The intensity of bleeding depends on the shape of the uterine fibroids.
By the number of myomatous nodes:
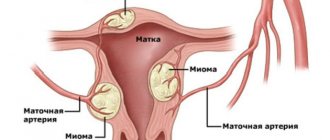
- single form - one myomatous node;
- plural form – several nodes.
By localization of nodes in the uterus:
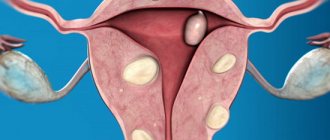
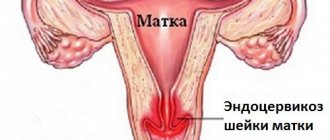
- Submucosal fibroids (submucosal) are a rare form of fibroids with a close location to the uterine cavity. Due to the presence of a thin stalk at the submucosal nodes, they are able to descend into the vagina and cervix. It is with submucous uterine fibroids that bleeding most often occurs.
- Interstitial form (intramural) - with this fibroid, intermuscular nodes are localized in the wall of the uterus.
- Subserous form - subperitoneal nodes are located outside the uterus, on its surface.
- Intraligamentary form – interligamentous myomatous nodes.
- Cervical form - a tumor on the cervix.
The most common form of uterine fibroids is interstitial, affecting 50-61% of women, subserous - 26-35%, submucous fibroids - up to 13%.
Causes
Women with a hereditary factor, excess weight, early menstruation, physical inactivity, inflammation of the genital organs, nulliparous women exposed to constant stress are predisposed to the occurrence of uterine fibroids. The risks are increased in women who have been treated with antihypertensive drugs for 5 years in a row, with a history of frequent curettage of the uterine cavity. In premenopause and menopause, when ovarian activity and estrogen production are suppressed, the likelihood of developing a tumor is significantly reduced, but it exists in almost all women of any age, with any general and reproductive health condition.
The mechanism of development of fibroids: damage occurs in one cell of the myometrium, from which the growth of a subserous, submucosal, intramural, interligamentous or cervical node begins, depending on which part of the organ the defect occurred. Only one tumor-like formation can grow from each damaged cell. If several cells of the muscle layer are damaged, then a multiple form of fibroids will appear, and some of the nodes die on their own, while others develop.
According to one version, cells are damaged during embryogenesis, which explains the development of fibroids in girls at an early age. According to another version, a defect in myomatous cells occurs under the influence of various factors (abortion, inflammation, injury to uterine tissue).
https://youtu.be/irw2FZTu8Wc
Therapeutic measures
Treatment for bleeding in young girls or women during menopause is the same. If the patient is not pregnant, then curettage of the uterine cavity is prescribed. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. It is used to stop hemorrhage and determine the cause of such a symptom.
Further treatment tactics may vary depending on the woman’s condition. Both conservative and surgical treatment are possible. In the first case, hormonal pills are prescribed. They help in reducing the size of the tumor.
If surgery is not necessary, then after the bleeding has stopped, intervention is performed. There are several methods of therapy:
- Myomectomy, in which only the tumor is removed.
- Embolization of the uterine arteries, the essence of which is to stop blood circulation in the tumor, which leads to its death.
- Complete removal of the uterus and fibroids. This radical method is used only in extreme cases. Moreover, most of the patients to whom it is prescribed are women who are in the climacteric period.
After the operation, strict adherence to the gynecologist’s instructions is required for successful rehabilitation of the body.
Types of bleeding with uterine fibroids
| Types of bleeding | Characteristics |
| Menorrhagia | Daily blood loss during menstruation is 80 ml or more, with a norm of up to 60 ml. Blood clots may be released |
| Menometrorrhagia | Bleeding during menstruation and between cycles |
| Metrorrhagia | Acyclic discharge (only between cycles) in women of reproductive age. Metrorrhagia in premenopausal and menopausal women always indicates the presence of fibroids or another tumor. Metrorrhagia is dangerous because it occurs suddenly |
| Hyperpolymenorrhea | Menstruation is not only heavy, but also prolonged, and there is a danger of large blood loss, which leads to anemia and the development of asthenic syndrome |
The mechanism for the development of bleeding in fibroids: the surface of the endometrium becomes unequal during the disease. This causes the contraction of different areas of the mucosal layer at different times. Some sections are rejected during menstruation, the rejection of other fragments does not coincide with menstruation, so acyclic bleeding occurs.
The occurrence of bleeding is facilitated by weakened myometrial tone, defects on its surface, damage to the vessels of the muscle layer, and an increase in myomatous nodes. It is when they grow that bleeding occurs in most cases. This condition requires appropriate treatment, otherwise serious complications will arise.
Treatment of uterine fibroids
When faced with a problem, most women begin to think about what to do to stop the bleeding. This is not the most correct way to pose the question. First of all, you need to understand that bleeding from fibroids requires treatment of the disease itself as a whole, and not getting rid of just one symptom.
The nature of therapy is determined based on several criteria: the degree of the disease, the nature of the bleeding, the age and characteristics of the patient’s body.
With the help of medications
Conservative therapy for bleeding from fibroids involves taking hormonal medications. This method is indicated under the following conditions:
- The size of the formations is less than 12 weeks;
- There are no strong pain sensations;
- The disease did not affect the organs adjacent to the uterus;
- At the time of treatment there is no significant blood loss.
This method is also prescribed to girls who have not reached puberty, and to women who have had surgery to remove fibroids, and less than six months have passed since the operation.
Medicines prescribed by a doctor are aimed at performing the following functions:
- Stopping uterine bleeding with fibroids;
- Elimination of the inflammatory process;
- Strengthening blood vessels;
- Restoration of hormonal levels.
As a rule, the complex of drugs includes coagulants, antiprogestogens, progesterone-containing medications, hormonal contraceptives, etc.
The doctor’s qualifications play an important role in this matter. If prescribed incorrectly, the situation may worsen and the tumor may begin to grow.
Surgical method
The most effective method of treating fibroids, and therefore stopping bleeding, is surgery. Indications for it are:
- Large size of neoplasms;
- Active tumor growth;
- Severe pain in the pelvic area;
- Excessive blood loss;
- Presence of endometriosis.
The most effective method of treating fibroids is surgery.
In most cases, surgery allows you to remove fibroids while preserving the reproductive organ.
There are three types of surgical intervention:
- Laparotomy. Abdominal surgery in which the anterior abdominal wall is dissected. This type is indicated when there is a risk of injuring the arteries and causing large blood loss. If there is an incision, the surgeon has maximum control over the course of the operation;
- Laparoscopy. The procedure is carried out using an endoscopic device. Tumor formations are removed through punctures, after which sutures are applied to them. The patient's recovery is quite fast;
- Hysteroscopy. Allows removal of fibroids through the cervical canal. Endoscopic equipment is also used for this.
There are also minimally invasive procedures, such as arterial embolization. It is used to block arteries feeding tumor nodes. As a result, they die and are excreted in the blood.
Another procedure in the form of curettage is aimed at removing thickened endometrium. With its help, bleeding is stopped and the volume of the upcoming operation is assessed.
Folk recipes
Many women, in search of an answer to the question of how to stop bleeding, turn to traditional medicine. Such therapy is not capable of defeating the disease on its own, but may well act as an addition to the main medical treatment.
A decoction of shepherd's purse is an effective hemostatic agent.
Among the methods of alternative medicine are:
- Infusion of nettle and yarrow. Dry crushed herbs are mixed, 25 grams of each. The resulting mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water and left for at least two hours in a warm place. You need to drink the solution one third of a glass 3 times a day for 10 days;
- Tea made from mint and rowan. The fresh leaves of these plants are brewed into herbal tea. You need to drink it 3 times a day;
- A decoction of shepherd's purse. This plant with an unusual name is brewed in the proportions of 1 tablespoon per 250 milliliters of boiling water. Take a tablespoon of the decoction 4 times a day at regular intervals;
- Decoction of cucumber lashes. Dry cucumber lashes in the amount of 50 grams are poured into a thermos and poured with 500 milliliters of boiling water. Infuse the liquid for an hour. You should drink the decoction 120 milliliters 3 times a day;
- Tincture from boron uterus. It is made by mixing 50 milliliters of vodka and 50 grams of dry grass. The solution is infused in a cool, dark place for a month. Drink tincture 40 drops 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 21 days.
Before using traditional medicine, you should consult your doctor. This is the only way to choose the optimal treatment method and avoid possible complications.
Signs and complications of the disease
Each form of uterine fibroids has its own characteristics. In half of the cases, there are no symptoms of fibroids if the tumor is small and located intramural or subserous. The most pronounced symptoms are with submucous fibroids, especially if there is not one but several lesions. Without proper timely treatment of submucosal and other types of myomatous nodes, they can grow to enormous sizes, which causes significant deformation of the uterus and compression of nearby organs.
Compressing the uterus, bladder and intestines, the submucosal node causes uterine bleeding, frequent or involuntary urination, urinary retention, constipation, pain in the lower abdomen, intensifying during menstruation (algomenorrhea), painful intimate contact (dyspareunia), and cycle disorders. The most intense, sharp pain occurs when the pedicle of a submucous myoma is torsed, which requires urgent radical treatment.
Sometimes the first symptom may be acyclic bleeding. This sign cannot be ignored. If at this stage a woman turns to a specialist, she will avoid dangerous complications and complex treatment. If you ignore the bleeding, the tumor will grow further, which will lead to unpleasant consequences.
Bleeding leads to the development of anemia and asthenia. The woman experiences weakness, fainting, tachycardia, fever, and hypotension. If a pedunculated submucous tumor prolapses through the cervical canal, then they speak of the “birth” of a node.
With a large tumor, ascites, thrombosis, venous insufficiency, and intestinal obstruction are possible. Infertility develops in 3% of cases, spontaneous miscarriages – in 10% of cases. During gestation, the tumor increases in 10% of cases.
Don't self-medicate
Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Causes of myomatous bleeding
The formation of fibroids in the uterine cavity leads to the active development of a vascular network, similar to the state of the organ in pregnant women (it is no coincidence that when diagnosing a myomatous tumor, its size is determined over weeks, as during pregnancy). Myoma increases in size and begins to affect neighboring organs. In addition, myomatous nodes provoke the following changes:
- hypertrophy of the venous system;
- loss of vascular tone;
- loss of elasticity of the vessels of the uterine organ;
- uneven thickening of the endometriotic layer;
- proliferation of the myomatous layer;
- increased blood supply to the uterus.
The above factors lead to a decrease in the contractility of the uterine organ, creating an ideal environment for the development of bleeding.
Diagnostics
Often, fibroids are discovered accidentally during a medical examination or after heavy bleeding. The diagnosis is made based on diagnostic data:
| Type of diagnosis | results |
| History taking | The patient should be prepared for the doctor to ask not only general questions, but also questions related to the intimate sphere. The truthfulness of the answers affects the final result when making a diagnosis. |
| Gynecological examination | During a bimanual examination, the doctor determines the size and shape of the uterus, the intensity of pain, and the presence of bleeding. |
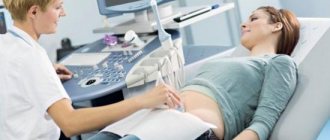
| Ultrasound sonography transvaginal or transabdominal | The main method of examination for fibroids. On an ultrasound image, the tumor is visualized as dense, round-shaped foci; the location, number, and size of the foci are determined. |
| Smear for microflora and STDs | Identification of pathogenic pathogens with possible inflammation. |
| Oncocytological smear | Detection of dysplastic processes in the uterus and appendages. |
| Hormonal panel | The level of estrogen and pituitary hormones is determined. |
| Blood and urine tests | Exclusion of the inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, determination of complications of bleeding (anemia). |
| MRI | To clarify the diagnosis. |
| Biopsy | For differential diagnosis and exclusion of a malignant process. |
For each patient, a set of studies is selected individually; all of the above methods are not necessarily used.
General characteristics of the pathology
The formation of fibroids is associated with hormonal imbalance. With hormonal imbalance, the likelihood of rapid growth of the muscle tissue of the uterus increases, with the formation of nodes and uneven thickening of the endometrium.
The result of such changes is a disruption of the physiological process of rejection of the formed layer of cells, which becomes the cause of delayed menstruation or prolonged uterine bleeding.
The presence of fibroids in the uterus becomes an obstacle to its complete contraction and narrowing of the arteries, as a result of which the blood does not stop.
Therefore, to the question of whether there can be bleeding with uterine fibroids, the answer is affirmative. Yes, it is a frequent companion to a benign tumor. Attempts to stop it on your own lead to a significant deterioration of the condition. The lack of a timely, qualified approach to their elimination leads to a situation where surgical intervention is required, including removal of the reproductive organ.
To prevent such complications, it is necessary to become familiar with the causes and symptoms of the pathological condition. This will make it possible to pay attention to deviations from the norm in a timely manner, undergo a high-quality examination and an adequate course of therapy.
Why does fibroid bleed?
Myoma (fibromyoma, leiomyoma) is a tumor consisting of smooth muscle and connective tissue cells. The formation grows in the thickness of the myometrium and can extend into the uterine cavity or beyond the genital organ. The location of fibroids directly affects the likelihood of bleeding. Mostly submucosal nodes located in the organ cavity bleed. Bleeding also occurs with interstitial formations located in the wall of the uterus. Subserous tumors almost never cause such complications.
Other factors that influence the likelihood of bleeding:
- Leiomyoma size. Tumors up to 2.5 cm in diameter are usually asymptomatic and do not cause bleeding. The exception is submucosal formations on the stalk, which give the clinic even in small sizes;
- Presence of concomitant pathology. When fibroids are combined with endometriosis, endometrial hyperplastic process or polyps, the risk of bleeding increases;
- General condition of the woman. Pathology of the blood coagulation system can cause bleeding.
It is important to know
Uterine bleeding is considered to be the leakage of blood from the genital tract in a volume exceeding 80 ml. A simple test is performed to determine the amount of discharge. A woman should put on a clean pad (normal or plus) and time the time it takes for it to fill. Normally, hygiene products last for at least 1.5 hours. If the pad fills in an hour or less, we are talking about uterine bleeding.
With pathological uterine bleeding, a woman is forced to change pads almost hourly.
The immediate causes of increased bleeding with fibroids include the following conditions:
- An increase in the size of the uterus and the area of the endometrium - the inner layer that is shed monthly;
- Concomitant hyperplastic changes in the uterine mucosa;
- Impaired contractility of the muscle layer.
- Increase in the number of vessels (venous plexuses);
- Decreased tone and elasticity of blood vessels.
All these phenomena provoke changes in the structure of the organ and lead to disruption of its function with the development of uterine bleeding.
First aid algorithm for myomatous bleeding
What to do in a situation when bleeding caused by uterine fibroids begins?
- If a large loss of blood is detected (determined in the manner described above by identifying the filling rate of the pad), you should call an ambulance.
- Then take a Vikasol or Dicinone tablet.
- Put cold on your stomach.
- Lie down and wait for the doctor to arrive.
Other methods of self-medication are unacceptable, as they can only aggravate the condition. Further treatment involves a hospital stay using drugs that help contract the uterus and stop bleeding. The main therapeutic regimen is prescribed on the basis of a diagnostic examination in order to identify the cause of heavy blood loss.
Symptoms of uterine bleeding
Uterine bleeding due to tumor formation can be accompanied by anemia and severe fatigue. At the same time, the woman feels constant weakness in the body. The main symptoms may be frequent pain in the lower abdomen, menstrual irregularities and the appearance of intermenstrual bleeding. A woman may suffer from chronic constipation and frequent visits to the toilet due to improper bladder function. Pain in the legs and back can also occur due to uterine bleeding. They are caused by pinched nerves.
Symptoms appear depending on the growth of fibroid nodes and their location. They can form on both the posterior and anterior wall of the cervix. A woman may experience the following symptoms of uterine bleeding:
- menstruation lasts more than a week;
- blood clots are released;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen with a pulling effect;
- flatulence;
- sexual intercourse is accompanied by bloody discharge;
- elevated temperature;
- nausea;
- deterioration of the general condition of the body;
- fainting.
Types of fibroids
By localization:
- Subserous is a subperitoneal fibroid, which is located on the surface of the uterus and increases towards the peritoneum.
- The wall of the uterus grows in depth, causing it to enlarge.
- Subendothelial - a neoplasm in the middle of the myometrium, after the endothelial layer of the uterus.
Subserous fibroids:
- intramural-subserous;
- interstitial subserous;
- pedunculated subserous fibroid.
Causes of intramural fibroids:
- An increased level of estrogen accompanies the appearance of fibroid nodes. Often during menopause, myomatous nodes resolve, which is associated with a natural decrease in estrogen levels;
- late first birth or no birth at all;
- polyps and erosions;
- chronic, inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- abortions, caesarean sections, other surgical penetrations of the uterus.
Risk factors for the appearance of intramural nodes are if a woman has diabetes, arterial hypertension, obesity, or has a hereditary predisposition.
Therapy tactics
How to stop bleeding with uterine fibroids? You should contact your gynecologist with this question. Depending on the characteristics of the clinical course of the condition, the doctor chooses the most effective method - drug treatment or surgical intervention.
Therapeutic tactics
To stop bleeding from uterine fibroids, hormonal hemostatic drugs are used, which have the ability not only to stop the discharge, but also to have an inhibitory effect on tumor growth.
Positive dynamics are observed when using Etamzilate, Tranexam, Ascorutin.
As an emergency measure, drugs from the COC group (combined oral contraceptives) can be prescribed.
The initial dose is the maximum dosage followed by a gradual reduction.
Also, to correct this condition, the use of medications from a number of gestagens, analogues of gonadoliberins or antigonadotropins is practiced.
The choice of effective medications should be left to a qualified specialist. The result of self-medication is a prerequisite for deterioration of the condition, the likelihood of intensive growth of the tumor and the ensuing negative consequences and complications.
Uterine artery embolization
The most effective and minimally invasive method of stopping bleeding in myomatous pathology is the introduction of special substances into the uterine arteries - emboli. Their impact leads to the cessation of bleeding and the gradual regression (death) of the fibroids themselves.
Hysterectomy
In the presence of multiple tumor formations, tumor growth to a significant size, or the presence of cells of atypical etiology, there is a need to take radical measures, that is, surgical intervention.
Hysterectomy is a method of treating bleeding from uterine fibroids
Instead of abdominal surgery to remove the uterus, they often resort to using a more gentle option - hysteroscopic myomectomy.
This method is used in the absence of positive dynamics of drug treatment and the failure of embolization.
The indication for removal of the uterus is the inability to stop bleeding, which poses a serious threat to the patient’s life.