After forty, a woman may experience changes in her menstrual cycle. Most often, they are provoked by physiological changes, which are considered normal and represent a decline in the function of the reproductive system due to age and hormonal changes.
Treatment of menstrual irregularities at 40 years of age is mainly aimed at reducing the activity of the manifested symptoms of perimenopause.
Physiology of a woman after 40
For most women, the childbearing period ends at 40–45 years. This is due to age: the aging processes of the reproductive system are activated in the body, starting with the depletion of the ovaries and a decrease in their sensitivity to the effects of follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing (LH) hormones produced by the pituitary gland. The ovaries stop producing estradiol, causing its blood levels to drop.
The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland begins to actively produce gonadotropic hormone, the level of FSH and LH in the blood increases, which is why hormonal levels and the menstrual cycle are disrupted after 40 years.
Gonadotropins provoke severe depletion of the ovaries, and critical days can occur, but their duration may vary. Gradually, under the influence of such irregularities in the menstrual cycle at 45 years of age, its duration increases. As a result, there is a complete cessation of menstruation.
Along with these processes, disruptions in the cyclical release of gonadotropins are provoked in the pituitary gland. Gradually, they cease to have an effect on the ovaries, which are in the active stage of exhaustion. The listed reasons for cycle disruption after 40 years provoke inhibition of ovarian function, and this is associated with the occurrence of structural changes in them, such as:
- activation of the process of oocyte death;
- atrophic processes in primordial follicles;
- thinning of granulosa, stroma;
- sclerosis of hyalinosis.
The listed factors provoke disruption of the cyclicity of menstruation after 45 years due to the lack of possibility of ovulation and insufficiency of the luteal phase. This affects what happens to the woman’s body: oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea develops.
Women of different ages depend on female sex hormones; after 40–45 years, hormonal imbalance causes depletion of the endometrium of the uterus. Also during this period, opposite processes may occur - diffuse, focal hyperplastic changes. Gradually, the size of the uterus decreases to 4–5 centimeters.
The indicated reasons for the disruption of the menstrual cycle also affect the general condition of the woman. This is due to the fact that many tissues and organs have receptors that sense estrogen levels, and during menopause or premenopause it decreases significantly.
Most often, such changes are smoothed out with the help of the body’s adaptation mechanisms, blocking the processes of the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. But in some women the activity of these functions is insufficient, which is why menopausal syndrome manifests itself.
Features of disorders at different periods of life
The cycle can go astray at any age, both teenage and elderly. Each period is characterized by individual changes, which will be discussed below.
Adolescence
During the first 1-2 years, a girl’s cycle is established; during this period it is important to monitor it in order to know its duration and suspect irregularities. Delays and early menstruation are associated with hormonal levels. But there are a number of factors that affect the regularity of menstruation:
- Sclerocystic ovaries;
- Frequent colds;
- Infection of the brain and genital organs;
- VSD – vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Traumatic brain injuries.
The regularity of the ovarian-menstrual cycle is affected by strict diets, weight loss, hypovitaminosis, early sexual activity, bad habits, and genetic factors. Often teenagers are faced with juvenile uterine bleeding, anemia, and poor health against this background. This is usually due to nervous tension and the presence of infections in the body.
Childbearing
During reproductive age, a woman complains of irregularities in cyclicity, delays and bleeding. Disturbances are caused by physiological and pathological factors. Normally, menstruation disappears during pregnancy and lactation, as well as after childbirth. In addition, disruptions in the menstrual cycle occur after the installation of an intrauterine device or due to the use of oral contraceptives.
Reasons for failure:
- Follicle persistence - the condition is characterized by the absence of ovulation, the appearance of a follicular cyst, and excessive growth of the uterine mucosa.
- Insufficiency of the second (luteal) phase - prolonged bleeding during the period of ovulation in large quantities.
- Consequences of abortion - it can be either spontaneous or medical.
After removal of the fertilized egg, the cycle usually lengthens and is restored after 3 months. If the abortion had complications, rehabilitation is longer and is accompanied by acyclic menstruation, as well as algomenorrhea.
Premenopause and menopause
Menstrual irregularities after 40 occur in the premenopausal period. The decline of reproductive function is often accompanied by delays, menopausal syndrome, bleeding, and changes in cyclicity. If menstruation resumes during menopause, you need to urgently go to the doctor, and bleeding during this period indicates an oncological process.
Periods of a woman's life after 40
After forty years, many women begin to experience suppression of their reproductive function. The process of menstrual irregularities is divided into several stages:
Perimenopause combines premenopause, menopause, and 2 years after the last normal menstruation.
Menopausal transition period
The main cause of menstrual irregularities after 40 years of age is premenopause. It begins at the age of 40–45 years and lasts until the end of menstruation. It is characterized by the beginning of a decrease in the activity of the hormonal function of the ovaries and the appearance of primary symptoms of menopause. This period passes unnoticed for only 5–10% of women.
Menopause
At the age of 45, menstrual irregularities caused by premenopause move to the next stage - menopause, which occurs with the last normal menstruation after 45 years and lasts a year.
Menopause in a woman’s life is premature if it begins at 37–40 years old, early – at 41–45. This stage may occur a couple of years earlier due to smoking, fasting, or alcohol addiction.
Perimenopause
It begins at the age of 40–45 and ends by the age of 55. This age is characterized by a decrease in ovarian function associated with the aging of the reproductive system. The perimenopause phase includes perimenopause, menopause and the 2 subsequent years.
Postmenopause
This stage begins from menopause, that is, after the onset of the last normal menstruation, as well as for 1 year after it. The postmenopausal stage is observed up to 65–70 years, gradually flowing into the senile period.
Reasons for lack of menstruation
Any irregularities in the menstrual cycle are a serious problem. The reasons for the absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) can be associated both with the physiological characteristics of the female body and with dangerous pathologies.
Factors that provoke amenorrhea:
- Failure in the functioning of the endocrine system. When thyroid hormones are not produced in sufficient quantities, menstruation may be absent for a long time.
- Pregnancy. It's no secret that there are no periods during pregnancy. This is the only reason explaining the presence of this phenomenon in a healthy woman. To confirm or refute the fact of conception, it is recommended to use a special test.
- Climax. Menopause usually occurs after age 45. The reproductive function disappears, just like menstruation during menopause. In this case, the absence of menstruation is a physiological norm, which means there is no reason to worry.
- Disorders of the pituitary gland. The presence of a tumor in one of the subcortical centers of the brain provokes a disruption of the menstrual cycle, as a result of which there is no discharge for a long time.
- Ovarian dysfunction. Failure in the functioning of the ovaries may be associated with hormonal imbalances. Due to dysfunction of the uterus and ovaries, severe nagging pain in the lower abdomen will occur throughout the entire cycle.
- Use of oral contraceptives. Taking some birth control pills provokes hormonal imbalance, as a result of which menstruation may not occur for a long period.
- Bulimia and anorexia. The diseases are associated with a sharp change in weight category. They are often accompanied by a lack of discharge. In this case, this phenomenon is a protective reaction of the body, because any blood loss due to such pathologies, including menstrual bleeding, is life-threatening.
- Venereal diseases. Some sexually transmitted diseases cause absence of menstruation.
- Alcohol and drug abuse. A woman who regularly uses drugs and alcohol may not have periods for a long time. The fact is that bad habits have a destructive effect on the reproductive system.
- Psycho-emotional tension, stress. Nervous shocks that are experienced regularly provoke disruptions in the functioning of internal organ systems, including the reproductive system. As a result of disruption of its functioning, there is a risk of lack of menstruation.
Symptoms of menopause
Symptoms of menopause are divided into 3 groups:
- early - appear before the cessation of menstruation (during the transition to menopause);
- medium-term – begins 2–4 years after menopause;
- late – appear 4–5 years after menopause.
In almost 50% of women, menopause is severe with pronounced symptoms. A mild form of transition is observed only in completely healthy representatives of the fairer sex, while menstrual cycle disturbances are observed later in them.
Early
Failure of the menstrual cycle in the fifth decade is manifested by vasomotor and psycho-emotional symptoms.
Irregular and short-lived menstruation provokes the appearance of vasomotor symptoms, such as:
- feeling of heart rate;
- feeling of rising temperature;
- increased sweating;
- hypertension.
With a physiological delay in menstruation, a change in the psycho-emotional state and the appearance of the following symptoms are noted:
- memory impairment;
- insomnia;
- irritability;
- decreased libido;
- depression;
- headaches and dizziness.
Medium-term symptoms of menstrual irregularities include the appearance of dryness, itching, burning sensations in the vagina, pain during sexual intercourse, urinary incontinence, wrinkles on the skin, increased fragility of the nail plates, hair loss and weakening.
All of the above symptoms can manifest themselves within five years after menstrual irregularities at 45 years of age.
Late
These menopausal symptoms are associated with the development of diseases of vital systems and organs. The reasons for the failure of the menstrual cycle after 40 years lead to the appearance of such problems as:
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- postmenopausal osteoporosis;
- Alzheimer's disease.
To avoid the development of dangerous pathologies, it is necessary to begin treatment of menopausal syndrome in a timely manner. Hormone replacement therapy is considered the only effective method. It should be started when early signs of menopause appear. On average, this takes 1–3 years, but the duration can be increased to 5 years.
Recommendations
In cases where the reasons for the disruption of the menstrual cycle are not serious and are not interrelated with pathological processes and changes, then the woman needs to reconsider her diet and lifestyle in general. 14 days before the onset of menstruation, a woman is advised to follow a special diet that includes eating vegetables, fruits and whole grains.
During this period, it is necessary to completely avoid eating fast food, foods that contain large amounts of fat, as well as alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks. If the cause of the disruption of the monthly cycle is bloating, then it is necessary to reduce the amount of salt consumed. Reducing the use of sugar and caffeine is also helpful.
Physical exercise will help reduce the severity of pain during menstruation. The regularity of such exercises is more likely to give a positive result. Very important in this situation is the individual selection of the necessary set of exercises, which is performed taking into account the characteristics of the woman and the possible presence of problems with her health. This complex must be compiled by a qualified specialist.
It is necessary to take into account that not only physical exercises can normalize the condition. Having regular sex life also plays an important role in the life of every woman.
In order to prevent the occurrence of diseases caused by harmful microorganisms, it is necessary to regularly carry out hygiene procedures using a special intimate hygiene product. Particular attention should be paid to hygiene during menstruation.
In addition, gynecologists recommend changing tampons and sanitary pads every 4 to 5 hours. There is no need to use overly scented hygiene products, as they can cause irritation of the intimate area.
You need to be extremely careful and not abuse a procedure such as douching in order not to disturb the microflora inside the female genital organ. To keep your body clean, you need to shower twice a day.
Failure of the menstrual cycle - causes after 40 years
As we age, levels of progesterone and estrogen, two important hormones produced by the ovaries to control the menstrual cycle, begin to decrease, leading to erratic symptoms, cycle irregularities, and other less-than-pleasant symptoms. This condition is called perimenopause.
At the same time, most women after 40 years experience many changes in the body, which, as a rule, appear gradually and spontaneously, but indicate a decrease in the function of childbearing and the woman’s entry into a new phase of her life.
After 40 years the cycle becomes shorter. Below is a typical picture of a menstrual cycle disorder, which causes confusion among many, but at the same time is natural:
- At 20 years old the cycle is approximately 31 days
- At 30 – approximately 28 days
- At 40 it’s already 24-27 days.
Due to hormonal imbalance, there are three main types of menstrual cycle disorders:
- Menstruation becomes lighter and decreases. This scenario is more typical in women who have always had fairly light periods, and especially in women who are not overweight and have low estrogen levels.
- Periods can become extremely heavy and irregular due to hormonal fluctuations, and this lasts for 3-5 years before menopause. In some cases, the body actually produces more estrogen, causing thicker endometrial lining and heavier bleeding. It can also be caused by the presence of uterine fibroids or adenomyosis.
- Some women will not experience any change in their cycles, but find that their cycles first become closer together and then become more irregular.
Contact your doctor if:
- you have several menstrual cycles shorter than 21 days in a row,
- several cycles that last three days longer than usual.
Types of menstrual irregularities:
- absence of menstruation for six months or more (amenorrhea). This condition is normal during pregnancy, breastfeeding, during menopause and in girls who have not yet reached puberty. In all other cases, this is a pathology;
- infrequent menstruation (menstrual cycle more than 35 days);
- frequent menstruation (menstrual cycle less than 21 days);
- violation of the duration of menstruation (too short - less than 2 days; too long - more than 7 days);
- too scanty menstruation (blood loss less than 20 ml.) or heavy (more than 150 ml.);
- menstruation outside the cycle.
Restructuring the body during premenopause
To understand the changes in your cycle that occur after age 40, it is important to learn about menopause and its different stages. The first stage of menopause is premenopause.
The body will also begin to change with decreasing hormone levels and menstrual periods. During this time, most women become less likely to become pregnant and may experience irregular and sometimes heavy periods.
The changes that occur during perimenopause can be a gradual onset of symptoms and often resemble PMS:
- anxiety,
- weight gain,
- depression,
- nervousness,
- general weakness,
- sleep problems.
- decreased bone density,
- dry skin.
Perimenopause is a transitional phase that can begin after age 35 and usually lasts from two to ten years until menopause.
Below are some of the symptoms that premenopausal women experience:
- Mood swings.
- Mild chest pain.
- Severe premenstrual syndrome.
- Decreased libido.
- Hot tides.
- Fatigue
- Irregular periods.
- Dryness in the vagina, causing discomfort during sex.
- Urine leakage when sneezing and coughing.
- Increased need to urinate – incontinence.
Changes in the menstrual cycle at 40 years old - types and treatment
- Cramps during menstruation
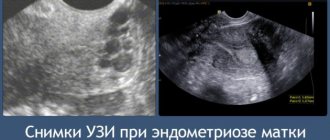
Dysmenorrhea or menstrual cramps are common cycle changes after age 40, usually accompanied by lower abdominal pain. According to some doctors, endometriosis is a common cause of dysmenorrhea, which leads to the formation of adhesions of the pelvic organs and the development of cysts in the ovaries.
Oral contraceptive pills and analgesics are common forms of treatment in this case; surgery is a last resort option, which is used if the cyst reaches a large size or there are other serious problems that cannot be eliminated without surgery.
Heavy bleeding
Heavy bleeding during menstruation is known as menorrhagia and is associated with the passage of blood clots in the early days. Heavy periods before menopause can lead to fibroids, which in turn lead to anemia and cause symptoms such as fatigue and lethargy. The severity of symptoms and the number and size of fibroids determine the treatment method. Treatment options include:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Ibuprofen, Nurofen),
- birth control pills, tranexamic acid.
- in some cases surgery is required to excise the fibroids, and in some cases the only option is complete removal of the uterus.
- Irregular cycle
28 days is the average time between two cycles. The last of them may become irregular before menopause: - start earlier - once every two weeks,
- infrequent - sometimes the break can reach more than 3 months.
Menopause or dysfunctional uterine bleeding can cause irregular periods and be accompanied by:
- insomnia,
- hot tides,
- mood swings.
Achieved by most women by age 50. These symptoms are purely physiological and begin approximately two years before menopause. Osteoporosis is common in long-term menopause, so calcium supplements and exercise are generally recommended for all women over 50.
Bleeding during the menstrual cycle
Irregular bleeding that occurs before or after menstruation is called intermenstrual bleeding and refers to the period after 40 years. This is not like having irregular periods. Women suffering from intermenstrual bleeding are advised to:
- have a Pap smear to rule out cervical cancer,
- carry out an ultrasound scan of the pelvis to check the uterus,
- perform dilation hysteroscopy to check for uterine cancer.
When to see a doctor
During perimenopause, irregular cycles are completely natural. However, there are other signs that can change the course of your menstrual bleeding. You should consult a doctor immediately if:
- Menstrual blood contains blood clots.
- Cycles are longer than usual.
- Discharge after sexual intercourse.
- The cycle is shorter than usual.
Reasons for violation
Menstrual cycle irregularities (MCIs) are a deviation with which modern women most often turn to a gynecologist. One-time failures caused by stress, overload or climate change do not pose a threat to health. Another thing is the complete lack of regularity of menstruation.
Constant delays, which can last up to 6 months, or too frequent periods are not the only reasons for concern. A change in the duration of an established cycle, as well as the duration and intensity of discharge, are sufficient reasons to consult a doctor.
The main reasons for the disruption of the menstrual cycle:
- Overweight or underweight. The fat layer is the main reservoir of female sex hormones - estrogens. Its deficiency or excess can cause disruption of the menstrual cycle. Young girls, fixated on unhealthy thinness or keen on “cutting”, usually do not pay attention to delays in menstruation. Women who are overweight, in addition to irregular or complete absence of menstruation, may experience uterine bleeding caused by excess estrogen.
- Lack of vitamins. Even with a balanced diet, the body does not always receive the full amount of necessary microelements. Strict diets and restrictions lead to metabolic disorders and hormonal disorders. Vitamin deficiency can cause the cancellation of regular processes (including menstruation), which are not a priority for life support.
- Psychosomatic factors. Nowadays, the life of the average working woman is one big stress. Lack of sleep, inability to eat right, psychological stress caused by the number of problems that need to be solved: all this signals the body that now is not the right time to reproduce. The cycle fails. Changes in climate and time zone can also lead to irregular menstruation.
- Insufficient uterine tone. Weak contractile functions of the smooth muscles of the uterus do not allow blood clots to be effectively expelled, so the body is rebuilt, reducing the regularity and abundance of menstruation. The cause of decreased tone may be insufficient physical activity or reduced levels of substances that stimulate contractions.
- Hormonal imbalance. In this case, the cycle failure is a post-effect of taking hormonal drugs that affect the functioning of the endocrine system, for example, oral contraceptives. After stopping medication, the body needs some time to restore the regularity of menstruation. However, incorrectly selected medications can cause the failure to recur. In this case, you need to consult a doctor.
- Pregnancy and lactation. Hormonal changes associated with pregnancy and breastfeeding are designed to prevent re-conception. During lactation, prolactin, the hormone responsible for milk production, is actively produced. It blocks the generation of ovarian hormones, which leads to absence of menstruation. As a rule, the cycle stabilizes immediately after breastfeeding stops.
- Problems with the hematopoietic system. During “critical days,” a woman loses on average up to 100 ml of blood. Anemia or decreased blood clotting can cause your menstrual cycle to increase or stop completely.
- Infectious diseases of the reproductive organs. Most sexually transmitted diseases are asymptomatic in the initial stage. However, if you notice uncharacteristic discharge with an unpleasant odor or pain in the appendage area, you should immediately consult a doctor. Infections and accompanying inflammatory processes affect the regularity of the cycle and can cause adhesions.
- Ovarian dysfunction. Stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs, malfunctions of the endocrine system, as well as sexually transmitted diseases can cause the appearance of neoplasms in the genital organs and, as a result, NMC. Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the most common diseases that requires timely treatment.
- Diseases not related to gynecology. Any change in the functioning of the reproductive system can become a symptom of the development of a more serious disease, for example, the formation of a malignant or benign tumor, damage to the central nervous system, or the development of diabetes mellitus. The regularity of menstruation is one of the main indicators of the normal functioning of the body, which is why it is so important to monitor your cycle, even if pregnancy is not planned.
- Genetic abnormalities. For approximately 5% of women, lack of regularity in the menstrual cycle is normal. This makes it difficult to plan a pregnancy because it is difficult to track the moment of ovulation, but there are no health problems.
Monitoring the regularity of menstruation is one of the main conditions for preventing problems with the reproductive system. Nowadays, in order to distinguish a single failure from a serious disorder of the menstrual cycle, it is enough to install the appropriate application on your mobile phone.
Long menstrual cycle - probable causes
- The long gap between cycles sometimes reaches several months; the ovaries cannot produce predictable levels of estrogen and progesterone. This imbalance can lead to the uterine lining becoming too thick, and then leaving the body completely after the first pause.
Prolonged bleeding may indicate the presence of polyps in the uterus, due to which bleeding lasts longer than usual.
Prolonged bleeding may also indicate a high probability of fibrosis - a non-tumor tumor that grows in the muscular wall of the uterus (or it could be multiple fibroids).
Bleeding during menopause
If there is bleeding during menopause, the patient must be prescribed curettage of the uterine cavity. After all, bleeding may indicate serious pathologies, in particular the development of atypical hyperplasia or endometrial adenocarcinoma . Sometimes a doctor may decide to perform a hysterectomy .
Sometimes a patient during menopause is prescribed gestagen medications: Depo-Provera , Duphaston , 17-OPK .
During treatment, antiestrogenic drugs can also be prescribed - Danazol , Gestrinone , 17a-ethynyl testosterone .
Abnormal uterine bleeding - treatment
Menstrual irregularities at 40, the treatment of which ranges from the use of painkillers to surgery depending on the diagnosis, its severity, medical history and doctor's recommendation, are not always the result of perimenopause. Sometimes the causes can be much more serious, so examination by a doctor is necessary.
In all cases, less invasive treatments are considered first. The choice of treatment depends on age, desire to maintain fertility, and the cause of abnormal bleeding (dysfunctional or structural). Some treatments can reduce menstrual bleeding to normal.
Drug therapy is often successful and is a good option. True, the result lasts only as long as the medications are taken, so this treatment is long-term:
- Low doses of birth control pills, progestins, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help control heavy or irregular bleeding caused by hormonal imbalances.
If your periods have stopped, oral contraceptives and birth control pills are very effective in restoring a regular cycle, but they do not address the reason why the bleeding stopped. They may also help reduce menstrual bleeding, improve and control menstrual patterns, and relieve pelvic pain.
An oral contraceptive containing a form of progesterone called drospirenone and sold under the names YAZ, Yasmin, Ocella, Gianvi and Zarah, may reduce some mood-related symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, tearfulness and tension.
Natazia, which contains the synthetic estradiol valerate, is the first birth control pill approved for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding that is not caused by a uterine condition. The combined estrogen-progesterone pill may help women who do not have risk factors and do not plan to become pregnant.
Birth control pills may not be an appropriate choice for treatment if you smoke, have a history of pulmonary embolism (blood clots in the lungs), or other side effects from this medication. The risk of these side effects is even higher if you use the IUD for birth control because it contains higher levels of estrogen.
Treatment of cycle disorders in women of childbearing age
Treatment of menstrual cycle disorders in this case is similar to the treatment regimen for such disorders in adolescents. Both at the age of twenty, and treatment of menstrual irregularities at the age of 40 with bleeding is carried out by curettage. It is carried out for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Next comes hormone therapy. Combined oral contraceptives are prescribed and used according to the usual regimen. If the second (luteal) phase is incomplete, progesterone analogues Utrozhestan or Duphaston ; they must be taken in the second phase of the cycle. It is also possible to take 17-OPK , Norkolut .
It is important to replenish the volume of circulating blood, for which colloidal solutions are used. Antianemic treatment and symptomatic hemostasis are also practiced. Provided that curettage does not work, the doctor may decide on hysterectomy or ablation (burning out) of the endometrium.
It is also important to properly treat those concomitant diseases that could provoke a cycle disorder. So, for hypertension, it is important to take prescribed medications and limit salty and liquid intake. If you have liver pathology, you should follow a proper diet and take hepatoprotectors.
Some women also practice treatment with folk remedies. However, such methods must be practiced very carefully, since without consulting a doctor there is a risk of missing a serious pathology. And even irregular menstruation after 45 years of age, perceived by a woman as the beginning of menopause, is a reason to consult a doctor.
Since cycle disruptions can cause infertility , women of childbearing age, if necessary, are prescribed Choriogonin and Pergonal - medications to stimulate the development of active follicles. To stimulate ovulation, you should take Clomiphene .
Cutting pain in the lower abdomen, periods are painful
If you regularly experience severe stabbing pain in your lower abdomen (called dysmenorrhea), your doctor may recommend trying prescription and over-the-counter medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as Ibuprofen and Naproxen, can be purchased without a prescription. Treatment works best if started several hours before pain begins. If the pain begins, the likelihood of it decreasing after taking medication is low, so you should start taking pills before it starts - according to the instructions. This will also help reduce heavy bleeding.
Oral contraceptive pills are also effective for menstrual cramps. If the active tablets are taken continuously for 90 to 120 days in a row, periods will only occur three to four times a year.
Other ways to relieve symptoms include warm compresses to the abdominal area and mild exercise.
Approaching the age of 40, most women notice that undesirable changes occur in the body. Feeling worsens, vigor and optimism are replaced by fatigue and depressed mood. The reasons for all this are the decline of reproductive function and hormonal changes. The number of produced eggs decreases, the ratio between progesterone and estrogens changes.
A phenomenon that does not go unnoticed by any woman is irregular periods after 40 years and a change in the amount of bleeding. In some women, ovarian or uterine diseases are added to hormonal imbalance. Age-related changes can provoke polymenorrhea, bleeding, delay and other disorders.
Normal menstruation after 40 years
This age period is characterized by delays in menstruation, lengthening and shortening of the cycle. It also happens that spotting occurs 2 times a month. They can be abundant or scanty, and under certain conditions doctors consider this to be normal. However, we cannot exclude pathologies that also cause all of the above phenomena. After 40 years, a woman should monitor her periods very carefully, paying attention to their intensity, duration, color and consistency.
What menstruation may indicate a deviation from the norm:
- Abundant. In rare cases, heavy bleeding is a sign of perimenopause. Possible pathologies are cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids.
- Delayed. Symptoms of incipient menopause or a sign of pregnancy, which can occur after 40 years.
- Scarce. The cycle is extended to 35-40 days or shortened to 19-21 days. With scanty periods, the reason after 40 years is usually the approach of menopause.
- Frequent. Bleeding twice a month or between menstrual periods is called polymenorrhea. The reason is the decline of ovarian function and the production of a small amount of estrogen. Sometimes polymenorrhea indicates cervical cancer, endometriosis or a cyst.
- Long lasting. Menstrual bleeding that lasts a week or longer is a reason to see a doctor immediately. Long periods occur with blood clotting disorders, infectious diseases, pathologies of the ovaries and uterus. Taking oral contraceptives can also cause a prolongation of the menstrual period.
Cycle failure after 40 years: options for menstruation disorders
After reaching a certain age, a woman’s ability to conceive decreases every year. While the menstrual cycle has not completed, it is still possible to conceive, carry and give birth to a child. If menstruation fails after 40 years, the likelihood of such an event is reduced to a minimum. However, this does not eliminate the need to take contraceptives or use barrier methods.
There are different types of menstrual irregularities. Most often, doctors diagnose the following:
- heavy bleeding without irregularity;
- shortened cycle, when menstruation occurs once every 1.5-2 weeks;
- prolonged scanty bleeding (smearing continues without interruption);
- bleeding occurs after or before menstruation, as well as instead of the main menstruation;
- scanty discharge;
- cycle delay in the absence of pregnancy.
After 40 years, any of these phenomena is a reason for medical consultation. There are other symptoms of perimenopause. For example, before the onset of menstruation, a woman feels a worsening mood, experiences irritability, dizziness, headache, and palpitations. This is how the body reacts to the decline of ovarian function and hormonal imbalance, accompanied by endocrine changes.
Painful periods: ICD 10 code No. 94
Painful periods according to ICD 10 mean:
- Pain that occurs approximately in the middle of the cycle.
- Dyspareunia. This disorder involves pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse. This item does not include psychogenic dyspareunia.
- Vaginismus. The disorder is understood as convulsive contractions of the vaginal muscles of a spastic nature that occur when attempting to examine or have sexual intercourse. Gynecologists do not include psychogenic vaginismus in this category.
- Syndrome of the so-called premenstrual tension. This is a complex of various symptoms characteristic of phase 2 of the cycle. PMS is individual in nature and usually includes psycho-emotional disorders and headaches.
- Primary dysmenorrhea. Painful menstruation is observed in women from menarche to the age of 30. The disorder is usually caused by hormonal disorders.
- Secondary dysmenorrhea. Pain that accompanies menstruation often appears due to gynecological diseases.
- Dysmenorrhea (unspecified). This diagnosis can be made for menstrual pain of unknown etiology.
- Other conditions (specified) that are directly related to the menstrual cycle and reproductive organs.
- Unspecified pathologies associated with the cycle and genitals.
Causes of scanty periods in women over 40 years of age
When the hormonal system fails, the endometrium, the protective membrane that covers the uterine cavity from the inside, suffers. With each monthly cycle, the thickness of the mucous layer becomes thinner. This makes the uterus vulnerable to infection and causes the amount of bleeding to decrease each month. At this time, it is important to undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
If there are no gynecological diseases, there is nothing to worry about. Scanty periods are a sign that perimenopause will soon give way to menopause. However, if the phenomenon continues for several months, in addition to examination, hardware diagnostics may be necessary. Some pathologies of the reproductive sphere can only be identified in this way. Here's how spotting and spotting can appear:
- instead of normal menstruation, at the appointed time;
- during the intermenstrual period, before and after menstruation.
You need to see a doctor as soon as possible, because timely detection of pathology significantly increases the chances of a successful treatment outcome.
Spotting instead of menstruation
The regularity of the menstrual cycle must be monitored every month. A woman can mark a calendar, use an app, or use another method. It is important to be able to conveniently monitor the duration, intensity and frequency of discharge.
Common causes of scanty menstrual bleeding:
- consequences of a previous infection (flu, sore throat, pneumonia, otitis media);
- the body's reaction to physical overload, stress and nervous tension;
- endometriosis of the uterus or ovaries, fibroids, cysts, hyperplasia;
- pathologies in the appendage area, loss of hormonal function of the ovaries;
- a sharp increase or decrease in body weight caused by illness, dieting, or the transition to a normal diet after a weight loss course;
- exacerbation in women with thyroid pathologies, diabetes mellitus;
- deterioration of the condition with chronic adnexitis;
- disruption of the kidneys, liver, pancreas;
- pregnancy.
The latter option cannot be called a typical reason for the absence of menstruation in women after 40 years of age, but it should not be excluded. If your last period was scanty or spotty, you should be examined by a gynecologist and take a pregnancy test. Many women over 40 are able to carry and give birth to a healthy baby. In this case, severe pathologies should be excluded and make sure that the development of the fetus is not in danger.
Why do you have long periods after 40?
Hormonal changes are often accompanied by heavy, prolonged and frequent menstrual flow. Instead of once a month - 2-3, each time for several days. The condition is difficult to tolerate, and concomitant diseases may develop against its background. It is necessary to identify the cause as quickly as possible, since severe blood loss is dangerous to a woman’s health.
Typical causes of frequent and prolonged periods in women over 40 years of age:
- polyps in the uterus;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- complication of endometriosis;
- formation of a malignant tumor;
- atypical changes in endometrial tissue that developed against the background of a hyperplastic process;
- intramural or submucosal leiomyoma;
- other pathologies of the reproductive organs.
Heavy and prolonged menstruation cannot be treated using traditional medicine methods. In the case of a precancerous condition, such negligence can lead to the development of a malignant tumor.
How to stop heavy periods
Vaginal or uterine bleeding cannot be stopped on your own. There are several methods, but which one to use for a heavy menstrual cycle in a woman over 40 years old is decided by the gynecologist. Possible options:
- taking hormonal medications;
- use of hemostatic drugs;
- scraping.
The latter method is used when you need to obtain information about the condition of tissues. A sample of the material is sent for histological examination. Based on the results, treatment is prescribed.
Causes of failure in adolescents
Most often, problems with the cycle occur in very young girls . In most cases, gynecologists urge not to see this as a cause for alarm. The young body has just entered the maturation phase; the hormonal levels have not yet stabilized during puberty.
During the first few years, a teenage girl’s menstrual cycle is just establishing itself. Menstruation may come irregularly , with long gaps between cycles.
Often there are anovulatory cycles, as a result of which menstruation does not occur. The internal reproductive organs continue to form, menstruation can be painful, prolonged and heavy. Sometimes the situation manifests itself in the opposite form: menstruation comes rarely , lasting no more than 2-3 days.
There is no need to worry too much about such disruptions, since for most women a stable cycle is established only by the age of 18-20 or after the birth of a child. But it is necessary to monitor the situation by regularly visiting a gynecologist . To regulate the menstrual cycle, girls are often prescribed light oral contraceptives, which help normalize hormonal levels. Taking pills on your own without consulting a doctor is not recommended so as not to harm the developing body.
Why do I get my period twice a month?
Normally, critical days should occur every 21-25 days. Small deviations in one direction or another are not considered pathology. However, a frequency of 2 times a month requires medical consultation. It does not matter whether the discharge is heavy or scanty, or whether it is accompanied by pain, weakness or other symptoms. You need to go to the doctor in any case.
Usually the reason for frequent periods after 40 years is pathological changes in the tissue of the uterus, appendages or ovaries. In such cases, adequate treatment is prescribed.
Causes of irregular periods
The main reason for an irregular menstrual cycle, if there are no unpleasant symptoms and the discharge itself has a typical color and consistency, is the approaching menopause. At first, menstruation occurs once every 1.5-2 months, then less often, and after a while it stops.
During the transition period, phenomena arise that are considered to be satellites of the menopausal syndrome. However, you should not reassure yourself that hot flashes, headaches, palpitations and high blood pressure are normal. In fact, before menopause, a trip to the doctor is mandatory. It is better to visit a gynecologist whenever your health condition causes concern.
Delayed menstruation: what is the reason
The most common causes of missed periods after 40 years are menopause and pregnancy. The symptoms of these conditions vary, so a woman can easily distinguish one from the other. The delay can also be caused by pathologies or postoperative conditions.
The most common reasons:
- taking hormonal and non-hormonal medications;
- endocrine disorders;
- malnutrition;
- chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys, bronchi, pancreas;
- post-infectious conditions;
- fibroids, polyps, curettage;
- psychogenic diseases.
Other reasons for delay are stress, overwork, and regular lack of sleep.
Main reasons
Normally, there are only two natural causes of failure or cessation of the menstrual cycle - pregnancy and menopause. Everything else is the impact of negative factors on the body or a consequence of pathological processes.
Why does the monthly cycle shorten after 40 years? The natural reason is that the body enters a state of premenopause. The production of female hormones by the ovaries decreases. This is reflected in the menstrual cycle, which by its nature is a hormone-dependent process. The monthly cycle can either shorten or increase, and discharge can change in volume.
But this is not always the case for such a natural reason. Many things can cause a cycle to fail:
- Endometriosis.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Inflammatory processes in the body.
- Abortion or miscarriage.
- Taking hormonal contraceptives.
- The period after childbirth.
- Serious physical activity.
- Chronic stress conditions.
- Abnormal change in body weight.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Taking certain medications.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Let's look at these reasons in more detail.
Other cycle disorders
Menstruation in women over 40-45 may resume a few months after completion. This condition is not normal.
Bleeding is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- heaviness in the stomach;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- constipation;
- diarrhea;
- heartburn;
- bloating.
You need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist, do an ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries, and colposcopy. The woman is also sent for a blood test and cytological examination. In adulthood, the main thing is to exclude or detect cancer early. Proper treatment will allow you to avoid complications.