The nature of discharge from uterine fibroids depends on concomitant conditions complicating the disease. Normally, vaginal mucus does not cause discomfort to a woman. The discharge is clear or milky and has no odor. When the appearance of fibroids is accompanied by colored discharge, we are talking about pathology. Uterine bleeding often accompanies a benign tumor.
If the discharge becomes unusual, you should consult a doctor to perform a differential diagnosis. It will be impossible to get rid of unpleasant symptoms without finding out their cause.
Reasons and factors
The cause of a benign neoplasm in the uterus is hormonal instability. If earlier the pathology was detected mainly in patients in adulthood, now fibroids are detected at the age of 20-30 years. At the same time, not every woman produces unusual mucus from the vagina. If the tumor size is small, there are no disturbing signs at all.
Numerous studies have made it possible to establish the factors on which the formation of myomatous nodes depends. Women at risk include:
- Having a hereditary predisposition (if your grandmother and mother had fibroids).
- Self-administering hormonal medications.
- Those who have not completed their childbearing function before the age of 35 years.
- Those with chronic pathologies of the uterus and other reproductive organs.
- Suffering from blood diseases.
Kinds
With fibroids, there may be blood discharge, which becomes heavy during menstruation, and in the middle of the cycle looks like spotting. The patient may also complain of prolonged periods, which significantly impairs her well-being. Often, the discharge contains endometrial clots that look lumpy. The absence of menstrual bleeding also sometimes accompanies myomatous nodes. In this case, the discharge is scanty and occurs over a long period of time. Often this condition is accompanied by changes in the functioning of the ovaries.
Myometrial dysfunction may be accompanied by yellow or greenish discharge, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
If the mucus is white, contains lumps and has a sour smell, then the woman has fibroids and thrush.
Based on the nature of the discharge, separate conditions can be assumed. However, only an examination will help confirm your guesses: a smear, blood test and ultrasound.
To the smooth ones
Small nodular fibroids are often accompanied by bloody discharge that has a liquid consistency. They are protracted and exhausting for the body. The reason for the formation of this symptom is the uneven growth of the mucous layer of the reproductive organ, caused by a hormonal imbalance. The separation of endometrial cells at the site of the node is uneven. It occurs gradually, so the patient observes prolonged bleeding, which she considers to be unusual menstruation. Menstruation with a benign tumor can be delayed for 2 weeks. At the same time, the interval between bleedings is reduced.
If the separation of the endometrium occurs in the middle of the cycle, small amounts of blood are released. The patient complains that she has spotting after her period. The volume of bloody mucus is insignificant, there are no clots or lumps in it.
Heavy menstrual bleeding in women is the first sign of a benign neoplasm. Small tumor sizes do not cause additional symptoms, but the size of the uterus is already becoming larger. Therefore, during a gynecological examination, this pathology can be assumed on the basis of an increase in the volume of the reproductive organ, taking into account complaints about blood discharge.
Scarlet blood from the vagina can be released when fibroids are located in the cervical cavity.
The prolapse of the node is accompanied by pain and a change in the consistency of vaginal mucus. In addition to prolonged menstruation, the patient complains that she has copious watery discharge during the menstrual cycle.
K brown
In addition to the fact that menstruation becomes more abundant, a woman may be bothered by brown vaginal mucus. This symptom indicates the submucous appearance of the node and its significant size. The active growth of a benign tumor causes stretching of the myometrium. As a result, the mucous membrane lining the uterine cavity also stretches. The walls of the vessels cannot withstand the stress and rupture. The blood coagulates and takes on a dark hue.
Myoma, accompanied by brown discharge, usually has an impressive size. At the same time, the patient may experience pain in the lower abdomen. They intensify during physical activity and sexual contact. After intimacy, the volume of brown smear increases. A large benign neoplasm can prevent pregnancy in the future.
Brown discharge, caused by damage to the vascular wall, often leads to anemia, deterioration in general health and decreased performance. The patient complains of drowsiness, apathy and chronic fatigue.
yellow
If menstrual function is not impaired due to fibroids, and the discharge between bleedings has a yellow tint, it is highly likely that we can talk about an infection and an inflammatory process. The cause of the development of the disease is the proliferation of pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms. They are able to penetrate the vagina, and from there enter the uterus after unprotected sexual intercourse. Also, inflammation of the reproductive organs can occur when pathogens spread through the bloodstream or lymph flow.
Bacterial vaginosis is a common companion to fibroids. The disease is characterized by the proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms as a result of a decrease in the body's resistance. The pathology is not considered dangerous and can be easily treated, but in the absence of timely assistance it becomes more complicated.
Vaginitis and endometritis are considered more serious diseases, in which a woman develops yellow discharge from the genital tract. Myoma is not associated with these pathologies, but can be combined with them.
Metritis - inflammation of the myometrium - is a frequent companion to fibroids. The disease can be determined using laboratory diagnostics. With yellow discharge, the patient also has complaints:
- itching of the labia;
- burning in the perineum;
- abdominal pain;
- discomfort during urination and sexual intercourse;
- infertility;
- menstrual irregularities;
- increase in body temperature.
Consistency
When a myomatous node forms, the consistency of vaginal mucus changes. The determining role for this indicator is played by the type of pathological process and the size of the tumor.
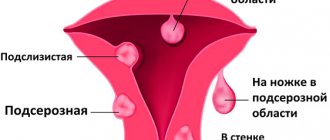
If a subserous myoma with a stalk has formed, then the mucus practically does not change. The neoplasm grows towards the abdominal cavity and does not deform the endometrium. It should be noted that such fibroids have mild symptoms and do not prevent pregnancy.
Treatment
If the patient is bothered by white, yellow, brown or red discharge caused by the formation of fibroids, then treatment is prescribed. The regimen is selected individually, taking into account the type of tumor, its size, concomitant diseases of internal organs, the patient’s age and the need for reproductive function in the future.
The use of hormonal drugs can achieve positive results for small fibroids. With the help of medications it is possible to regulate the menstrual cycle. Correcting the functioning of the ovaries can make bleeding less profuse and short-lasting.
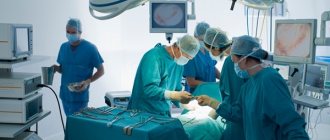
If the fibroids are large, the patient is prescribed removal of the tumor-like formation. Depending on the location of the fibroids, a suitable technique is selected. If the tumor grows inside the myometrium, then the arteries feeding the tumor are “switched off”. The manipulation is minimally invasive and minimally traumatic. When the node grows into the pelvic cavity, surgical intervention is performed, which involves removing the tumor.
The radical method of treating fibroids is hysterectomy. Surgery is prescribed for large tumors when treatment with alternative methods is not possible.
After surgical treatment of fibroids, a woman experiences slight bleeding. Bloody discharge is a natural reaction of the body. The cavity of the reproductive organ contracts, and damaged vessels cannot be restored instantly. Therefore, in the first days after surgical treatment, a woman’s discharge is bright red, and by the end of the week it becomes brown. Gradually the ichor brightens, the mucus becomes barely pink. By 10-14 days after the operation, the discharge ends and becomes normal.
P prognosis
For small fibroids the prognosis is favorable. The neoplasm responds well to treatment. Relapse with the appearance of discharge is observed in only 2 patients out of 100. If you refuse therapy, the probability of tumor growth will be 50%. It is safe to say that strange discharge will appear over time.
Vaginal mucus without blood (except during menstruation) is normal. Changes in color, consistency, structure and other organoleptic characteristics are considered a deviation. At the first signs, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination. Myoma is a benign tumor that is not prone to malignancy. However, it needs to be monitored. Growth control allows doctors to prescribe correction in a timely manner and avoid complications.
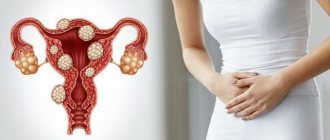
Fibroids are characterized by the growth of nodes in the muscle tissue of the uterus. The most commonly present symptoms of a benign neoplasm in a woman’s reproductive organ are discharge from the genital tract and pain.
It is after the discharge begins that patients consult a gynecologist, after which the disease is diagnosed.
The consistency and color of the secretion is influenced by the degree of damage to the uterus, the number of myomatous nodes, the localization of the growth, the size of the tumor, the complicated course of the disease, as well as the individual characteristics of the girl.
Different colors of discharge indicate different progression of uterine fibroids. As the pathological process develops, the nature of the rejected secretion changes.
Intermenstrual bleeding is the most common manifestation of uterine fibroids, both at the first stage of development and in the advanced form of the disease. They are associated with an uncontrolled increase in the endometrial layer due to changes in hormonal levels and the formation of hyperplasia. The inner surface of the uterus grows unevenly - it becomes very thick in one place and thinner in another. Due to this, endometrial cells are torn away in uneven parts or immediately completely from the structural surface, violating the integrity of the blood vessels. Because of this, a bloody secretion of a pinkish hue is released. If the endometrium is completely rejected, then severe bleeding with a bright red color is observed, which cannot be stopped with vasoconstrictor drugs.
Often, as a result of increased endometrial rejection, the volume of blood released during menstrual periods increases. The period of menstruation becomes longer, and the consistency of the blood becomes thinner. The color of bloody clots varies from light pink to dark red.
The presence of myomatous nodes can provoke a constant discharge with a small amount or a break between blood loss of several days. On average, blood rejection occurs up to three times a month for three to seven days.
Often the symptom is supplemented by nagging painful sensations in the lower third of the abdomen, radiating to the lower back. Due to significant blood loss, signs of iron deficiency anemia develop. The woman complains of general weakness of the body, drowsiness, chills, headaches, pale skin. Some girls note an increase in the number of menstruation and a reduction in their abundance.
If the blood from the genital tract smells unpleasant or an admixture of pus is found in it, then this fact is the beginning of the inflammatory process. You should seek medical help immediately.
Bloody discharge is most often characteristic of a submucous type of benign neoplasm in the uterine cavity. The fact is that submucous fibroids develop in the inner muscle layer and grow inside the uterus. The venous system of the uterus hypertrophies, and the blood filling of the organ increases. As the size of the growth increases, the tumor interferes with the normal outflow of blood during menstruation, so blood is released outside the usual period. The amount and abundance of blood is greater in women of reproductive age.
Blood loss with the intramural variety is less common.
The yellowish color of genital secretions is much less common. He reports the development of a complicated process of uterine fibroids. As a rule, a benign growth is aggravated by a bacterial infection or the inclusion of fallopian tubes in the process. Localization of a benign tumor causes purulent rejection. This process is called "salpingitis".
First, thick leucorrhoea appears, which gradually turns yellow as the pathological process increases and begins to smell unpleasant. The intensity of the color indicates an increase in infectious inflammation of the genital organ. Over time, the yellow discharge intensifies and an unpleasant odor appears.
Periods after removal
Causes
The first periods after UAE are quite scanty. They are spotty in nature and begin exactly on time. If previously, during embolization, patients experienced delays for a period of one month to six months, now such manifestations are rare, thanks to the use of large-diameter emboli.
Separately, it is worth noting cases in which the “birth” of a myomatous neoplasm is observed. It is accompanied by heavy periods after embolization. The process involves an initial normalization of the quantity - however, at “birth”, menstruation again becomes abundant, returning to normal after expulsion.
After surgery to remove fibroids, the woman must be monitored for a certain period while remaining in a medical facility. Vaginal interventions or laparotomy require hospital treatment for at least a week, and after laparoscopic surgery - up to three days. During this period, complications that pose a danger may arise, namely:
- inflammatory process at the incision site;
- seam divergence;
- purulent discharge from the wound surface;
- pain when urinating;
- peritonitis.
Restoration of tissue at the site of the stump may be accompanied by discharge with an unusual color, but in the overwhelming majority they quickly return to normal. If such changes do not go away for a long time, then it is necessary to seek medical help, as this may be a sign of inflammatory processes.
The following changes should also cause alarm in the postoperative period:
- abundance of discharge;
- the appearance of a bright red color;
- with purulent impurities;
- the appearance of a large number of clots.
The discharge of dark mucus, accompanied by an unpleasant odor, can serve as a manifestation of severe complications, the identification of which requires additional research. Initially, it is important to exclude inflammation of the suture, which can develop into infection and peritonitis. The volume of discharge also deserves attention; if it is too abundant, a repeat laparotomy may be required.
After removal of a tumor with the uterus, menstruation usually does not occur, except in cases where the ovaries are preserved, but the discharge in this case is much smaller in volume and repeats in accordance with the previously observed menstrual cycle.
Almost always, after removal of fibroids, menstruation occurs, which lasts for a week. This happens due to excision of the tumor, which is carried out along with a small area of the endometrium. As a result of the operation, the uterus is not able to contract for a certain time and the vessels are not compressed and continue to bleed.
The contractility will return after four to five days, and the full menstrual cycle will be established after a couple of months. The exact time it will take for complete recovery depends on the individual's capabilities and ability to recover, as well as the size of the tumor removed.
Myoma: what is it?
To make it easier to understand how the nature of vaginal discharge can change, you need to find out what fibroids are.
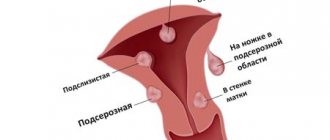
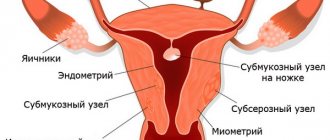
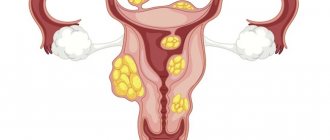
This is a benign tumor. It is located in the body of the uterus, in the myometrial layer, and consists of those cells that form the muscles of the uterus. There are several types of fibroids. In gynecology, fibroids are classified as:
- submucosal;
- subserous;
- intramural;
- interstitial.
If subserous fibroids grow into the abdominal cavity, and therefore no symptoms may be observed until the tumor reaches an impressive size, then with submucous fibroids the nodes grow directly into the uterine cavity. It is this subtype that forces women to consult a doctor about heavy and painful bleeding during menstruation.
Intramural fibroids grow directly in the muscle wall.
The majority of diagnosed myomatous nodes are interstitial. Discharge from uterine fibroids in such cases manifests itself as prolonged menstrual bleeding. The woman loses a lot of blood and begins to complain of fatigue and weakness. But this is observed only when the tumor reaches a significant size.
Reviews
Reviews existing online regarding the nature of the symptoms accompanying uterine fibroids are mostly positive. They say that treatment and diagnosis, as well as monitoring the condition of the tumor, do not cause any particular problems, and recovery after surgery occurs at a fairly rapid pace. Moreover, the degeneration of a tumor into a malignant state occurs in isolated cases, and the further state of the body quickly returns to normal.
You can leave your feedback in the comments line on the post, they will be useful to other users of the site!
Throughout her life, a woman must pay close attention to the nature of discharge from the genital tract. Those observed during the intermenstrual period are called leucorrhoea. Normally, leucorrhoea is light, whitish or transparent, and there is very little of it - no additional measures to protect the linen are required, for example, panty liners. If there are any diseases, leucorrhoea changes its color and consistency. What is the discharge like for uterine fibroids - a neoplasm that occurs in every second woman of the reproductive period?
Discharge from fibroids
It is impossible to predict with 100% accuracy exactly how the nature of menstruation will change and what kind of discharge will appear when a benign uterine tumor occurs. It's very individual. Patients present various complaints. But some patterns can be traced.
With fibroids, there may be bloody discharge - this fact is confirmed by the majority of women who are faced with the problem.
The first feature is that menstruation proceeds somewhat differently, differing from the scenario that has become familiar over many years. They can be:
- scarce (although they used to be plentiful);
- too long and strong, with clots (despite the fact that the norm for this patient until recently was moderate three-day periods);
- painful;
- smearing and long-lasting.
What is the color of the discharge from uterine fibroids?
Directly during menstrual bleeding, they can be the same as menstrual blood itself.
Forecast
For small fibroids the prognosis is favorable. The neoplasm responds well to treatment. Relapse with the appearance of discharge is observed in only 2 patients out of 100. If you refuse therapy, the probability of tumor growth will be 50%. It is safe to say that strange discharge will appear over time.
Vaginal mucus without blood (except during menstruation) is normal. Changes in color, consistency, structure and other organoleptic characteristics are considered a deviation. At the first signs, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination. Myoma is a benign tumor that is not prone to malignancy. However, it needs to be monitored. Growth control allows doctors to prescribe correction in a timely manner and avoid complications.
Causes of fibroids
A benign myometrial tumor is hormonal in nature. If previously it was found mainly in women of late reproductive age due to the “dance of hormones” before the approaching menopause, now the diagnosis of “fibroids” is often given to young, 20-25-year-old patients. The reason is the abundance of stress factors in the modern lifestyle, which have a tremendous impact on the functioning of the reproductive system.
The appearance of fibroids is also affected by:
- heredity;
- late (after 35 years) childbirth;
- absence of childbirth;
- chronic gynecological diseases.
Under the influence of such unfavorable factors, an imbalance of the “main” female hormones: estrogen and progesterone may occur. Cells begin to divide incorrectly, and a tumor appears in the muscle layer of the uterus.
It’s worth making a reservation right away: fibroids never degenerate into a malignant neoplasm! You should not panic when it is discovered during a routine examination: in most cases, it is successfully treated: it either stops developing or gradually decreases in size.
Treatment
Myoma can be limited not only to a feeling of discomfort and some pain. The danger lies in the serious complications that this disease threatens. It does happen, although not often, that a benign tumor, which is essentially a fibroid, can degenerate into a malignant state. Often the tumor grows rapidly and the fibroids become large. In this state, it compresses nearby organs and impedes their functioning. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to contact a medical facility in a timely manner and carry out proper treatment. Several methods are used for this:
- conservative method of treatment;
- surgical method with complete removal of the organ or partial excision of fibroids.