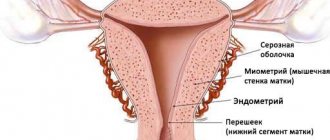
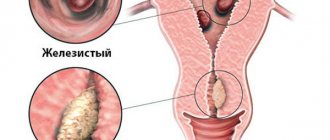
Any pathological changes in the structure of the endometrium have a negative impact on a woman’s reproductive function (cycle disruption, infertility and miscarriage, development of neoplasms).
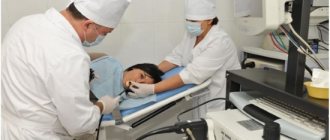
One of the most modern diagnostic methods is pipell biopsy of the endometrium. During the operation, a particle of the uterine mucosa is removed, then a histological examination is performed. The operation allows you to identify atypical changes and establish the cause of menstrual irregularities or infertility.
Depending on the technique, there are several ways to extract tissue: partial curettage, surgery, hysteroscopy.
Description of endometrial biopsy
The purpose of an endometrial biopsy is to study to identify the causes of infertility, miscarriage, and menstrual irregularities. The procedure is also used in preparation for IVF. Allows you to obtain complete information about the condition of the mucous membrane.
Aspirate from the uterine cavity is also taken in case of hormonal abnormalities, a history of miscarriages, uterine bleeding that is not associated with menstruation, hyperplasia, and malignant neoplasms.
During the procedure, mucous particles are surgically removed. Depending on the tactics of execution, tissue sampling is performed using a tube, a vacuum apparatus or a syringe. In conventional curettage, a surgical curette is used for diagnostic purposes. Material for research can also be obtained during hysteroscopy using a probe. Equipped with a video camera, the device has a small surgical instrument that takes precise samples from the lining of the uterus (endometrium).
Modern equipment allows you to take a sample of the mucous membrane in the desired area - the uterus, the cervical canal - without damaging healthy tissue. The possibility of complications and discomfort during the operation is minimized. A biopsy is considered a minor surgical procedure. It is usually performed routinely for diagnostic purposes, but in rare cases it is performed as part of the main operation or as an emergency.
Indications
What does a pipel biopsy show? For what conditions and diagnoses is it prescribed?
- Pipel endometrial biopsy before IVF or natural pregnancy is performed in order to establish or deny the presence of obstacles to pregnancy;
- In case of infertility or frequent miscarriages, especially in the early stages, it is considered a necessary and informative diagnostic procedure;
- It is carried out for uterine bleeding of unknown origin, as it helps to establish their cause;
- Necessary if an oncological process is suspected;
- Quite often it is also carried out if hyperplasia or endometriosis is suspected;
- Sometimes it is carried out when viral, bacterial, or fungal infections are suspected;
- It is often carried out for hormonal abnormalities in order to establish their effect, nature, and sometimes the cause, for further effective treatment.
In some cases, such a diagnosis is also carried out for other diagnoses and suspicions of them.
https://youtu.be/4f6fpO_w6Ss
Carrying out diagnostics
Diagnosis using aspiration biopsy or another type of material collection is carried out for various uterine defects, absence of menstruation, and bleeding during menopause.
If the study is carried out as planned, the operation is preceded by the following diagnostic measures:
- taking a smear for cytology and flora;
- colposcopy behavior;
- Ultrasound of organs located in the woman’s pelvis;
- General analysis of urine and blood.
An emergency biopsy is performed in case of suspicion or precise establishment of the presence of a malignant neoplasm in the uterine cavity or cervix, and the day of the cycle is not taken into account.
Also, as part of the preparation, it is recommended:
- refusal to take drugs that affect blood clotting and anticoagulants;
- temporary abstinence from sexual activity (at least three days before surgery);
- refusal to douche;
- exclusion from the menu of dishes that cause gas formation.
Improper preparation for surgery can cause various complications, such as vascular damage (resulting in bleeding), endometrial rejection, and cycle disruption.
Preparation
It is in order to exclude potential contraindications that a number of studies are carried out before prescribing this manipulation. You need to do the following:
- Perform an ultrasound examination to confirm or refute the presence of pregnancy;
- Take a vaginal smear to determine sterility in order to exclude the presence of infections, including sexually transmitted ones;
- A coagulogram is necessary for those who do not know exactly what their blood clotting ability is.
In addition to such research, a number of other measures need to be taken:
- Avoid sexual intercourse for 3 days before the intervention;
- Maintain good hygiene;
- Stop taking medications that thin the blood at least a week before the intervention, as they reduce blood clotting, which may result in bleeding (cancellation is possible only in consultation with the doctor);
- Stop taking hormonal medications (strictly in consultation with your doctor) at least a week before the procedure;
- Carry out the procedure strictly on the established day of the cycle, as this can have important diagnostic significance.
On what day of the cycle is a pipel biopsy performed? It depends on the purposes for which it is carried out. Usually, the most optimal day of the cycle is prescribed by a specialist. Proper preparation for pipell endometrial biopsy is very important, as it affects the information content of the procedure.
When to take aspirate from the uterine cavity
An endometrial biopsy is performed according to indications determined by the doctor observing the woman. Taking an aspirate from the uterine cavity is necessary in the following cases:
- suspicion of tumor growth;
- scanty menstruation or uterine bleeding, including dysfunctional;
- in the presence of inflammatory processes of the endometrium;
- determining the cause of infertility, spontaneous abortions or missed pregnancies;
- amenorrhea without pregnancy for unknown reasons;
- preparation for the IVF procedure;
- pregnancy pathologies.
Scraping the endometrium allows you to determine its structure and identify atypical cells. Its thickness and exact location are also determined.
The procedure is used if, after a standard gynecological examination and ultrasound, the doctor detects pathological changes in the endometrium. Diagnosis is always carried out before removing fibroids or myomas, polyps, or malignant neoplasms.
Contraindications
The list of contraindications is the same for all variants of this diagnostic procedure. Pipelle biopsy is not performed in the following cases:
- Pregnancy. Even in the presence of unprotected sexual intercourse before the operation, when determining conception is impossible with a standard home test, a test is done to determine the level of hCG to accurately determine the fact of fertilization.
- Blood clotting disorders. In such cases, aspiration biopsy is not performed. Sometimes the diagnostic measure is preceded by treatment of the underlying pathology.
- Presence of infection (chronic or acute process). Pathology is indicated by pain, itching, bleeding not associated with menstruation, and purulent discharge.
- Contraindications also include hemophilia, a high degree of anemia, and some chronic diseases in the acute stage.
The list of contraindications is strictly taken into account before diagnosis in order to avoid side effects after surgery.
Suspicion of cancer pathology is a direct indication for diagnostics, and an emergency one at that. In this case, the biopsy is performed with a minimum number of contraindications.
Decoding the results
The interpretation of data is carried out exclusively by a specialist. Decoding is done under a microscope. A woman can receive the final result a week after the procedure.
The conclusion will have four parts.
Information content
An uninformative sample means that the material does not contain a sufficient number of cellular structures of endometrioid tissue.
An informative biopsy is characterized by the presence of a sufficient number of mucosal cells in the area under study.
Microscopic description of biomaterial
In this column, the specialist indicates data on the type of epithelium, the shape of stromal cells, its deciduality and fibroplasticity and other indicators.
Macroscopic description
In this case, data will be provided on the color, weight of the samples, consistency, presence of blood clots and blood clots.
Diagnosis
Based on all the data, the gynecologist makes a final diagnosis.
What is the procedure
Endometrial biopsy is performed using different methods, but the aspiration option is most often used. It is less traumatic, there is absolutely no discomfort during the procedure, the risk of complications and side effects is minimized, and the information content of the study is quite high.
The analysis is taken after appropriate preparation for the procedure, which begins 3 days before the procedure. Immediately before the examination, the intestines are cleansed with an enema.
A biopsy of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal or uterus lasts no more than 3 minutes (on average 30–60 seconds depending on the qualifications of the doctor). Rarely, a woman may need anesthesia. The absence of nerve fibers allows manipulation to be performed with minimal use of painkillers.
A biopsy for erosion involves taking material from the cervical or uterine canal using a vacuum/syringe/tube/curette. Additionally, the doctor can remove polyps.
Curettage of the uterine lining and further histological examination of the material are carried out for women of any age, including during menopause, before or after childbirth and pregnancy.
Technique of the procedure
Taking a biopsy using a pipell instrument is an innovative research method and has a slightly different execution technique from a conventional biopsy.
The procedure consists of several stages:
- the woman is located in the gynecological chair;
- the doctor conducts an initial examination and palpation;
- A plastic tube is inserted through the cervical canal of the cervix.
After its tip rests against the wall of the uterus, the gynecologist extends the piston, which leads to the suction of the contents of the uterine cavity and pieces of epithelium into the pipe.
After all the manipulations are completed, the instrument is removed, and the biological material contained in it is placed in a container with a special solution and sent to the laboratory. In terms of time, a pipel biopsy of the endometrium of the uterus takes less than a minute, and together with the initial examination, its duration will not exceed a quarter of an hour.
Timing and technique of performing a biopsy
Endometrial biopsy is performed at certain periods of the cycle depending on the diagnostic goals pursued:
- When clarifying the factors of infertility against the background of anovulatory cycles and the minimum luteal phase, the analysis is done one day before the onset of menstruation or on the first day of bleeding.
- In the case of acyclic bleeding not associated with menstruation, curettage of the mucous membrane is prescribed on the first or second day of menstruation.
- When diagnosing polymenorrhea, manipulation is carried out between the fifth and tenth days of the cycle.
- To determine the cause of hormonal imbalance, a sample is taken in the second phase of the cycle between the 17th and 25th days.
- If the presence of benign or malignant neoplasms is suspected, a scraping is taken regardless of the day of the cycle (emergency).
Any study involves the insertion of a special device into the vagina to collect a sample of the endometrium. The methods differ in duration, possible side effects, and information content.
Scraping
Biopsy curettage is both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. Curettage was previously used not only to identify endometrial pathology, but also for emergency treatment of bleeding.
Curettage of the cervix is used less frequently today than other methods, since it is performed blindly, sometimes under the control of an ultrasound machine or visualization of the organ using a hysteroscope. The manipulation is performed under general anesthesia, often intravenous.
This procedure not only makes it possible to identify the cause of changes in the structure of the mucous membrane, but also has a therapeutic effect:
- emergency stop of bleeding from the uterus;
- removal of the damaged area of the mucosa;
- removal of glandular polyps and other neoplasms (except malignant ones).
The optimal time for curettage is considered to be the 3-4th day before menstruation, and in case of cycle disorders, the first day of the appearance of acyclic blood discharge.
The total operation time takes up to 20 minutes; intravenous anesthesia is preferable for pain relief. During the operation, the external genitalia are disinfected with iodine-containing preparations, and urine is removed using a catheter.
After a short-term anesthesia is administered, the cervical canal is opened with a special instrument, the material is scraped out with a surgical curette and placed in a special bottle. After this, a hysteroscope is used to examine the mucous membranes of the uterus, then with a larger curette, material is again taken from the inner surface of the organ. The resulting sample is placed in a separate bottle and sent for histology.
On what day of the cycle is it done?
If the main task of the diagnostic measure is to determine the level of infertility, then the analysis is recommended to be done the day before the onset of the menstrual cycle or on the first day after its onset.
If polymenorrhea is diagnosed, then a study is done on days 5 and 10.
In cases where the presence of acyclic bleeding is noted, a biopsy is scheduled 1-2 days after menstruation begins.
On this topic
- Biopsy
Can a biopsy be wrong?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- October 16, 2020
When the goal is to determine benign or malignant neoplasms, the analysis is carried out regardless of the cycle.
If there is a suspicion of hormonal imbalance, a CG biopsy is used. It is necessary to collect biomaterial at intervals of 7-8 days during the 1st menstrual cycle.
Aspiration biopsy
The aspiration technique for obtaining tissue samples is used more often than curettage. With this technique, expansion of the cervical canal is not required, since the procedure is quite painful. The flexible tube used during the procedure reduces the risk of trauma to the uterine wall to zero.
The aspiration tube allows you to obtain material from any part using sterile devices, which reduces the risk of infection. Also, if an aspirate is used, the biopsy is taken almost painlessly, the uterus recovers faster, and the woman can return to her normal life immediately after scraping.
Negative factors of performing aspiration biopsy include the impossibility of simultaneously examining the structure of all areas of the endometrium. There is a risk that local small areas of damage will remain unexamined.
The results of histological examination of material selected in this way are highly informative.
The collection of particles from the uterine mucosa is carried out on different days depending on the tasks:
- to remove a polyp immediately after the end of menstruation;
- on the 1st day of the cycle with atypical blood discharge;
- when carrying out hormonal treatment - on the 17th–24th day of the cycle (including to monitor the prescribed treatment);
- in case of long and painful periods - on the 7th–10th day;
- to clarify the factors of infertility - 2–3 days in advance;
- regardless of the day after/before menstruation when determining a malignant neoplasm.
Aspiration biopsy is performed using several methods: collecting tissue particles directly into a syringe, placing tissue samples in saline, or using a vacuum unit.
Curettage
The classic method is to collect the endometrium with a curette. During the procedure, the cervix is dilated and fixed, then the surgeon uses a sterile curette to scrape the mucous layer.
As a rule, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia. In this case, intravenous or mask anesthesia is more often used. In this regard, a woman should undergo a preliminary examination, if necessary, stop taking certain medications, and not take food or water after 6 pm the previous day.
Curettage is performed for hyperplasia of the mucous membranes, pathological bleeding, non-developing pregnancy, or suspected neoplasm.
Aspiration biopsy
In this case, the collection of material for research is carried out using vacuum aspiration. Aspiration curettage is less traumatic than classical. During the procedure there is no need to dilate the cervix, and there is virtually no pain. In case of increased sensitivity, short-term drug anesthesia can be used.
Preparation for vacuum aspiration involves avoiding douching, sanitary tampons, and sexual intercourse for 3 days before the procedure. In the evening before the biopsy, it is recommended to do a cleansing enema. Since during manipulation there is a risk of infection of the uterine tissue, measures are taken to eliminate infectious and inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity.
An aspiration biopsy is performed to diagnose uterine pathologies. A disadvantage of the procedure is the relatively smaller volume of material for research than with classical curettage.
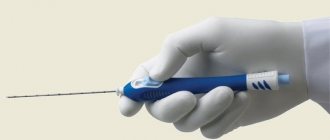
Pipelle biopsy
The Pipelle biopsy method is carried out according to a similar scheme with aspiration, but using a special thin tube with a diameter of 3 mm. The method does not require expansion of the uterus, is low-traumatic and does not lead to the development of complications.
The procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis, the preparation is the same as before aspiration. A Pipel biopsy is performed using a special Pipel tip, which is inserted into the uterine cavity. Next, when the piston is activated, a fragment of the endometrium is separated for biopsy.
As a result of this procedure, no wounds are formed on the mucous membranes, which reduces the risk of infection, and the biopsy is painless. Pipelle biopsy is recommended for young women who have not yet given birth to diagnose endometrial pathologies, identify the causes of infertility, and determine hormonal receptors.
CUG biopsy
During CUG biopsy, the cervical canal is not dilated. The surgeon removes the endometrium in thin strips along the entire cavity using a small curette. A procedure is prescribed to identify the body's response to hormone therapy, determine the degree of maturation of the mucous membranes at physiological hormonal levels during the cycle (several biopsies are assumed at different phases).
CUG biopsy is a low-traumatic and safe manipulation in which a slight sampling of the endometrium is carried out in the form of thin strokes. Sufficient information content is ensured by collecting several strips of mucous membrane from different areas of the uterine cavity.
Pipelle biopsy
This diagnostic method is preferable to aspiration biopsy and curettage. During diagnosis, the catheter replaces a small plastic cylinder. At one end, placed in the uterine cavity, there is a small hole on the side, at the other there is a piston. When the material is removed, a vacuum is created, the hole is attached to the wall of the uterus, and mucosal cells are literally sucked into the device.
The procedure is also performed at certain periods of the menstrual cycle, depending on the type of examination. The technique has a number of advantages:
- painless, no anesthetics are used;
- no side effects;
- carried out without dilation of the cervix;
- most informative;
- a flexible tube allows you to control the depth of insertion, which reduces the risk of injury to the internal walls of the uterus;
- no hospitalization required;
- fewer contraindications, possible use in women with serious chronic or acute diseases.
This technique also makes it possible to identify the causes of hormonal disorders, infertility, and assess the growth of tumors.
Consequences
If the preparatory recommendations are not followed, as well as if there are violations during the manipulations, some complications may arise.
Perforation of the uterine fundus
This condition occurs if the procedure was performed by a doctor with little experience. In such a situation, severe blood loss will be observed, which is the basis for visiting a medical facility.
Bleeding
Minor discharge after a biopsy is considered normal. In addition, with this condition, the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen is often noted. If the bleeding is intense and does not stop for a long time, you should consult your doctor.
Infection of the uterine body
Penetration of infection into the uterine cavity is one of the most dangerous complications. The reason for this problem in most cases is non-compliance with recommendations during preparation and rules for performing a diagnostic study.
When infected, severe pain, intoxication of the body, and brown discharge with an unpleasant odor are noted.
Zug biopsy
This technique is one of the least dangerous and least traumatic compared to endometrial aspiration biopsy or curettage. Can be executed a maximum of three times per loop.
This technique is not used to diagnose cervical precancer or malignant neoplasms.
To determine the cause of uterine diseases, the cervical canal is artificially expanded, and a small curette is carefully inserted into the organ cavity. With its help, tissues are collected from the surface of the inner layer.
Line scraping of the endometrium is carried out from the depths outward up to the internal os of the cervix. Two samples of material are collected at a time.
The procedure is performed on the 1st–2nd day of menstruation or after it. The taken uterine material is also sent for histology, which makes it possible to accurately identify the causes of infertility, hormonal changes, uterine bleeding, and the location of tumors.
Period after the procedure
After a pipel biopsy, women often feel satisfactory and there is no need for hospital observation. You may experience discomfort, similar to menstruation, for 24-48 hours after the procedure. In the first days, there may be various types of bleeding from the vagina. During this period, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse. After 3-4 days, intimate relationships can be resumed, making sure to use contraception.
After aspiration biopsy of the endometrium, menstruation occurs on time or with a delay of up to 7-10 days. If the delay is longer, you should consult your gynecologist. It is also important to tell your doctor if you feel unwell in general, fever, dizziness or fainting.
Infertility procedure
Endometrial biopsy is considered one of the leading methods for clarifying the factors that provoke infertility, miscarriage, spontaneous abortions, interruption of fetal viability and other disorders of female reproductive function. In addition, it is possible to establish the causes of uterine diseases with a biopsy, and increase the chances of embryo implantation during IVF.
The procedure helps not only to identify factors of infertility. Even pregnancies that occur as a result of in vitro fertilization are observed more often. A high percentage of successful IVF was noted. Positive effects were recorded when the biopsy was performed in the month preceding fertilization.
To clarify the factors of infertility, the operation is performed according to the same scheme as the usual diagnostic procedure. Examination of the material allows us to identify the presence or absence of atypical cells, including precancerous conditions, hormonal disorders, inflammatory processes, hyperplasia and other factors leading to lack of conception.
https://youtu.be/bzv8jkje9G4