Yellow vaginal discharge before menstruation can have several causes. In most cases, this symptom should not be a cause for concern, but sometimes it indicates an infection or is an early sign of pregnancy.
Vaginal discharge in women can be of different colors. Their color and consistency are affected by numerous factors, such as diet, medications, stress and sexual activity.
Yellow vaginal discharge is relatively common and does not usually indicate any health problems. It can be an indicator of several body conditions. The causes of yellow discharge vary. They can occur as a result of the natural functioning of the body or become a consequence of infectious diseases and pregnancy.
It is important to note that if a woman is concerned about the color or consistency of her vaginal discharge, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms, she should talk to her doctor about the problem.
Three common causes of yellow vaginal discharge are listed below.
Sparse and watery yellow vaginal discharge
Yellow vaginal discharge can be caused by several reasons
Rare and watery yellow vaginal discharge in most cases does not indicate pathological conditions in the body. As a rule, they indicate that a woman is close to her period and will soon begin a new menstrual cycle.
In most cases, the yellow tint is the result of mixing early menstrual blood with mucus.
Other signs that your period is approaching include symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. These include the following:
- acne or other skin changes;
- breast tenderness or tenderness;
- feeling tired;
- abdominal cramps;
- problems with bowel movements, such as constipation or diarrhea;
- bloating or gas accumulation;
- headaches or mood swings;
- feeling of irritability;
- depression.
Women who do not experience symptoms indicating the onset of their period, or are confident that yellow vaginal discharge is not associated with an impending period, should understand that this symptom may indicate the presence of an infection.
https://youtu.be/1JzeFKsiEAQ
What to do if suspicious discharge appears
Considering that discharge can be both normal and pathological, great attention must be paid to your own feelings. You will also need to decide on the phase of the menstrual cycle. The following possible actions are:
- if there are no signs of pathological processes, and the appearance of yellow secretion occurs in the second phase of the cycle, you can calm down and wait for the start of menstruation;
- if there is a delay, a test is required to determine the presence of pregnancy;
- when, in addition to mucus, itching, burning or pain occurs, a visit to the gynecologist is necessary;
- It wouldn’t hurt to analyze sexual contacts of the last three months – that’s how long the incubation period of certain sexually transmitted diseases lasts;
- if the cause is an allergic reaction, you will need to eliminate allergens - change your underwear, giving preference to natural materials, refuse panty liners, carry out hygiene procedures using only warm water twice a day. You may need to take antihistamines and use topical agents.
If diseases are detected during a gynecological examination, full therapy is necessary. The danger of incompletely cured infections is their progression into chronic disease and the possibility of damage to other organs.
https://youtu.be/HX8DySp-UUU
Before menstruation, before ovulation, and even in the first weeks after conception, discharge sometimes changes in consistency and color under the influence of hormonal changes in the body. Yellow discharge before and after menstruation often helps to assess the degree of condition of a woman’s genitourinary system.
Sometimes there may be yellow discharge before your period
Thick yellow vaginal discharge
Thick, yellow, odorless vaginal discharge can also be a sign of menstruation, but sometimes it indicates pregnancy. A yellow tint indicates the presence of new or old blood in the mucus. The yellow color can also result from implantation bleeding in the very early stages of pregnancy. Therefore, in such situations, a woman should take a pregnancy test, especially if she has not had her period.
In fact, many women are unaware that bleeding occurs during implantation, which often appears as small spots rather than full-blown bleeding.
Other signs of early pregnancy include the following:
- fatigue;
- changes in appetite, which can include both aversion to food and strong cravings;
- nausea;
- slight dizziness;
- constipation;
- bloating;
- abdominal cramps;
- mood swings.
These symptoms are very similar to those of menstruation, so if a woman thinks she may be pregnant, she should purchase a test at the pharmacy.
However, in situations where a woman becomes pregnant a few days before her period, the test does not always immediately give a positive result. A woman can more accurately determine a possible pregnancy some period after the moment when she was supposed to have menstruation. In addition, more accurate results may be obtained some time after the woman begins and passes minor bleeding.
If a woman discovers she is pregnant, she can expect an increase in discharge throughout her pregnancy. Such discharge, which is commonly called leucorrhoea in medicine, is usually odorless or has a slight odor and a milky white color. They are not associated with any disturbances in the functioning of the body.
What does the discharge depend on?
The “correct” menstrual cycle is characterized by regularity, painlessness, and constant intervals between menstruation and duration of bleeding.
Discharge in women is due to the proper functioning of the reproductive organs. They help the vagina to be moisturized, cleansed, and the cells of the mucous membrane are renewed, while at the same time protecting against infections.
The type, color, and frequency of vaginal discharge are influenced by the state of the microflora and hormonal balance. Any change in hormonal levels or the appearance of pathological microorganisms entails a change in the nature of the vaginal secretion.
A woman’s microflora is represented by lactic acid bacteria, various opportunistic microorganisms that do not cause disease with normal immunity and proper functioning of the vaginal mucosa.
Yellow vaginal discharge with odor
Vaginal discharge with a strong and unusual odor may indicate an infection
Yellow vaginal discharge with a strong odor usually indicates an infection. This could be anything from bacterial vaginosis to sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). An example of an STD that causes yellow vaginal discharge is trichomoniasis.
Millions of people around the world have trichomoniasis, but only 30% of them develop symptoms, which include the following:
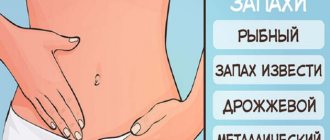
- discharge with an unusual fishy odor;
- sensitivity, itching, redness and burning;
- an increase in vaginal discharge, which may be yellowish, but also white, clear or green.
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
When a woman suspects that she is infected with trichomoniasis, she should consult a doctor. If trichomoniasis is left untreated, it can bother a person for several months or even years.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on complaints and a typical clinical picture. The medical history and the presence of sexual intercourse without a condom are clarified. If necessary, the doctor prescribes an additional consultation with a dermatovenerologist. A gynecological examination is mandatory.
It is also necessary to donate blood for a general analysis. To identify the pathogen, vaginal swabs are taken for culture. At the same time, bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics is determined.
One of the modern laboratory tests is the PCR method. With its help, pathogens of sexually transmitted infections are identified. Additional studies include ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs and MRI of the abdominal cavity.
What is yellow vaginal discharge?
Every day, the female body produces vaginal discharge. Their quantity and consistency help determine the phase of the cycle. Before ovulation occurs (in phase 1 of MC), a little clear mucus is secreted. With the onset of ovulation, the mucus more closely resembles egg white. Then there is more discharge. Its consistency is thick, and its color is white with a slight tint of yellow.
Thus, light yellow discharge before menstruation is normal. At the beginning of menstruation, droplets of blood join them. The mucus becomes pink or brownish. Its smell is light and specific. The woman does not feel any unpleasant symptoms.
The reason for the appearance of yellow discharge in different phases of the cycle can also be non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. Initially white mucus, as it remains on the laundry for a long time, it turns into yellow stains. Lack of timely care for the intimate area leads to the fact that discharge begins to accumulate and pathogenic bacteria multiply in it. They make the discharge yellow. Next, an inflammatory process develops, vaginitis or thrush.
Yellowish discharge before menstruation may also appear due to allergies. Unpleasant reactions are provoked by synthetic and lace fabrics of underwear or unsuitable intimate hygiene products. An allergy in the groin is manifested by itching, burning and redness. But the discharge does not have an unpleasant odor.
The type, color and frequency of vaginal secretion determine the hormonal status and state of the local microflora. An imbalance in the ratio of hormones or harmful and beneficial microorganisms changes the nature of vaginal discharge.
What is considered normal
It is a rare woman who can boast of complete compliance with the norm; situations are often observed when, before the onset of menstruation, vaginal discharge of a pathological color appears - greenish with an admixture of a yellowish tint, whitish, brown or deep yellow. It cannot be said that secretion is a pathological process, since in this way the body organizes the protection of the genital organs from the effects of pathogenic agents and their excessive reproduction. But normally, such mucus does not cause any discomfort. Before menstruation, the discharge is quite abundant, but under the influence of body temperature, most of it evaporates and a small amount comes out.
Discharge in the first and second half of the menstrual cycle is different, let’s look at what is considered normal:
- The volume of mucus in accordance with the day of the cycle can vary within 0.06–4 ml/day. Before menstruation, the amount released increases, but if the fluid is completely absent, this is also not considered a pathology - the woman may not feel minor discharge.
- Often before menstruation, yellow, odorless discharge is observed if the woman is completely healthy, or it may be slightly sour. On the remaining days of the cycle, the unpleasant vaginal odor should be completely absent, otherwise the development of pathologies can be suspected.
- In the middle of the cycle during the ovulatory period, the secretion becomes viscous and resembles the white of a raw egg. As menstruation approaches, the mucus begins to acquire the consistency of a cream; immediately after the critical days, the secretion becomes liquid again.
- During the entire cycle, the structure of the mucus is homogeneous or includes small lumps that are formed from particles of epithelial tissue.
- In the first half of the cycle, a clear or slightly cloudy colorless liquid is observed from the vagina; as it approaches the critical days, it becomes white. Mucus that gets on laundry may have a yellow tint due to a reaction with oxygen.
- Yellow discharge before menstruation may be normal, but it should not cause discomfort or cause itching - unpleasant sensations indicate pathological processes occurring in the reproductive system.
https://youtu.be/qqBR_7hVDnI
Physiological causes of yellow discharge before menstruation
If a woman does not experience pain when urinating and during sex, and the presence of yellow discharge before menstruation does not affect her well-being in any way, and the discharge is completely odorless, the causes of this condition can be called natural.
Various factors provoke yellow spotting shortly before menstruation:
- Activity of beneficial bacteria. Lactobacilli protect their habitat and do not allow pathogenic pathogens to cause inflammatory processes. The slightly acidic environment of the vagina suppresses microbes, which results in the formation of protective yellowish mucus.
- Contact of mucus with oxygen. When exposed to air, vaginal secretions oxidize and, without timely care for the delicate area, acquire a specific color.
- Taking hormonal contraceptives. Contraceptives correct hormonal levels, which in turn affects the nature of the discharge.
- Physical fatigue and stress. Labor-related and psycho-emotional overloads have a bad effect on the functioning of the female body. An unfavorable psychological environment, overwork and insufficient hours of rest have a negative impact on the endocrine and reproductive systems.
- Age-related changes and diseases of the reproductive organs. Disruptions in the endocrine and gynecological sphere can provoke yellowish vaginal discharge.
What does yellow discharge with an unpleasant odor mean?
When rich or brownish-yellow vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor appears, such symptoms may indicate an infection of the internal genital organs or the development of a gynecological disease.
A visit to a specialist cannot be postponed, since many pathologies are very dangerous.
Let's look at why yellow, foul-smelling discharge occurs before menstruation:
- Vaginosis. The composition of the microflora is disrupted due to weakened immunity, taking antibiotics or endocrine disease. Pathogenic agents of Gardnerella penetrate the genital tract and begin to actively multiply, which inevitably leads to increased production of secretions. Gardnerellosis is very dangerous during pregnancy, as bacteria can cause miscarriage or premature birth.
- Endometriosis. The growth of the mucous membrane that lines the uterus from the inside occurs due to hormonal imbalance. The pathology is manifested by painful periods and brown or dark yellow spotting with an unpleasant odor.
- Colpitis. The causative agents of the disease are chlamydia, trichomonas and streptococci. The first symptoms of colpitis are foul-smelling yellow-green discharge, itching and burning in the genital area. The labia and vaginal mucosa appear swollen.
- Salpingitis. The infection affects the fallopian tubes and triggers an inflammatory mechanism. Acute salpingitis occurs with symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen, hyperthermia, chills, nausea, and yellow vaginal smear. The process affects the ovaries, uterus and bladder. The cause of salpingitis is infection of the genital tract by intestinal microbes. A nonspecific type of disease can bother a woman after an abortion, birth trauma, insertion (removal) of an intrauterine device, or during vaginal prolapse. Pain is felt not only in the abdomen, but also in the lower back, sacrum and rectum. The nature of the discharge is serous-purulent. The shade is yellow.
- Cervical erosion. Concerns young girls who began sexual activity too early and adult virgins under 30 years of age. Other causes of changes in uterine tissue are abortions, injuries to the internal genitals, hormonal disorders, sexually transmitted infections and weak immunity. The main signs of erosion are brown or dark yellow spotting in the middle of the cycle, painful urination and impaired circulatory function. Active infectious strains make mucous secretions purulent and yellow.
- Adnexitis. The ovaries and fallopian tubes are involved in the inflammatory process. The disease disrupts a stable cycle and provokes abnormalities such as adhesions, cysts, and infertility. Adnexitis is caused by sexually transmitted infections and intestinal microbes. Inflammation irritates the vaginal mucosa, causing a burning sensation inside and swelling in the organs. Foul-smelling discharge is yellow in color.
- Chlamydia. Yellow, smelly mucus may contain purulent inclusions. Sexual intercourse is painful, urination is accompanied by burning. I am concerned about itching in the vagina. Gonorrhea. Yellow discharge before menstruation becomes purulent and greenish. Then the woman feels itching and burning. The rhythm of the cycle may be disrupted.
- Trichomoniasis. The color of the discharge varies from yellow to yellow-green. The smell is reminiscent of rotten fish. The genitals itch, swell, and turn red.
Normal discharge has a slightly sour odor. They do not cause any discomfort and do not stain laundry much (the permissible daily volume is about 2 ml). Abundant, opaque mucus of a strange color indicates the development of the disease and requires medical advice.
Can yellowish discharge before menstruation indicate pregnancy?
Consider yellow spotting before menstruation as a sign of pregnancy.
Yellowish leucorrhoea after menstruation ends
Normally, after menstruation, a woman should not be bothered by vaginal discharge. Detection of problems after the end of critical days is due to the following factors:
- Chronic inflammation in the uterus and appendages (endometritis, adnexitis);
- Vulvovaginitis (inflammatory process in the lower parts of the reproductive organs);
- Polyp in the uterus or in the cervical canal (a benign neoplasm provokes a cycle disorder);
- Adenomyosis (endometrioid damage to the walls of the uterus);
- Submucous fibroid (benign nodule growing into the cavity of the reproductive organ);
- Ovarian cyst (hormonal disorders due to tumor).
The reasons can be varied, so it is important not to try to self-medicate: it is necessary, together with the doctor, to find the main factor that provokes the entry of small amounts of blood into the vagina.
Or sick
The following signs will indicate an infectious nature or inflammation (for example, as a result of hypothermia): itching, swelling, burning, unpleasant odor, rash on the genitals.
Let's look at what diseases may be manifested by discharge with a yellowish tint. And you check with your observations and feelings. But don’t diagnose yourself, much less prescribe treatment. I am giving you information for general information so that you do not guess, but when going to the gynecologist, you know approximately what to expect. Cervical erosion. Scanty yellowish discharge, often with blood streaks or pinkish patches.
Adnexitis. Yellow purulent discharge with a characteristic odor; in chronic adnexitis, it is more scanty, but is accompanied by visible irritation.
Chlamydia. Itching when urinating and not only, pain during sex. The discharge, as with adnexitis, is yellowish and purulent.
Salpingitis. Copious discharge, sexual intercourse with pain and the appearance of pinkish mucus after it. During menstruation, the stomach hurts greatly and appetite decreases.
Trichomoniasis. Greenish tint, may bubble a little. The smell of rotten fish is characteristic. Redness and severe itching are noticeable on the external genitalia.
Gonorrhea. Almost the same symptoms as with trichomoniasis: itching, burning, irritation, “greenness”. Possible delay of menstruation.
Allergy. Apart from a yellowish tint and slight irritation or rash, nothing to worry about.
Main reasons
Natural yellow discharge does not provoke irritation of the mucous membrane of the genital organs and the skin in the groin area. In this case, no therapy is required. It is enough to comply with standard hygiene standards. Causes of yellowish, odorless and itchy discharge may include:
- an increase in the amount of mucus before the menstrual cycle, during pregnancy or after the birth of a child;
- hormonal imbalances associated with age-related changes;
- diseases of the mammary glands;
- hormonal imbalance as a result of pathologies of the endocrine glands;
- taking hormonal contraception;
- stressful situations and psycho-emotional disorders.
Hygiene and “scented” pads
Observe carefully, if such discharge, without any special “side effects,” appeared once and did not recur, then carefully observe the hygiene of the genitals, wash with a weak solution of potassium permanganate to eliminate allergies, do not use pads with fragrance and purchase special soap for intimate hygiene . It does not disturb the normal acidic environment of the vagina.
If there is severe itching, pain, or bloody discharge is added to the yellow discharge, immediately make an appointment with a gynecologist. Neglected female “diseases” like chlamydia or trichomoniasis lead to infertility, and cervical erosion is generally the first harbinger of a malignant tumor!
Remember, for women everything is interconnected. Your well-being, mood, skin and hair condition often depend on the health of the genitourinary system, so you must treat it more carefully.
Here's a little reminder of what discharge normally looks like. You will check with it and know whether you should worry or not.
Prevention
If you have yellow, odorless discharge, there is no need to worry or panic. In such situations it is enough:
- wear underwear made from natural materials;
- choose only high-quality products for personal hygiene;
- observe hygiene standards;
- Be careful when having sex, use condoms.
If leucorrhoea causes itching in the perineum, burning, pain, is accompanied by a strong unpleasant odor or frequent urination, you should immediately seek advice from a qualified specialist. Only a competent examination and tests will help determine the correct diagnosis and identify the cause of the disorders.
The vaginal microflora is a rather complex system that is easily disrupted as a result of illiterate therapy. Because of this, in the future you will have to spend a lot of time on treatment and restoration of its natural environment. Sometimes this takes several years. Therefore, under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Only a gynecologist is able to determine the cause of the failure and prescribe quality therapy.
Similar articles
Sour Discharge Odor in Women (No Itching)
10621 Kokh V. A.
Vomiting With Fever Without Diarrhea in a Child
2212 Super User
Treatment
If there are complaints of pathological discharge, complex therapy of the underlying disease is carried out. Moreover, if it is caused by a sexual or other infection, an important principle is the simultaneous treatment of both partners.
Infectious pathology is treated with antibiotics. Local treatment is done by douching and using vaginal suppositories.
In combination therapy of both infectious and non-infectious inflammations, anti-inflammatory drugs are used. If cycle disruption is caused by a hormone imbalance, it is corrected with hormonal medications.
Regular intimate hygiene is mandatory. For this purpose, both special means and decoctions of medicinal herbs are used.