Author of the article: Victoria Stoyanova, category 2 doctor, head of the laboratory at the diagnostic and treatment center (2015–2016).
Article publication date: 01/13/2016
Article updated date: 12/02/2018
The reasons leading to pain in the right hip joint are no different from the causes of pain in the left joint. There are no specific, specific diseases that selectively affect the right hip joint.
The main pathologies that can occur with pain in the joint (both right and left):
- Injury.
- Coxarthrosis.
- Osteoporosis.
- Arthritis.
- Bursitis.
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
- Oncology.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease.
Injuries and coxarthrosis “prefer” right-sided localization, since for most people it is the right leg, as well as the right hand, that are the “leading workers”: a person primarily leans on his right leg when standing, a football player kicks the ball with his right foot, etc. With these ailments, right-sided lesions are more common (although localization on the left is quite possible).
Treatment of pain in the hip joint on the right is no different from that for left-sided localization: it is prescribed by a doctor (arthrologist, orthopedic traumatologist, neurologist, surgeon, oncologist or others), and the scope of measures is determined by the nature of the disease and its severity. With appropriate timely treatment, some ailments can be eliminated quite quickly, others can only be alleviated, removing the most painful symptoms.
Below we will talk about the nine most common causes of pain in the right hip joint, their characteristic symptoms and treatment methods.
Injury
Hip injuries often occur in athletes: football players, skiers, figure skaters
When people of any age complain of pain in the hip joint, it is first necessary to rule out injury. This could be simply a bruise of the soft tissues of the thigh or a much more serious condition - a fracture of the femoral neck in the right hip joint.
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Causes | Falling on your side, road accidents and other traumatic situations. |
| Symptoms | In addition to pain, external changes are characteristic - swelling, hematoma (bruise) over the joint area. With fractures of the femoral neck, there is an inability or severe pain when supporting the right leg, the inability to lift the leg from a lying position (symptom of “stuck heel”). |
| Treatment | Treatment is carried out by a traumatologist. In case of a bruise, it is enough to provide rest for 1-3 days; on the first day after the injury, it is recommended to apply cold and take painkillers (baralgin, ketorol, nurofen). For femoral neck fractures, immobilization is necessary - this is carried out by applying a plaster cast to the entire leg from the groin fold to the heel. Young people may undergo surgery to treat a fracture. Additionally, calcium supplements are prescribed to speed up bone healing, and painkillers are prescribed to relieve pain. The prognosis for a hip fracture depends on age: the older the patient, the harder and longer the bones heal. In elderly, weakened patients, the bone may not heal, and the function of the joint is irretrievably lost. In young people, the fracture heals and performance is restored. |
Pain in the hip joints: causes and treatment of coxarthrosis
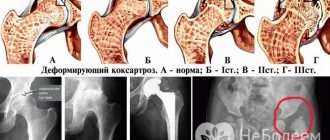
Coxarthrosis is characterized by destructive and degenerative processes in the tissues of the hip joints. The disease most often affects older people. With age, the cartilage tissue of the joint loses its elasticity, becomes thin, and begins to wear out. Increased loads on the joint cause the destruction of thin cartilage tissue, friction of the joint bones against each other and the development of the inflammatory process. The body's protective reaction leads to the appearance of outgrowths on the bone, which significantly limits the movement of the joint - deformation begins, which is accompanied by severe pain.
The reasons for the development of coxarthrosis, in addition to age-related changes, can be diabetes mellitus, trauma, congenital subluxation of the hip, flat feet, poor posture, long-term use of hormonal drugs, and purulent arthritis. Treatment of the disease depends on the severity of the joint damage; it can be medicinal, surgical, including endoprosthetics. If it is impossible to install an endoprosthesis, palliative treatment is used.
Coxarthrosis
Arthrosis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis) is a disease that occurs due to the destruction of articular cartilage with subsequent deformation of the femoral head. Coxarthrosis is the most common cause of pain in the right hip joint (not associated with trauma) in middle-aged and elderly people.
On the left is a healthy hip joint, on the right is coxarthrosis
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Causes | The reason is essentially a discrepancy between the load on the joint and its ability to withstand this load. Provoking factors: age-related changes, thinning of cartilage, excess weight, prolonged standing work, concomitant endocrine diseases. |
| Symptoms | Chronic pain in the hip joint on the right, worsening at the end of the working day and with changes in weather. Increasing lameness. In advanced cases, the inability to walk, lean on the leg, or make movements in the hip joint. |
| Treatment | Treatment is carried out by a traumatologist-orthopedist or arthrologist. They use therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy, and medications - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (nurofen, diclofenac, nimesulide), chondroprotectors (teraflex, artrum). If a joint is destroyed, crutches are needed to facilitate movement; joint replacement surgery (prosthetics) is indicated, but not many people can afford this expensive intervention. It is impossible to cure coxarthrosis, but it is quite possible to get rid of excruciating pain. |
Causes and nature of pain
Regardless of the intensity of pain, whether it occurs during movement or at rest, you need to go to the hospital. Some joint diseases in the initial stages do not manifest themselves as pronounced pain, but in the later stages they are difficult to treat.
Severe pain is often of traumatic origin. If pain in the hip joint is not caused by injury, then the cause may be infectious or inflammatory diseases. Pain syndrome occurs with the following diseases:
- osteoarthritis;
- arthritis, including infectious;
- osteoarthritis.
In degenerative-dystrophic processes, pain is not concentrated in the sacrum and hip joints, it spreads to the entire thigh and lower limbs, reaching the lower leg. Stiffness of movements appears.
Aching pain in the hip joint
The appearance of aching pain in the hip joint, which subsides while lying down, may be associated with fungal arthritis. Its peculiarity is that it is difficult to relieve with painkillers and is disturbing mainly during movement.
If the muscles of the hip joint begin to ache, this indicates damage to the nerve endings as a result of injuries or operations. Congenital abnormalities in the development of muscle fibers are also the cause. The pain is aching in nature and radiates to the groin and buttocks.
The tendon of the hip joint may hurt due to damage to the musculo-ligamentous apparatus. Nagging pain occurs when sprains, myositis, or muscle strain.
Hip pain on the right or left side
If the hip joint hurts only on the right or left side, then this most often indicates an injury to the articular joint.
Piriformis syndrome may also be a cause. The pain is caused by damage to the lumbar spine. The pain syndrome is acute and occurs after physical exertion or injury. The pain spreads to the back, buttocks and legs, and does not go away even at night. It hurts for a person to raise a straightened leg or bend forward, but there is no stiffness in the joint.
With bursitis, pain is most pronounced in a horizontal position, if you lie on the affected limb.
Hip pain at night
Night pain in the hip joint may indicate muscle atrophy due to necrosis of the femoral head. The pain syndrome manifests itself around the clock.
The cause of acute pain in the hip joint on the right or left can be piriformis syndrome. With this diagnosis, a person cannot find a comfortable position while sleeping.
The reason why the hip joint hurts at night is arthritis. The pain syndrome is most intense at 3-4 am, and stiffness appears after sleep.
Hip pain in women
The following diseases can cause pain in the hip joint in women:
- polymyalgia rheumatica;
- trochanteritis;
- femoral neck fracture.
Diseases that lead to pain in the hip joint in women occur during menopause.
Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause pain. This is an autoimmune disease that is difficult to cure. Symptoms of this hip disease in women are:
- morning stiffness;
- redness and swelling of the skin;
- the pain, which intensifies in the evening, radiates to the groin and buttocks.
Pain in the pelvis also occurs in pregnant women in the third trimester.
Hip pain in men
Pain in the hip joint in men is most often caused by aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. This disease is usually diagnosed in young men aged 20-45 years, as well as in older men. Predisposing factors:
- alcohol abuse;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- anemia;
- diseases of the circulatory system, which are manifested by blood clotting disorders;
- increased cholesterol levels;
- diabetes;
- obesity.
Acute unbearable pain in the hip joint
Burning pain indicates purulent arthritis. With this disease, the hip joint hurts, body temperature rises to 39-40˚C, headache and nausea appear. The damaged area turns red and swells. The pain is caused by the accumulation of purulent exudate. It is so strong that the patient cannot walk and does not stop even at rest.
The cause of acute pain in the hip joint, radiating to the groin, front of the thigh and lower back, can be aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. Pain syndrome can occur unexpectedly, without previous symptoms.
The pain in the hip joint is sharp. The patient cannot lean on the sore limb; even while sitting, he feels pain in the pelvis. The attack lasts for several days, and then the pain disappears. Over time, the pain syndrome recurs, but is accompanied by new manifestations, for example, lameness.
The cause of pain in the hip joint when getting out of bed or from a chair can be coxarthrosis. The pain syndrome is intense, but goes away with rest. It intensifies after physical activity, and problems with hip mobility appear. Pain in the hip joint appears when abducting the leg, trying to bring the knee to the chest, putting on shoes, or when lifting the limb. It extends to the front of the thigh and reaches the knee.
Arthrosis in most cases is associated with age-related changes, so it is more common in older patients.
If pain in the hip joints occurs after prolonged sitting or while walking, the cause may be trochanteritis (inflammation of the hip tendons). Soreness spreads along the outer surface of the thigh.
Unbearable pain may indicate benign or malignant cancer.
Constant pain in the hip joint
If the hip joint constantly hurts on the right or left side, then it could be sarcoma of the femoral neck, or bone cancer. The disease leads to destruction of the articular joints and fractures. Against the background of severe pain, symptoms of intoxication appear.
If the right or left hip joint constantly hurts, then it is worth examining for infectious arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis. If the lumbar spine is damaged, in particular the spinal cord roots, pain can be regular. Pain is felt in the hip joints and lower back.
Osteochondrosis and spondyloarthrosis also lead to pain that radiates to the thigh and buttocks. In addition to pain, numbness and tingling occur. The pain decreases at rest and increases with movement. The cause of pain can also be a herniated disc, muscle spasm, or injury.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic metabolic disease in which there is a decrease in bone density and an increase in their fragility.
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Causes | The reasons are varied - genetic factors, changes in endocrine levels (during illness, after menopause), lifestyle features (poor diet, bad habits), etc. |
| Symptoms | Aching pain in the joint, bones. Habitual, frequent fractures of the femoral neck and other locations with a relatively low force of exposure to the traumatic factor. |
| Treatment | Treatment is carried out by an orthopedic traumatologist together with an endocrinologist, therapist and doctors of other specializations. In case of completed fractures, the primary task is immobilization of the affected limb and pain relief. To prevent subsequent fractures and strengthen bones:
The disease is incurable, but with the right approach it is possible to prevent fractures. |
Hip pain: how to treat avascular necrosis
Aseptic necrosis most often affects men and is characterized by poor circulation in the area of the femoral head. The pathological condition leads to the death of bone cells and the functionality of the joint is impaired. The cause of this process can be: old injuries, alcohol intoxication, long-term use of hormonal drugs, treatment with radiation therapy, in some cases the cause cannot be determined. The first symptom of the disease is pain in the joint, then it can spread to the groin, anterior thigh, and lower back.
Over time, lameness appears and limb muscle atrophy begins. Treatment of the disease consists of restoring blood supply to the joint area, eliminating pain, restoring the normal state of the muscles of the limb, and maintaining the functionality of the joint. The patient is prescribed vitamins, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and additionally prescribed courses of physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy. It is recommended to wear orthopedic shoes and use additional support when moving.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
Osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine that begins with damage to the intervertebral disc and then affects other parts. When the roots of the spinal nerves are pinched, the so-called radicular syndrome occurs, one of the manifestations of which is back pain radiating to the leg (including the hip joint).
Osteocondritis of the spine. The two upper intervertebral discs are healthy, the two lower ones are damaged
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Causes | Very different. Provoking factors: age, excessive load on the lumbar region (prolonged standing, sitting), obesity, etc. |
| Symptoms | Back pain radiating (radiating) to the hip joint. Difficulty bending and turning the body. |
| Treatment | The treatment is complex, prescribed by a neurologist. Therapy includes exercises and lifestyle changes. Medicines include anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, nimesulide) in tablets and topically (creams, gels), chondroprotectors (structum, rumalon). Massage and physiotherapy courses are used. The disease is incurable, but with proper treatment, symptoms can be relieved. |
Treatment
Therapy should not be started until the cause can be found. In case of severe pain, the patient needs first aid. Painkillers such as Ibuprofen or Paracetamol can help relieve pain. It is important to provide rest to the sore limb and avoid any stress. When lying down, you should lean on your healthy leg.
Often, a splint or cast is applied to provide rest to the affected joint.
If the pain is caused by overexertion or excessive physical exertion, then thermal procedures that help relax the muscles are suitable. You can apply a warm (but not hot) heating pad to the source of pain or take a bath (water temperature up to 35 ˚C).
For arthritis, myositis, and bursitis, you cannot do without local non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They reduce pain and inflammation. Fastum or Voltaren gel is effective. Infectious forms of arthritis are treated with antibiotics. If pus has collected in the joint cavity, then the cavity is drained.
For arthrosis, NSAIDs will not be enough. You cannot do without chondroprotectors; in some cases, injections of hyaluronic acid and corticosteroid drugs are used. Muscle relaxants are effective for muscle spasms. Sirdalud and Mydocalm quickly relieve spasms.
To restore joint mobility and improve blood flow, you cannot do without manual therapy and physical therapy; exercises in water are useful.
Massage and exercise therapy are contraindicated during periods of exacerbation of arthritis.
In advanced stages of cocarthrosis, surgery cannot be avoided. The destroyed parts of the joint are replaced with prostheses. If the operation is not performed, the person will remain disabled. Oncological formations also require surgical intervention.
Quite a long and complex treatment of necrosis of the femoral head. Unfortunately, it is impossible to cure the disease. The goal of therapy is to prolong remission. If conservative methods are ineffective, then surgery is performed to remove dead tissue and replace it with healthy ones. If the damage is severe, the joint is replaced with a prosthesis.
Oncological diseases
Tumors may appear in the right hip joint, or tumors from neighboring areas metastasize (relatively speaking, “multiply”) there (with cancer of the uterus, ovaries, and colon).
Various localizations of cancer
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Causes | Diverse and not fully explored. The main role is played by exposure to carcinogens (from food, the environment, tobacco smoke) and genetic predisposition. |
| Symptoms | Severe chronic pain that does not respond well to medications. Cancer cachexia (exhaustion, nausea, decreased or complete lack of appetite). |
| Treatment | Treatment is carried out by oncologists, choosing a method depending on the form of cancer, the presence of metastases, the age of the patient and other factors. It is possible to radically remove the tumor surgically with replacement of the joint with an endoprosthesis, or the use of radiation therapy and chemotherapy. The prognosis depends on the stage of the tumor and its type. |
Diagnosis of joint diseases
Inflammatory processes of the joints in the pelvic area have different etiologies. To diagnose the causes that influenced the occurrence of inflammation, the following methods are used:
- Examination by highly specialized doctors: therapist, neurologist, cardiologist and others for a general examination of the patient;
- Clinical tests of blood and urine to determine indicators in terms of identifying markers of the inflammatory process, which allows us to determine the type and nature of the disease;
- CT scan. The examination method is similar to radiography, but shows advanced equipment and a more detailed image of the diseased joint. Used when it is not possible to conduct an MRI.;
- ECG, electrocardiogram. Instrumental method for determining heart function;
- MRI, magnetic resonance imaging. Allows you to identify deviations from the norm in the condition of soft tissues thanks to a clear picture of the internal structure of the body. It is carried out using a specialized device - a tomograph. Effective in identifying the disease at an early stage of development;
- Ultrasound, ultrasound examination. An examination based on images of the internal structure of the body using ultrasonic waves that generate a picture in real time. Provides an opportunity to track the state of the organs being studied over time.
A comprehensive examination of the body will allow the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and begin timely treatment of the hip joint when the first signs of inflammatory or metabolic-dystrophic processes appear.
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is a purulent process in the bone and adjacent tissues.
The process of development of osteomyelitis in bone
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Causes | The introduction of infection with blood, lymph, in case of injury with damage to soft tissues, less often - as a complication of surgical interventions. |
| Symptoms | General, usually severe intoxication (high fever, severe weakness, headaches, vomiting), pain in the leg and hip joint, impaired motor function. Swelling, redness of the soft tissues over the area of suppuration. |
| Treatment | Treatment is carried out by surgeons in a hospital. Powerful antibiotic therapy is prescribed (2-3 antibacterial drugs are administered intravenously, intramuscularly), detoxification (intravenous administration of glucose-saline solutions), vitamins, immobilization of the limb with a plaster cast, and in some cases, surgical treatment. The effect of therapy depends on the time of treatment; in most cases, the disease is completely cured. |
Diagnostics
If pain occurs in the legs, lower back and tailbone, a thorough diagnosis is required.
The following research methods can be used:
- Ultrasound and x-rays are used for any disease of the hip joint.
- General and biochemical blood tests allow you to assess the condition of the body and determine the presence of rheumatological diseases.
- Urine examination. This determines transparency, density and color.
- Computed tomography displays bone tissue, joint and its density in several projections.
- Osteoscintigraphy is performed by administering osteotropic radiopharmaceuticals. At the same time, the state of metabolic processes and blood flow is visualized.
- Dopplerography is an examination of vascular patency.
Patients are also examined and interviewed. At the same time, attention is paid to joint mobility and accompanying symptoms, such as headache, swelling and local hyperemia.
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, bone destruction not associated with infection, primarily affects children and adolescents.
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Causes | Unknown. |
| Symptoms | Pain in the leg and joint, lameness. |
| Treatment | Children are sent to sanatoriums for treatment. It is necessary to unload the joint (bed rest, walking with crutches). Medications include drugs that improve microcirculation (no-spa), antiplatelet agents (trental), and multivitamins. Carry out therapeutic exercises. The treatment process is long, but usually the disease can be completely eliminated. |
Symptoms of hip diseases
Characteristic symptoms of inflammatory processes in the hip region at different stages of the disease manifest themselves in a similar way:
- pain in the groin area spreading along the lower extremities to the feet;
- decreased mobility of limbs prone to pain;
- crunching sounds while walking and other physical activity;
- shortening of one leg compared to the other;
- lameness, pain in the knee, loss of sensation in the thigh muscles;
- pain from mild to intense;
- reduction and disappearance of pain after movement;
- increased pain after physical activity;
- increased temperature, swelling, redness, swelling in sore areas of the body;
- localization of pain in the buttocks or thighs on the outside with impact in the knees;
- muscle tightness in the thigh area, especially in the morning.
The listed symptoms, which appear during a normal lifestyle, are a signal to consult a doctor. It is much easier to treat diseases at an early stage with non-surgical methods, allowing you to prevent serious complications associated with the complete loss of joint mobility.
Seeing a doctor
Folk remedies
In folk medicine, there are many successful methods for treating coxarthrosis:
- Tinctures and decoctions used internally (there are many recipes for the preparation of medicinal folk medicines, which include garlic, lemons, mumiyo, various parts of plants, honey, etc.);
- Ointments based on various natural ingredients (ointments from celandine, eucalyptus oil, aloe and other plants);
- Compresses and baths (application of cabbage leaves, baths with Jerusalem artichoke, etc.).
When using all folk remedies, it is necessary to remember that there is no guarantee of 100% recovery.
Orthopedic devices and physical therapy
Treatment for diseases of the hip joint includes the use of orthopedic products. Most often they are used after injuries, when complete or partial immobilization is needed for several weeks or even months. Thus, for fractures, a rigid fixation orthosis is used, which, unlike plaster, does not cause irritation and allergies.
If a person has to lie down for a long time, he definitely needs an anti-bedsore mattress. During rehabilitation after an injury, walkers, canes, and crutches are used for support. With symphysitis, pregnant women are recommended to wear a pelvic corset with rigid ribs. It is equally important during treatment and for prevention to wear orthopedic shoes that relieve the load on the foot.
Physiotherapy is also indicated to improve the condition of the hip joint. This treatment eliminates symptoms, relieves pain, and optimizes blood circulation. During course therapy, inflammation decreases, swelling goes away, and the process of tissue repair begins. Laser therapy has proven itself best - laser beams heat tissue up to 10 cm thick, quickly relieve pain, and relieve inflammation.
Other physiotherapy techniques used are:
- electrophoresis;
- darsonval;
- magnetic therapy;
- shock wave therapy;
- balneotherapy;
- microcurrents;
- turpentine baths.
It is also recommended to regularly use the Kuznetsov applicator at home - it increases blood circulation and helps reduce pain. In the acute stage of the disease, it is used for 5 minutes up to 5 times a day; in the chronic stage, the time is increased to 20 minutes three times a day.
Video gymnastics for arthrosis of the hip joint
Exercises to combat and prevent coxarthrosis should be carried out carefully. Movements during exercise therapy should be smooth and not cause pain. Exercise therapy for the treatment of an illness should be aimed mainly at strengthening the muscles themselves and not loading the joints. A good way to prevent coxarthrosis is swimming, especially in salt water.
- starting position: lie on the floor, stretch your arms and legs along your body. Slowly raise the sore leg, straightened at the knee joint, 15 cm from the floor and hold it for about half a minute. After this, lower your leg and repeat the exercise with the other leg;
- starting position: lie on your stomach, stretch your legs and arms along your body. Raise your straight legs 15 cm up, bring them together, and then spread them apart. Everything should be done slowly.
The patient should remember that some exercises for arthrosis of the hip joint from exercise therapy may be difficult for him due to his physical fitness. They are quite effective methods of preventing various ailments, therefore they are included in the exercise therapy system both for arthrosis and for other diseases.
Perthes disease
Perthes disease of the hip should also be considered. It is worth noting that this disease most often affects children aged 3 to 12 years. At the same time, boys are more likely to get it. However, in girls the course of the disease is more serious.
What is Perthes disease of the hip joint? So, this is a special pathological process when normal blood circulation in the femoral head is disrupted, which causes a problem such as necrosis. It is important to note that there are both unilateral and bilateral damage.
Today, doctors have not yet come to a common conclusion about what the main cause of this disease is. The stages of Perthes disease are as follows:
- After the normal blood supply to the femoral head begins to cease, tissue necrosis develops.
- Secondary fracture of the bone head in the area of destruction.
- Necrotic tissue gradually resolves. This leads to shortening of the femoral neck.
- Connective tissue grows at the site of necrosis.
- Connective tissue is gradually replaced by bone.
The recovery process in this case depends on the advanced stage of the disease. If treatment is started in time, full recovery is possible. Otherwise, the head may fall apart into several parts, which often leads to its incorrect, deformed fusion.
They will talk about what Perthes disease of the hip joint looks like, photos. It is enough to look at the pictures of sick children to understand that this disease also causes changes in appearance (i.e., there may be lameness and shortening of the limb itself). This disease is also accompanied by pain. At first it will be dull and will begin to appear while walking. There may be a slight limp or falling on the affected leg. No other clinical symptoms are observed. This is the whole danger, because people rarely turn to an orthopedist with such complaints. If a compression fracture occurs, the pain intensifies significantly, lameness already manifests itself sharply, it is clearly noticeable to others. There is limited movement, walking becomes difficult. Body temperature may rise to low-grade levels.
The disease is diagnosed using radiography. Treatment takes place in the orthopedics department, then on an outpatient basis. Duration of conservative therapy: approximately 12-14 months. Surgery may be indicated only in the most severe cases.
In the end, it is worth noting that if various diseases of the hip joints in children are considered, we are most often talking about this particular disease.
Pain treatment
Once the exact cause of the pain is discovered, appropriate treatment must be started immediately. For this, complex therapy is used. Its components are:
- Drug treatment. To alleviate the condition, medications are used to eliminate inflammation and pain. For these purposes, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets or warming ointments. Examples of such drugs: Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Ibufen, Voltaren, etc. In severe forms of joint diseases, steroid drugs and chondroprotectors should be used.
- Physiotherapy. These procedures help improve the condition of the affected joint by warming it up and improving local blood circulation. For this purpose, the following physiotherapy procedures are used: electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, phonophoresis, UHF, massage, physical therapy.
- Surgical intervention. If degenerative-dystrophic changes in the hip joint occur (they are usually observed in advanced stages of joint diseases), then the attending physician recommends surgical intervention. Its essence is to replace the affected areas with prostheses.
Prevention
In order to prevent diseases of the hip joint, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of injury. It is necessary to take vitamins, eat right, and maintain weight within normal limits. Do not forget that this joint bears the weight of the upper body, so obesity is fraught with injury to the joint.
Women during menopause should monitor their hormonal levels, take vitamin complexes, and chondroprotectors. This will avoid joint problems.
Hip pain can indicate various diseases. It doesn’t matter whether they are aching or acute, treatment should be started as early as possible.
Arthrosis
Initially, you need to talk about such a problem as the disease “coxarthrosis of the hip joint”. In ordinary language, in everyday life this disease is simply called arthrosis. It is important to note here that this particular disease ranks first among various problems of the human musculoskeletal system.
This disease begins from damage to the articular cartilage. It gradually fragments and depletes, which leads to the loss of its shock-absorbing properties. In this case, the bone of the joint is also affected, and bone growths may appear. Other problems that may also arise due to coxarthrosis:
- formation of cysts in the head of the femoral bone;
- cysts can also form in the tissues of the acetabulum, where the head of the bone is located;
- Sclerosis of the plates of the joint surfaces often occurs.
Very often the cause of the development of this disease is a disease such as dysplasia (of course, of the hip joint). This is underdevelopment of bone tissue, as well as a difference in the size of the acetabulum and head. In this case, insufficient blood supply occurs, which causes a problem such as arthrosis.
Among the causes of the development of the disease, doctors identify various injuries and bruises. If we are talking about microtraumas, then their regularity can also cause the development of this problem. And, of course, it is especially important to treat various inflammatory processes in a timely manner. After all, they can also turn into arthrosis.
Endoprosthetics
The third stage of the disease can only be treated surgically. The patient is recommended to undergo joint replacement surgery, or endoprosthetics. The surgeon cuts off the head of the femoral bone and inserts a metal pin into the cut, onto which the artificial head is attached.
The prosthesis itself can be unipolar (replacement of only the head) and total (replacement of both components). Already on the next day after the operation, some elements of exercise therapy are performed while lying in bed; the patient can stand up, but for now without supporting the leg; after a few days - on crutches. After 2-3 months, crutches will no longer be needed and full weight bearing on the leg will be allowed.
Patients who have undergone endoprosthetics are recommended to undergo rehabilitation consisting of physical therapy, massage, and physical therapy. In most cases, limb function is restored. The service life of the prosthesis is from 10 to 20 years, then it is replaced with a new one.
Tactics of drug treatment
Drug treatment is aimed at improving the patient’s well-being. For this purpose, drugs of various clinical and pharmacological groups are used:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Nimesulide, Ketoprofen, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam, Indomethacin, Ketorolac. Injection solutions are used to relieve acute pain, and tablets, dragees, ointments, and gels help eliminate pain of mild or moderate severity;
- glucocorticosteroids - Triamcinolone, Diprospan, Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone, Flosterone. They are used in the form of intra-articular blockades in combination with the anesthetics Novocaine, Lidocaine;
- muscle relaxants - Mydocalm, Baklosan, Sirdalud. Included in treatment regimens for spasms of skeletal muscles, pinching of sensitive nerve endings;
- drugs that improve blood circulation in the joint - Nicotinic acid, Eufillin, Pentoxifylline. Prescribed to patients to improve tissue trophism and prevent disease progression;
- chondroprotectors - Teraflex, Structum, Artra, Dona, Alflutop. Effective only at stages 1 and 2 of arthrosis.
Rubbing in ointments with a warming effect (Viprosal, Apizartron, Finalgon, Dikul balms) helps eliminate mild pain. The active ingredients of external agents are capsaicin, cinquefoil
, camphor, menthol. These substances are characterized by a locally irritating, distracting, analgesic effect. Compresses on the joints with Dimexide, bischofite, and medical bile will help you cope with puffiness and morning swelling of the thigh. Patients are recommended classic, acupressure or vacuum massage for coxarthrosis. An excellent prevention of further progression of arthrosis is daily physical therapy exercises.
Treatment with gymnastics
Performing a complex of therapeutic exercises, individually developed by a competent specialist for a specific patient, will help increase the range of movements in the problem area, improve the functions of the TB department, and correct muscle balance. Special physical training in an adequate mode will allow you to competently relieve the sore area of the musculoskeletal system, reduce the severity, duration and frequency of pain, increase vitality and generally improve well-being.
Exercise therapy courses should be conducted in a rehabilitation gym under the supervision of medical personnel regarding the recovery of patients with musculoskeletal disorders. In any case, until the person perfectly masters the techniques of rehabilitation exercises recommended by the doctor. Patients are recommended to have at least a certain range of aerobic training with and without machines, but with the exception of force loads on the affected joints. Loads are selected strictly taking into account the main diagnosis, concomitant diseases, weight and age of the patient, and his physical capabilities.
Activities organized in the pool - therapeutic aqua gymnastics, swimming - provide invaluable benefits. Measured walking and gentle exercise on an exercise bike are encouraged.
Bursitis
Another disease that also needs to be considered is hip bursitis. In this case, we are talking about an inflammatory process in the synovial bursa, the main task of which is to prevent friction.
Let us further consider such a part of the human body as the hip joint. Symptoms of the disease with bursitis are as follows:
- Pain. It can be sharp, intense, burning. Localization: most often it is the outer part of the thigh.
- As the problem progresses, the pain may become dull. However, its area of distribution is increasing.
- Pain increases during hip flexion and extension. It may also be painful for a person to lie on their side on the affected side.
- With purulent bursitis, the pain is so severe that it makes it impossible to even move normally.
The main diagnostic methods: examination of the patient, palpation, listening to complaints. To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is sent for an X-ray or MRI. Mostly treatment is conservative. In rare cases, when the disease is advanced, surgical intervention may be required.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
The hip joint is a large, articulated synovial joint, which is called the most powerful because it bears a greater range of loads. It is formed by the spherical head of the femur and the cup-shaped cavity of the pelvic bone (acetabulum), the surfaces of which are covered with smooth hyaline cartilage. Together they represent a hinge, where their musculoskeletal contact interaction occurs.
Every day, this unique mechanism performs the most important functions, which include maintaining the weight and position of the body in an upright state (standing, sitting), ensuring motor activity during movement (walking, running, jumping, etc.), and moving parts of the body relative to each other.
The forces passing through the hip joint apparatus are quite significant. For example, in the usual position of “standing on two lower limbs” the joint experiences a load of 1/3 of a person’s weight, while standing on one limb - 2.5 times higher than the body weight, when walking and running - a load of 2-6 times exceeds the person's original weight. Experts definitely attribute the fact of significant loads to one of the explanations for the high susceptibility of the joint to destabilization and wear, and, consequently, to the development of osteoarthritis. However, to say that the cause of the disease is the natural functional physiology of the joint is fundamentally incorrect; without an aggravating factor, the pathological process is impossible.
And another important point: for the hip joint to function well, it must have a sufficient range of movements with very good stability. And this, in turn, is possible provided there are strong ligamentous muscle groups that control movement and support functions in the joint, as well as a strong articular capsule that protects and holds the bone joint. The depth of insertion of the spherical element of the femur into the acetabular bed of the pelvis also plays a huge role. Failure of the designated structures and/or incorrect anatomical parameters can clearly lead to degeneration of the articular surfaces.
This is what the joint cavity looks like through an arthroscope.
All of the above is general introductory information, it is also important to know and understand. Of course, we will not leave readers without an answer to the burning question: what specific reasons cause such a complex diagnosis? Experts name the following root causes that most often lead to osteoarthritis of the hip joints:
- genetic defects in the development of the hip joint, characterized by congenital disorders of the development and growth of bone, cartilage, ligamentous, and muscle structures of the joint (dysplasia);
- old age, since against the background of age-related changes, cartilage hydration, muscle elasticity, blood circulation in joints, etc. decrease;
- systemic pathologies, where osteoarthritis is one of the consequences (gout, rheumatism, collagenosis, diabetes, complex types of allergies, etc.);
- various chondropathy leading to modifications of bone structures related to the joint;
- chronic arthritis (long-term inflammatory phenomena in the joint due to infection, autoimmune and metabolic disorders);
- avascular osteonecrosis of the femoral head (death of bone tissue) as a consequence of local circulatory disorders of traumatic or non-traumatic origin;
- hormonal imbalance, especially in women during menopause, when the level of estrogen, which protects joints, sharply decreases;
- obesity of any stage (excess weight is the worst enemy, since it significantly increases the load on the TB department and on the limbs in general);
- previous injuries localized to the pelvis and femur (fractures, dislocations, bruises, etc.), as well as a history of surgical manipulations on the hip region;
- orthopedic disorders, in particular valgus and varus deformities of the limbs, flat feet, spinal curvatures;
- a sedentary lifestyle, which causes a deficiency of muscle mass, ligament laxity, poor blood supply and limited supply of nutrients to the hip joint, which contributes to the onset and progression of osteoarthritis;
- constant overload of the hip region and lower extremities due to intense sports training, performing work while standing with heavy lifting, long monotonous poses (especially in static positions “standing” in one place, “sitting”), long walking forced by the nature of the activity.
It is impossible not to ignore the fact that smoking and alcohol abuse also have an adverse effect on the condition of the joint. Toxic products of nicotine and alcohol lead to a critical disruption of blood circulation around the musculoskeletal organ, to depletion and irreversible death of osteochondral tissues.
ethnoscience
Treatment with folk remedies is effective only in the initial stages. Ointments, compresses and tinctures are used to relieve pain. Medicines are prepared based on flowers and herbs (valerian, cinquefoil, lilac). Bile, honey and propolis are added from natural ingredients. For thermal effects, compositions with pepper and turpentine are used.
Important!
Traditional recipes should not be used on young children and pregnant women. A possible allergic reaction may have negative consequences.