Incidence of appendicitis in women
Appendicitis can often be difficult to diagnose because early signs and symptoms are mild and nonspecific and may include loss of appetite, nausea, and a general feeling of malaise—symptoms that can indicate many other health problems.
Symptoms only become more severe as the condition worsens. Despite the distinct nature of pain usually associated with appendicitis, experience shows that in women, pain from appendicitis is often confused with gynecological pain and menstrual cramps. On the other hand, gynecological diseases are also easily disguised as appendicitis due to the proximity of the right ovary, fallopian tubes and uterus.
This is the most common symptom of appendicitis. The pain occurs due to pressure exerted by the inflamed appendix and usually varies around the navel. As the inflammation progresses, the pain moves down to the right side of the peritoneum. Over the course of 24 hours, the pain becomes more severe.
Body temperature Low temperature is often present with inflamed appendicitis, but not always. The presence of a temperature above 37 degrees is only a weak factor indicating this condition, which cannot be accurately diagnosed, but in combination with other symptoms it gives a more accurate picture of the general condition. However, some patients experience high fever, especially when the appendix ruptures.
Gastrointestinal SymptomsLoss of appetite is a very common symptom of appendicitis. As the obstruction and inflammation of the appendix worsens, progressive loss of appetite and nausea will develop. Vomiting, constipation and diarrhea may also be present.
Appendicitis is a disease accompanied by inflammation of the appendix. The appendix is a small extension of the cecum, worm-shaped. The disease is eliminated through surgery.
In women, appendicitis most often develops between the ages of 20 and 40. Pregnancy is considered one of the provoking factors. As a result of fetal growth, organs become displaced. This causes inflammation of the appendix.
Appendicitis in medical practice
At one time, the statistics of deaths from appendicitis was alarming.
Medical practice has shown that the optimal solution is complete surgical removal of the problem organ. He constantly threatened the patient's life. The danger remains potential, even in the absence of inflammatory processes. It was also found that difficulties with the appendix can arise for the most unexpected reasons: from stress to overeating. In particular, children suffered from inflammation of the appendix due to poor, insufficient chewing of food. The appendix became clogged with small particles of food, difficult to digest, for example, the husks of seeds. The result was inflammation.
At the moment, some changes can be noted in the traditions of treating appendicitis. There are possibilities for more detailed examination and thorough drug treatment, suppression of inflammatory processes. In this regard, the picture of mass removal of appendicitis that was in the 80s and 90s of the last century is no longer observed. Let us dwell on the key differences between treatment methods.
Where is the appendix located?
| Medication | Surgical |
| The appendix cannot be removed | Surgical intervention with complete removal of the problem organ affected by inflammation |
| The organ is preserved, which will then perform its functions. However, the risk of inflammation also remains | A person loses an organ. This completely eliminates the risk of inflammation followed by sepsis, which is life-threatening. A 100% cure guarantee is given. |
| Despite the remaining risk, many experts still believe that avoiding surgery with air and microparticles entering the abdominal cavity is a great victory for medicine | Surgical removal, surgery, especially in the peritoneum, is always associated with a certain risk to the patient’s life. The result will be determined by the patient’s general health, tolerance to anesthesia and the skill of the surgeon. However, it is worth remembering that surgery prevents the risk of death due to appendicitis, but is dangerous in itself. This is the most radical treatment method with its own side effects. |
But you should understand that drug therapy can only be used for chronic forms of appendicitis! If the inflammation is acute, then the only treatment option is surgery.
In general, we can talk about the controversial issue: treat chronic uncomplicated forms of appendicitis with medication or radically remove the organ surgically. At the moment, many surgeons prefer to preserve the organ. Of course, the approach in such complex cases should be strictly individual.
Inflamed appendix
https://youtu.be/dit6BBgqEVA
The first signs of the disease
There are several reasons that provoke the development of acute appendicitis:
- Blockage of the appendix with undigested food particles and fecal stones. It is not for nothing that the vermiform appendix bears this name - not only is it thin and narrow, but the appendix also has great mobility. Blockage of the appendix leads to stagnation of its contents and inflammation of the wall.
- Entry into the wall of the appendix of conditionally pathogenic and pathogenic intestinal flora - Escherichia coli, staphylococci, enterococci, streptococci, anaerobes in the presence of certain conditions - hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue, bending of the appendix and the impossibility of emptying it;
The first and second causes of appendicitis are interrelated, since stagnation of the contents of the appendix creates ideal conditions for the pathological proliferation of bacteria and their penetration into the wall of the appendix.
- In the West, a separate cause of exacerbation of appendicitis is identified - the ingress of fusobacteria, causing necrotization of the tissues of the appendix. These bacteria are characterized by the ability to quickly cause purulent-inflammatory processes, but are very sensitive to the action of antibiotics. In our country, it is not customary to classify the fusobacterial theory of appendicitis in a separate column, and conservative treatment of appendicitis, which is very common in Western countries, is used extremely rarely.
- Infectious and parasitic diseases of the intestines - typhoid fever, yersiniosis, amebiasis, tuberculosis and others.
- A diet with a high content of protein foods, which contributes to the excessive formation of protein breakdown products in the intestines and the development of putrefaction processes.
- A tendency to constipation is the inability to empty the intestines in a timely manner and the creation of conditions for the active proliferation of bacteria.
Symptoms of appendicitis in adults, characteristic of the typical course of appendicitis, have a cyclical nature and manifestations corresponding to the progression of the pathological process. What are the first signs of appendicitis in adults?
Appendicitis can occur at absolutely any age. But more often young women encounter it. The causes of the disease are as follows:
- disturbance of the blood flow of the appendix or its displacement;
- inflammatory process in nearby organs;
- intestinal infection;
- excess serotonin;
- blockage of the organ with small objects (seeds, bones, etc.);
- clogging of the lumen with feces.
In women, appendicitis often occurs due to gynecological diseases. One of the most common causes of the disease is considered to be an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs. Diet, lifestyle and stress have no less influence on the condition of the appendix. The development of the disease occurs in stages:
- The initial stage of inflammation is called catarrhal.
- The next stage is characterized by the formation of purulent ulcers.
- The phlegmonous stage is characterized by an increase in the appendix and its filling with pus.
- At the last stage, the appendix ruptures.
In addition to pain, acute appendicitis in women has other manifestations. Usually the disease manifests itself suddenly, often in the evening and at night. Its first signs include:
- loss of appetite;
- an increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 °C (in adult women over 40 years of age, this symptom may be absent; on the contrary, the temperature may decrease);
- chills, increased heart rate - general symptoms of inflammation and intoxication;
- dry mouth;
- yellow coating on the tongue;
- bloating;
- upset stomach, loose stools;
- frequent urge to urinate.
In some cases, symptoms of appendicitis in women can mimic food poisoning, an attack of cholecystitis and other diseases of the digestive tract. In addition, the manifestations of this surgical pathology are similar to the clinical picture of ectopic pregnancy, rupture of an ovarian cyst, and inflammation of the appendages.
Pregnant women represent a special category of patients with appendicitis. Compression of the abdominal organs by the growing uterus creates the preconditions for the development of inflammatory processes in the intestines. Often expectant mothers associate discomfort and pain with their special situation, which in the case of appendicitis can be very dangerous.
In pregnant women, the disease proceeds according to the standard scenario. In most cases, pain develops in the epigastrium, and only after a few hours it “descends” to the right iliac region (Kocher’s symptom). Most patients characterize it as acute, of moderate intensity. At the first signs of pathology, it is important to consult a doctor, who will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of the disease. Appendectomy (an operation to remove an inflamed appendix) is well tolerated by pregnant women and does not harm the unborn child.
Causes
The attack usually begins suddenly. Immediately before it starts, the person feels great. Typically, the first signs of the disease appear in the evening or at night.
Here are the main causes of appendicitis that make up the clinical picture:
- Individual features of the structure of the appendix;
- Infection from the intestines or through the blood;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Inflammation begins due to disturbances in the circulatory system of the appendix;
- There are cases when inflammation of the appendix spreads from the genital organs.
- Obstruction or mechanical blockage of the process. Due to the fact that the lumen is blocked due to a foreign body or fecal stone, the contents stagnate in the appendix, an infection occurs and a rapid inflammatory process begins. Blockage occurs due to enlarged lymph nodes, due to parasites, due to the appearance of some tumors or neoplasms.
In this regard, among the preventive measures for appendicitis in women are:
- Fight allergic conditions, which also contribute to decreased immunity;
- Try to prevent the development of dysbacteriosis;
- It is advisable to minimize the number of stressful situations;
- Proper nutrition to help eliminate the problem of constipation, diarrhea and indigestion. This means that you need to have a sufficient amount of fiber, and you also need to eat less fatty and hard-to-digest foods;
- Maintain immunity (frequent inflammatory diseases can lead to infection in the appendix) Chronic diseases of the stomach, pancreas, intestines, genitourinary system organs and persistent inflammation of the tonsils are especially dangerous.
The causes of appendicitis in adults have not yet been precisely established. However, scientists agree that there is no single cause of appendicitis that is common to all patients. Each patient may have their own reason. In most cases, appendicitis is caused by a blockage in the entrance of the appendix to the rectum.
Bacteria also play an important role in the occurrence of appendicitis: enterococci, streptococci, staphylococci and E. coli. Most often there is a combination of both of these factors. Stagnation of the contents of the appendix leads to a weakening of its internal immunity and the introduction of pathogenic bacteria into the mucous membrane.
Factors contributing to the disease include a tendency to constipation, poor intestinal motility, lack of plant fiber in food, overeating, many infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and the presence of parasites. The appearance of the disease can also be influenced by hereditary factors, as well as decreased immunity due to bad habits, stress, and lack of vitamins and microelements.
An increased incidence of appendicitis in pregnant women has also been noted, due to displacement of the appendix caused by an increase in the size of the uterus. In the case of some diseases of the uterus, it is possible that the source of inflammation can be transferred from it to the appendix.
Clinicians include stagnant processes as the main causes of the disease: mechanical blockage of the opening of the appendix with waste products of helminths, coprolites, bones, seeds, or due to neoplasms.
Also provoking factors are:
- chronic diseases of the pelvic organs;
- difficulty defecating;
- atypical structure of the process;
- production of large amounts of serotonin;
- frequent stress;
- endocrine disorders;
- hormonal changes;
- bad habits.
Appendicitis does not select people; everyone is susceptible to it, regardless of gender and age. The exact reasons for its appearance have not yet been established - they are individual for each person, and it is impossible to single out a single cause for all patients. The main factors that can provoke this disease are:
- blockage of the appendix at the entrance to the rectum, which leads to inflammation of the walls of the appendix. It can be caused by various foreign bodies, poorly digested food, fossilized feces and the presence of adhesions;
- the presence of pathogenic bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci and E. coli), which, when the immunity of the appendix deteriorates, successfully penetrates the mucous membrane of the organ;
- the presence of fusobacteria in the appendix, which can lead to serious purulent-inflammatory processes in a very short time;
- intestinal diseases caused by infections and parasites (tuberculosis, typhoid fever).
- the body’s predisposition to frequent constipation (a polluted intestine is the best place to activate bacteria);
- unhealthy diet high in proteins and deficiencies in plant foods, overeating;
- abdominal trauma, heredity.
How does appendicitis hurt: the nature of the pain
- When the appendix becomes full, the pressure inside it increases, causing generalized pain around the belly button.
- Since the pressure increases even more every hour and the inflammation progresses, the pain usually moves to the right lower abdomen - to the location of the appendicitis itself and becomes more severe and intense within several hours.
- Sometimes the pain can spread to the pelvic area or the center of the lower abdomen.
- The pain gets worse when walking, sneezing or coughing.
- If stretched too much, the process may burst. In this case, abdominal pain sometimes decreases for a short time after it ruptures.
- Without treatment, the pain can eventually spread throughout the abdomen, causing generalized peritonitis, an inflammation of the lining of the abdominal cavity.
To distinguish the pain of appendicitis from other more common abdominal pain, you need to trace the nature of the pain:
- pain continues and occurs suddenly over several hours or lasts throughout the day,
- it is often possible to trace the path of pain (from right to left, from the navel down, etc.),
- acute pain may radiate from the navel to the area directly above the location of appendicitis 12 to 24 hours after symptoms first appear.
When alarm signals occur, it is necessary to pay attention to the local location of painful sensations. The appendix is located on the right side, so the greatest concentration of sensations is noted there. Pain is noted in the area from the navel to the lower abdomen, where the ovaries are located in women.
A few hours after the first symptoms appear, discomfort spreads to other organs. Discomfort appears in the epigastric region, aching pain in the lower back develops, and discomfort when walking increases.
The most common symptom indicating inflammation of the appendix is pain. It can hurt in different ways, depending on the location, intensity and nature of the pain; doctors make a preliminary diagnosis.
The inflammatory process always occurs the same way, but the area of pain will depend on the anatomical structure of the appendix. Unpleasant sensations are clearly felt in the abdominal cavity when pressing on the abdomen, especially at the site of inflammation. It becomes hard and swollen to the touch. The patient cannot find a comfortable place for himself, it hurts him to sit and stand.
Symptoms of an inflamed intestinal appendix in children are difficult to recognize, especially when the child cannot explain the pain in which area he is concerned about. Taking this into account, every parent should be attentive when their child is bothered by alarming symptoms.
Symptoms
The problem of how to determine that the symptoms indicate appendicitis is especially acute for the surgeon if the request for help was delayed. At the catarrhal stage, in both men and women, the symptoms are very similar to food poisoning - diarrhea, nausea and vomiting are accompanied by pain.
With the same probability, we can assume an exacerbation of cholelithiasis (in women it occurs more often than in men), with similar symptoms and localization of pain.
If you continue to endure it at home, after 16 hours (and sometimes earlier) the second, more dangerous stage begins - phlegmonous. It differs from catarrhal only in more pronounced pain attacks, which become difficult to ignore and impossible to stop. This is the only way to determine that it is impossible to eliminate a dangerous condition at home.
External relief of the symptoms of appendicitis occurs at the gangrenous stage. In the affected area, the nerve endings die, and they stop transmitting pain impulses to the brain. There is no way to treat this condition with conservative methods, since at home the next stage begins - perforation.
The walls of the appendix are destroyed, necrotic areas form on them, and then holes. Ultimately, the purulent contents of the appendix spill into the abdominal cavity. It is not possible to cure peritonitis even in an operating room in all cases, and if this happens at home, the prognosis is often negative.
Symptoms in women
Even experienced surgeons do not know how to determine that a woman has acute inflammation of the appendix without laboratory and hardware tests. Nausea and vomiting, loss of strength, and disgusting health are characteristic of any inflammatory process in the body that occurs in the acute stage.
Such symptoms may indicate food poisoning, acute cholecystitis, liver pathologies, pyelonephritis, colitis and intestinal obstruction. Pain in the right side indicates fewer possibilities, but the anatomical location or specific condition of pregnancy in women makes it difficult to determine appendicitis.
Here are common symptoms that are also characteristic of other pathologies:
- high temperature is a sign of any acute inflammatory process or viral infection;
- nausea and vomiting are a sign of many emergency conditions, poisoning, exacerbations of a chronic process;
- lack of appetite, high fatigue and decreased performance are characteristic of any severe disease;
- pain in the right side can signal not only the appendix, but also liver or gall diseases;
- during pregnancy, pain can be caused by spasms of smooth muscles, a state of threatened miscarriage, false contractions;
- during the menstrual cycle, pain from the reproductive system radiates to part of the gastrointestinal tract, since the genitourinary system and intestines are located in close proximity.
It is almost impossible to name symptoms that absolutely indicate acute appendicitis unless this issue has been specifically studied. But even experienced surgeons can confuse its manifestations with other emergency conditions due to uncharacteristic signs, features of the anatomical structure, size and location of the insidious appendix.
The location of pain on the right side does not always mean the presence of acute appendicitis, but should always be accompanied by a full examination.
Abdominal pain is often confused with an ailment of the digestive system, but there are distinctive signs that make it possible to recognize suspected inflammation:
- Pain syndrome in the abdominal area. Only at the beginning of the inflammatory process is discomfort felt near the navel, with a gradual movement to the right, to the lower corner, to where the appendix is located. The attack and pain occur unexpectedly, it is impossible to take a deep breath. The pain syndrome intensifies many times when a person begins to cough or laugh.
- Body position. When the appendix becomes inflamed, the human body involuntarily takes a certain position in which the pain is not so strong. A man walks in a bent position. In the supine position, both the adult and the child lie on their sides with their legs pulled up.
- Nausea, vomiting develops. The inflammatory processes occurring inside also affect the intestines, causing a feeling of nausea and regular vomiting, which does not bring relief. In rare cases, gagging occurs 1-2 times; the majority of patients complain of ongoing discomfort. Schoolchildren and teenagers suffer from appendicitis more often, which is why vomiting occurs more often during this period. Adults experience vomiting much less frequently. If the disease develops in an elderly person, such symptoms are not observed.
- Body temperature. When the body tries to cope with any inflammation, the overall temperature rises. As a rule, the thermometer shows 37.5 - 38 degrees. In a child’s body, the temperature can reach 40. An increase in thermometer readings indicates an increase in the inflammatory process and the progress of the disease.
- Defecation disorder. It is rare for an upset bowel symptom to occur. Only if the location of the appendix itself is atypical, then there may be a lack of stool or diarrhea. It is worth noting the state of a person after defecation is liquid. If after the process there is temporary relief, then there is poisoning; if there is no relief, it is appendicitis.
- Feeling of dry mouth and plaque. The appearance of these signs clearly indicates the development of inflammatory processes in the cecal appendage.
In rare cases, pain may occur when urinating. This occurs due to the location of the appendix next to the bladder and pressure on it (sometimes it is believed that the kidney hurts). Pain may appear in the lumbar spine or in the groin. It all depends on the specific position of the appendix in the human body. Sometimes it is difficult to diagnose the disease when children develop a runny nose and a cold cough.
At home, determining the presence of acute appendicitis is not so easy. It is extremely important to be able to distinguish the signs, since any delay is life-threatening. It is necessary to seek qualified help at the first symptoms.
Let's look at the key signs of acute appendicitis.
Symptoms of appendicitis in an adult
Floating pain
As a rule, at first abdominal pain does not have a clear localization (usually in the periumbilical or epigastric areas). But within several hours, the pain shifts to the right lower quadrant of the abdomen, when the parietal peritoneum is involved in the inflammatory process. Often, patients believe that their gastritis has worsened, or that the unpleasant sensations are associated with poisoning or overeating. Often, this symptom (Kocher's symptom) becomes the most important in early diagnosis and is the reason for hospitalization.
Possible locations of pain in appendicitis
Constancy
A characteristic sign of pain with appendicitis is persistence. At the same time, it may subside a little, and then sharply increase again. However, it continues steadily for a long time. The pain syndrome noticeably increases due to physical tension, muscle contractions: when coughing, inhaling and exhaling, turning, walking and running, transferring the body from one position to another.
If the pain suddenly subsides, this is an extremely dangerous sign. In this way, the body signals the transition of inflammation of the appendix to a stage when the threat to the patient’s life sharply increases. You cannot be happy if this severe, ongoing pain suddenly stops. It is very likely that the appendix ruptured, followed by purulent blood poisoning, with the contents rupturing directly into the abdominal cavity.
The first symptoms of appendicitis
How to identify the signs
The main symptom of appendicitis is abdominal pain. It gets worse when laughing or moving. In some cases, discomfort radiates to the right leg. At the initial stages, it is difficult to understand the symptoms of appendicitis in women; how to determine their manifestation at home, you need to learn in advance. Inflammation develops rapidly, so it is important to consult a doctor in time.
There are certain signs that you should pay attention to. At the initial stage, the pain is aching in nature. It can radiate to any area of the peritoneum. Its signs can easily be mistaken for cholecystitis, gastritis or gynecological diseases. A little later, the clinical picture becomes more pronounced.
External
External signs of appendicitis include low-grade fever. It is characterized by fluctuations in body temperature in the range from 37.1 to 38 degrees. Deterioration in health is accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring significant relief. Pregnant women experience abdominal stiffness and shortness of breath. The skin becomes pale, the tongue becomes covered with a yellowish coating.
Domestic
With inflammation of the appendix, appetite may disappear. There may be difficulty urinating and bowel dysfunction. Diarrhea occurs most often. Clinical symptoms depend on the location of the process. When it is located behind the cecum, the pain is muted. Localization of the appendix in the pelvis leads to atypical pain.
Internal signs of appendicitis are determined by palpation. The right iliac region and umbilical ring are examined. With light palpation, the tone of the anterior peritoneal wall increases. When you take a deep breath, you feel an increase in pain.
At the early stage of inflammation, symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite, and deterioration of health often appear. Few people associate such sensations with an impending illness, but they can help quickly make a diagnosis and avoid complications. Do you experience pain when breathing? This may be the first sign of appendicitis.
This option is rare, but stands out as a separate disease. Diagnosis is complicated by the unclear nature of the pain. They appear rarely and may become worse after eating or during menstruation. One of the signs of a chronic disease is a decrease in muscle tone on the right side of the abdomen.
What should you do if you suspect appendicitis?
At the slightest suspicion of appendicitis, you should call a doctor. The reason to consult a doctor is any persistent pain in the abdominal area that does not go away within 6 hours. Before being examined by a doctor, you should not take laxatives, antibiotics or other gastrointestinal drugs, and especially analgesics, as all these drugs can blur the clinical picture and make diagnosis difficult.
It is also prohibited to place a heating pad on the right side of the abdomen, since an external heat source can accelerate the development of the disease. Bed rest is indicated. You should refrain from eating. When the doctor arrives, you need to tell him about all the symptoms, how your stomach hurts, and allow him to conduct an examination.
Principles of diagnosing appendicitis
The diagnosis of acute appendicitis is made on the basis of:
- patient survey data;
- physical examination data;
- laboratory blood test (leukocytosis in dynamics);
- data from an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity (American experts consider ultrasound a low-informative method for determining appendicitis, which has many diagnostic errors, recommending CT);
- temperature reaction.
It is necessary to differentiate this pathology from acute gastroenteritis and pancreatitis, covered perforation of a gastric or duodenal ulcer, intestinal dyskinesia, renal colic, pleuropneumonia. With an atypical location of the appendix, the disease is differentiated from gynecological and urological pathology, cholecystitis.
If there is doubt about the diagnosis, they resort to laparoscopic examination of the appendix. This diagnostic procedure allows you to accurately establish the diagnosis and, if it is confirmed, immediately begin laparoscopic appendectomy.
If pain occurs, appendicitis can be diagnosed using one of the following methods:
- The Sitkovsky test involves the patient initially lying on his right side, after which he turns over to his left. Symptoms should completely stop or subside on the right side. When turning to the left side, the intensity of the pain increases.
- Obraztsov's symptom. The patient should take a horizontal position and straighten his legs. Later, you need to carefully lift your right leg, which is not bent, up. If a person has an inflamed appendix, the intensity of pain will increase significantly. With advanced forms of pathology, the patient may not be able to cope with the task at all.
- The Rovsing test consists of palpating the side where the appendix is located. Manipulations should be jerky in nature. During pressing, pain should not appear; it occurs when releasing the hand.
Diagnosis of appendicitis is based on clinical examination data and specific clinical symptoms (Shchetkin-Blumberg, Obraztsov, etc.). The type of inflammation can be determined and the diagnosis can be confirmed using additional methods - ultrasound, laboratory tests. In difficult diagnostic cases, laparoscopy is prescribed.
Self-diagnosis and self-treatment of appendicitis is unacceptable. However, you can check at home whether you really have this surgical pathology. For this:
- Bend your index finger slightly and tap the iliac crest with it. With appendicitis, abdominal pain will intensify.
- Try coughing loudly: increased pain also indicates the development of inflammation of the appendix.
- Lightly press the palm of your hand onto the skin in the sore area. Hold for 5-10 seconds: during this time the discomfort decreases. Then suddenly release your hand: the return of acute pain is one of the signs of appendicitis.
- Lie on your right side and assume a fetal position. The pain will ease at this point. A similar position on the left side, on the contrary, will lead to increased discomfort.
If appendicitis is suspected, only a doctor can palpate (feel) the abdomen. Failure to comply with the procedure technique can lead to rupture of the inflamed appendix.
The final diagnosis is made by specialists. There is no need to take any measures on your own. If you suspect appendicitis, you should not drink water or engage in active movements. This will prevent premature rupture of the appendix. It is advisable to wait for an ambulance in a horizontal position. At temperatures below 38 degrees, antipyretic drugs are not required
You can distinguish appendicitis from other diseases at home. The main thing is to carry out all manipulations carefully. Initially, the symptoms of appendicitis in women are assessed; how to determine the source of pain at home is no less important. You need to press your fingers into the place on two fingers to the right of the navel and quickly release them. The pain at this moment will be more intense.
In the hospital
After entering the hospital, diagnostic tests are carried out. It includes the following steps:
- examination by a surgeon;
- visit to the gynecologist;
- blood donation;
- Ultrasound monitoring.
The gynecologist conducts an examination for the presence of gynecological diseases. If they are not there, the woman is referred to a surgeon. He will palpate the abdominal area and ask questions about your stool and last meal. Donating blood helps determine the level of leukocytes and ESR. An increase in indicators indicates an inflammatory process. An ultrasound examination is prescribed if doctors have doubts about making a diagnosis.
Features of the disease during pregnancy
Pregnancy can provoke the appearance of an inflammatory process in the appendix, due to changes, movement of organs in the abdominal cavity, growth of the uterus, as well as gastronomic preferences. The peculiarity of appendicitis in women during pregnancy is that the symptoms are very different and may be incorrectly recognized as another disease at the primary stage.
This disease is most dangerous starting from the second trimester, when placental abruption, intrauterine infection and, as a consequence, fetal loss can occur.
If you suspect appendicitis, a pregnant woman should definitely go to the hospital for tests, undergo an ultrasound or laparoscopy, in order to provide timely assistance in emergency cases. Operations are carried out using both classical and modern methods. After the operation, the pregnant woman remains in the hospital for 10-14 days, under the supervision of doctors with a course of antibiotic therapy.
A woman after an appendectomy is at risk of premature birth or miscarriage. Symptoms of appendicitis manifest themselves differently in adult women than in men, but they can also be treated successfully if you do not neglect to visit a doctor or call an ambulance.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Features of the flow
According to the nature of inflammation, acute appendicitis is:
- catarrhal (when the mucous layer of the appendix is inflamed) - develops in the first hours from the onset of the disease;
- purulent or phlegmonous (characterized by severe swelling of the walls of the organ and the formation of purulent exudate) - on the first day from the onset of the disease;
- gangrenous (accompanied by necrosis - death of appendix tissue) - within a few days after the development of inflammation.
Perforation of the wall of the appendix and entry of inflammatory exudate into the free abdominal cavity is accompanied by the development of peritonitis, a life-threatening condition.
In rare cases, the female body develops chronic appendicitis, a disease in which the inflamed appendix is limited to a dense appendiceal infiltrate. As a result, the first attack of abdominal pain goes away, but after a while it appears again. The pathology is characterized by a wave-like course, in which exacerbation is replaced by remission.
The danger of appendicitis is the possibility of death. In the absence of timely assistance, peritonitis develops. The inflammatory process may be sluggish. In this case, the pain is not very pronounced, but the following symptoms periodically appear:
- vomit;
- pain during bowel movements;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- decreased performance;
- discomfort in the abdomen after eating, while laughing or hiccups.
Causes of chronic appendicitis and its types
The following types of chronic appendicitis are distinguished:
- Primary chronic appendicitis. In this case, the causes of inflammation have not been precisely established, and a number of authors generally consider this form of the disease to be non-existent. Such a diagnosis is established only after a thorough examination and exclusion of any other pathology of the abdominal organs.
- Secondary chronic appendicitis. He can be:
- residual - occurs after acute appendicitis, which was not operated on,
- recurrent - repeated attacks of acute appendicitis periodically occur with a minimum number of symptoms between them.
Recurrent appendicitis can develop even after removal of the appendix for acute appendicitis, if a stump of more than 2 cm in length remains.
The development of chronic inflammation in the appendix is facilitated by cysts, adhesions, hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue, kinks in the appendix, and circulatory disorders in this organ.
Possible complications and consequences
If you do not take the necessary measures for the primary symptoms of inflammation of the appendix of the cecum, life-threatening complications may develop, for example: pylephlebitis, abscess, formation of abscesses and peritonitis.
Only a surgeon can identify the consequences of pathology based on the examination results. As a rule, when the appendix becomes inflamed, during surgery it is possible to get rid of all undesirable consequences, but the development of complications during the recovery period should not be ruled out.
Let's look at the most common postoperative complications:
- Formation of postoperative hernia. It is most often formed due to divergence of seams.
- Peritonitis is diagnosed, as a rule, in adults who came to a medical facility late. Accompanied by high fever, weakness, pain in the peritoneum.
During the postoperative period, all necessary rules must be followed. Firstly, it is important to avoid overeating and exclude spicy, fried and fatty foods from your diet. Physical activity is contraindicated, otherwise the seams may come apart.
Complications of acute appendicitis include: limited abdominal abscess, appendicular infiltrate, diffuse peritonitis and pylephlebitis.
If appendectomy is performed in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. If appendicitis is complicated by peritonitis, more extensive surgery is required, followed by drainage of the abdominal cavity and serious antibiotic therapy, the recovery period is prolonged.
If a person does not seek medical help, the disease can lead to death from peritonitis and acute intoxication of the body. It is extremely rare that appendicitis resolves spontaneously with the formation of an inflammatory infiltrate. However, you should not count on this, since in the future such an outcome of acute appendicitis results in the formation of adhesions and foci of inflammation in the abdominal cavity.
Any acute pain in the abdomen, aggravated by coughing or movement, accompanied by a slight fever, nausea, diarrhea or constipation, as well as involuntary tension of the abdominal muscles, is a reason to immediately consult a doctor!
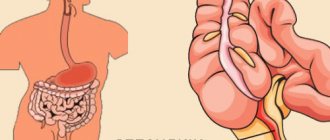
What is the appendix
The appendix (appendix vermiformis) is the vermiform appendage of the cecum. The physiology of its occurrence occurs from the lateral entry of the small intestine into the large intestine, forming a kind of dome with an appendage. It is located on the right side in the ileum region below the liver, and sometimes behind the cecum.
Depending on the physiological characteristics of the structure of each person, it is located closer to the pelvis or liver on the right side. There are exceptions; those people who have a mirror image of the structure of their internal organs may experience pain from inflammation of the appendix on the left side.
The appendix performs a protective function of the body, which partially affects the human immune system.
It contains a large number of beneficial bacteria that allow you to restore the intestinal microflora, especially after infection and antibiotic therapy.
Appendectomy
The operation to remove appendicitis is performed using a classic appendectomy or laparoscopy. Appendectomy is a classic abdominal operation. Laparoscopy is an operation that does not require abdominal incisions in the skin. It is less traumatic, but has a number of significant contraindications. Classic appendectomy is performed much more often.
Before the operation, general anesthesia is given. Then access to the affected organ is provided. In the case of laparoscopy, small punctures are made in the skin. The appendix is completely removed, after which the abdominal cavity is drained. The final step involves placing stitches on the puncture or incision sites.
Results
Everyone should know where the appendix is located and what signs accompany its inflammation. This pathology can cause life-threatening complications. It is strongly recommended not to delay contacting a specialist. Timely surgical intervention to remove the appendix significantly reduces the likelihood of developing undesirable consequences.
You can get appendicitis once in a lifetime, but despite this, you cannot treat the disease negligently. Many leading experts are of the opinion that it is possible to prevent inflammation of the appendix by observing preventive measures.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the doctor prescribes antibiotic therapy. Medicines and their regimen are selected on an individual basis. If there is a predisposition to thromboembolism, anticoagulants are prescribed.
A scar measuring up to 10 cm is formed at the site of the operation. It heals for about six months. Immediately after the operation, it has a burgundy tint, and over time it turns white. To resolve it, specialized ointments and creams are prescribed. Following your doctor's recommendations ensures a quick recovery. With proper care, the likelihood of wound suppuration is significantly reduced.
Diagnosis is simplified by specific symptoms of appendicitis in women; how to determine the disease at home becomes clear after studying physiology. The main difference is the location and nature of the pain. But only a specialist can make a final diagnosis.
Diagnostics and treatment in a hospital setting
The anatomical feature of the female body does not always allow one to quickly and accurately determine inflammation of the appendix. Since there may be another organ at the location of the inflamed appendage. Many women experience similar pain (pulling and aching) during the menstrual cycle.
- inflammation of the diverticulum. This organ is localized near the appendix and, when inflamed, also causes pain in the lower abdomen. The diverticulum is removed surgically;
- diseases of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. These organs are located very close to the appendix. Therefore, infectious diseases of the genital organs cause identical pain;
- diseases of the organs of the upper peritoneum. In case of stomach ulcers, problems with the genitourinary system, liver damage and other diseases, fluid can flow into the lower right half and cause pain in the lower abdomen;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- poisoning due to intestinal obstruction;
- kidney diseases.
Calling emergency help will help make a diagnosis and begin treatment as quickly as possible. If the presumptive diagnosis turns out to be false, the surgeon will refer the patient to a gynecologist for further examination.
Diagnosis begins with a physical examination, which allows a preliminary diagnosis to be made. Today there are many techniques and methods by which appendicitis is identified.
For example, a woman’s pain intensifies:
- when pressing on a painful area of the abdomen, and then quickly sharply removing it;
- when you press on the area where the cecum is located;
- when touching the painful area of the abdomen and lifting the right leg;
- when palpating the area of inflammation: from the navel to the right upper iliac region.
Despite the fact that an accurate diagnosis has been made, ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic tomography and endoscopy are mandatory examinations.
Tests confirm the clinical picture:
- Blood analysis. If there is an infectious inflammatory process in the body, the patient's leukocytes are elevated. At the initial stage of appendicitis, the number of blood cells may remain unchanged, but at a later stage it necessarily changes, which also indicates inflammation of the appendix.
- Analysis of urine. This analysis is highly likely to determine inflammation of the genitourinary system, since it significantly increases the number of microbes, red and white blood cells. If the urine test is normal, this will confirm the diagnosis.
If for any reason there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, laparoscopy is performed. This is a modern method that allows you to examine the cecum through a special camera introduced into the body through a small incision.
External changes in the appendix are immediately noticeable and the patient will be referred for surgery. Today it is often carried out in the same way. Manipulations using laparoscopy leave a cosmetic, almost imperceptible suture, which distinguishes this method in comparison with open surgery.
In the hospital, the doctor must determine appendicitis and exclude the presence of other pathologies using palpation, laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Ultrasound or radiography is performed;
- the patient donates blood and urine for tests.
X-rays and ultrasound images will help identify pathological changes characteristic of appendicitis:
- accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the cecum, between the layers of the peritoneum or in the pelvis;
- increase in the thickness of fatty tissue;
- swelling of the intestinal walls located near the appendix;
- modifications of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract;
- increase in size of the appendix, thickening of its walls.
In some cases, when it is difficult to detect the disease, a laparoscopic examination is performed. This procedure allows you to assess the condition of the internal organs and the type of appendicitis. A movable tube with a camera at the end is inserted into a small incision, which transmits the image to the monitor. If cells begin to die and necrotic changes progress, this indicates gangrene.
Ultrasound and blood tests
To perform laboratory tests for appendicitis, the patient is given blood and asked to provide urine. This is necessary to exclude other diseases of the pelvic and abdominal organs. When examining blood against the background of an inflammatory process, a high level of leukocytes with a predominance of neutrophils is observed.
To identify inflammation of the appendix of the cecum with an intra-abdominal abscess and determine its atypical locations, an ultrasound examination is performed.
For diagnosis, visual inspection and palpation are used primarily. The main symptoms are a tense abdomen and pain in the lower right part. However, these methods are not always reliable. Diagnostic methods such as ultrasound, MRI and computed tomography, blood and urine tests are also used.
It should be noted that recognizing the disease can be difficult, since the symptoms of acute appendicitis are largely similar to other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. These include acute gastroenteritis, pancreatitis, ulcer (especially if it is perforated), intestinal or renal colic, inflammatory processes of the uterus, stretching or rupture of the abdominal muscles. Therefore, it is important to differentiate appendicitis from other diseases, which in most cases do not require urgent surgical intervention.
Acute appendicitis requires surgical intervention already in the first hours of the development of pathology.
Lack of timely treatment results in severe complications for the patient, so it is important to establish an accurate diagnosis in time and, based on it, select a treatment method.
Diagnosis of appendicitis must be extremely accurate, since this disease is often disguised as other diseases.
Suspicion of the development of acute inflammation of the appendix in a person usually appears already at the stage of development of the first symptoms, since some signs are characteristic of appendicitis.
If you experience prolonged abdominal pain, dyspeptic disorders, nausea, or symptoms of intoxication, you should seek help from a medical facility.
The doctor will be able to presumably determine what caused the changes in well-being, and based on this, prescribe examinations and consultation with specialists. If appendicitis is suspected, the entire examination usually takes place in several stages, these are:
- Examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis.
- Palpation and percussion of the abdomen.
- Lab tests.
- Instrumental methods for diagnosing diseases.
- If possible, diagnostic laparoscopy.
At each stage of the examination, the surgeon records deviations from the norm and, based on the totality of changes, makes a diagnosis.
Patient examination
When a patient enters the emergency room, the surgeon immediately focuses on the person’s behavior and posture. Appendicitis can be suspected by the tense position of the body - pain in the iliac region on the right forces a person to carefully sit down; in a lying position, the patient often pulls his legs towards his stomach. With tension, that is, a change in body position, coughing, or laughter, it is clear that the pain intensifies.
During the examination, the doctor collects all complaints. It is important to find out where in the abdomen the pain started, how long it lasts, and whether there are symptoms of intoxication.
Palpation is carried out with caution. With appendicitis, you can feel, by palpating the abdomen, tension in the abdominal wall at the lower right or at the site of the atypical location of the appendix. The doctor also conducts special tests, during which certain symptoms indicating appendicitis are recorded.
- Sitkovsky's symptom. The patient should lie on his left side, and when the appendix is inflamed, the pain in the lower right increases. This is due to the fact that the mesentery of the appendix is stretched and, accordingly, the walls become tense, and the pain increases.
- Obraztsov's symptom. The patient must raise his right leg straightened at the knee joint; the pain also intensifies due to the tension of the mesentery.
- Razdolsky's symptom consists of lightly tapping the abdominal wall with the edge of the palm. As appendicitis develops, the pain increases.
- The Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom consists of pressing the fingers on the right iliac region with a sharp removal of the hand after about three seconds. A positive symptom is increased pain.
- Rovsing's symptom consists of palpation with jerky movements of the large intestine in its lower parts. With inflamed appendicitis, the movement of gases during such palpation increases the pain.
There are dozens more tests used by surgeons to rule out or confirm appendicitis in people of different ages.
By palpation, an experienced doctor can identify a conglomerate in the area of the appendix, which suggests an appendiceal infiltrate formed due to inflammation. Certain difficulties arise when determining inflammation of the appendix during palpation in pregnant women.
The tests used during this period of a woman’s life can be distorted, and pain due to displacement of the appendix is localized above its typical location for appendicitis.
When a patient with suspected appendicitis is admitted to the hospital, a gynecologist is usually invited to examine her. This is due to the fact that inflammation of the female genital organs and ectopic pregnancy have a pathology similar to appendicitis.