Among gynecological disorders, endometriosis of the uterus is recognized as a difficult disease to diagnose due to the varied symptoms characteristic of other pathologies.
The disease affects women in their reproductive period; after 50 years, endometriosis does not develop in women.
Endometriosis of the uterine body is called a dyshormonal immune-dependent pathology, which is characterized by benign tissue proliferation (endometrial hypertrophy).
The disease code according to ICD-10 is N80.0.
Types of disease
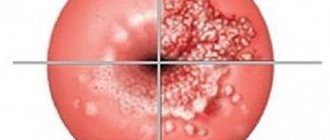
Separation of pathology according to the form of growth (shown in the photo below):
- The diffuse form of the pathology is a uniform lesion of the endometrium.
- The focal form corresponds to damage to individual areas of the endometrium.
- Nodular endometriosis is characterized by pathological foci in the form of nodes.
The disease can develop in four stages, differing in the depth of penetration of pathological foci:
- The lesions concern the superficial layer of the myometrium.
- The lesion extends to the middle of the myometrial layer.
- The disease affects the entire muscular layer of the uterus.
- The fourth degree is characterized by the spread of endometriosis to the peritoneal tissue.
What is endometriosis?
Photo of endometriosis
The endometrium is the tissue lining the inner lining of the uterus (mucosal layer).
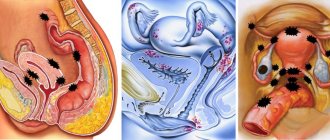
Uterine endometriosis is a condition in which endometrial tissue is found outside the uterus. It is "trapped" in the pelvis and lower abdomen, and, less commonly, in other areas of the body.
Foci of the spread of the disease
Endometriosis is a common gynecological pathology, ranking third in frequency of occurrence after inflammation and uterine fibroids. Most often, uterine endometriosis is detected in women of reproductive age - from 25 to 40 years.
Pathology can also appear in girls during the formation of menstrual function and in women during menopause. It should be borne in mind that difficulties in identifying pathology and the asymptomatic course of the disease allow us to conclude that the endometrioid process is more common.
Symptomatic manifestations
Symptoms of uterine endometriosis :
- Intense and cyclical pain syndrome, especially manifested in premenstrual days.
- Excessive bleeding during menstruation.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Painful sexual intercourse.
- Disturbed menstrual cycle.
- Infertility.
- Spotting and spotting between periods.
- Fatigue, general weakness.
Symptoms of endometriosis
If the disease is not asymptomatic, it is accompanied by clinical signs:
- pain in the pelvic area during menstruation (dysmenorrhea);
- spotting before and after menstruation;
- 5% of patients have nausea and vomiting during menstruation;
- long menstruation (more than 8 days) and severe bleeding (menorrhagia); anemia;
- uterine bleeding not associated with menstruation;
- bloating during menstruation;
- 20% of patients have pain when urinating and defecating;
- pain during intercourse;
- infertility, cervical cyst, mastopathy.
Causes
The reasons for the development of pathology remain unclear . According to one theory, the pathological process is triggered by retrograde menstruation.
There is an assumption that endometrial cells move through lymphatic and blood channels.
Causes and psychosomatics of the disease :
- Hormonal disorders.
- Frequent abortions, diagnostic curettages, complicated childbirth.
- Weakened immunity.
- Genetic predisposition to the disease.
- Thyroid dysfunction.
- Long-term inflammation of the genital organs.
- Physical inactivity, obesity.
- Bad ecology.
NOTE!
Periodic checking of hormone levels and gynecological examination prevent the development of most gynecological disorders.
Degree of disease development
In medicine, there is not yet a unified theory about the causes of the development of endometriosis. There are several causes, the most common of which is retrograde menstruation (meaning the flow of menstrual blood back).
When a number of conditions are combined, endometrioid cells attach to various organs and resume their ability to function cyclically. During menstruation, the presence of endometrium, localized on uncharacteristic organs, provokes microbleeding and inflammation.
Thus, those women who have retrograde menstruation may develop endometriosis, but not in all situations. The likelihood of developing pathology increases due to the following features:
- hereditary predisposition;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- surgical interventions;
- environmental factors (properties of the environment that affect your body).
Progression of endometriosis is also possible with surgical interventions on the uterus. For this reason, after any surgery, it is important to be observed by a doctor for timely diagnosis of possible pathologies.
There are also a number of other theories about the causes of endometriosis, which include:
- theory of gene mutations;
- deviations in the interaction of receptor molecules with hormones;
- dysfunction of cellular enzymes;
- embryonic theory.
There are several main groups of women predisposed to the progression of endometriosis:
- women with a shortening menstrual cycle;
- women with metabolic disorders (obesity);
- using intrauterine contraceptives;
- age over 30-35 years;
- women with pathologically high levels of estrogen;
- women with pathologies that suppress the immune system;
- have undergone surgery on the uterus;
- smoking women.
Diagnostic measures
An accurate diagnosis of the disease is established based on the following studies:
- Hysterosalpingography, x-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy.
- Ultrasound scanning of the pelvic organs.
- Biopsies.
- Gynecological examination of the vagina and cervix.
- Laparoscopy is the most accurate method for detecting pathological foci of endometriosis
What does the disease represent?
To understand what endometriosis is, it is necessary to understand the anatomical features of the female reproductive system. The entire internal cavity of the uterus is covered with a layer of endometrium - tissue, the thickness of which varies depending on the period of the menstrual cycle. If the growth of the inner lining extends beyond the organ and is noticeable on the cervix, doctors diagnose “suspicious endometriosis” and recommend that the patient undergo additional diagnostic testing.
The disease develops differently in each individual case. It is difficult for doctors to predict the dynamics of pathology progression. Moreover, in the early stages of the disease, it is difficult to diagnose it only by visual examination. After all, the focus of endometriosis is located inside the uterine cavity.
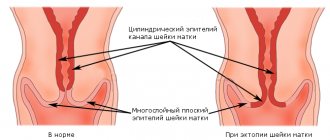
Cervical endometriosis
External genital endometriosis with damage to the vaginal mucosa of the cervix and cervical canal is called cervical endometriosis.
The disease is characterized by hormone dependence, the pathology regresses during menopause. Cervical endometriosis can be superficial, affecting the vaginal portion of the cervix, or deep, developing in the distal cervical canal .
What does the disease look like? The pathology can occur without pronounced clinical symptoms. There may be bloody spotting outside of menstruation or after sexual intercourse.
Objective tests are needed to detect cervical endometriosis:
- Gynecological examination with speculum.
- A week before the onset of menstruation, a colposcopy is performed.
- Targeted biopsy of the cervix.
- Ultrasound.
The pathology is eliminated with hormonal agents under the supervision of the attending physician . Complex treatment also includes taking immunomodulatory drugs, non-steroidal and anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
In cases where conservative methods fail, pathological growths are removed surgically. The methods used are cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, radiocoagulation, and laser vaporization .
IMPORTANT!
Doctors do not recommend using tampons if you have endometriosis of the uterus. The created artificial barrier complicates the natural outflow of blood and can provoke a reverse flow of blood into the fallopian tubes and peritoneum.
Possible complications
With timely diagnosis, complications with cervical endometriosis are very rare.
The most common are:
- anemia due to severe blood loss;
- spread of the inflammatory process to neighboring organs;
- infertility.
The chances of endometrial cells degenerating into malignant ones and the development of cervical cancer also increase.
Due to hemorrhages and scar formation in endometriosis, adhesions are provoked in the abdominal organs and pelvis. Quite often, as a result of pathology, cysts are formed on the ovaries, which are filled with menstrual blood. Both adhesions and endometrioid cysts can cause infertility.
Also, with endometriosis, compression of the nerve trunks can be observed, which leads to the development of neurological symptoms. Due to significant blood loss, manifestations such as:
- anemization;
- irritability;
- constant weakness.
Foci of endometriosis in some cases undergo malignancy (malignancy).
Treatment methods
Endometriosis is treated using hormone therapy and surgery. The goal of therapeutic measures is to stop the pathological process of growth, relieve the symptoms of the disease, while maintaining reproductive function.
Hormone therapy simulates the artificial onset of menopause by taking gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists . The course of treatment is at least six months.
Progestin therapy includes the use of intrauterine devices, contraceptive implants, or contraceptive injections.
Surgical treatment involves removing endometriotic lesions using laparoscopy. Minimally invasive surgery eliminates lesions using cauterization .
The use of laparoscopy ensures rapid recovery and eliminates the formation of adhesions. The operation is indicated in the absence of positive results of drug treatment , large foci of growth, or relapse of the disease .
In case of advanced endometriosis with severe complications, hysterectomy is performed, complete removal of the organ and appendages.
Currently, a combination treatment method is more often used . First, treatment is carried out with hormonal agents, then the foci of endometriosis are removed by surgery.
Sometimes it is possible to combine traditional treatment of endometriosis with folk remedies, in particular using boron uterus.
Therapy
When choosing treatment methods, the form of endometriosis, its location on the cervix, its prevalence, as well as the woman’s age and her plans to give birth are taken into account.
Only after a complete examination does the doctor decide how best to treat this form of endometriosis in a particular case. The following types of treatment are used:
- surgical;
- hormonal;
- additional medication.
https://youtu.be/qLcUlIYJFZ0
Surgical method
Even decades ago, cervical endometriosis was regarded as a tumor disease, so the choice was made in favor of surgery.
For this reason, many young women were deprived of childbearing function. Modern gynecology uses surgical treatment only for certain indications:
- if conservative treatment carried out for 3-4 months has no effect;
- when there is spread of the disease beyond the uterus and appendages - to the pelvic organs, abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space, with severe pain, impaired intestinal function;
- if the patient does not intend to give birth again or has already passed childbearing age.
An interesting rare case: the parents of a 12-year-old girl came to see her about lower back pain and blood in her urine. The examination revealed endometriosis spreading to the kidney, and the child underwent surgery.
Among surgical methods, preference is given to minimally invasive organ-preserving interventions - endoscopic, laparoscopic, which do not require incisions, and the removal of nodes is performed under the control of a video camera through a probe.
Laser vaporization (evaporation) of lesions, as well as cryodestruction (removal by cold), ultrasound and radio wave coagulation are widely used and produce good results.
https://youtu.be/DSbxc9QKAz4
Complete removal of the uterus with the cervix and appendages is performed in advanced cases of the disease, as well as in women past fertile age.
Hormonal effects
The treatment strategy for newly diagnosed endometriosis is to correct hormonal levels in order to suppress the process of active growth of the endometrium under the influence of excess estrogen.
Hormonal treatment today is the leading method of combating endometriosis. The choice of drugs and their dosage is based on laboratory determination of the content of sex hormones in the blood.
Among the estrogen antagonists, Tamoxifen, Leuprolerin are prescribed, as well as progesterone antagonists (Gestrinone), antagonists of sex hormone synthesis (Danol, Nafarelin).
In mild cases of endometriosis, the course begins with the prescription of tablet contraceptives, which normalize the proportions of hormones (Zhanine, Novinet, Lindinet and other analogues).
When estrogenic activity is too pronounced, they resort to the prescription of male sex hormones - androgens (Methyltestosterone and analogs).
Patients who have already been treated in the past with hormones and who have a relapse of the disease are subject to removal of lesions on the cervix by one of the methods.
Additional conservative methods
Regardless of whether the patient has undergone surgery or is receiving hormonal treatment, it is mandatory to prescribe medications that eliminate the symptoms of the disease, increase the protective properties of the woman’s body, and improve tissue repair processes.
These include:
How does it affect pregnancy?
The pathological process of endometriosis leads to the formation of adhesions, which causes infertility.
Despite the fact that endometriosis often prevents conception, the chance of becoming pregnant remains.
There are often cases when gynecologists offer the patient, in the absence of contraindications, to give birth to a child. The natural cessation of menstruation associated with pregnancy and the subsequent period of breastfeeding stops the disease process .
Before a planned pregnancy, a course of treatment is required.
If a woman manages to become pregnant with a diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia, the pregnancy process will be difficult . The patient should be under constant medical supervision and follow all prescriptions.
CAREFULLY!
Endometriosis does not have a negative effect on the development of the child, but it increases the likelihood of miscarriage and premature birth.
Causes
Experts in the field of gynecology say: “endometriosis of the cervix never develops in a vacuum,” this is confirmed by clinical practice and medical statistics.
The disease usually develops against the background of women’s health problems, these include:
- Abortion.
- Previous operations on the pelvic organs.
- C-section.
- Complications during childbirth.
- Multiple births.
- Cervical erosion treated with coagulation.
- Intrauterine contraceptives.
- Ovarian hyperfunction, excess estrogen.
There is also a so-called risk group, which includes women with inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, weakened immunity, anemia, liver failure, hypovitaminosis, diabetes mellitus, obesity, and leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Hereditary predisposition also plays a significant role, which occurs in 10-15% of patients.
Diet and lifestyle
A proper diet and a certain lifestyle can significantly increase the chances of curing the disease .
- Smoking and alcohol have a detrimental effect on women's health. First of all, you should give up these bad habits.
- The consumption of carbonated drinks and coffee should be kept to a minimum.
- For endometriosis, you should increase your diet with iron-containing foods: buckwheat porridge, liver, dried apples, dried fruits, rose hips, fresh herbs.
- Half of your diet should consist of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- You should avoid fatty, spicy, smoked, and pickled foods.
- Fatty dairy products are not recommended.
- The diet should include lean meat, no more than 2-3 times a week; sea fish and seafood.
- Recommended: sports, walks in the fresh air, active recreation. Yoga classes, static inverted poses, are especially useful for women's diseases.
- A woman’s emotional stability is of no small importance. Negative emotions and stressful situations should be avoided, and positive life attitudes should be followed.
Endometriosis is recognized as a difficult-to-treat pathology, with a number of serious consequences . All women should be attentive and careful about their health.
In conditions of increasing environmental stress, a healthy and active lifestyle is especially important, which makes it possible to resist various diseases.
How to treat uterine endometriosis?
Today, in the arsenal of experienced specialists, there are many different ways to cure endometriosis. Many doctors have used pseudopregnancy and pseudomenopause to eliminate this disease. However, modern methods are more effective and humane. These include the use of medications and surgery.
If surgery is not indicated, you can eliminate a disease such as endometriosis at home. The consequences of taking Now-foods drugs will not take long to appear. Along with remission comes an improvement in well-being, restoration of the body’s immune forces and normalization of the functioning of all internal systems. Why are Now-foods drugs so useful, and why are they indicated for ovarian endometriosis? The treatment is very gentle and effective.
It can also be argued that this complex is a kind of treatment with folk remedies, since it contains natural components and biologically active elements that have a beneficial effect on the female body.
How is endometriosis diagnosed?
To make a diagnosis, the doctor needs to collect a detailed medical history of the patient, listen to her complaints, and conduct a chairside gynecological examination. An examination by a gynecologist should be carried out just before the onset of menstruation. If a pathology is suspected, a woman is sent for the following examinations:
- Ultrasound - transvaginal ultrasound provides 85-90% accuracy, performed on the eve of menstruation;
- hysteroscopy - the most informative examination, allows you to differentiate pathology from fibroids, uterine polyps, and cancer;
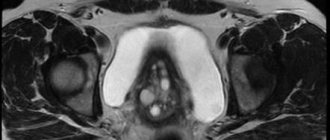
- MRI;
- laboratory testing of blood and urine to determine hormone levels and the presence of anemia [7].
Degrees of endometriosis
There are 4 degrees of endometriosis:
- 1st degree: single pathological foci of endometrial growth form on the surface of the uterus;
- 2nd degree: pathological foci are located within the uterus, growing into its deep layers;
- 3rd degree: multiple deep foci of proliferation of endometrial tissue in the uterus with transition to the ovaries and peritoneum with the formation of cysts;
- 4th degree: numerous endometrial foci that have grown deep into the uterus, bilateral ovarian cysts, germination into the vagina and rectum, the formation of adhesions.
Types of endometriosis
There are genital and extragenital endometriosis. With both types, different organs can be affected.
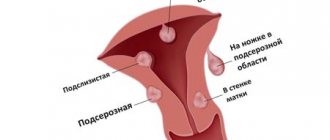
Uterine endometriosis is a lesion of the entire uterus with deep growth of endometrial cells into its layers (adenomyosis). The uterus increases significantly in size. Clinical manifestations: intense pain during menstruation. Pathological foci are located in different parts of the uterus, spread throughout the entire wall or have the form of nodes growing from the muscle layer.
Ovarian endometriosis is the formation of ovarian cysts filled with old blood (“chocolate cysts”) with a diameter of 2-50 mm. Complicated by rupture of cysts and heavy uterine bleeding.
Cervical endometriosis is an asymptomatic form of the disease. It is characterized by the formation of endometrial lesions up to 5 mm in diameter. In 70% of cases it is detected during a gynecological examination.
External - the endometrium grows in the ovaries, cervix and on the inner surface of the uterus;
Internal - localized only in the uterus and is characterized by deep germination of the muscle layer with the formation of fibroids.
Extragenital endometriosis - damage to non-genital organs; Along with cyclic menstruation, bleeding is observed in the affected organ.
When the bladder is damaged during menstruation, the urine turns red. The patient is experiencing pain in the pelvis, which gets worse with urination. Without treatment, endometrial cells gradually grow into the walls of the bladder with the formation of adhesions and chronic pain.
If the intestines are damaged during menstruation, blood is found in the stool; patients report pain during bowel movements. Typically, the descending colon and rectum are affected.
Endometriosis of a postoperative scar is the growth of the endometrium in a postoperative wound. It is more common after cesarean section, perineal rupture during childbirth, and operations on the abdominal organs. A red or blue cyst forms in the area of the surgical wound, which decreases after menstruation. Patients complain of aching pain in the wound area during menstruation.
Prevention of endometriosis
To avoid the disease or detect it at an early stage:
- See a gynecologist regularly (2 times a year), especially after surgical interventions on the uterus;
- for menstrual pain, consult a gynecologist;
- promptly and completely treat acute and chronic gynecological diseases;
- when choosing contraception, consult a gynecologist;
- avoid sexual intercourse during menstruation;
- normalize body weight;
- quit smoking, avoid stress.
Endometriosis: treatment
Now let's figure out how endometriosis is treated.
The following treatment methods are distinguished:
- conservative - hormonal, anti-inflammatory, vitamin preparations, immunomodulatory agents, hepatoprotectors;
- surgical - depending on the stage of the disease, the patient’s age and her general condition, radical (hysterectomy, removal of the uterus and appendages) or organ-preserving (coagulation of pathological foci) surgical interventions are performed [8];
- combined.
At the initial stages, conservative therapy is prescribed; if it is ineffective, surgical treatment is indicated[9].
Coagulation is prescribed for the following symptoms:
- hyperplastic endometrium;
- adhesive process;
- purulent inflammation;
- ineffectiveness of hormonal therapy lasting more than three months;
- presence of contraindications to hormonal therapy.
It is recommended that the patient try to become pregnant no earlier than 6 months after undergoing conservative treatment or endocoagulation. The issue of hysterectomy is considered in the following cases:
- progression of the pathological process in patients over forty years of age;
- ineffectiveness of drug treatment and organ-preserving surgical interventions;
- h degree of diffuse type adenomyosis;
- nodular form of the disease in combination with uterine fibroids;
- threat of development of a malignant process.
Since during pregnancy a woman does not have menstruation and significant hormonal changes occur, this period has a positive effect on the course of the disease.
Adenomyosis is a chronic pathology prone to recurrence. After a course of conservative treatment and organ-preserving surgery, approximately 20% of women under 40 years of age are diagnosed with a relapse. Over a five-year period, recurrence is observed in 70-75% of patients. Shortly before the onset of menopause and during menopause, the prognosis is favorable, which is explained by the decline in the production of hormones by the ovaries. In many cases, women of menopausal age recover without therapy [10].
Why do patients choose the Good Forecast Specialized Clinic?
PROFESSIONALISM – highly experienced doctors, doctors of the highest category, candidates of medical sciences, authors of modern clinical treatment protocols and innovative techniques
- Organ-preserving techniques
- Minimally invasive operations
- Modern operating rooms and departments
EXPERIENCE – we have been treating and operating for 10 years, since 2009
CARE for patients
- Patient support 1 month after surgery – free
- Observation of patients after recovery - clinical examination
- Individual approach to out-of-town patients
CONVENIENCE
- Clinic in Kyiv - easy to reach us
- We consult and operate daily – Mon-Sat 8:00-22:00
- 24/7 – 24-hour hospital in Kiev – we are always ready to provide our patients with support and emergency hospitalization
TRUST of our patients - read and see reviews about us! This is our best reward!
When identifying endometriosis, it is important to exclude other gynecological pathologies that occur with similar symptoms. Diagnostic search includes the following activities:
- Anamnesis collection. It is important to take into account not only the patient’s clinical symptoms and complaints, but also family history, that is, cases of pathology among family members. It is also necessary to clarify whether gynecological operations were performed.
- Gynecological examination. Can be vaginal, rectovaginal, or in speculum. The most informative is to carry it out a few days before the start of menstruation.
- Colposcopy and hysterosalpingoscopy. They are carried out to clarify the location and parameters of the lesion, as well as to obtain a biopsy sample.
- Ultrasonography. It is necessary to clarify the location of foci of pathology and the dynamics of the condition during therapy.
- Spiral computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. These methods make it possible to clarify the nature and localization of endometriotic lesions.
- Laparoscopy. The method allows you to visually assess the number, maturity, and activity of endometriotic lesions.
- Hysterosalpingography is an examination of the uterus and fallopian tubes using x-rays.
- Hysteroscopy is an endoscopic examination of the uterus to detect adenomyosis.
- Laboratory tests: identifying tumor markers CEA, CA-125, CA 19-9 and performing a RO test. These indicators increase significantly in the case of endometriosis. Laboratory diagnostics are also carried out to detect anemia in patients with endometriosis.
Some diagnostic techniques are worth considering in more detail.
This technique is important for identifying internal endometriosis (adenomyosis or endometriosis of the uterus). The study is carried out with a water-soluble contrast agent on days 5, 6 or 7 of the cycle. The presence of contour shadows is noted on the x-ray.
Tomography
Computed tomography can provide information about the boundaries of the pathological process. Magnetic resonance imaging is more informative for endometriosis.
Ultrasound image of an illness
This technique allows you to characterize the pathology according to clear criteria. An ovarian cyst of endometrioid origin is characterized by the presence of a dense capsule and hyperechoic contents.
In the case of adenomyosis, examination can reveal areas with increased echogenicity, unevenness and jaggedness of the border areas of the endometrium and myometrium, and round inclusions about 5 mm in diameter. Nodular variants of adenomyosis are accompanied by the formation of cavities with fluid with a diameter of about 30 mm.
Hysteroscopy
This technique makes it possible to accurately identify endometriotic ducts and the roughness of the relief of the uterine walls in the form of crypts or ridges. In 1997 V.G. Breusenko and co-authors developed a hysteroscopic classification of the prevalence of the endometrioid process:
- The first stage: unchanged relief of the walls of the uterus, endometriotic ducts in the form of “eyes” of a blue hue or bleeding foci are detected. The uterine wall is characterized by unchanged density.
- Second stage: uneven relief of the uterine wall in the form of ridges or disintegrated muscle tissue. Endometriotic ducts are identified. The uterine cavity does not stretch well. The wall has a higher density.
- Third stage: the inner surface of the uterus includes many protrusions of varying sizes that do not have clear boundaries. Sometimes endometriotic tracts are noted on the upper part of the bulges. The uterine wall is very dense.
Differential diagnosis is necessary to distinguish between endometrioid cysts and ovarian tumors. The final diagnosis is made based on medical history and ultrasound examination. With ovarian endometriosis, there may be no pain, but with an oncological process, non-localized pain may appear.
In cancer and endometriosis, there is an increase in the level of CA-125. Therefore, an increase in the concentration of this substance does not confirm only one diagnosis. In some cases, a definitive diagnosis is only possible during laparoscopic surgery.
In the case of rectovaginal localization of endometrioid lesions, a differential diagnosis with metastases of chorionic carcinoma is required. To make a final diagnosis in this case, a correct medical history and a study of the hCG concentration are required (in this case, signs of pregnancy are also determined).
The tubo-ovarian inflammatory process in the form of an abscess is difficult to diagnose due to the erased clinical inflammation (for example, chlamydial etiology) and the difficulty of distinguishing the process from a benign tumor or cyst of endometrioid origin.
Also, in the case of endometriosis, differential diagnosis with endometrial hyperplastic process may be required. With the retrovaginal nature of the lesion and endometriosis of the ligamentous apparatus of the uterus, it is imperative to exclude malignant neoplasms in the organs of the digestive system.
The tactics of therapeutic correction are determined by the following parameters:
- age;
- number of pregnancies;
- number of births;
- prevalence of the pathological process;
- location of lesions;
- clinic intensity;
- accompanying illnesses.
There are the following treatment methods for endometriosis:
- Medication.
- Surgical – laparoscopy with elimination of endometrioid lesions or radical removal of the uterus and ovaries.
- Combined.
The goals of therapeutic correction of endometriosis are not only to eliminate symptoms, but also to prevent unfavorable processes in the form of adhesions, cysts and other pathologies.
Conservative treatment (non-surgical) of the disease is carried out if endometriosis is asymptomatic, the patient is young or premenopausal, and there is a need to preserve reproductive functions.
The basis of conservative treatment is hormonal therapy with the following groups of medications:
- Combined estrogen-progestin drugs. These include Nonovlon, Silest, Marvelon. These medications contain small doses of gestagens and suppress estrogen synthesis and the ovulatory process. They are prescribed in the initial stages of endometriosis, since combination drugs do not have an effect in the case of widespread endometriosis or the presence of cysts. Possible side effects if used: nausea and vomiting, pain in the mammary glands, spotting during the intermenstrual period.
- Gestagens. These include Duphaston, Nemestran, Utrozhestan, Norkoput. Prescription is possible at all stages of the endometriotic process. Treatment with these drugs is carried out over a period of six months to 8 months. Possible side effects: intermenstrual bleeding, depression, pain in the mammary glands.
- Antigonadotropic drugs. These include Danol, Danogen, Danazol. The mechanism of action is to suppress the synthesis of gonadotropic hormones in the hypothalamic-pituitary system. A continuous course lasting from six months to 8 months is prescribed. Not used in case of hyperandrogenism. The following side effects are possible: hot flashes, sweating, fluctuations in body weight, roughness of voice, increased oily skin, increased hair growth.
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists. These include goserepine, triptorelin and some other drugs. The advantages of taking medications from this group include the possibility of short-term use and the absence of significant side effects. These drugs suppress the ovulatory process, reduce the concentration of estrogen, which together suppresses the prevalence of endometriotic lesions.
- Auxiliary medications: immunostimulating drugs, antispasmodic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory drugs.
Prognosis and prevention
Timely diagnosis and treatment guarantee a positive result. Women who have undergone surgery leave positive reviews, and there are no relapses.
The chances of a full recovery increase with the parallel use of hormonal drugs that prevent the re-growth of endometrial cells.
There are no specific conditions for the prevention of internal endometriosis. Doctors give the following recommendations:
- avoid abortion if possible;
- promptly treat postpartum injuries;
- treat inflammatory processes of the reproductive system;
- eliminate bad habits and lead a healthy lifestyle;
- if you have a genetic predisposition, stop taking oral contraceptives;
- undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist.
Questions from patients - answers from Botkin.pro doctors:
Endometriosis: when to take the first Zoladex injection
Good evening! My diagnosis is endometriosis. After the operation (laporoscopy), three injections of Zoladex were prescribed. Please tell me when is it necessary to give the first injection? Is there a loop binding? Thank you very much in advance!
Endometriosis ranks second in the structure of female diseases, affecting the cervix in 30% of patients, manifests itself in rather unpleasant symptoms and requires professional treatment.
The pathology is typical for reproductive age (28-45 years), but the number of cases in young women and the overall incidence are increasing, which allows specialists to consider endometriosis a disease of the 21st century.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
For ordinary women who visit a gynecologist once a year, and then as promised, the terms endometritis and endometriosis have absolutely no differences. Of course, they are consonant, but in fact, these are completely opposite diseases, each of which brought quite a few bitter tears and disappointments to beautiful young ladies. In a nutshell, endometriosis is the growth of the endometrium, and endometritis is inflammation of the endometrium. And the endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. In this article we will talk about what endometriosis is and how to treat it.
Definition of the concept . Endometriosis is a problem for women of reproductive age, although there are exceptions. There is a misconception that this process refers to tumor processes or, at least, pre-tumor ones. In fact, this is a deep misconception! Endometriosis does not have cellular atypia, so characteristic of tumors, but is capable of growth, germination into surrounding tissues, as well as metastasis through the blood and/or lymph. The uterine mucosa, the endometrium, is lined with endometrioid cells containing highly specific receptors for sex hormones and special spiral glands (crypts). There are no such cells anywhere except the endometrium in a woman’s body. But this is normal. In pathology, the opposite is true. These endometrioid cells migrate to different organs and tissues of the body, without ceasing to function there. And their main function is to menstruate! It turns out that this is the case.
Classification . Depending on where the endometrial cells end up, there are: Endometriosis of the uterine body (adenomyosis), in which the following forms are distinguished: diffuse, focal and nodular, as well as 4 degrees of its development, up to the germination of the endometrium to the pelvic organs; Cervical endometriosis , localized in the canal of the cervix, its outer part (ectocervical endometriosis), or internal (endocervical); Ovarian endometriosis (in the form of pseudocysts); Endometriosis of the fallopian tubes, which is very often complicated by adhesions and the tube becomes impassable. These are all forms of internal endometriosis. External endometriosis: Vaginal endometriosis ; Endometriosis of the perineum. Extragenital (external) endometriosis: Pelvic endometriosis; Intestinal endometriosis; Endometriosis of the navel; Endometriosis of the eye, etc., that is, it can affect almost any tissue of the body. According to statistics, genital endometriosis prevails by more than 90%. Causes of occurrence . So how do endometrial cells end up where they don't belong? There are many diverse theories for this, a couple of which are still the most probable: Endometrioid cells migrated, shifted into the thickness of the uterine wall, were transferred retrogradely with menstrual blood on their own, or “sprouted” with the help of a doctor, after surgical interventions - abortion, complicated childbirth , caesarean section and other manipulations. That is, roughly speaking, the movement of cells is purely mechanical in nature. Embryonic theory. Areas of endometriosis appeared during the girl’s prenatal development. Some of the cells from which the endometrium of the uterus will subsequently grow have shifted in the wrong direction, and pathology has arisen. This theory explains the development of endometriosis in young ladies who have not even begun to menstruate, some of whom, in addition to endometriosis, have various congenital malformations, for example, anomalies of the genitals. Symptoms . There are no specific signs and manifestations here, but some symptoms should definitely alert the young lady: spotting dark bloody discharge from the genital tract 2-5 days before and after menstruation, especially if these same menstruation is quite heavy and prolonged; The same spotting may occur during sexual intercourse; Uterine bleeding during the intermenstrual period (metrorrhagia); Pain of varying intensity, even acute, can be localized in the lower abdomen, radiating to the groin area, anus, or leg. The pain either occurs in the first days of menstruation and disappears with its end, or does not leave the woman throughout the entire cycle, but after the end of menstruation they weaken. Symptoms associated with chronic blood loss are weakness, pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, increased fatigue and drowsiness. There is a high risk of developing anemia.
None of these symptoms, or the presence of all of them together, gives the right to confirm the diagnosis of endometriosis. These are just the warning beacons that should prompt an immediate trip to the gynecologist! Diagnostics . Depending on the form, type, and degree of development of endometriosis, the range of diagnostic measures varies quite widely, from ultrasound of the pelvic organs to diagnostic laparoscopy. Treatment . Perhaps the first question that women ask when voicing a diagnosis of endometriosis is: is surgical treatment necessary? Of course, this depends, first of all, on the localization of the process, and secondly, on the degree of its severity. For example: with vaginal endometriosis, surgical excision of areas of endometriosis is necessary; with grade 1 adenomyosis, you can get by with ablation (resection) of the damaged endometrium. If adenomyosis is combined with uterine fibroids, then in this situation it is necessary to remove the uterus; The same operation will have to be undergone by women in whom hormonal therapy for adenomyosis has not led to proper relief of the symptoms of the disease. More gentle methods are used for endometriosis of the cervix, its outer part - here cryodestruction (cold treatment), electrocoagulation, applications with a solution of solkovagin are possible. If its internal part is damaged, radiocoagulation, laser vaporization or conization of the cervix (excision of its sections) is used. These are, of course, invasive methods, but still organ-preserving. As for extragenital endometriosis, the decision to treat the patient should be made together with a surgeon, urologist, ophthalmologist, etc., depending on the location. Most often, the decision is made to surgically excise the endometriotic lesion. After any surgical intervention, hormonal therapy is prescribed for up to 6 months to prevent relapse. Conservative treatment . If surgical treatment is not indicated for a woman, then conservative hormonal therapy is carried out. Currently, there are a huge number of hormonal drugs for the treatment of endometriosis, here are the most promising of them: Progestogens (Duphaston®), Antigonadotropins (Danazol®); Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Zoladex®). Other groups of drugs that “help” in the fight against painful symptoms of the disease: NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-inflammatory therapy);
Antispasmodics and analgesics (pain-relieving effects); Sedatives (elimination of neurological manifestations); Immunomodulators (normalization of impaired immune status); Vitamins A and C (correction of deficiency of the antioxidant system); Iron supplements (elimination of the consequences of chronic blood loss); Physiotherapy. New data .
Scientists from the United States recently conducted a study in which 248 women diagnosed with endometriosis and 538 healthy women took part. During the study, scientists determined whether the women's blood contained pesticides - substances that are used in agriculture. The results of the study were stunning! Two pesticides were found in the blood of women with endometriosis: lindane and mirex.
Although these pesticides have not been used for more than 30 years, they can enter the human body through consumption:
- spring water;
- cow's milk;
- river fish.
https://myfamilydoctor.ru/
Series of messages “Medicine for you - 7”:
Medicine for you - 7
Part 1 - Quick and gentle treatment of colds. Part 2 - Atrial fibrillation. ... Part 13 - Five important questions about intimate women's health in the spring. Part 14 - Vitamin D and its properties. Part 15 - What is endometriosis and how to treat it? Part 16 - Atrophic colpitis (vaginitis). Symptoms. Treatment. Part 17 - How not to grow old? ... Part 47 - How to get rid of a double chin and maintain the shape of your face. Part 48 - The Scourge of Bachelors. Prostatitis is not as simple as it seems Part 49 - How diets affect hairstyles.