Chronic giardiasis is a common type of infestation, since it is very easy to become infected with this parasite. In addition to the intestines, Giardia can affect the liver of its carrier. In the first stages, the invasion is asymptomatic, which complicates the process of its detection.
Detection of infection occurs by chance or during the onset of the acute stage, when a person begins to complain of negative symptoms. If the necessary treatment measures are not taken in a timely manner, lamblia in the liver can cause enormous harm to human health.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
Giardia
Treatment of lamblia in the liver in adults
Treatment of Giardia in the liver in adults should be carried out by a parasitologist.
Self-prescription of drugs is unacceptable. Therapy involves the implementation of three stages: preparatory, basic and restorative. Preparatory stage of treatment of lamblia in the liver. First, it is necessary to create conditions in the body under which Giardia will stop actively reproducing. For this purpose, the patient is transferred to a dietary regimen with the consumption of bran, cereal porridges, fruits and vegetables. At the same time, limit carbohydrate foods as much as possible, and primarily sugar.
Patients should periodically undergo fasting days. In parallel, antihistamines and choleretic drugs are prescribed. To normalize digestive function, the patient is prescribed enzyme preparations: Festal, Creon, Pancreatin, etc.
The main stage of treatment for lamblia in the liver. The main stage of ridding a person of parasitic infestation comes down to taking antiprotozoal drugs. The most commonly used drugs are: Metronidazole (Trichopol), Tinidazole, Nimorazole, Ornidazole (Tiberal), Furazolidone, Albendazole (Nemozol). As a rule, the doctor prescribes 2 courses of treatment.
All of these drugs are well tolerated and have high anti-Giardia activity.
Restorative stage of treatment of lamblia in the liver. The last stage of treatment is aimed at restoring the human body. To do this, he is prescribed enterosorbents, vitamin complexes, and immunostimulants. It is possible to use herbal medicine. The need to take a particular medicine is determined by the doctor.
As for the prognosis, with proper implementation of the treatment regimen, its effectiveness reaches 95%. Although re-infection cannot be ruled out in the future, since the body does not develop immunity. In this regard, you need to follow the basic rules for the prevention of giardiasis: do not drink raw water, especially from open sources, keep your hands and room clean.
Author of the article: Tatyana Vyacheslavovna Danilova, infectious disease doctor, especially for the site ayzdorov.ru
Infection of the body with protozoal infections is always serious, because even protozoan parasites can cause significant harm to health. These include lamblia in the liver. Only correct and timely therapy in adults and children will avoid unpleasant complications and speed up recovery.
Diet for giardiasis
During the entire course of therapy directed against Giardia, the patient is shown a special diet for Giardiasis according to Pevzner (Table 5). It is permissible to include the following products in the diet:
- Cereals and cereal porridges (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat, etc.);
- Any soups with vegetable oil or vegetable broth;
- Fish and meat of low-fat varieties;
- Fermented milk products in the form of yogurt, cottage cheese, kefir;
- Whole grain bread with bran;
- Greens, fruits and vegetables;
- Some desserts in the form of marmalade, honey and marshmallows.
It is strictly forbidden to eat the following foods:
- Fish and meat of fatty varieties;
- Strong rich broths;
- Margarine and lard;
- All legumes;
- Mushrooms in any form;
- Chicken egg (no more than 1 per day and only as part of dishes);
- Fresh pastries and desserts with chocolate and rich creams;
- Any hot seasonings and smoked foods;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Ice cream and coffee.
It is worth knowing that with proper therapy, it is possible to get rid of Giardia in 96% of cases. However, this does not exclude re-infection with parasites, since the main cause of infection by which one can become infected with parasites is dirty hands, water and fruits/vegetables. Infection can be prevented only by observing basic rules of personal hygiene and eating high-quality, washed food and clean water. Remember, it is always easier to prevent an infection than to fight it later.
https://youtu.be/hCGWctx6ffA
Causes of Giardia in the liver in adults
The source of the spread of Giardia is an infected person. It is he who releases mature parasite cysts into the external environment. They leave the patient's body along with feces.
Giardia can be carried by dogs, cats, rabbits and other animals. Various insects can carry Giardia larvae on their paws: cockroaches, flies, ants, etc. The mechanism of infection is fecal-oral. Giardia cysts can enter the human body through water, food and household contact.
Therefore, the following causes of parasitic infestation can be identified:
Violation of personal hygiene rules. Dirty hands are especially dangerous in this regard.
Eating contaminated fruits, herbs, vegetables, salads, berries, etc.
Drinking unboiled water. Although all tap water entering residential premises goes through several stages of treatment, Giardia cysts may be present in it. They can get there through damaged pipes or when filtration technologies are violated. Naturally, the risk of infection increases significantly when drinking water from natural sources.
Poor sanitary living conditions. In this case, we are talking about the abundance of insects in the living room, since they are spreaders of infection.
Use of common items without proper pre-treatment.
Any contact with soil poses a potential hazard.
The infestation rate of the adult population will be higher, the more severe the environmental pollution, the worse the condition of the water supply and sewerage system, the higher the crowding of groups, the lower the level of sanitary education work in a particular locality. These factors explain the high percentage of patients among the adult population in developing countries.
It is worth noting that the risk of infection in adulthood is not as high as in childhood. The fact is that the digestive system of an adult is more advanced and has a more aggressive environment for parasites. Therefore, if several Giardia cysts enter the gastrointestinal tract, infection may not occur.
The likelihood of infection increases if the following predisposing factors are present:
Congenital defects and developmental anomalies of the biliary tract.
Diseases of the digestive system, accompanied by low acidity and deterioration of enzymatic activity.
Surgical interventions on the stomach and duodenum.
Adherence to low protein diets.
Errors in nutrition leading to dystrophy.
The maximum surge in the incidence of giardiasis is recorded in spring and summer.
Preventing infection with liver parasites
Specific prevention against Giardia has not been developed. To protect the liver from parasites, you just need to follow the rules of hygiene: wash your hands before eating, rinse vegetables and fruits well before eating, do not drink untreated water, especially from open sources.
In areas of giardiasis, anti-epidemic measures are being taken. Sanitary supervision must prevent fecal pollution of the environment.
Giardiasis of the liver, specifics of the disease
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
A remedy for getting rid of parasites that works immediately...
>>>
Giardiasis is an infectious disease that develops as a result of infection of the body with Giardia. There are two forms of the disease: vegetative and trophosiodic.
In the vegetative form, parasites live in the small intestine. They attach themselves to the walls of the organ using special suction cups and begin to multiply. After 40 days, they enter the large intestine and are excreted from the body, dying. In trophozioditis, helminths live in the liver. They can turn into cysts and remain able to reproduce for several months.
Parasites feed on broken down food debris that enters the human body. The results of their vital activity enter the bloodstream and negatively affect all human organs and systems.
Symptoms of giardiasis of the liver
The disease in the initial stages may be asymptomatic. And those signs that appear some time after infection are often attributed to intestinal disorders. Giardiasis of the liver may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
a white coating appears on the tongue, and an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth; the patient is worried about frequent stomach rumbling and bloating; frequent belching; pain in the right hypochondrium; most patients note a sharp deterioration in appetite and a change in taste preferences; weakness, rapid heartbeat; loose stool.
In the form of an effective cure for parasites, doctors
It is advised to take the drug “Intoxic”.
The product is based on active elements of exclusively natural origin, they were grown only in places with a 100% clean environment, and have a proven effect that allows you to quickly deal with any type of worms.
Get rid of parasites..."
If giardiasis of the liver is not treated, it becomes chronic and manifests itself with the following symptoms:
rashes appear on the skin, it begins to peel off; patients are bothered by itching on the skin of the face, abdomen and hands; Unpleasant sensations appear in the abdomen: cramps, pain, constipation.
In children, additional signs of the disease are redness of the lips, the formation of ulcers and peeling on them. After infection, stool becomes thin and watery, and body temperature may increase.
Causes and routes of infection
Infection occurs through contact with an infected carrier: animal or person. Their feces also contain a large number of helminths, which may not die in the external environment if they have become cysts. Most often, infection occurs in the following ways, from which lamblia appears in the liver:
through raw tap water; through unwashed foods: fruits, vegetables and berries; through household items if an infected person has come into contact with them (towels, dishes, children's toys); children become infected through dirty hands after playing in sandboxes; On the fur of domestic animals that are infected with giardiasis, worm eggs can remain viable for some time.
Children and families who keep pets at home are most at risk of infection. Often, infection occurs as a result of non-compliance with hygiene rules when cleaning pets' toilets.
Disease prevention
Prevention for giardiasis is a synonym for the words “personal hygiene”. Teach children to observe basic hygiene rules: wash their hands, do not eat dirty vegetables and fruits. Supervise children while playing outside, and do not allow them to eat food with unwashed hands after playing outside.
Recommendations for protection against infection:
- do not be lazy to wash your hands more often after contact with dirt, money, or after being in public places;
- Wash any food with soap before cooking or eating;
- drink boiled water, the high temperature kills microbes;
- swim carefully in bodies of water, do not swallow the water;
- take a shower with soap after swimming in rivers, lakes, or after visiting the pool;
- disinfect the plumbing fixtures at home, renew the textiles used in everyday life.
What ailments occur? There are strange sensations in your stomach, but are you chalking it up to poisoning? Don't self-diagnose. The sooner a correct diagnosis is made, the easier it is to eradicate the infection.
Classification
Depending on the type of pathological process, giardiasis can be acute or chronic. The disease can also occur in the following forms: asymptomatic carriage, subclinical variant, established (manifest) variant. Experts also distinguish three variants of giardiasis depending on the clinical manifestations:
- intestinal. Characterized by the development of duodenitis, gastroesophageal reflux, enteritis, intestinal disorder;
- extraintestinal. Astheno-neurotic syndrome develops, and toxic-allergic symptoms also appear;
- biliary-pancreatic. Biliary dyskinesia, cholecystitis and acute reactive pancreatitis appear.
Giardiasis practically never occurs in children with strong immune systems.
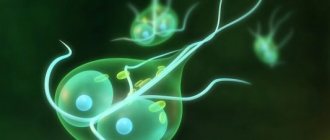
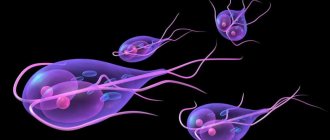
Giardia infection as a disease
Giardia are the simplest single-celled microorganisms that can parasitize the intestines, gallbladder and duodenum. The main location in the human body is the lumen of the small intestine (about 85% of cases). Cases of damage to liver tissue by microorganisms are quite rare due to the lack of a favorable nutrient environment, but with a long course of the disease, Giardia creates the necessary conditions for pathogenic life activity. The hepatobiliary form of giardiasis is a serious disease, as it is combined with damage to the bile ducts. Giardia in the liver can provoke gastritis, gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, cholestasis and biliary dyskinesia. There are two forms of existence of Giardia:
- Vegetative. Giardia in this form is capable of parasitizing inside the host’s body.
- Cysts. They are spore forms when active life activity stops. Existence in the form of cysts is necessary to maintain viability outside the host body.
The vegetative form is transformed into cysts after microorganisms enter the carrier’s large intestine, from where they are excreted with feces into the external environment. Cysts can exist outside the human or mammal body for many months before entering a new body. Giardiasis of the liver is the subject of research among gastroenterologists, parasitologists and pediatricians (in pediatric practice).
Myths and truth about Giardia
It’s hard to say why, but of all the parasites, it was Giardia that received the “honor” of being recognized as almost one of the main threats to humanity. These single-celled organisms have been studied quite well, and therefore anyone interested can learn enough about them if they wish.
Moreover, it is not clear why there are so many myths around giardia and giardiasis, which, by the way, are actively supported by medical workers themselves:
- “Giardia is very dangerous!” It is a myth. Even in the active vegetative stage, during the reproduction period, protozoa cannot be considered dangerous, since they do not pose any threat to the life of the child. The harm that Giardia causes to a child’s body is greatly exaggerated.
- “Your child has problems with his gallbladder because he has Giardia!” This is no longer just a myth, but real medical obscurantism. These protozoan parasites cannot exist anywhere except the small intestine, and the bile environment is completely destructive for them. Therefore, any problems with the digestive organs (cirrhosis, biliary dyskinesia, etc.) should in no way be explained by the presence of Giardia in the child’s stool.
- “If giardiasis is not treated, the child will develop giardia in the liver and other organs.” This myth is apparently financially supported and fueled by manufacturers of pharmacological agents to combat parasites. And some doctors quite seriously say such words to the parents of their young patients.
- “Giardiasis can be treated with folk remedies.” Decoctions of herbs, pureed onions and garlic and other recipes from the arsenal of alternative medicine can, in principle, affect Giardia, but such treatment will be long and ineffective, and it is unlikely that it will be possible to completely get rid of the parasites. Therefore, it is better to resort to a course of treatment with traditional drugs; it will not take more than 5 days.
- “If you wash your hands often, you won’t get giardia.” It is a myth. Hand washing is an excellent habit that protects a child from many pathogenic bacteria and some viruses, but it practically does not protect against Giardia. It is enough for a child to play in the sandbox, in which a cat carrying Giardia was previously sitting, in order to bring microscopic cysts on his shoes. And only 10 individuals are enough for infection.
- “Because of Giardia, the child began to get ARVI more often.” It is not true. The presence of parasites in the small intestine does not in any way affect the likelihood of contracting the virus and has virtually no significant effect on the immune system.
- "Giardia is a source of allergies." Giardia cannot cause an allergic reaction on the skin, since their waste products are not strong toxins or allergens. Skin ailments, including those of allergic origin, should not be associated with giardiasis.
- “Giardiasis can be cured once and for all.” This is a common misconception. After one batch of parasites has been dealt with, the baby may become infected with a new one, and on the same day.
- “Every fifth child has Giardia.” It's true. According to test results, about 30% of children aged 3 to 7 years actually have these parasites in their bodies. However, they do not have any complaints or pathologies or diseases with dire consequences. Their parents learn about Giardia only from the results of a stool test. In this case, there is no talk of intestinal giardiasis, because the presence of cysts is not yet a disease.
A little about the parasite
The causative agents of the disease are Giardia - single-celled organisms that parasitize the intestines and liver. They are also called giardia. With their vital activity they irritate the mucous membrane, disrupting the digestive processes. They attach themselves to the intestinal walls with flagella, absorb nutrients and actively reproduce. Giardia is often confused with helminths.
The main feature is that the causative agents of giardiasis, despite the fact that they consist of only one cell, function as a single integral microorganism. Giardia leads a parasitic lifestyle. After the cysts enter the stomach along with food, under the influence of digestive juice, their protective shell dissolves. Then young forms emerge and move further along the gastrointestinal tract.
The life activity of Giardia occurs in two main stages:
- Vegetative, or also called mobile. Active parasitic activity. At this stage, parasites enter the intestines through the stomach, after which they actively absorb nutrients.
- Inactive. At this stage, cysts form. Giardia is divided into larvae, which are covered with a shell - a cyst. This period can be called a state of sleep or inactivity. Under these conditions, parasites can survive various negative conditions, such as high or low temperatures. Only after entering the duodenum does the cyst open and the microorganism begins its pathogenic activity.
Giardia cysts can live in water, soil, fruits and vegetables. Cockroaches and flies contribute to the contamination of food products. In the small intestine, molecules of vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are broken down into small fractions, which provide a breeding ground for parasites. This is why vitamin deficiency develops along with giardiasis.
Giardia life cycle
Each cyst, after entering the intestine, is divided into two parts, from which, respectively, two lamblia are obtained, which begin to actively multiply in the thin section. During the active reproduction of pathogens, the mucous membrane of the small intestine is injured. The production of hormones that are responsible for digestion processes is also disrupted.
If the disease is not cured within several months, it can cause serious complications in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) in the form of enteritis, irritable bowel syndrome, increased gas production, constipation or diarrhea. The waste products of pathogens can cause the development of allergic reactions, skin diseases, as well as disorders of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Carefully! Giardia can “wait” for a long time, especially in water. Their cyst is a reliable protection against the aggressive effects of external factors.
In unfavorable conditions for Giardia, they can begin to change. Parasites surround themselves with a powerful protective shell, which not every medication can penetrate. In this form, they are excreted from the intestinal tract. In environmental conditions, pathogens can persist for up to three months. They are not even afraid of icy water and the scorching sun.
What is lamblia
Giardia is an insignificant microbe from the order of parasites. It is this that causes the disease called giardiasis. It was discovered at the end of the seventeenth century by the inventor of the microscope, Anthony Van Leeuwenhoek.
Then it was studied in more detail by Professor Lambl, whose name practically became the name of this parasite. This microbe carries out its parasitic effect in the human intestine, as well as in its bile system.
This parasite can be in two states - mobile (vegetative) and immobile (in the form of a cyst). Giardia has eight flagella and a disc equipped with suckers. With the help of these devices, it is held on the inside of the intestinal walls.
The disease caused by Giardia is called Giardiasis. It is much more common in children than in adults.
If you examine this microbe under a microscope, you can see a very active “creature” moving at high speed along the intestinal walls. As you know, the inside of the intestine consists of villi, which, by processing the beneficial substances contained in food, transfer it to the body.
It is on these villi that Giardia parasitize, simply taking for themselves everything that was intended for the human body. There can be several tens of billions of microbes in the intestines of an infected person at the same time!
In a favorable environment, they are capable of multiplying at a tremendous speed - on the order of the rate of cell division. When leaving the small intestine into the human rectum, Giardia takes on the appearance of a cyst, creating a protective membrane around itself.
In this form, they are excreted from the human body and, if they enter an environment favorable to them, they can cause infection of another person, once in whose intestines they will again turn into a vegetative form.
In the human body, these creatures manifest themselves in two forms:
- vegetative, adult individual (trophozoites), this form dies quickly;
- cyst (protective form), created in case of unfavorable conditions for Giardia. This form is not destroyed by antibacterial drugs. Inside the body, trophozoites are released from the cyst and are suitable for reproduction. Some of them again form cysts, which are released into the external environment with feces.
Clinical picture
Important!
A healthy liver is the key to your longevity. This organ performs a huge number of vital functions. If the first symptoms of a gastrointestinal or liver disease have been noticed, namely: yellowing of the sclera of the eyes, nausea, rare or frequent bowel movements, you simply must take action.
We recommend that you read the opinion of Elena Malysheva about how to simply and quickly restore the functioning of the LIVER in literally 2 weeks...
Read more…
Giardia in the liver and other organs parasitizes for a long time without any special symptoms, but after some time patients can already feel signs of a general decrease in body tone, symptoms of mild intoxication. Parasitic activity provokes inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, malabsorption, secondary fermentopathy, endogenous intoxication and the development of dysbiosis.
Giardia secretes a special toxic component that negatively affects organs. The disease has two main forms:
acute process; chronic form.
An acute pathological condition requires immediate treatment due to the high risk of becoming chronic. Protozoal invasion is accompanied by discomfort in the epigastric region, the patient experiences constant nausea and the urge to have a bowel movement. Young children and adults are often infected.
Common symptoms for all types of giardiasis
pain in the hypochondrium or abdomen; excessive pallor of the skin; change in the color of the palms and feet, up to a rich red hue; dry skin.
The disease is characterized by the appearance of arrhythmia, general weakness, and sweating. Some patients complain of continuous nausea and other dyspeptic disorders (loose stool, vomiting), emotional instability and fatigue occur.
The main symptoms of giardiasis of the liver
the appearance of a milky coating on the tongue; changes in the structure of liver tissue (enlargement, thickening); bloating and strong rumbling.
The lack of adequate timely treatment leads to complications of the disease (intoxication, dysfunction of some organs and systems), as well as to the emergence of a chronic form of the disease.
Signs of chronic giardiasis of the liver
feeling of heaviness in the stomach; nagging pain in the navel area; signs of cholecystitis; weight loss; fatigue, short temper or apathy; the appearance of bitterness in the mouth.
Factors such as poor diet, excessive food intake, bad habits and poor hygiene can contribute to relapses of the disease. The risk group for the occurrence of a chronic form of giardiasis of the liver is considered to be children aged 2.5 to 5 years.
Signs of illness in children
With giardiasis of the liver, symptoms in children are more pronounced.
In children, intoxication quickly increases, the temperature may rise, and diarrhea appears. There is a risk of rapid dehydration, which leads to irreversible processes in the body, including loss of consciousness and coma. The initial stages of the development of the disease are manifested by rumbling and pain near the navel. After just a few days, the symptoms increase and are rapid in nature, for example, the development of reactive pancreatitis, dyskinesia of the bile ducts and biliary tract. An important aspect of successful treatment of acute giardiasis is careful diagnosis. The main task of differential diagnosis is to exclude other diseases of the liver and biliary tract.
Symptoms
The presence of cysts cannot be felt in any way. The child does not complain or get sick. We can say that the development of pathology associated with the proliferation of Giardia begins when the parasites begin to irritate the intestinal mucosa. This process may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- unpleasant sensations in the navel area, in the upper abdomen, moderate nagging pains that are not acute or pronounced, the sensations are not constant;
- loss or disturbance of appetite, change in taste preferences, feeling of mild nausea;
- The baby’s tummy is quite often swollen, and after eating you can hear rumbling;
- stool instability - diarrhea is replaced by constipation and vice versa;
- prolonged diarrhea (several days);
- feces have a yellow or yellowish color and uneven consistency, in some places there are inclusions of mucus;
- general weakness, irritability, capriciousness of the child;
- if the baby was previously diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, an exacerbation may begin;
- body temperature is usually normal, very rarely it rises to subfebrile levels (37.0 - 37.9 degrees).
The most common symptom is weight loss. As we have already found out, Giardia sucks many useful substances from the small intestine that get there with food. And if you consider that the child already has a reduced appetite, then the weight will actually begin to change downwards. Babies will experience slow weight gain or the weight will stay the same.
Diagnostic methods
When parasitizing the liver, Giardia can affect its function. Accurate diagnosis is often difficult due to the wide range of possible manifestations of the disease. In case of a burdened clinical history or a tendency to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver, additional diagnostic methods are often required to exclude pathological changes in organs, systems, as well as tumor-like formations. The main methods for detecting infection are:
visual examination of the patient (skin, oral cavity); interviewing the patient for complaints; study of clinical and life history; blood sampling for biochemical testing; urine test (sometimes for sterility); stool analysis for bacteriological culture; parasitological research (detection of cysts in biological materials).
When giardiasis manifests itself, it is necessary to conduct a whole range of laboratory tests. Among others, specialists often use the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method and ELISA test (blood serum antibodies). This allows you to more accurately understand how to treat the infection.
Diagnostic measures
A diagnostic examination for suspected giardiasis is given particular importance. This is explained by the diversity that is characteristic of the disease presented. In particular, the symptoms are varied, indicating not only Giardia in the liver area, but also other lesions of the organ and gastrointestinal tract systems. It is also noteworthy that there are no characteristic pathognomic symptoms - all this indicates that laboratory diagnostics must be carried out.
The material for the examinations is feces and duodenal contents. Speaking about duodenal contents, it should be noted that it allows parasitic trophozoites, solid feces - cysts, and semi-formed or liquid feces - both cysts and trophosites.
In order for liver treatment - this applies to both adults and children - to be successful, it is important to carry out diagnostics at each stage of therapy. As you know, Giardia is prone to frequent relapses and rapid infection of internal organs
That is why it is so important to take into account all the symptoms, which will prevent the worsening of the general condition.
Efficiency
Drugs that form the basis of antiparasitic treatment, such as Metronidazole, Furazolidone and all products based on them, gradually lose their effectiveness due to the fact that parasites appear that are very resistant to the active substance of these drugs. Giardia, which left the body at the stage of antiparasitic treatment and did not die, but only became cysts, acquires such resistance.
The next time they cause infection, giardiasis will be much more difficult to respond to drug therapy. The modern pharmaceutical industry is working on this issue, and almost every year new drugs appear on the market. Doctors are usually aware of new products, and will definitely suggest another remedy for Giardia if Metronidazole does not work.
If a child is diagnosed with parasites, and they lead to illness, then both adults and other children in the family should take the medications prescribed for the baby. The dosage for each family member is determined by the doctor.
Sometimes there is a need for a second course of treatment. In order to make sure that all the parasites have left the body, the child must have stool tested several times after completing the first course. He is required to undergo clinical observation for six months, during which time it is advisable to have his stool analyzed for Giardia cysts at least three times.
Methods for diagnosing giardiasis
Before you begin to treat the disease, it is necessary to detect and identify the pathogen. The patient is prescribed a series of tests, according to which an accurate diagnosis can be made. These include:
- Ultrasound - the liver will be enlarged in size, signs of inflammation can be detected;
- a general blood test will show an increase in the level of leukocytes and eosinophils - specific cells that are produced by the immune system in response to the presence of parasites;
- a biochemical blood test will indicate an increase in the activity of liver enzymes (ALT, AST);
- Giardia cysts can be detected by microscopy of stool samples.
After the examination, the doctor will explain what giardiasis is, in what form it occurs in the patient, and also prescribe treatment. The difficulty of diagnosis is that Giardia cysts are not constantly excreted, and in some samples they may be absent. If the result is negative, but other points are consistent, repeat stool microscopy is prescribed. The fact is that Giardia rarely parasitizes exclusively in the liver. In most patients, they can be found both in the small intestine and in the organs of the hepatobiliary tract.
Giardia has a complex life cycle, which allows them to persist in the environment for a long time
Liver tests and blood tests for antibodies
To determine the parasitic infection of the liver and the degree of damage to the organ, a biochemical blood test is taken. Key indicators of liver tests:
- Bilirubin level. A deviation from the norm indicates damage to liver cells or a violation of bile excretion.
- Protein level. Deviation from the norm indicates a violation of the synthetic function of the liver.
- Activity of the enzymes alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Elevated levels indicate liver cell destruction.
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity. Increased activity indicates a violation of the patency of the bile ducts.
To determine antibodies (immunoglobulins) to Giardia antigens, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is performed. The presence and level of immunoglobulins of the class IgA, IgM, IgG are determined.
Treatment tactics
So, how to get rid of Giardia? What treatment tactics do specialists use? Treatment of Giardia in the liver tissue in adults and children takes place in several stages. The main medications in conservative therapy are Tiberal, Furazolidone, Trizopol. The chronic form of the disease is usually not immediately treated with antiparasitic synthetic drugs due to the high risk of toxic and allergic complications. In case of exacerbation of the chronic form of giardiasis of the liver, treatment is carried out in stages.
First step:
- improvement of enzymatic activity of the gastrointestinal tract;
- correction of immune status;
- an adequate diet with limited carbohydrates;
- taking choleretic drugs:
- carrying out enzyme therapy;
- prescription of antihistamines.
The first stage is aimed at gradually preparing the body for the effects of drugs.
Second step:
- taking enterosorbents (activated carbon, Polysorb, Enterosgel);
- Tiberal, Furazolidone, Trichopolum;
- antihistamines (Zyrtec, Zodak, Suprastin).
The course of drug treatment for Giardia in the liver depends entirely on the degree of damage to the body, the severity of symptoms, and the level of general intoxication. The drugs can remove parasites in a short period of time.
Third step:
Third stage therapy is aimed at strengthening the body after drug treatment and consolidating the achieved results. The main methods include:
- prescribing a long-term therapeutic diet;
- correction of the body's immune response;
- introduction of prebiotics and lactobacilli to prevent dysbiosis.
The duration of the stage varies from 2 to 4 weeks. The chronic form of the disease requires fairly long periods of therapy to prevent relapses of exacerbations in order to increase the period of stable remission.
Alternative medicine
Traditional methods of treating Giardia and other parasites have gained immense popularity even in the medical community. Some recipes are effective and expel parasites within a week.
- Cabbage brine. To destroy Giardia, you need to drink up to 100 ml of brine before meals 3-4 times a day.
- Coconut pulp. Effective for expelling Giardia in children. To prepare the recipe, you need to open the fruit and remove the liquid into a separate container. The pulp must be thoroughly crushed and combined with milk. The composition can be given to the child several times a day before meals, 1 tablespoon. The therapeutic course lasts about 7 days, after which a two-week break is taken. If necessary, treatment can be continued for a long time. The child will be happy to continue the tasty therapy.
- Flax-seed. To prepare the recipe you will need to combine flax seeds with cloves in a 1:1 ratio. The composition must be crushed and added to food. The daily dose of powder is 30 grams. Flax helps to safely and quickly remove Giardia from the liver.
Treatment with folk remedies may be contraindicated in people with a burdened clinical history
Before getting rid of lamblia in the liver on your own, it is important to consult a specialist
Prevention
Preventive measures include simple recommendations, which, if followed, significantly reduce the risk of infection. Compliance with personal hygiene, rules for visiting public places (swimming pool, sauna, ponds), drinking and eating habits, rules for communicating with animals will help preserve the health of not only adult patients, but also their children for a long time. The effectiveness of treatment measures is about 95%, but the likelihood of re-infection is always present. The attending physician will select the necessary preventive therapy. To prevent repeated episodes of protozoal infection, repeated courses of treatment are required. After recovery, the patient is registered at the dispensary for about a year and undergoes the necessary tests to determine the likelihood of parasites. The prognosis with adequate therapy is almost always favorable.
How to remove lamblia from the liver
You can cope with the disease only with the help of a comprehensive approach. Treatment of giardiasis of the liver should be aimed at increasing the body's immune response, improving stomach function, and motility of the small and large intestines. As a rule, the course of treatment lasts no more than 5-7 days with subsequent monitoring of the condition. Full recovery occurs a week after the onset of the acute phase of liver damage by Giardia. With reduced immunity, the process may take several months.
Tablets for Giardia in the liver
In the acute phase of the disease, doctors usually prescribe antihistamines and imidazole derivatives. In this case, much attention is paid to preventing the occurrence of toxic-allergic complications. It is important to note that a cure for Giardia in the liver that instantly eliminates the infection has not yet been invented. Antiparasitic therapy involves the use of a number of medications, among which are the following:
- medicines against Giardia and other protozoa (Metronidazole or Trichopolum, Furazolidone, Tiberal);
- enterosorbents (Activated carbon, Smecta);
- plant adaptogens (Schisandra, Eleutherococcus);
- probiotics and prebiotics (Linex, Bifiform);
- enzyme preparations (Pancreatin);
- hepatoprotectors (Heptral, Liv 52);
- choleretic drugs (Flamin, Insadol).
Diet for giardiasis
The nature of nutrition most directly affects the success of each stage of antiparasitic therapy. Hepatic giardia enters the reproduction stage only if they do not have any problems with food. For this reason, to transform active parasites into cysts, doctors recommend that patients completely review their diet. The diet for the treatment of lamblia involves avoiding the use of:
- dairy products;
- Sahara;
- complex carbohydrates;
- some vegetables (potatoes, beets)
- sausages;
- sweet fruits;
- fried fatty foods;
- porridge with the addition of whole milk;
- chocolate;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- cabbage;
- coffee.
Causes
Doctors identify several ways of infection by helminthic infestations, due to which Giardia penetrates the liver. Giardia enters the adult body in several ways:
- Through dirty and unprocessed food, dirty hands.
- Domestic route: through contact with an infected person.
- Using untreated tap water, swimming in ponds and swallowing water.
Liver infection is characterized by the life cycle of the parasite. Once in the digestive tract, the cysts are transformed into trapozoids under the influence of bile. In this case, the vegetative form of the parasite develops in the intestine, attaching to the walls. The danger lies in the fact that, feeding on the juices of the walls of the esophagus, the worms consume all the nutrients that are necessary for the normal functioning of the body. At the same time, nutrients and minerals cannot be absorbed.
Prolonged stay of Giardia in the body leads to inflammation of the small intestine and the appearance of atrophic changes that suppress the functions of the digestive tract. These changes lead to dysfunction of the liver and biliary tract.
When contacting a specialist and the presence of giardiasis, the doctor interviews the patient. The main symptoms of liver damage by Giardia in an adult are as follows:
- Rumbling in the intestines.
- White coating on the tongue.
- Enlarged liver.
- The patient notes that he is bothered by pain in the umbilical area.
- Belching, heaviness, loss of appetite.
- Giardiasis also causes a hypertensive crisis, which is associated with fainting.
- Arrhythmia may occur.
In the chronic form of the disease, the skin is affected and anemia is noted. Also, with this form of pathology, relapses are observed. Chronic pain occurs in both adults and children. In this case, the following symptoms of lamblia are characteristic when localized in the liver:
- Constipation alternating with diarrhea.
- Loss of appetite.
- Body weight decreases.
- Children are lagging behind in physical development and have general malaise.
- Skin problems appear: urticaria.
As clinical manifestations develop rapidly, the immune system weakens and is unable to protect the body. Therefore, Giardia in the liver in adults quickly gains strength, resulting in complications.
Giardiasis in children
Giardia in children is quite common; its symptoms are more pronounced than in adults and treatment takes longer. Children, due to their immature immunity, are more susceptible to infection. Almost every child is at risk, because they can simply become infected while playing with children in the yard or in kindergarten (for example, through toys).
If a nursing mother is a carrier of parasites, she can infect her baby through breast milk.
If the child is healthy and has strong immunity, then the body itself gets rid of helminths within 5-6 weeks. In most cases, lamblia in a child makes itself felt over time in the form of unpleasant symptoms.
- through toys, household items,
- water from dubious sources,
- swimming in bodies of water (swallowing water when diving),
- a child's tendency to bite his nails,
- poorly cooked meat products, unwashed fruits,
- consumption of food and catering establishments.
Symptoms of the presence of Giardia in the liver of a child
When a child develops lamblia in the liver, symptoms may not appear immediately. Often the first signs appear when parasites have settled in the liver and small intestine.
Symptoms that mothers should pay attention to:
- low-grade fever, which lasts for a long time in the absence of viral diseases,
- change in the structure of stool,
- indigestion (flatulence, stomach turmoil, bloating, nausea),
- grinding teeth during night sleep,
- sudden attacks of coughing, ending in suffocation (usually at night),
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- skin rashes,
- pain in the liver and navel area,
- sudden weight loss,
- depressed mood, decreased activity.
They appear both individually and in combination.
Diagnostics
For children under 10 years of age, the most popular diagnostic method is scatology (stool examination). Under a microscope, the laboratory technician detects cysts, if any. But the method is not always effective.
The second most effective is a blood test to detect special antibodies that the body produces as a response. The method is effective in the first 2-3 weeks after infection with parasites.
Duodenal examination - consists of examining the child’s bile. A very effective method. The disadvantage is that the procedure is carried out from a certain age; for children this process is difficult.
Treatment of children
Treatment of Giardia in children should be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. The medications and the duration of their use are determined by the doctor; the course depends on the severity of the disease. The treatment regimen for giardiasis in children includes a set of measures: diet, directly getting rid of parasites with the help of anthelmintic drugs, strengthening the immune system and restoring intestinal microflora.
Diet means giving up flour and sweet products, sausages, sugary drinks and other foods high in carbohydrates.
Often, at the beginning of taking antiparasitic drugs, there is a sharp deterioration in the child’s well-being - a normal reaction of the body. If your baby is bothered by frequent vomiting, you need to take measures to prevent dehydration. Before removing Giardia from the child’s body, in order to avoid re-infection, it is recommended that all family members be tested.
In general, treatment of giardiasis in children is carried out individually depending on the stage, and the treatment regimen can be changed by the doctor. Sometimes, in order to remove Giardia and normalize liver function, treatment is not complete without choleretic medications.
Reasons for the formation of Giardia in the liver
Giardia can enter the body of adults and children not only through food, but also in other ways. In particular, they live in reservoirs and sewer water - which is why such liver lesions occur quite often in places where sanitary conditions are poorly developed. After entering the body, Giardia penetrates the area of the small or large intestine, where they begin to multiply. In order for the development of giardiasis to begin, at least 10 cysts must penetrate the body.
It is noteworthy that another condition is a low degree of acidity of gastric juice, which negatively affects the general condition of the liver and provokes various symptoms. In connection with the routes of penetration of bacterial components, three types are distinguished, namely water, food and contact-household
Treatment largely depends on how exactly Giardia affected the body - this is very important not only for adults, but also for children
I would like to draw attention to some features of the transmission routes of giardiasis. In particular, speaking about the contact and household method of transmission, experts note that accumulation is noted on household items, which include clothing, dishes, toys and everything else
Noting the peculiarities of Giardia transmission through food, it should be noted that the reason for this is the lack of optimal heat treatment of products. It is in this case that the parasitic components survive, subsequently affecting the liver area
However, before starting treatment, it is necessary not only to carry out the appropriate diagnosis, but also to differentiate all the symptoms of the disease.
Experts identify several forms of the disease in adults, namely acute and chronic. The first form occurs in people with weakened immune systems and causes symptoms such as fever, vomiting, and a rash that is similar to rubella or measles.
It is equally important that lamblia in the liver leads to anorexia and sharp pain in the epigastric region
In some cases, even if treatment was successful, manifestations of the disease may recur. This is typical for colds and stressful situations immediately after therapy in relation to acute giardiasis. In general, treatment of the disease is successful only after the earliest possible recovery course.
Folk remedies
Parasites can disappear from the body thanks to alternative treatment. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to consult with specialists, because certain people may be intolerant to a particular drug or it may be contraindicated.
Sauerkraut brine
Some useful recipes:
- Sauerkraut brine should be taken before meals in small quantities. This cheap and effective remedy can get rid of Giardia.
- Coconut is an effective substance against giardiasis. It is recommended to grind the coconut pulp and add a little coconut milk to it to obtain a tender mass. It should be taken in small quantities before meals for 2 weeks.
- Some experts recommend consuming coconut on an empty stomach. After taking a certain amount of nut, you must refrain from eating (up to 3 hours). If you really want to eat, then it is permissible to eat some fruit.
- Flax seeds are an excellent remedy against Giardia. You should grind them in a coffee grinder and add a little cloves. The mixture can be used as a spice, or eaten in small quantities throughout the day.
Causes
To begin with, I’ll briefly tell you what the disease is. Giardiasis, or giardiasis, is a protozoal disease caused by protozoa: single-celled parasites Lamblia intestinalis (also called Giardia intestinalis, Giardia duodenalis, Giardia lamblia).
They are transmitted:
- With water.
- Through food.
- By contact (for example, when sharing towels, toys).
Giardia cysts, the entry of which into the body leads to an infectious process, can be found on animal fur, in ready-made dishes (if hygiene rules during food production are violated); They are well preserved on vegetables, fruits, and herbs. There is a risk of infection when swimming in bodies of water.
Its migration to nearby anatomical structures is possible, but bile has a detrimental effect on Lamblia intestinalis, and therefore permanent invasion of the ducts does not occur. Disorders of the hepatobiliary system are associated with intoxication and reflex dyskinesia.
Expert advice
You probably know that even successful therapy for giardiasis does not guarantee the absence of the risk of re-infection. It is impossible to “get over the disease” so that you develop lasting immunity to parasites.
Therefore, it is worth remembering about prevention:
- observe the principles of personal hygiene;
- follow the rules for preparing and storing prepared food;
- drink boiled or filtered water;
- Wash fruits, vegetables, herbs thoroughly or consume them only in heat-treated form.
Persons who have contact with a patient with giardiasis are subject to mandatory examination.
These are members of a family or an organized group (for example, in a kindergarten or school for children). If infection is confirmed, staged therapy is carried out according to the previously described principles.
Classification
Invasion of giardiasis etiology is a systemic process - that is, a general one. Despite the strict localization of parasites, their presence affects the entire organism as a whole. At the same time, there is a fairly wide variety of forms of manifestation.
Clinical classification
Giardiasis occurs:
- typical (classical, with the presence of signs characterizing the disease in accordance with any specific form of the disease);
- latent, or hidden;
- subclinical, or erased.
Giardia carriage is also isolated - a person is infected, but has no signs of intestinal damage or other symptoms of parasitic infestation.
In addition, there is a practical classification:
| Flow type | Form | Syndromes and manifestations |
| With predominant damage to the digestive structures | Intestinal | Duodenitis, enteritis |
| Biliary | Cholecystitis, cholangitis, hepatitis | |
| Gastric | Stomach damage | |
| Combined | There are signs of all the options mentioned before | |
| Masking | Intoxication-allergic | There is a rash, itching, urticaria |
| Asthenoneurosis | Nervous system involvement | |
| Anemic | Decreased hemoglobin levels, possibly red blood cells | |
| Mixed | Combinations of different symptomatological complexes are observed |
The biliary form can be combined with the pancreatic form - that is, with damage to the pancreas.
Classification of flow features
Giardiasis has periods:
- Incubation.
- Vivid manifestations (manifest).
- Convalescence (recovery).
- Chronization.
The flow phases are divided as:
- acute – lasts no more than 1 month, manifests itself with bright manifestations reminiscent of an intestinal infection, and may be accompanied by the development of complications, including liver damage;
- subacute – duration from 1 to 3 months;
- chronic - occurs after 12 weeks of the existence of an active infectious process.
Pathology can be considered as:
- Complicated.
- Flowing without any peculiarities.
It acts as a primary or concomitant disease.
Complications
The consequences of giardiasis are divided as:
- Specific (this is an allergy in the form of urticaria, Quincke's edema, damage to the eyes (ophthalmopathy), joints (arthritis)).
- General (immunodeficiency, exhaustion).
The presence of parasites in the liver can lead to the development of complications such as:
- cholecystitis;
- cholangitis;
- pancreatitis;
- hepatitis;
- abscess;
- sepsis.
Children are at risk of developing bronchial asthma and atopic dermatitis. Although these diseases do not always have a direct connection with giardiasis, the parasitic infection creates a favorable background for the worsening of the condition. The occurrence of intestinal dysbiosis in patients of different age groups is also characteristic.