Women almost always associate pain in the lower right side with appendicitis. This comparison, although not always correct, is favorable: if appendicitis is suspected, an ambulance is always called, and any acute pathology will be under the supervision of a doctor.
The causes of pain in the right side of the lower abdomen in women are associated with damage to nearby organs and are quite diverse: the gastrointestinal tract, reproductive and urinary systems, lymph nodes and blood vessels. The nature of the disease that provoked the pain syndrome can be guessed from the accompanying symptoms. However, only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease and provide appropriate medical care.
Causes of pain in the right lower abdomen associated with the gastrointestinal tract
Damage to the gastrointestinal tract is a common cause of abdominal pain localized to the right and bottom. Patients often develop symptoms of an “acute” abdomen, in such cases emergency medical care is required. Sometimes the pain is dull and prolonged, while the woman often tries to lie down, while the disease progresses in the meantime and can lead to serious consequences. List of diseases and their symptoms that provoke pain in the lower abdomen on the right side:
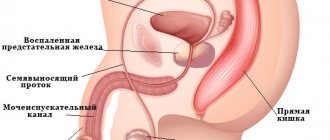
- Appendicitis
Initially, the pain is aching and quite tolerable, localized in the navel and epigastrium. Only then is the pain center identified in the right iliac region, the pain increases, signs of an “acute” abdomen appear (board-shaped abdomen, specific tests of Shchetkin-Blumberg, Voskresensky, Obraztsov, etc.). In this case, the woman notes an increase in temperature, nausea, and single vomiting.
As inflammation progresses, after 1-2 days, appendix necrosis and peritonitis develop. With acute inflammation of the peritoneum, the patient’s general condition changes greatly: decreased a/d, pale skin covered with sweat, confused consciousness, temporary subsidence of pain and its resumption with renewed vigor.
- Pancreatitis
The picture of acute pancreatitis is very specific. Severe girdling pain, affecting the lower abdomen on the right, forces the patient to take a knee-elbow position. The temperature rises, uncontrollable vomiting does not bring relief. Shortness of breath, hiccups, and bloating appear.
- Strangulated inguinal hernia on the right
Severe pain occurs in the area of the hernial protrusion, peristalsis in the strangulated intestinal loops cannot be felt, and the hernia cannot be reduced. Subsidence indicates the onset of intestinal necrosis.
- Right intussusception, intestinal obstruction
The pain quickly spreads throughout the abdomen, bloating and lack of peristalsis are noted. Signs of intoxication and a state of shock quickly increase. Intussusception is often caused by large-scale helminthic infestation.
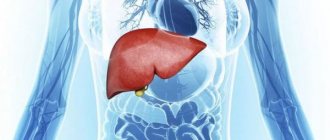
- Gallbladder and liver diseases
Pain in the lower right with cholecystitis, cholelithiasis and hepatitis is often radiating in nature (the epicenter of pain is located higher). Aching pain indicates chronic cholecystitis, paroxysmal pain is a sign of gallstones or acute cholecystitis, pressing pain occurs with hepatitis (absent in the initial stage).
- Enteritis
Cramping pain is localized near the navel, often radiating down the abdomen on the right to the area of the ileocecal valve (the junction of the small and large intestines).
- Colitis
Inflammation of the ascending colon leads to a constant feeling of heaviness on the right side, nagging pain periodically intensifies. Possible chronic constipation, diarrhea (with Crohn's disease).
- Intestinal diverticulum
Protrusion of the intestinal wall is often the result of chronic inflammation (enteritis, colitis) and constipation. In this case, the accumulated feces harden and turn into stones, and periodically there is quite a strong stabbing pain.
- Oncopathology of the intestine
At an early stage, the malignant process is manifested by frequent painless diarrhea that is not amenable to conventional treatment. Patients lose weight and become anemic. Pain occurs only when the tumor reaches a large size (closing the intestinal lumen) and metastasizes, accompanied by signs of obstruction (vomiting after eating) and critical exhaustion.
Important! Acute processes in the gastrointestinal tract - appendicitis, strangulated hernia, diverticulum rupture, etc. - are fraught with the development of peritonitis. Medical assistance must be provided as an emergency.
Ischemic colitis
There are a number of pathological processes in which obstruction and/or blockage of venous vessels in the intestine occurs. These diseases include: diabetes mellitus, vein damage, vascular atherosclerosis. As a result, inflammation develops - ischemic colitis.
This pathology is characterized at the first stage by severe cramping pain in the lower abdomen, then spreading to the affected side. At the second stage, after some time, pain decreases.
They are becoming widespread. To establish a correct diagnosis, in addition to pain, it is necessary to notice the following symptoms:
- decreased appetite;
- nausea;
- bloating and rumbling in the abdomen;
- indigestion;
- severe pain when pressing with your hand in the affected area;
- with the development of the acute stage of the disease (infarction of the intestinal walls), blood may be detected in the stool.
When are urinary system diseases to blame?
A nagging, aching pain in the lower right side is often a consequence of severe pyelonephritis (inflammation of the right kidney). In this case, there is irradiation of pain in the groin and thigh, an increase in temperature to 38ºC and above, cloudy urine, severe intoxication (headache, weakness). Often, severe pain in the lower right abdomen is a consequence of kidney stones.
Acute symptoms of renal colic develop as the stone moves through the ureter. Cramping pain is accompanied by nausea, fever, urinary retention and false urges. You can visually notice blood in the urine.
Important! Pain in the lower abdomen associated with kidney pathology is always accompanied by a change in the composition of urine. With indolent kidney damage, symptoms of intoxication, swelling, and increased blood pressure come to the fore.
Duodenitis
This disease is nothing more than inflammation of the duodenum. Most often, the disease affects males. Signs of this disease, along with a cylindrical lump and pain to the right of the navel, are excessive salivation, dizziness, high blood pressure, vomiting with bile, general malaise, and dry mouth.
The stronger half of society is most susceptible to inflammation of the duodenum. Symptoms of duodenitis include: an increase in the amount of saliva, dizziness, increased blood pressure, a sluggish state of the body and, of course, pain near the navel. Sometimes vomiting with stomach bile may occur.
The cause of pain is pathology of blood vessels and lymph nodes
Often the cause of pain in the groin and lower abdomen is lymphadenitis. Inflamed lymph nodes, often mobile and painful with infectious lesions of the genital organs and bladder in women. Lymph nodes enlarged due to cancer pathology are painless and fused with the surrounding tissues.
Vascular diseases that cause pain in the side are a difficult group of diseases to diagnose. Painful sensations occur with atherosclerotic lesions of the iliac artery and the formation of an aneurysm, inflammation of the deep inguinal veins.
With arterial pathology, the pain is pulsating in nature. Diseases are detected by instrumental examination of blood vessels (Doppler ultrasound, etc.), an increase in coagulability, an increase in cholesterol and other changes in the blood are also detected.
Above
In the upper left part of the peritoneum there is: the spleen, diaphragm, stomach, pancreas, intestinal loops. Some diseases can cause the spleen to become enlarged or even rupture. The cause may be an injury or blow, when there is severe pain, a bluish seal near the navel from above.
Other causes of discomfort:
Gynecological problems with characteristic pain symptoms
Pain in the right lower abdomen can be caused by both acute and chronic gynecological diseases. Some of them pose a high threat to life, so pain in the lower right side of women, combined with severe general condition and bleeding, requires urgent hospitalization.
- Right-sided adnexitis - provokes attacks with radiation to the lower back. The disease often simulates renal colic, but with adnexitis there are no changes in the urine. With chronic inflammation, pain intensifies during sexual intercourse.
- Ovarian cyst - characterized by constant aching pain in the lower abdomen on the left or right. The syndrome is more pronounced during menstrual bleeding. Rupture of the ovary, torsion of the cystic pedicle are manifested by a sharp increase in pain (“dagger” pain), a state of shock quickly develops (confusion, nausea/vomiting, etc.). A woman’s acute condition is associated with physical activity or sexual intercourse.
- Adhesive disease, chronic inflammation of the uterus, fibroids - pain in long-term diseases of the uterus is usually mild and aching. Strengthening occurs in the premenstrual period and the first days of rejection bleeding. Often, white or bloody discharge appears from the vagina.
From below
A seal near the navel from below is observed if it is:
- pinched hernia;
- protrusion of the sigmoid colon;
- rupture of the walls of the diverticulum;
- inflammation of the pelvic organs in women;
- intestinal obstruction in the lower sections;
- increased gas formation in the walls of the large intestine;
- localization of the tumor in the genital organs of men.
A lump in the lower abdomen can be caused by: IBS, intestinal inflammation, compression by nerves (extending from the spinal column), or movement of a kidney stone down the ureter.
Lower abdominal pain and pregnancy
When carrying a child, a number of physiological changes occur, leading to the appearance of pain in the right side. Softening of the ligaments, changes in the position of the uterus and its growth, displacement of intestinal loops - all this provokes nagging pain in the lower right side during pregnancy. However, physiologically caused pain is not pronounced and does not affect a woman’s life. Pathological symptoms during pregnancy can be caused by:
- Ectopic pregnancy - severe, sharp pain occurs when a tube ruptures (approximately 3-4 weeks of pregnancy). Painful shock is accompanied by confusion, vomiting, and tension in the anterior abdominal wall.
- Hypertonicity of the uterus - can be detected from the early stages of pregnancy. Constant nagging pain intensifies when walking, lifting even a small weight (there is a feeling of a dense lump in the lower abdomen) and weakens in a sitting or lying position with the knees brought to the stomach. This condition is regarded as a threat of miscarriage. Fetal rejection is accompanied by increased symptoms (often cramping) and bleeding.
- Placental abruption in the later stages provokes pain, but external bleeding does not always occur. Often, blood accumulates between the amniotic sac with the placenta and the uterine wall, forming a hematoma. A growing hematoma provokes dull, less often cramping, pain. Pain in the lower right side during pregnancy complicated by placental abruption and in the absence of external bleeding indicates the localization of a hematoma. The epicenter coincides with the site of placental abruption. Even with intrauterine hemorrhage, placental abruption is diagnosed, among other things, by disturbances in the cardiac activity of the fetus.
Important! The development of other acute pathologies in pregnant women cannot be excluded. Pain on the lower right side can be caused by appendicitis, kidney stones, or iliac artery aneurysm. Therefore, if you experience even minor pain, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment measures
Methods are selected exclusively by the attending physician. It is possible to prescribe medications based on the results of diagnostics, other studies, tests, blood and urine tests. So, for example, if a hernia is detected, a correction is required, which means surgical intervention. The main thing is not to give the pathology a chance to develop further.
Additionally, in the case of a hernia in the area of the umbilical ring in infants, it is recommended to massage, place the baby on the tummy more often, and apply a copper coin to the navel.
Reviews from women are such that in some cases the umbilical hernia resolves on its own. The main thing is to start preventive or therapeutic measures in time.
Often in infants a hernia is caused by poor ligation of the umbilical cord or accumulation of gases. It is enough to carry out simple manipulations in a timely manner, which will certainly help to avoid complications and surgery in the future.
Of course, in some diseases, a protrusion at the navel carries a mortal danger:
- peritonitis;
- abdominal aortic aneurysm;
- duodenitis;
- inflammation of the intestine, duodenum.
Conclusion
Immediate assistance from specialists is required. Connivance and lack of reaction to a protrusion in the abdomen on the part of parents can lead to irreversible consequences and death.
What to do if you have pain in the lower abdomen?
Any woman should forever remember a simple truth: under no circumstances should you take painkillers for pain in the abdominal cavity, including the right side!
Even a mild but growing symptom may indicate the development of an acute pathology. Help in such cases, and often even save life, can only be done with the help of emergency medical measures. The only correct tactics in case of abdominal pain that lasts more than 30 minutes:
- Put the patient to bed.
- Apply an ice pack or any cold to the pain area.
- Call emergency assistance.
Making an appointment with a local physician or gynecologist is permissible only in cases of mild pain, no worsening signs of the disease and no worsening of the patient’s condition. Only timely, complete diagnosis using laboratory tests and instrumental studies will help determine the true cause of pain and choose the right treatment tactics.
Tags:
my stomach hurts
Intestinal tumors
Oncological diseases of the intestine are relatively rarely manifested by clearly localized pain. Often, both the patient and the doctor learn about the tumor itself only during surgery for intestinal obstruction. However, if the tumor compresses or invades neighboring organs, pain can still appear quite early.
Treatment
For oncological pathology, the entire range of antitumor measures is used:
- radiation therapy;
- chemotherapy;
- use of immunosuppressants;
- surgery to remove the tumor (if technically possible).
Umbilical hernia
One of the obvious indicators of an umbilical hernia is a hard seal in the peri-umbilical area, which does not disappear when pressed with fingers, but, on the contrary, becomes more noticeable and causes severe pain. In addition, the patient will be disturbed by bloating, constipation, vomiting and rapid heartbeat. The hernia may be strangulated and reducible. In both cases, the help of an expert is required, who in the first case will prescribe surgical intervention, and in the second, he will independently correct the existing seal.
Sutures after caesarean section
Women often experience hardening of their sutures after a caesarean section. Naturally, not in all cases the compaction indicates a disease. However, a caesarean section is a complex operation, and during it doctors are forced to cut tissue in the abdominal area, then fasten it with medical materials and sew the tissue with a ligature. During recovery, the sutures are covered with scar tissue, but in some cases a growth appears in the abdominal area due to an autoimmune reaction, the use of low-quality materials, the appearance of an abscess under the skin, and tissue infection. It is suppuration that can become a very dangerous phenomenon if the subcutaneous tissues have been damaged, cells have died, and dead tissues have mixed with keratinized skin particles. Bacteria may enter, which can cause tissue compaction, structural changes and infection. Additionally, burning, itching, and ichor occur in the abdominal quadrant.
What can hurt in the lower abdomen is interesting to many.
Trephine biopsy of the iliac bone
Trepanobiopsy of the iliac bone is a type of diagnostic examination, the conduct of which involves the selection of bone marrow particles, as well as tissues.
The main purpose of the procedure is their histological examination, aimed at determining the health of the bone tissue structure. Doctors receive comprehensive information about the quality of the cellular composition of the bone marrow, the percentage of adipose and hematopoietic tissue, the condition of blood vessels and stroma.
Histological analysis makes it possible to determine the presence of a benign or cancerous neoplasm if signs of a tumor process are found in the structure of the ilium. Biological material is collected using a needle puncture. The patient is under general anesthesia, and the diagnostic procedure itself is a simple surgical operation.
The first signs of colorectal cancer
If every person over 40 had regular colonoscopy, colorectal cancer would become rare. Alas, this is still far from happening.
The main risk group is people over 60 years of age, but among the patients, about 20% are those who are still very far from retirement.
The exact causes of this, as well as any other cancer, are not completely clear. But one thing is clear: colon and rectal cancer is a disease of civilization. In those corners of the world where people still earn their living by hunting and fishing, where it is customary to move not on wheels, but on foot, where the air is saturated with the smells of earth and grass, and not gasoline and asphalt, we have heard about this disease haven't heard of it.
In what cases should you go to the doctor?
If the pain is intense, does not stop for several hours and, in principle, interferes with normal activities, you need to consult a doctor.
First, you should visit a gynecologist and gastroenterologist . If necessary, they will refer you to other doctors, such as an infectious disease specialist or even an oncologist.
Since diagnosis with such a vague symptom is quite difficult, it is recommended to carry out a number of tests:
- General blood analysis;
- Urinalysis, including culture and antibiotic susceptibility testing;
- Diagnosis of pregnancy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs to detect tumors;
- If inflammation is suspected, a church mucus test is performed;
- Culdocentesis, which determines the presence of fluid in the area of the uterus and rectum;
- X-ray of the peritoneum;
- Laparoscopy of the pelvis.
Find out on our website about medications for the treatment of cystitis in women! Look for a list of popular and effective ones in our article.
What are the causes of ureaplasma in women? You will learn everything about this disease and its effective treatment from our review.
We will tell you how hormonal imbalance manifests itself in women and what the correct treatment should be like here: https://beautyladi.ru/gormonalnyj-sboj/.
Discomfort in the stomach during pregnancy
Pregnant women often experience pain in the lower abdomen. Is this normal? To answer this question, you should pay attention to the deadline.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, frequent pain in the right side may indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
This pathology leads to the fact that a fertilized egg gets stuck in the fallopian tube. Over time, it stretches, and if the girl is not given medical assistance in time, it ruptures.
Also, a painful right side in a pregnant girl can signal the possibility of a miscarriage. Typically, discomfort in this area occurs when walking.
To establish the exact cause of this phenomenon, a pregnant girl needs to undergo a medical examination. After examining the patient and collecting the relevant tests, the doctor will prescribe her treatment.
It is also worth highlighting a separate group of factors that provoke discomfort in the right side during pregnancy - obstetric pathologies.
- Spontaneous abortion. With a spontaneous abortion, a girl may experience severe pain. This pathology develops in early pregnancy. Pain syndrome with this pathology is accompanied by heavy vaginal bleeding. There is a risk of large blood loss and infection of the birth canal.
- Premature birth. This pathology occurs in late pregnancy. Pain in the lower abdomen during premature birth is combined with toxicosis. To eliminate the risk of death of the baby, the woman must be urgently hospitalized.
Why there is pulling in the right side: common diseases for men and women
A symptom such as nagging pain in the right half of the abdomen may accompany acute appendicitis, chronic cholecystitis or pancreatitis, inflammation of the kidneys and pathology of the spinal column.
Acute appendicitis
In 80-90% of cases, pain in acute appendicitis is acute and accompanied by nausea and fever. But inflammation of the appendix can masquerade as another pathology, especially if it is in an atypical location:
- In an ascending position, the process is located near the liver. When it is inflamed, patients often complain that the right side of the abdomen is pulling; the pain is often dull and moderately intense. The severity of symptoms of intoxication depends on the duration of the process and its prevalence. In such cases, acute appendicitis can easily be confused with cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), an abscess in the liver, or even pneumonia, in which abdominal syndrome is often observed.
- With a medial or median location of the appendix, the pathological process can imitate inflammation of the mesenteric lymph nodes or diverticula (congenital protrusions in the form of pockets in the small intestine), in which there may also be a complaint of pulling on the right side.
- In the case of retrocecal (that is, behind the cecum) localization, acute inflammation of the appendix can be confused with an ovarian cyst, adnexitis, since with these diseases there is also a nagging pain that occurs in the right side of the abdomen.
Classic symptoms of the disease (Shchetkin-Blumberg, Rogozin, Kocher, etc.), an increase in signs of intoxication within 24 hours of observation, the absence of pathological changes on ultrasound of the ovaries, gall bladder and liver, intestinal lymph nodes, an increase in ESR help the doctor make a diagnosis of acute appendicitis. and leukocytes in peripheral blood.
Chronic cholecystitis
Frequent stressful situations, abuse of fatty, spicy and fried foods, concomitant pathology of the gastrointestinal tract lead to stagnation and retention of bile in the bladder with the subsequent development of chronic inflammation in it.
If there is a metabolic disorder, in particular fat metabolism, stones may form in the cavity of the gallbladder, which also injure its wall and disrupt the outflow of bile. Mostly, patients with chronic cholecystitis complain that they have a pulling on their right side under the ribs, morning sickness and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth. Stool disorders in the form of constipation or diarrhea may occur.
Upon objective examination, the doctor sees a tongue coated with a white or brownish coating and pain on palpation in the right hypochondrium. Thus, such complaints from the patient as pulling on the right side and nausea allow the doctor to suspect the presence of chronic inflammation in the gallbladder.
Treatment of chronic cholecystitis is mandatory, otherwise the following complications may develop: biliary hepatitis and reactive pancreatitis (reversible inflammatory changes in the head of the pancreas), in the case of stone cholecystitis - hepatic colic or peritonitis due to rupture of the gallbladder.
Chronic pancreatitis
The development of this pathology is influenced by:
- Nutritional factor (fatty, coarse and spicy foods).
- Smoking and alcoholism.
- Chronic stress.
- Some previous infections (for example, mumps).
- Autoimmune factor (when the human body produces antibodies directed at pancreatic tissue).
One of the main manifestations of the disease is a dull nagging pain in the right side, which, when worsened, becomes spastic in nature. Most often, the pain is girdling, that is, it engulfs the upper abdomen and back, either in the form of a half-belt on the right or left.
In addition, characteristic symptoms are nausea and vomiting, which brings relief, loose stools mixed with undigested food (this indicates a deficiency of glandular enzymes).
During the examination, the doctor identifies painful points in the projection of the pancreas and can palpate its enlarged head or tail through the anterior abdominal wall.
Acute pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis refers to inflammation of the kidney tissue involving the pyelocaliceal system.
Most often, the disease develops against the background of an existing infection in the body:
- Acute cystitis or urethritis (bacteria ascend through the ureters into the kidneys).
- Acute or chronic tonsillitis (in this case, microorganisms are carried by the bloodstream).
- Anomalies in the structure of the genitourinary system, pregnancy, general hypothermia and urolithiasis also contribute to the development of pyelonephritis.
Against the background of intoxication (fever, weakness), pain occurs. As a rule, patients complain of pulling the right side and lower back on one or both sides. Symptoms of dysuria appear: frequent and painful urination, imperative urge. The urine itself may become cloudy with sediment in the form of a whitish suspension.
The disease progresses quickly and requires timely treatment with antibiotics, uroseptics, antioxidants and detoxification therapy (intravenous administration of glucose-saline solutions to eliminate toxicosis).
Degenerative diseases of the spinal column
Osteochondrosis and osteoarthritis of the spine occur equally in both men and women of any age.
Incorrect posture, excessive physical activity, excess weight, impaired metabolism and deficiency of microelements and vitamins in the body - all this leads to the development of degenerative processes in cartilage and bone tissue. On both sides of the spinal cord, spinal roots consisting of nerve fibers extend. For example, if any thoracic root on the right is pinched due to osteochondrosis, the patient may have a complaint, voiced by him as “pulling the right side from the back.”
The pain is dull, less often aching, and is constant. In addition, some physical capabilities of a person are limited, since pain intensifies when walking and sitting for long periods of time.
Additional symptoms include:
- impaired sensitivity in the projection of the innervation of the roots;
- crawling sensation or so-called paresthesia;
- pain along the spinal column.