Why can menstruation stop early?
- Genetic reasons - when malfunctions in the ovaries are programmed into the girl’s DNA after her conception;
- Psychological reasons - a life filled with constant severe stress and shock, loss of loved ones, work associated with frequent nervous overstrain can hasten the aging of the female system and the whole body;
- chronic mental illnesses, diabetes of various types, diseases of the heart and blood vessels, liver, oncology;
- socio-economic prerequisites - a higher status in society, in which a woman does not lack funds for her life, and her body is not worn out by hard work, pressure on the psyche in the work collective, makes it possible to maintain the normal course of menstruation much longer;
- geographical location - in places where there is a lot of sun and heat, girls begin puberty earlier, menstruation comes earlier and ends later;
- behavioral reasons - if sex has an active meaning in a woman’s life, and she experiences satisfaction, disruptions in menstruation are postponed to a later age.
When should you see a doctor?
In general, a woman does not necessarily need to contact a doctor to be diagnosed with perimenopause, but sometimes it is necessary to do so. You may be experiencing individual symptoms of a natural transition process, but there are some signs that you should contact a specialist if you encounter them. Do this if you experience:
- absence of menstrual cycles;
- blood clots during menstruation;
- bleeding after sex;
- longer periods than usual.
Sometimes the cause of hormonal imbalance is fibroids, most of which can be cured . It is important to know that an accurate diagnosis also helps eliminate the potential possibility of cancer.
In addition, medical help should be sought if perimenopausal symptoms interfere with daily life activities.
https://youtu.be/x-Cau7D-d48
What is menopause and when does it occur?
Menopause in general is a period of complete extinction of the reproductive system, divided into several stages:
- Premenopause - preparation for menopause
- Menopause is the period from the last menstruation until the decline of reproductive function.
- Postmenopause is the complete cessation of reproductive function and further restructuring of the female body.
On average, the first signs of premenopause appear in women after 45 years of age, and then this period can last from 2 to 10 years. In 10% of cases, this stage in women makes itself felt from the age of 35. In this case, the woman is faced with the concept of early menopause.
Early menopause can occur due to several reasons: heredity, poor lifestyle and bad habits, sexually transmitted infections. Find out what are the signs of menopause in women at 40 years old.
Also, menopause can occur at a later date - about 50 years.
During the transition to premenopause, the hormonal secretion of the ovaries changes, and as a result, the content of estrogens and progestins decreases, and the level of follicle-stimulating hormone, on the contrary, increases. The amount of production of male sex hormones by the adrenal glands - androgens, which are transformed into estrogens in adipose tissue, also increases.
New cells and tissues are actively formed in the uterus and mammary glands due to the excessive action of the hormone prolactin, which was previously responsible for the regular onset of menstruation and ovulation. During this period, menstruation may still occur from time to time, but such hormonal “slides” cause significant disruptions in the menstrual cycle. This is why premenopause and menstruation are closely related, inseparable processes.
It is worth noting that this is only the beginning of hormonal changes and female hormones are still in sufficient quantities in the body, so all “critical days” will pass with ovulation, in 57%, until the onset of menopause. Therefore, the chances of getting pregnant during this period are quite high. It is imperative to use contraceptive methods if conception is not planned.
Menopause is a hormonal change in the body, accompanied by a gradual cessation of the production of estrogen, which is responsible for the functioning of the ovaries. During menopause, which lasts from 2 to 15 years, the menstrual cycle gradually increases, leading to the complete cessation of bleeding and the end of a woman’s reproductive capacity.
Menopause is divided into 3 periods:
- Premenopause. Normally it begins after 45 years of age (but can occur earlier or later than this age) and consists of a gradual decrease in estrogen production. Premenopause lasts from 2 to 10 years.
- Menopause is the last menstruation before the final end of fertility.
- Postmenopause is the 12 month period following the date of the last menstrual bleeding. Differs in early postmenopause (5-8 years) and late.
Most women experience menopause at age 50. At this point, the supply of oocytes is excised and estrogen production stops.
Gynecologists also distinguish:
- Early menopause, occurring before the age of 40.
- Late menopause, which becomes more active at the age of 60.
Early menopause most often occurs in women living in large cities who work in professions that involve being in long-term stressful situations.
The main reasons for early menopause are:
- hormonal pathologies of the thyroid gland, such as obesity and diabetes;
- previous multiple abortions;
- frequent gynecological diseases and their subsequent treatment;
- improper use of hormonal contraceptives;
- bad habits;
- oncological pathologies;
- bad environment;
- constant stress;
- genetic predisposition of a woman.
Late menopause is the most favorable for the body and is associated with a longer period of aging.
Occurs most often in women:
- having serious gynecological diseases;
- suffering from tumors that cause active release of estrogen;
- after previously undergoing oncology of the genital organs, accompanied by chemotherapy and radiotherapy;
- who have used antibacterial therapy for a long time;
- following a Mediterranean diet;
- often eat seafood.
Menstruation is possible only during premenopause. The appearance of bleeding 1.5-2 years after the completion of the last menstrual bleeding indicates the formation of a pathology of the reproductive system (caused by a strong proliferation of endometrioid tissue) and requires an immediate visit to the gynecological office.
Menopause (menopause) is the decline of the reproductive system in a woman’s life. The medical definition of the onset of menopause is when a woman has not had a menstrual cycle for 12 consecutive months.
The time preceding menopause is called premenopause, and this is the first stage of menopause with all its symptoms.
There is no strict medical definition of perimenopause, but it generally refers to the age approaching menopause during which a woman begins to experience symptoms of decreased estrogen levels. The process lasts until full menopause, which is the time when the ovaries stop producing eggs.
Perimenopause is not a disorder or disease, but a normal physiological process. And, despite the fact that it is not always asymptomatic, there is no cure for it.
What changes occur in the female body during perimenopause?
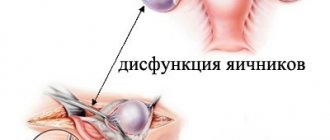
The ovaries are the main hormonal gland of a woman at reproductive age. They perform several functions at once:
Generative.
They produce eggs to reproduce offspring.
Vegetative.
They influence the formation of primary and secondary female sexual characteristics.
Hormonal.
They synthesize hormones to carry out reproductive function and to regulate the activities of various organs and systems.
The hypothalamus, located in the brain, controls the activity of the ovaries, including the secretion of estrogen and progesterone. These hormones ensure a two-phase menstrual cycle, egg fertilization and pregnancy.
As the hypothalamic structures age, they begin to lose their regulatory role, so the ovaries produce less estrogen. The follicles can no longer reach the required maturity, and ovulation does not occur. This is how the premenopausal period begins, characterized by a change from ovulatory cycles to anovulatory ones.
To compensate for the lack of estrogen, the pituitary gland intensively produces follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), but the hormonal balance still remains unstable.
It is not only the reproductive organs that are the target of these changes. The female body has structures that are dependent on estrogen and hormonal imbalance. The people most affected by premenopausal syndrome are:
- Mammary gland;
- Brain, pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- The cardiovascular system;
- Musculoskeletal system;
- Urinary system;
- Connective tissue;
- Intestines;
- Hair and skin.
With a deficiency of estrogen, changes occur in these organs and tissues that bring considerable discomfort to the woman. The severity of manifestations of hypoestrogenism depends on the compensatory capabilities of the body. This includes lifestyle, heredity, the presence or absence of somatic diseases and many other factors.
Healthy women go through the premenopausal period without any problems or negative symptoms, especially at the beginning of this process, when the influence of estrogen is still present.
As menopause approaches, hormones become less and less, and their absence is practically not compensated for by FSH. But even in this case, some women live ordinary lives without feeling significant changes.
If there are disorders of the endocrine, cardiovascular system, gynecological diseases, the woman endures serious physical and mental stress, has bad habits, the symptoms of premenopause are pronounced, and the woman cannot always cope with them without the help of a specialist.
These manifestations are conventionally divided into 2 groups: the first are symptoms associated with menstrual dysfunction, the second are symptoms associated with a lack of estrogen.
Signs of the onset of premenopause:
- Unequal menstrual cycles with varying duration and volume of blood loss;
- Dysfunctional bleeding;
- Enlargement and tenderness of the mammary glands before menstruation;
- Development of mastopathy;
- Single “hot flashes”, characterized by a feeling of heat, increased sweating, redness of the skin of the face and neck;
- Decreased libido;
- Increased fatigue;
- Irritability and increased emotionality;
- Sleep disorders – insomnia or increased sleepiness;
- Vaginal dryness, causing discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- Deterioration of hair and nails;
- Increase in body weight;
- Frequent headaches;
- Increased heart rate;
- Blood pressure surges.
If premenopause syndrome gives a woman negative feelings, she should consult a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
In addition to a gynecological examination and ultrasound of the pelvic organs, the doctor studies the woman’s hormonal background. It may be unstable, so studies are carried out several times and the results are compared.
How to recognize the onset of menopause
Unfortunately, menostasis (that is, menopause) does not pass without leaving a trace; most women feel unpleasant physiological sensations.
For example:
- Tides. One of the most common and unpleasant signs of the onset of menopause is accompanied by a sudden onset of a feeling of heat, lasts no more than a minute and goes away abruptly. Some women experience hot flashes quite rarely, which does not cause them any inconvenience or discomfort. For others, this feeling can bother up to 50 times a day, often occurring at night, after which the woman may not get enough sleep and feel tired and irritable.
- Increased sweating is directly related to hot flashes, occurring precisely after them. Sweating can be so severe that marks can appear on clothing and on the face in the form of beads of sweat, which is very uncomfortable and unpleasant.
- Insomnia. It often occurs due to hot flashes, but a woman suffering from insomnia cannot always feel the hot flashes, often waking up in the middle of the night without other unpleasant sensations. Due to insomnia, a woman may often experience feelings of sleep deprivation, fatigue, irritability and inattentiveness.
- Tension and headache. Tension arises due to the inability to relax, the facial muscles remain tense, hence the headache, and the outside of the face looks constantly gloomy. Migraine can also be attributed to this symptom, because a sharp attack of headache, darkening of the eyes and dizziness often occurs due to constant tension in the facial muscles.
- A sharp change in emotional background. Often a woman after 50 years of age may experience a sharp change in mood from cheerful and playful to irritated and offended. The symptom is in many ways similar to PMS (premenstrual syndrome).
- Depression often accompanies other unpleasant sensations. Experiencing hot flashes, increased sweating, insomnia, headaches and sudden mood swings, a woman often becomes depressed and sad.
- A lump in the throat that you can neither swallow nor spit out. This sensation is not accompanied by pain, only slight discomfort, and often goes away on its own and quickly.
- Absent-mindedness, forgetfulness - the influence of hormonal levels.
- Frequent desire to go “small”.
- Dryness and itching in the vagina (the effect of hormonal changes in women over 50 years old).
Insomnia leads to constant fatigue
Causes of perimenopause
Perimenopause is a natural process characterized by a decrease in hormone levels that comes with age.
These hormonal changes can be explained by the following types of reasons. Internal reasons. Hormone fluctuations manifest in the signs and symptoms of perimenopause. We are talking about natural fluctuations in hormone levels that occur as the body matures and ultimately lead to the cessation of menstrual cycles. External reasons. While women experience an internal process of hormonal changes, these changes can be accelerated by external factors. These factors include bad habits such as smoking, as well as extreme stress, hysterectomy, chemotherapy and radiation exposure.
Treatment of symptoms and medications
The treatment regimen for uterine bleeding after menopause is prescribed by a doctor based on the reasons that caused it. If these are extragenital pathologies, the underlying disease is subject to treatment. For dysfunctions of the genitourinary and reproductive systems, a course of drug therapy is prescribed, but in some cases urgent and surgical interventions may be necessary.
If there is sudden heavy bleeding, emergency treatment may be needed. She usually ends up in an inpatient setting.
- If the doctor suspects an intrauterine pathology, he performs an emergency hysteroscopy. If polyps and other growths are found in the endometrial cavity, they are resected.
- If the cause of bleeding is hyperplasia, an endoscopic operation to curettage the uterus is performed.
- If a clinical gynecological examination reveals the absence of organic causes, hemostatic therapy is used.
This is followed by further examination of the body in a stationary mode.
Subsequent treatment directly depends on the abnormality that caused the bleeding. In medical practice, hormone replacement therapy is most often used to restore the balance of progesterone and estrogen. If any neoplasms or tumors occur, they are often eliminated through surgery.
If there are concomitant diseases of the thyroid gland and internal organs, the patient is prescribed a course of drug therapy and a special diet (especially for hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism). Often, the doctor prescribes corrective therapy with multivitamin complexes. Oncological diseases are cured by surgical resection of the tumor; if necessary, treatment continues with chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
When experiencing uterine bleeding during menopause, a woman needs to understand that this symptom is extremely specific, and in some cases only it can signal the presence of oncology. Therefore, timely seeking qualified help in this case is simply necessary.
The period of menopause is a complete restructuring of the body due to its hormonal instability. Many women say that menopause is very difficult to endure, almost impossible, that this period is filled with nervous breakdowns, worries and poor health. However, statistics stubbornly prove the opposite.
When you haven’t had your period for exactly a year or more, you can say that menopause has arrived.
Uterine bleeding can be divided according to the principle of its occurrence:
- Diseases of the female reproductive system. If menstruation began more than six months after its expected end, then this indicates an inflammatory process in the organs of the reproductive system: the uterus, ovaries, vagina, fallopian tubes, cervix, etc.
- There are such bleedings, the occurrence of which is to blame for hormones, or rather disruptions in hormonal balance. The lack of female sex hormones causes atrophic processes in the organs of the reproductive system. This causes bleeding, but they cannot be confused with menstruation, because they differ significantly in consistency, quantity, and color.
- Some bleeding may occur as a side effect of certain hormone-based medications.
- Uterine bleeding can be caused by hormone therapy, which was originally used to relieve the symptoms of menopause in cases where a woman has complications with menopause. By the way, this type of bleeding is not at all as scary as it might seem at first. It also has a right to exist during menopause. This suggests that the cycle has been restored and will appear as regularly as during reproductive age. This type of discharge will be somewhat different from menstruation in the usual sense. There will be little discharge, there will be no clots. A woman will experience this condition every month for 3-4 days, and usually it goes away easily, without any noticeable complications.
- Bleeding may be caused by disturbances not only in the functioning of the reproductive system, but also in the internal organs. Such disorders include cirrhosis of the liver, pathologies in the thyroid gland and some other conditions.
In addition, you need to find the reason that provokes these bleedings. To do this, you need to undergo diagnostic procedures.
In addition to the basic medications to maintain a woman’s health, the following medications are prescribed, which must be taken over a long period of time:
- Amymocaproic acid.
- Drugs that reduce the permeability of vascular walls.
- Drugs that affect prothrombin synthesis.
- Calcium gluconate, which serves to strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
- Mix mistletoe, shepherd's purse grass, yarrow, crooked bread root, viburnum root, horsetail root, meadowsweet flowers, dried nettle. Brew with boiling water, let it brew and take half a glass half an hour before meals three times a day.
- Mix silver cinquefoil, bergenia root, snake knotweed, arnica, hawthorn fruit, sandy immortelle, rose hips. Pour boiling water over and cool. Drink instead of tea for a month.
- Mix plantain, shepherd's purse, geranium herb, bird cherry fruits, blueberry leaves. Pour boiling water and drink half a glass three times a day, regardless of meals.
Changes in the physical condition of a woman during premenopause are quite large. But if you begin to be embarrassed by heavy or too long periods, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Some dosage forms come to the rescue in preventing undesirable consequences:
- hormonal pills (oral contraceptives);
- phytohormones, if hormonal drugs are contraindicated for a woman;
- intravaginal products with estrogens;
- hemostatic agents: prescribed only because of long and heavy periods;
- herbal preparations;
- vitamins for women.
Remember! Never self-medicate, otherwise you may cause irreparable harm to your health.
If you carefully monitor how changes in discharge manifest themselves during premenopause, then entering menopause will be subtle and successful.
Treatment is aimed at reducing the severity of unpleasant symptoms of the onset of menopause and preventing possible potential risks. The use of hormonal agents is pathogenetically justified, but in mild cases nonspecific treatment without drugs is possible.
Non-drug methods
With mild severity of menopausal syndrome, a woman is recommended to follow a daily routine. For proper rest, 7-8 hours of sleep is necessary. To increase tone, physical activity and general strengthening activities are important. Some people find that wiping with cold water, hardening procedures, and contrast showers help.
Nutrition correction is required. If you are prone to high blood pressure, limit your salt intake. It is recommended to reduce the amount of animal fats; preference is given to plant foods, cereals, and fermented milk products. Sweets, fatty foods, and starchy foods lead to excess weight gain and worsening premenopausal symptoms and metabolic disorders. Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol is mandatory. For mild depressive disorders during premenopause, individual or group psychotherapy helps; the support of loved ones, relatives, and spouse is important.
Conservative therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is prescribed for moderate and severe premenopause; it is started at any age when the first signs of pathology appear. The drugs are selected individually in the absence of contraindications such as a tendency to thrombosis or diseases of the cardiovascular system. Hormonal drugs are prohibited if there is a suspicion of malignant tumors of the mammary glands or reproductive organs, uterine bleeding of unknown origin, or acute liver pathologies. The following groups of drugs are used for HRT:
- Combined estrogen-progestogen agents. In young women, monophasic or triphasic oral contraceptives are used, and after 50 years, drugs based on natural estrogens with the inclusion of a gestagen component are used. Premenopausal women are prescribed estradiol valerate in combination with cyproterone acetate, levonorgestrel, nogestrel, medroxyprogesterone.
- Gestagens. Recommended for women with uterine fibroids, endometriosis and other contraindications to estrogen. Dydrogesterone and micronized progesterone preparations can be used orally cyclically from days 5 to 25 of the cycle. An intrauterine system with levonogrestrel, which is installed once every 5 years, is effective.
- Pure estrogens. They are used when the uterus has been removed, since there is no risk of developing proliferative processes that can develop into endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. Estradiol tablets, a hormonal patch or gel are used for application to the skin.
- Phytohormones. In case of absolute contraindications to HRT or a woman’s refusal, ready-made extracts of the plants of Circimfuga, Melbrosia, Raponticin, which contain phytoestrogens, are used. These include isoflavonoids, lignans, and coumestans. They have an estrogen-like effect, but this occurs with long-term use.
First signs of menopause
For most women, by the age of 40-45, the so-called period of menopausal transition begins. It is not included in the concept of premenopause and is manifested by mild and nonspecific symptoms.
In fact, this period is a preparatory period, allowing the body to more easily endure the onset of menopause.
Most often, women are concerned about menstrual irregularities, manifested by irregular menstruation. May also be noted:
- scanty menstruation;
- delayed menstruation;
- change in the cycle towards increasing the time between menstruation.
Methods for determining the beginning of menopause
For the initial establishment and subsequent confirmation of the diagnosis of menopause, a full comprehensive diagnosis of the woman is required, carried out by specialized specialists - an endocrinologist, mammologist and gynecologist.
Main events:
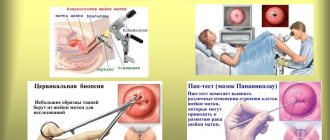
- Preliminary assessment of the symptoms of the syndrome using the Kupperman indices;
- Papanicolaou smear - cervical cytology;
- Blood chemistry;
- Coagulogram;
- Determination of blood lipid spectrum;
- Ultrasound of all pelvic organs;
- Osteodensitometry;
- Mammography;
- Regular measurement of pulse and blood pressure.
Determining the levels of FSH, LH and estradiol in the blood makes it possible to confirm the primary diagnosis with almost 100 percent probability and prescribe maintenance therapy if necessary.
- Analysis for follicle-stimulating hormone. It is used to diagnose the causes of infertility, one of which is menopause. During menopause, the level of FSH in the blood increases significantly;
- Blood test for estradiol. Determination of this steroid hormone produced in the ovaries allows us to instrumentally determine the stability of the menstrual cycle and detect possible causes of its disruption;
- Blood test for luteinizing hormone. This element stimulates the production of estrogen and is a “litmus test” for the stability of the ovaries. During menopause, its concentration is increased, and the direct ratio with FSH reaches 2 (follicle-stimulating hormone is twice as much as luteinizing hormone).
What to do with symptoms of perimenopause
The most important things you need to know about premenopause, symptoms and treatment. Signs will help you understand that a new life period is approaching. And therapy can make it more acceptable.
You cannot be a hero and tolerate manifestations of the decline of ovarian function, especially if it occurs abruptly. This happens in 10% of women and causes severe menopause. But a smoother transition from one hormonal state to another does not occur completely unnoticed.
Therefore, premenopausal treatment can be very different for different women. And you shouldn’t choose it based on the experience of your friends yourself.
Hormones
If the premenopausal period is severe, treatment with hormonal drugs is prescribed. Experts consider it important to stabilize the cycle before the complete extinction of ovarian function, since it is during long delays that all its symptoms become intensely manifest. Premenopausal hormones are presented in the following types and treatment regimens:
- Progestogens. These include Norkolut, Pregnin, Turinal. The drugs lead to a more stable cycle, since the main active ingredient stimulates the onset of its second phase, that is, the rejection of the basal layer of the endometrium. After menstruation, the amount of discharge in which will decrease, the symptoms of premenopause practically do not bother you. Such treatment is indicated for 2-3 months. There is the possibility of a longer-term effect of progesterone on the body if it is necessary to reduce menstrual bleeding - Mirena IUD;
- Combined. Products containing estrogens and gestagens balance the balance of both substances. Such drugs are also necessary to prevent pregnancy. After all, at this stage it is still possible, but for most women it is undesirable. Therefore, they are prescribed hormones containing small doses of Marvelon, Janine, and Silest. If the main goal is to stabilize the general condition, relieving severe symptoms of premenopause, then Klimen, Divina, Klimonorm, Cyclo-Proginova are better suited. They are drunk in cycles, in between which menstrual-like bleeding occurs.
If in premenopause the main undesirable manifestations occur in the intimate area, that is, they concern the condition of the mucous membranes and urination, it is advisable to use local hormonal agents: creams and suppositories. Ovestin, Ovipol Clio, Estrocad, Estriol will help with this problem without affecting other tissues and organs.
Homeopathy and herbal remedies
Premenopausal preparations of herbal and homeopathic origin make it possible to use in many cases. Synthetic hormones have contraindications, and you should not use them right away if there are safer means to reduce the impact of menopause.
You can even out the balance of substances, make premenopause less uncomfortable for the body, and smooth out its manifestations with the help of medications:
- Klimadinon;
- Remens;
- Klimaktoplan;
- Klimakt-Hel;
- Estrovel.
They contain plant hormones from soybeans, red clover, cohosh, and some of them contain immunity-stimulating snake and bee venoms.
Herbal medicines and homeopathic remedies are easier to tolerate by the body, do not provoke cardiovascular problems and tumors, and are acceptable even if a woman already has similar diagnoses. True, the effect from them is not as fast and pronounced as from treatment with hormones.
We recommend reading the article about taking Remens during menopause. You will learn about the effect of a homeopathic medicine on a woman’s body and its benefits during menopause, instructions for use.
Discharge during menopause, what is possible
During menopause, a variety of discharges are possible:
- At the premenopausal stage, spotting is observed, as during menstruation. After the complete cessation of ovarian function, you may notice a mucous, transparent discharge of uniform consistency.
- Unnatural is discharge that has an unpleasant odor, uneven consistency, dark or yellow color, not transparent or watery.
If a woman sees unnatural discharge, she should immediately consult a doctor. Since these can be diseases that threaten a woman’s life.
Premenopause, perimenopause and menopause
To give a clear definition, you need to remember that menopause is divided into 3 stages:
- premenopause, in which changes in the body are just beginning, the main symptoms appear gradually, are mild, conception is still possible;
- menopause, characterized by the cessation of menstruation, increased hormonal chaos, large-scale restructuring of body systems, exacerbation of menopausal syndrome;
- postmenopause, which lasts until the end of life, during which physiological changes in the reproductive system end, its reduction, transformation, and degeneration of tissue into connective tissue occur.
Perimenopause captures a period of active changes, this is premenopause and part of menopause, lasting for 2 years after the last menstruation.
Is pregnancy possible?
Pregnancy during premenopause is possible. This is typical for the initial stages, when the female system is practically normal and is capable of producing offspring. However, despite this, there are some limitations, which we will talk about now.
During premenopause, a woman's body weakens slightly due to a lack of hormones that are so necessary during pregnancy. Because of this, it can be more difficult, and this in turn indicates a threat to the mother. The child absorbs many maternal substances, which she does not have in sufficient quantities. Therefore, it is possible to get pregnant, but it is not advisable. Also, if there has been no menstruation for more than a year, the probability of getting pregnant is 0.
Premenopause is a rather important and difficult period in the life of every woman. It is important to notice changes in your body in time and seek help from specialists. After all, with the right treatment tactics you can achieve good results.
Vitamins for menopause
During menopause, a woman needs to consume the following vitamins in sufficient quantities:
- Retinol. An antioxidant that prevents the development of tumors and slows down the aging of the epithelium;
- Vitamin E. Stimulates the activity of the ovaries, prolonging their work, participates in the formation of female hormones;
- Ascorbic acid. Prevention of complications after menopause;
- Vitamin B1 and B6. Regulate the functioning of the nervous system, ensuring its normal functioning against the background of hormonal changes;
- Vitamin D. A catalyst for calcium absorption, which helps fight osteoporosis, a common concomitant complication of menopause.
In addition to vitamins, a woman’s body during menopause requires increased doses of microelements - magnesium, calcium and zinc.
Menopause treatment
The mainstay of treatment for menopausal symptoms is hormone replacement or maintenance therapy. Treatment should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Self-medication is strictly prohibited and can cause irreparable harm to a woman’s health.
Indications for hormonal therapy are:
- severe menopausal disorders (hot flashes, arterial hypertension, insomnia, heart rhythm disturbances);
- development of atrophic changes in the mucous membrane of the genitourinary organs;
- prolapse or prolapse of the uterus;
- urinary incontinence;
- the need to prevent osteoporosis, arthrosis, and fractures.
In addition to hormonal therapy, courses of sedatives, antioxidants, and special vitamin complexes are indicated.
Features of pathological menopause
Menopause can be natural or artificial. In medicine, these types of ovarian function decline are defined as physiological and pathological. The latter is due to the following factors.
- Surgical intervention. This involves removing the ovaries separately or together with the uterus. In the case when only the appendages or only the uterus are removed, menopause does not occur immediately, but earlier than the natural period. If two ovaries are cut out at once, the decline of reproductive function occurs within a few days.
- Medicinal effects. Taking potent drugs for infertility and endometriosis temporarily inhibits ovarian function. Hormone deficiency helps reduce the manifestations of diseases. This treatment restores the chances of getting pregnant and having a favorable perinatal period.
- Radiation exposure. Menopause occurs due to excessive radiation exposure, often after radiation therapy.
Also, the concept of premenopause is used to characterize severe menopause syndrome; you can read about this by visiting the premenopause forum. This period is accompanied by pronounced symptoms, exacerbation of chronic diseases and the development of new ones that affect the target organs of menopause.