From this article you will learn: for what reasons pain appears in the elbow joint on the inside of the arm. Symptoms, treatment and prognosis for pathologies that cause such a symptom.
Author of the article: Victoria Stoyanova, category 2 doctor, head of the laboratory at the diagnostic and treatment center (2015–2016).
Article publication date: 06/17/2019
Article updated date: November 29, 2019
Why does my right or left elbow joint hurt on the inside? Such a symptom is rarely isolated (pain at a certain point without other manifestations), and most often it indicates pathological processes or damage to the anatomical structures of the limb.
Pain in the elbow on the inside can occur with:
- tendinitis;
- myositis;
- injuries;
- medial epicondylitis;
- arthrosis;
- tunnel syndrome;
- tumors in the elbow joint.
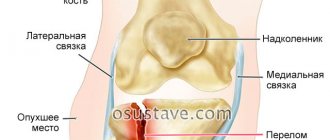
1 – medial epicondylitis;
2 – dislocation of the elbow joint; 3 – cubital tunnel syndrome; 4 – arthrosis of the elbow joint The first positions in the risk group are firmly occupied by young and middle-aged people (from 20 to 40 years):
- athletes - tennis players, golfers, football players;
- people whose profession involves performing monotonous movements - pianists, programmers;
- people in difficult, traumatic professions - masons, plasterers, miners.
The exception is degenerative changes in the structure of cartilage and joint destruction or arthrosis. This disease most often affects older people (after 65 years).
All pathologies or injuries that cause pain on the inner surface of the elbow are dangerous in their own way and can provoke the development of various disorders of the elbow or limb. Some of them are relatively easy to treat, some are more difficult, but you can relieve pain and improve your condition with the help of competent therapy in any situation.
If a symptom appears, you should consult a general practitioner, who will refer you to a specialized specialist. Arthritis is treated by a rheumatologist, arthrosis by an orthopedic surgeon, injuries and injuries by a traumatologist.
Tendinitis
Tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendons that attach muscles to the bones of the skeleton. The pathology is usually diagnosed in people engaged in heavy and monotonous physical labor and in athletes.
Causes:
- Exercise stress.
- Repetitive movements.
- Damage.
- Natural aging of fabrics.
- Infections, metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus).
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatic arthritis).
Symptoms: Pain in the elbow joint on the inside causes inflammation of the biceps tendon.
Biceps tendonitis
Symptoms increase gradually:
- At first, aching pain occurs at the peak of the load and subsides with rest;
- then bothers you with normal movements;
- intensifies to a burning sensation, intense when bending the elbow, straining the biceps and pressing on the tendon;
- spreads along the tendon, capturing the anterior surface of the forearm;
- Swelling and redness may appear in the area where the tendon attaches.
Characteristic diagnostic signs are cracking of the tendons during movements, absence of pain when bending a limb with the other hand.
Prognosis: with early treatment, it is completely cured in 80–90% of cases. Over time, chronic tendonitis can be complicated by thinning and rupture of tendon fibers, lead to improper fusion and ossification of tissue (contracture, ankylosis), and limit the range of active movements in the elbow.
Characteristics and types of pain
Often, pain in the limbs can be caused by reasons hidden in other parts of the body. Therefore, self-medication in order to eliminate them can lead to negative consequences . In this case, you may even miss the onset of a serious illness. It is important to listen to the body and distinguish between the types of pain and their nature.
Strong pain
It is characteristic of arthritis and bursitis . This may occur suddenly and intensify with wind and cold.
Hand movements can also cause and worsen pain.
In addition, severe pain is typical for fractures.
It's a dull pain
It can be caused by inflammatory processes in the body and salt deposits in the joints. It may be worse at night and lessen at rest. Often this pain intensifies when coughing or sneezing, and sometimes it is accompanied by fever.
Nagging pain
It happens with inflammation of the joints that occurs due to a cold or in humid weather. In this case, muscle twitching and stiffness of the limb may occur. Relief may occur with warming and slight movements of the elbow. In addition, such pain can occur due to a fall, which can pinch a nerve, which requires examination by a doctor.
Burning pain in the elbow joint
A burning, unbearable pain in the elbow is characteristic of gout. At the same time, it intensifies with movement, in the cold wind, in the evening and at night, as well as in a lying position on the sore side. Sometimes accompanied by fever or redness of the skin in the painful area.
Constant pain
Painful sensations become constant if you do not pay attention to them in time. Usually at first they are not so pronounced, but over time they become permanent.
May be accompanied by swelling and redness of the elbow area , and also signal the presence of some disease in the joints.
Pain during flexion and extension
This pain can occur mainly due to injury. A person can hit himself on public transport, get injured during training, during sports, and in everyday life. In this case, pain during extension and flexion is very pronounced, and in some cases is accompanied by swelling and redness of the periarticular tissues.
IMPORTANT. Sometimes such pain can occur due to repetitive occupational activities. Often, pain during extension or flexion can be a signal of the presence of a serious pathology, such as arthrosis, therefore, for any type of pain, consultation with a doctor is required.
Pain when pressing on the elbow
If pain occurs when you press on your elbow, you should fix it for a while before contacting a doctor. Such pain can also occur due to injury, bruise or due to heavy lifting. In this case, pinching of the nerve ending can occur, which leads to unpleasant sensations in the elbow. In addition, such pain may occur due to sprained ligaments or tendons, which requires contacting a traumatologist.
Pain during physical activity (lifting heavy objects)
Pain during exercise is usually a sign of arthrosis or chondrocalcinosis. Sometimes it is accompanied by a crunching sound and intensifies with movement. In advanced cases, the arm remains half-bent. In addition, such pain is typical for people who perform constant mechanical actions due to their profession.
Additional symptoms
Bruising and crunching in the elbow joint are characteristic of a fracture. At the same time, it becomes more difficult to move the hand, sometimes it becomes completely motionless.
Crunching also occurs with arthrosis. At the same time, it becomes more difficult to straighten and bend the arm at the elbow, and the temperature may rise.
Sometimes patients may complain of numbness or decreased sensation in the limb. This occurs due to compression of certain nerve endings in the structure of the elbow joint. This phenomenon can occur after exercising or lifting weights.
Read the articles -
Medial epicondylitis
Inflammation of the tendon in the area of muscle attachment to the internal epicondyle (protrusion) of the humerus.
Medial epicondylitis is inflammation of the flexor and pronator tendons at the site of their attachment to the internal protrusion of the humerus (on the inside of the elbow).
A rarer form than lateral epicondylitis (10 times). It is diagnosed mainly in people engaged in monotonous sedentary work (programmers). In the left elbow, inflammation occurs 2 times less often than in the right.
Causes: overexertion, strain on the forearm muscles.
Symptoms:
- medial epicondylitis develops gradually;
- in the initial stages, discomfort or aching pain appears in the area of the elbow joint on the inside;
- symptoms intensify with load, flexion of the hand, pressure on the epicondyle area and subside with rest;
- Over time, pain appears with any basic movements.
Joint mobility is maintained.
Prognosis: in 90% of cases it is cured without a trace. Occasionally, after treatment, slight muscle weakness persists, which does not affect the person’s quality of life.
Treatment of the joint
Which doctor should I contact if such ailment occurs? First you need to visit a therapist. He will conduct a survey and a detailed examination of the patient, palpating the affected area. After this, the patient is sent for hardware studies, such as ultrasound diagnostics, magnetic resonance imaging, x-ray, arthroscopy. Based on the research, the therapist prescribes treatment together with a rheumatologist or traumatologist.
Treatment largely depends on the cause of the discomfort. The basis for it is the elimination of pain and inflammatory processes. For this, the following groups of drugs are used:
- analgesics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- in advanced cases - glucocorticosteroids;
- when cartilage tissue is destroyed - chondroprotectors.
Also, comprehensive treatment of the elbow includes physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy, and massage. The dynamics of recovery should be monitored by the attending physician, who should be visited regularly for examinations during the treatment period.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Cubital tunnel syndrome occurs as a result of damage or compression of the nerves that run through the elbow. The appearance of pain in the elbow joint on the inside causes compression of the musculocutaneous nerve at the level of the elbow bend.
Compression of the ulnar nerve in the cubital canal. Click on photo to enlarge
| Causes | Symptoms |
| Damage, injuries | Pain localized on the inside of the elbow joint and forearm, intensifies when extending the elbow and rotating the arm |
| Exercise (tennis, swimming, heavy physical work) | Numbness of the anterior forearm |
| Diseases (arthritis, arthrosis) | Limited mobility of the elbow (it cannot be fully extended) |
In 50% of patients, the pathology occurs with severe symptoms (burning pain, severe numbness).
Prognosis: with timely treatment, it is completely cured in 70% of cases. If the causes of compression cannot be eliminated, it can lead to persistent disorders of blood circulation, limb function, muscle atrophy (loss of strength and volume) and other unpleasant consequences.
Elbow pain
Elbow joint
formed by the articulation of the humerus, radius and ulna. The articular surfaces of the bones are covered with hyaline cartilage, which promotes soft and smooth movements in the joint. The elbow joint is a complex part of the body, since three smaller joints can be distinguished in its cavity: radioulnar, humeroulnar and brachioradialis.
Diagnosis of various diseases of the elbow joint usually does not cause difficulties for specialists. This is due to the fact that the elbow joint is well accessible for examination and various diagnostic procedures.
Elbow pain can occur for many reasons. A thorough clinical examination to confirm the diagnosis can be supplemented by a variety of functional tests. Particular attention should be paid to the position of the elbow. With joint effusion, thickening of the synovium and degenerative joint diseases, the arm will be slightly bent at the elbow.
Diseases and causes that cause pain in the elbow joint:
1.
Osteochondrosis
, inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout, chondrocalcinosis, tumors, tendonitis and osteoarthritis are the most common causes of pain in the elbow joint. However, compression syndromes such as cubital tunnel syndrome can also occur in the elbow joint due to osteophytes narrowing the ulnar nerve groove.
2.
One of the most common causes of elbow pain is
lateral epicondylitis
or tennis elbow. Less common is medial epicondylitis, also called golfer's elbow.
In addition to local pain upon palpation, typical signs include the occurrence of pain in the corresponding area of the elbow during passive movements: extension - “tennis elbow”, or when bending the hand - “golfer’s elbow”, as well as pain from muscle tension.
Specific tests help distinguish symptoms of epicondyle pathology from symptoms associated with other diseases.
3. External epicondylitis (“tennis elbow”)
Attached to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus are the muscles involved in wrist extension—the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis (the clenched fist muscles) and the brachioradialis muscle. Inflammation of the tendons of these muscles where they attach to the bone is called lateral epicondylitis. The muscles are weak flexors of the forearm, so if they are damaged, the function of the elbow joint is practically not affected.
This pathology usually affects people over 35 years of age. The appearance of pain in the elbow joint is preceded by an unusual load - working in the garden, playing sports after a long break, etc. The patient accurately indicates the place of greatest pain, corresponding to the external epicondyle of the humerus. Pain may radiate down the outer surface of the forearm to the hand. The pain is easily reproduced by resistance to active extension of the wrist joint.
4. Internal epicondylitis (“golfer’s elbow”)
The tendons of the muscles attached to the medial epicondyle are affected - the pronator teres, the ulnar and radial flexors of the hand, and the long palmaris muscle. Medial epicondylitis is less common than external epicondylitis. Palpation pain is detected at the site of muscle attachment. Pain may radiate along the ulnar surface of the forearm to the hand.
5. Olecranon bursitis
The superficial bursa of the olecranon process is located above the eminence of the olecranon process, and does not communicate with the cavity of the elbow joint. Inflammation of the bursa occurs in isolation as a consequence of chronic injury to the posterior-inferior surface of the elbow (in car drivers resting their elbow on the door), or in combination with arthritis due to gout and RA. In the area of the olecranon, a low-painful round formation the size of a chicken egg with a soft consistency appears. It becomes clearly visible when the arm is extended at the elbow joint. With isolated bursitis, the function of the elbow joint is not noticeably affected.
Other causes of elbow pain:
1. Lesions of one elbow joint are often observed in hemophilia and Charcot neurotrophic arthropathy
. Monoarthritis of the elbow joint, as well as deforming arthrosis, are rare.
2. The cause of “articular blockades” may be osteochondritis dissecans of the epiphysis of the humerus or synovial chondromatosis
. In these diseases, “articular mice” are often found in the cavity of the elbow joint.
3. Limited mobility of the elbow joint, in the absence of visible changes, can be caused by diffuse fasciitis. With this pathology, the skin on the inner surface of the forearms and shoulders becomes like an orange peel, it cannot be folded, and an absolutely painless lump can be felt underneath it.
4. Pain in the elbow joint can also be referred. It may be caused by pinched nerve roots
for osteochondrosis of the spine or intervertebral hernias localized in the C5 - C6 and ThI - ThII segments. With this pathology, there is a violation of flexion in the elbow joint, disorders of skin sensitivity on the surface of the forearm, and the possible development of atrophy of the biceps muscle.
5. Elbow injuries
. Most often, posterior dislocations of the elbow joint are observed, less often - anterior and lateral ones. Dislocations can be combined with fractures of the bones that make up the elbow joint, as well as with tendon separation. Mechanism of injury: fall on the hand, sports, industrial, automobile injuries.
With a posterior dislocation, the elbow joint is deformed
, the forearm is shortened, the protruding olecranon process is visible. I am worried about severe pain, movements in the joint are severely limited. When attempting to extend the joint, spring resistance is detected.
With anterior dislocation
the forearm is elongated compared to the healthy limb, and retraction is detected in the area of the olecranon. With lateral dislocations, the forearm is displaced inward or outward. With anterior and lateral dislocations, there is often damage to the ulnar or median nerve with loss of sensation in the hand.
When a tendon ruptures, the biceps brachii muscle most often suffers; sometimes the tendons of several muscles can be torn off. In this case, the function of active movements of the upper limb is impaired, the strength of flexion in the elbow joint is reduced, asymmetry in the shape of the muscles occurs compared to the uninjured limb, and swelling and pain are noted.
HOW TIBETAN MEDICINE ELIMINATES ELBOW JOINT PAIN
Tibetan medicine has truly vast experience in treating diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which dates back thousands of years. Tibetan doctors consider lifestyle and nutrition correction to be one of the main principles of treatment. That is, a person should avoid hypothermia, wear clothes appropriate for the season, keep the body (hand) warm, and not carry out hardening procedures (dousing with water). Food should be warm (hot); cold food and drink should be excluded from the diet. Doctors of Tibetan medicine also pay attention to the psycho-emotional state of a patient with a similar illness. Disruption of the functions of the nervous system (“wind”), affecting the entire body, “hits” the most vulnerable and weak points of a person. Therefore, such warming procedures as moxotherapy (warming with wormwood cigars), the Mongolian method of oil-herbal massage “Khorme” have a sedative effect on the nervous system, coupled with the doctor’s conversations and his recommendations.
What do doctors at the Naran Tibetan Medicine Clinic do first:
- Diagnosis is carried out by questioning, examination, pulse diagnostics, palpation
- Based on the combined data of oriental diagnostic techniques, the exact cause of pain
- Relieve pain in one or two sessions using proven acupuncture
- They begin treatment by combining several methods, taking into account the characteristics of the disease that caused a similar symptom.
RESULTS OF TREATMENT AT THE NARAN CLINIC
- Pain relief
- Restoring mobility of the elbow joint
- Improving blood and lymph circulation and nutrition in cartilage tissue
- Improving the conduction of nerve impulses
- Elimination of general and local stagnation of energy flows
- Boosting immunity
- Normalization of metabolism
- Elimination of muscle spasms
The Naran Clinic celebrates its 30th anniversary in 2019, which, of course, is modest in comparison with “eternity,” but is impressive on the scale of Russia. Be the first to open a clinic of Tibetan medicine in Moscow, and then branches in the largest cities of St. Petersburg, Kazan, Yekaterinburg, Vienna (Austria), maintain a high bar for thirty long years, be in demand by discerning Muscovites, cure thousands of people, earn their recognition, Of course, this speaks of high-class doctors, professionals in their field.
RECOMMENDATION
Unfortunately, many patients do not pay attention to such “little things” as unpleasant pain in the joints. Find time and contact specialists who have been treating such diseases for a long time. Come at the first signs of ill health, this will avoid much suffering in the future. If you think that joint diseases are the lot of “old people” and you are far from this, do not flatter yourself too much. If you are 40 now, then at 60-70 you will want to be as mobile and active as you are today. Moreover, now age limits have expanded and people remain strong and attractive for a long time.
Myositis
Myositis is inflammation of the muscles. The most common form is myositis of the muscles of the neck and lower back; inflammation of the muscles of the forearm and shoulder is diagnosed much less frequently.
Myositis is characterized by pain in the affected muscle
| The causes of inflammation are varied | Symptoms |
| Injuries | Pain spreads throughout the inflamed muscle |
| Intensive loads | Intensifies when bending the elbow and pressing on the biceps |
| Hypothermia | The muscle is dense to the touch, tense |
| Infectious diseases (flu, ARVI) | Joint mobility is slightly limited |
| Autoimmune pathologies (rheumatoid arthritis) | If the cause of myositis is an infectious process, the symptoms include redness, swelling, increased local and general temperature |
| Parasitic infections (echinococcosis) |
Acute pain in the elbow joint on the inside is caused by inflammation of the biceps brachii muscle.
Prognosis: with timely treatment, local myositis (inflammation of one muscle) due to hypothermia or stress is cured in 99.9% of cases.
If the cause cannot be eliminated, it becomes chronic, in which case it can cause a persistent but minor limitation of mobility (the arm cannot be fully extended at the elbow).
Non-drug treatment
If the joint in any elbow hurts, experts most often recommend complex treatment. In the acute stage, medication is indicated, and after the inflammation subsides, physiotherapy and exercise therapy are required. Without them, the risk of chronic pathologies is high. Physiotherapy methods are usually prescribed:
- Microcurrents;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Laser;
- Ozokerite;
- Paraffin;
- Mud;
- Electrophoresis;
- UHF.
Orthopedic treatment methods will also help reduce pain - resting the arm, observing a work and rest schedule, wearing an orthosis and a bandage on the elbow joint. For advanced arthrosis, a course of shock wave therapy is recommended. Many patients also benefit from treatment with a chiropractor, massage, and acupuncture.
In severe cases, only surgery will help. Replacement of a joint in this location with an endoprosthesis is almost never practiced. Basically, drainage of synovial bursae is performed in the presence of pus, and aspiration of joint fluid is performed in case of excessive accumulation. Hygromas, cysts and other tumors are also removed if they spread to the elbow joint.
Injury
Fracture of the olecranon: 1 – without displacement;
2 – with displacement Trauma is a violation of the integrity of any tissue in the area of the elbow joint (bone, connective, muscle, nervous).
Causes:
- Injury.
- Hit.
- Push.
- A fall.
- Rotate your wrist inward or outward.
The more serious the injuries, the brighter and more acute their symptoms. Fractures, cracks, ruptures of ligaments, tendons and capsules, displacement of joint bones are accompanied by:
- acute, unbearable pain that radiates to the forearm, shoulder and wrist;
- severe swelling;
- hematoma in the area of damage (hemorrhage from ruptured vessels).
Any movements are severely limited and cause intense pain, including on the inside of the arm.
Minor and moderate injuries (bruises, sprains of muscles and ligaments located on the inside of the arm) are accompanied by less pronounced symptoms. The pain is quite severe immediately after the injury, gradually subsides, movements in the joint are almost unlimited, and the condition does not always require treatment.
The first stage of treatment of any injuries and injuries is first aid:
- an ice compress is applied to the site of injury (on the first day - for 15 minutes for every hour);
- the limb is immobilized with a fixing bandage thrown over the neck, or with a splint (if the joint is not deformed);
- the patient is given an anesthetic (Nimesil, Ketoprofen).
Treatment in traumatology:
- If necessary, excess fluid is removed from the joint capsule.
- They combine articular surfaces, bone fragments, and restore tissue integrity (if there are no contraindications).
- A plaster cast is applied to the limb until complete recovery.
- Painkillers (for pain) and physical therapy are prescribed until complete recovery.
Prognosis: minor and moderate injuries heal in 90% of cases without consequences for the limb.
Treatment of severe injuries does not always end successfully. In most cases, they are complicated by various disorders of joint mobility and hand functions - from minor limitations to complete loss of ability to work.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you experience acute pain caused by an injury, you should contact an emergency room or a trauma surgeon. In all other cases, you need to visit a therapist, who, if necessary, will refer you to a specialist or prescribe an examination. A rheumatologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune pathologies, in particular rheumatoid arthritis.
Diseases of a neurological nature that arise as a result of compression (pinching) of nerve endings, as well as osteochondrosis and its complications (hernia, protrusion) are under the jurisdiction of a neurologist. If it is necessary to correct various deformations of bone structures, the therapist will refer you to an orthopedist for consultation.
Because the bones of the forearm are firmly connected by the annular and interosseous ligaments, they tend to dislocate together. Most often, posterior dislocations occur; lateral dislocations occur somewhat less frequently. In isolated cases, anterior and isolated dislocations of the radius and ulna are recorded
Injuries
The elbow can be most severely damaged during a fall, when, due to loss of balance, half-bent arms instinctively stretch forward and serve as a kind of shock absorption. It is the emphasis on the elbows that most often leads to dislocations and fractures. It should be noted that elbow injuries require timely diagnosis and treatment to avoid complications in the future.
Most often, the consequences of injuries occur due to scar-fibrous formations in the tendons. Untreated dislocations are diagnosed somewhat less frequently, and in isolated cases, improper fusion of bones after a fracture.
Sprains can occur during sports training or when performing heavy work. Sudden movements of the shoulder or forearm sometimes lead to partial or complete rupture of the ligaments. Damage to the ligamentous apparatus is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain and swelling;
- subcutaneous hemorrhage (bruise);
- pain increases with touch and movement;
- motor ability decreases.
The stronger the pain, the more serious the damage: with a normal sprain, the pain is mild or moderate. Severe pain indicates a rupture of one or more ligaments, and may also be a sign of a dislocation or fracture.
Diagnosis and treatment
X-rays are taken to rule out more serious injuries and determine the extent of damage. Treatment consists of immobilizing (immobilizing) the affected arm and taking anti-inflammatory drugs. To limit involuntary movements, the arm is fixed with an elastic bandage or secured with a scarf.
To reduce swelling and prevent extensive hematoma, it is recommended to apply cold compresses. It is advisable to do this only on the first day after the injury.
Dislocations and fractures
A dislocation in the elbow joint is accompanied by severe pain, as well as difficulty flexing and extending the arm. The elbow is visually deformed, the soft tissues are swollen, movements are severely limited. It is impossible to either bend or straighten the arm, which depends on the location of the dislocation.
It is worth noting that pain when bending and extending a joint can also occur for other reasons, which you can read about here.
When bones are displaced relative to each other, nearby structures are often damaged - nerve endings, blood vessels, cartilage tissue and periosteum. The synovial capsule, ligaments, and tendons may also rupture. Serious dislocations sometimes result in fractures of individual bones or condyles.
A dislocation in the right or left elbow requires immediate attention to a traumatologist. Self-alignment of bones is strictly prohibited! First you need to find out what kind of dislocation occurred, since there are several types - anterior and posterior, external and internal, as well as divergent. In the latter case, the radius and ulna bones of the forearm are displaced so that the distance between them increases.
Only after determining the type of dislocation, the doctor performs its reduction using local anesthesia. X-rays may be taken using a contrast agent to reveal damage to the joint capsule and surrounding ligaments.
Fractures occur in different situations when the arm is subjected to strong mechanical stress. Most often these are road traffic accidents, sports competitions, walking on icy sidewalks, as well as domestic and work injuries.
The fracture can be open or closed. With a closed fracture, the pain increases with palpation, the joint swells, and the skin becomes bluish. It becomes impossible to move your hand.
With an open fracture, bone fragments are visible on the surface, and a wound occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the skin. Open fractures can be complicated by bleeding, infection and painful shock.
Diagnosis and treatment
Therapeutic tactics depend on the type of fracture, which can break one bone or several. In addition, the fracture can be comminuted, when the bone is literally crushed, and mixed, combining a simple and comminuted fracture. To assess the severity and nature of the damage, x-rays and computed tomography are performed.
If a simple fracture is diagnosed, not accompanied by displacement of bone fragments, the patient is given a cast for 1-2 months. Healing takes place at home, after which the plaster is removed.
If there is displacement, the bones are surgically repositioned in an anatomically correct position.
Epicondylitis
Epicondylitis refers to degenerative-dystrophic pathologies and develops at the sites of attachment of muscle tendons on both the outer and inner sides of the elbow. The cause of occurrence is the systematic performance of similar movements. With external epicondylitis, this is extension of the elbow and external rotation of the forearm. Internal epicondylitis is caused by flexion movements and inward rotation of the forearm.
A characteristic symptom of the disease is pain when putting stress on the arm. The pain intensifies when lifting and carrying heavy objects, and also interferes with activities that require rotational force, such as difficulty turning a wrench, a tight water faucet, or working with a screwdriver for a long time.
Pain during exercise is not only characteristic of epicondylitis; it also accompanies other disorders. To find out which ones, click here.
It should be noted that at rest there is no pain and motor ability is completely preserved. There are also no external signs of inflammation or deformation. However, there is another typical symptom: with epicondylitis, the bone in the elbow joint hurts. These are the so-called condyles of the humerus - bony protrusions on either side of the joint that serve as attachment points for muscle tendons.
The lesion with epicondylitis is usually unilateral - right-handed people usually complain of soreness in the right arm, and in left-handed people it occurs in the left elbow.
Diagnosis and treatment
The presence of characteristic signs suggests epicondylitis; an x-ray or computed tomography is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis. The main principle of treatment is the exclusion of traumatic movements, not only of the elbow, but also of the wrist joint. Patients are advised to wear a fixative bandage, apply cold compresses and use anti-inflammatory ointments based on Diclofenac and Ibuprofen.
Arthropathy
If the elbow joint is painful, red, and enlarged, pyrophosphate arthropathy may be the cause. This condition occurs against the background of systemic pathologies and metabolic disorders. Characteristic signs appear due to deposits of calcium salts in the joint, which is more common in older people.
Pyrophosphate arthropathy can occur periodically or cause constant aching pain. Attacks of the disease usually begin unexpectedly, and the pain intensifies within several hours. Having reached its peak, the pain gradually passes and disappears completely after a week or two. However, after a while she returns again.
The clinical picture has some similarities with gout, in which uric acid salts are deposited in the tissues of the joints. The difference is that the progression of arthropathy leads to joint deformation and the appearance of bone spurs, causing pain and limiting movement.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnostic measures are carried out by a rheumatologist who refers the patient for an X-ray examination or computed tomography. A joint puncture may be prescribed, which is necessary to identify calcium pyrophosphates in the synovial fluid and exclude infection.
In some cases, arthroscopy is performed to assess the condition of the joint cavity and carry out differential diagnosis with other diseases. During the procedure, biomaterial is also collected for cytological examination, through which the presence of pyrophosphate crystals is determined.
The main focus of arthropathy therapy is correction of the underlying disease. To relieve pain and inflammation, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and the anti-gout drug Colchicine are prescribed.
Arthrosis
Arthrosis of the elbow joint
Arthrosis is a chronic disease. It begins with a malnutrition of the joint cartilage under the influence of various factors and ends with the destruction and deformation of the articular surfaces. Arthrosis of varying severity is diagnosed in 85% of people over the age of 65 years.
Causes and provoking factors:
- excessive load;
- injuries;
- metabolic disorders (gout);
- inflammatory diseases (arthritis);
- congenital defects in joint development;
- age.
The disease develops gradually. In the initial stages, pain in the elbow occurs with exertion (flexion-extension) and intensifies in the evening. The patient may be bothered by dull vascular pain around the joint at night, which usually goes away after getting up.
Symptoms at stages 2 and 3 of elbow arthrosis:
- aching pain occurs more and more often, intensifies, affects the entire joint from the inside, outside and sides;
- the elbow changes shape;
- muscles weaken (atrophy);
- the limb is shortened.
The range of active movements in the elbow is limited (it is impossible to fully bend or straighten the elbow). A characteristic sign is clicking and crunching in the joint when moving.
The pain in the elbow becomes sharp and severe during exacerbations of arthrosis, which occur more often in the later stages.
Prognosis: the disease is incurable. In the early stages, it is successfully and permanently stopped by physical therapy. In the later stages, endoprosthesis replacement (installation of a prosthesis) is most effective, but the elbow joint is rarely destroyed to a critical condition.
Methods for treating elbow pain
The elbow of the right hand hurts (it must be treated immediately) - in case of a serious injury, the doctor suggests orthopedic devices to immobilize the damaged joint:
- fixing bandage;
- bandage;
- gypsum;
- splint;
- orthosis
The specialist can also recommend medications suitable for each specific case.
Medications
They are the mainstays in treating elbow problems. The most commonly prescribed drugs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Their action is quite fast, but superficial. Non-steroids fight inflammation and eliminate pain, but not the cause itself. They are designed to eliminate pain in order to alleviate the patient's suffering.
There are currently dozens of NSAIDs available in various forms.
The most common of them:
| Name | Form | Approximate cost |
| Diclofenac | Ointment/Gel, 30 g Solution for injection, 25 mg/ml Tablets, 50 mg | From 16 rub. From 42 rub. (for 5 – 10 ampoules) From 27 rub. (for 20 tablets) |
| Nimesulide | Tablets, 100 mg | From 30 rub. (for 20 tablets) |
| Indomethacin | Ointment 10%, 40 g Tablets, 25 mg Rectal suppositories, 50/100 mg | From 36 rub. From 15 rub. (for 30 tablets) From 52 rub. (for 10 pcs.) |
| Celecoxib | Capsules, 200 mg | From 141 rub. (for 10 capsules) |
| Meloxicam | Solution for injection, 15 mg/ml Tablets 7.5/15 mg | From 291 rub. (for 5 ampoules) From 152 rub. (for 10 tablets) |
| Ketorolac | Solution for injection, 30 mg/ml Tablets 10 mg | From 51 rub. (for 10 ampoules) From 15 rub. (for 10 tablets) |
| Ibuprofen | Ointment 5%, 25 g Tablets, 200 mg | From 28 rub. From 28 rub. (for 50 tablets) |
| Naproxen | Tablets, 250 mg | From 131 rub. (for 10 tablets) |
| Piroxicam | Capsules, 10/20 mg | From 19 rub. (for 20 capsules) |
Ibuprofen will help relieve pain in the elbow of the right hand.
These medications should not be used constantly. They are sold without a prescription, but have many side effects.
Another group of drugs prescribed for elbow pain are chondroprotectors. Their functions are the healing of cartilage tissue, while relieving pain, and leveling the process of dystrophy. The basis of such drugs are 2 components – chondroitin and glucosamine. They are a natural building material of cartilage tissue.
Treatment with these drugs takes a long time - over 3 months. First they are prescribed in injections, and then in tablets. To maintain maximum effect, the course of treatment is repeated annually.
The most popular chondroprotectors:
| Name | Form | Approximate cost |
| Structum | Capsules, 500 mg | From 1200 rub. (for 60 capsules) |
| Alflutop | Solution for injection, 10 mg/ml | From 1453 rub. (for 10 ampoules) |
| Chondroxide | Cream 8%, 50 g Gel 5%, 40 g Tablets, 250 mg | From 499 rub. From 318 rub. From 500 rub. (for 60 tablets) |
| Teraflex | Cream 30/50/100 g Capsules | From 307 rub. From 979 rub. (for 60 capsules) |
| Noltrex | Syringe 2.5 ml | From 2500 rub. |
| Chondrolone | Solution for injection, 0.1% 1 ml | From 778 rub. (for 10 ampoules) |
For severe pain, injections may be prescribed directly into the joint. Such injections provide quick relief. But doctors do not recommend using this treatment constantly - along with the injection, an infection can be introduced into the joint.
For intra-articular injections use:
- chondroprotectors;
- hyaluronic acid;
- corticosteroid hormones
The last group of drugs has an almost immediate effect on the sore joint, effectively copes with inflammation, but has many contraindications. However, they are extremely popular with patients.
Most often used:
| Name | Form | Approximate cost |
| Diprospan | Suspension for injection | From 110 rub. (for 1 piece) |
| Kenalog | Suspension for injection, 40 mg/ml | From 451 rub. (for 5 pcs.) |
| Flosteron | Suspension for injection | From 3950 rub. (for 5 pcs.) |
| Metipred | Powder for injection, 250 mg | From 199 rub. (for 1 piece) |
| Depo-Medrol | Suspension for injection, 40 mg/ml | From 678 rub. (for 1 piece) |
Injections are prescribed 1 every 2 weeks. A full course includes 3-5 injections. Corticosteroids do not affect the disease itself, so they cannot provide complete treatment.
My right elbow hurts (can also be treated with hyaluronic acid) as a result of injuries or joint diseases. The drug is injected into the joint when there is a lack of fluid in it. As a result, nutrition improves and restoration of cartilage tissue accelerates.
Today, the following medications with hyaluronic acid are used:
| Name | Form | Approximate cost |
| Ostenil | Syringe, 20 mg/2 ml | From 2800 rub. |
| Fermatron | Syringe, 1% solution, 2 ml | From 3190 rub. |
| Sinokrom | Syringe, 1% solution, 2 ml | From 2950 rub. |
Traditional methods
There are plenty of non-traditional remedies used to treat joints. But not everyone is suitable for elbow pain.
Here are some of the most effective recipes:
- Compress. You will need the shells of 4-5 chicken eggs and 500 g of sour milk. The washed shells are dried and crushed to a powder state. Then it is mixed with sour milk. From the resulting pulp, apply a compress to the elbow and carefully wrap it with thick cloth. After an hour, the bandage is removed. The course of treatment is 1 time per day for 5 days.
- Baths. Ranunculus flowers are poured with a glass of boiling water and infused for about 5 hours. Then another 4.75 liters of boiling water is added to the broth. You need to dip your elbows into the resulting liquid. The duration of such elbow baths is 1 hour. At night you can make compresses from this decoction. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Homemade ointment. You will need a bottle of camphor alcohol (40-50 ml), 2 egg whites, 3 tbsp. l. mustard powder. The ingredients are mixed into a paste. The resulting ointment is applied to the elbow and wrapped in a thick cloth. Wrapping is done at night. The course of treatment is 5 procedures.
You can also take physiotherapy courses. In terms of effectiveness in treating the elbow of the right or left hand, they can compete even with medications. If all previous methods do not help to cope with the disease, then the doctor may suggest surgery.
Author: Iha-rock
Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma is a malignant neoplasm of the elbow joint. It arises from cartilage tissue cells and affects bones. A common type of tumor (from 7 to 16% of the total number of bone tumors), but elbow sarcoma is quite rare (1.5%).
Chondrosarcoma of the distal humerus (X-ray). Click on photo to enlarge
Causes: It is still not clear why cancer cells develop. Predisposing factors include heredity, trauma, the influence of radiation exposure, toxic substances, and unfavorable environmental conditions.
The disease most often develops gradually.
Symptoms:
- at the initial stages, a person experiences discomfort and mild pain in the elbow joint, which intensifies at night and weakens slightly when taking painkillers (but does not disappear at all);
- the tumor noticeably deforms the elbow;
- the pain becomes constant, unbearable;
- the pain is localized around the affected joint (the elbow hurts equally strongly on the inside, outside and sides).
The patient's general condition noticeably worsens, weakness, fatigue appear, and appetite disappears. When the tumor compresses the nerve bundles, the pain radiates along the affected endings.
Treatment: In the early stages, the disease is treated by surgical removal of the tumor. In later stages, the likelihood of limb amputation is high. Sarcoma does not respond well to chemotherapy and radiation.
Prognosis: removal of sarcoma in the early stages prolongs the life of 90% of patients by 5 years. At stages 2 and 3 – 45–30% of patients.
Aching pain - other causes
If any elbow joint hurts, and injuries and inflammation are excluded, this may be a symptom of arthrosis. This degenerative disease occurs most often after 50 years of age, but with certain work or other conditions, the elbow joint can wear out faster. The cartilage tissue becomes thinner, the joint space becomes narrower, so bone movements cause pain. Usually the right joint begins to suffer first, and later the second one becomes affected.
The following pathologies are more rare:
- Malignant tumor. In addition to the pain syndrome - persistent, constant, increasing over time - a person also exhibits general symptoms. He loses weight, body temperature may rise, fatigue and weakness are observed. The tumor is almost always noticeable visually, because it grows quickly. Sometimes the first sign is a spontaneous fracture due to weakening of the bone tissue by the tumor.
- Chondrocalcinosis. The cause of the pathology is the deposition of calcium salts in cartilage and ligaments. It occurs only in older people and is associated with diseases of the parathyroid glands, metabolic pathologies, and heredity. The disease can cause only minor discomfort and is often detected by chance.
- Hygroma. A benign formation appears due to the accumulation of water in the tendon sheath. It is formed along the tendons and can also cover the elbow joint.
- Neuritis and cubital tunnel syndrome. Damage or inflammation of the nerve processes is manifested by pain from the elbow to the hand, numbness, and tingling in the arm. The disease occurs due to an injury to the elbow, infection, or diabetes.
- Osteochondritis dissecans. After part of the cartilage and bone are separated, these fragments block the joint itself, causing severe pain. The disease occurs very rarely, the causes have not yet been discovered.
Also, a prerequisite for pain is sometimes tuberculosis, syphilis, osteochondrosis of the neck, hemophilia, myocardial infarction.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the cause of pain in the elbow joint, various methods are used:
- Examination, questioning, diagnostic tests (palpation, active or passive flexion and extension of the arm) - help to establish the cause of pain, determine some deviations, changes in the joint and periarticular tissues.
- X-rays are informative in the later stages of joint diseases, when bones are involved in the process or the disease occurs with the deposition of crystals in soft tissues.
- MRI, ultrasound or CT scan - allow you to determine pathological changes in the joint and periarticular tissues in the early stages of disease.
- Arthroscopy - helps to identify any intra-articular changes. To do this, a probe with an optical device at the end is inserted into the capsule.
- Diagnostic extraction of intra-articular fluid (puncture) - allows you to identify pathogens, determine the cause and nature of the pathological process.
- Laboratory tests of blood, pieces of tissue from the lesion, fluid extracted from the joint help confirm a pre-established diagnosis and exclude diseases that are similar in symptoms.
1 – inspection; 2 – ultrasound of the elbow joint; 3 – arthroscopy; 4 – diagnostic puncture
If necessary, and to clarify the diagnosis or condition of the affected tissues, the doctor may prescribe other studies:
- densitometry (determination of bone density);
- scintigraphy (x-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent to determine a malignant tumor or its metastases).
Diagnosis of elbow pain
You can find out the reason why problems arise in the elbow of your right or left hand with your local therapist. Having the patient’s medical record in hand, he can quickly diagnose the problem and prescribe treatment. Sometimes, in more complex cases, a conclusion from a more specialized specialist - a neurologist, cardiologist or surgeon - is necessary.
Again, a local doctor can write a referral to them. But if the problem is not obvious, additional research will be needed. Some of them can be carried out at a local medical facility, while others can only be carried out in hospitals or medical centers for an additional fee.
| Type of study | Where to spend | Approximate cost |
| X-ray of the elbow joint | Hospital, medical center (MC) | 350 – 9100 rub. |
| Blood analysis | Clinic, hospital, MC | 0 – 980 rub. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the elbow joint | Hospital, MC | 2000 – 20300 rub. |
| Arthrography of the elbow joint | Hospital, MC | 1500 – 9100 rub. |
| Puncture (fluid collection) from the elbow | Hospital, MC | 990 – 3000 rub. |
Folk remedies for pain relief
What to do if your hand hurts? An inexpensive and fairly reliable way to get rid of elbow pain and other symptoms is home remedies prepared according to folk recipes:
- For pain due to myositis. Take 1 tsp. turpentine, 1 egg yolk, 1 tbsp. l. apple cider vinegar and mix. Rub into the damaged muscle at night, wrap with a warm cloth. In this way, myositis is treated until complete recovery.
- For pain and swelling due to tendinitis and epicondylitis. Mix fresh chicken protein with the same amount of medical alcohol (70%). Add flour to the mass, knead the dough so that you can form a flat cake and apply it to the sore tendon. Secure the cake with a bandage and hold it on your hand until it begins to dry out. Do compresses every day until complete recovery.
- To prevent exacerbations of arthrosis. Dry wheatgrass rhizomes (4 heaped tablespoons) pour boiling water (3 cups), boil over heat to 1/4 volume (150 ml). Strain and drink a tablespoon twice a day. Continue treatment for up to 8 months, take a break of 7 days every 4 weeks.
How to treat elbow pain with folk remedies?
Traditional medicine has been used for centuries to relieve a person from discomfort in the elbow joint. Such recipes are simple and always effective because, firstly, they cannot cause harm, and secondly, they are aimed at reducing the inflammatory process with herbal components and easing pain.
Ways to treat elbow pain:
- To ease the pain, you can perform a light massage with essential oil or eucalyptus tincture. This product can be easily purchased at a pharmacy, or you can prepare it yourself by pouring about five grams of propolis with a glass of pure vodka or alcohol. This mixture is infused for a week in a dark place, after which it is successfully used to treat pain and reduce inflammation.
- It is good to regularly use a simple honey massage. To do this, a small amount of natural honey, slightly heated in the microwave, is rubbed into the sore forearm. After a gentle massage, it is recommended to apply a burdock leaf to the sore elbow joint and leave it under a bandage overnight; the elbow can be wrapped in a warm scarf for greater effectiveness.
- Regular compresses of laurel oil will help relieve pain in your elbow. It can be purchased at pharmacies, or can be prepared at home. A piece of gauze is soaked in this oil, after which the elbow is wrapped in it and held for some time.
- Warm baths with sea salt will be extremely beneficial for the elbow joint. Buying such salt is not a problem at all, but if you don’t have it, you can easily replace it with rock salt
- Other effective compresses can be made from Kalanchoe tincture, celandine juice, and clay masks. Clay is purchased at a pharmacy and applied to the joint for at least two hours, after which it is washed off with warm water. It is best to give preference to white or red clay. You can dilute the clay with sour cream
- A compress made from birch leaves is considered extremely effective for treating elbow pain. To do this, pour boiling water over a handful of fresh leaves, steam for several minutes, drain the water and apply the greens to the joint. For greater effectiveness, wrap the joint with a bandage and hold it for at least thirty minutes.
Treatment with traditional recipes for pain in the elbow joint
Causes of contracture
There are many reasons causing this pathological condition. They can be divided into two large groups: injuries and diseases (congenital and acquired).
Injuries
Damage leading to pathology:
- Bruise is the most common injury. Usually it affects the olecranon, periarticular tissues, humeral condyle, and ulnar nerve.
- Partial or complete ligament ruptures.
- Various dislocations of the bones that form the joint.
Injuries also include fractures, which most often affect the internal joint of the ulna.
Fractured elbow as a result of falling on it
Signs of damage
The first sign of injury is acute, severe pain at the time of injury to the elbow. Then the injured area begins to swell and the color of the skin changes. Any attempts to move the injured limb are extremely painful. Pathological mobility cannot be ruled out. There may be numbness in the forearm, hand and fingers. When a fracture occurs, bone fragments may clearly protrude under the skin.
Consequences of fractures and bruises
After an injury, immobilization contracture may develop:
- Due to mechanical obstacles, if reposition was not carried out (comparison of bone fragments for their optimal fusion) or it was not done in the best way. In both cases, the bones do not heal properly, and mobility in the joint is limited.
- If scars have formed after ruptures of the ligaments or periarticular bursa.
- When a person, after a fracture, is forced to wear a plaster cast for a long time.
- If the brain has been damaged.
Diseases
The cause of impaired mobility may lie in congenital:
- Clubbing. There are two types of pathology (ulnar and radial). In the first case, the ulna bone is absent or underdeveloped, in the second - the radius. The latter type of pathology is most often observed.
- Dislocation of the radial head.
- Synostosis, which is a fusion of the ulna and radius bones.
Congenital bone abnormalities are accompanied by disturbances in the development of muscles, tendons and ligaments that serve the corresponding bones.
Two types of epicondylitis
Acquired diseases
Often the factors causing the development of styloiditis are:
- Excessive physical activity. One of the diseases of this nature is epicondylitis - “tennis elbow”. Due to constant overload of the forearm muscles, an inflammatory process begins in the places where the muscles attach to the bones.
- Long monotonous movements that a person is forced to perform in the course of one or another production activity. The tendons that attach to the styloid or olecranon process become inflamed.
- Bursitis or inflammation of the joint capsule, which negatively affects the range of motion in the joint.
- Various forms of arthritis. With this disease, which can be caused by many reasons, almost all joint structures (synovium, capsule, cartilage and others) suffer from inflammation.
Acquired pathologies also include arthrosis, a chronic disease leading to degenerative changes in the joint.
Pain on the inside of the arm
Sharp pain in the arm on the inside of the elbow is a clear sign of epicondylitis.
This disease can occur due to physical overload and severe stretching of the tendons. During normal movements, the patient does not experience any discomfort in the elbow area, but with increased physical activity or frequent repetition of the same movements, weakness in the arm and aching pain may suddenly appear. People over 40 years of age whose profession involves constant stress on their hands are at greatest risk of developing this disease. At risk are loaders, builders, programmers, drivers, artists, athletes (especially weightlifters, tennis players and golfers). Minor injuries and inflammation caused by overexerting the inside of the arm can lead to cramping, scar tissue growth, and salt deposits.
This joint is formed by the bones of the shoulder, elbow and radius. The joints of the bones are covered with cartilage, which ensures their soft, smooth movement.
Diagnosing elbow diseases does not cause difficulties for specialists, although pain in it occurs for various reasons. To diagnose the disease, pay attention to the mobility of the elbow and the sensations caused by it.
In this article we will look at the reasons why the elbow joint of the right hand hurts and how to treat the disease.
Elbow pain varies in nature, depending on the type or severity of the disease. Based on this characteristic feature, a preliminary diagnosis can be made. To determine why the elbow joint of your left or right hand hurts, you should pay attention to the nature of the pain.
Each cause has a specific nature of pain.
Painful sensations manifest themselves in the following types:
- aching;
- sharp;
- strong;
- acute;
- pulling;
- shooting;
- reflected.
The aching type of pain is caused by chronic and degenerative changes.
The acute nature of the discomfort develops against the background of injury or inflammation. If a burning sensation occurs, then this is a reflective pain that occurs during angina pectoris or a heart attack, radiating to the left shoulder.
The nagging nature of the discomfort bothers a person with the cubital canal or with neuritis. With this disorder, an additional symptom occurs - numbness of the fingers. Shooting occurs when nerve endings are pinched. This phenomenon occurs against the background of a herniated intervertebral disc or damage to the spine by osteochondrosis.
Inflammation
Bursitis and other inflammations of the elbow joint are accompanied by pain.
Most cases of pain in the elbow bend of the arm are associated with the development of such diseases:
- arthrosis;
- acute arthritis, including rheumatoid;
- bursitis;
- tendinitis;
- cyst;
- purulent infection.
When bending and straightening, the elbow hurts due to various reasons. Extending or bending the elbow brings discomfort when arthrosis of a deforming nature occurs. Any movement is accompanied by pain due to bursitis or arthritis. The inflammatory process against the background of a purulent infection is accompanied by acute pain, which intensifies when touched.
Injuries
Injuries include dislocations, subluxations, or broken bones (fractures). Often such injuries are accompanied by swelling, hematoma, and impaired joint mobility.
Among the chronic ailments that cause discomfort are the following:
- gout;
- arthritis;
- osteoarthritis;
- disorders of the cervical spine;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- epicondylitis of the elbow joint.
Such diseases can also provoke swelling and limited movement. In some cases, a person cannot even hold a small load with his hand.
Prognosis for recovery
The prognosis of pain in the elbow joint depends on the pathology that caused it.
If applied in a timely manner:
| Disease | Forecast |
| Tendonitis and epicondylitis | Cured in 90% of cases (with early treatment - within 2 weeks, with chronic disease - within 4 months) |
| Arthrosis | Incurable, progresses throughout life and gradually causes joint destruction |
| Arthritis | Allergic is successfully treated within 2–3 weeks, rheumatoid is incurable and after 5 years from the onset of the pathology it becomes the cause of disability in 40% of cases |
| Carpal tunnel syndrome | Treatment takes from 1 to 6 months, but in 30–40% of patients some disorders remain - for example, fixation of a limb due to improper fusion of muscle fibers |
| Injuries | Mild damage disappears without a trace within 2 weeks, medium damage can take from 14 days to 1 month, severe damage can be treated for up to 3 months, and in 70–80% of cases, various joint mobility disorders remain afterward. |
Cervicothoracic osteochondrosis
Destruction of spongy bone tissue entails impaired mobility of the arm , clavicular plexus, and brachial plexus. Precursors to the disease include a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, poor posture, constant hypothermia, frequent colds, and disruptions in the endocrine system.
Signs will be asthenic syndrome, headaches, squeezing sensations from the chest, heart area, numbness of the fingertips, variable pressure, noise, dizziness, goose bumps before the eyes.
Nature of pain
Compressive in the chest area. Constant, aching from the cervical and shoulder regions, affecting the hand.
Diagnosis and treatment
A vertebroneurologist, chiropractor or traumatologist will examine the patient. Based on the complaints received, they will be sent for x-rays, ultrasound, MRI, electrocardiography, electroencephalography. Nonsteroidal medications such as Ketanov, Ketalong, Indomethacin, steroid hormones, and paravertebral novocaine blockades are used. Chondroprotectors Chondroitin, Chondroxide, Mucosat, Artra. Immunostimulants, vitamin supplements Complivit. A good outcome is provided by reflexology, magnet, electrophoresis, exposure to heat, light, mud therapy, massage, and therapeutic exercises. Traditional methods include ingesting peppermint, mountain arnica, and oregano.
Herbs eliminate headaches and normalize blood pressure, which worries the patient with this diagnosis.
Arthritis and arthrosis
The two ailments should not be confused with each other. Arthritis is an inflammatory formation in the bone . Manifestations include rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, metabolic disorders, and autoimmune diseases. Arthritis is indicated by tissue hyperemia, redness, temperature of the lesion, it is impossible to bend and straighten the limb, rotational functions are preserved. Arthrosis is understood as a degenerative-dystrophic change in bone mass and cartilage. Fortunately, pathologies are prevented by heredity, endocrine disorders, a person’s lifestyle, hypothermia, influenza, ARVI, bursitis, and an excess of certain elements in the body. When bending, a crunching sound is heard, there is slight swelling, and loss of mobility.
Affects the right or left elbow.
Nature of pain
When arthritis is expressed, intense, it occurs during movement or at rest. Moderate in arthrosis, appears only with maximum activity.
Diagnosis and treatment
A rheumatologist, orthopedist, and arthrologist gives an accurate picture. It is necessary to do a biochemical blood test, ultrasound, micro-resonance tomography, arthrography, and a sample of synovial contents. Non-steroidal drugs Nimesulide, Meloxicam, Piroxicam, Celebrex are selected. Chondroprotectors Chondroitin Sulfate, Glucosamine, Structum. Salicylic ointments, Hemosol, Solcokerasal, Viprosal, Apizatron, Ungapiven. The infectious nature is eliminated with the help of antibiotics and immunostimulants. Physical procedures are required: paraffin baths, laser, electrophoresis, mud pads, massage. The diet is followed, and in the future you should give up bad habits of smoking and alcohol.
Folk remedies include rubbing, infusions of medicinal herbs, the use of bee honey has a beneficial effect.
Treatment methods
Treatment of pain that occurs when pressing on the elbow bone consists of complex therapeutic measures. Treatment is carried out in several stages:
- First the pain is relieved. If necessary, the joint is fixed with orthopedic devices. This could be an orthosis, a bandage, a splint. For injuries, a plaster cast is applied. Keeping the joint still and providing pain relief are first aid measures for elbow pain.
- A course of medications. First, external medications are prescribed to relieve pain. These are gels and ointments. Drugs in tablets or injections are prescribed if external agents do not give the expected result. Drugs from the group of nonsteroids, glucocorticosteroids, and chondroprotectors are used as drug therapy. If necessary, injectable agents containing hyaluronic acid are administered.
- Physiotherapy sessions are carried out in combination with a course of medications. Physiotherapeutic treatment is aimed at enhancing the effect of medications. The type of physiotherapeutic procedure depends on the type of pathology and the severity of the disease. Procedures such as cryotherapy, laser and magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, and special thermal baths are indicated.
If the hand loses mobility, then a massage is prescribed. Massage movements not only help restore motor activity of the limb, but also relieve muscle spasms.
As an additional technique, folk remedies are used. You can treat the joint with a cold compress.
If a tumor is detected in the elbow joint, surgery should be performed as the most effective procedure.
The surgical technique is also used in case of ineffectiveness of drug therapy, with purulent inflammation of the ulna. Sometimes surgery is the only way to eliminate elbow pain.
After the surgical intervention, a fixing splint is applied to the elbow. During the recovery period, drug therapy is carried out. If necessary, the hand is developed using special exercises.
Epicondylitis or tennis elbow
The disease refers to damage to the muscle tendons that are attached to the inner condyle of the shoulder bone. It is facilitated by the same, repeated movements, physical activity in a certain position, for example, the professions of a turner, carpenter, dentist. It affects golfers and tennis players, hence the name. There is internal and external epicondylitis. The first is indicated by pain going down to the hand, noticeable on palpation. The external one appears in the elbow during flexion and extension, and rotation of the limb.
Additionally, fluid accumulation in the capsule, slight redness, swelling, and decreased muscle tone are possible.
Nature of pain
Strong, constant, spreading from the inside or outside. It gets worse when you try to squeeze the hand. There are no cramps at night.
Diagnosis and treatment
You need to contact a rheumatologist, orthopedist-traumatologist. Get an X-ray, MRI, ultrasound. A splint, bandage, or special bandage is applied to the affected limb. NSAIDs are prescribed: Ibuprofen, Ortofen, Ketorolac, Indomethacin. External ointments with cooling properties. Electrophoresis with anesthetic and analgesic composition, magnetic therapy, laser, cryomethod, exercise therapy.
If there is no positive dynamics, an operation is performed to excise the extensor muscles affected by the inflammatory process.
Diagnostic examination
To prescribe treatment for pain in the elbow, comprehensive diagnostic measures are first carried out:
- asking the patient about the location of pain;
- studying the nature of pain using palpation. During the examination, pressure is applied while the hand is in a calm state;
- an x-ray allows us to examine the presence of pathological processes and structural changes in the joints;
- Ultrasound examination;
- laboratory diagnostics of blood and urine.
If necessary, the therapist schedules consultations with an oncologist, neurologist and cardiologist.
Traumatic injuries
These include fractures, cracks in bones , tendon ruptures, muscle sprains, blows, and bruises. When a fracture occurs, unbearable spasms occur.
With a severe bruise or blow, a hematoma in the area, profuse hemorrhage, swelling, pain on palpation, and hotness of the area are observed.
Nature of pain
From strong, sharp, to aching, aching.
Diagnosis and treatment
If signs appear, you need to visit a traumatologist or surgeon. For an accurate diagnosis, the patient must take x-rays. Analgesics Baralgin, Analgin, Nise are used. Ointments with absorbable action Heparin, Ketonal, Febrofid, Nise. In case of a fracture, a plaster cast is applied. Physiotherapy: laser, magnet, lotions with Dimexide, massage.
No exposure to heat!
Gout
Gout is considered to be the deposition of uric acid in the blood , as well as urate in the joint tissues. Deposits are formed due to excessive consumption of foods such as red wine, chocolate, seafood, due to obesity, kidney failure, high blood pressure, strong addiction to alcoholic beverages, heredity, and inhibition of urate excretion along with urine.
The main features will be exhausting spasms, swelling, redness, inflammation of the joint capsule, compaction on the extensor surface, and the presence of local temperature.
Nature of pain
Sharp, pungent, exhausting with a burning, burning sensation.
Diagnosis and treatment
A rheumatologist deals with pathology therapy. It is necessary to conduct samples of intra-articular fluid, ultrasound, MRI, radiography, biochemical blood and urine tests. The patient is required to follow a strict diet, take NSAIDs Ibuprofen, Butadione, Reopirin, Prednisone. Specific agents Allopurinol, Uridan, Allomaron. Uricodepressive and uricosuric drugs. During the period of remission, Finalgel, Fastum-gel, Diclofenacol creams. UHF, electrophoresis with potassium and lithium ions, compresses with Dimexide, ozokerite, paraffin baths. Sanatorium-resort treatment with radon, hydrogen sulfide, iodine-bromine baths.
Home methods include turnip patches, chicory, chamomile baths, drinking an infusion with St. John's wort, and an ointment based on poplar buds.
Diagnostic methods
Any doctor first examines the patient to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. He collects anamnesis, listening to the patient’s complaints, because pain is only one of the symptoms of the disease; in addition to it, swelling, changes in skin color, limited mobility and many others may occur.
In addition, the specialist prescribes tests, primarily blood tests. A blood test helps to detect the inflammatory process in the body, as well as the content of certain substances that are not present in the plasma of a healthy person. Urinalysis also helps to draw conclusions about certain types of disorders. So, with gout, the exchange of salts is disrupted, which will also affect the composition of biological fluids.
Instrumental examination methods are mandatory in diagnosis:
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- CT.
They allow you to “look” inside the joint and see changes in its structure. If necessary, a puncture may be prescribed, during which a sample of synovial fluid is taken; its composition can also determine the presence of certain diseases.
One of the diagnostic methods is palpation of the affected area.
Possible causes of pain
The occurrence of pain can be triggered by various injuries and pathological conditions.
These include:
- Inflammation of the joint due to certain diseases;
- Joint overload due to heavy lifting;
- Joint dislocations;
- Tendinitis;
- Tendon injury (stretch or rupture);
- Epicondylitis;
- Tumors;
- Bursitis;
- Synovial chondromatosis;
- Pinched nerve roots due to manifestations of osteochondrosis, with damage to the vertebrae of the thoracic and cervical spine;
- Ulnar nerve compression syndrome.
It should be remembered that myocardial infarction can provoke pain that covers the arm from the elbow joint to the shoulder.
Identifying the cause and treatment
Therapy is carried out in the traditional way or using folk remedies. They adhere to combined tactics:
- To relieve pain, restore joint mobility and slow down degenerative processes, medications are prescribed.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures help improve tissue trophism and blood circulation.
- If there is excessive accumulation of fluid inside the synovial bursa, drainage is done.
- Compresses, rubbing, and massage help slow down the development of elbow joint disease.
Surgery is resorted to when conservative treatment has failed. The patient has a damaged joint replaced or bone fragments collected in case of a severe fracture. For cracks, a plaster cast is applied to the affected area and bed rest is prescribed. The prognosis is favorable in many cases.
Treatment of the elbow joint is carried out externally (ointments, gels), with injections or tablets. The patient is prescribed:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) – Colchicine, Arthrozan, Diclofenac. They have an antipyretic and analgesic effect.
- Chondroprotectors – Artra, Chondroxide, Noltrex. Restore damaged cartilage tissue.
- Corticosteroids – Flosteron, Kenalog, Metipred. They relieve inflammation and have an immunomodulatory effect.
- Vitamin B complex – Compligam B, Milgamma, Combilipen. The drugs relieve neurological pain.
- Medicines with hyaluronic acid – Sinokrom, Ostenil. Improves cushioning of cartilage tissue.
- Muscle relaxants – Baclofen, Mydocalm. Eliminate muscle spasm.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out along with drug therapy. The patient is prescribed:
- Electrophoresis with Dimexide. Under the influence of direct current, the medicine penetrates deeply into the tissues and relieves inflammation.
- Cryotherapy. Special installations apply a jet of liquid nitrogen to the affected area. They relieve swelling and improve blood circulation in the joint.
- Laser therapy. Activates cell regeneration processes, helps supply tissues with oxygen in case of arthrosis and arthritis.
- Applications with mud or paraffin. Relieve pain, improve blood circulation in case of ligament damage, arthritis, joint diseases.
Specific treatment cannot be prescribed without a diagnosis. For pain, you can use painkillers. However, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first opportunity so that the doctor can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Such pain is treated using various methods. First of all, it is necessary to relieve the pain syndrome, and then apply complex treatment.
Treatment of a disease that causes pain in the elbow joint involves the use of external medications. Such drugs are especially effective if the patient cannot tolerate oral medications. Drugs for the treatment of joint diseases are divided into several groups:
- Preparations based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which include ointments Ketonal, Nise, Indomethacin and others. They have the ability to reduce fever and relieve joint pain.
- Capsaicin-based drugs that have a “burning” effect. These include Nicoflex, Capsicam, Golden Star balm and others.
- Preparations based on salicylic acid, namely Viprosal, Efkamon and others.
- Combined and homeopathic remedies, for example, Dimexide.
In addition to ointments, tablet and injection forms of medications can be prescribed.
Physiotherapy
Drug treatment of joint pain can be supplemented with physiotherapeutic methods. These include electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, paraffin, mud procedures and others. These methods can be supplemented with massage and compresses.
Folk remedies
Elbow pain is also treated with folk remedies. There are many recipes for pain relief. For example, propolis-based tinctures are considered the most popular remedy.
You can lubricate the elbow area with this liquid and make compresses from it, thereby relieving swelling and pain. You can also relieve these sensations with the help of baths based on sea salt, pine needles and cones.
For arthritis or arthrosis, the following recipe can help: fresh milk should be mixed with crushed eggshells, then the mixture is applied to gauze or a napkin and applied to the joint. This procedure is carried out before bed for several days.
For bursitis, the following is recommended: you need to take a mixture of burdock, chamomile and yarrow leaves and pour boiling water over it. Then the mixture is infused for several hours, filtered and taken orally before meals, half a glass.
In terms of variety and range of motion, the elbow joints can be considered the most mobile in the human body, regardless of age, gender and social status.
When we work, eat, rest or even sleep, we constantly make various movements with our right or left hand, which involve the elbow joint. It is not surprising that unpleasant sensations often arise in it.
To maintain the functionality of the joint, and therefore the quality of life, and prevent complications, it is important to identify the cause of pain in the elbow and promptly carry out the necessary treatment.
What we call in everyday life the elbow joint is actually not one, but three joints located in a common articular capsule. The humerus goes up from the elbow, and the radius and ulna bones go down, forming the forearm. All of them are connected to each other in pairs, forming three joints:
- humeroulnar;
- brachioradial;
- proximal radial.
Each of these joints has a different structure, direction and range of motion from the others.
The humeroulnar is a trochlear joint with a helical structure of articulating surfaces. It is formed by a notch (groove) in the trochlea of the humerus and a corresponding ridge in the trochlea of the ulna.
This joint allows flexion and extension of the forearm in a range of up to 140 degrees. The brachioradialis is a classic ball-and-socket joint. It is formed by the rounded head of the condyle of the humerus and the fossa in the head of the radius.
The proximal radius connects the ulna and radius and is capable of rotational movements.
Thanks to it, we can not only bend and straighten the arm at the elbow, but also turn the forearm with the outer or inner side up, increasing the variety of possible movements.
The articular surfaces are covered with hyaline cartilage, which provides soft gliding. The muscles attached to the joints with the help of tendons make them functional, and the fixation of the common joint capsule is due to the presence of four ligaments.
The elbow joint is easily palpable on the arm; it is not surrounded by a large amount of soft tissue. And active movements often become a source of pain and injury.
Everyone knows the sharp pain of an unsuccessful elbow strike.
In addition, high physical activity and work intensity can cause conditions where pain becomes a symptom of a developing disease.
General systemic diseases, damage to joints and other organs can also lead to pain in the elbow area.
Injuries
The most serious injury is considered to be a fracture. It is accompanied by severe swelling: the joint increases in size literally before our eyes, turns red, and one or more hematomas appear, which can merge. When trying to move, a sharp pain is felt, and a distinct crunch may occur.
A fracture occurs in the joint itself, then they speak of a U-shaped or T-shaped fracture of the condyle, a fracture of the head of the radius or ulna, or a fracture of the trochlea of the humerus. There are also combined fractures, when the joint is damaged in several places at once.
Elbow pain can also be caused by fractures of the bones near the joint or avulsions of the condyles.
You can dislocate your elbow due to an unsuccessful fall, blow, or accident.
A dislocation is accompanied by severe pain, swelling, loss of sensation in the injured limb below the elbow, and blood circulation may be impaired.
Bruising occurs much more often.
A fall, an awkward movement - and now the victim winces in pain, holding his elbow. After the first minutes, the bruise is characterized by swelling in the elbow area. The joint may be hot to the touch.
Movements are difficult.
Elbow pain often occurs in athletes or people who, due to their professional activities, perform a large number of monotonous movements.
In older people, discomfort is often associated with tissue wear, in particular, degenerative changes in cartilage.
Sometimes a tingling sensation and even pain can occur due to a temporary circulatory disorder associated with compression of small vessels during sleep or prolonged forced stay in an uncomfortable position.
Acute pain that occurs for no apparent reason or prolonged pain is most likely caused by some disease.
1. Epicondylitis - inflammation of the tendons. The epicondyles are bone formations near the elbow joints. Muscle tendons are attached to them, providing flexion and extension movements of the fingers and hands. Frequent monotonous exercises, increased loads, and heavy lifting can cause undesirable changes in these tendons and provoke the development of an inflammatory process.
The peculiarity of epicondylitis is that it affects only one arm, the one with the most load. Usually for right-handers it is the right, and for left-handers it is the left.
Lateral (external) epicondylitis affects the tendons on the outside of the elbow joint. This disease is often called “tennis elbow” because the specific loads in tennis have the greatest impact on this area.
A clear sign of lateral epicondylitis is a feeling of pain in the elbow when shaking hands.
2. Osteochondrosis. It would seem that there could be a connection between the elbow and spinal disease. However, with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, pain in the elbow and throughout the arm is one of the characteristic symptoms. Painful sensations are accompanied by numbness of the limb and intensify with fatigue or, conversely, during a night's rest. 3.
Arthrosis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process in cartilage and bone tissue caused by degenerative changes. Arthrosis is characterized not only by pain, but also by forced limited mobility. Each movement is accompanied by a noticeable crunch in the elbow area. If treatment is not started, the disease progresses, the joint becomes deformed, as a result of which the pain becomes even stronger. 4.
Arthritis can be a local inflammation or a systemic disease. If the elbow not only hurts, but is also red, hot to the touch, and swelling is noticeable, then we may be talking about the onset of a serious illness that gradually affects all joints. Arthritis can be infectious, gouty, rheumatoid and reactive. These terms characterize the causes of the disease.
Identification of diseases by symptoms
Problems of the elbow joint are characterized by different symptoms. For example, when the elbow hurts when bending the limb, and the sensations are accompanied by a crunching, stiffness, the prerequisites may lie in arthrosis. Pain from physical activity during inflammation is combined with:
- Edema;
- Redness;
- Painful sensations during palpation;
- Restriction of movement.
If the pain syndrome is intense, it is worth remembering what injuries preceded the situation. Surely the matter lies in a sprain, a ligament rupture, a fracture, and a large bruise and large swelling appear on the elbow.
Other “provocateurs” of unpleasant feelings in the elbow joint:
- Increased feeling when pressed - arthritis, bursitis, additional signs - redness, swelling;
- Persistent pain – tumors in late stages (they can be felt in the bone or joint);
- Aching pain with “goosebumps” – osteochondrosis, cubital canal syndrome;
- Sensations occur after training - sprain, bruise, subluxation;
- Pain when shaking hands or when pulling up – epicondylitis, bone fracture;
- Night, morning pain in the left elbow, right elbow - gout, neuritis, tumor;
- A burning sensation in the right or left elbow joint in combination with pain in the heart, behind the sternum - unstable angina, an attack of ischemic heart disease;
- Shooting sensations – clamping of the spinal roots due to osteochondrosis;
- Pain with a crunch – arthrosis, possibly with osteophytes (bone spines).