Today, herpes during pregnancy is a very hot topic due to more frequent infections and relapses. If you are wondering whether herpes is dangerous during pregnancy, yes, it is, but not always. Below we will talk about how herpes infection affects pregnancy, whether there can be a miscarriage if herpes was detected in the early stages of pregnancy, and what drugs are used in its treatment.
What can be dangerous about colds on the lips during pregnancy?
The relative harmlessness of labial herpes during pregnancy is explained by the tropism of the virus to nerve cells and only local spread in the body.
When you have a cold on the lips, viral particles actively multiply in skin cells and tissues that are not very deep underneath it. Those virions that infect the processes of nerve cells introduce their genetic material directly into their replication centers, located in the nerve ganglia far from the site of symptoms (usually this kind of “refuge” is the cells of the spinal cord, which, however, do not suffer seriously from this) .
The virus infects tissues only where its manifestations are visible. With a cold on the lips, it is the facial tissues and facial nerves that are affected, but viral particles do not penetrate into the abdominal cavity, and, especially, into the uterus with a developing embryo.
What is genital herpes and how is it transmitted?
Herpes virus type 2 (and it is this virus that most often causes genital herpes during pregnancy) can be found in the body of most people, almost every second person.
But clinical manifestations are observed in only a third of those infected. To understand the reason for this, you should follow the development cycle of the virus:
- Entering the body. It can happen in different ways, but it always comes down to the fact that the virus cells end up in the internal environment.
- Incubation period. The virus moves through the circulatory system through the body until it reaches its destination. In the case of genital herpes, these are nerve nodes, mainly related to the spinal cord.
By integrating into the cells of the nerve ganglia, the virus takes root in the body. The immune system most often cannot cope with it completely, but keeps it within limits, preventing it from multiplying and capturing key nodes. However, if for some reason the immunity drops, the virus begins to multiply uncontrollably and its waste products poison the body.
https://youtu.be/SkvWaYc5G5g
The more virus cells that get inside, the greater the chance of developing symptoms. Penetration can occur in one of four ways:
- Airborne. It is almost impossible to cause genital herpes in a pregnant woman in this way - the body must be too weak for the virus, which was drawn in with the air, to take root and reach intimate areas. However, there is still a small chance. And in this case, the source of the virus is a person with an exacerbation of herpes, coughing and sneezing.
- Sexual. The most obvious and common. It is easiest for them to catch herpes in the 1st trimester. The source is a carrier with an exacerbation of herpes; the virus passes from one organism to another through the mucous membranes during sexual contact.
- Domestic. Not very common, but possible option. The source of the virus is not only the carrier with an exacerbation, but also his intimate hygiene items. Transmission is possible by using one pair of underwear, a toothbrush, a washcloth, and also by kissing.
- Vertical. Herpes in the intimate area during pregnancy can also appear due to the fact that the woman has been infected since birth. In this case, the source is the infected mother, and the virus enters the child’s body either during childbirth or in the prenatal period.
It is not only vaginal sex that is dangerous, but also anal and oral sex. With an untested partner, it is better to have sex with a condom.
It is important to know the routes of transmission so as not to catch genital herpes during pregnancy. It is also important to know what can lead to an exacerbation if the virus is already in the body.
Treatment methods
A dermatologist has knowledge of how to treat herpes on the lips of pregnant women. The principles of therapy for expectant mothers are not much different from generally accepted methods. Only when prescribing medications does the specialist take into account the patient’s situation and select medications for her that do not include pregnancy among the contraindications.
Complex treatment of herpes blisters on the lips consists of three points:
- The use of antiviral ointments . You can’t take pills without your doctor’s knowledge, but you can use external remedies. Pregnant women carry out safe treatment of facial herpes with the help of drugs - Acyclovir, Virolex, Zovirax, Supraviran. Medicines treat the disease superficially, without penetrating into the internal tissues and bloodstream. Prevention of bacterial infection of herpetic rash is carried out using ointments - tetracycline, oxolinic or erythromycin.
- Folk remedies . Healing methods, together with pharmaceutical drugs, most effectively treat herpes on the lip of pregnant women. At the first symptoms, it is better to “nail” only with medication. From the 3rd day, when the blisters begin to open and become crusty, it is necessary to use gentle means to accelerate the regeneration of affected tissues.
- Diet + strengthening the immune system . An unbalanced diet, depleted of vitamins and microelements, inhibits the defense system and worsens the mother’s appearance, and also affects the baby’s health. For this reason, it is necessary to review the menu and enrich it with products with a high content of vitamins, amino acids, and protein components. To do this, a woman just needs to eat a lot of vegetables, fruits, sea fish and lean meat. On the advice of a gynecologist, you can take vitamin complexes for pregnant women. Lysine helps slow down the replication of the herpes virus. The amino acid is found in excess in chicken meat and fruits. It is better not to eat raisins and chocolate during an exacerbation of HSV. Their component arginine promotes the spread of infection.
If a pregnant woman experiences hyperthermia with herpes on her lip, she is prescribed antipyretic drugs Ibuprofen and Paracetamol.
Treatment
Based on the data obtained during diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. Treatment of herpes during pregnancy takes place in different ways, adjustments are made in accordance with the duration and type of disease.
- 1st trimester. If infected early in pregnancy, doctors recommend terminating the pregnancy, since the risk to the fetus is highest. If the disease relapses, topical ointments are prescribed. When using local drugs, the risk of the active substance entering the blood is minimized. The most effective and safe drug is Acyclovir ointment. Used for course treatment.
2nd and 3rd trimesters. Treatment of herpes in pregnant women is carried out using:
- antiherpetic ointments for topical use;
- medications to strengthen the immune system.
oral antiherpetic drugs;
When herpes in pregnant women is diagnosed in the second trimester, treatment is carried out and a natural birth is planned. 2 weeks before birth, rashes are prevented with the help of antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Famciclovir, Viferon).
When the genital herpes virus is detected in the last month of pregnancy, a caesarean section is recommended. This will help avoid infection of the newborn. If the membranes rupture before the planned operation, labor is carried out through the natural birth canal.
In addition to using medications, doctors may recommend increasing the proportion of foods containing lysine in the diet.
Lysine is an amino acid that inhibits the development of the virus during the reproduction stage. These products include chicken, fruits and vegetables. Limit chocolate and raisins. These products contain large amounts of arginine, which is activated by the virus.
Onset of the disease in the first trimester
According to statistics, colds on the lips most often appear in the first trimester. This is due to the phenomenon of the so-called natural immunosuppression of the mother’s body (suppression of immunity) - in order to avoid rejection of a fetus that is not genetically identical to her.
It is known that relapses of herpes most often occur precisely when the immune system is weakened. In a normal state of the immune system, protective cells constantly destroy viral particles produced by infected nerve cells, and the infection exists in the body in a state of a kind of dynamic equilibrium that does not manifest itself in any symptoms.
Early in pregnancy, the interaction between the invading cells of the embryo and the maternal cells of the uterine lining is critical for the further development of the fetus. The attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus and the formation of its membranes, on the one hand, must be stimulated, and, on the other hand, strictly controlled by the depth of penetration into the endometrium. In addition, the fetus itself, as a carrier of paternal genes foreign to the mother’s body, must be protected from the immune system of the mother’s body by an appropriate immunosuppressive barrier.
Thus, in the early stages of pregnancy, functional immunosuppression develops, providing control over gestation without immunological conflict. Weakened immunity at this time does not always have enough resources to control the virions emerging from the cells, which successfully move (“roll down”) along the axons of nerve cells to peripheral tissues and re-infect them in those areas where the primary infection once occurred.
According to statistics, of all cases of herpes developing on the lips in pregnant women, more than 72% of relapses occur in the 1st trimester. This confirms the theoretical basis of the entire process.
At the same time, reactivation of a herpetic infection even in the early stages of pregnancy is not dangerous: the virus cannot spread beyond the tissues in contact with infected nerve cells, and the likelihood of the infection spreading to the abdominal cavity or genitals is almost zero.
Danger to mother and child
If a woman has had a herpes infection before pregnancy, the risk to the fetus is minimal. The mother has antibodies that provide protection to the unborn child. The probability of infection is 5-7%. Primary infection of a pregnant woman is much more dangerous.
The consequences of fetal damage are determined by the trimester and the state of immunity . During gestation, he is in a depressed state to ensure the existence of an organism foreign to the mother.
HSV can affect the normal course of pregnancy and lead to the following complications:
- non-developing pregnancy;
- spontaneous interruption;
- premature birth;
- antenatal fetal death.
A non-developing, or frozen, pregnancy is a failed spontaneous miscarriage.
The embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus, but does not develop. For some time, the woman’s condition remains normal, then signs of intoxication and bleeding appear. According to the results of ultrasound, only the fetal membranes are determined in the uterine cavity. This condition is an indication for curettage. https://youtu.be/IV2pSmw_3OA
If the influence of herpesvirus on an interrupted pregnancy is established, then treatment is prescribed for at least 6 months.
Complications from the fetus due to intrauterine infection or neonatal herpes include the following pathologies:
- damage to the central nervous system, epilepsy;
- skin manifestations;
- long period of newborn jaundice;
- blindness and deafness;
- micro- or hydrocephalus;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- defects of various organs;
- hemorrhagic syndrome (internal and external bleeding).
Often developmental defects are incompatible with life. Children are born disabled or die soon. Primary infection in the mother leads to infection of the child in 50% of cases. Caesarean section reduces the risk of infection, but does not exclude perinatal transmission of the pathogen. For premature babies, the prognosis is the most unfavorable.
Complications
Complications of labial herpesvirus include expansion of the affected area beyond the nasolabial triangle, damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose. With primary infection during pregnancy, damage to the oral mucosa is possible, followed by the development of herpetic gingivostomatitis.
In addition, complications during pregnancy include frequent recurrent herpes, which appeared even before conception and recurs more than 10 times a year. Recurrent herpes negatively affects the quality of life of a pregnant woman, but is practically not dangerous for the unborn child.
Complications of labial herpesvirus include expansion of the affected area beyond the nasolabial triangle, damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose.
Prevention of herpes before and during pregnancy
Nobody wants to get sick, especially during a wonderful period in the life of every woman - carrying a baby. Therefore, in order to eliminate the possibility of herpes appearing during pregnancy or to avoid contracting the virus if you have never had it, the expectant mother should undergo a full examination before pregnancy, take all measures to strengthen the immune system, and also take preventive measures:
- Give up bad habits, engage in active sports and strengthen your body. Avoid hypothermia or overheating.
- If you are prone to recurrent herpes, when going outside, use sunscreen to protect your skin, as ultraviolet light activates the virus.
- Do not contact people with obvious signs of herpes skin lesions. It is especially dangerous to use shared household items, towels and bed linen. Always practice good personal hygiene. tree.
- Strengthen your immune system by including chicken, vegetables, and fruits in your diet. Avoid eating chocolate and raisins - they contain the amino acid arginine, which activates the virus. Drink more water, juices and drinks containing large amounts of vitamin C. Rosehip decoction, green tea with lemon, and freshly squeezed juices are useful.
- Avoid nervous tension and stressful situations; proper rest and sleep are also important.
Herpes during pregnancy should not be ignored and self-medicated. Consultation with a doctor is mandatory. The doctor will prescribe laboratory tests to clarify the type of herpes viral infection, and also identify its nature (primary herpes or relapse). In case of primary infection, in addition to blood tests, the gynecologist prescribes additional ultrasound examinations of the fetus to detect the presence of intrauterine herpetic infection. Timely treatment and prevention of viral infection during pregnancy will help avoid dangerous consequences and give birth to a healthy baby.
https://youtu.be/iklFcsfZSiI
Prevention
First of all, it is important to find out whether a pregnant woman is a carrier of herpes or whether the infection has occurred for the first time. To do this, a laboratory blood test is performed, which detects the presence of antibodies to this virus.
If they are present, then there is nothing to fear and no measures need to be taken. If the analysis does not detect antibodies, the situation changes dramatically - there is a high risk of infection of the fetus.
To avoid becoming infected with the herpes virus during pregnancy, a woman should avoid any contact with people who have herpes rashes. If an infection occurs in one of the family members, it is important not to stay in the same room with him for a long time, use individual personal hygiene items and observe basic sanitary standards.
Gynecologists strongly recommend that every woman at the stage of pregnancy planning undergo a blood test to detect the presence of herpes in order to reduce the risk of infection of the fetus and the likelihood of an unsuccessful pregnancy outcome.
When the first signs of the disease appear, it is important to consult a doctor and treat the disease under his supervision, since an exacerbation of a herpes infection can cause other pathological phenomena in the body.
Author: Olga Rogozhkina, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
Relapse of viral infection
Exacerbation of infection threatens less consequences for the fetus than primary infection. In the early stages of normal pregnancy, mother's antibodies reliably protect the child from infection. There is concern that a relapse may occur just before delivery. The threat of infection in this case is 1% during vaginal delivery.
To minimize the likelihood of illness in a newborn, it is necessary to plan the onset of pregnancy and sanitize foci of infection: chronic infectious diseases of internal organs, carious teeth. It is recommended to perform an analysis for specific immunoglobulins. In terms of preparing for pregnancy, women are prescribed antiviral drugs Acyclovir, Valciclovir and vitamin restorative drugs.
In case of relapse, childbirth is carried out through the natural birth canal, since the risk of infection is minimal .
After birth, such children are prescribed antiviral therapy to prevent the development of the disease. https://youtu.be/ualPorJ9Bn8
Primary infection
Primary infection of the lips with herpes during pregnancy is dangerous in three cases:
- The infection occurred in the last week of pregnancy - and the risk of neonatal infection of a newborn from a sick mother is very high;
- The mother has serious immunity problems;
- The pregnant woman and her sexual partner continue to practice oral sex. If the partner has not previously been infected, then there is a possibility of infection and transfer of the infection to the genitals of the expectant mother with the development of genital herpes. In this case, there is a high probability that infection of the fetus may occur in the early stages of pregnancy, and in the later stages a caesarean section will be indicated.
Primary infection more often than relapse occurs with a complicated clinical picture. In this case, normal symptoms are:
- A characteristic rash on the lips with severe pain;
- Increased body temperature;
- Headache;
- Nausea;
- General malaise.
In the hospital, blood tests can be taken from the pregnant woman, and based on the results of an immunological examination, it can be determined whether the infection is primary or recurrent. However, in practice this is done extremely rarely due to the harmlessness of colds on the lips for the fetus.
Sometimes the primary infection of a pregnant woman is asymptomatic, or the signs of the disease are blurred. For example, there may be no rash on the lips, but the patient’s general condition will temporarily worsen and her body temperature will rise. The frequency of asymptomatic herpes is approximately 43% of cases.
If a pregnant woman does not have immunodeficiency diseases, then even primary infection of the lips with herpes will most likely not harm the fetus.
Herpes symptoms
All types of herpes affect different areas of the skin and mucous membranes, but they have the same clinical symptoms and course of the disease. At the very beginning, red spots appear, in place of which erythematous papules (vesicles) form. As the virus cells multiply, the lymph nodes become enlarged and painful sensations appear in the affected area. After some time, the papules burst and shallow ulcers form, covered with crusts. After they fall off, pigmented areas of the skin remain, in which for a long time the nerve endings give out a signal of pain.
Other signs:
- increased body temperature;
- chills and general weakness;
- burning and itching in the affected area;
- muscle pain.
Important! Even after the initial rash has completely disappeared, the virus continues to cause harm to the body.
Symptoms
Herpes virus type 1 during pregnancy affects the entire body, but outwardly manifests itself as a characteristic rash in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
The initial stage is characterized by the manifestation of symptoms that are precursors of the disease. This is itching, burning, pain. During pregnancy, there may be a deterioration in the general condition of the body, the appearance of fever, headache and other signs of intoxication.
As the process progresses further, the woman may notice that her lip is swollen as a result of the swelling.
The swelling may progress for some time. 3-5 days after the first symptoms appear, regional lymph nodes may become enlarged. Then the appearance of small, grouped papules is observed, which later take on the appearance of vesicles filled with liquid. These can be either single or multiple formations measuring 1-4 mm. There is a possibility of fusion of vesicles and the formation of large multi-chamber vesicles.
The third stage of the disease during pregnancy is characterized by clouding of the serous contents and further opening of the vesicles with the formation of erosions and ulcers. Subsequently, they become covered with yellowish-brown scabs, under which epithelial regeneration occurs. Due to the fragility of the latter, cracks and bleeding may occur. At this stage, increased sensitivity of the skin in the affected area is clearly expressed. The disease lasts 7-14 days from the development of the first signs to the completion of epithelial regeneration.
- What are the stages of herpes on the lips?
Localization and types
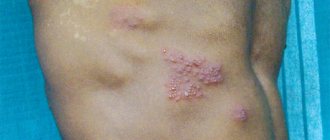
Herpes during pregnancy behaves as usual in relation to the pregnant woman herself; the most common strains are:
- Herpes type 1. during pregnancy, it is also localized in the form of bubbles near the labial borders and on the lips. Labial herpes is most often transmitted through close contact with a virus carrier.
- Herpes type 2 during pregnancy causes the same herpetic rash in the groin and genital area, which brings much more discomfort during pregnancy. One of the types of genital herpes is vaginal herpes; during pregnancy, it can lead to infection of the fetus.
- Type 3 virus – chickenpox and herpes zoster. Shingles during pregnancy forms rashes around the torso, less commonly around the legs or around the forearms and arms. In the case of primary viral infection, shingles is the well-known chickenpox.
- Virus type 4 (Epstein-Barr) – causes infectious mononucleosis. The disease does not form a blistering rash.
- Type 5 of herpes. Cytomegalovirus in pregnant women occurs without rashes. A characteristic manifestation is increased body temperature and symptoms of colds. Diagnostics – laboratory examination of a blood test.
What to do if herpes appears on the labia?
The so-called “Genital herpes” is an infectious disease caused by the herpes virus, which is characterized by rashes on the mucous membranes of the genital organs and the cervix. It is most often transmitted through sexual contact, and less commonly through household methods.
- There are primary herpes (a woman fell ill for the first time in her life):
- And secondary (an infection that already lives in the body is activated).
Important! The most dangerous is primary herpes, in which the probability of infection of the fetus is 60%.
Statistics on the danger of herpes for the fetus
Let's look at the dangers of herpes during pregnancy. There is no point in objecting to medical statistics on herpes during pregnancy. Regarding this disease, she provides the following information and figures:
- literally 90% of people on Earth are carriers of the herpes virus of the first type, as well as the second type;
- with primary infection with genital herpes during pregnancy, the risk of infection of the fetus in utero is thirty to fifty percent, for recurrent herpes three to seven percent;
- herpes in the early stages of pregnancy becomes the basis for spontaneous miscarriage in thirty percent of cases;
- herpes during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester will cause late miscarriage in fifty percent of cases;
- in forty percent of newborns, intrauterine infection actively leads to the formation of latent virus carriage with the possible development of dysfunctional disorders at a later age;
- Women who have had the disease asymptomatically or in atypical forms give birth to sick children in seventy percent of cases. Infant mortality in this group itself is approximately fifty to seventy percent of cases. About fifteen percent of babies are born healthy.
It is important to note that treatment of herpes during pregnancy can be carried out at any stage. The more timely the expectant mother contacts an obstetrician-gynecologist at the clinic, the more timely the diagnosis will be carried out and both therapeutic and preventive measures will be prescribed. Otherwise, numerous complications of various types may arise.
In case of extensive rashes on the lips, nose, face, possibly on the mucous membrane of the genital organs or in any other part of the body, the attending physician will refer the pregnant woman for additional studies, the purpose of which will be to identify the type of herpesvirus that has entered the body. Herpesvirus type 1 is not as dangerous as the genital one. In this case, it is clear how herpes affects the condition of a pregnant woman and that the virus can cause serious complications.
Management of pregnancy and treatment of the disease during this period
Fundamentally, the tactics for treating colds on the lips during pregnancy are similar to the management of the disease outside the gestation period, differing only in a few nuances:
- During pregnancy, medications for systemic use are contraindicated - tablets Valtrex, Famvir, Zovirax, injection drug Foscarnet, etc.;
- Antiherpetic ointments should be used strictly with the permission of a gynecologist;
- Systemic means of symptomatic treatment are used only when absolutely necessary;
- If the disease appears frequently, you should undergo examination at a clinic and find out the cause of weakened immunity.
First-line drugs for the treatment of colds on the lips are ointments based on acyclovir - Acyclovir-Acri, Herperax, Zovirax and others, Panavir gel, Fenistil Pencivir, ointments of general antiviral action Viru-Merz Serol, Priora, Erazaban. Any ointment from this group acts locally, and its components practically do not penetrate into the blood. However, these drugs also have a risk of developing side effects, so they should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Review: “At the eighth week, herpes appeared. He was gone for three years, and then he appeared on you. At the pharmacy I took Zovirax - tablets and ointment, but did not use it immediately, but called the gynecologist. She immediately forbade me to take the pills and asked what herpes itself looked like. He looked bad, his entire upper lip was broken, even a little on the right side of his nose. The doctor allowed me to smear it, but said that if there were only a few bubbles, then I could do without it. After two days, all the blisters were covered with crusts and no longer hurt. But I applied it strictly according to the instructions for 5 days...” Alla, from correspondence on the forum.
Apply each of the above ointments to the affected surface in a thick layer, rubbing the product into the skin. As the product dries, the area with the ulcers needs to be smeared again. Treatment should continue for at least 5 days, even if the papules have crusted over and dried out.
The sooner the use of antiherpetic ointments is started, the less pronounced the unpleasant symptoms will be and the faster they will pass. If you start applying the ointment to the skin at the stage of characteristic tingling, then bubbles on the skin may not appear at all.
If severe pain occurs on the lips, they can be treated with products such as Menovazine or benzocaine ointment. Moisturizing lip creams protect the crusts from cracking, and some folk remedies such as aloe or sea buckthorn juices can enhance the effect of antiherpetic ointments. But the use of these drugs without antiviral therapy will have virtually no effect on the course of herpes.
To avoid consequences for the fetus and complications, it is necessary to support the immune system with a healthy diet and taking vitamin complexes, and abstain from oral sex. If herpes appeared in a pregnant woman in the last week and its symptoms have not completely disappeared even after childbirth, then you should not kiss the baby until the crusts are completely peeled off, and breastfeeding should be done in a cotton-gauze bandage.
Be healthy!
Useful video about the serious problems that the herpes virus can create for your sex life
Medicines
Genital herpes in pregnant women requires treatment as carefully as possible. You need to act in such a way as not to harm the body in attempts to help it. Use:
- Acyclovir. An ointment that is prescribed to all pregnant women, even in the first trimester. It needs to be applied several times a day and as a result the symptoms will be relieved quite quickly. In the second and third trimesters, tablets of the same name are used. They not only relieve symptoms, but also fight the virus.
- Panavir. A gel that has a similar effect to acyclovir and is also used even in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Famvir. An expensive drug that acts exclusively on those cells that are affected by the virus. It is prescribed at any stage of pregnancy and is often used during planning.
In addition to medications, therapy aimed at relieving symptoms can be supplemented with folk remedies:
- Chamomile decoction. Pour water over dried flowers and boil for 5 minutes. Strain and use to wash the affected area.
- Calendula infusion. Pour boiling water over dried flowers, wrap them and put them in a warm, dark place for several hours. Remove, strain, and use for rinsing.
- Essential oils - sea buckthorn, calendula, rose hips, fir. Add a few drops of oil to a glass of warm water and use for rinsing.
Any folk remedies should be used only after consultation with your doctor.
Ways of infection with herpes
Like most viruses, herpes has several varieties - 8 types, of which only the first 6 have been studied quite well:
- simple;
- genital;
- chicken pox;
- Epstein–Barr virus;
- human cytomegalovirus;
- Roseolovirus - also known as 3-day fever.
Most often in modern realities the first 2 categories are found. Despite the lack of a 100% working cure for herpes, scientists have identified all the main transmission routes for each type.
The most common:
- direct tactile contact with the patient (kiss or, if we are talking about genital herpes, sexual intercourse);
- through household items - improperly washed cutlery, mugs, touched toothbrushes;
- due to the general use of cosmetics (lipstick, etc.);
- airborne droplets - during sneezing or coughing with droplets of saliva:
- in 65% of cases, a child can become infected from the mother if she has genital herpes in the acute stage at the time of birth;
- eating food from the same container as the patient.
There is a misconception that herpes can occur as a result of hypothermia or stress. The myth arose because rashes often occur during illness. In fact, herpes is a virus and cannot appear from the cold, like a common cold, but it often manifests itself during a period of weakened immunity.
Complications in pregnant women with herpes
In pregnant women, all the body's forces are concentrated on internal restructuring. Reduced immunity is a favorable factor for the development of an insidious disease.
Pregnant women infected with herpes are diagnosed with:
Missed miscarriage (frozen pregnancy) is the most common complication that occurs during the first trimester.
Although pregnancy begins safely (since the fertilized embryo is securely attached to the muscular layer of the uterus), its subsequent development does not follow (only the membranes develop).
The problem is that the woman may not feel the presence of the disease in any way and fetal rejection does not occur, but the products of the decay of the embryo can cause intoxication of the female body, as a result of which the following are observed:
- inflammatory processes of the endometrium;
- thrombosis, bleeding and other disorders of the hematopoietic system.
It is extremely important to promptly notice that the fetus has stopped developing. As a rule, it is removed using vacuum extraction under general anesthesia with curettage or scraping.
Subsequent treatment for genital herpes is 6 months or more.
It should be noted: during pregnancy there is a fairly low probability of infection of the fetus with herpes, with the exception of the primary infection of a woman with HSV-2.
The probability of infection of the fetus with the virus may be 50%.
Primary infection after 32 weeks of pregnancy can cause skin ulcerations, cerebral necrosis, cataracts, and choriomeningitis in the child.
Immunity to herpes means a guaranteed healthy baby.
There is no need to immediately conclude that herpes is incompatible with the birth of a healthy child. Only primary herpes in pregnant women is dangerous.
Many women who have had genital herpes give birth to completely healthy children, since the fetus is reliably protected by the mother's antibodies.
The risk of infection of a newborn is influenced by the severity of the disease in the pregnant woman and the duration of contact of the fetus with contaminated amniotic fluid.
To prevent this from happening, you should get tested 2-4 weeks before giving birth. If the result is positive, it is advisable to perform a planned caesarean section.
Do pregnant women need to treat herpes?
While carrying a child, the use of any medications can be dangerous, and this fact forces some mothers to refrain from treating minor diseases, including herpes. Doctors say this is fundamentally wrong. Herpes rashes may not go away for up to three weeks if you do not help the body in fighting them.
During pregnancy, such a delay will only cause problems, while there are a lot of drugs approved during pregnancy and lactation. Even if herpes is recurrent, you need to immediately begin treatment, not to mention the more dangerous primary form.
What are the dangers during gestation?
At first glance, it may seem that herpes is not so terrible during pregnancy if we are talking about types I or II. In women, it can manifest as rashes on the skin, lips, and genitals. This really won’t cause much harm to maternal health, but the following situations are dangerous to the fetus:
- if your mother gets herpes for the first time;
- if episodes of exacerbation are frequent;
- if the rash appeared on the eve of childbirth.
At the initial encounter with the virus during pregnancy, the female body does not yet have protective antibodies, so HSV also reaches the fetus, disrupting its development and can cause defects. First of all, the nervous system suffers. The virus affects and provokes pathologies of the heart (myocarditis, organ failure), liver (hepatitis, underdevelopment of the bile ducts), and brain (increased intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus). In severe cases, it can provoke intrauterine fetal death. Similar consequences are also possible if the herpetic infection worsens frequently - several times a month.
If you detect any rashes similar to herpes types I and II, you should immediately consult a doctor. Also, you should not ignore taking tests when registering, since they often help identify this disease or immunity to it.
Risks during childbirth
The risk of fetal infection with HSV exists not only during pregnancy. Often the virus is transmitted to the child when it passes through the birth canal, and its outer layer comes into close contact with the mother’s mucous membrane. Infection in this case can result in a generalized herpetic infection, pneumonia, and slow healing of the umbilical wound.
If there are signs of rashes in the genital area on the eve of childbirth, it is recommended to perform a cesarean section while the mother is treated with antiherpetic drugs. So the risk of infection of the child is minimal.
Vitamins
In case of herpes infection, the doctor will definitely prescribe special vitamin complexes for the pregnant woman.
In addition to this measure, it is necessary to include in your diet foods enriched with microelements:
- amega-3 acids – sardine, tuna, cod, lean meats;
- vitamin E – rose hips, prunes, oatmeal, spinach, buckwheat porridge;
- vitamin A – cod and animal liver, fish oil (capsules);
- B vitamins – wheat porridge, eggs, fish, beans, brown and brown rice, broccoli;
- vitamin C – black currants, strawberries, all types of green salads, apricots, bell peppers.
Recurrent herpes in pregnant women
Important : Recurrent herpes during pregnancy is not dangerous.
If a pregnant woman has had relapses before, then the antibodies blocking the effect of HSV will provide reliable protection for the fetus.
The risk of infection of a newborn child from the mother is about 1%.
A set of measures is necessary so that during pregnancy herpes does not bring unpleasant surprises to the expectant mother and her baby.
When planning a future pregnancy, you should eliminate foci of infection (gastritis, sinusitis, dental caries), forget about bad habits and undergo a course of restorative therapy.
It is imperative to undergo tests for the presence of immunoglobulins.
Acyclovir or Valacyclovir, as well as vitamin complexes, are prescribed as preventive measures.
Clinical picture
Herpes on the lips during pregnancy is quite easy to recognize even without the help of a doctor. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of itching, redness and a rash in the form of blisters filled with cloudy liquid. The disease occurs in several stages:
- Itching on the lips. It is this sign that indicates the onset of the disease. In this case, the woman experiences not only itching, but also general local discomfort.
- Formation of bubbles. The rash often looks like one or several blisters with a cloudy liquid filling.
- The appearance of erosion on the lips at the site of the lesion. Erosion forms after spontaneous or artificial opening of the bubbles. It is important to know that their contents contain the largest number of pathogenic agents. To prevent the spread of infection, you need to regularly disinfect the affected area.
- Crust formation. After the ulcers heal, dry crusts form in their place. Under no circumstances should you rip them off. This can lead to bleeding, pain, infection, and scarring on the lips.
If the labial virus has relapsed and the disease is mild, there is no danger to the mother and fetus during pregnancy.
You should immediately consult a doctor if rashes appear on other parts of the body, for example, on the genitals (genital herpes). There is a possibility of intrauterine damage to the fetus, and therefore the woman requires immediate treatment.
The effect of herpes virus type 2 on pregnancy
Recurrent herpes on the labia does not have a serious effect on the course of pregnancy.
In the presence of maternal antibodies, the fetus is protected. However, the likelihood of ascending infection with vaginal and cervical (on the cervix) herpes is slightly higher than with rashes on the external genitalia. New-onset genital herpes has approximately the same probability of infection in all trimesters of pregnancy. The disease can lead to consequences identical to those caused by infection with HSV-1.
Recurrence of genital herpes in the last weeks of pregnancy can cause infection of the fetus during natural childbirth. Therefore, before them, the woman must undergo a course of treatment to transfer the disease to the latent stage. If therapy does not help or genital herpes occurs several days before birth, surgical delivery by cesarean section is recommended.
https://youtu.be/bjhvlVguuWc
Folk remedies: effective recipes
It is permissible to use alternative medicine recipes for the treatment of labial herpes only in mild cases of the disease, in which there is no severe itching and pain.
Folk remedies:
- Apply grated raw potatoes to the affected area. The starch contained in the vegetable will dry out the vesicular vesicle and reduce inflammation and redness.
- Moisten a small swab with propolis tincture and apply to the vial. Has a cauterizing effect.
- Apply a small amount of toothpaste to the affected area to speed up the breakthrough of fluid from the bubble.
- Apply a little calendula ointment to the crust formed after the liquid has poured out from the vesicular vesicles. The ointment will soften the crust and prevent its premature cracking.
- Tea tree oil, aloe juice, and fir oil will help speed up regenerative processes in the affected area. A small amount of any liquid is applied to the sore spot several times a day.
- For compresses, use a soda solution. In 100 ml. dissolve 5 g of water (half a teaspoon without a slide) of soda. Soak a swab in the solution and apply to the affected area.
- Brewed black tea also helps fight the virus. Brew black tea in a mug without adding sugar. Place a teaspoon into the hot liquid. Wait until it warms up. Apply a hot spoon to the area where the herpes appears and leave until it cools completely.
- Homemade garlic-honey ointment is a surefire way to fight herpes. Mix liquid honey and garlic juice in equal proportions. Mix and apply 6 times a day to the sore spot.
Treatment of herpes during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the main direction of treatment is to eliminate the external manifestations of the disease and reduce the risk of relapse. During primary infection, therapy is carried out aimed at preventing infection of the unborn child. There is no cure for the herpes virus, so it should be fought with drugs that weaken the influence of the pathogen and strengthen the immune system.
A complicating factor in treating the disease while pregnant is that many antiviral drugs are prohibited for pregnant women. Therefore, self-medication is excluded, and the necessary therapeutic course is carried out under medical supervision after diagnosis.
Diagnostics
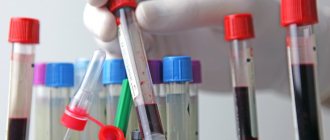
The type of disease is determined by identifying antibodies to the infectious pathogen: a blood test is performed for immunoglobulins (IgM and IgG). A positive result for IgM indicates a primary infection or an acute period of a chronic disease. The presence of IgG indicates that herpes has been present in the blood for a long time.
The most reliable method for determining HSV is PCR analysis, which examines material from the cervical canal. The analysis allows you to determine the presence of the virus even at low concentrations.
The type of disease is determined by identifying antibodies to the infectious pathogen: a blood test is performed for immunoglobulins (IgM and IgG).
How to treat
When the first signs of HSV appear, you should use an ointment or gel with an antiviral effect, the use of which is permitted during pregnancy. Among the most popular external remedies are ointments with acyclovir (Acyclovir, Zovirax, Herperax), preparations based on plant extracts (Panavir gel).
Rectal suppositories Viferon and Genferon are also used, approved for the treatment and prevention of relapses of the disease from the middle of the 2nd trimester. These drugs allow you to stimulate the production of antibodies and increase the immune defense of the female body during pregnancy.
What types of ointments are there for herpes?
Folk remedies
For the safety of the unborn child, you can use alternative medicine methods to treat a viral infection, which will help alleviate the symptoms of the disease. The greatest effect will be obtained by using the following means:
- Aloe juice. Squeeze a few drops from the leaves of the plant and apply the moistened swab to the sores for half an hour.
- Tinctures of calendula or chamomile decoction, tea leaves. Apply a tampon moistened with a healing infusion several times a day to the affected areas.
- A strong solution of salt and soda. Treat the blisters with the solution several times a day.
- Fir, sea buckthorn oil or tea tree extract. Treat rashes every 2-3 hours, and after crusts form, wipe the wounds several times a day.
Folk remedies do not have an antiviral effect, but they will help get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease and relieve inflammation.
Prevention
During pregnancy, timely examination for the presence of antibodies to the herpes virus and taking the necessary measures to strengthen the body's protective properties (giving up bad habits, hardening, playing sports, proper balanced nutrition, proper rest) will help to avoid the threat of disease.
In case of relapse of the disease, a set of protective measures is necessary to prevent the activation of the virus: hypothermia and overheating, nervous stress, and excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin should be avoided.
Review of safe tools
Labial herpes (rashes on the lips) in pregnant women is treated topically with the following drugs, available from pharmacies without a prescription:
- acyclovir in the form of ointments, creams, gels;
- iromontadine ointment;
- alpizarin ointment;
- oxolinic ointment;
- Zovirax;
- herpetad;
- agerp;
- Viferon;
- virolex.
The drugs are aimed at suppressing the activity of viruses at the site of application. In some cases, an interferon solution is prescribed by injection. Treatment of lip herpes that appears during pregnancy involves taking pills to stimulate a woman’s immune system.
Herbal preparations that affect the general condition of the body and are prescribed by a doctor:
- dietary supplements;
- ginseng;
- echinacea;
- Eleutherococcus;
- vitamin complexes.
After the blisters open and begin to dry out, balms or capsules with vitamin E (tocopherol, aevit) are applied to the lips to speed up healing. Traditional medicine claims that raw potatoes and calendula ointment have a positive effect on the speed of rash healing.
Necessary examination
A comprehensive examination to determine the presence and type of HSV includes two stages:
- examination by a specialist;
- laboratory research.
The following are considered the main methods that can reliably confirm the presence of infection.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A simple way to determine the virus, even if it is in the body in a small concentration. The essence of the method is to repeatedly copy a section of the pathogen's DNA and further identify its species. The material is collected from the suspected source of infection - from the site of rashes on the lips, genitals, and from the cervical canal. PCR allows you to indicate whether HSV is currently active. A negative result indicates no active infection, but not complete cure.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Allows you to identify antibodies of the IgM and IgG types and determine their quantity. This way the phase of the disease is determined.
- Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF). The taken biological material is treated with a special substance, after which the antigens begin to glow. This allows them to be detected under a microscope. Used less frequently.
A breakdown of test results for HSV types I and II is presented in the table.
Table - Correct assessment of test results for HSV types I and II
| IgM ELISA | IgG ELISA | PCR | Result |
| Not executed | Not executed | Negative | — There is no active infection; — immunity to the pathogen is unknown |
| Not executed | Not executed | Positive | — Active infection; — immunity to the pathogen is unknown |
| Positive | Negative | Positive | — Active infection; - first contact with a pathogen |
| Positive | Positive | Positive | — Active infection; - exacerbation of chronic form |
| Positive | Negative | Negative | — Acute infection, but there is no pathogen in the study site; - first contact with a pathogen |
| Positive | Positive | Negative | - Exacerbation of chronic infection; — there is no virus in the PCR material |
| Negative | Positive | Negative | Suppressed infection |
| Negative | Positive | Positive | Subacute course |
Additional research methods include the following.
- Cultural. The biomaterial is placed in a nutrient medium where viruses are expected to grow. If it is not there, there is no infection.
- Immunogram. Blood test for immune cells. Does not indicate the presence/absence of a virus.
- Vulvocolpocervicoscopy. Examination of the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix with a colposcope. You can detect signs of herpetic lesions.
When registering, a woman must undergo testing to detect TORCH infections (toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes types I and II). And knowing the immune status before pregnancy, you can promptly identify the pathogen and prevent primary infection during pregnancy.
Recommendations
To maintain a weakened immune system when herpes is in the active stage of development, it is necessary to promptly replenish the reserves of microelements and vitamins in the female body. To do this, it is recommended to adhere to a proper diet. The expectant mother and the baby growing inside need large quantities of amino acids, proteins and vitamins, which can be obtained from sea fish, fresh fruits, lean meats and vegetables. Taking multivitamin complexes is an excellent support for a weakened body during pregnancy, but they should be prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
It is extremely important to follow standard medical recommendations. It is necessary to drink enough healthy fluids:
- Tea with lemon added.
- Warm decoction of rose hips.
- Herbal tea with honey.
Compliance with the water regime is indicated if there are no signs of kidney dysfunction.
Features of pregnancy
If a woman is diagnosed with herpes during pregnancy, then dynamic monitoring is required. At an early stage of about 12 weeks, the first screening ultrasound is performed, which determines the presence of internal organs and the thickness of the collar fold. If gross malformations incompatible with life are discovered during this period, the woman is offered to terminate the pregnancy.
The next ultrasound is performed at 20-24 weeks. Pathologies that were invisible for a short time become visible. Suspension in intrauterine waters, thickening of the placenta, cysts in the brain or liver, an increase or decrease in the amount of water indicates an intrauterine infection. Pathology is indicated by intrauterine growth retardation and fetoplacental insufficiency.
If ultrasound results are distorted, additional examination is required. In each trimester and immediately before birth, a blood test for antibodies is prescribed.
The most accurate diagnostic method is PCR . The reaction allows you to determine the DNA of the herpes simplex virus. To search for antibodies, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunofluorescence reaction are used. The study can be performed before treatment and during the use of drugs: they do not distort the result.
For childbirth, the woman in labor is hospitalized 2 days before the expected date. In a hospital setting, an additional examination for antibodies is carried out, and the vagina is sanitized.
Herpes in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters
Herpes causes the least harm in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, when the main systems and organs of the fetus are already formed, and infection cannot provoke the development of serious pathologies.
In the 2nd trimester, the placenta is at risk. Due to violations of its function by herpetic components, the fetus suffers from hypoxia. Children who have suffered a viral attack are often born underweight and with a weakened immune system.
Primary infection with herpes from 34 to 38 weeks of pregnancy increases the risk of developing severe brain pathologies in the fetus. In the third trimester of pregnancy, it is easier for the virus to penetrate the placental barrier, resulting in such dangerous consequences as fetoplacental insufficiency, including placental abruption, premature birth and death of the child.
Effect of the virus on the fetus
Every expectant mother, upon discovering the first symptoms of the disease, asks herself: is herpes on the lips dangerous during pregnancy? And how to treat this disease. It is quite difficult to answer, because how herpes affects pregnancy depends on many factors. The main ones are the type of pathogen and the time of infection.
https://youtu.be/WibJgFK4nxY
Herpes simplex
The typical course of the disease, when herpes appears in the nose and lips, with adequate treatment most often does not harm the pregnant woman and the fetus. Only in the first months after conceiving a child there is a small risk of the virus entering the woman’s blood, which can lead to the development of fetal pathologies and even its death. Herpes in the blood during pregnancy of more than 20 weeks is not dangerous for the child; the already developed placenta well protects the fetus from infection. The immunity of a woman who is infected long before conceiving a child will sooner or later become more active and suppress the effect of the virus. But during primary infection there are no antibodies in the body, so the risk of the spread of dangerous cells into the systemic bloodstream increases. Herpes simplex during pregnancy requires surgical treatment; at the initial stage it is not dangerous to the fetus.
Genital herpes
If a parasitic virus covers the genital area not for the first time, then there is practically no threat to the child. Only if the woman’s immunity is excessively reduced can the virus reach the fetus through the placenta. Primary herpes in the intimate area during pregnancy occurs with complications and requires serious treatment. In 50% of infected pregnant women, the virus enters the bloodstream. At the same time, the answer to the question of why herpes is dangerous for the fetus is based on statistical data.
A viral infection causes:
- nervous system disorders – 35% of newborns;
- damage to the eyes and skin - 45% of infants;
- intrauterine fetal death in mid-pregnancy – 90% of cases;
- infection at 32-34 weeks is 60-80% fatal.
Important! Herpes type 2 during pregnancy affects the very process of development of the baby in the womb. Infection of the fetus in the 1st trimester leads to fading and spontaneous miscarriage, and at the end of pregnancy to premature birth and stillbirth.
Even if the child survived and was born, he has serious health problems. Children often develop heart defects and hydrocephalus from the herpes virus, the functioning of the central nervous system is disrupted, and the risk of internal and external bleeding increases. Such children often become blind and deaf, have developmental delays and epileptic seizures.
Nutrition
If you have a herpes infection, it is recommended to follow a diet that will reduce the severity of the signs of the disease:
- Avoid alcoholic drinks (especially beer).
- Limit the consumption of smoked meats, salty, spicy foods, fried foods, canned food, fatty broths, spicy spices and coffee.
- Increase the consumption of fermented milk products, which help restore the microflora of the intestinal tract.
- As for protein products, it is recommended to include fish, dairy products, and lean meat in your diet.
- Add soybean, pea, and bean dishes to the menu.
- Eliminate fast carbohydrates and introduce complex carbohydrates into the menu, found in vegetables, cereals, fruits and whole grains.
- Foods rich in an amino acid called arginine are removed from the diet. It is found in seeds (most of all in pumpkin seeds), nuts, especially peanuts, chocolate, raisins, dishes with gelatin, and white bread.
Deciphering the analysis of herpes simplex during pregnancy
Modern research has established that antiviral antibodies to type I herpes are observed in 80% of women of reproductive age, and to type II - in 30%.
Many pregnant women are often worried because the ELISA test showed herpes in the blood.
Such fears may be unfounded, since IgG antibodies detected in the blood do not pose a serious threat to the fetus.
On the contrary, they greatly reduce the risk of transmitting herpes to the fetus, indicating that the mother is immune to this virus.
Since M antibodies (IgM) arise during several weeks after the initial infection, they may also indicate reactivation of existing herpes.
IgM remains in the body for a maximum of 2 months, and IgG remains throughout life (seropositivity). Primary herpes infection is represented as IgM.
Recurrent herpes, as a rule, is diagnosed by elevated IgG levels, and the presence of IgM in such patients is regarded as a signal of exacerbation of the disease.
If the IgM results are questionable, the doctor will order a repeat test within two weeks.
It is worth emphasizing that sometimes even experienced medical specialists cannot distinguish the symptoms of herpes from the manifestations of other diseases.
That is why you need to undergo the appropriate tests, and then plan for the birth of a child.
HSV during pregnancy: symptoms
HSV type 1, as mentioned above, manifests itself in the form of specific blisters on the lips, which can itch and itch. They appear, as a rule, against the background of a general decrease in immunity and can be accompanied by high fever, weakness, sore throat, runny nose, etc.
As for HSV type 2, the main symptoms include:
- Redness of the skin in the perineum, lower abdomen or thighs.
- Watery discharge.
- Pain when going to the toilet.
- Cold symptoms: fever, sore throat, runny nose, cough.
HSV type 2 is transmitted during pregnancy exclusively through sexual contact. In the case of primary infection of a pregnant woman with genital herpes, the virus is easily transmitted to the unborn baby through amniotic fluid, or during childbirth by passing through the birth canal.
A positive test result for HSV and CMV carriage: what does it mean?
The risk of transmitting the virus to a child largely depends on the timing of infection. For example, if the period is 20 weeks, then the likelihood of the baby becoming infected is low, but if this happens, the pregnancy will result in serious consequences, including miscarriage. If a woman becomes infected in the third trimester, then the likelihood of a threat increases, since HSV transmission occurs in 50% of situations. There are three options for a child becoming infected:
- during pregnancy in the womb,
- during childbirth,
- after childbirth.
In 90% of cases, transmission of the infection occurs during childbirth if the woman in labor has a rash in the genital area. The same statistics apply to the transmission of cytomegalovirus - CMV.
Herpes on the lips in early pregnancy
Doctors say that in the 1st trimester, women during pregnancy are bothered by herpes on the lip more often than in other periods. This is explained by spontaneous suppression of the immune system, which does not want to accept a foreign body, namely the embryo.
Recurrences of herpes are also associated with a weakening of natural defenses. In an ideal state, the body is able to fight viral agents that have become active and have gone beyond the nerve cells. Gestation makes the body vulnerable. Herpetic infection in expectant mothers can be aggressive or asymptomatic; it all depends on the level of immunity in a particular period of time.
Thus, in the development of herpes on the lips in the early stages of gestation, the main role is played by functional immunosuppression. This condition ensures normal gestation without immunological conflicts. Oppressed by the current situation, the defense system is not able to control the virions, and they, in turn, reach peripheral tissues and infect them at the sites of initial damage.
Herpes does not pose a danger in the first trimester of pregnancy, since the strain does not spread beyond the tissues that come into contact with infected axons. This means that the likelihood of the virus spreading from the lips to the abdominal cavity and reproductive system is negligible (almost zero).
Diagnostics
All women expecting a child are prescribed a test for the herpes virus. Two tests are most effective: ELISA and PCR.
Determination of avidity for herpes using ELISA
When prescribing ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), the avidity index for the herpes virus is important. Avidity characterizes the strength of the antigen-antibody bond. When the virus enters cells, the immune system produces Igm antibodies, then IgG antibodies. In the latter, avidity is initially low, then, as immune reactions progress, the avidity of IgG antibodies increases, that is, antibodies closely bind to antigens. These high-avidity antibodies persist for life, and their number increases with exacerbation of herpes. Thus, by the number of antibodies one can judge at what stage the disease is:
- High values of IgM and low avidity IgG indicate primary herpes (IA up to 40%).
- A small amount of waxy IgG - the virus is present in a latent form (IA exceeds 60%).
- A large number of high-avidity IgG - the disease has entered the acute stage (AI from 40 to 60%).
Ideally, there should be no IgM antibodies, and IgG should be highly avid.
Carrying out PCR during pregnancy
The polymerase chain reaction method is highly informative. It can be used to detect STIs, including herpes. The essence of the method is to restore cell DNA using various enzymes. In this case, DNA copying is possible if it is present in the sample being studied. This analysis determines not only the active phase of the disease, but also the presence of antibodies to it.
How to reduce the risk to the fetus?
Therapy of the herpes virus in pregnant women is difficult, since not all drugs can be prescribed during this period:
- Primary herpes is treated with antiviral drugs only in case of pronounced symptoms and only after 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- In the first trimester, drugs for external use are allowed: ointments, creams, solutions (Acyclovir, Gerverax).
- Immunomodulators (Viferon, Interferon) are necessarily prescribed, which increase immunity, forcing the body to fight infection.
- A woman should also take a vitamin complex that contains zinc and vitamin E.
You can reduce the severity of symptoms with proper nutrition. Chocolate and raisins should be excluded from the diet, as they contain arginine, which helps activate the virus. You need to eat foods rich in lysine (chicken meat, vegetables, fruits). This amino acid has a detrimental effect on the virus.
To prevent recurrence of infection, expectant mothers must follow simple rules:
- Protect yourself from infectious diseases.
- Eat properly.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Avoid being in drafts.
- Do not communicate with people who have signs of herpes.
- Use strictly your own hygiene products, cosmetics, and cutlery.
https://youtu.be/8aA6YEueLvk
HSV during pregnancy: prevention
If a person does not have antibodies to HSV in his blood, only standard preventive actions can save him:
- Use separate utensils in cases where symptoms of the disease appear in one of the family members. Everyone should have their own fork, spoon, mug and plate. The same goes for a toothbrush, lipstick, pillowcase, towel and other household and hygiene items.
- Do not finish other people's food or drink other people's drinks.
- Avoid kissing and oral sex during pregnancy. If the bubbles appear in the genital area, you will also have to give up classic sex for a while. Changing partners, of course, is also unacceptable!
- If possible, isolate the sick family member in a separate room, constantly ventilating the entire apartment.
- At the first symptoms, be sure to see a doctor!
HSV infection during pregnancy: consequences
If the expectant mother catches HSV again, the risk of infection of the fetus is minimized and is no more than 1%.
However, if the infection is primary, then in more than half of the cases the disease is transmitted to the unborn baby. Although if a woman notices the development of the virus in time, the consequences can be minimized.
HSV during pregnancy: first trimester
In the first trimester, all vital organs and systems are formed in the fetus. HSV caught during this period can lead to a fatal outcome:
- frozen pregnancy;
- miscarriage;
- development of defects incompatible with life;
- heart disease;
- disruption of brain function.
HSV during pregnancy: second trimester
When the fetus is already formed, the tiny heart is beating, the brain is functioning at full capacity, there is a good chance that the baby will be born on time, but he will have to live with chronic and difficult diseases:
- anemia;
- pneumonia;
- sepsis;
- malnutrition;
- epilepsy;
- jaundice;
- hepatitis.
In some cases there is a risk of premature birth.
HSV during pregnancy: third trimester
In the third trimester, it is also possible for a baby to be born prematurely, but the chances of saving it are greater - after all, the closer to the expected date of birth of the baby, the more developed and perfect the baby lies in the expectant mother’s tummy.
However, the consequences of primary HSV infection can also be detrimental:
- liver necrosis;
- spleen diseases:
- possible developmental delay;
- Possible deafness or blindness.
Treatment provided
If a woman was infected before pregnancy, and the virus is in a “dormant” state and does not bother the woman in any way, careful monitoring and preventive measures to improve health must be carried out. However, you must always remember that at any stage of pregnancy, every exacerbation of herpes cannot remain without due attention.
This disease is unpredictable and from ordinary herpes on the lips can turn into generalized forms with damage to the meninges or even the death of the child. Therefore, in any situation, a thorough examination and treatment if necessary are required, because the cost of negligence in this case is very high.
| Variant of the course of the disease | Scope of treatment measures carried out |
| Simple and genital herpes with local lesions |
|
| Generalized forms for any type of infection |
|
| Genital herpes with a high risk for the baby | The question of premature delivery by cesarean section is raised |
Attention: any therapy option should be prescribed and monitored only by a doctor. A pregnant woman should understand the possible risks; lack of therapy or spontaneous self-prescription of medications is fraught with serious complications.
Treatment of pregnant women with active herpes
HSV during pregnancy: diagnosis
It is quite difficult to diagnose HSV on your own, since outwardly it manifests itself as a mixture of a standard acute respiratory viral infection and slight irritation on the skin. Therefore, it is very important to visit your doctor regularly and inform him of any changes in your condition.
To fully diagnose the disease, the doctor may offer one of several research options:
- Virological. In this case, blood and substances from the placenta are placed in a special environment in which the virus can progress at an increased rate. This will help to find out how strong the virus is, whether it has penetrated into the amniotic fluid, and whether the pregnant woman’s immunity can cope with it.
- Gene diagnostics. The secretions of the expectant mother are examined, in which the DNA of the virus is isolated.
- When planning and with the onset of pregnancy, an analysis is required for the presence of antibodies in the blood to certain viruses.
Consequences for the fetus
Possible negative developmental outcomes for the fetus vary. This depends on the duration of infection of the pregnant woman.
- 1st trimester. Miscarriage, threatened miscarriage, frozen pregnancy, congenital deformity, complete or partial damage to organs at the developmental stage;
- 2nd and 3rd trimesters. Early untimely birth, heart disease, pneumonia, serious disruption of the liver, disruption of the spleen.
Treatment of newborns who became infected in utero rarely gives a positive result. The baby either dies or is born disabled. Due to infection of the fetus, the results may be as follows:
- cerebral palsy;
- deafness;
- blindness;
- epilepsy and other consequences.
The neonatal virus expresses itself at varying levels of manifestation. As a rule, a baby is born with symptoms of herpes on the skin, rarely on the genitals. A virus that attacks the nervous system is fatal in 50% of cases.
When the herpes simplex virus develops at any time, before birth, herpes is transmitted to the child. Only 6% of babies are born with symptoms of focal lesions during relapse of the disease.
To summarize, it is worth recalling that during pregnancy it is most dangerous to become infected with genital herpes for the first time. Since primary infection will be more dangerous for the fetus, because the pregnant woman does not have antibodies to herpes in her blood, which means herpes can penetrate to the fetus and disrupt proper development. If a relapse of herpes occurs during pregnancy, then it is necessary to urgently begin treatment, and it is better to consult a venereologist rather than a gynecologist, since genital herpes is much easier to diagnose by a venereologist.
Pills
The following tablets are mainly prescribed:
- Acyclovir – 200 mg five times a day, treatment period from 5 to 10 days
- Valocyclovir or Valtrex – 500 mg twice a day. Duration of treatment 5-10 days
- Vitamin complexes to strengthen the immune system
https://youtu.be/mL0eUgrIOhA
You should take the tablets regularly, strictly following the instructions. If it is prescribed to use for 10 days, then the treatment period cannot be shortened, even if the infection is visually eliminated.
It should be understood that this virus not only has a long incubation period, but also periods of extinction and recovery.
The disease can last 30-40 days. Therefore, you cannot let your guard down. If you notice the slightest deterioration in your health from the prescribed tablets, you should immediately consult your doctor.
The course of pregnancy with herpes
HSV ranks second after rubella in terms of teratogenicity (the ability to form malformations in the fetus). It has been established that intrauterine HSV infection can occur:
- transplacentally - through the vessels of the placenta;
- ascending from infected genital tracts, especially with premature rupture of membranes, long anhydrous period;
- from the pelvic cavity through the fallopian tubes.
If the expectant mother becomes infected with genital herpes for the first time during pregnancy, the fetus may suffer. As a rule, if infected before the 10th week of pregnancy, fetal death and miscarriage occur. Damage to the developing organs of the fetus and the occurrence of congenital deformities are possible.
Infection in the second - third trimester, and especially after 36 weeks of pregnancy, is fraught with damage to the fetal nervous system, skin, liver, and spleen. Despite the treatment prescribed after birth, up to 80% of newborns with a primary episode of genital herpes in the mother die or become severely disabled.
The primary episode of genital herpes and the associated loss of a desired pregnancy is a severe psychological trauma for both potential parents. But the next pregnancy will proceed against the background of recurrent genital herpes, and antibodies will circulate in the mother’s blood for life, which will preserve and protect the unborn child, penetrating through the placenta into his body. During pregnancy from a mother with recurrent genital herpes, the virus is transmitted to the fetus in only 0.02% of cases. Therefore, recurrent genital herpes is not so dangerous during pregnancy and does not cause deformities or damage to internal organs. However, with recurrent herpes, the incidence of placental dysfunction, intrauterine growth restriction, and miscarriage increases. These complications are most often associated with autoimmune processes in the mother’s body against the background of a herpes infection, when the immune system “does not recognize” its own tissues and cells and produces antibodies to them as to foreign proteins. Such processes affect, in particular, the process of blood clotting, while the fetus suffers secondarily as a result of damage to the blood vessels of the developing placenta.
Therefore, if you have a recurrent herpetic infection, you need to carefully follow the schedule of all studies performed during pregnancy in order to promptly eliminate possible complications.
Congenital herpes If a woman has active rashes during childbirth, newborn babies cannot always avoid infection when passing through the mother's infected genital tract. The incidence of infection in newborns whose mothers were isolated with herpes virus at the end of pregnancy is 40-60%. According to WHO experts, 0.03% of all newborns were infected with HSV during childbirth. In addition to the above mentioned routes of transmission of infection, during childbirth, infection is possible through direct contact during passage through the birth canal, as well as after birth from the mother if she has active rashes. In newborns, skin rashes are detected; in severe cases, damage to the brain and other organs (liver, lungs, adrenal glands) is possible. The mortality rate for newborns with primary herpes infection is about 50%, and half of those who survive have ocular or neurological complications.
Back to contents
How to prepare for childbirth
Prevention of genital herpes before childbirth is carried out as follows:
- If primary or recurrent HSV-2 is diagnosed in the third trimester of pregnancy, the woman is recommended to have a cesarean section to exclude the possibility of infection of the child;
- Pregnant women who for some reason cannot be operated on are prescribed suppressive treatment 2 weeks before birth. This method involves long-term use of antiviral tablets in a certain dosage in order to suppress the activity of the virus.
Immediately before birth, the walls of the birth canal are treated with chlorhexidine. Suppressive therapy in combination with antiseptic treatment of the birth canal can almost completely reduce the risk of infection of a newborn with genital herpes.
Clinical manifestations
In accordance with the international classification and depending on the clinical manifestations, primary and recurrent genital herpes are distinguished. The latter, in turn, is divided into clinical forms:
- Typical, which is accompanied by the presence of characteristic lesions on the skin and mucous membranes of the external genitalia.
- Atypical, or latent, presenting significant difficulties in terms of diagnosis. It is characterized by the presence of chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the internal genital organs in the form of colpitis, vulvovaginitis, endocervicitis, endometritis, salpingoophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes) with laboratory (bacteriological and microbiological) confirmation of the herpetic nature of these inflammatory processes, which is not always possible.
- Asymptomatic with virus isolation - as a result of a virological examination of material (smears) from the genitourinary tract, the herpes simplex virus is sown, but there are no clinical symptoms of damage to the skin of the genitals and the mucous membrane of the genitourinary tract.
It is very important to be examined and identify genital herpes when planning pregnancy. Most often, a primary genital tract infection does not cause any symptoms, especially among people who have previously had a disease caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1. In these cases, infection with the second type of virus occurs in the form of a recurrent form or latent carriage.
At the same time, the acute phase of the disease or relapse of genital herpes during pregnancy is not always detected using standard laboratory microbiological and bacteriological methods. As a result, the woman does not receive the necessary specific treatment. She becomes a virus carrier and a source of infection of the fetus.
Pregnancy and genital herpes
There are several forms of the virus. One of them is genital herpes. Infection occurs through sexual contact. The skin of the external genitalia and the genitourinary system (mucous) are affected. Microorganisms are spread throughout the body through the circulatory and lymphatic systems. The incubation period lasts up to 11 days. Once in the human body, this form remains in it forever. At the same time, it may not manifest itself, being in a “sleeping” state. In order for the virus to manifest itself, it, like any other form of herpes, requires favorable conditions, as discussed above.
The appearance of watery blisters, rashes on the labia majora and minora, ulcers, erosive lesions, burning, redness, itching, swelling - all these are signs of genital herpes. In parallel with this, pain occurs in the groin and discharge (from the urethra and vagina). Urination is accompanied by pain and burning.
Additional symptoms may also be present: headache, malaise, fever (slightly above normal), poor sleep. If the virus manifests itself atypically, then its only sign is vaginal discharge.
Genital herpes during pregnancy is a dangerous disease. Its negative impact is second only to rubella in terms of impact. The virus infects the placenta, its membrane, and amniotic fluid. This can cause disturbances in the formation and development of the fetus. In this case, infection may not manifest itself immediately, but only after the baby is born. Premature birth, miscarriage, abnormalities in the development of the child are the consequences of exposure to genital herpes.
If a woman gets sick with this form of herpes for the first time, and this happens during pregnancy, the risk is maximum.
The first trimester is the time of formation of the organs of the unborn child. Encephalin, microcephaly (underdeveloped brain), hydrocephalus (accumulation of fluid in the skull), heart defects are consequences of genital herpes.
Infection in the second trimester leads to fetal death and miscarriage. If the baby remains alive, then the list of congenital anomalies is also huge: jaundice, pneumonia, thrombosis, impaired functioning of the organs of hearing and vision.
Primary genital herpes is also dangerous for the expectant mother herself. Spreading throughout the body, the virus causes diseases such as hepatitis, meningitis, and encephalitis. If assistance is provided improperly, there is a high probability of death.
CMV and HSV during pregnancy
HSV 1 during pregnancy
According to the latest data, the herpes simplex virus type 1 is present in more than 90% of the world's population. Usually it lies dormant in the peripheral nervous system and does not pose any threat to humans. As soon as the immune system weakens, the herpes virus becomes active - this usually manifests itself in the form of a cold on the lips. In addition to being aesthetically unattractive, such blisters can be very itchy and itchy. In such cases, we are talking about the herpes virus type 1, and it is usually not dangerous.
HSV 2 during pregnancy
The real danger lies in the type 2 virus, when blisters appear directly on the genitals! This type of virus is much less common, but it also causes more severe consequences during pregnancy. Moreover, antibodies to the virus of the 1st body against the virus of the 2nd type are completely powerless.
It is no secret that with the onset of pregnancy, the expectant mother’s immunity weakens significantly, and the risk of contracting HSV, like any other virus, increases significantly.
In ordinary life, despite the fact that the virus does not appear outwardly, it is stored throughout the body:
- in blood;
- in the lymph;
- in saliva;
- in tears;
- in urine;
- in sperm.
Since there are already antibodies in the blood against the first type virus, there is no danger to pregnancy, health and development of the baby. However, the second virus can be harmless only in case of re-infection, when antibodies are also already present in the pregnant woman’s body.
The most serious danger lies in cases when infection with genital herpes occurs for the first time, that is, when a pregnant woman does not yet have antibodies to the virus in her blood.
CMV during pregnancy
CMV or cytomegalovirus belongs to the group of herpes viruses. It occurs quite often, but does not cause much harm to the body. The virus cannot be cured completely - it remains forever in the nerve cells in a dormant state, becoming more active in some cases of weakened immunity.
Primary infection usually occurs in early childhood and outwardly resembles an ordinary acute respiratory viral infection.
Content
- CMV and HSV during pregnancy HSV 1 during pregnancy
- HSV 2 during pregnancy
- CMV during pregnancy
- HSV during pregnancy: first trimester
Some of the most dangerous viruses include HSV (herpes simplex virus) and CMV (cytomegalovirus). HSV during pregnancy is an extremely dangerous condition that requires urgent medical intervention. It is not dangerous for an adult, but it can cause irreparable damage to a fetus developing in the womb.
Types of herpes
It should be noted that there are 2 main stages of a viral infection in the body:
- Primary – develops when the virus enters the recipient’s body for the first time.
- Recurrent – accompanied by periodic exacerbation of symptoms. In this case, the viral form is in a “dormant” state in the body and manifests its activity when the immune system is weakened.
Let's look at the main types of herpes virus:
- Type 1 is considered the simplest. It appears in the form of small bubbles filled with liquid, their location is lips, face, mucous membranes;
- Type 2 – includes the genital herpes virus. It spreads to the woman’s genitals, with symptoms similar to those of herpes simplex;
- Type 3 is the virus that causes chickenpox and shingles. It is worth noting that these forms are quite rare among pregnant women;
- Type 4 This includes the well-known Epstein-Barr virus, which affects the lymph nodes, internal organs and systems of the recipient;
- Type 5 – cytomegalovirus infection. It tends to affect the liver, spleen and causes disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
The last two forms of herpes are considered especially dangerous during pregnancy. Infection can occur both before and after fertilization of the egg. That is why, among the mandatory studies, these two forms of herpes are paid the most attention.
Causes
About 95% of the entire population are carriers of the virus. Primary herpes occurs as a result of infection through contact, blood transfusion and organ transplantation. Routes of transmission: sexual, airborne, blood.
The virus enters the body and can remain latent for a long time. It is activated as a result of weakening of the body (during pregnancy, immunity sharply decreases).
Causes of herpes during pregnancy:
- overwork, nervousness, stress;
- colds, hypothermia;
- hormonal changes;
- taking antibiotics;
- chronic diseases in acute form;
- deficiency of vitamins in the body.
Relapses
Like all herpes viruses, herpes simplex, once in the body, never leaves it. People who have had genital herpes once usually experience recurrences of the disease. This happens when the virus moves from the nerve ganglia - its permanent place of residence - along nerve fibers to the skin and mucous membranes.
Repeated episodes are easier, and their frequency can vary from several throughout life to very frequent, more than 12 times a year. There are two fundamentally different approaches to the treatment of recurrent genital herpes.
Laboratory diagnostics
The diagnostic process includes a mandatory test for antibodies to this virus, types 1 and 2. Only a specialist can decipher them. But to have a general idea, you need to know:
- If the result is negative, both IgG and IgM are negative. This indicates that the woman is 100% healthy and does not contain the virus in her body. There is no cause for concern, but to avoid infection it is worth taking preventive measures.
- If IgG is positive, while IgM is negative, this means that the body has the virus, but has developed strong immunity. In this case, planning a pregnancy is possible; the risk of infection of the child in the womb is 3%.
- If IgG is negative and IgM is positive, this indicates a recent onset of infection and the absence of stable immune protection. It is recommended to make an appointment with an infectious disease specialist and postpone pregnancy.
- If both indicators have a positive value, it is worth considering two scenarios: the infection happened recently or a long time ago, but the virus has become more active. It is best to postpone conception until high-quality antiviral therapy has been carried out.
Based on the results of laboratory diagnostics, a conclusion can be drawn about the presence or absence of the disease and its severity.
The course of pregnancy with confirmed HSV carriage
If the progression of the virus appeared before the moment of conception, and it is primary, with repeated inflammation the risks are minimal. To confirm the diagnosis, a woman must visit her doctor. The results will determine the level of immune protection and the degree of risk for the child. During pregnancy complicated by symptoms in the form of a rash, acyclovir is prescribed. The dosage and duration of treatment are prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis.
Herpes on the lips in the second trimester
Primary infection with HSV in the second trimester is no longer as dangerous for the fetus as in a short period of gestation. He already has the basic structures of his organs, so the herpes virus does not cause developmental abnormalities. But you cannot relax and not treat herpes, since in the 2nd trimester it disrupts the functioning of the placenta and provokes fetoplacental insufficiency. Its consequence for the fetus is chronic oxygen starvation. This condition delays intrauterine development, and the baby is born either too weak or underweight.
Severe HSV in the mother is fraught with pathologies of the fetal nervous system. This part of the future human body is actively formed during pregnancy in the second trimester, or more precisely, at its very beginning, from the 12th obstetric week. Underdevelopment of the nervous system affects the newborn with meningitis or viral encephalitis. Negative consequences for the baby’s body are usually associated with the mother’s immunodeficiency state.
When a periodically recurrent infection is reactivated, the risk of fetal pathology in the 2nd trimester is minimal. Antibodies produced by the mother's body are transferred to the child through the placenta and protect him from the virus.
Revealing the secrets of herpes
Herpes is an intracellular virus that parasitizes the cells of the human body, because it needs this biological material to reproduce. Today, there are 8 main types of herpes, but the most common is the herpes simplex virus (abbreviated HSV) - these are types 1 and 2.
Photo of herpes virus
Herpes type 1 or labial
The first type is the most favorable. This herpes virus in the blood of pregnant women provokes the appearance of blistering rashes on the lips and mucous membranes of the mouth, which is why it is also called herpes of the lips. The infection can be contracted through airborne droplets, as well as through household contacts and during a kiss.
Symptoms of the labial form manifest themselves in four stages of development:
- At the first stage, burning, itching, and discomfort on the lips and mucous membranes begin. Some women may experience increased body temperature, a feeling of body aches, weakness and general malaise.
- At the second stage, painful sensations appear on the lips and swelling appears, in place of which vesicular rashes filled with exudate develop. After some time, they burst and a colorless liquid flows out of them.
- The third stage of the disease is dangerous because the exudate of the burst blisters contains a large amount of infection. After this exudate flows out, ulcerative wounds remain at the site of the rash.
- Stage 4 is characterized by the formation of scabs (crusts) on the affected skin. Recovery is coming
If you are wondering whether herpes is dangerous during pregnancy in the first type of course, the answer in this case will be the following - with a favorable course, the labial form rarely causes complications. But you need to understand that no one can give a 100% guarantee that the pathogen will not begin to progress and will not enter the systemic bloodstream.
During the initial stages of pregnancy, the placenta is not yet well formed, which means that the baby is absolutely unprotected and is in potential danger in the form of severe malformations and antenatal death.
Herpes rash on lips
Formation of crusts
Herpes type 2 or genital
In this case, there is already a serious danger of herpes during pregnancy compared to the previous option. You can become infected with a genital infection through household and sexual contact.
The latter method is prevalent and is observed during unprotected sexual contact. Often, genital herpes can be combined with other infectious venereal diseases: mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, ureaplasmosis, etc.
This type is manifested by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of slight watery vaginal discharge , which can last about a week. In some situations, this is the only symptom indicating this pathology.
- Rashes in the form of small blisters filled with colorless liquid localized on the mucous walls of the vagina and lining of the cervix, as well as on the skin of the external genital organs. Afterwards, these rashes burst and leave behind ulcers that do not heal for a long time.
- This rash is preceded by itching and a burning sensation . Such symptoms are also harbingers of the disease.
- Signs of general intoxication of the body in the form of headache, malaise, weakness, muscle pain, increased body temperature to febrile or subfebrile levels.
Attention: in case of exacerbation of genital herpes immediately before childbirth, the question of performing a caesarean section is raised.
Genital herpes
What do rashes look like?
Herpes type 3 or varicella zoster virus
This virus belongs to the same family and resembles other herpes viruses in its structure and function, but is the causative agent of two different diseases - shingles and chickenpox. The infection is highly contagious and is transmitted by airborne droplets.
In case of infection with chickenpox, a strong immunity is formed. After recovery, the infection remains in the body and persists for a long time in the sensory nodes.
When the “dormant pathogen” is activated (this can happen after many years), the development of herpes zoster is observed. Repeated incidences are extremely rare.
Shingles
As we have already understood, herpes zoster during pregnancy appears if a woman has previously had chickenpox (popularly called chickenpox), through close contact with an infected person, or through decreased immunity.
This type of disease manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a unilateral widespread rash on the skin along the large nerve trunks;
- the occurrence of neuralgic pain in the area of the rash, due to the fact that the infection “lives” in the nerve cells;
- the addition of symptoms of intoxication in the form of weakness, increased body temperature, malaise, etc.
Also, herpes zoster during pregnancy can have other forms of occurrence - Ramsay-Hunt syndrome, motor and ophthalmological. Cases of atypical variants in the form of abortive, hemorrhagic, cystic and gangrenous forms cannot be excluded.
This type of infection is especially dangerous in the last stages, when the pathogen can easily penetrate the placenta. For the purpose of prevention at birth, the child is given an immunomodulatory course and antiviral therapy.
Herpes zoster variant
Now is the time to talk about chickenpox. This is another type of disease that the infection presented can cause.
In frequent cases, chickenpox appears in childhood, after which, as we have already said, strong immunity develops. However, situations cannot be ruled out when a pregnant woman has not yet had it, that is, there are no antibodies, and she can easily become infected with it.
Chickenpox is very dangerous when carrying a baby, especially when it comes to the early stages. Here, pregnancy fading or miscarriage is possible. Herpes in the last month of pregnancy also easily penetrates the placenta and enters the child’s body, which subsequently affects its chronic course.
Clinical severity appears quite late and carries the following symptoms:
- weakness and malaise;
- increase in body temperature;
- headache;
- the appearance of a characteristic rash, represented by small blisters that itch, causing severe discomfort.
The appearance of such signs implies a mandatory visit to the attending physician.
Chickenpox