Psoriasis (translated from Greek “psora” - “skin disease, scabs”) is a chronic pathology of a non-infectious nature, also known as scaly lichen, which mainly affects the skin areas on the knee and elbow joints, lower back and head. Psoriasis of the joints, bones, nails, external genital and internal organs is also found, but these forms are diagnosed quite rarely. The pathology is difficult to cure, so when the first symptoms or red rashes appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How does psoriasis manifest at the initial stage?
The disease progresses in waves. One stage replaces another. Psoriasis has three stages:
- progressive or initial;
- stationary;
- regressing.
The symptoms of each period differ depending on the type of psoriasis.
Early symptoms in adults
A lot of factors can give impetus to the development of skin pathology. It could be genetics, infection, cuts, problems with internal organs. But sometimes it’s enough just to get nervous, and the skin will immediately “respond” to the stress with a psoriatic rash.
Psoriatic papules
At the beginning, a small nodule (papule) appears. It has a reddish color and clear boundaries. Soon similar rashes appear. Papules merge with neighboring plaques and grow more and more. They are very itchy, inflamed and painful.
In order not to confuse papular rashes with ordinary skin irritation, you need to know the signs of the psoriatic triad:
- at the beginning there is a stearin stain. This effect has a characteristic feature: if you scrape a papule or accidentally damage it, the peeling will increase. Even if there were no visible epithelial scales on the plaque before, as soon as you start scratching them, they will appear. The plates are separated painlessly. They are dry, silvery in color and resemble ground paraffin drops. The cause of this symptom: disruption of intercellular contacts;
- thermal film. When all the scales are removed from the plaque, a shiny reddish surface is exposed. Cause: acanthosis;
- blood dew. If you scrape the papule further, small droplets of blood will begin to appear on its surface, not merging with each other. Cause: damage to the capillaries of the dermis.
Early symptoms vary depending on the type of psoriasis:
- pustular . It is characterized by rashes in the form of bubbles filled with clear liquid. The body temperature, although not significantly, rises, and the person experiences weakness. If you scratch the blisters, there is a high probability of infection getting into them, which can lead to suppuration and inflammation;
- vulgar . It is recognized by reddish thickened formations (papules) with a scaly whitish coating. If the affected area is small (3% of the skin), the rash may go away on its own;
- teardrop- shaped In this case, the plaques look like droplets, they are so small. The color of the papules is intensely red. At the initial stage, their number is small, but if treatment is delayed, the rash will cover the entire body;
- psoriatic arthritis . Its peculiarity is that against the background of dermatosis there is damage to the joints. They become inflamed, painful and difficult to bend;
- nail psoriasis . The initial stage is characterized by changes in the nail plate. Grooves and small pits appear on it. Gradually the nail thickens.
Knowing the symptoms, you can most likely diagnose psoriasis yourself.
Early manifestations of the disease in children
The primary symptoms of psoriasis in children may appear on the face or under the hair.
But more often the disease begins with redness between the skin folds. This is observed in children wearing diapers. Therefore, psoriasis at this stage can be confused with allergies or diaper dermatitis. The difference lies in the clear boundary between the affected area and healthy skin.
Causes
The etiology (cause) of psoriasis is unknown!!!
First, I will talk about the pathogenesis (mechanism of development) of the disease, and then I will talk about the possible causes.
Pathogenesis of psoriasis:
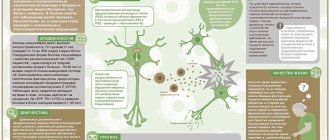
- Cells of the surface layer of the skin (epidermis) - keratinocytes - begin to multiply intensively. Their number increases several times. Their life cycle is shortened, meaning they become covered with scales much earlier than normal skin cells. Externally, this process is manifested by thickening and redness of the skin, the surface of which is also covered with whitish scales.
- Immune cells - lymphocytes: T-killers and T-helpers penetrate into the thickness of the changed skin cells (read more about the cells and organs of the immune system). These cells secrete special substances that attract other cells of the immune system - macrophages and neutrophils. An inflammatory reaction develops in the skin without the involvement of infection. This reaction is called autoimmune, that is, the immune system is directed against its own body, and not against bacteria or viruses.
And now about the reasons.
Scientists are still arguing about what the triggering mechanism is – a sharp growth of keratinocytes, in response to which a mass of immune cells comes into the skin? Or is the autoimmune reaction in the skin primary, and keratinocytes subsequently begin to grow excessively and develop rapidly?
In any case, no one has yet gotten to the main reason - WHAT IS THE IMPACT for the launch of one or another mechanism at the beginning of the development of psoriasis?
And again an interesting fact. It is known that in HIV patients the immune system is suppressed, primarily T-lymphocytes. It seems that psoriasis should not develop in them. However, there is an increase in the incidence of psoriasis in HIV patients. And the course of the disease in patients with AIDS is more severe.
Provoking (trigger) factors of the disease
- Heredity: if one parent is sick, the risk of psoriasis in children is 7%, if both parents are sick, the risk is 40%.
- Skin injuries: - mechanical - scratches, cuts, abrasions, - chemical - solvents, varnishes, paints, detergents, household chemicals, perfumes, - thermal - hypothermia, burns.
- Endocrine diseases - diabetes, hypothyroidism, hormonal changes in the body.
- Stress.
- Infectious skin diseases - staphylococcal, streptococcal, fungal infections.
- Alcohol abuse, smoking.
- HIV infection.
What does psoriasis look like at the initial stage?
In addition to the psoriatic triad, there are several other symptoms that confirm psoriasis:
- Koebner phenomenon . Characteristic for the initial stage. If you damage (scratch or cut) healthy skin, then after 2 weeks new papules will form in this place;
- Pilnov's rim . In this case, psoriatic plaques have a red border that exactly follows the contours of the lesion. This symptom indicates the progression of the pathology;
- papules are formed symmetrically . They are raised above the healthy surface.
Typical locations: bends of the arms and legs, nail phalanges, outer side of the knees, elbows, scalp, abdomen. Tight clothing can also cause a rash. In places where it constantly rubs the skin (straps, trouser waistbands, tight underwear), psoriasis will develop first.
The initial stage lasts several weeks. But its duration can be reduced by using competent treatment tactics.
The rash that appears on the skin will be very itchy. If you have taken into account all the symptoms and suspect that you have psoriasis, do not delay your visit to the dermatologist.
It is difficult to make a diagnosis on your own, since this type of pathology is multifaceted in its manifestations and has several varieties. And each case has its own special treatment.
You can live with him
If you think that this disease affects very few people, you are deeply mistaken. According to statistics, psoriasis affects every 20th inhabitant of planet Earth. Such legendary figures as Benjamin Franklin, Winston Churchill, John Rockefeller, Henry Ford, Joseph Stalin, Vladimir Nabokov suffered from this disease.
How do you find yourself surrounded by Cameron Diaz, Tina Karol, Britney Spears, Kim Kardashian? But they are also victims of psoriasis. By the way, the famous American model Caridi English even released a series of photographs of herself, in which she showed close-up her ideal body, affected by this disease. In her opinion, “psoriasis is not a disease, but a lifestyle.”
This lifestyle is quite easy to maintain, especially if you take into account some very useful tips from those people who have accepted the disease and learned to live with it.
Is hair falling out on the back of the head a sign of illness or not?
Indeed, the scalp (hairy area) often suffers with psoriasis.
To stop the spread of the lesion, it is important to know its symptoms:
- At first, slight peeling of the skin on the affected areas is observed. Most often on the back of the head;
- Peeling gradually spreads to other areas of the scalp. There is minor itching and irritation;
- then the itching becomes more and more intense. The patient begins to comb the sore spots. As a result, bleeding wounds and cracks appear on the skin;
- at the next stage the situation worsens: the plaques increase in size, the skin becomes rougher.
Next, the active exfoliation process begins on the papules. Gray scales appear. If left untreated, the lesion will extend beyond the hair area: to the neck, back of the ears, forehead.
Psoriasis is rarely the main cause of hair loss, since it affects only the upper layers of the dermis. The hair follicles are usually not affected because they are located deeper. And only an advanced form of the disease can damage the base of the hair.
It is important to recognize the disease at an early stage. This is difficult to do on your own, since people mistake a psoriasis rash for simple irritation, and scales for dandruff.
Therefore, if you suspect scalp psoriasis, you should immediately consult a dermatologist. You should not practice self-medication, since this dermatosis is similar in symptoms to seborrheic dermatitis, and only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Localization of psoriasis
Hands
In most cases, the rash appears on the surface of the elbows or between the fingers. Less commonly, papules are noted on the forearm.
Attention! The hands are characterized by a plaque form of pathology, but others also occur. Its sign is small red spots that quickly become covered with white scales; the affected skin becomes rougher.
Legs
Psoriatic formations mainly occur on the legs in the knee area, but it is possible that they can also form on other parts of the legs.
The first rash is single and small with a clear outline, but loose, inflamed and very flaky. Such pinpoint papules spread quickly, forming conglomerates.
Head
Often develops against the background of seborrhea, affecting the hairline, forming the so-called psoriatic crown. Skin formations gradually grow and spread over the entire surface, resembling dandruff. This localization occurs quite often; less often, the rash appears on or behind the ears.
Nails
The nail plate can be affected by the following types:
- Thimble is a point form of psoriasis. Small pits appear on the nails, which resemble marks from needle pricks.
- Onychomycosis - the nail changes color, becomes dull, noticeably thickens and begins to peel off. A psoriatic papule, similar to an oil stain, is visible through the plate, surrounded by a reddish rim.
Body
Usually manifested by characteristic papules that merge with each other. Psoriasis is more common on the back, less often on the neck, abdomen, hips; formations can be drop-shaped, dotted and plaque-shaped.
Face
It is rarely affected, the rashes are located in the nasolabial folds, in the temples and eyebrows, around the eyes. Rarely, the pathology affects the border of the lips; the rash resembles herpes.
Palms and feet
Both zones are affected simultaneously, but there have been cases where pathology developed only on the feet or palms. On the soles, the disease is often combined with fungal pathology, which greatly complicates diagnosis and therapy.
This type of psoriasis is divided into 3 types:
- Papular-plaque – formations are dense, do not protrude above the skin, scales are difficult to separate from the plaque. The rash occurs in the marginal areas, accompanied by swelling and keratosis.
- Psoriatic callus is a round, dense papule consisting of keratinized epidermis. The layer of skin gradually thickens and becomes rougher. As a result, it is easily injured and cracks occur. There is practically no redness, the size of the growths is from 2-3 millimeters to 2-3 centimeters.
- Vesicular-pustular - manifests itself in the form of serous-purulent papules. The bubbles reach 2 millimeters in diameter and are prone to coalescence.
Joints
Pathology can affect human joints, which leads to changes in the structure of their tissues, which, as it progresses, leads to pain and deformation. External symptoms: a reddish rash appears on the skin. Internal signs - joints hurt, especially during sleep, there is stiffness of movement, swelling.
Important! First, psoriasis affects the small joints of the feet and hands, then spreads to the knees and elbows, and at an advanced stage, the intervertebral joints are already affected.
Does the body itch at the beginning of the disease?
Itching can be called the first sign of illness. It is always observed at the beginning of the pathology.
This happens because psoriasis causes a malfunction of the immune system. And abnormally rapid cellular growth begins, forming plaques on the surface of the skin. At an early stage of pathology, the body reacts to these changes in the form of itching, which can be unbearable or mild and not particularly irritating.
You can relieve itching with special ointments, and sometimes it is enough to change your diet.
Classification of the disease
How psoriasis begins, how it manifests itself, what its effect on the body is - all these points are determined by the specific type of pathology. Today there are several classifications of the disease. One of the most common divides psoriasis into two types:
- non-pustular;
- pustular.
The non-pustular (or simple) form is a chronic pathology characterized by a stable course. This group also includes erythrodermic psoriasis, the main symptom of which is damage to most of the skin.
The pustular variety includes:
- annular pustulosis;
- Barber's psoriasis;
- von Zimbusch psoriasis;
- psoriasis of the palms and soles.
A separate category are:
- drug-induced form;
- seborrheic;
- Napkin psoriasis;
- “inverse psoriasis” (develops on the flexor surfaces).
Depending on the localization of the pathological process and the characteristics of the manifestation of the first symptoms of psoriasis, the following are distinguished:
- psoriasis of the scalp;
- facial skin psoriasis;
- elbows;
- hands;
- legs;
- joints;
- nails (onychodystrophy);
- plantar;
- plaque-shaped;
- teardrop-shaped;
- pustular;
- spotted;
- seborrheic;
- psoriatic arthritis;
- psoriatic erythroderma.
What diagnostic methods help to recognize the disease?
To diagnose psoriasis, an experienced doctor only needs to examine the patient’s skin. Typical symptoms of the disease allow you to quickly determine the type of pathology and prescribe appropriate therapy.
However, there are also complex cases that require additional information. A mandatory study in this case will be a biopsy of a sample of the affected skin . It will allow you to accurately determine the pathology.
A potassium oxide test is also performed (if a fungus is suspected). When dermatosis affects the joints and causes arthritis, you should consult a specialized specialist.
He will prescribe x-rays and necessary tests. UV radiation will also help clarify the diagnosis. When the papules are cleared with an excimer laser, the glow of the flaky areas will be visible.
Since psoriasis has similar symptoms to other dermatoses, differential diagnosis is necessary.
Differential diagnosis will allow you to exclude such pathologies as:
- ringworm;
- Reiter's disease;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- neurodermatitis, etc.
The listed studies will allow the dermatologist to prescribe the most effective therapy to the patient.
Course of the disease
Like any psoriatic process, the disease is chronic and flows in waves, alternating stages of progress and regression of the rash. Neglect of the case and the lack of special treatment not only creates problems with the patient’s appearance, but also leads to various complications, including psoriatic arthritis.
Interesting to know! With timely rational therapy, compliance with medical recommendations and avoidance of all kinds of triggers (stress, for example), the prognosis for the disease is quite favorable.
The disease not only worsens the condition of the skin, but also affects the psychological status of a person, contributing to the development of anxiety and depression. Stress and anxiety, in turn, lead to the progression of psoriasis.
How to treat the initial form of the disease?
At the initial stage, psoriasis should be treated comprehensively. Today there are enough highly effective drugs that, although they will not give a complete recovery, will eliminate the flaky formations that so spoil the patient’s life.
Modern treatment tactics have undergone changes in favor of non-hormonal drugs (gels, solutions, emulsions) and aromatic retinols.
Shampoo Friederm
Popular ointments for psoriasis:
- tar-based : Antipsorin and Colloidin, Friederm (shampoo);
- based on solid oil : Kartalin and Cytopsor;
- from petroleum : Naftaderm;
- emollients : Belosalik and Salicylic ointment.
A variety of physiotherapy procedures are practiced (paraffin or radon baths, PUVA therapy). For severe itching, antihistamines should be taken.
Psoriasis and its treatment in adults and children
Having found out what psoriasis is and seen a photo of the disease, you should pay special attention to the treatment of the pathology. Uncomplicated forms of the disease can be treated at home. Therapy consists of using topical products in the form of gels, ointments, creams, shampoos, and soaps. In addition, it is necessary to follow a diet, give up bad habits, and eliminate other factors that provoke the disease.
In complicated forms, therapy is more serious; drug treatment is used in the form of ointments, tablets, and physiotherapeutic treatment methods are also used.
Treatment with ointments
Products in the form of ointments can be hormonal and non-hormonal. Non-hormonal drugs are used for mild forms of pathology. These include:
- salicylic;
- sulfuric;
- grease-based ointments;
- naphthalene;
- tar;
- Vishnevsky ointment.
These medications rarely cause side effects and are well tolerated by patients.
Among hormonal drugs for external treatment of wounds, corticosteroids (hormonal drugs) are used. The most popular are:
- cortisone;
- hydrocortisone;
- prednisolone ointment.
The disadvantage of such drugs is the high risk of side effects. With prolonged use, dry skin, stretch marks, and redness may occur. The negative side of treatment with hormonal drugs is the addictive effect. Despite all this, in many cases it is impossible to do without steroid drugs, especially in such severe forms as pustular psoriasis and erythroderma.
Use of tablets
Therapy of the disease will be successful only if the treatment has a competent, comprehensive approach using all necessary medications. In addition to ointments, the following groups of drugs are used to get rid of rashes:
- Antiallergic drugs - help eliminate itching, redness, swelling (Diazolin, Zyrtec, Loratadine).
- Hepatoprotectors – support the normal functioning of the liver (Allohol, Karsil).
- Enzyme preparations – promote the production of necessary enzymes (Mezim, Pancreatin).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - eliminate the inflammatory process (Meloxicam, Ketoprofen).
- Calming - normalize the psychosomatic state of the patient (Persen, Tonorma, Sedavit).
Drugs that normalize the functioning of the immune system play an important role in the treatment of the disease. Immunomodulators for psoriasis are Methotrexate, Remicade, Timodepressi and others.
All products are used under the supervision of a physician with strict adherence to dosage and dosage schedule.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is an important treatment method for the development of pathology. The following methods are used to get rid of stains:
- Ultrasound irradiation.
- Selective herbal medicine.
- PUVA therapy.
- Cryotherapy.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Laser treatment.
- Baths with added salt.
In addition, such unconventional methods as hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches), ichthyotherapy (using fish) and many others are often used.
Diet for psoriasis
Nutrition during illness should consist of maximum limitation of allergens, spicy, sour, salty foods. The patient should avoid smoked meats, marinades, and citrus fruits. You need to exclude chocolate, honey, eggs, nuts, and red fruits.
Preference should be given to cereals, vegetable soups, low-fat dairy products, fish and lean meats. Avoid drinking alcohol and large amounts of caffeine.
Maintaining proper nutrition, following all doctor’s instructions and paying close attention to your health will help you get rid of the disease and prevent its recurrence for many years.
Unconventional methods of treatment
Here are some folk remedies that are effective at the initial stage of pathology:
- linseed oil . Apply topically to affected areas;
- grease . They lubricate the affected areas once a day before bedtime;
- celandine juice . It is effective for mild forms of psoriasis.
Traditional medicine knows many completely safe recipes for skin regeneration, but when using them, you should also remember some difficulties:
- It takes a lot of time to prepare the product (several days). It is very important to strictly follow the proportions. The slightest carelessness will ruin all efforts;
- controversial effectiveness. Since folk remedies have not undergone clinical trials, you should not expect a complete cure from them;
- intolerance to components. When the homemade medicine is ready, test it: treat a small area with it. If itching or redness appears, then the product is not suitable for you.
Symptoms
Stearic stain
The first sign of psoriasis, part of the triad of pathological symptoms. It is characterized by increased peeling after scraping the affected surface with a spatula. Over time, silvery-white scales separate from the papules. Their removal is not difficult, as they become loose and weakly adhere to the psoriatic papule. The surface of the new formations (rashes) turns white, and the particles crumble and resemble shavings.
The first phenomenon of the triad is explained by the development of parakeratosis (improper functioning of the epithelium, which leads to disruption of the formation of the stratum corneum). To combat deviations at the initial stage, local non-hormonal agents (creams, ointments) are used.
Terminal film
It is characterized by the removal from the papules of a thin layer of tissue that has a shiny structure and looks like polyethylene. It comes off easily under any influence (pressure, friction, etc.) after removing dried scales.
The terminal film is the last layer that is removed from the skin. Further scraping leads to the last stage of the triad - drip bleeding.
At this stage, medicinal herbal baths, drugs with an antiallergic effect, and natural-based ointments (without corticosteroids and hormones) are used.
Pinpoint bleeding
After removing the terminal film on the affected area of the skin, drip bleeding occurs (Auspitz's symptom or “bloody dew”) and accelerated growth of neoplasms is noted, which sometimes reach the size of a pea and are called lenticular. In some cases, the papules increase to the diameter of a small coin and are differentiated as nummular. As the disease progresses, their growth increases and when they join, psoriatic plaques form.
Retinoids, immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physiotherapy are used for treatment.
Others
The disease can be recognized by other characteristic signs, the main ones of which are 4:
- Pilnova is a red rim, not covered with scales, that forms around the papules.
- Caberna - small rashes are visible on a clean area of the skin (usually appears before the progressive stage of psoriasis).
- Kartamysheva is a symptom that helps to distinguish psoriasis from seborrheic dermatitis and is characteristic of the active stage of the pathology. It is accompanied by the appearance of papules with clear boundaries on the scalp; this does not happen with seborrheic dermatitis.
- Voronova - a light shiny rim of skin appears around the formation. The symptom is characteristic of the stage of regression of the disease and appears when the papules disappear.
Factors that provoke the development of psoriasis
Both patients and attending physicians know that there are certain triggers that cause the disease itself or provoke an exacerbation. Such reasons include:
- Stress, nervous tension, psychological trauma;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Taking certain medications: antibiotics, B vitamins, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Mechanical skin injuries: cuts, burns, deep scratches;
- Infectious diseases: tonsillitis, otitis, sinusitis, as well as infections caused by streptococcus - scarlet fever, erysipelas, etc.;
- Alcohol consumption, non-compliance with the regime, poor diet, smoking;
- Sudden climate change, prolonged exposure to the sun.
Nutrition and diet
When using complex therapy to treat psoriasis, you must follow a strict diet. Restriction in the consumption of a certain group of products should be aimed at harmonizing the following processes:
- normalization of metabolism;
- reduction in exacerbation of psoriasis;
- reduction of inflamed areas and rashes;
- normalization of the gastrointestinal tract system.
Currently, there is a specialized diet developed by physician-scientist John Pegano. The main principle of its action is to reduce the level of acidity in the bloodstream and block the production of autoimmune antibodies, as well as to establish the proper functioning of the intestines. The doctor believes that the diet should consist mainly of the following products:
- alkaline-forming foods (vegetables, fruits, berries, grains), except prunes, plums, currants and cranberries.
- the remaining part should be occupied by acid-forming foods (meat, fish, legumes, cottage cheese and fermented milk products, eggs).
However, it should be understood that there are allergenic products that can provoke allergies as a secondary reaction of the body and provoke the progression of psoriasis. Allergy sufferers should carefully select their diet.
For psoriasis, diet should be based on the consumption of the following foods:
| Recommended | Excluded |
| leafy vegetables; | baked goods and bread products; |
| fruits and natural juices; | artificial additives, dyes, preservatives; |
| bird, rabbit; | smoked sausages, canned food, red meat; |
| low-fat milk-containing products; | sugar, honey, carbonated sweet drinks; |
| vegetable oil; | alcoholic products; |
| pumpkin seeds, flax seeds, sunflower seeds, almonds; Brown rice; | fatty and fried foods; |
| wholemeal bread; | rice, nightshades, citrus fruits. |
It is necessary to refuse to visit catering establishments and fast foods. In addition to junk food, such places may offer food containing preservatives and unnatural ingredients. With proper adherence to the diet, the patient’s skin begins to clear, the general condition improves, and the frequency of relapses is reduced to a minimum.
How not to make a mistake with the symptoms?
Timely detection of signs of the disease will help to begin treatment in a timely manner and prevent damage to large areas of the skin, as well as prevent the spread of symptoms to internal organs.
You can determine that the signs described above indicate psoriasis by the following steps:
The scales will easily peel off when the plaque is scraped off;
- When the scales are scraped off, thin, smooth, pink skin remains;
- At the site of scraping, droplets of blood begin to appear.
The first signs of psoriasis most often affect those places that are most susceptible to friction:
- Palms, elbows, feet;
- Inguinal cavities;
- Knees;
- Lower back;
- The scalp under the hair.
At the first symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Pseudopsoriasis
Pseudopsoriasis is another dermatosis that visually resembles the traditional disease. It is also accompanied by auxiliary symptoms (itching, flaking, general deterioration in a person’s well-being, dry skin).
The pathology, like psoriasis, remains poorly studied. The two diseases can be distinguished by the absence of the traditional triad of symptoms for pseudopsoriasis. It is characterized by the “wafer phenomenon.”
When carefully removing the scales from the surface of the papule, they separate completely in a single layer. The treatment for a specific illness also differs. It is based on the use of the following groups of medications:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Antimalarial drugs.
- Desensitizing agents.
- Vasoprotectors.
The question of a complete cure for pseudopsoriasis remains open. He is put into remission and preventive medications are used to consolidate the result. In any case, therapy should be carried out by a specialist.
Psoriatic triad
Despite the fact that psoriasis has many types, characterized by different symptoms, in medical practice there is still a certain concept that is suitable for all forms of the disease. This is the so-called psoriasis triad.
The psoriatic triad includes the following manifestations:
Appearance of stearin stain
The onset of the disease is characterized by the appearance of spots densely covered with scales. When you try to remove them, the husk easily peels off. Externally, the picture resembles stearin. It is also worth noting an increase in the intensity of peeling.
Terminal film
When all the scales on the patient's body are removed, a red, smooth surface is exposed. The film is very thin and easily damaged. In medical practice, this phenomenon is called terminal film.
Bloody dew
The third stage, the name of which speaks for itself. Drops of blood are observed on human skin after accidental or artificial removal of the film. Bloody dew can be observed throughout the plaque, being more intense at its edges.
The manifestations of psoriasis are quite extensive. Symptoms depend on the type of disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. Timely consultation with a doctor and early diagnosis will help get rid of unwanted manifestations of the disease and possible complications.
Features of the course of psoriatic arthritis
The first signs of psoriasis in women and men with this type of pathology can be in the form of pain in the affected joints, general weakness, a feeling of malaise and depression.
Psoriatic arthritis is rare and most often results from complications of other forms of pathology.
This type of disease mainly affects the phalanges of the fingers, less often larger joints and the spine.
Patients note severe pain, as well as changes in the shape of joints and ligaments, which is also noticeable externally. The phalanges of the fingers become less mobile, swollen and curved.
Manifestations of psoriasis of the palms and feet
Another type of pathology is palmoplantar psoriasis. The signs of psoriasis in women and men with this form of the disease are absolutely identical. The main symptom is severe coarsening and layering of dermal cells on the palms and soles. Sometimes the pathology resembles many calluses with small cracks.
The course of the disease is aggravated by mobility of the arms and legs. This provokes injury and bleeding in the affected areas.
Palmoplantar psoriasis in most cases occurs simultaneously on the feet and palms, but often occurs separately.
Related articles:
Psoriasis in children: types, treatment and folk remedies Diagnosis of psoriasis Stages of psoriasis and their treatment Diagnosis of psoriasis in children How to quickly relieve an exacerbation of psoriasis
Treatment of psoriasis of the scalp
- An important part of the treatment of psoriasis on the head is taking vitamins A and B, preparations with calcium and nicotinic acid, and the use of ascorbic and folic acid.
- The most effective is the use of corticosteroid drugs.
- A good effect can be achieved using salicylic ointment.
- As an aid, it is recommended to moisten the scalp with decoctions of herbs with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect: celandine, chamomile or sage.
- Separately, it should be said about the Soderm solution, which many experts consider the most reliable way to get rid of psoriasis on the head. It is applied to the affected areas in the mornings and evenings. If there is a noticeable improvement, you can limit yourself to using the drug once, then use it every other day, etc.
Unconventional methods for treating psoriasis on the scalp
Traditional medicine also offers many ways to get rid of this type of psoriasis.
- A compress based on celandine juice relieves pain and inflammation.
- Alcoholic extract of string - should be taken orally three times a day, about 20 drops.
- A mask based on sea salt and clay (applied to the affected scalp).
The best remedies for Psoriasis
Add to cart
Antipsoriasis cream 990 rub.
Add to cart
Magnipsor ointment RUB 1,490
Add to cart
Ultraviolet lamp Dermalight ® RUB 14,900.
Psoriasis in intimate places
When studying the localization of psoriasis, patients susceptible to this type of disease are interested in whether there can be psoriasis in intimate places. In fact, the localization of lesions in intimate areas is a fairly common occurrence. It usually manifests itself in men; women can suffer from psoriasis during periods of hormonal changes in the body. Symptoms of this type have characteristic features:
- the initial symptom of the disease is characterized by the appearance of small rashes in the groin, on the pubis; in women, psoriasis is localized on the labia; in men, psoriasis occurs on the head of the foreskin and the shaft of the penis;
- reddish papules have a round/oval shape;
- On dry areas, grayish scales form on top of the papules; on moist skin, there are practically no scales on the papules.
In men, psoriasis on the penis appears as clearly defined, reddish, raised papules covered with a small number of scales. On the penis, psoriatic plaques can also hide in the fold of the foreskin. Diagnosing the disease can be difficult, because inflammation in intimate places can be visually similar to the manifestations of sexually transmitted infections. Often, a dermatovenerologist prescribes a biopsy or histological examination of the contents of the papule. The development of pathology depends on the stage of psoriasis. Initial manifestations can be removed with the help of ointments and creams; more advanced manifestations must be treated with hormonal and antifungal drugs to prevent secondary infections.
Dependence of symptoms on the stage of the disease
The manifestations of psoriasis vary depending on the specific season and stage. Many patients experience a “winter” version of the disease, in which periods of exacerbation occur in late autumn or winter. In the warm season, due to the intensity of ultraviolet radiation, improvement occurs. The “summer” type is quite rare. During the pathology there are three stages:
- Progressive, in which new elements constantly appear, the active growth of existing plaques, the presence of a pink zone around them, severe peeling, and itching are recorded.
- Stationary – the growth of papules stops, new rashes do not form, small folds are noticeable on the top layer of skin, around the plaques.
- Regressive - there is no peeling, plaques begin to disappear, and as the disease subsides, areas with increased pigmentation remain in their place.