Pain in the groin on the left and right. Many men around the world turn to doctors complaining of pain in the lower abdomen, usually on the right, but sometimes on the left. Often, such pain can shift closer to the groin area, which creates additional discomfort. An integrated approach to diagnosing this symptom will reveal what exactly the problem is. The difficulty in determining the cause lies in the fact that the source of the problem may be quite far from the source of pain and at the same time radiate to a certain area of the groin area. In some cases, to determine the causes of groin pain in men, a private consultation will be sufficient, but sometimes serious diagnostics cannot be avoided.
What diseases cause nagging pain
For pathologies of the prostate gland in men, a clear localization of pain in the groin area is not typical, although they can give periodic “shots” in one of the thighs during an acute process.
Cystitis and urethritis also usually give diffuse, poorly localized sensations of a burning or aching nature. Causes of various types of groin pain may include:
- nephritis – a group of inflammatory diseases of the kidneys, their pelvis and parenchyma;
- urolithiasis - usually provoking nephritis or accompanying it;
- cystitis - sepsis of the bladder caused by an ascending infection of the genital organs or autoinfection with chronic urinary retention;
- urethritis - inflammation of the urethra, usually infectious, but scenarios of mechanical irritation and malignant lesions can also be observed;
- orchitis - inflammation of the testicles (usually the left, but also the right), caused by third-party microflora, trauma, congenital disorders of blood and lymph flow, damage to the tubules that excrete sperm;
- epididymitis - a septic process in the appendages of the testicles, almost always accompanying orchitis;
- varicocele - varicose veins of the inguinal veins, almost exclusively of hereditary nature;
- hydro- and spermatocele are congenital or traumatic phenomena in the form of accumulation of fluid from the abdominal cavity (first) and sperm (second) in the tissues surrounding the testes. Both deviations manifest themselves for a long time as a discomforting growth of the neoplasm, and pain in the lower scrotum occurs only in the last stages;
- Testicular torsion is an extremely dangerous and acute condition. It involves the rotation of the testis around its axis, as a result of which its blood supply and the outflow of lymph with sperm are completely stopped. When torsion occurs, the symptoms increase rapidly, emergency assistance is required, and its causes remain a mystery to science;
- cancer - any organ or tissue that forms the scrotum and reproductive apparatus of a man, including the foreskin. The cause may also be malignant tumors of the rectum, appendix, bladder;
- spasm or rupture of the pelvic muscles - a typical symptom of which is urinary incontinence;
- prostatitis – inflammation of the prostate gland under the influence of hormonal imbalance (often age-related, premenopausal) or infection, injury;
- adenoma - a benign growth in the tissues of an organ of purely endocrine origin;
- prostate abscess - a purulent focus in it with prostatitis;
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a predominantly psychogenic phenomenon formed by a variety of uncritical but unpleasant manifestations, from indigestion and gas to alternating constipation with diarrhea;
- the already mentioned appendicitis - with pain most likely in the right groin (the vermiform appendix is located on the right);
- inguinal hernia is a congenital developmental defect that disappears on its own or can be operated on in childhood, but can recur in people with heavy physical labor and weightlifters.
The causes of pain in men in the groin (both right and left) also often lie in processes occurring in the bones, joints, nerve trunks and pelvic muscles that are pinched by them - myositis (inflammation of the muscle heads), arthritis, arthrosis, bursitis, lumbago, sciatica , intervertebral hernias. Among their causes are old injuries that make themselves felt after many years - sprains, previous interventions, blows to the groin, fracture of the penis (during intense sex or having it with an incomplete erection) or bones.
Exacerbations of this kind in the vast majority of cases occur after hypothermia of the lower body, heavy lifting, long walking or running, playing sports, or shaking. After 40 years, they can be triggered by the change of seasons, food poisoning, the development of stomach ulcers, cardiovascular abnormalities, and menopause.
Various disorders and disruptions in the functioning of the body lead to the appearance of unpleasant sensations near the organs of the urinary system. Such symptoms will be a significant reason for a visit to a specialist. Initially, you need to visit a therapist, and then he will refer the patient to a specialist.
During the examination, the doctor discovers the exact location of the pain and its nature. Pain sensations can cover the entire groin area or be concentrated on the left or right.
Painful and aching sensations can be caused by damage to some internal systems:
- kidney;
- Bladder;
- ureters;
- urethra;
- prostate gland;
- testicles;
- penis;
- large intestine;
- groin muscles;
- inguinal ligaments;
- lymph nodes;
- lumbar nerves.
Establishing the location will allow you to eliminate the unpleasant pathology in the shortest possible time.
The groin area is located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity adjacent to the thighs. It contains various muscle groups, intestinal loops, large vessels, and the spermatic cord.
Only a doctor can determine which disease has become the source of pain after carrying out a series of diagnostic measures.
The main pathologies manifested by pain in the hip joint
Let's take a closer look at the main diseases that can cause similar symptoms:
- Arthrosis (coxarthrosis) of the hip jointDeforming arthrosis of the hip joint is diagnosed in every third person who comes to see a doctor about lower back pain radiating to the groin. However, qualified experts say that true coxarthrosis occurs only in about 30% of cases.
The disease develops mainly after 40 years of age and is more common in women. It affects both one joint and both at once. Most often, the disease is not diagnosed at the initial stage, because the symptoms are few and sometimes completely absent. Gradually the disease develops and passes from one degree to another. This period is approximately a year, two or three. Sometimes the rapid development of the disease is provoked by injuries in the hip area, severe stress, and unsuccessful movement. All this accelerates the pathological process. Then the disease will develop to a severe degree within a few months. In the presence of coxarthrosis, pain will be felt on the front and side of the thigh, and will radiate to the groin area.
Often there is severe aching in the buttock, and sharp pain is transmitted to the knee. All pain is observed during movement or when loading the joint, if the pathology is in an early stage.
Advice! Pay close attention to your health and, if you have similar symptoms, consult several specialists to be completely sure of the diagnosis.
According to statistics, 30% of people with similar symptoms suffer from trochanteritis
This is a systemic disease that is diagnosed in only 1% of cases when a person goes to the hospital with pain in the lower back and groin. It occurs more often in women over 50 years of age who have suffered severe stress or even nervous shock.
Causes of pain on the right side
Unpleasant sensations in the groin area can appear under the influence of various factors, and in order to prescribe effective therapy, it is important to establish what triggered the pathology. If pain occurs in the groin in men, the reasons may be the following:
- Inguinal hernia. This pathology can develop with sudden power loads and heavy lifting with weak abs. In addition, constant constipation, obesity and systematic cough can cause this disease. Characteristic signs of this pathology are swelling of the skin in the groin area and the appearance of pain.
- Inguinal lymphadenitis. Such inflammation of the lymph nodes can develop as a consequence of a sexually transmitted disease, infection in the genitourinary system, or the formation of a tumor. A swelling appears in the left groin area, which has a dense consistency, but does not cause pain. With further progression of the pathology, purulent exudate accumulates in the swelling, the skin becomes very red and severe swelling develops.
- Chronic prostatitis. This pathological condition is accompanied by the appearance of nagging pain localized in the groin area. Discomfort spreads to the testicles, and the process of urination becomes frequent, difficult and painful.
- Renal colic. The main reason for the development of this pathology is the accumulation of stones in the ureter, bladder and kidneys. A man complains of sharp pain that appears in the left side and radiates to the groin. Over time, the pain becomes simply unbearable and additional symptoms appear, such as vomiting, bloody urine, weakness and problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In such a pathological condition, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible, otherwise the consequences may be unpredictable.
- Inflammation of the testicles or appendages. Often this disease begins to progress with injuries and damage to the testicles, as well as when infection penetrates into the organs of the genitourinary system. Any movements cause increased pain in the left groin, and swelling of the scrotum is observed. The patient complains of nausea, migraine, fever and vomiting.
- Cystic formation on the spermatic cord. Mostly this disease is diagnosed in men after 35-40 years of age and is characterized by swelling of the scrotum. Aching, fighting sensations in the groin may be disturbing, and this is due to the fact that the cyst begins to put pressure on nearby vessels and nerves.
- Testicular torsion. With this disease, a man is bothered by acute pain that cannot be relieved by anything. Some of the scrotum becomes enlarged, swollen, and may turn blue. Possible increased body temperature and attacks of nausea with vomiting.
Injuries
Another cause of pain in the left groin can be osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. With this pathology, severe discomfort and pain occurs in the lumbar region, which radiates to the groin, perineum, legs and hips. With osteochondrosis, pain can appear suddenly in the form of attacks, be aching and weak after being in one position for a long time.
[flat_ab id=”4"]
Prostatitis occurs due to the following reasons:
- Poor circulation in the body.
- Inactive lifestyle.
- The presence of sexually transmitted diseases in a representative of the stronger sex.
- Hypothermia.
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Lack of regular sexual relations.
In the chronic course of prostatitis, representatives of the stronger sex experience nagging pain in the groin area. Painful sensations often radiate to the testicles. Chronic inflammation of the prostate gland is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Difficulty, painful urination.
- Weakening of sexual function.
- Weakness.
- The appearance of pain in the lumbar region.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis involves taking antibiotics and drugs belonging to the group of alpha-blockers. Physiotherapeutic procedures and massage sessions provide a pronounced therapeutic effect. In severe cases, extensive surgery is resorted to.
Pain in the groin on the left side of men may indicate the presence of an inguinal hernia. This pathology appears due to weakening of the abdominal muscles against the background of increased physical activity. An inguinal hernia can be caused by heavy lifting. The likelihood of pathology occurring increases if a representative of the stronger sex is overweight, has a lingering cough, or has chronic constipation.
Pain in the groin on the left, radiating to the testicle, may be a manifestation of orchitis. If a man has this pathology, the following unfavorable symptoms occur:
- redness of the scrotum;
- nausea;
- swelling of the scrotum;
- the appearance of headaches;
- lethargy;
- pain in the scrotum area;
- elevated body temperature.
If pain in the left groin in men radiates to the testicle, you should undergo a full examination. A similar symptom may also indicate the presence of epididymitis in a representative of the stronger sex.
Discomfort in the groin area can also be caused by a cyst of the spermatic cord. This disease is most often diagnosed in men who have crossed the thirty-year mark. With a spermatic cord cyst, a slight swelling appears in the scrotal area. With this pathology, aching pain in the groin on the left side in men occurs with a rapid increase in the size of the tumor. The cyst begins to put pressure on the adjacent vessels and nerves.
With varicocele, dull pain also occurs in the left groin area. Representatives of the stronger sex often complain of a feeling of heaviness in the genital area. With the purulent form of inguinal lymphadenitis, a sharp increase in lymph nodes is observed. There is swelling in the left side of the groin. The skin around the tumor swells and turns red. When you touch the groin area, severe pain appears.
When testicular torsion occurs, pain in the groin in men on the left often becomes acute. One half of the scrotum appears swollen and increases in size. The skin in the affected area takes on a slightly bluish tint. In some cases, the patient experiences adverse symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
Unpleasant sensations can be caused by renal colic. It occurs when there are stones in the kidneys, bladder or ureters. With renal colic, a representative of the stronger sex experiences sharp pain in the left side. Pain often radiates to the groin. In addition to severe pain, if a patient has renal colic, other symptoms may be observed:
- the appearance of bloody impurities in the urine;
- vomit;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- pain in the head area;
- lethargy;
- frequent urination.
A patient with renal colic needs qualified medical assistance.
The choice of a specific treatment regimen largely depends on the severity of the disease in question. For example, if a man has a purulent form of inguinal lymphadenitis, antibiotics are recommended. Anti-inflammatory medications are used for local treatment of the affected area. If severe suppuration occurs, surgery is performed. In some cases, when treating inguinal lymphadenitis, physiotherapeutic sessions are indicated.
Complex treatment of orchitis involves, first of all, the prescription of drugs with antimicrobial properties. If there are septic complications, the patient requires surgery.
Right groin pain in men can be a dangerous symptom. Sometimes this is a sign of appendicitis. In this case, there is first severe pain on the right side of the abdomen, and then it goes down. Unpleasant sensations are accompanied by nausea. In this condition, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, as emergency surgery may be required.
A similar condition can be caused by renal colic. In men with urolithiasis, stones can become lodged in the ureters. This causes an attack of severe pain, which first occurs in the right side, and then radiates to the lower back, groin area and leg.
The attack can last from several minutes to several hours.
Right groin pain in men may be associated with a right-sided inguinal hernia. This formation infringes on the intestinal loops, which causes an attack. this disease is quite common. In this case, the pain does not radiate to the groin, but occurs directly in this area. Often an attack occurs after heavy physical work. If this happens, emergency medical care and surgical treatment are required.
Pain in the left groin in men can also be associated with a hernia. In this case, the disease develops on the left side. In this case, you may notice a slight swelling in the groin area.
Renal colic can also occur on the left side. If the stone has descended into the lower parts of the ureter, then pulsation appears in the groin area.
Pain in the left groin in men is quite often associated with infections of the genitourinary organs. Usually, unpleasant sensations radiate to the lower back. Patients complain of pain when urinating, discharge of blood and mucus from the urethra.
Aching pain in the groin in men is often observed. The reason for this may be excessive physical activity during sports training. However, this is often a symptom of pathology.
Such pain often indicates an exacerbation of chronic cystitis. Unpleasant sensations can have different localizations. Usually this is the lower abdomen. This disease must be treated urgently, as the inflammatory process can spread to nearby organs.
There are other possible causes of aching pain:
- Bladder injuries.
- Hypothermia.
- Congestion in the pelvic area.
- Hormonal disorders.
Sharp pain in the groin in men often signals serious illness. This symptom never goes away on its own. The most dangerous cause may be a tumor of the genitourinary organs. This requires immediate diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of aching pain
A number of pathologies do not have obvious manifestations and are detected by chance during a routine examination. A person occasionally feels a mild aching pain, but in the future it becomes more pronounced.
Aching pain is a companion to the following diseases:
- cryptorchidism – hormonal imbalances, problems with conception, delayed puberty in adolescents;
- prostatitis – problems with urination and potency, the appearance of adenoma, infertility;
- cancer - weight loss, fever, poor health, sensation of a foreign body inside;
- cyst - unilateral enlargement of the testicles;
- lymphadenitis – single and multiple swellings with adhesions;
- abscess – impurities in the urine, rash, problematic emptying, discharge.
Aching pain will be the main symptom of acute cystitis. This is an acute inflammation localized on the mucous membrane of the bladder. The culprits of the acute form are various infections. Manifestations of the acute form: cloudy urine, aching pain, frequent urination with pain, the appearance of blood in the urine, nausea, high fever.
The likelihood of developing cystitis increases:
- injury to the surface of the bladder;
- hormonal imbalances;
- simple blood in the pelvic veins;
- decreased protective functions;
- hypothermia.
Aching pain is provoked by malignant neoplasms in the rectal mucosa. She talks about the growth of the tumor and the spread of malignant cells into the tissue of nearby organs, the process becomes irreversible. Symptoms: constant constipation, loss of appetite, bloating, bloody stool, feeling of weakness, pale skin.
The essence of the technique
Reviews after the article
Meirama pillow
We accept pre-orders.
Order
Exact location and accompanying symptoms
To understand what causes groin pain, you need to determine the location of the pain and the accompanying symptoms.
One of the most common conditions that cause groin pain is a hernia in the groin area. This pathology is formed when the supporting tissues are weakened and is characterized by the movement of intestinal loops from the abdominal cavity to the groin area.
Symptoms of an inguinal hernia include:
- pain in the groin area, aggravated by coughing, sneezing, physical activity (may radiate to the sacrum or lower back);
- the presence of a characteristic protrusion in the groin;
- discomfort when walking and other physical activity.
In some cases, an inguinal hernia causes constipation and dysuria (frequent urination, urinary retention, discomfort and pain in the urethra).
What to do
If women treat pain relatively calmly, then in a man the appearance of painful discomfort in the groin causes a panic attack and strong fear for male strength. But don't panic. Before deciding what to do, you should calm down a little and assess your condition :
- The nature of pain discomfort. A nagging or aching pain indicates the chronic nature of the pathological process. Most likely, the groin has been pulling for a long time, but before the man tried not to pay attention to the suspicious sensations. It is dangerous when the groin pain is acute and the pain syndrome intensifies.
- Localization. Pain in the left side of the groin allows us to exclude appendicular inflammation in a man. But you should not ignore the symptoms that have arisen if the groin hurts acutely. This may turn out to be testicular torsion, a strangulated hernia in the groin and some other acute processes.
- Connection with movement. Any pain discomfort increases when trying to move. But if there is almost no pain at rest, but pain appears when walking or turning the body, then it is worth considering a joint pathology or a neurological disorder.
Any pain in the groin should be a reason for a man to visit a doctor. Without timely treatment, even such “harmless” causes as constipation or joint diseases due to reflex irritation of the inguinal nerves and congestion in the pelvis can cause erectile dysfunction and other irreversible processes.
Interesting1Not interesting0
Methods for eliminating pathology
To diagnose factors that provoke pain in a given part of the body in men, various research methods are used.
Patient Interview
A diagnostic measure that must begin with interviewing the patient or taking an anamnesis. During its implementation, the specialist identifies the patient’s complaints, their origin, general information, and important information about the development of the disease.
After interviewing the patient, the specialist proceeds to objective diagnostic methods - examination, palpation, listening. Often they enable the doctor to quickly identify the pathological process that provoked pain in a given part of the body.
To identify a pathological process or confirm the initial diagnosis, laboratory research methods are used. They are aimed at analyzing the patient’s biomaterial. For diagnostic purposes, the following tests are prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- general urine analysis;
- urethral swab;
- secret analysis.
Discomfort on the left, right in the groin and throughout the entire surface of the abdominal cavity in males appears due to various factors. You need to take unpleasant signs seriously, as they can indicate disorders in the body. Timely diagnosis contributes to the prescription of effective therapy and elimination of unpleasant pathology as soon as possible.
To identify the cause that provoked the pain in the left groin, a thorough diagnosis is carried out. A man is recommended to consult specialists such as a urologist, neurologist, therapist, surgeon and oncologist. First of all, a man undergoes the following tests:
- a general examination of urine and blood can identify inflammatory processes and infections;
- blood for biochemistry helps determine the functioning of internal organs, metabolic processes and diagnose the lack of microelements in the body;
- a smear from the male organ is carried out to assess the general condition of the microflora in the genitourinary system and identify the causative agent of infection;
- determination of the condition of the prostate gland.
The following instrumental diagnostic methods occupy an important place in identifying the cause of pain in the left groin:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and genitourinary system helps to identify stones and inflammatory processes occurring in the male body;
- Endoscopy will be used to identify neoplasms such as tumors, ulcers and erosions in the genitourinary system and intestines. If indicated, tissues and cells of individual organs are collected for additional research.
- X-rays can reveal inflammation, tumors, fractures and bruises of the hip bones in a man.
After establishing the cause that provoked the pain in the groin on the left, treatment begins.
The choice of one or another method of therapy is made taking into account the cause that provoked the pain.
Drugs
When pathologies such as epididymitis and orchitis are identified, drug therapy is carried out using antibiotics of the fluoroquinolone and macrolide groups, as well as non-steroidal medications and analgesics. Such drugs as Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, and Indomethacin, Ketoprofen and Analgin have a good effect in the treatment of diseases. If an accumulation of pus is detected, then surgical intervention is performed.
Renal colic is accompanied by the development of pain, so analgesics and antispasmodics are prescribed to relieve it. In order to speed up the removal of stones from a man’s body, medications such as Olimethin, Cystenal and Avisan are used. In addition, for renal colic, special nutrition is indicated.
Treatment of inguinal lymphadenitis is carried out using antibacterial drugs such as Penicillin, Streptomycin, Azithromycin and Doxycycline. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as Nimesulide, Ibuprofen and Diclofenac are prescribed. Elimination of such pathology is carried out using homeopathic remedies in combination with physiotherapeutic methods.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy plays an important role in the treatment of pathologies that are accompanied by pain in the left groin:
- UHF therapy helps to get rid of severe pain and inflammation, as well as normalize blood circulation;
- electrophoresis is the effect of electrical impulses on human organs and the administration of medications through the skin using a special device;
- Magnetic therapy can eliminate discomfort in the groin, stabilize blood circulation and improve immunity.
If indicated, surgical intervention is performed. Inflammation of appendicitis, which is accompanied by sharp pain in the left groin, is considered a common occurrence. In this situation, a standard operation such as appendectomy under local anesthesia is performed.
For an inguinal hernia, surgical intervention such as hernioplasty is indicated, which is usually performed without complications. Removal of stones from the ureter is carried out using a urethroscope or under the influence of magnetic waves. During the procedure, the stone crumbles and leaves the male body naturally.
[f[flat_ab id=»5"]p>
As a rule, the cause of pathological pain in the groin area is:
- Inguinal hernia. Such a violation can occur during sudden power loads. If a person has weak abs and lifts heavy weights, a hernia often forms. Chronic constipation, excess weight, and systematic cough can also lead to this pathology. The skin in the groin swells, protrudes, pain is felt on the left in the groin area. Sometimes nausea and a gag reflex also occur.
- Renal colic. The reason for this is the formation of stones in the ureter, kidneys, and bladder. Sharp pain occurs in the left side, felt in the groin. Patients with such symptoms moan and even scream. The pain becomes unbearable. This symptom is often accompanied by bloody urine, vomiting, gastrointestinal dysfunction, depression, migraines, and weakness. In this case, emergency medical attention is required.
- Inguinal lymphadenitis. This is an inflammation of the lymph nodes, the prerequisite for which may be a sexually transmitted disease, infection of the genitourinary system, or their tumor lesion. There is swelling in the left groin. It is dense to the touch, but painless. Over time, the swelling fills with pus. Redness and swelling in the groin are observed. When palpated, the swelling hurts.
- Inflammation of the testicles or their appendages. Such diseases often occur due to injury to the testicles or infection in the genitourinary organs. With inflammation of the testicles, pain on the left side of the groin intensifies with movement. The scrotum is swollen. A person experiences a migraine, nausea, fever, general weakness, and a gag reflex. With epididymitis, that is, inflammation of the appendages, the symptoms are similar, but the pain is less pronounced. They get worse when walking.
- Chronic prostatitis. This disease is mainly manifested by nagging pain in the groin area. They pass into the testicles. On the left, in the groin area, it constantly hurts. The urination process becomes difficult, frequent and painful. Potency weakens.
- Spermatic cord cyst. This pathology occurs after thirty-five years. In men, a round, soft and elastic swelling appears around the scrotum. It's painless. But sometimes aching pain appears on the left in the groin area. This is due to an increase in the size of the cyst, which compresses the vessels and nerves located nearby.
- Varicocele. Dull, diffuse, nagging pain periodically engulfs a person. There is a feeling of discomfort in the groin area, heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- Testicular torsion. Acute pain does not give rest. Part of the scrotum swells, swells, increases in size and even turns blue. The injured testicle is displaced. Body temperature increases. Nausea and vomiting occur.
- Osteochondrosis of the lower back. This disease affects the entire lumbar spine. Pain sensations radiate to the groin, perineum, thighs and even legs. The pain is sharp, shooting and sharp. They manifest themselves in periodic attacks. At times the pain becomes weak and aching. As a rule, they intensify if a person sits for a long time.
To eliminate pain on the left side in the groin area, you need to identify the causes that provoked the pathological manifestation.
An inguinal hernia is treated with surgery. It is adjusted and the hernial sac is removed.
To eliminate renal colic, antispasmodic and analgesic drugs are used. In some cases, it is recommended to apply a hot heating pad to the lumbar area. To facilitate the passage of stones, doctors prescribe Olimetin, Avisan, Cystenal. A balanced diet is also important and must be strictly followed. Otherwise, therapeutic measures will be in vain.
To treat chronic prostatitis, alpha-blockers, antibiotics, prostate massage, and various physiotherapy are prescribed. If the disease is advanced and male gland hyperplasia is diagnosed, then surgical treatment is necessary.
To eliminate inguinal lymphadenitis, antibiotics, vitamins, and local treatment with special ointments that relieve inflammation are prescribed.
To cure inflammation of the testicles and their appendages, antimicrobial and physiotherapy are used. If septic complications of diseases are diagnosed, then surgical intervention is advisable.
Surgery is usually performed to eliminate spermatic cord cysts, as well as testicular torsion.
If pain in the left side of the groin is caused by progressive osteochondrosis, then physiotherapeutic procedures, reflexology, massage, manual therapy, and physical therapy are prescribed. To eliminate pain, various local gels and ointments, as well as painkillers, are sometimes used.
Why does a man's groin still hurt?
Let's look at other possible reasons why the groin area hurts in men:
- Inguinal hernia. In addition to moderate discomfort in the groin, it is manifested by external swelling of the abdominal wall. Has different sizes. Most noticeable when the man is standing. When an inguinal hernia is strangulated, acute pain occurs.
- Orchitis. Inflammation of the testicles is accompanied by severe pain discomfort, which intensifies when walking. Groin and testicles hurt. Men complain that during sexual intercourse the pain increases sharply.
- Inflammation of the hip joint (coxoarthrosis, arthritis). At the same time, discomfort appears in the groin, and the leg hurts. The pain intensifies with movement and may completely disappear with rest.
- Testicular torsion. Painful sharp sensations appear in the scrotum and radiate to the groin. Additionally, men feel dizziness, weakness, and nausea. The twisted testicle is dense and slightly enlarged in size.
- Inflammation of the lymph node in the groin. The cause may be diseases of the pelvic organs, sexually transmitted infections or a tumor process. It is typical for lymph node damage that the pain in the groin intensifies when pressing on the node or with sudden movements.
As you can see, a man’s groin can hurt both due to pathological processes in the genitourinary area and for other reasons. But any painful manifestations indicate that not everything is in order in the body, so the resulting pain syndrome should not be ignored.
Causes: diseases and other factors
Other causes of groin pain include:
- traumatic injuries to the groin area;
- proptosis is a disease that occurs in a chronic form and promotes displacement of the abdominal wall;
- herpes;
- neoplasms;
- a cyst developing in the spermatic cord;
- femoral artery aneurysm;
- varicose veins of the large vein of the lower limb.
Any discomfort in the groin requires a thorough medical examination and treatment appropriate to the case.
Causes
Pain in the groin of men occurs due to pathologies of any organ. To be more precise, this includes the genitourinary, locomotor systems, and digestive tract.
The digestive tract allows you to process food to extract the necessary vitamins and minerals for the body. There are a number of diseases of the digestive system
that can lead to pain in the groin:
- Disorder of intestinal activity. It can manifest itself as either too fast or too slow work of the muscles of the intestinal wall. It is she who, by contracting rhythmically, helps move digested food. The disorder manifests itself as diarrhea or constipation. This condition is usually caused by a malnutrition.
- Intestinal obstruction. The movement of overcooked food products is partially or completely disrupted. May be provoked by mechanical or dynamic factors
that provoke blockage. - Chronic constipation. The frequency of bowel movements is less than 2–3 times per week. There are many reasons causing this disorder. The main ones are ischemia, poor nutrition, and certain medications.
The urinary system forms, accumulates and removes the resulting urine from the body. The following can cause discomfort in the perineum:
- Urolithiasis. Impaired metabolism leads to the appearance of stones in any component of the urinary system.
- Cystitis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane is observed, and trigonitis may begin.
- Urethral cancer. A malignant neoplasm
affecting the urethra. - Urethritis. Inflammation of the urethra. The origin is conventionally divided into infectious and non-infectious.
- Bladder cancer. A malignant neoplasm located on the wall of the bladder.
The reproductive system is necessary for human reproduction.
A man has internal (seminal vesicles, vas deferens, prostate gland, Cooper glands, testicles) and external (penis, scrotum) genitalia. Painful sensations are caused by the following pathologies:
- Prostatitis. Pathological process affecting the prostate. Microorganisms enter its structure and cause pathogenic processes.
- BPH. The formation of a benign neoplasm due to excessive growth of glandular tissue.
- Vesiculitis. Inflammation in the seminal vesicles.
- Epididymo-orchitis. A disease characterized by inflammation of the testicles or appendages
. - Balanoposthitis. A pathological process localized on the head of the penis or its foreskin.
Note!
Lumbar osteochondrosis often causes pain radiating to the groin.
Diseases of the nervous and locomotor system that provoke discomfort in the perineum can be divided into:
- Groin injuries. Mainly among athletes. Accompanied by edema and swelling.
- Lesion in the lumbar plexus of nerve fibers. Caused by injuries, inflammation, tumors.
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of nagging groin pain, you must:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- reduce the number of sexual partners, give preference to protected sex with a condom;
- drink at least 1.5-2.5 liters of water per day;
- replenish the deficiency of vitamins and microelements;
- give up easily digestible carbohydrates, fried foods and animal fats in favor of fiber-rich carbohydrates, lean fish and lean meat;
- pay due attention to physical activity;
- promptly treat any infectious diseases;
- visit a urologist at least twice a year.
The preventive measures listed above will help avoid the development of genitourinary diseases and the appearance of associated symptoms.
Since the main culprit of nagging pain in the groin in men is a hernia, it is worth saying a few words about the prevention of this pathology.
To prevent the development of a hernia, you should:
- avoid lifting heavy objects or use a special corset designed for these purposes;
do not gain excess weight;- stop smoking;
- strengthen your abdominal muscles with special exercises;
- drink plenty of fluids, give preference to a healthy diet;
- promptly treat pulmonary diseases;
- Avoid constipation if possible.
In order to prevent the appearance of pain in the groin, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle and promptly treat foci of infection identified in the body. If unpleasant symptoms appear, it is necessary to begin therapy only after determining the cause that provoked the disease. When pain occurs, it is necessary to determine its location, intensity, frequency and nature.
Sudden pain in the groin on the left side of men may be the first sign of any dangerous disease progressing in the man’s body. It is for this reason that it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible and undergo the necessary treatment.
No one has yet been able to predict all cases of injuries to the genital or musculoskeletal system in the groin. But men should remember that their health, unlike the whole body, is supported by relatively thin muscles and blood vessels with their own “nuances” of structure. Therefore, throughout your life you should lift weights exclusively using the correct technique:
- from a half-squat, without rounding the back;
- without jerking, controlled and smooth movement;
- infrequently (if possible).
A sedentary lifestyle, prolonged daily standing motionless on your feet, interrupted and prolonged sexual intercourse are also harmful to blood circulation in the groin.
Treatment of groin pain
Treatment is selected strictly individually for each patient, depending on the causes of the illness. First, a man needs to see a therapist; after an examination, he will select the necessary therapy or write a referral to a surgeon or urologist.
The causes of groin pain in men are treated:
- medicinally;
- surgically;
- physiotherapeutic methods.
Therapy using folk remedies can be used as an adjunct
to the main treatment and only after the doctor’s approval.
Important!
Before visiting a specialist, you should not take painkillers, antibacterial or other drugs. Otherwise, the overall picture of the disease will be blurred.
Treatment
If you experience nagging pain in the groin, you should make an appointment with a doctor. The specialist will examine the patient, listen to his complaints, and prescribe a number of diagnostic procedures, such as:
- Ultrasound of various organs;
CT scan;- Analysis of urine;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbar spine;
- examination by a surgeon (if appendicitis or hernia is suspected);
- determination of the level of prostate-specific antigens in the blood;
- TRUS of the prostate, rectal examination by palpation (if prostate cancer is suspected);
- biochemical and general blood test;
- smears, bacteriological culture (if there is a suspicion of sexually transmitted infections).
Thus, the first thing that is examined for nagging groin pain is the kidneys, prostate and bladder. Once the diagnosis is made, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
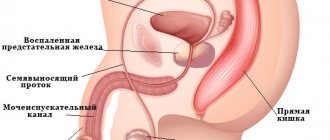
Prostatitis
The disease most often affects elderly and senile people, but it can also occur in young men.
© shutterstock
Causes
Can provoke inflammation of the prostate gland:
- genitourinary infections;
- hypothermia;
- hormonal imbalance;
- age-related changes in the body;
- irregular sex;
- frequent delayed ejaculation to prolong sexual intercourse;
- sexual abstinence;
- physical inactivity;
- venereal diseases.
Chronic prostatitis often affects older people; young people usually develop an acute form of the disease.
Characteristic signs
Symptoms depend on the characteristics of the disease.
In the chronic form, a nagging pain occurs in the groin. Added to the pain are :
- frequent desire to go to the toilet for a little while;
- feeling that evacuation is not complete;
- increased discomfort in the groin during urination;
- erectile dysfunction;
- increased pain during ejaculation.
In acute prostatitis, the symptoms are more pronounced. Sharp stabbing pain appears in the lower groin, which intensifies when trying to empty the bladder and during bowel movements. Acute pathology often occurs with acute urinary retention and signs of intoxication (fever, headache, weakness).
Treatment
Therapy is selected taking into account the severity of the disease. A man is prescribed :
- analgesics and antispasmodics for severe pain in the groin;
- antibiotics;
- NSAIDs for moderate non-infectious inflammations.
In severe cases, when the inflamed prostate impairs urinary function, a soft catheter is installed for the constant outflow of urine.
Who to contact
If pain in the groin is accompanied by urinary disorders, you should consult a urologist or andrologist.
What diseases are typical for the development of aching pain in men?
The first symptom of the development of cystitis is aching pain. Characteristics of the disease:
- When an infection gets inside the bubble, all the symptoms of inflammation develop;
- Cystitis can also be caused by urethritis and prostatitis;
- Acute inflammation in the bladder.
Factors:
- Violation of the integrity of the bladder following injury;
- Failure in the release of hormones;
- Hypothermia;
- Decreased functioning of the immune system;
- Blood stagnation occurs in the pelvis.
Acute cystitis and its symptoms:
- During the process of urination, pain and discomfort are observed;
- The urge to urinate increases;
- The bladder is not completely emptied;
- Urine becomes cloudy;
- Increase in body temperature.
First aid for severe groin pain
In case of acute pain in the groin, symptomatic therapy aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition is first needed:
- take a horizontal position;
- try not to move;
- Apply cold to the perineum (for example, a bottle of water).
If a man has severe groin pain, this may be a sign of a dangerous condition (for example, appendicitis), so you should immediately call a doctor at home.
It is not recommended to take painkillers until the ambulance arrives, or to apply heating pads or warm compresses to the sore groin.
Prostate
The prostate gland (prostate) is a single organ through which the urethra passes, responsible for the production of secretion, which is an important component of seminal fluid.
Externally, the prostate gland resembles a capsule of dense elastic tissue , but inside it is filled with glandular tissue, whose glands produce a secretion that is discharged into the prostatic part of the urethra through contraction of the smooth muscles of the gland during ejaculation.
The secret looks like an opaque white liquid , intended to dilute sperm and ensure their rapid movement through the ducts.
Also, an increase in the total amount of seminal fluid provides a rich and vibrant orgasm.
The prostate is fully formed by the time puberty ends in men; subsequently, its growth and development stop.
Abnormal development of the external genitalia in men
There are certain norms for the development of external genitalia. Deviation from these norms is anomalous .
Here are some examples of abnormal penis development:
- Congenital phimosis is the inability to fully open the head due to fused or underdeveloped foreskin. The disease threatens the development of all kinds of infections and the complete impossibility of sexual intercourse, but is usually diagnosed in the first years of a child’s life and can be successfully treated either through exercises or through surgery.
- Congenital absence of the penis or developmental anomalies of any of its parts, which include both the absence of the head and any violations of the integrity of the shaft (hidden in the body, for example, or forked).
- Ectopia of the penis (another name, micropenis) is a developmental anomaly in which the penis grows to one or two centimeters, and even in an active state does not increase by more than 3-4 centimeters, which naturally makes sexual life completely impossible. Some men complain about the size of their genital organs and in vain call their penis small, although, according to world medical standards, it is of normal, average size and does not require any enlargement.
- Hypospadias is a developmental abnormality of the urethra (the opening from which urine and semen exit). The anomaly is that the urethral opening may be located in an inconvenient place for a man, for example, on the scrotum. There are various forms of hypospadias. Generally, as a measure, surgeons perform surgical treatment of hypospadias in children so that this disease does not interfere with the person in adult life.
Seminiferous tubule
The seminiferous tubule is an organ designed to supply the testicle with blood and remove sperm from it .
with a total length of no more than 9 centimeters extend from the epididymis
They are surrounded by connective, rather loose tissue, penetrated by many blood vessels. The convoluted tubules are connected into straight ones , forming a single testicular network. The result of such a merger is a dozen efferent tubules flowing into the epididymal duct.
Penis
The penis (penis or phallus - this is what the male external genital organ is called in medicine and literature) is the external organ of a man, intended for sexual intercourse, the purpose of which is the release of seminal fluid and the removal of urine from the bladder .
On average, according to anatomical statistics, the size of the external male genital organ (member) in a calm state ranges from 4 to 8 centimeters, increasing by 2-4 times when excited.
In the anatomy of the penis, one should distinguish:
- Root (base).
- The body (trunk), which is a cavernous body, similar from the inside to a sponge with many internal voids designed to quickly fill with blood during preparation for intercourse.
- The head of the penis, covering the ends of the shaft and covered with delicate foreskin - the thinnest skin. In the central upper part of the head there is an opening, the so-called urethra, through which sperm and urine are discharged. Also, the head, due to the huge number of nerve endings, is very sensitive to any touch, which plays an important role in arousing men.
In an excited state, the penis increases in volume due to filling with blood and acquires density and elasticity.
A long-term erection is possible due to the fact that the root of the penis consists of special, quite powerful muscles that can block the movement of blood flow in a couple of seconds. After the end of the act , they gently relax, the penis falls off and decreases in size . The head differs from the excited shaft in its softness and tenderness, which allows you to avoid injury to the vagina even during very active sex.
During sexual intercourse, two types of fluid are released:
- Smegma (a familiar lubricant) is a secretion of the glands of the foreskin (the fold of skin covering the head) to reduce friction of the head and avoid the occurrence of microtraumas. The lubricant consists of fats and colonies of mycobacteria. New discharge is white and plastic, but over time it turns yellow and acquires a pungent odor.
- Sperm (also known as seminal fluid) - consisting of two components: seminal plasma - a hodgepodge of products from the activity of various glands and sperm, the final product of the male reproductive system.
Damage to the urinary system
Various lesions of the urinary system can lead to pain in the right side. The most common pathologies are:
- Urolithiasis disease. It is characterized by the formation of stones of different composition and size. If there are stones in the right ureter, the patient is bothered by acute pain in the groin area and lower abdomen. Discomfort intensifies when the stone is moved, traces of blood may appear in the urine, and disruption of urine excretion processes may occur.
- Cystitis. The pathology is characterized by damage to the bladder, which may be of an infectious nature. The disease develops in both male and female populations. It is accompanied by acute painful sensations in the groin area, which intensify significantly when visiting the toilet, and radiate to the lower back. Another characteristic symptom is an increased urge to urinate.
- Urethritis. Inflammatory lesion of the urethra, which can be infectious or non-infectious in nature. The disease causes discomfort in the groin in men, and is also accompanied by periodic burning sensations and pain when visiting the toilet.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Diseases of the lumbar spine can cause severe pain in the groin when moving. These pathologies are regularly diagnosed in both men and the female half of the population, namely:
- radiculitis of the sacrolumbar region - destruction of the roots of the spinal cord, which leads to pinched nerve endings, pain in the upper part of the buttocks, hip joints (during walking, acute pain occurs, radiating to the leg, as well as to the central part of the groin area);
- compression compression of the nerve ending located between the 1st vertebra of the sacral region and the 5th lumbar - in this case, the feeling of pain is so strong that the person feels it radiating into the leg, hindering the activity of the musculoskeletal system (when raising the leg, reflex compression is possible fingers, which indicates the beginning of the inflammatory process in the nerve root);
- intervertebral hernia formed between the 3rd and 4th vertebrae of the lumbar region - pain in the leg is localized in the groin area, and sudden lumbago may also occur, penetrating the entire lower limb (while walking, these symptoms only intensify).
The basis of therapy for the above diseases are anti-inflammatory drugs, therapeutic exercises, massage, and spinal traction. In some cases, surgery may be indicated.
Hip joints
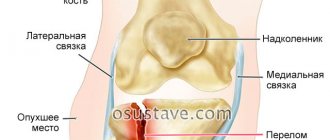
If your leg hurts in the groin area, this may indicate damage to the hip joints.
Similar symptoms are typical for the following types of diseases:
- coxarthrosis - inflammation of the connective and bone tissue of the joint occurs with further deformation, a person experiences severe pain in the groin, and while walking it only intensifies and is felt along the entire limb, right up to the knee (occurs against the background of a hereditary predisposition, hormonal imbalance, after mechanical injuries);
- Perthes disease - as a result of its development, there is a lack of blood supply to the head of the femur, which subsequently affects the condition of the tissues of the articular cartilage (the last stage of the disease is necrosis);
- rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic pathology of connective tissue that leads to dysfunction of the hip joint (accompanied by severe pain in the groin, localized on the right or left, depending on which joint is affected by the disease).
It is possible to eliminate pain in the groin that occurs when walking, which is caused by the destruction of the hip joint, but this will require systemic therapy for the source of the disease. In such cases, strong anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers are used, as well as surgery to replace the joint with an implant if its own tissue has been destroyed by the disease.
Weakening of muscle fibers
This pathology most often occurs in men and women who lead a sedentary lifestyle, suffer from excess body weight and large amounts of fat deposits in the abdominal cavity. The result of weakening muscle fibers is the occurrence of the following diseases, which cause pain in the groin that occurs when walking:
- deformation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, it can lead not only to a feeling of pain in the groin, but also to disrupt the functioning of the bladder, as well as the organs of the reproductive system;
- inguinal hernia - unlike a similar disease in the anterior abdomen, this pathology is localized exclusively in the lower abdomen, which causes aching pain that becomes acute when walking.
Causes of discomfort in the groin and their diagnosis
To make a correct diagnosis, the patient undergoes the following methods of examination and diagnosis of the disease:
- Taking the patient's medical history;
- Conducting an objective and complete examination;
- Diagnosis using laboratory tests;
- Application of instrumental examination methods.
Our readers recommend!
To quickly and reliably improve potency, our readers recommend a natural remedy that has a comprehensive effect on the causes of erectile dysfunction. The composition contains only natural ingredients with maximum effectiveness. Thanks to natural ingredients, the drug is absolutely safe, has no contraindications or side effects. Read more "
Lymphatic system
Pain in the leg that radiates to the groin may indicate the presence of a disease such as lymphadenitis. Medical practice shows that the inguinal and axillary nodes are most often affected. In addition to the characteristic pain syndrome present on the right or left side, the following symptoms are possible, which are characteristic of this disease:
- the lymph nodes in the groin area become dense and increase in size by 2-3 times;
- upon palpation, it is felt that several nodes are fused together;
- the skin over the inflamed area becomes red, and when touched it feels hot.
Pain in the leg in the groin area continues until drug or surgical therapy is carried out aimed at relieving inflammation in the lymph nodes. When there is an accumulation of purulent infiltrate, surgical intervention is a prerequisite for effective treatment, since the pathological process may spread to adjacent tissues.
How to recognize these diseases
To know what disease may be causing groin pain, let's look at the symptoms that most often accompany these disorders:
- Chronic inflammation of the prostate - in about half of the cases of pathology, there is a constant nagging pain in the groin area, radiating to the testes. Distinctive signs are painful, frequent urination, weakening of sexual desire and potency. In acute prostatitis, the pain is more pronounced, but is not observed constantly, but at times.
- Adenoma - pain and problems with urination are more pronounced than with prostatitis. A condition where pain is accompanied by enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes located on the left side of the groin is very dangerous for the male body. This indicates the presence of an infectious-inflammatory disease of the genitourinary system, which threatens the development of erectile dysfunction, sexual disorders, and infertility.
- Renal colic - the sharpest pain is most pronounced in the left side, from where it radiates to the groin area. Unbearable pain, combined with difficult painful urination, frequent urge to go to the toilet, and the release of small portions of urine mixed with blood, make it easy to diagnose the disorder.
- Inguinal hernia - a swelling appears in the left part of the groin area, which is most pronounced when standing and tensing the abdominal muscles, and can disappear in a lying position. Sharp pain is felt, as a rule, when parts of the internal organs prolapse into the hernial cavity and the hernia is strangulated. Depending on the degree of damage, nausea, vomiting, constipation and other symptoms are added to the pain syndrome.
- Orchitis and epididymitis - the main signs of pathologies are pain in the groin and testicles, which intensifies with walking and physical activity (with orchitis the pain is much stronger). Swelling and hyperemia of the scrotum, increased temperature, deterioration of general condition, and nausea are also noted.
- Varicocele - constant pain has a pulling, diffuse nature, and at times radiates to the right side of the groin.
- A spermatic cord cyst develops in men over forty years of age and is manifested by the appearance of a painless formation in the scrotum area. Pain in the left side of the groin area occurs when the enlarged cyst compresses the blood vessels and nerve endings.
- Testicular torsion - acute pain is combined with swelling of the damaged testicle, which is located higher than the healthy one.
- Inguinal lymphadenitis - the lymph nodes located in the groin area become painful and swollen, the skin turns red and swells.
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region - pain is felt not only in the groin, but also in the hips and legs, and the perineal area. Attacks of acute pain resemble neuralgia, and aching painful sensations usually occur immediately after waking up in the morning or after sitting for a long time.
Abnormal development and diseases of the internal genital organs in men
If the abnormal development of the external genital organs leads to the impossibility of sexual intercourse, then any changes in the internal part of the male reproductive system lead to the production of non-viable sperm, and, accordingly, to infertility.
The causes of dysfunction of the internal genital organs can be different:
- Congenital or acquired as a result of surgery, the absence of one or two testicles.
- Diseases suffered in adulthood, accompanied by a sharp and prolonged increase in temperature, such as influenza, mumps or measles.
- Pseudohermaphroditism, expressed in the presence of part of the female genital organs and atrophy of the testicles and prostate, which makes both full sexual intercourse and the possibility of conception impossible.
- Cryptorchidism is a disease in which one or two testicles do not descend into the scrotum, but remain in the abdominal cavity or groin.
- Groin injuries leading to testicular dysfunction or rupture of the spermatic duct.
- Inflammatory processes caused by sexually transmitted diseases.
- Consequences of inflammation caused by the last stages of hemorrhoids, prostate or urinary cancer.
Only the joint work of both external and internal male genital organs will ensure the possibility of high-quality functioning of the entire reproductive apparatus.
A short video on the structure (structure) of the internal and external male genital organs: find out what functions they perform and how the reproductive system works
A man of impressive size is what every member of the stronger sex wants , but, unfortunately, not everyone has been blessed with it by nature.
You may think that a small penis is a death sentence and accept it, or you can use one of the many methods to enlarge it at home, without resorting to surgery. Which one will help is purely individual.
How to enlarge the penis at home? Is it real? This will be discussed in this article. Read more.
The groin area is the part of the abdominal wall from below that attaches to the femur. The inguinal canal is located in the same area. The large femoral vessels, spermatic cord and urethra pass through this canal.
The groin resembles a triangular shape. The anatomy of the groin area in males is more prone to the formation of an inguinal hernia than in females. Men perform more strenuous physical work and are susceptible to pathologies such as prostatitis and phimosis. These factors are key in the spread of a hernia in the groin.
Vas deferens
The vas deferens are special ducts into which seminal fluid enters from the epididymal duct.
These are two organs, each about half a meter long, designed to release sperm. Starting from the epididymis, they pass through the inguinal canals and unite into a common ejaculatory stream, which, after passing through the prostate gland, ends in the posterior part of the urethra.
Scrotum
The scrotum is a musculocutaneous organ designed to store the testicles, epididymis and the beginning of the seminal canal.
Each individual organ is enclosed in a kind of muscle capsule inside, which is especially clearly visible by the connecting suture that every man has. The color of the skin on the scrotum is darker than the rest of the body , the skin is covered with hair, its thickness can vary.
The purpose of the scrotum is obvious - it creates optimal conditions for maintaining important internal reproductive organs. For example, to produce healthy sperm, the body temperature must be two degrees lower than normal human body temperature.
The scrotum allows this to be achieved using a unique system for maintaining the required temperature - so in the cold the scrotum tightens, and in the heat it moves away from the body as much as possible.
The structure of the anatomical region in representatives of the stronger sex
The reproductive organs of the stronger sex are divided into those located inside and outside.
Organs that are located externally:
Inside the reproductive system are:
- Testes and epididymis;
- Vas deferens;
- Prostate.
Purpose of the urinary and reproductive system in males:
- The genitals, which contain receptors, are considered an erogenous zone;
- The penis performs the act of intercourse.
Ejaculants
The paired male glands that are located inside the reproductive system are called testes.
The main task of the testicles is:
- Sperm production;
- Release of testosterone into the blood.
The testicles are oval-shaped, approximately 25 grams per testicle. The testes are located in the middle of the scrotum. The right testicle is higher than the left testicle. The testes are placed in a special shell and separated from each other by a crossbar.
The testicle is attached with the help of the spermatic cord; it consists of the following components:
- The duct through which sperm flows out;
- Nerve connections;
- Blood and lymph vessels;
- Muscles.
The testicular appendage consists of:
The peritoneal cavity surrounds the testes and creates a serous space that closes off. On the outside, the testes are covered with a tunica albuginea and under it is the testicular parenchyma. They divide the testicle into 2900 pyramidal particles.
In the middle of one of the lobules there are three tubules, which have a tortuous shape and a length of 90 mm. The seminiferous tubules are interconnected. 15 seminiferous tubules arise from here.
Duct for excreting seminal fluid
Near the prostate, the base of the vas deferens expands and a so-called ampulla is formed. It consistently narrows at the bottom and is directed into a narrow channel.
Spermatic cord
These bubbles are located in the middle of the pelvis, behind and to the side of the bottom of the bladder.
The seminal vesicles contain:
- The wide end, which is called the base;
- Body;
- The tapered end that moves into the duct to release seminal fluid.
The walls of the seminal vesicles contain many tortuous chambers containing protein fluid. It is part of the seminal fluid.
Prostate
The prostate gland has the following structure:
- Right and left lobes;
- Isthmus;
- The outer side of the gland is covered with a capsule; septa extend from it into the middle of the gland;
- The gland consists of glandular and smooth muscle tissue.
Bladder
There are two holes in the back wall of the bladder.
The ureters enter through them. The continuation of the neck of the bladder is considered the urethra. The bladder performs the following functions:
- Its capacity is approximately 350 ml;
- It can empty completely;
- The man has the urge to urinate and urine is released;
- With the help of the lower sphincter, a person has the ability to hold urine.
Rectum
The rectum is designed to collect stool. The intestine is approximately 16 cm long. 13 cm refers to the pelvic region and 3 cm in the anus. The wall of the rectum is covered with mucous and muscular membranes.
Functions of the rectum:
- Discharge of feces;
- Fecal masses collect in the rectum, where they are freed from liquid and formed into compressed feces;
- Approximately 4 liters of fluid enter the intestine per day;
- Water, alcohol, glucose and some medications are absorbed in the rectum;
- Serves as a reservoir;
- Gases and feces accumulate in it.
Penis
The penis consists of:
- Base or root;
- Trunk or middle part;
- Heads.
Scrotum
The scrotum is a muscular organ covered with skin. In its middle are the testicles, epididymis, and the beginnings of the spermatic cord. All these organs are separated from each other by partitions inside and outside by the embryonic suture. The top of the scrotum is covered with hair, and her skin is darker than normal skin color.
The scrotum contains many sebaceous and sweat glands, which emit a specific odor. The temperature in the scrotum is 2 degrees lower , which creates optimal conditions for sperm production. If it's cold outside, the testicles are pressed closer to the body; in warm conditions, they drop back into the scrotum. The scrotum is also an erogenous zone in men. If you experience itching in the scrotum, read here.
Urine channel
The channel for the emission of urine is a thin tube that has increased elasticity. In representatives of the stronger sex, the size of the canal is about 22 cm. The urethra starts from the bladder and comes out at the head of the penis.
How to get rid of prostatitis without the help of doctors, at home?!
- so that the pain stops
- normalize urination
- so that sexual desire appears and the opportunity to have sexual intercourse. Shaken men's health can and should be restored! with a timely course of treatment. Read more "
Male genitourinary system
In men, the organs of the reproductive and excretory systems are susceptible to inflammatory processes, the occurrence of which can provoke pain during fast or slow walking.
The following pathologies of the male genitourinary area are identified, which cause pain in the groin area when moving:
- varicocele is an expansion of the blood vessels that supply the epididymis and the testis itself; the right testicle is most often in the affected area (after taking 2 steps, the man is forced to stop moving, since the pain in the testicle is so severe that it radiates to the limb, and the pathology can only be treated with the help surgical intervention);
- prostatitis is an acute or chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the prostate gland; during examination, a man often complains that he has pain between the leg and groin, and also radiates to the perineum and anus (the disease is successfully treated with the drugs Prostamol, Escusan, Prostanorm , Prostatilen);
- testicular torsion - displacement of the epididymis with twisting of the spermatic cord, which entails a violation of local blood circulation in the organ (mechanical reduction of the testicle or surgical operation is required);
- hydrocele - a disease expressed by the accumulation of an excess amount of serous fluid in the membrane of the testis (during movement it can cause both acute and aching pain in the groin area);
- urethritis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra, it can spread to neighboring organs of the genitourinary system located in close proximity to the source of pathology.
If the cause of pain in the groin that occurs at the slightest movement is associated with diseases of the male genitourinary system, then in this case additional symptoms may occur in the form of: changes in the color of urine (turbidity, acquisition of darker tones, presence of bloody discharge); a burning sensation in the pubic area, which intensifies during urination; frequent urge to go to the toilet; loss of strength, physical weakness; increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees Celsius; erectile dysfunction.
If there is pain in the groin due to pathologies of the male reproductive system, then the discomfort in this part of the body increases in proportion to the severity of the inflammatory process. The pain syndrome can be localized in the center of the groin, closer to the perineum, or radiate to the lower limb.
Testicles
Testicles (testicles) are a double gland responsible for the formation of sperm and the release of the hormone testosterone into the blood, which is responsible for sexual arousal in a man. The size of the testicle on average ranges from four to six centimeters in length.
The location of the testicles is the scrotum, where the testicles are separated by a special membrane (externally expressed by a suture on the scrotum). It is normal that the testicles may be different in size or located at different heights.
The testicles are perhaps
the most vulnerable organ of the male reproductive system .
For example, overheating is strictly contraindicated for them , because too high a temperature interferes with the development of sperm. The norm for good testicular function is a temperature not exceeding 32-33 degrees.
The scrotum is responsible for regulating temperature, but it may not cope with the task if, for example, a man enjoys hot baths, has a sedentary job, or wears excessively tight underwear.
Diseases of the genital organs in men
The importance of all organs in the body is high, but representatives of the stronger sex are most horrified when they notice any unpleasant symptoms of diseases of the genital organs.
They are right to be horrified, I must say. And I must also say that it is necessary to take the most important measure - consult a doctor. A doctor who can examine and identify diseases, pathologies and anomalies of the male genital organs (inflammation, infectious, congenital, etc.) and in most cases can independently carry out treatment, taking into account the age characteristics of the patients, is an andrologist. He can identify purely male diseases, or common diseases, but they manifest themselves differently in women.
The figure clearly shows the cross-sectional structure of the male genital organ system:
Scroll down to read a description of the physiology of the internal male genital organs.
For the harmonious functioning of the male reproductive system, the participation of both external and internal genital organs is required. What do the internal male genital organs include?
The internal genital organs are divided into : testicles, vas deferens, prostate gland, spermatic cord and prostate.
It is worth taking a closer look at the features and work of each of these organs.