Abdominal organs The pancreas is an important part of the digestive system of the human body. It helps break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats, thanks to the production of insulin and glycogen, and is also directly involved in regulating the digestion and breakdown of food. If the pancreas malfunctions, the entire gastrointestinal tract suffers. The body warns that the gland cannot cope with the load. Pain in the pancreas can indicate a number of pathologies. The causes of pain should be identified in time and treatment of pancreatic diseases should be started in order to prevent serious consequences.
Symptoms and signs of pancreatic inflammation
The gland is located behind the stomach and close to the gallbladder, so if it hurts, the disease spreads to the pancreas. At the beginning of the development of inflammation, the signs and symptoms of pancreatitis are standard:
- girdling nature of pain;
- burning pain in the lower thighs from the back;
- decreased appetite;
- increased gag reflex;
- when bending forward, the pain decreases;
- Sometimes an increase in temperature is characteristic.
Patients often confuse pancreatitis with osteochondrosis, pyelonephritis, and even herpes zoster. But an experienced doctor quickly identifies inflammation of the pancreas, since the onset of the disease always occurs with acute pain. It is easy to determine that it is not the spine that is hurting with the help of palpation: with osteochondrosis or pyelonephritis, tapping in the painful area is noticeable, but with pancreatitis, it is not.
Acute form
The acute form of pancreatitis can be treated in a hospital, and doctors must “calm down” the pancreas quickly, otherwise the disease threatens to develop into necrosis (tissue death) and death for the patient. Therefore, at the first pain in the epigastric region or inflammation of the hypochondrium, you should immediately consult a doctor. Acute gland disease leads to mortality in 15% of cases due to untimely contact with a specialist. The main signs of acute inflammation of the pancreas:
- tachycardia;
- vomit;
- sharp pain around the navel;
- temperature increase;
- diarrhea.
Chronic
If acute pancreatitis occurs against the background of activation of pancreatic enzymes, then its chronic form is formed by various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis or hepatitis. Signs of a chronic disease:
- aversion to fatty foods;
- pain in the hypochondrium during physical activity;
- bowel dysfunction;
- sudden loss of body weight;
- loss of appetite.
Depending on the symptoms, doctors distinguish several forms of chronic pancreatic disease: asymptomatic, painful, recurrent and pseudotumor. In the first form, the patient is unaware of the disease, in the painful form, he feels periodic pain under the ribs, and in relapses, pain appears, but disappears after a course of treatment. The pseudotumor form of inflammation of the pancreas occurs when its head enlarges, overgrown with fibrous tissue.
Symptoms of pain in the pancreas and how to get rid of them
When pain occurs in the pancreas, you need to know what to do to relieve the syndrome and try to find out the cause. Since pain symptoms can be caused by other diseases, you need to carefully study the symptoms of the disease, and in the best case, consult a doctor.
The pancreas has certain symptoms of pain, which makes it possible to confidently determine the disease - pancreatitis.
The symptoms of acute and chronic inflammation of the pancreas are significantly different, and the clinical picture of the course also has its own characteristics. The symptoms of chronic pancreatitis are not clearly expressed, but as for the acute type of inflammatory process of the gland, the attack is pronounced and carries possible severe complications of a person’s health.
In the acute phase, only calling an ambulance and hospitalization with a strict diet will prevent the development of pathologies of other organs and the appearance of necrosis of pancreatic tissue. Often, during remission of the disease, after treatment with hunger, the pancreas is restored and treated using folk methods and means.
propolis to eliminate nausea
To eliminate nausea, pain and other symptoms of pancreatitis, it is recommended to use propolis. The pure product (propolis) is chewed when signs of exacerbation occur. The product relieves the inflammatory process and heals open internal wounds well, restoring the functioning of the gland.
raisins for compote will help with indigestion
And also with pancreatitis, the main symptom and manifestation is diarrhea and intestinal upset. These symptoms are well removed by fresh raisin compote. Take 4-5 sips until diarrhea completely stops.
A decoction of burdock root will help restore pancreatic function.
Decoctions of medicinal herbs are widely used. Brewed burdock roots bring good benefits. To prepare, take 2 tablespoons of roots and pour 300 ml of boiling water. Take 50 ml 3-4 times a day in between meals. Within a month, the symptoms go away and the functioning of the pancreas is restored.
oatmeal jelly for pancreatic self-healing
Eat oatmeal jelly. This remedy, in addition to quenching thirst for hunger, brings benefits with its properties. Envelops the walls of the stomach, pancreas, and intestines, which provides a kind of respite and the possibility of self-healing.
How does the pancreas hurt during acute pancreatitis?
Pain in the pancreas is a sign of developing pancreatitis. The disease itself has two forms of development, acute and chronic. In acute inflammation, it passes abruptly and provokes the very digestion of the pancreatic organ. In this situation, timely access to a hospital will bring the possibility of quick treatment. In a different scenario, there are consequences and death. What symptoms of pain in the pancreas indicate developing acute pancreatitis of the pancreas:
- gagging, severe vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- severe cutting pain moves from the stomach to the back.
hospital treatment for acute pancreatitis
Treatment in a hospital, where the patient will be under round-the-clock supervision, and constant diagnostics will ensure timely stopping of the development of the disease. This pathology leads to a latent form of diabetes mellitus, so it is necessary to carry out a full diagnosis and treatment in hospital.
How does chronic pancreatitis hurt?
Pain in the pancreas with chronic pancreatitis, also with its own characteristics. How to relieve pain in the pancreas, what are the symptoms of this pathology?
Chronic disease is a gradually progressive process. The variability of the pain state, from a severe attack to a smooth progression and mitigation of symptoms, does not create a very pleasant clinical picture. In this type of disease, the pancreas develops both in the tail of the pancreas and in the head of the gland.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis:
- inflammation of the head of the gland - pain in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region;
- if the source of inflammation is in the tail, the left hypochondrium hurts;
- if the entire pancreatic organ is affected, then the pain is encircling, radiating to the back and the left scapular part of the body;
- There is also a shooting pain in the groin, in the tailbone, and radiates to the thigh.
To fully diagnose the disease, tests are necessary. Since, the inconstancy of pain and jumps in pain symptoms roll from a strong cutting syndrome to a constantly aching one, which corresponds to an acute attack of pancreatitis.
Localization of the inflammatory process
If the pancreas is inflamed, then the pain can be different: aching, cutting, stabbing, with a specific localization, for example, under the right rib, or without localization at all throughout the abdominal cavity, in the back or groin. The type of this pain directly depends on which part of the gland is inflamed: the body, head or tail. When the localization of pain is blurred, doctors often talk about a complete disease of the organ.
Aching pain in the middle part of the abdominal cavity indicates that the body of the pancreas is inflamed; if the pain is felt in the right side, the head of the gland is inflamed, and if in the left, the tail is inflamed. The presence of the last two cases is much worse, because a space-occupying formation (tumor) forms in these parts.
- An attack of pancreatitis - symptoms, first aid at home, treatment methods and diet
- Treatment with drugs of the pancreas for symptoms of diseases
- How to treat pancreatitis of the pancreas at home
Pancreatic diseases
In the head of the pancreas
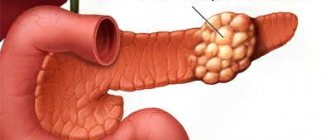
A general change in the size of the pancreas is much safer than enlarging any part of it. The head of the gland has a special shape and unique structure: in an adult it is located at the level of the first two vertebrae, and in a newborn baby it is slightly higher. In adulthood, the normal size of the head of the pancreas should reach up to 35 mm, and if it is smaller or larger in size, then this is considered a pathology.
A mass formation in the head of the pancreas is usually detected during an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and is considered a dangerous disease. It can be benign or substandard, which requires immediate removal. This disease often occurs in people over 60 years of age. Even visually, an experienced doctor can detect the first signs of inflammation of the head of the gland: a change in skin color and yellow coloration of the whites of the eyes. Treatment of this form of the disease occurs in a hospital setting.
In the tail
The tail of the pancreas has an upwardly curved pear-shaped shape and comes close to the spleen. In an adult healthy person, the optimal width of the tail of the organ is 20-30 mm, and its length is about 15 cm. A severe pathology of the tail of the gland is its expansion or thickening, against the background of which obstruction of the splenic vein or subrenal form develops.
A tumor in the tail of the gland occurs rarely: about a quarter of all gastrointestinal diseases. But if it is diagnosed, then often the tumor is immediately malignant and almost impossible to treat, since it is discovered late, when it has already reached a significant size. When operating on a tumor in the tail of the pancreas, doctors often have to remove nearby organs.
What is the pancreas - functions, structure
The pancreas in humans is the largest exocrine and intrasecretory digestive organ. The intrasecretory function of the organ is the implementation of digestive enzymes - pancreatic juice. By producing biologically active organic compounds, the pancreas provides the body with the regulation of fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism. Another important functional purpose of this organ is the active production of insulin, which helps reduce the level of glucose concentration in the blood. Hormonal disruption due to inflammation of the pancreas can lead to impaired insulin secretion, which will lead to the development of diabetes mellitus.
The structure of the pancreas
The anatomical structure is an elongated lobular formation of a grayish-pinkish color, located in the abdominal cavity of the upper section on the posterior wall of the abdomen behind the stomach with the organ in close contact with the duodenum. In an adult, the length of the pancreas reaches 14-25 cm, with a mass of about 70-80 g. The macroscopic structure is the head, body and tail. The head of the pancreas is adjacent to the duodenum through the minor duodenal papilla.
It is through the head of the digestive system that the portal vein passes, collecting blood into the liver from all unpaired organs of the abdominal cavity - the stomach, spleen and intestines.
The body of the pancreas has a triangular configuration - anterior, posterior and inferior. The tail of the pancreas is cone-shaped or pear-shaped and extends to the spleen. The gland is supplied with blood through the pancreaticoduodenal arteries, which branch from the superior mesenteric and hepatic arteries.
It is typical that in newborns the pancreas measures from 3 to 5 cm in length, with an organ weight of 2.5-3 g. The formation of a gland characteristic of adults occurs by the age of 5-7 years.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, the causes of pancreatic disease are associated with alcoholic beverages. Moreover, it does not matter what was drunk the day before: expensive vodka or homemade wine. People are used to thinking that alcohol puts the main burden on the liver, which leads to cirrhosis, but up to a certain point it copes with alcohol with the help of its enzymes. The pancreas does not have such proteins at all, so alcohols directly hit the organ, which is unable to defend itself.
The following factors are also considered to be the causes of organ inflammation:
- Diseases of the biliary tract . When bile is thrown into the pancreas, special substances accumulate, which activate the gland’s own enzymes, creating tissue swelling, damage to blood vessels and various hemorrhages. If you do not take into account alcoholic pancreatitis, then this form of inflammation accounts for 70% of all pancreatic diseases.
- Formation of rock or sand . In the pancreatic duct, under the influence of improper nutrition, stones often form, which, when released, block the duct, causing inflammatory processes in the “pancreas”.
- Diseases of the duodenum or stomach . A stomach ulcer, gastritis or any other inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract contributes to the release of unprocessed intestinal contents into the pancreatic ducts, which leads to an exacerbation of pancreatitis.
- Hypertension, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, pregnancy . In these cases, normal blood circulation is disrupted, limiting the nutrition of the pancreas, developing inflammation.
- Chemical or food poisoning . In case of poisoning with alkalis, acids, toxins, intoxication or helminthic infestation, pancreatic enzymes are activated, which often leads to pancreatitis.
- Uncontrolled use of medications . Some medications activate gland enzymes, so they must be taken strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
- Binge eating . If fat metabolism in the body is disrupted with a tendency to overeat, then the risk of pancreatitis increases significantly. Especially if a person abuses fried, fatty and spicy foods.
- Wounds or injuries to the abdomen . With wounds, blunt trauma or unsuccessful surgical interventions on the gastrointestinal tract, the risk of developing acute inflammation of the organ increases.
- Infections . Chronic hepatitis, chicken pox, liver failure, tonsillitis, mumps, purulent processes in the abdominal cavity, intestinal sepsis or dysentery increase the risk of pancreatitis.
- Genetics . Genetic disorders often cause inflammation of the pancreas in a child immediately after birth.
Signs of organ imbalance
Pathological changes occurring in the pancreas affect all human organs. This is explained by their close relationship in the coordinated work of the human body. Dysfunction of one part immediately affects the functioning of another.
The triggered mechanism of disturbances leads to an imbalance throughout the human body.
The signs of pancreatic disease in women are the same as in men. Based on the nature of their manifestation, they are divided into several groups:
- pain symptoms;
- symptoms of indigestion;
- skin manifestations;
- specific symptoms.
Symptoms of pancreatic pain are associated with dysfunction of the organ. These manifestations are decisive and most common in the diagnosis of organ disease. Pain syndrome is provoked by inflammatory reactions occurring in the gland.
How to determine that the pancreas hurts? Of course, only a doctor can decide this, although there are symptoms by which the disease can be detected independently. When the pancreas hurts, the patient experiences dyspeptic disturbances in the functioning of the body. Pathology manifests itself with appetite disturbances in both adults and children. After eating, there is a feeling of heaviness, even if a small amount of food was consumed. Subsequently, men and women with organ dysfunction develop a feeling of nausea and gag reflexes. Often vomiting does not bring adequate relief. The bile released along with vomit turns it yellow and gives a bitter taste.
Important information: Symptoms and treatment of pancreatic tumor
Prolonged vomiting can lead to dehydration, which makes you feel thirsty. The resulting symptoms of digestive imbalance are aggravated by stool disturbances (diarrhea alternates with constipation) and flatulence.
In the chronic form of imbalance, skin ailments appear. This happens due to a violation of the secretion of pancreatic juice into the duodenum. As a result, the acidic environment in the intestines is not neutralized, and enzyme functioning is disrupted. Against the background of these processes, bacteria begin to actively multiply and destroy the intestinal protective barrier. Patients present with symptoms of food or bacterial allergies in the form of skin rashes or atopic dermatitis.
If, as a result of inflammatory or other processes, the volume of the pancreas increases and it begins to compress the bile ducts, then the patient’s skin may acquire a yellowish tint. So-called obstructive jaundice occurs.
Also, an enlarged organ can put pressure on the intestines, thereby disrupting blood flow in the abdominal area.
Sometimes the pancreas hurts with the manifestation of specific symptoms, which only a doctor can determine. These include:
- pain on palpation of the left costal angle (Mayo-Robson symptom);
- pain when pressing on the area below the navel 2 cm (Dudkevich's symptom);
- push-like pressure on the epigastric region of the abdomen causes severe pain (Chukhrienko's symptom);
- The Blumberg-Shchetkin symptom manifests itself as sharp pain upon palpation of various areas of the abdominal cavity.
Laboratory tests of blood and urine can reveal the presence of serious pathologies in the gland. If inflammation or destruction of the pancreas is suspected, clinical and biochemical blood tests are performed. The density of urine, the presence of proteins and leukocytes, ketone bodies and sugar are also assessed.
Methods for relieving inflammation and treating pancreatitis
For any pain in the gastrointestinal tract, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Treatment of pancreatitis usually occurs in a hospital setting. During the acute period, doctors anesthetize the pancreas, suppressing its secretory functions. They also relieve spasm of the excretory flows with medications and prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics to prevent inflammatory changes or secondary complications. If complications in the pancreas are serious, surgical intervention is used.
Exacerbation of a chronic disease is treated on an outpatient basis. The patient is prescribed a thermally gentle diet with steamed dishes. Proper nutrition is combined with taking medications that block active gland enzymes. In case of severe exacerbation of inflammation of the “pancreas”, painkillers, antispasmodics, enzyme medications and vitamins are also prescribed.
- Medicines for pancreatitis - features of their use
- Reactive pancreatitis - symptoms and treatment
- Treatment of the liver and pancreas with drugs and folk remedies
How to treat with herbs and folk remedies
An ancient and effective method of treatment is herbal therapy. In addition to a proper diet for pancreatitis and avoidance of fried, fatty and spicy foods, in order to relieve acute inflammation in the pancreas, you need to drink choleretic herbs. To do this, take 10 g of dry herbs:
- celandine;
- corn silk;
- anise fruit;
- dandelion root;
- tricolor violet;
- bird knotweed.
Grind everything, mix, pour ½ liter of boiling water and boil for 3 minutes. After cooling, the decoction should be drunk during exacerbation of the disease three times every day before meals for two weeks in a row. Then you need to prepare a drink from the following herbs:
- dill, peppermint 30 g each;
- immortelle flowers, hawthorn fruits 20 g each;
- chamomile flowers 10 g.
Pour ½ liter of boiling water over the crushed herbs and leave for 20 minutes, then strain and take three times daily after meals for a month. It is also useful to drink sauerkraut juice without carrots and spices. The juice will quickly relieve acute pain, because it contains lactic acid, which is especially useful for exacerbation of pancreatitis.
Medications
Medicines primarily eliminate the primary cause of the inflammatory process in the pancreas, as well as:
- restore digestive function;
- relieve pain;
- compensate for endocrine insufficiency.
To achieve these results, doctors prescribe medications such as analgesics, antispasmodics aimed at relieving pain in the gland, enzymes designed to restore normal pancreatic function, as well as antacids - drugs that suppress the secretion of hydrochloric acid by the stomach. For acute inflammation of the glands, no-shpu, papaverine or atropine are used in medium doses.
What tests are needed
If inflammation of the pancreas is suspected, the patient is sent for a comprehensive examination. He is prescribed:
- abdominal ultrasound;
- overview image of an x-ray examination;
- computer, magnetic resonance imaging;
- laparotomy.
If the doctor has diagnosed pancreatitis, then you need to constantly monitor the condition of the pancreas, so you will regularly need to undergo the following laboratory tests (tests):
- general clinical blood;
- biochemical blood;
- urine, feces;
- saliva.
Treatment and first aid for pain in the pancreas and prevention of the disease
Treatment of the liver and pancreas with folk remedies is strictly prescribed by a gastroenterologist. There is no need to engage in amateur activities or drink packs of painkillers. If the pain is unbearable, you should immediately call an ambulance.
In case of acute inflammation, it is necessary to abstain from food for a while
The following will help to numb the pain for a while:
- Antispasmodics can temporarily relieve pain, but they cannot be delayed; medical supervision is necessary;
- In the hospital they can give you intramuscular pain relief;
- A cold compress will also help reduce pain;
- Drink plenty of fluids, at least two liters per day;
- Refusal to eat, switch to warm broth;
- Hospitalization.
Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor. The first step is usually to relieve pain to reduce the production of stomach acid. To reduce the destruction of the gland enzyme, prescribe: Pantoprazole or Omeprazole . To facilitate the work of the glands, they may prescribe: Pancreatin , Festal . During hospitalization, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. Medicines are prescribed to neutralize hydrochloric acid in the stomach. A special diet is introduced. In acute cases of the disease, surgery may be performed.
Let's give up bad habits
Disease prevention:
- Monitor nutrition and diet;
- Getting rid of bad habits;
- Do not indulge in medications unnecessarily;
- Treat gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases in a timely manner;
- Eat 5 times a day, drink 2 liters of water;
- Drink folk medicine daily: parsley, lemon with peel, grind garlic and drink 1 tablespoon.
A person destroys his own health with his own hands. With a healthy lifestyle, pancreatic pain and symptoms can be avoided. Health to you!
How to relieve an attack of pain in a child
Doctors strongly do not recommend relieving an attack of acute pancreatitis in a child at home. With any symptoms of the disease, the baby should be taken to the hospital. But in life there are different situations, for example, medical care is not available. In such situations, you should try to relieve acute pain in the pancreas yourself, and then be sure to send the child to the nearest medical facility. To do this you will need:
- Strict fasting.
- Complete rest of the body.
- Give your child ¼ glass of water every 30 minutes.
- You should not give medications such as Creon or Panzinorm, as well as any others containing enzymes, so as not to aggravate the situation.
- It is better, if possible, to inject papaverine (2 ml) or replace it with no-shpa.
- Place an ice pack on the pancreas area from the back.
- Place the child in a sitting position, bending the body forward.
Pain and causes of inflammation
So why does the pancreas hurt, and what are the causes of this pathology? Pain in the pancreas occurs to a greater extent with alcohol abuse or inflammatory processes in the gallbladder (urolithiasis).
causes of pancreatic inflammation
This risk of pathology accounts for 80% of all visits to medical institutions, according to statistics from the Ministry of Health. True, with the main reasons, there are others that also provoke inflammatory processes in the gland, and there are plenty of them. They will appear in conjunction with pancreatitis, which aggravates the already difficult situation of the patient. So why does the pancreas hurt and factors that provoke an increase in the inflammatory process:
- ulcers;
- duodenitis;
- injuries to the abdominal area and internal organs;
- drug poisoning;
- misuse of drug treatment and abuse of non-prescription pills;
- viral infections, hepatitis of all types and forms;
- helminthic infestations;
- metabolic disease;
- weak immune system;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- heredity to the disease;
- constant stress;
- abuse of alcohol and smoking.
healthy pancreas and pancreatitis
Therefore, before treating pancreatitis, after carrying out diagnostic measures, the primary source of provocation of the pancreas is eliminated first, and only then the symptoms of the disease are relieved. Mostly, attacks of pancreatitis occur at home in the evening, so you need to know how to calm the pancreas while at home. To do this, check out some tips:
- If an attack occurs at home, the victim needs to take a curled up position (embryo) and slightly tilt his torso forward. In this position, the pain will become much quieter for a short period of time, which will make it possible to wait for the ambulance to arrive.
- When the pancreas aches and hurts, you should not apply warm compresses to the painful area. Only cold lotions (including frozen foods) to the site of focal pain and complete rest of the patient are allowed. Cold objects that will be used to relieve the source of pain must be wrapped in a thin cloth to avoid frostbite of the skin area.
- At the time of an attack of pancreatitis and in the next 3 days, food should be completely excluded from the patient’s diet; what is possible is only drinking liquid (still mineral water, decoctions of medicinal herbs, weak tea drink). Drinking liquid will not provoke inflammatory processes and will remove the bulk of toxins and harmful substances from the body.
- After 2-3 days of therapeutic fasting, during the period of complete relief of pain symptoms, it is allowed to eat simple and light food: oatmeal, jelly, boiled or baked vegetables, lean fish and meat.
Cooking should only be done by boiling or baking; food should only be consumed in ground pulp form. Completely avoid salty, sour, bitter, fried and smoked foods. Anything that will provoke a repeated attack and irritation of the pancreas.
medications for an attack of pancreatitis
Medication methods are used to relieve pain. In case of an acute attack of pancreatitis, the following medications are allowed:
- Baralgin;
- Paracetamol;
- antispasmodic No-shpa;
- Papaverine;
- Mezim, Creon, Festal will help relieve acidity.
It will also help relieve the symptoms of pancreatitis at home using traditional methods of treatment. It is advisable to coordinate all these methods with your doctor in order to avoid individual intolerance to the body and the occurrence of side effects:
- Drink fresh potato juice 30 minutes before meals.
- Taking a decoction of oatmeal.
- Eating peppermint;
- Decoction of rosehip, chamomile, hawthorn.
All these methods require coordination, since some types of products provoke a repeated attack of pancreatitis.
folk remedies for the treatment of pancreas
It is also necessary to understand that the disease does not like amateurs and improper treatment. Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) is an insidious disease that will bring sad results from neglect of health and provoke other side diseases.
Nutrition and diet
Regardless of the form of the disease, to treat inflammation of the pancreas it is necessary to follow a strict diet. If the disease worsens, you should not eat any food in the first two days. Only rosehip decoction, still mineral water or weak and unsweetened tea are allowed. It is imperative to exclude from the diet during exacerbation of the disease:
- alcohol;
- spices, seasonings;
- fatty, fried;
- sausages, smoked meats;
- pickles, canned food;
- confectionery, chocolate, sour juices.
What products can
If inflammation of the pancreas is chronic, then doctors allow the following products:
- Dairy products: non-acidic cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir.
- Low-fat fish: pike, bream, pike perch.
- Meat products in the form of puree, cutlets, soufflé from rabbit, veal, beef, turkey or chicken.
- Boiled grated vegetables.
- Rusks or dry wheat bread.
- Steamed egg omelet.
- Cereal, chicken, noodle or vegetable soups.
- Oils: refined sunflower, olive, butter.
- Pasta, grated cereals.
- Sweet jellies, jelly, compotes.
- Baked pears, apples.
- Wheat bran decoction, weak tea, rosehip decoction, still mineral water.
What is the pancreas and why is it needed?
A person should not forget that he has a pancreas. Pain that requires immediate treatment should never be ignored. The situation is significantly complicated by the fact that this organ has a good margin of safety and does not make itself felt for a long time until serious problems arise. However, the pancreas performs 2 important functions in the body:
- Production of pancreatic juice, which enters the duodenum. It contains many essential enzymes that help digest food.
- Production of insulin and glucagon. These hormones take part in the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Therapeutic tactics for diseases of the pancreas
Tablets for pancreatitis
The form of the disease and the individuality of its course determine its severity, the localization of inflammatory foci, the patient’s general history, and other important factors. Treatment of pancreatic diseases is carried out comprehensively and is aimed at eliminating the causes in the first place. Symptoms of the disease can be provoked by other serious diseases in the patient’s body, so even a doctor is not able to immediately identify pancreatic disease from, for example, pyelonephritis, without tests and other diagnostic methods. The main algorithm of the therapeutic approach is to treat the very causes of the disease, treat the pathological condition with medications, prescribe vitamins, herbal preparations (for example, liver preparation) and homeopathic remedies, adherence to a special therapeutic diet and physical activity regimen.
Other methods of treating the disease include anti-enzyme therapy, which is aimed at restoring the functions of the pancreas after destruction. To begin with, the patient must comply with bed rest, a starvation diet with parenteral nutrition in acute or advanced form, and a different diet due to the severity of the disease. Such restrictions are imposed for approximately a period of 3 weeks. Symptoms of an acute illness should go away by this time. After this period, doctors again examine the patient and continue to develop treatment tactics. Choleretic, sedative, and mucosal cavity-enveloping medications are used as medications.
Locations of pain and accompanying symptoms of diseases
When a person stands upright, the pancreas is located at the level of the 1st lumbar vertebra. The pancreas itself consists of three sections: “body”, “head” and “tail”. The “body” is located behind the stomach, the “head” is near the duodenum, and the “tail” is near the spleen. Pain may be felt in the hypochondrium area or localized to the right under the scapula; it may be felt in the upper abdomen, intensify and spread throughout the abdomen. This location of pain indicates inflammation of the pancreatic tissue or pancreatitis.
Other symptoms of pancreatitis include:
- prolonged constipation;
- bloating and heaviness of the abdomen;
- bad breath;
- as the disease develops, it may begin to hurt in the right side (in the place where the pancreas is located). The pain becomes so severe that the person is unable to move or even turn, and the side reacts even to touch;
- then the temperature rises significantly;
- apathy and weakness begin;
- nausea and vomiting appear, some suffer from diarrhea;
- pulse quickens;
- the sclera of the eyes turns yellow.
With acute or chronic pancreatitis, the symptoms are different.
In the chronic course of the disease, the following symptoms may appear:
- when the head of the gland is inflamed, pain is felt in the epigastric region and right hypochondrium;
- when the source of inflammation is located in the “tail”, pain is felt in the left hypochondrium;
- when the entire pancreatic organ is affected, the pain is girdling in nature, radiating to the back and left shoulder blade;
- There may be shooting pain in the tailbone, groin, which radiates to the thigh.
Reactive pancreatitis
Examination by a doctor - to diagnose pancreatitis
Due to the fact that reactive pancreatitis is a special type of disease, it is formed as a result of the pancreas reacting to inflammatory processes in other organs of the human body.
It mostly affects children due to their special sensitivity. The culprit of this form of the disease is the consumption of fatty heavy foods.
The development of pathology is accompanied by the manifestation of certain unpleasant symptoms. These include:
- sudden severe pain in the abdominal area near the navel;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile limits, sometimes reaching the thermometer mark of 38 C;
- intestinal disorder;
- vomit;
- feeling of dryness in the throat
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- belching;
- flatulence;
- bad feeling.
In no case should you ignore the presence of disturbing symptoms in a child or attribute everything to the child’s increased capriciousness. Inflammation can take a chronic course and cause a number of serious complications, as well as adverse health consequences, including diabetes mellitus, pancreatic necrosis, and internal bleeding.
Acute pancreatitis
This disease causes sudden, intense pain in the epigastric region, which often radiates to the back. Most often, acute pancreatitis is caused by cholelithiasis or alcoholic beverages. Symptoms may worsen after eating. If the disease is caused by stones in the bile ducts, it develops very quickly. When the disease occurs after alcohol, its symptoms progress a little more slowly, over a period of several days.
Nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, fever, jaundice, and changes in blood pressure can be combined with epigastric pain in acute pancreatitis. Often the pain is very severe, making it difficult to cough and breathe deeply. In addition to cholelithiasis and alcohol consumption, acute pancreatitis can be caused by an infectious process (salmonellosis, legionellosis, hepatitis B), autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome), and injuries. In 15% of cases, the exact cause cannot be determined.
Types of disease
Childhood pancreatitis is a dangerous disease
The course of childhood pancreatitis can be acute or chronic. During an acute inflammatory process, swelling of the pancreas occurs. A severe form of the disease is accompanied by hemorrhage with the possible formation of local tissue necrosis of any part of the organ.
Pancreatitis is divided into types based on the type of pathological disorders:
- acute edematous;
- hemorrhagic;
- purulent;
- fatty pancreatic necrosis.
The chronic course of the disease is indicated by the duration of the inflammatory process for more than 5 months. The progressive nature of pancreatitis entails vascular sclerosis, the formation of fibrosis with further atrophy of pancreatic tissue, as well as negative changes in its activity.
The acute form of the disease in childhood is extremely rare. Among schoolchildren, the most common chronic type of disease is in a latent or recurrent form.
Latent pancreatitis is not characterized by obvious clinical severity, despite the fact that when it is repeated, there are periods of exacerbation and subsidence of the inflammatory process.
According to the nature of its origin, the disease is divided into types:
- primary;
- reactive (secondary);
- genetic (autosomal dominant type of inheritance).
In the case of accurate implementation of correctly selected therapeutic therapy for the underlying disease that caused the development of pancreatitis, it is possible to stop the disease, otherwise there is a danger of its developing into the true form.
Treatment of inflammation
First aid for exacerbation of inflammation of the gland involves taking measures to alleviate the patient’s condition.
To reduce the load on the organ, it is forbidden to eat. Regardless of the form in which the disease occurs, you should not eat anything for 1–2 days. It is allowed to drink only rosehip decoction or still mineral water in a volume of 1-1.5 liters.
Before the doctor arrives, you should not take enzyme preparations - Festal, Creon, as this can only worsen the patient’s condition. A person needs complete rest and bed rest. To relieve pain, a cold compress can be applied to the area of the affected organ. Also, to reduce pain, you should tilt your body forward.
You should not take painkillers on your own because it can be dangerous. But for chronic inflammation of the pancreas, treatment is allowed with Papaverine, No-Shpa.
Symptoms
Symptoms of inflammation of the pancreas in men and women are the same and resemble intoxication of the body: the stomach hurts, the person feels sick and vomits. But at the same time, other signs of pancreatitis also appear, which depend on the form in which the disease occurs.
With acute inflammation, colic and repeated vomiting appear. After some time, a girdle pain occurs in the upper abdomen, radiating to the shoulder blades. Subsequently, it becomes aching, and its intensity gradually decreases.
The following symptoms are observed:
- bloating and constipation;
- enlarged belly;
- pale facial skin;
- cardiopalmus;
- foul-smelling, foamy stools containing undigested food particles;
- increased body temperature, trembling;
- lack of appetite.
If such signs appear, you should urgently call a doctor. An acute attack can provoke bleeding in the gland.
If pancreatitis is not treated, then the acute form becomes chronic after some time. A person constantly experiences poor health, which may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- yellowness of the skin;
- pain in the upper abdomen after eating fatty foods or overeating;
- weight loss;
- diarrhea.
A long-term disease destroys the gland and changes the structure of its tissues. This leads to the development of diabetes mellitus, secretory deficiency and malabsorption syndrome.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic program can be based on the following examination methods:
- general laboratory analysis of blood, urine, feces;
- blood chemistry;
- tumor marker test;
- pH-metry;
- ELISA;
- PCR test;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- endoscopic examinations of the gastrointestinal tract;
- CT, MRI;
- X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
The diagnostic program will be compiled on an individual basis. The data that was collected during the initial examination and the current clinical picture are also taken into account. Based on the results of the examination, it will be determined why the pancreas hurts and treatment will be prescribed.
Drugs for treatment
The acute form of pancreatitis is treated in a hospital, the chronic form - at home. Thanks to complex treatment, medications normalize the function of the gland. The choice of drugs depends on the form of the disease and on concomitant diseases:
- Antiseptic intestinal agents. They have an anti-inflammatory and astringent effect. These include De-Nol.
- Antispasmodics and analgesics. Thanks to painkillers (Papaverine, No-Shpa), spasm of smooth muscles and pain are relieved. Analgesics Aspirin and Paracetamol relieve severe pain.
- H2 blockers. In order to suppress pancreatic secretion, Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine are used. In some cases, hormones are taken that reduce the production of acid in the stomach - Glucagon, Somatostatin.
- Enzyme preparations. They are used to normalize digestion and improve the absorption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. These include Festal, Pancreatin, Creon.
- Antacids. Thanks to these medications, the production of hydrochloric acid is neutralized and reduced. The doctor prescribes Controloc, Gastrozol, Phosphalugel.
- Antibiotics. Such broad-spectrum drugs eliminate inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, prevent the spread of infection in other organs, and reduce the development of complications. These include Gentamicin, Ampicillin.
- Drugs that reduce toxicity. This is saline solution, Hemodez, Ringer's solution.
Etiology
It should be noted that if the pancreas hurts, this does not mean that the pathological process is developing directly in this organ. A symptom of this nature may indicate a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, liver or kidneys. Therefore, self-medication in this case means increasing the risk of complications.
If the pancreas hurts, then the reasons directly related to this organ are as follows:
- pancreatitis, that is, inflammation of the organ;
- cyst formation;
- pancreas cancer;
- organ injury.
You should also highlight the following reasons that the pancreas hurts:
- cholecystitis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- cholelithiasis;
- bile duct dyskinesia;
- pyelonephritis;
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- enteritis;
- osteochondrosis;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- shingles.
Intercostal neuralgia
In more rare cases, the pancreas hurts due to factors such as:
- binge eating;
- alcohol abuse;
- incorrectly composed diet;
- complications after surgery;
- medication abuse;
- excessive physical activity.
Thus, the range of factors that provoke this symptom is quite extensive, so it is strongly not recommended to independently compare symptoms and treatment. This can lead to extremely negative consequences.
Why does it occur in children?
Gross violation of diet is the cause of pancreatitis
The formation of pancreatitis in childhood is caused by the negative impact of enzymes secreted by the pancreas, which, when activated, carry out the process of self-digestion.
In this case, damage to tissues, vessels, and ducts of the organ occurs with the development of inflammation, and the release of enzymes with harmful substances into the circulatory system leads to general intoxication of the body, damaging other important organs.
The sources of the disease are:
- improper outflow of pancreatic secretion;
- blunt abdominal trauma;
- helminthiasis;
- weakness of the muscle tissue connection;
- endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, obesity);
- complications after acute infectious diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- malignant tumor of the pancreas.
In addition, increased activation of organ enzymes often occurs due to the characteristics of the child’s nutritional diet. These include:
- overeating, especially abuse of fatty foods;
- non-compliance with food intake;
- use of various types of fast foods, carbonated drinks, crackers, chips, spicy dishes in the menu.
Also, the culprits in the development of inflammation of the pancreas in children are a powerful toxic effect, allergic manifestations to certain foods and medications.