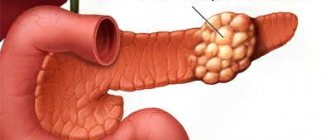
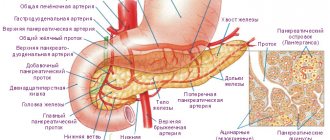
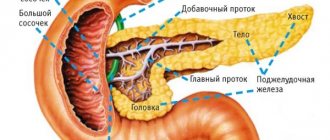
Underfunction and hyperfunction of the pancreas are quite serious diseases that can lead to death if timely treatment is not carried out. It should be remembered that this disease is rare. The development of this pathology in most cases is caused by a dysfunction of the nervous system, as well as a low level of glucose in the human blood.
Symptoms of the disease
The manifestations of symptoms of pancreatic hypofunction depend on the individual characteristics of the body. Among the main ones:
- rapid weight loss or gain that is not related to eating habits or diet;
- feeling of thirst and dry mouth, especially in the morning;
- frequent urination;
- weakness, fatigue;
- nausea, vomiting;
- discomfort in the abdomen, pain
- loss of consciousness, dizziness.
If a patient experiences similar symptoms from time to time, he should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment. After all, hypofunction of the pancreas can provoke a diabetic coma. Excessive glucose in the blood causes destruction of cells and tissues of the body and, in its advanced form, can lead to partial or complete loss of vision, gangrene, and strokes.
Hyperfunction of the gland
Causes
The disease occurs much more often in women than in men.
Determining the root cause of hyperfunction will become the basis for further treatment. Pancreatic hyperfunction occurs when glucose levels decrease. The body responds to this with a sharp increase in insulin production (which it subsequently cannot neutralize).
The increased function can be distributed according to gender: in women the disease is much more common than in men. The reason for this is the differentiation of the hormonal system, as well as the distinctive characteristics of the female body (the disease progresses on a large scale with a shorter time interval).
To track the first manifestations of the disease, you should pay special attention to:
- diet;
- blood glucose levels;
- general condition of the body.
Symptoms
The symptoms are not pronounced. It is for this reason that patients do not notice changes in the usual rhythm of life, ignoring a visit to the doctor. The initial symptoms of increased glucose levels are more similar to typical fatigue or nervous feelings. Basic symptoms include:
- fatigue, weakness of the body;
- high degree of fatigue, which is not justified;
- drowsiness;
- apathetic state;
- cramps in the limbs;
- loss of consciousness.
The faster you respond to the manifestation of symptoms due to pancreatic hyperfunction, the more effective and efficient the treatment will be. If timely treatment is not started, the consequences can be irreparable, even death.
Over time, the symptoms will become more pronounced and cause great discomfort to the patient, thereby disrupting his usual routine.
Advice: take care of your own health and undergo routine examinations by specialists, which include an additional list of tests. This way you can increase your chances of a speedy recovery.
Diagnostics
CT scan.
Diagnosing a disease consists of several stages, each of which provides the doctor with extensive information about the state of the body and a specific organ. Diagnostics consists of:
- determination of glucose content;
- determination of insulin content;
- determination of proinsulin content;
- functional test, which is taken by the method of daily fasting;
- conducting computed tomography of certain areas of the body.
Treatment
Attacks of the disease can be neutralized by intravenous administration of glucose or glucose solutions. The patient can refuse intravenous administration and take any sources of glucose when he feels a sharp deterioration in his condition. Increased function is accompanied by the formation of a tumor in a specific organ. Treatment of the disease consists of surgical removal of the tumor.
In some cases (due to the individual characteristics of the patient), such surgical intervention is prohibited. The patient should adhere to a special diet, take special medications and strictly follow medical instructions.
https://youtu.be/ptUJcUKCvpw
Please note: the conservative method is less effective than timely tumor removal.
Doctor's comment on diet
It is important to follow the diet prescribed by your doctor. When the patient's body recovers, he is allowed to eat a small amount of sweets. You can drink a glass of lemonade. The patient's diet should include foods rich in carbohydrates. It is advisable to avoid fatty, spicy and starchy foods. You should not drink alcoholic beverages.
After therapy, the patient must constantly monitor his health, and if the first signs of pathology appear, consult a doctor. Prevention involves monitoring glucose levels.
Source: giwot.ru
By
Pancreas in Chinese medicine
According to Chinese medicine, the pancreas and spleen are part of the same functional system of the human body, controlling blood, digestion, metabolism, and muscle mass.
But the main role of the gland is to establish the natural balance of nutrients in the body. And since among the Chinese, the formation of Qi energy and the composition of the blood are associated with the harmonious distribution of nutrients, it is difficult to underestimate the role of the pancreas for human health.
The gland is a kind of regulator, a dispenser of energy and nutrients to each and every human organ. The pancreas and spleen regulate water metabolism, improving the tissues of the human body, giving it “lightness and mobility.”
The correct functioning of the gland-spleen tandem is:
- the cause of a healthy oral cavity;
- good appetite;
- elastic muscle mass;
- strong sense of taste.
And, on the contrary, if the system malfunctions, then problems begin in the oral cavity, lips become flaccid, muscles become flabby, bleeding, bruising, and heavy discharge in women are possible.
Causes and symptoms of excessive gland function
Hyperfunction of the pancreas helps reduce the amount of glucose in the blood. Most often, this phenomenon occurs for the following reasons:
- non-compliance with the rules for treating diabetes mellitus and the use of incorrect insulin dosage;
- development of neoplasms of various localizations, in particular in the brain;
- formation of insulinoma (a benign tumor that increases insulin levels, located in the gland itself or in other organs of the digestive system);
- the formation of glucagonoma (a neoplasm, most often localized on the islets of Langerhans, which very often degenerates into a malignant tumor).
Regardless of what factors contributed to the disease, the development of hyperfunction is a rather dangerous problem. Therefore, it is very important to identify pathology in the pancreas in the early stages of development.
The symptoms that accompany hyperfunction are caused by the occurrence of hypoglycemia, which is the main symptom of the disease. Since this disease is very rare, it can often be confused with another disease that has similar symptoms. If the pancreas produces too much secretion, this leads to the following symptoms:
- It is very difficult for a person to concentrate in the morning. He becomes absent-minded, often repeats the same actions, and cannot quickly answer certain questions.
- There is pronounced psychomotor agitation. The patient constantly rushes about, cannot find a place for himself, which causes the feeling that the person is drunk.
- Seizures that have some similarities with epileptic seizures occur, but are of shorter duration.
- Neurovegetative disorders appear, which manifest themselves in the form of sudden changes in blood pressure, increased sweating, heart rhythm disturbances, and redness of the skin on the face.
- The rapid progression of disease of the endocrine glands can provoke the appearance of confusion, which can be of varying severity.
- In some cases, a dream-like state appears in which a person goes to an unknown place without realizing it. After this, he does not understand where he is and how he got there.
Complications
The inevitable consequence of untreated such pathologies can be diabetic coma. Such conditions are serious and require intensive treatment, with low chances of success.
With hyperfunction of the pancreas, tumors can form in this organ, which requires immediate surgical removal.
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most difficult cancers to treat with a high mortality threshold, so if you suspect any dysfunction of this organ, you should definitely visit a doctor.
Diagnostic methods
Symptoms of hypofunction and hyperfunction of the pancreas in the early stages of development are mild and nonspecific, which makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. As a result, diagnosis is difficult, and the patient is often misdiagnosed.
To correctly diagnose the problem, after a detailed survey and examination, the doctor should prescribe the following examinations:
- Blood analysis. First of all, the doctor prescribes a blood test to detect the levels of insulin, proinsulin and glucose. Blood sampling for testing is carried out on an empty stomach.
- Functional tests. If at the time of the blood test the patient has no signs of hypoglycemia, then a functional test with fasting is performed. To do this, you refuse to eat for 2-3 days. To confirm the diagnosis of hypoglycemia, another test may be prescribed, in which the patient is given an injection of insulin, after which the blood is examined.
- CT. Allows you to detect a pancreatic tumor at an early stage, study in detail the structure of the formation and the nature of its growth. Tomography is also used to track the condition of the organ throughout treatment.
- Angiography. Helps detect changes in the pancreas, identify a tumor, determine its location and size.
If a malfunction of the pancreas is suspected, a urine test is also prescribed. If necessary, other diagnostic measures and consultations with various specialists may be prescribed.
Trophological deficiency syndrome
Diarrhea is one of the symptoms of pancreatic disease.
This syndrome occurs when digestion is impaired due to enzyme deficiency. It is noteworthy that the main indicators of trophological deficiency syndrome are:
- Atrophy of subcutaneous fat in the abdominal area
- Darkening of the skin color at the location of the pancreas
- Rapid weight loss
- Psychological disorder
- Visual impairment
- Skin turning gray
- Loss of coordination
- Exocrine disorder syndrome
If a person develops a disease of the pancreas, which is accompanied by exocrine insufficiency, then this disease will be very difficult to resolve.
This is explained by the fact that with exocrine insufficiency, up to 90% of the parenchyma dies, and, as a result, there is a reduced production of enzymes involved in the metabolic process. There are several symptoms of pancreatic disease caused by decreased excretory function:
- Diarrhea
- Steatorrhea
- Exhaustion
This video will tell you about pathologies of the pancreas:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QsOoCbB0MJY
There are a number of diseases that are accompanied by a violation of the exocrine function of the pancreas. For example:
- Chronic pancreatitis. Characteristic features of this disease are weight loss and the development of steatorrhea, and quite often this disease provokes the development of diabetes mellitus.
- Cystic fibrosis. An autoimmune disease in which there is a high probability of developing exocrine insufficiency, and, as a result, the formation of cysts and atrophy of the pancreas.
- Shwachman's syndrome. Characterized by decreased production of trypsin and lipase. There is a failure in the development of the skeleton and bone marrow neutropenia.
- Pancreatic resection. Doctors decide to remove the pancreas if a chronic form of pancreatitis with increased intraductal pressure is detected, as well as with necrosis or cancer of the pancreas.
Characteristic signs
At the initial stage, the symptoms of pancreatic hyperfunction are mild and are similar to other common diseases. In this regard, the disease progresses and remains unrecognized for a long time. The initial signs of the disease manifest themselves in general weakness and fatigue, constant drowsiness, and apathetic states.
Subsequently, periodic convulsions and loss of consciousness join them. As the disease progresses, the clinical picture worsens:
- Loss of orientation, especially in the morning after a night's sleep.
- Prolonged seizures, similar to epileptic ones.
- Neurovegetative disorders: pressure surges, increased sweating, cardiac arrhythmia.
- Severe psychomotor agitation, reminiscent of alcohol intoxication: incoherent speech and meaningless movements. A person loses control over his actions and actions.
- Impaired consciousness of varying degrees of severity, the most dangerous of which is coma.
Treatment
The primary task here is to normalize blood glucose levels, since this parameter greatly affects the activity of the entire body, especially brain productivity. Depending on the stage of the disease and the nature of its course, the following methods are used:
- If instrumental examinations show the presence of a tumor process, the neoplasm is removed surgically. If insulinoma is found, it is removed along with some fragments of gland tissue;
- In the event of an acute attack of hypoglycemia, the patient should be given an intravenous injection of glucose solution as soon as possible. The patient must be under constant medical supervision, and a blood glucose test is performed once an hour;
- If the patient has become worse in a chronic condition, he is advised to eat food and drinks rich in simple carbohydrates (sweet tea, chocolate, cookies, etc.);
- During routine therapy, the patient is prescribed drugs that suppress insulin production, such as Diazoxide, Octreotide, as well as medications that increase glucose - the most common of these are glucagon injections. If a patient, some period after the start of therapy, shows signs of enzyme deficiency (and this occurs due to an artificial reduction in the load on the gland, as a result of which it minimizes the production of both hormones and digestive enzymes), medications with enzymes may be prescribed.
It is advisable to recognize the hyperfunction of secretory activity in time, which is complicated by the fact that the early symptoms of the disease process have much in common with the usual signs of accumulating fatigue, among which the patient is often not aware of the problem. However, insulin hypersecretion is dangerous for the entire body. Sometimes it is associated with tumor phenomena. Therefore, this problem must be recognized as early as possible in order to provide the body with relevant therapy.