Pancreatic insufficiency symptoms, which almost no one pays attention to, are a very serious disease. If it is present, all necessary and beneficial substances are not absorbed properly in the body.
Everything is due to the fact that the gland stops producing the required amount of enzymes and hormones.
The essence of the problem
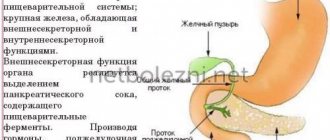
The pancreas performs 2 main functions:
- Exocrine.
- Endocrine.
The first is the production by the gland of substances involved in the process of digesting food (pancreatic juice and more than 20 types of enzymes). This part of the pancreas consists of acini (gland cells) that synthesize enzymes (trypsin, lipase, chymotrypsin, amylase, etc.) that break down proteins, fats and carbohydrates that enter the body with food in the duodenum.
Lipase ensures the breakdown of fats into fatty acids in the bile environment of the intestine.
The endocrine part of the gland is the islets of Langerhans, which are located between the acini and consist of insulinocytes that produce insulin, glucagon, somostatin and various polypeptides involved in glucose metabolism and regulating blood sugar levels. Islets consist of A, B and D cells. Glucagon is produced in type A cells (25% of all cells); B cells (60% of all cells) produce insulin, and type D cells (15%) synthesize other polypeptides.
Pancreatic failure is caused by the destruction of normal tissues and cells in the organ and their gradual replacement with connective tissue (fibrosis), which subsequently leads to a decrease in the functional activity of the gland in the production of necessary enzymes and hormones. Thus, pathology can lead to malfunctions in all body systems.
Reasons for the development of disorders
The organ produces special enzymes in the body, without which the process of digesting food is impossible. Sometimes the normal functioning of the pancreas is disrupted and the amount of components produced decreases; such a pathological failure is called pancreatic insufficiency. The main reasons for the development of the condition in the organ may be the following:
- damage to the tissues that make up the organ;
- the occurrence of vitamin deficiency in the body;
- drop in protein concentration in the blood;
- reduced hemoglobin content in red blood cells;
- incorrect diet, leading to disruptions in the body.
In addition to the listed reasons for the formation of disorders, there are a large number of factors that can influence the formation of malfunctions in the gland. In some cases, a person’s heredity plays a huge role in the development of malfunctions in the glands. In such cases, even with a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition, pancreatic disorders occur. Malfunctions of the gland can cause various forms of diseases.
Exocrine insufficiency, like other disorders in the body, has a number of specific symptoms and manifestations that make it possible to clearly establish the presence of this type of disorder in the body. The main symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency are as follows:
- intolerance to fatty and spicy foods;
- the appearance of heaviness in the stomach after eating fatty and spicy foods that are not fully absorbed by the body;
- the presence of fatty, mushy stools;
- the occurrence of bloating;
- the appearance of colic in the abdomen;
- the occurrence of pain in the bones.
In addition to the listed symptoms, malfunctions of the gland are characterized by the occurrence of rapid heart rate, muscle cramps, shortness of breath, abnormalities in the system that ensures the functioning of blood clotting, dry skin and some others. The occurrence of these symptoms is due to a lack of fats and fatty acids in the body. Due to a violation of their digestibility, problems appear that cause enormous discomfort, greater than the disease itself.
Medical specialists have identified several reasons leading to the development of pathological disorders in the gland. Depending on the influence of certain causes on the body, a certain disorder develops. The main reasons for the development of violations are the following:
- reduction in the mass of exocrine glandular tissue;
- the outflow of secretions into the cavity of the duodenum;
- insufficient participation of enzymes in the process of food processing;
- use of certain medications in the treatment process.
The main way to normalize the functioning of the pancreas is to maintain proper nutrition. The basic principles of proper nutrition, which contributes to the normalization of organ function, are:
- the use of fractional food consumption, in which the number of meals is increased while simultaneously reducing the amount of food consumed at one time;
- limiting the amount of fatty foods you consume;
- limiting food consumption late, before bedtime and in the middle of the night;
- refusal to drink drinks containing alcohol.
The foods that are allowed to be eaten are regulated by the attending medical specialist, who monitors the patient’s diet. If the consumption of fatty foods of animal origin is limited, it is replaced with plant foods containing vegetable fats. A large number of vegetables and fruits are introduced into the diet.
For those suffering from exocrine disorder, carbohydrate-containing foods come to the fore in nutrition, which must be consumed in sufficient quantities in order to provide assistance to the body in the fight against the disorder. The main thing that is required is to get carbohydrates from healthy foods, and not from sweets.
In addition to dietary nutrition, a patient with this type of disorder is required to use medications during treatment, the action of which is aimed at restoring the functions of the organ. Such medications include Creon, Pancreatin, Mezim and some others. Most often, such drugs are taken simultaneously with food. If this phenomenon occurs, then you should eat bran.
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is one of the types of organ dysfunction, which is manifested by a lack of production of juices by the glandular tissue of the organ for digestion.
The main symptoms of the development of this disorder are:
- poor digestion of food;
- increased level of gas formation in the stomach;
- disruption of the process of feces formation;
- feeling of nausea;
- the appearance of a feeling of heaviness.
The reasons for the violation may be the following:
- disruption may be caused by irreversible changes;
- stomach problems;
- dysfunction of the duodenum;
- problems with the gallbladder;
- eating disorders;
- alcohol abuse;
- food starvation.
Treatment of this type of pathological disorder begins with determining the causes of its development. If the cause of the disorder is diet or alcohol abuse, then it is necessary to begin adjusting the patient’s diet and eliminating alcohol consumption.
Disturbances in the pancreas in children are especially dangerous, since malfunctions in such an important organ lead to serious pathological disorders in a child’s developing body. Failures in the pancreas lead to metabolic disorders; such changes can lead to disruptions in the development of the child.
pancreatit.pro
Pancreatic enzyme insufficiency has very different symptoms, depending on the type of malfunction that develops. The pancreas is one of the most important human organs. This organ is responsible for performing a large number of functions that ensure the normal functioning of all body systems.
With enzymatic deficiency of substances produced by the pancreas, the digestion process becomes difficult and incomplete.
One of the pathological disorders is pancreatic enzymatic insufficiency.
Types of pancreatic insufficiency and their signs
Pancreatic diseases are classified into 4 main types:
- Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, caused by a decrease in the activity of special secretory substances that break down food into substances that are freely absorbed by the body, or a violation of the secretory outflow of pancreatic juice into the intestine due to narrowing of the flow channels due to tumors or fibrosis. When enzyme activity is disrupted, the secretion becomes thick and viscous and does not break down food well. When the flow channels are narrowed, an insufficient amount of fermenting substances enters the intestines, which do not fully cope with their task. Its main symptoms: intolerance to spicy and fatty foods, heaviness in the stomach, diarrhea, bloating and colic; minor: shortness of breath, tachycardia, pain throughout the body, convulsions. Fats entering the intestines are not processed and are excreted in undissolved form along with feces (pancreatic steatorrhea). Fatty acid deficiency leads to brittle bones, decreased blood clotting, seizures, impaired night vision, and impotence. A decrease in protein fermentation causes shortness of breath, tachycardia, anemia, general weakness, and fatigue.
- Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is a consequence of a decrease in the production of pancreatic (pancreatic) juice, which is responsible for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. It manifests itself as indigestion, nausea and heaviness in the stomach, excess gases in the intestines and disruption of its activity; is the cause of diabetes mellitus. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency can be relative or absolute. The first is reversible, the integrity of the organ in this case is not impaired, the malaise is caused by the immaturity of the pancreas or a violation of secretion, and is more common in children. Absolute deficiency is accompanied by atrophy of the acini and fibrosis of pancreatic tissue, and a decrease in the production of enzymes. It is a consequence of diseases such as chronic or acute pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.
- The lack of enzymes in the gastric juice involved in the digestive process is pancreatic enzymatic insufficiency. Symptoms indicating insufficiency of enzymes for digesting food: flatulence, nausea and vomiting, foul-smelling diarrhea, dehydration, general weakness, etc. The most significant and characteristic sign of enzyme insufficiency is changes in stool: increased frequency of bowel movements, stool with excess fat, which is bad flushed from the toilet, acquiring a gray color and a putrid stench.
- With endocrine insufficiency of the pancreas, the production of the hormones insulin, glucagon, and lipocaine decreases. This form of failure is dangerous because it causes a malfunction of all human organs and has irreversible consequences. The symptoms are similar to those characteristic of a deficiency of pancreatic enzymes. Insulin is responsible for the supply of glucose from the blood to the body's cells and lowers the sugar level, while glucagon increases it. The normal level of glucose in the blood is 3.5-5.5 mmol/l. Changes in the norm lead to the development of diseases - hyperglycemia (increased glucose levels) and hypoglycemia (respectively decreased). Impaired insulin production leads to increased blood glucose levels and the development of a disease such as diabetes. The main signs indicating a lack of insulin hormones: increased blood sugar after meals, thirst, frequent urination; in women - itching in the genitals. With a decrease in glucogan production, the following set of symptoms is characteristic: weakness, dizziness, tremors of the limbs, changes in the psyche (anxiety, depression, causeless restlessness), convulsions, loss of consciousness. If, for insulin deficiency, treatment is prescribed by an endocrinologist, then for glucogen deficiency, the help of a psychotherapist is also necessary.
Important information: What medications should be used to treat the pancreas?
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency: symptoms, causes and treatment
Exocrine deficiency is understood as a lack of juices, which, if properly available, act as a guarantor of proper digestion of food. Exocrine insufficiency is characterized by:
- Bloating;
- Stool disorder;
- Feeling of heaviness in the abdominal area;
- Nausea;
- Poor digestibility.
Most often, this type of deficiency is caused by problems with the digestive system (diseases of the stomach, intestines, gall bladder), diet abuse and refusal of foods necessary for the body, as well as excessive addiction to alcoholic beverages.
However, symptoms alone cannot determine the diagnosis. To do this, you need to undergo a number of mandatory tests, including blood sugar tests, because diabetes mellitus is one of the most common complications of this type of deficiency.
Treatment is based on the exclusion of alcoholic beverages and foods that negatively affect the health of the gland. In particular, the diet is enriched with vitamins A, C and E. Medicines designed to stimulate the synthesis of enzymes also play an important role.
Causes of pancreatic failure
Factors contributing to malfunction of the pancreas may be the following:
- degenerative changes in the gland;
- vitamin deficiency (lack of vitamins B, C, E, PP, nicotinic acid), which provokes liver disease and the development of cholelithiasis;
- decreased protein content and anemia;
- errors in eating - a lot of fatty, spicy foods in the diet, alcohol abuse;
- infectious diseases of the stomach, pancreas, duodenum;
- exacerbation of pancreatitis or chronic pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas;
- helminthiasis;
- long-term use of medications;
- improper fasting;
- metabolic disease;
- disorders of the small intestine and duodenum, degenerative changes in the intestinal microflora;
- congenital malformations of the pancreas.
In this case, necrosis of the pancreas tissues occurs and they are replaced by scar growths and, as a consequence, they lose their functional abilities.
Main causes of pathology
Rarely diagnosed diseases include enzyme deficiency, characterized by a complete absence of enzymes. But most often, the pancreas reduces the production of one or more enzymes. Gastroenterologists identify the following causes of the pathological process:
- eating a large amount of food, for the breakdown of which there are simply not enough enzymes produced;
- acute and chronic pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas);
- helminthic infestations;
- cholelithiasis, accompanied by a violation of the outflow of pancreatic juice;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- enteritis, gastroenteritis, gastritis - inflammatory processes in the small intestine and (or) stomach;
- diseases of the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, in which bile does not activate pancreatic enzymes;
- hypoacid gastritis, characterized by insufficient production of hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes;
- Crohn's disease, amyloidosis, systemic autoimmune diseases in which cells of the intestinal mucosa die;
- consequences of surgical interventions - excision of part of the gastrointestinal tract;
- nutritional errors or fasting, leading to a deficiency of vitamins and microelements.
Pancreatic insufficiency can be caused by congenital anomalies. Symptoms of enzyme deficiency and digestive disorders are observed in children almost immediately after birth. This pathology cannot be treated, but it is quite possible to correct the condition. Lifelong replacement therapy and a strict diet are indicated for children and adults with congenital enzyme deficiency.
If the pathological process is provoked by any disease, then the prognosis for complete recovery is favorable. It is necessary to follow medical recommendations and review the diet. But sometimes the damage is irreversible, for example, when the intestinal walls are damaged. In these cases, the patient will also have to monitor his diet and take medications with enzymes.
Enzyme deficiency is caused by damage to pancreatic cells.
Diagnosis of pathological changes in the pancreas
First of all, the attending physician conducts a survey of the patient and finds out the symptoms that distinguish pancreatic enzyme deficiency. To diagnose the disease, laboratory blood tests are performed (for the content of hemoglobin and biochemical substances, for sugar levels), studies of the presence of enzymes in the urine, stool analysis and coprogram for fat content (normally no more than 7%), elastase-1 and the state of absorption and processing food by the body.
To identify degenerative changes in organs, abdominal ultrasound, CT and MRI are prescribed. An important diagnostic method is endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (examination of the pancreatic ducts and bile ducts for their patency and the presence of keloid formations). To clarify the diagnosis, a method of direct study of secretions obtained from the pancreas by aspiration of the pancreas is used, which allows one to determine the content and volume of pancreatic juice.
Important information: What should be the diet for pancreatic cancer
Endocrine insufficiency is tested by glucose tolerance testing—blood collected on an empty stomach and blood collected 2 hours after a meal or 75 g of glucose. This test shows the body's ability to produce insulin and process glucose.
The following indicators indicate a disturbance in glucose metabolism: blood glucose level of at least 6.7 mmol/l; 2 hours after taking 75 g of glucose - 7.8-11.1 mmol/l. Normally, the blood glucose level should not exceed 6.4 mmol/l. If the blood glucose level taken on an empty stomach is 7.8 mmol/L or more than this value, then diabetes occurs.
Types of disease
At the diagnostic stage, the type of enzymatic deficiency and the stage of its course are established. Each form of pathology has its own specific symptoms and causes. Further treatment will depend on the type of disease.
Warning: “If enzyme deficiency is at an early stage, then therapy does not take much time. Sometimes it is enough for the patient to adjust his diet so that the functional activity of the digestive organ is completely restored.”
Exocrine
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency develops as a result of a decrease in the mass of exocrine parenchyma or the outflow of digestive secretions into the cavity of the duodenum. Experienced diagnosticians can identify this type of pathology only by its specific symptoms:
- indigestion after eating fatty or spice-rich foods;
- feeling of bloating and heaviness in the abdomen;
- loose stools with a significant content of fat not absorbed by the body;
- painful cramps in the lower abdomen, radiating to the sides.
Malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract lead to chronic intoxication of the body. Due to insufficient absorption of vitamins and microelements, a person’s skin becomes dry and gray, shortness of breath appears, and the heartbeat increases.
Exocrine
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency occurs after irreversible damage to its tissues. The causes of the pathological process are the lack of treatment of the duodenum, gall bladder, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Exocrine insufficiency is found in people whose diet is unbalanced and monotonous. Abuse of strong alcoholic drinks also provokes a decrease in the functional activity of the gland and the development of the inflammatory process. What signs are characteristic of this species:
- insufficient absorption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increased gas formation;
- irregular bowel movements;
- loose stool.
Long-term digestive disorders lead to decreased motor activity, neurological disorders, lethargy, apathy, and drowsiness.
Enzymatic
This type of deficiency most often develops under the influence of external factors. The cause of the pathology is a course of treatment with pharmacological drugs that damage pancreatic cells. Tissue damage can occur after pathogenic infectious agents penetrate the digestive organ. Symptoms of pancreatic enzyme deficiency:
- seething and rumbling in the stomach;
- diarrhea;
- decreased appetite and weight loss;
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- pain in the navel area.
The main symptom of the pathology is frequent bowel movements, during which loose stools with a specific foul odor are released.
Endocrine
The disease develops against the background of damage to the islets of Langerhans. These areas of the pancreas are responsible for the production of insulin, glucagon, and lipocaine. With insufficient production of biologically active substances, not only digestive disorders occur, but also endocrine pathologies, for example, diabetes mellitus. What symptoms does enzyme deficiency cause?
- chronic diarrhea;
- bouts of vomiting;
- lack of appetite, low body weight;
- bloating, belching;
- drowsiness, emotional instability.
This type of enzyme deficiency is dangerous due to the development of dehydration due to fluid loss during vomiting and diarrhea.
Diet is the basis for treating enzyme deficiency
Consequences
Ignoring enzymatic deficiency leads to the development of all kinds of complications. First of all, a person will constantly complain about feeling unwell. Integral companions of the disease are nausea and frequent episodes of vomiting. Over time, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract will deteriorate. As a result: loss of appetite, weight loss, diarrhea, constant pain, flatulence, bloating, belching.
Against the background of enzymatic deficiency, chronic intoxication of the body develops. As a result, a person’s cardiovascular system is disrupted, the condition of the skin worsens, the degree of motor activity decreases, and neurological and endocrine diseases appear.
It is important to remember that enzyme deficiency is not independent. It is always a symptom of some disease. Ignoring the disease leads to the fact that the underlying pathology progresses. As a result, a threat is created not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient.
Food as the main source of enzymes
The main enzymes that help digestion are found in large quantities in food. Most of these microelements are found in fermented milk products (cottage cheese, kefir and various yoghurts).
Additional sources of natural enzymes are:
- Sauerkraut.
- Apple vinegar.
- Bananas.
- Soy sauce.
- Apples.
- Horseradish.
- Garlic.
- Avocado.
- Papaya.
- A pineapple.
- Mango.
- Kiwi.
- Legumes.
- Broccoli.
- Cabbage (white cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli).
Also, enzymes are found in large quantities in freshly squeezed juices not only from fruits, but also from vegetables, so it is very useful to drink such liquids at least three times a week.
It is important to know that vegetables and fruits should be consumed mainly raw, since after steaming they lose most of their beneficial substances.
The task of food enzymes is that they give the body the necessary “forces” for normal functioning. Also, such microelements promote the removal of toxic substances and protect the body from harmful effects.
Symptoms of enzyme deficiency in children
The clinical picture of enzyme deficiency is clearly manifested in the digestive system. The main symptoms of the pathology are: vomiting in the child several hours after feeding, frequent nausea, which causes anxiety and whims in the baby. Very often there is bloating, very liquid stool and general weakness. Due to poor digestion, the child sharply loses weight, his appetite decreases, or he completely refuses food.
A severe form of enzyme deficiency leads to delayed physical development. This is due to the fact that the required amount of vitamins and minerals is not absorbed by the body. In the absence of proper treatment, a number of other pathologies develop.
In children after one year of age, symptoms are not as acute. After taking dairy products, the child develops abdominal discomfort, suffers from flatulence, colic, and nausea. They develop diarrhea, and the stool is foamy and has a strong sour odor. Children become lethargic, complain of weakness and completely refuse dairy products, which can lead to calcium deficiency.
Celiac disease is manifested by excessive dry skin, the development of stomatitis, the child does not gain weight well, but the abdomen is very enlarged due to severe bloating. The baby often suffers from diarrhea, the stool is foamy and has an extremely unpleasant odor. Sometimes the child suffers from severe nausea and vomiting.
Phenylketonuria is manifested by delayed mental and physical development. Such children are prone to various mental disorders.