Causes of the disease
Myoma usually has the form of nodes, but diffuse growths without definite contours are also found. Diagnosis of intramural fibroids is not difficult due to uterine enlargement, dysuric disorders and defecation disorders. The diagnosis can be confirmed using ultrasound, Dopplerography or hysteroscopy.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease:
- Burdened heredity;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Frequent abortions;
- Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- Overweight;
- Bad habits;
- Stress;
- Climax;
- Metabolic diseases.
This video shows the surgical treatment of fibroids in 3 formats:
Diagnostics
In most cases, intramural fibroids are detected during examination by a gynecologist. When examining a patient using expanding mirrors and bimanual examination, the doctor determines the increase in the size of the reproductive organ, its position, deformation, and can even palpate large nodes.
To accurately determine the location of nodes and their sizes, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Ultrasound of the uterus, appendages and ovaries using the transvaginal and transabdominal method;
- Dopplerography of uterine vessels;
- Hysteroscopy (contrast radiography);
- Computed or magnetic resonance imaging;
- Diagnostic laparoscopy.
The patient's blood must be taken to study hormonal levels. In some cases, cancer is diagnosed, since fibroids can rarely act as a precancerous pathology.
Symptoms of the disease
Basically, intramural fibroids are asymptomatic until the myomatous nodes reach a significant size, at which point they cause compression of neighboring organs. Subsequently, the symptoms of the disease are caused by deformation of the uterine cavity. It causes pain in the lower abdomen, heavy and prolonged menstruation, infertility, and bleeding.
Complications of the disease include tumor necrosis and significant compression of neighboring organs with disruption of their function. This requires emergency hospitalization with urgent surgical intervention.
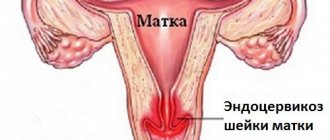
Types of myomatous nodes:
- Interstitial. They are characterized by uniform enlargement of the uterus due to multiple myomatous nodes in the muscles of the uterus and heavy menstruation.
- Subserous. They are distinguished by the erased symptoms of the disease and are not detected for a long time. Myomatous nodes form on the outside of the uterus and can affect the pelvic area.
- Submucosal. The nodes are localized under the endometrium and are accompanied by intense pain. The uterus quickly increases in size. The body's excretory systems suffer.
- Intramural. Multiple myomatous nodes affect the middle layer of muscles. Symptoms of the disease include menstrual irregularities, enlarged uterus as during pregnancy, and pain in the lower abdomen.
Diagnostic methods
Intramural uterine fibroids can be diagnosed using the following methods:
- Study of anamnesis. The doctor pays attention to the presence of factors that can provoke pathology. The risk of developing fibroids is increased by abortion, changes in hormone levels, and surgery;
- Examination of a woman on a gynecological chair. With the help of such a study, it is possible to identify nodular formations and deformation of the uterus if the fibroids have reached a large size;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. During the procedure, it is possible to detect a hypoechoic node located in the uterine cavity;
- Hysteroscopy. This diagnostic method makes it possible to identify intramural fibroids at the very beginning of their development. Thanks to this study, it becomes possible to assess the size of a benign tumor and prevent tissue necrosis;
- MRI and CT. Using such diagnostic methods, it is possible to take a series of layer-by-layer images. MRI is considered more sensitive to soft tissues; it allows one to see small nodes and determine their location.
If there are any doubts about the diagnosis or the node grows quickly enough, diagnostic laparoscopy and tomography may be prescribed.
Surgical excision
If a woman with a small intramural fibroid located in the wall of the uterus plans to become pregnant in the near future, then such fibroids are simply controlled by recommending visiting a doctor once every 6 months. If pregnancy occurs against the background of such fibroids, then most likely it will proceed normally, and the fibroids will decrease in size. Myomatous nodes that rapidly increase in size are subject to surgical removal. In this case, young women undergo organ-saving operations. In this case, only the fibroid is removed.
We recommend watching a video from the operating room where fibroid embolization takes place:
If there is an intramural node of size “up to 12 weeks of pregnancy” located externally, laparoscopic removal of the tumor should be performed. A laparoscope is a device that allows, with minimal invasive intervention (3-4 punctures), by inserting special instruments through minimal holes, to remove a tumor. The operation is carried out under video control.
If a tumor grows inside the uterus, hysteroscopy is performed - an operation in which a probe with special equipment is inserted into the uterus through the genital tract and the tumor is also excised under visual control.
Important! It is not possible to remove large myomatous nodes using laparoscopic and hysteroscopic methods, therefore, for such tumors, other treatment tactics are used.
In this case, hormonal therapy is prescribed, and after the tumor has shrunk in size, gentle surgical intervention is performed. In some cases, there is still a need for laparotomy - a simple surgical procedure with a large incision under general anesthesia. After such an operation performed by a qualified specialist, the woman subsequently has the opportunity to plan a pregnancy and successfully bear a child. Delivery after such an operation in the vast majority of cases is carried out by caesarean section.
Indications for the operation:
- Progression of myomatous node;
- Malnutrition of fibroids associated with torsion of the leg;
- Large size fibroids (more than 14-16 weeks of pregnancy);
- Softening of education;
- Hormonal therapy;
- Debilitating bleeding leading to anemia;
- Compression and disruption of adjacent organs;
- Malignant degeneration of fibroids.
Treatment
Treatment for intramural fibroids depends on how quickly they grow and in what part of the uterus they are located. An equally important factor for selecting therapy is the woman’s age. For young patients, doctors try to prescribe treatment that allows them to maintain the ability to conceive and give birth to a healthy child. Hormone therapy is usually prescribed. It is a preventive measure, since after the tumor is removed surgically, there is a possibility that fibroids may appear again. Sometimes hormonal drugs do not have the desired effect, and the tumor continues to grow; in this situation, other treatment methods are selected, for example:
Conservative treatment
- The most common treatment is medication. This is a non-surgical form of tumor control. Especially suitable for women who want to have a child in the future. This method is also used after surgery to avoid relapse of the disease;
- Immunomodulators;
- Sedatives, sedatives. Used to eliminate stressful conditions that provoke the growth of tumors.
Alternative medicine
This type of therapy should treat the disease if the doctor conducted examinations and found small nodes. To prevent them from continuing their development, it is better to take the necessary measures, for example, start treatment with folk remedies. It helps improve the functioning of the female body and is a good way to improve its health. There are two ways to treat fibroids using unconventional methods: the first is means taken orally and the second is the insertion of tampons soaked in a decoction of herbs into the vagina or douching.
Herbs used in therapy:
- Antitumor general use - plants are poisonous. These include mistletoe, celandine, cinquefoil, fly agaric;
- Antitumor localized action - they are not poisonous, restore hormonal balance, due to this, tumors are reduced;
- Hemostatic - shepherd's purse, nettle, yarrow;
- Immunomodulatory - these are ginseng, lemongrass fruits, kopeck, radiola rosea, eleutherococcus, aralia.
In addition to herbs, the following are used in the treatment process:
- Quail eggs - you need to drink six eggs daily on an empty stomach for three weeks;
- Tincture of walnut partitions - available at the pharmacy or you can prepare it yourself. To do this you will need 30 grams of walnut partitions. They need to be filled with one glass of vodka. The resulting infusion should be allowed to brew in a dark place for three to four weeks. The course of treatment is one month. You need to take 30 drops of tincture with a glass of water half an hour before meals.
Surgical methods
- Embolization is a method that does not require surgery. To carry it out, the vessels that provide nutrition to the myomatous node are blocked;
- Myomectomy – surgical removal of a tumor. The recovery period lasts a year. After the procedure, the woman retains her reproductive function;
- Hysteroestomy - the meaning of the procedure is the complete removal of the uterus. Such surgical operations are performed in case of prolapse or prolapse of the uterus caused by a tumor or if there is a suspicion that the tumor is becoming malignant. An indication is also the size of the tumor exceeding 5-6 cm if it begins to bleed. The operation is performed when a woman no longer needs to become pregnant and give birth to children.
When fighting tumors, you must follow the doctor’s recommendations. This will help to avoid the recurrence of fibroids in the future.
Hormonal therapy for intramural fibroids
Not all types of fibroids can be reduced with hormonal treatment. But doctors sometimes prescribe this type of therapy, especially to young patients. Its course is long and reaches 7-8 months.
Typically, the following drugs are prescribed for this therapy:
- Androgen group drugs are drugs that reduce the activity of estrogen. The course of treatment is 7-8 months.
- Preparations of the gestagen group are effective for small size myomatous nodes.
- Combined drugs - used for fibroids no more than 2 cm. The course of treatment is 3-6 months.
- The Mirena system stabilizes the body’s hormonal balance and provides contraception. Issued for up to 5 years.
Progressive surgical method for removing fibroids
FUS - ablation evaporates the node, affecting it with ultrasound, while nearby tissues remain untouched.
Advantages of the procedure:
Painless and no blood loss. Good results for large fibroids. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis and without anesthesia. The nodes are reduced by 2-3 times. Normal tissues are not affected. No relapses or scars.
In addition, recently the method of uterine artery embolization has been successfully used, which prevents tumor nutrition and its regression.
Pain with fibroids is of the following nature:
- the girl constantly feels discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- aching pain appears in the suprapubic region;
- in the lumbar region the girl experiences aching pain;
- the lower abdomen begins to hurt during physical activity, or when walking for a long time;
- the pain is acute, cramping in nature.
Pain occurs periodically, usually due to tumor growth. The severity of pain depends on the size of the fibroid, as well as its location and “behavior.” For example, fusion of the peritoneum and tumor causes pain. In addition, pain may occur if the tumor stalk becomes twisted. Then the nutrition of the fibroids is disrupted, and therefore necrosis develops, leading to peritonitis. All this is extremely dangerous for the patient’s life.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy may well occur and develop normally in the presence of intramural fibroids. But sometimes an increased estrogen content and cervical localization of nodes can lead to miscarriage.
The location of the myomatous node is of great importance during pregnancy. If the attachment of the fertilized egg occurs on the unchanged mucosa and the fibroid is no more than 3-4 cm, then the pregnancy will proceed without any problems and delivery will occur naturally. During pregnancy, myomatous nodes, as a rule, become smaller or disappear completely; after childbirth, the nodes are observed to return to their previous size.
The location of the placenta near the node can lead to intrauterine growth retardation, premature birth or termination of pregnancy, as well as infection of the fetus. During pregnancy, as the fetus grows, the blood supply to the tumor is disrupted, which leads to increased tone and pain. Implantation of the fertilized egg near the tumor can contribute to placental abruption, frozen pregnancy or miscarriage. Patients with this disease need to undergo regular examinations (ultrasound of the placenta and node), as well as adhere to a work and rest regime, for this it is necessary to register with the antenatal clinic as soon as possible so that he can decide on the tactics of pregnancy and delivery, as well as give necessary recommendations.
The disease significantly complicates the course of childbirth; delivery usually occurs by cesarean section. Small intramural or subserous neoplasms are not an obstacle to natural childbirth.
Indications for surgical delivery may be:
Localization of nodes that interferes with the opening of the cervix and the advancement of the fetus. Myoma more than 10 cm or multiple nodes. Possible necrosis or degeneration of fibroids. A scar on the uterus in combination with fibroids. Malnutrition of fibroids.
During labor, complications may also arise that require immediate delivery: fetal hypoxia, premature rupture of water, impaired contractility, and abnormal placental attachment or concomitant diseases.
Possible consequences and complications
The presence of subserosal intramural fibroids is not a dangerous manifestation. However, this pathology is fraught with the development of a number of complications and negative consequences that threaten not only the health, but also the life of the patient. In most cases, they are associated with intensive growth and an increase in the size of intramural uterine nodes. Let's look at this issue in more detail:
- Myoma necrosis is considered one of the most common complications of the disease in question. It manifests itself in the form of general intoxication of the body with an increase in body temperature, bloody discharge and pronounced pain in the lower abdomen.
- Leg torsion is a dangerous condition that leads to death of adjacent tissues, sepsis, and in the absence of timely measures, even death.
- Fatty deformation of the myoma node is a pathological process leading to a rapid and significant increase in the size of the tumor. As a result, manifestations such as compression of closely located organs and tissues, pinched nerve endings, problems with urination, disorders and disruption of intestinal activity and the process of defecation are observed. In this case, the development of a number of concomitant diseases is possible.
- Rupture of the tumor, accompanied by severe bleeding and acute pain.
In addition, subserous fibroids located in the uterine angles can become a serious obstacle to the penetration of a fertilized egg, which is a common cause of pathological pregnancy or early termination. The following manifestations are also very likely:
- difficult childbirth;
- uterine bleeding during the birth process;
- pathologies in fetal development;
- premature placental abruption;
- miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- infertility;
- increase in body weight.
Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, it is recommended to undergo an examination and, if this pathology is present, to eliminate it before conception. In addition, if uterine intramural fibroids are detected, the necessary course of treatment should be completed to avoid the development of the above complications.
Diagnostic methods
In most cases, the presence of these tumor-like neoplasms is discovered accidentally during a general gynecological examination. To clarify the diagnosis, determine the size and localization of intramural subserous nodes, the patient is prescribed a series of studies. These include the following procedures:
- An ultrasound examination allows you to determine the presence and location of the tumor, its size and condition, and identify the possible presence of endometriosis.
- Palpation method.
- A study using a so-called transvaginal sensor, which allows you to obtain extremely accurate data on the condition of the uterus.
- CT scan.
- Hysteroscopy, which provides an opportunity to examine the tumor in detail and determine the possible presence of a number of complications, such as torsion of the leg or necrosis of fibroids in the initial stages.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is a highly productive study that allows you to determine the size and location of the tumor formation, the condition of nearby organs and tissues, the depth of the uterine lesion, etc.
- Laparoscopy. It is used primarily when there is a suspicion of the presence of a tumor-like neoplasm in the ovarian area.
- In some cases, to exclude the possibility of cancer, a biopsy procedure is performed - taking suspicious biological material for further examination.
Typically, such a pathology is diagnosed without any difficulties, which makes it possible to promptly identify the presence of the disease and, if necessary, take timely therapeutic measures.
Traditional methods of treating the disease
Treatment of intramural fibroids with celandine is a method proven over years of use. This medicinal plant contains biologically active substances that have a beneficial effect on many body systems. However, it should be remembered that celandine is a poisonous plant and uncontrolled use in large quantities can harm the body.
Please note! It is best to use preparations from celandine for the treatment of intramural joints in a comprehensive manner - orally and locally.
To make candles, you need to take 150 ml of celandine herb extract and 50-75 grams of beeswax.
Stages of making candles from celandine:
- To prepare the extract, take a kilogram of crushed celandine herb, add half a liter of water and boil in a water bath until the volume reaches 150 ml.
- Add pre-strained celandine extract into the melted wax. Simmer in a water bath, stirring until a homogeneous composition of the desired consistency is obtained. Pour into oblong molds or form candles by hand.
You can also use the pharmacy version of candles. Use a suppository at night vaginally or rectally for 2 weeks.
To prepare an infusion of celandine for internal use, you need to tightly place the chopped celandine in a clean glass jar with a capacity of 0.5 liters and fill it with vodka. The product should be infused for a month in a dark, cool place until ready.
Scheme for taking celandine drops orally:
- You should start with 2 drops of the product, and then increase the intake daily by 1 drop.
- Having reached 20 drops, stop taking it for a period of 19 days, and then resume it, bringing it up to 40 drops in the same way. After which you should begin to consistently reduce the number of drops by 1 drop per day.
- Gradually reducing, bring to 10 drops of the product and take a month break again.
- After a month, increase the intake of the drug consistently to 60 drops and reduce to 2.
Recipe for treating fibroids with boron uterus:
- Infuse 50 grams of uterus leaves into 0.5 liters of vodka for 2 weeks.
- Take 40 drops orally three times a day before meals.
Recipe to stop bleeding:
Take fresh carrot tops, cut them and pour boiling water over them (a liter of boiling water is taken for 2 cups of carrot tops). Leave for 0.5 hours and take as tea until bleeding stops.
Treatment of fibroids with calendula tincture
You can also treat small uterine fibroids with a pharmacy tincture of calendula:
To do this, dilute the tincture with boiled water in a ratio of 1:10. Douche the vagina with a warm solution at night.
Note! Treatment of fibroids with folk remedies is effective only in the initial stages of the disease and small fibroid nodes.
Indications for surgery
Absolute contraindications to intervention are:
- The size of the tumor corresponds to a period of more than 14 weeks of pregnancy.
- Any postmenopausal progression or rapid growth during reproductive age.
- Localization on the cervix.
- Prolonged menstruation with heavy blood loss.
- Necrosis of the node.
- Infertility, if its cause is identified as fibroids.
- Negative impact of neoplasms on the pelvic organs.
The choice of the method and extent of the operation is made depending on the woman’s age, the presence of concomitant diseases, and planning a pregnancy in the future.
Prevention of occurrence
Preventive measures to prevent the appearance of itramural fibroids include:
Adequate contraception to avoid unplanned pregnancy and, as a result, abortion. Correction of endocrine system disorders. Timely treatment of common chronic diseases. Prevention of sexually transmitted diseases, having a permanent sexual partner. Elimination of bad habits. Regular medical supervision during menopause. An active lifestyle to avoid congestion in the pelvis. Timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system.
Only careful attention to your own health, regular medical examinations and a healthy lifestyle can prevent the appearance of myomatous nodes. And if the disease could not be prevented, then it should not be allowed to progress to such a state where a complex operation under general anesthesia is required, but rather use a minimally invasive intervention. To do this, a woman should always be aware of her health status and modern methods of treating gynecological diseases.
What danger does subserous fibroid pose to a woman?
Intramural-subserous myoma of the uterine body photo The main danger lies in the twisting of the tumor stalk, as well as in the death of its tissue due to disruption of normal nutrition. If a tumor in the female abdominal cavity begins to collapse, immediate surgical intervention is required. In addition, rupture of fibroids poses a danger, since it can be caused by its excessive enlargement. In such a situation, a woman not only feels an attack of acute pain, she begins to bleed, which is extremely difficult to stop.