscle atrophy, and changes in tendon reflexes. Disorders in emptying the bladder and/or bowel may also occur. As a result of the formation of an intervertebral hernia, the arteries supplying the spinal cord are compressed. Ischemic areas are formed in which all nerve cells have died. A so-called neurological deficit occurs - movements are impaired, tactility is reduced, and trophism is disrupted.
Prevention of osteochondrosis
Is it possible to protect your body from the development of unpleasant pathologies? Doctors say this is quite possible. For such purposes, they developed special rules to ensure the prevention of osteochondrosis.
Doctors' recommendations are reduced to 3 main tips:
- Sit correctly. When working sedentarily, you should change your position frequently. It is not advisable to stay in one position for more than 25 minutes. If you have to sit all day, then from time to time you should get up and walk around the room.
- Stand correctly. This is true for many people who, due to the nature of their work, are forced to spend a long time on their feet. To protect your spine from the development of osteochondrosis, doctors recommend changing your position every 20 minutes. If this is acceptable, it is better to change the type of activity. For example, after washing the dishes, move on to ironing the clothes.
- Lie down correctly. In this case, you need to choose the right mattress. Doctors do not recommend sleeping on bare hard boards or soft feather beds. The best option is a special orthopedic mattress. It will significantly improve posture and protect against the development of osteochondrosis. Orthopedic mattresses allow you to completely relax and straighten your spine.
It is very important to remember to lift weights correctly. Sharp jerks often lead to exacerbation of pathology. Be sure to pay attention to physical exercise. In this case, you will not be afraid of any osteochondrosis.
Treatment tactics
Osteochondrosis cannot be completely cured, since no drugs have yet been synthesized that could help restore damaged intervertebral discs and vertebrae. But therapeutic regimens must include chondroprotectors—slow-acting symptomatic agents. Preference is given to drugs with the active ingredients chondroitin sulfate and (or) glucosamine sulfate (hydrochloride):
- Artra;
- Structum;
- Don;
- Teraflex;
- Alflutop.
The clinical effectiveness of these chondroprotectors is confirmed by the results of many years of research. With long-term use (from 3 months to 2 years) of the drug, partial regeneration of cartilage tissue occurs, as well as other connective tissue structures - ligaments, tendons, bursae. As glucosamine and chondroitin cumulate (accumulate) in the intervertebral discs, they begin to have a pronounced analgesic, decongestant, and anti-inflammatory effect. This allows you to reduce the doses of NSAIDs, glucocorticosteroids, muscle relaxants, thereby reducing the pharmacological load on the body.
Chondroprotectors are ineffective when taken irregularly or when used for the treatment of grade 3 osteochondrosis, when significant destruction of cartilage tissue is observed.
| Clinical and pharmacological group of drugs used to relieve pain in osteochondrosis | Name and therapeutic effect |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Nimesulide, Voltaren, Diclofenac, Ketorolac, Nurofen, Fastum, Artrosilene, Celecoxib, Ketoprofen. Pain-relieving ointments, tablets, injections, and patches relieve inflammatory processes in soft tissues caused by vertebral displacement, reduce the severity of pain, eliminate swelling and stiffness of movement |
| Glucocorticosteroids (synthetic analogues of hormones produced by the adrenal glands) | Diprospan, Flosteron, Kenalog, Triamcinolone, Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone. Painkillers are used in the form of drug blockades in combination with the anesthetics Lidocaine or Novocaine. Eliminate acute, severe pain, normalize the functioning of the immune system, have an anti-exudative effect |
| Muscle relaxants | Tolperisone, Sirdalud, Mydocalm, Baklosan, Baclofen. They are used when muscle spasms occur due to pinched nerve endings. Relaxes skeletal muscles, blocks polysynaptic spinal reflexes, has an antispasmodic effect |
| Products for external use with a warming effect | Finalgon, Capsicam, Apizartron, Viprosal, Nayatox. The active ingredients are capsicum extract, snake or bee venom. They irritate receptors located in the subcutaneous tissue, promoting a rush of blood. They exhibit pronounced distracting, analgesic, and anti-edematous activity. |
To eliminate vertebrogenic symptoms, which usually occur with cervical or thoracic osteochondrosis, drugs are used to improve blood circulation, nootropics, as well as Betahistine, a drug that improves microcirculation of the labyrinth, used for pathology of the vestibular apparatus.
If necessary, antidepressants (Paroxetine, Sertraline) and anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Gabapentin) are included in treatment regimens.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are used in the treatment of osteochondrosis: UHF therapy, magnetic therapy, laser therapy. Reflexology, massage, exercise therapy, hirudotherapy, swimming, yoga are used. If conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated for the patient. Microdiscectomy, puncture valorization of the disc, laser reconstruction or replacement with an implant are practiced.
Classification of pathology
Depending on in which department the signs of osteochondrosis are diagnosed, the disease can be:
- Cervical. This pathology often develops in people over 40 years of age. However, there are cases of the disease being diagnosed in patients aged 16 years. Among all musculoskeletal diseases, pathology accounts for approximately 9%. Patients experience neck pain and headaches due to osteochondrosis.
- Chest. This type of pathology is more common in women. According to statistics, thoracic osteochondrosis is detected in almost 17% of all patients suffering from musculoskeletal diseases. The disease is characterized by the occurrence of painful discomfort in the area of the heart.
- Lumbar. This is the most common ailment. Its share among musculoskeletal diseases is about 55%. Most often, lumbar osteochondrosis occurs in men. Symptoms of pathology are numerous. A characteristic manifestation of the disease is aching pain in the lower back.
- Sacral. This pathology is not common. Among diseases of the musculoskeletal system, it accounts for up to 7%. In women, this problem is diagnosed 2-3 times more often than in men. The disease develops in people over 60 years of age.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis with medications
Competent medications and a clear schedule for taking them will have a sufficient, proper effect, relieve the inflammatory focus, stop an attack of pain and prevent the occurrence of remission. Drug treatment should be prescribed exclusively by a medical specialist, indicating the individual method of taking the drug and dosage.
Tablets/Capsules
Analgesics can quickly eliminate pain for a fairly long period, but still they provide temporary relief, but without a therapeutic effect. These include: Analgin, Spazmalgon, Dexalgin.
Anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs are often prescribed in combination with analgesics; they enhance the effect of each other, reduce or completely eliminate the source of inflammation, respectively, when combining the two groups, a therapeutic effect will be provided, but still temporary. These include: Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ketoprofen.
Chondroprotectors - play the role of essential vitamins for cartilage and bone tissue; they are also prescribed for complex use with an anesthetic group of drugs; their function is to protect tissues and prevent their further destruction. Preparations: Chondroxide complex, Artiflex, Glucosamine.
Ointments/gels for external use
Local application of gels ensures the absorption of the product into the immediate source of pain, which has an additional, longer-lasting effect, eliminates inflammation and relieves swelling.
Preparations: Dolobene, Traumeel, Fastum gel, Chondroxide ointment, Finalgon, Viprosal, Nimid gel.
Injections
Injections cope with the task of eliminating pain and inflammation faster than other listed methods. Injections can relieve spasm, a feeling of pinching and tension in the lumbar muscles and fibers.
Often, to achieve a quick effect, they use the blockade method, that is, they inject a certain painful area with anesthetic drugs - Lidocaine, less often Novocaine, the effect occurs instantly and lasts up to 9 hours.
Injections to relieve pain, spasm, inflammation: Dicloberl, Ketonal, Milgamma, Spazmalgon, in combination with B vitamins.
Trental, Pentoxifylline - drugs for intravenous, drip administration for circulatory disorders. It is prescribed additionally for more complicated stages of osteochondrosis.
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy shows high effectiveness in treating illness and restoring the body.
This is one of the most common methods of physical therapy. When exercising, the level of physical fitness of the person should be taken into account.
Physical therapy in the initial stages always contains only small and gentle loads. If the pain intensifies, during the transition to more complex exercises, the load is reduced. Exercise therapy requires careful attention to body position during a set of exercises.
To reduce the load on the back, a special cushion is placed under the shins of a lying patient.
For unexpressed pain, training begins with daily light exercises:
- Slow tension and relaxation of the abdominal muscles;
- Flexion and extension of fingers and toes;
- Slow raises of arms extended along the body;
- Flexion and extension of the legs at the knees while resting the foot on a hard surface in a lying position;
- Breathing exercises.
Even such simple gymnastics are performed strictly after consultation and instruction with a specialist. If the attending physician considers it possible to move on to more serious loads, the following exercises can be performed:
- Flexion and extension of the legs at the ankle, from a lying position;
- From a lying position, with a sliding movement, pull the heel to the buttock;
- Slow lifts of the pelvis with legs bent at the knees;
- Bend forward from a standing or lying position; At the same time, you should try to touch your chest to your legs.
Such gymnastics cannot be performed during exacerbations.
You can see what physical therapy looks like in this video:
Exercise therapy helps restore the functions of the spine and strengthen the muscle groups that support it. This reduces the risk of complications and improves mobility.
Medical concept
Osteochondrosis is a common disease in which joints suffer and the cartilage between them is destroyed. In most cases, osteochondrosis affects the spine, where, as a result of tissue deformation of the intervertebral discs, very serious complications arise that lead to pain in various parts of the body.
According to ICD-10, spinal osteochondrosis belongs to the XIII class of diseases “Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue” (codes M00-M99), subclass “Deforming dorsopathies” (codes M40-M43).
Why is thoracic osteochondrosis dangerous?
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine often resembles the symptoms of other diseases, so many people unsuccessfully treat the stomach, stop non-existent attacks of angina, and eliminate symptoms of cholecystitis that do not exist. While treatment therapy is not carried out correctly, the disease progresses and often has severe consequences. Lack of treatment can lead to the following complications:
- protrusion of the thoracic spine;
- spinal cord compression;
- disturbances in the functioning of internal organs;
- gallbladder dyskinesia;
- intercostal neuralgia.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is much less common than its other types, but difficulty in diagnosing it often becomes the cause of the development of complications. Only a comprehensive examination and qualified assistance from a doctor will help identify the disease and prescribe the correct treatment.
Gymnastics for the lumbosacral spine
Therapeutic gymnastics is an essential element in the treatment of spinal diseases. A certain set of exercises is prescribed even in the most severe cases, when a person cannot get out of bed.
But you need to be aware that physical activity for osteochondrosis, especially during exacerbations, is a therapeutic agent. You need to take it very seriously and carefully follow the recommendations of doctors. You can't miss classes. You cannot increase the load on your own. You can’t “strive for records.”
A frivolous approach, careless movements, recklessness always lead only to an extraordinary aggravation and accelerated progression of the disease. Careless movements can result in a disc herniation and even the need for urgent surgery.
The main rule that must be observed during therapeutic exercises is that there should be no pain or even discomfort in the body. Standard sports approach “Overcome yourself! Work through the pain! Without pain there is no victory! in this case, it not only does not work, but becomes deadly.
With osteochondrosis, all movements should be smooth, exactly in the range prescribed by the doctor, and the introduction of each new exercise (even the simplest) must be coordinated with your doctor.
Diagnostics
Complaints for osteochondrosis are based on the duration, level of damage, and the nature of previous treatment. Diagnosis of osteochondrosis will be related to the individual characteristics of the disease. But the main points when identifying are:
- Complaints, anamnesis and clinical picture.
- Palpation and physical examination.
Instrumental
The instrumental methods are based on:
- Bone densitometry is an assessment of bone density.
- Spondylography - assessment of the condition of intervertebral discs.
- X-ray shows destruction of the vertebral bodies, enlargement of joint spaces.
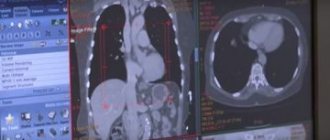
- CT or MRI are the most effective methods today. MRI signs of osteochondrosis make it possible to differentiate it from hernia, tumors, and trauma. MRI shows all components of the joint and inflammatory changes in surrounding tissues.
MRI is one of the methods for diagnosing the disease
Laboratory (Analysis)
There are no specific laboratory research methods for osteochondrosis. All of the above studies are aimed at searching for inflammation and differential diagnosis. Required appointments:
- UAC - shift in formula, increase in leukocytes and ESR;
- OAM - change in density, appearance of leukocytes;
- HD - change in the level of calcium, phosphorus, ASLO;
- blood for sugar.
Therapeutic exercise for osteochondrosis
In addition to taking medications, a special place in the treatment of osteochondrosis is given to physical therapy (physical therapy), which, when carried out regularly, gives excellent results. Physical exercises for osteochondrosis can strengthen the back muscles, reduce the load on the spine, improve blood circulation, increase the flexibility and elasticity of muscles and ligaments. Physical therapy has a positive effect on the entire spine. Let's look at a few simple exercises that can be used for both therapeutic and preventive purposes:
Exercise 1. Place the tips of four fingers on the forehead opposite each other, with light and soft movements press on the skin along the entire length of the forehead for 30 seconds. The same movements can be done on the temple and neck in the transverse direction. This exercise will help improve blood circulation.
Exercise 2. Sit on a chair, straight back, slowly move your head back a little, holding your chin and back of your head with your palms. Try to put a little pressure on your chin, turn your head to the right, then to the left, up, down. Perform the exercise for no more than 1 minute.
Exercise 3. Raise your shoulders up, while trying to reach your ears with them, then slowly lower them to your usual position. You need to do such exercises for 15 seconds, alternating - one shoulder up, the other down. Then rub your neck with your palms.
Exercise 4. Stand straight, feet shoulder-width apart. With slow and smooth movements, tilt your head to the right, then to the left, down and back. Allow 10 seconds for each position. Such head tilts must be performed 15 times in each direction.
There are other therapeutic exercises for the treatment and prevention of osteochondrosis, which should be developed by a doctor for each patient. Particular attention should be paid to physical education for thoracic osteochondrosis, since improperly performed exercises can harm health and further aggravate the course of the disease.
In combination with therapeutic exercises, patients with osteochondrosis are prescribed various procedures that have a positive effect on the spine, improve its flexibility, and relieve pain. Good results can be obtained from the following procedures:
- Physiotherapy: darsonvalization, electrophoresis, massage, thermal treatment, mud therapy. Such procedures can reduce pain, reduce inflammation and swelling in tissues.
- Reflex therapy: acupuncture, cupping massage, mustard plasters, iodine mesh.
- Manual treatment.
Only comprehensive treatment of osteochondrosis will help reduce the symptoms of the disease, relieve pain in the spine, and prevent further destruction of the intervertebral discs.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment are not inferior in effectiveness to medication, if treatment is started in a timely manner and does not start the inflammatory process. They can also be used in conjunction with traditional treatment methods in combination, then the chances of a speedy recovery are multiplied many times over.
Adam's root
Pour 200 grams of finely grated Adam's root into half a liter of vodka in a dark container and let it steep for 5 days. Use externally, to rub the sore spot, then wrap this part with a warm scarf, do not rinse. Analgesic and warming effects will be provided.
Burdock
Soak the burdock leaves over steam for 10 minutes, apply them to the pain location, wrap them up, and leave them for 1-1.5 hours. Birch leaves can also be used using the same method.
Horseradish
Squeeze the juice from grated horseradish and mix 1:1 with vodka or diluted alcohol. Rub the lumbar region up to three times a day, one of which, be sure to wrap yourself in a blanket before going to bed.
Pine bath
A pleasant and effective way to relieve pain and tension is to place 3-4 pine needle branches in warm water and add a few drops of the same essential oil.
The duration of the bath is no more than 15 minutes, after which dress warmly. The procedure is best performed at night; this method will help you further relax and improve the quality of your sleep.
Decoction
Place lingonberry leaves, cinquefoil, thyme, 10 grams of hop cones in 0.5 liters of water, bring to a boil, cover with a lid, leave for an hour. Strain, drink 50 milliliters three times a day after meals. The course is from one month to six months.
Ointment No.1
Mix mint herb, violets, pine buds, burdock root, plantain leaf, chamomile equally, grind the mixture to a powder. Three tablespoons, without a hill, of the crushed collection, pour 100 milliliters of boiling water and boil over low heat for five minutes, stirring continuously, mix while hot with warm, melted pork fat in a volume of 75 grams, cool and store in the refrigerator, no more than two weeks after preparation.
Use twice a day, applying a thin layer to the affected area until relief occurs.
Ointment No2
Combine 200 grams of melted lard with 75 grams of beeswax, 30 grams of marshmallow root powder, and one ampoule of lidocaine, mix until smooth, store in the refrigerator for no longer than 1.5 months. Use for intense pain in combination with injections or tablets; for mild pain, only ointment will be sufficient.
Physiotherapy and massage
The main goal of physiotherapy in treatment is the rapid relief of inflammatory changes. The main treatment options currently used:
- Electrotherapy is exposure to alternating current.
- Magnetotherapy is exposure to strong magnetic fields.
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy is the action of high frequency ultrasound.
- Reflexology – action on reflexogenic zones.
Manual therapy and massage restore muscle tone. This is important in case of chronic damage, since the formation of contractures significantly reduces any motor activity.
Both methods are based on mechanical impact on the area of suspected damage.