Author: Volkova A.A., endocrinologist, practical experience since 2015. May, 2020.
Synonyms: rare periods, a variant of hypomenstrual syndrome.
ICD-10 code: N91.4
Secondary oligomenorrhea is an increase in the interval between menstrual bleeding, often in combination with a shortening of the bleeding period itself. It develops after the establishment of a normal menstrual cycle. Occurs on average in 2.5-3% of women. In addition to menstrual irregularities, it can be characterized by obesity, the development of male pattern hair, and mood instability. It is treated both medically (COC) and surgically, depending on the cause.
Classification
Secondary oligomenorrhea differs from primary in that the secondary form occurs against the background of an established cycle, and the primary form is observed in girls with a not yet established cycle.
There are different forms of secondary oligomenorrhea:
- shortened menstruation (duration of bleeding from several hours to 1-2 days);
- extended interval between menstruation (from 40 days to six months)
- mixed variant, in which shortened bleeding is combined with a large gap between them (most common).
Additionally, secondary oligomenorrhea is divided into physiological and pathological.
Important! Physiological oligomenorrhea can be considered during lactation, at the onset of menopause. In all other cases, the symptom is pathological.
Types of oligomenorrhea
Oligomenorrhea is divided into primary and secondary forms, each of them is characterized by certain causes and time of development. Deviations of this nature also include opsomenorea and hypomenorrhea.
Primary oligomenorrhea
Typically, primary oligomenorrhea can appear during the first menstrual cycle (menarche), indicating the readiness of a woman’s body to perform reproductive functions. But pregnancy at such an early age is unlikely, since puberty continues.
It is important to ensure that the onset of the first menstruation occurs on time. If menarche does not occur for a long time, you should consult a gynecologist. Timely intervention in the development of the reproductive and reproductive system will make it possible to eliminate problems associated with its functioning. If oligomenorrhea develops, it will be more difficult to bring everything back to normal.
Secondary oligomenorrhea
If we consider secondary oligomenorrhea, this process occurs when the menstrual cycle is established. The condition of this form is observed less frequently in female representatives. Such deviations occur in 3% of girls and women.
Typically, oligomenorrhea is acquired and develops against the background of inflammation in the organs of the reproductive system, hormonal imbalances, physical exhaustion and excessive stress on the nervous system. In addition, secondary oligomenorrhea can occur after an abortion.
https://youtu.be/rrKSFY5Bxag
Causes and risk factors
Secondary oligomenorrhea in most cases develops as a result of exposure to various negative factors on the female body. The most common reasons are:
- acute and chronic infectious processes affecting the uterus and ovaries (gonorrhea, chlamydia, candidiasis, ureaplasmosis, genital herpes);
- diseases of the reproductive system of an inflammatory or traumatic nature (salpingitis, endometritis, oophoritis, myometritis);
- various stressful effects, nervous shock, the presence of certain mental disorders (bulimia, anorexia);
- the influence of negative environmental factors (living in an environmentally unfavorable area, working in hazardous industries, etc.);
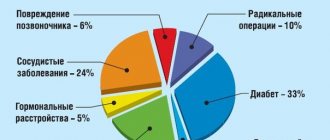
- decompensated (untreated) diseases of the pancreas, adrenal glands, thyroid gland (diabetes mellitus, adrenal insufficiency, hypo- and hyperthyroidism, etc.);
- surgical interventions on the uterus and ovaries, including abortions;
- disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, due to which the hormonal regulation of the body generally suffers;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels (with diseases of the cardiovascular system, the blood supply to the genital organs may be disrupted, which leads to a disorder in their functioning, and the body as a whole is weakened).
Doctors also identify risk factors that increase the risk of developing oligomenorrhea, but do not lead to it in 100% of cases. Among these factors:
- unfavorable environmental influences;
- regular stress;
- habit of eating poorly, going on irrational diets;
- taking hormonal medications without a doctor’s recommendation or neglecting the doctor’s recommendations;
- lack of vitamins;
- being overweight;
- sudden climate changes.
Professional female athletes are also at risk, as they constantly experience not only severe stress, but also have to cope with high physical activity.
Symptoms
The main symptom indicating the progression of the pathology is rare and short menstruation. It is also worth noting the fact that often women who have a history of this disease also experience infertility. Only ¼ of women experience physiological ovulation and can become pregnant.
Additional symptoms of oligomenorrhea:
- the appearance of acne on the back, chest and face;
- with oligomenorrhea, it can disrupt fat metabolism, so women with this disease often begin to gain weight;
- hirsutism;
- masculine physique and developed muscles;
- decreased libido.
Symptoms
The main symptom of secondary oligomenorrhea is short periods or a long interval between menstrual bleeding. A significant number of women ignore this symptom for a long time, not realizing that this is not a normal option, but a pathology. After all, the rarity or short duration of menstrual bleeding indicates that the uterine endometrium is renewed slowly and does not grow intensively enough. Such a change in the organ threatens infertility. Often a woman thinks about the need to visit a doctor for oligomenorrhea only after unsuccessful attempts to become pregnant and carry a child to term.
In addition to problems with pregnancy, the following symptoms may occur due to hormonal imbalance:
- disturbances in fat metabolism develop, which leads to the development of obesity;
- when there is an excess of testosterone in the female body, the figure changes to a male type (broad shoulders, narrow hips);
- acne appears on the skin, acne develops;
- hirsurtism develops (hair on the face, neck, back, abdomen according to the male type of hair growth), observed in 20% of patients;
- Libido decreases, sexual desire becomes less pronounced;
- There are sudden mood swings, increased nervousness and irritability.
In case of secondary oligomenorrhea, the symptoms may not cause significant discomfort to the woman for a long time, which is why she postpones seeing a doctor.
Signs and symptoms
The main symptom of oligomenorrhea is an increase in the intervals between menstruation. In adolescents, this condition may not present any additional symptoms, but in adult women, some symptoms are observed, the main one being hirsutism, accompanied by excess hair on the face and body.
Acne
In such cases, hair growth is observed in the places where it usually grows in men. Hair is present not only on the inner thighs, but also on those parts of the body where it usually does not grow in women - on the stomach, chest. The development of oligomenorrhea is usually caused by changes in the production of sex hormones. Among other signs of hirsutism, which was provoked by oligomenorrhea, there are the following changes:
- the menstrual cycle is disrupted;
- acne;
- extra pounds of weight;
- difficulties associated with conception;
- decreased libido;
- change in physique.
Changes in physique that oligomenorrhea causes forces female representatives to begin treatment as quickly as possible.
A normal mental state is the basis for the proper functioning of the reproductive system. Less than 29% of women experience oligomenorrhea in the absence of disorders in the nervous system. Patients do not deny that having reached the understanding that oligomenorrhea has developed, their quality of life changes, which is manifested by the following factors:
- deterioration of health;
- disturbance of peace of mind;
- lack of proper rest;
- changes in sexual activity;
- lack of material well-being.
Oligomenorrhea can have an extremely negative impact on a woman’s life, so diagnosis and treatment must be taken seriously.
Diagnosis of secondary oligomenorrhea
Secondary oligomenorrhea is diagnosed based on a combination of medical history, symptoms, results of laboratory and instrumental studies. During a conversation with the patient, the doctor clarifies when the first menstruation (menarche) occurred, how quickly the menstrual cycle became regular, whether the woman suffers from symptoms of premenstrual syndrome, whether she has a history of diseases of the reproductive organs or abortions. An examination in a gynecological chair is required.
From the studies applied:
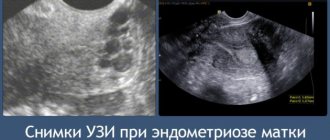
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (can be performed both transabdominally and transvaginally, the second option is preferable due to its greater information content) - pay attention to the size of the uterus and its appendages, their shape, structure;
- analysis of sex hormones - assess the level of progesterone, prolactin, estradiol, LH, FSH (an LH level of more than 15 mU/l should alert you outside the peak of ovulation, on days 1-14 of the cycle, as well as at the beginning of menstruation);
- hysterosalpingography is a method that allows you to assess the patency of the fallopian tubes;
- a group of tests to detect sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, etc.).
If a tumor of the pituitary gland is suspected, a woman may be recommended to have an MRI of the brain. If a disease of the adrenal glands is suspected, a urine test for 17-ketosteroids is taken, and if a pathology of the thyroid gland is suspected, a blood test is taken for thyroid hormones.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of a disease that causes menstrual irregularities is established on the basis of complaints and anamnesis, general objective and gynecological examinations, as well as an assessment of the state of the psycho-emotional sphere and neurological condition.
Additional methods for diagnosing oligomenorrhea include determining basal temperature with plotting a graph, ultrasound and MRI examination of the pelvis using a vaginal sensor, and magnetic resonance imaging of the skull. In addition, laboratory studies of the content of pituitary hormones (prolactin, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones) and sex hormones (progesterone, estradiol, testosterone), as well as glucose and cholesterol in the blood serum are carried out, the content of 17-ketosteroids in the urine is determined (to assess adrenal function) .
Treatment
Treatment of secondary oligomenorrhea should be comprehensive and selected depending on the cause of the disease. Therapy is jointly selected by a gynecologist and an endocrinologist. Treatment is possible with conservative and surgical methods.
Conservative therapy
Based mainly on the use of hormonal drugs. The purpose of the medications is to normalize the ratio of hormones and start the ovulation process. For this purpose, progesterone preparations (Duphaston, Inzhesta, Utrozhestan, etc.) or combined oral contraceptives are prescribed. They are suitable for women who do not plan to become pregnant or give birth in the near future. Progesterone preparations are taken in a course of 10-12 days a month until menstruation returns to normal. Combined oral contraceptives are taken according to standard regimens selected by doctors.
If a woman wants to get pregnant, she undergoes drug stimulation of ovulation under the supervision of a doctor.
In addition to drug treatment, it is necessary to eat well and rest, give up bad habits, and monitor your weight.
If it is determined that the cause of oligomenorrhea is an infectious disease, an antiviral, antifungal or antibacterial drug is selected with the help of a doctor, depending on the specific causative agent of the disease. In addition to the treatment of infection, drugs that stimulate the immune system, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physiotherapeutic procedures are used.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment of secondary oligomenorrhea is indicated for women in whom drug therapy does not produce results.
The operation is performed for polycystic ovary syndrome. Today, doctors mainly perform sectoral resection of the ovary with cauterization, removing the part on which the largest number of cysts are found. The operation is performed laparoscopically. The recovery period takes 4-6 weeks.
Treatment of NMC
Treatment of NMC directly depends on research results.
- Hormonal therapy. It is often used to eliminate NMCs caused by a lack of a particular hormone. Treatment is carried out with drugs based on hormones produced by the ovaries or thyroid gland - it all depends on the test results. For therapeutic purposes, oral hormonal contraceptives can be prescribed. This is especially true when treating an unstable menstrual cycle.
- Painkillers and antispasmodics. This group of drugs is prescribed for painful periods.
- Hemostatic agents and uterotonics. This treatment is carried out when bleeding is too heavy during menstruation. They are also prescribed for poor blood clotting. Aminocaproic acid contained in the preparations helps stop bleeding.
- Homeopathy and physiotherapy. Treatment often comes down to taking medications based on herbs and natural ingredients. The courses are complemented by a complex of physiotherapy procedures.
- Phytotherapy. To improve hormonal levels, eliminate pain during menstruation, and heavy bleeding, the attending physician can formulate a herbal-based treatment. Teas, infusions, douching based on tansy, shepherd's purse, elecampane, prutnyak, valerian will help eliminate many problems.
- Surgical intervention. Such treatment is highly undesirable for girls, but in the presence of neoplasms and pathologies of various origins, surgical intervention by a doctor is required. In case of serious diseases of the female organs, their partial removal may be required. To carry out these procedures, the patient goes to the gynecology department and is under close medical supervision before and after the operation.
- A course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. A antenatal clinic specialist prescribes this treatment when various types of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system are detected. The complex in each case is selected according to the situation.
Comprehensive preventive measures will prevent some gynecological diseases. For this there are the following rules:
Use only high-quality and proper products for food; vegetables and fruits are very healthy
They provide the body with a rich set of microelements, fiber and vitamins. It is important to avoid stressful situations and react to emerging situations without unnecessary emotions. Physical activity is important in every woman's life. A set of special exercises will prevent a number of gynecological problems
But you should understand that the load must be adequate, not exhaust the body, but train and harden. Excessive strength training can lead to an increase in the level of testosterone, the male hormone, which will inevitably affect menstruation. Excess weight means extra problems. Obesity often leads to hormonal imbalances, which should not be allowed. Under no circumstances should you use strict diets, especially during adolescence. The body loses vitality, which negatively affects the menstrual cycle. You should visit a gynecologist regularly. Even if a woman has no complaints and feels great, she should visit a doctor at least once every six months. There are a number of problems that do not cause any discomfort at the initial stage of development. But if a woman often experiences various types of NMCs, this should be done much more often.
You may be interested in: What is anovulation? Female infertility.
>What does luteal phase deficiency mean? Symptoms, causes and treatment
Complications, prognosis and prevention
The main complication of secondary oligomenorrhea, which is most feared, is infertility. According to statistics, in approximately 40% of cases a woman is not able to conceive or bear a child precisely because of the presence of secondary type oligomenorrhea. Also, hormonal imbalance in general negatively affects the body, increasing the likelihood of developing cancer of the reproductive system.
With timely initiation of treatment, the prognosis for secondary oligomenorrhea is favorable. A significant number of women, under the supervision of a doctor, manage to normalize hormone levels and regulate the menstrual cycle.
Prevention of the secondary form of oligomenorrhea is based on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, timely treatment of identified diseases, and regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
Primary oligomenorrhea: what is it?
Primary oligomenorrhea is a decrease in the duration of menstrual bleeding; it can occur from the moment of the first bloody discharge from the genital tract.
Menarche in girls is the first discharge from the uterus, which signals the beginning of the hormonal function of the reproductive system. Since only the formation of hormonal regulation in the girl’s body is still occurring, not only short menstruation can be observed, but also a decrease in the volume of menstrual flow, a shortening of the ovarian-menstrual cycle, as well as an increase in the interval between menstruation. If no pathological conditions are identified, then this is the picture is a variant of the norm. However, primary oligomenorrhea may indicate pathological conditions of the girl’s reproductive system. This clinical picture can be caused by congenital malformations of the uterus, infantilism (children's uterus), pathological processes of the brain responsible for the regulation of the cycle, as well as ovarian pathology, which does not allow them to be produced in the required volume.
Reasons for appearance
Secondary oligomenorrhea is a condition that always acts as a complication of some other disease or factor. It never develops independently, like the primary form, which is sometimes diagnosed in patients with a non-normal menstrual cycle.
The main reasons for the violation are the following:
- Hormonal disorders due to neurological or mental pathologies.
- Frequent diagnostic curettage of the uterus or artificial termination of pregnancy.
- Tendency to commit such violations.
- Ovarian cyst or polycystic disease affecting two ovaries at once.
- Hypoplasia of the uterus, in which the inner layer grows poorly as a result of various factors.
- Diagnosis of endometritis or endometriosis.
- Endocrine pathologies with disorders of the thyroid or pancreas, as well as the adrenal glands.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions, exposure to toxic substances on the body on an ongoing basis.
- Reducing the amount of vitamins and mineral components in the body, identifying chronic vitamin deficiency.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Obesity or anorexia, bulimia.
- Physical exhaustion of the body.
- Nervous tension, stress, severe mental disorders.
- Pathologies of the pituitary gland.
- Climate change.
- Incorrect uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs.
- Injuries of the pelvic organs.
- Infectious pathologies of the genital organs.
In addition, the cause may be constant heavy physical activity and emotional fatigue. Experts note that women who play sports professionally and have a minimal amount of subcutaneous fat are at risk.
This is due to the fact that sex hormones are deposited in large quantities in adipose tissue. If its quantity is insufficient, various disorders develop.
Does this disease need to be treated? How to choose the correct correction method?
You became aware of the symptoms that oligomenorrhea has. What it is is described above. It is worth saying that the problem cannot be left to chance. As you already know, in some cases it can lead to the development of cancer. The manifestation of unpleasant symptoms also unsettles any representative of the fairer sex from their usual rut.
Oligomenorrhea can be treated with medication and surgery. It all depends on the causes of the disease. That is why it is so important if the situations described above develop, consult a doctor and undergo the prescribed examination. Based on your complaints and additional data, the doctor will be able to make the correct diagnosis and correctly prescribe correction. Let's look at the main causes of oligomenorrhea and ways to eliminate them.
Treatment methods
Medicines, physiotherapy methods and some folk remedies are used to treat patients. In each case, the scheme may differ depending on the degree of neglect of the condition.
Medications
Secondary oligomenorrhea is a condition that, at the initial and progressive stages, can be quite successfully treated with medications. The treatment regimen always involves alternating progesterone drugs with contraceptives, but sometimes also includes medications from other groups.
The most effective means:
- Clomid is a drug that is used to restore the normal ovulation process in the body. The product helps to quickly restore reproductive function and eliminates the manifestations that accompany this disorder, and is considered very effective. The tablets are taken orally, 1 piece for 5 days, starting from the fifth day of the cycle. After this, a break is taken until the next menstruation and, if necessary, a repeat course is prescribed. No dosage increase is required. It is worth remembering that the remedy is not used for oligomenorrhea caused by a pituitary tumor. Price – from 750 rub.
- Clomiphene is a drug that comes in tablet form, is effective and helps normalize the maturation of the egg in the ovary. Prescribed according to the scheme, take 1 tablet for 5 days in a row, starting from the 5th day of the menstrual cycle. The crus can be repeated up to 3 times in a row if there is no effect. Price – from 600 rub.
- Utrozhestan is an effective progesterone-based drug that is used for 3-6 weeks to normalize hormonal levels. The patient takes the drug 1-2 capsules per day. If necessary, the course is repeated after a 2-3 month break. Usually the medicine is used in cases where the disorder was caused by polycystic disease. Price – from 500 rub.
- Novinet is an effective birth control pill, which is usually alternated with progesterone drugs to restore the menstrual cycle. Take the drug from the first day of the cycle, 1 tablet at the same time for 3 weeks. After this, a break is taken for 1 week and the course is repeated. Possibly up to 3-4 repetitions. The price of the product is from 400 rubles.
- Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is used when menstruation is accompanied by severe pain, cramping, or inflammation. The patient takes 2 tablets of the drug per day, treatment lasts 5 days. Usually the drug is prescribed in the acute period, it is effective and quickly eliminates the symptoms of the disorder. Price – from 70 rub.
In each case, the doctor determines the advisability of using a particular medication. Sometimes using one remedy is enough, in some cases it is necessary to take several medications.
Traditional methods
The pathology cannot be cured with folk remedies, but many women believe that some medicinal plants have therapeutic properties.
A decoction based on cherry leaves has a positive effect on the organs of the reproductive system. It should be prepared from 10 g of crushed leaves and 300 ml of water, cook for 4-5 minutes. After this, leave for 2 hours to infuse. Take the finished filtered product in small portions throughout the day. The course of treatment lasts 10-14 days.
Drinking aloe juice is considered a good way to improve your general condition and eliminate inflammation in the body. It is recommended to take 10 ml of juice daily, morning and evening, squeezed from the leaves of a plant that is at least 3 years old. Repeat treatment for 2 weeks. It is worth remembering that the juice is squeezed out immediately before consumption.
Oatmeal decoction is a general strengthening remedy for women of any age. For 1 liter of water you should take 2 tbsp. l. oatmeal, cook until tender. After this, filter the composition, separating the finished flakes, and consume the broth 150 ml 2 times a day. Treatment lasts up to 2 weeks. This method is not suitable for patients who suffer from acute intestinal diseases.
It is important to remember that folk recipes cannot be the only method of therapy, since they do not help normalize hormonal levels and do not treat concomitant pathologies. Their use must be agreed with a doctor.
Other methods
Secondary oligomenorrhea is a disorder for which auxiliary treatment methods can be used. After eliminating acute symptoms, it is allowed to use physiotherapy methods that affect the patient’s nervous system and improve the general condition, which has a beneficial effect on the reproductive system.
Ultrasound therapy is used in cases where oligomenorrhea is the result of pathologies of the reproductive system. The pelvic organs are exposed to ultrasound, which helps improve tissue nutrition and normalize blood circulation. After 10-15 sessions the patient feels improvement. They are carried out every 2-3 days and last 20-40 minutes.
Another additional treatment method is surgery, which is indicated in cases of advanced polycystic disease or progression of endometriosis and detection of multiple foci. The essence of the operation is to remove lesions using endoscopic instruments or open surgery. In this case, general anesthesia is used.
Secondary oligomenorrhea occurs against the background of other diseases
After the operation, the patient recovers in a hospital setting for 1-3 weeks, depending on the chosen method. At home, rehabilitation continues for 2-4 weeks after discharge. As a rule, rehabilitation involves taking antibacterial, hormonal and anti-inflammatory medications.