Many, eating tons of stress food, at first cannot even imagine that the problem requires radical therapeutic treatment. Bulimia – what kind of disease is it, how is it expressed and what can it cause? You should give yourself clear answers to all these questions so that you don’t unknowingly and accidentally put yourself at risk.
What is bulimia?
Bulimia – what kind of disease is it? Translated from Greek, the term “bulimia” means “wolf hunger.” In medicine, bulimia (or bulimia nervosa) is a mental illness, an eating disorder, characterized by regular uncontrollable outbreaks of hunger and overeating.
With bulimia, a person is constantly haunted by an obsessive thought about controlling his figure and the desire to reduce the negative impact of what he eats on his figure, even if his weight does not exceed normal values, which leads the patient to take extreme measures, for example, taking a laxative or provoking vomiting. Bulimia began to be considered as an independent disease in medicine relatively recently, which explains the lack of awareness of the population about this pathology.
There are several options for the mechanism of development of bulimia:
- Increased sensitivity of receptors to a slight decrease in blood sugar levels, for this reason it hurts to begin to feel hungry too early.
- Problems with the passage of signals from the stomach to the brain due to defects in the connection of nerve cells. As a result, the patient does not feel full.
- Disturbances in the functioning of food center areas.
Normal types of appetite formation:
- General appetite. Positive reaction to food in general. It occurs when blood, with a small amount of nutrients, affects the nerve endings of the hypothalamus. Failures in the formation of this type of appetite provoke the patient to absorb any food that does not combine with each other, possibly even spoiled, and the person never develops a feeling of satiety.
- Selective appetite. When there is a deficiency of necessary compounds in the body, a person begins to crave a certain type of food: salty, sweet or sour. On the surface of the cerebral cortex there are areas responsible for this mechanism and shaping eating behavior. When this mechanism is violated, a person begins to uncontrollably consume a certain type of product.
Causes
This eating disorder can be caused by stress, an ineffective diet, or an attempt to cope with painful emotions or feelings of imperfection in one's own body.
In general, there are many different reasons and factors why someone may develop bulimia. It is important to understand that eating disorders are often not about the food itself, and treatment must address the underlying thoughts and feelings that trigger the behavior.
Causes and risk factors
The causes of bulimia are mainly psychological in nature, but there are also physiological and organic factors that provoke this disease.
The occurrence of bulimia in most cases is explained by moral trauma or mental discomfort that the patient received or experienced in the past, for this reason there were failures in the “hunger-satiety” system.
Psychological traumas received in childhood that can cause bulimia:
- regular and prolonged feeling of hunger in infancy;
- parents’ beliefs that the child is too fat and should lose weight;
- lack of care and love from mother and father;
- difficult relationships with peers, bullying and bullying at school;
- food rewards for success, good behavior and grades at school.
In the examples above, food begins to be seen not as a need, but as a comfort and pleasure. Eating is safe, enjoyable and affordable. As a result of the formation of such an attitude towards food, it violates the main principle of proper nutrition - “Eat when you are hungry”, which causes disruptions in the functioning of the hypothalamus, which is responsible for the sensations of hunger and satiety.
In adolescence, young adulthood and adulthood, bulimia can also be caused by some social factors:
- An obsessive desire to meet modern beauty standards. The standards of appearance imposed by society, appropriate advertising, and the popularity of social networks in which users share their attractive photos make many people experience inferiority complexes and strive to meet the standard.
- Tactless remarks, jokes and comments about excess weight from people in your close circle. Suspicious and touchy people are sensitive to this kind of statements, worry about them for a long time and, ultimately, can decide to take extreme, unreasonable measures.
- Constantly comparing yourself with an attractive person from your environment, competing with him. It can be either a close person or a distant acquaintance or neighbor. A person prone to bulimia tries in every possible way to show that he is better, tries to look more attractive.
Physiological and organic reasons for which bulimia may occur:
- Metabolic disorders in general.
- Metabolic syndrome is a complex of changes in the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates, accompanied by an increase in a person’s weight and an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
- Diabetes. Impaired glucose absorption can often cause eating disorders. In addition, a certain diet for diabetes can provoke bouts of overeating in patients, who may even consume foods that are prohibited for them.
- Neoplasms in the hypothalamus or its toxic lesions.
- Pituitary cachexia is a pathology of the pituitary gland and hypothalamic nuclei, due to which the production of neurohormones of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus is reduced. Most often, damage to these areas occurs after infections: syphilis, tuberculosis, typhoid, malaria and others. In addition, the disorder can occur after surgery, against the background of vascular pathology and traumatic brain injury.
- Hereditary factor. The possibility of bulimia increases in individuals who have several relatives suffering from this disorder. This is due to genetic characteristics of the function of the endocrine system and a deficiency of hormones responsible for regulating feelings of hunger and satiety.
- Nutrient deficiencies caused by frequent dieting. With severe restrictions on food consumption, a person is very often unable to think about anything other than food. At one point he breaks down and starts eating uncontrollably. In this way, the exhausted body tries to restore strength and replenish nutritional deficiencies.
Suspicious and anxious individuals are most prone to developing bulimia, especially those experiencing feelings of guilt, low self-esteem and inferiority complexes, who are unable to fully experience satisfaction with certain positive events in their lives. As a rule, this type of people often suffers from prolonged depression.
Causes of bulimia
Bulimia nervosa is classified as a type of food addiction. If patients with anorexia refuse to eat, trying to show that they have control over themselves, then bulimics follow their emotions, destroying food as an abstract symbol and destroying themselves.
There are many reasons for the development of bulimia nervosa, since the issue in this case is purely individual, but among the most common are:
- authoritarian parenting style in the family;
- unconscious fear of loss of control;
- interpersonal conflicts in any area of interaction with others;
- change of usual way of life;
- death of a loved one or long separation from him;
- prolonged exposure to a stressful situation.
People suffering from bulimia nervosa experience feelings of loneliness, worthlessness, emptiness and disappointment in others, sadness, depression and melancholy. In this case, food acts as a way to lift your mood and combat stress.
Noticing weight gain, they try to regain control of themselves using mainly harmful methods, for example, diet pills, crash diets, and artificial vomiting. All this only leads to worsening the problem and deterioration of health.
Important
Often, unconscious feelings of envy, greed, and jealousy lead to the development of bulimia nervosa. Almost any negative emotions can become a fruitful platform for the formation of food addiction.
Signs and symptoms of bulimia, clinical picture
The main criteria to suspect the presence of the disease are the following symptoms of bulimia:
- Uncontrollable bouts of overeating. Moreover, they can be caused by both negative and positive events in life. Often appear at night. A person suffering from bulimia may chew something constantly.
- Inappropriate methods of weight loss. Refusal to eat, excessive, grueling physical activity, strict diets, taking laxatives, inducing vomiting. In cases where bulimia is accompanied by other serious disorders of the central nervous system, a person may cause physical harm to himself as a result of dissatisfaction with his appearance and self-hatred.
- A clear dependence of self-esteem and mood on body weight and physical fitness.
Some symptoms of bulimia are clearly visible to others. Signs of a person suffering from bulimia include:
- Constant conversations about excess weight, diets, gyms, models, physical fitness are common with bulimia. The ideal figure becomes an obsession for the bulimic, it occupies all his thoughts, and often he simply cannot carry on a conversation on other topics. At the same time, people suffering from bulimia quite often, in fact, do not have extra pounds in their weight.
- With bulimia, the patient is ashamed of his appetite and hides the fact that he eats a lot. He is officially on a healthy eating regimen or on a fad diet.
- Noticeable weight changes. A person can lose weight or gain weight by 5-10 kg in a very short time. Losing weight corresponds to the measures taken to reduce body weight, and gaining weight corresponds to a breakdown and bouts of overeating.
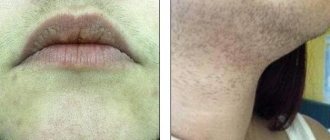
- Yellowing of teeth and wounds in the corners of the lips. Regular vomiting, which contains hydrochloric acid present in gastric juice, corrodes the oral mucosa and negatively affects tooth enamel.
- Damaged blood vessels of the eyeballs. Rupture of the ocular vessels is explained by a temporary increase in blood pressure that occurs during vomiting.
- Dry skin, deterioration of hair and nail structure caused by dehydration and lack of vitamins.
Symptoms of bulimia:
- A constant feeling of excruciating hunger, accompanied by pain in the stomach.
- Drowsiness, apathy, lethargy, depression, feelings of depression, impaired memory and attention, deterioration of mental activity due to lack of glucose in the body and constant dissatisfaction with one’s appearance.
- Dizziness and weakness.
- Inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity caused by constant vomiting.
- Frequent inflammation of the throat and tonsils. Sore throats and pharyngitis develop as a result of microtraumas of the throat mucosa by irritating vomit.
- Heartburn and spasms in the esophagus. These manifestations are caused by inhibition of the sphincters, which do not allow stomach contents to move up the esophagus and irritation of the esophageal mucosa by acidic vomit.
- Nausea. Constipation or diarrhea. Various types of disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract occur as a result of excessive food consumption, fasting, and the use of laxatives.
- Cramps. A deficiency of potassium and magnesium, which are excreted in the urine and are not properly absorbed due to frequent diarrhea or vomiting, disrupts normal muscle function, causing cramps.
- Disruption of the genitourinary system. In particular, decreased libido, menstrual cycle disorders in women and potency in men. These phenomena are observed against the background of hormonal disorders caused by inadequate methods of losing weight and pathological overeating.
- Constant feeling of guilt due to breakdown and overeating.
- Pathological need for the approval of other people.
Bulimia is a mental disorder, so the patient cannot adequately assess the situation, believing that his body weight is above the norm, even if in reality this is not the case.
Most often, bulimia occurs in adolescents aged 13-16 years or in girls 20-22 years old.
Classification of the disease
Scientists identify types of addiction that require close attention from a specialist.
- Primary bulimia, when patients feel constant bouts of irrepressible hunger.
- Bulimia as a residual phenomenon of anorexia. With this option, patients may alternate between bouts of uncontrollable gluttony and feelings of guilt, which is why they try to induce vomiting or drink laxatives.
The disease can progress in different ways. Some patients immediately after eating a large amount of food induce vomiting, diarrhea, and use enemas. In other cases, addicts exhaust themselves with diets and constant restrictions, from which they fall into the abyss of overeating. After this, food conditions have to be even more strictly limited.
Causes of bulimia nervosa: symptoms and treatment
To protect yourself as much as possible, it is worth thoroughly understanding what bulimia is and how it manifests itself. Often it becomes a consequence of organic or functional failures of the central nervous system. They can be psychological or physiological.
Physiological
- Hypothalamic-pituitary disorders.
- Elevated insulin levels.
- Tumors, both malignant and benign.
- Epilepsy, including the so-called vodka epilepsy.
- Old traumatic brain injuries.
Often, such disorders are directly associated with disruptions in the functioning of the food center of the cerebral cortex, all metabolic processes, and metabolic syndrome. Bulimia is caused by inherited problems or imbalances of chemicals and hormones in the brain.
Psychological
Statistics determine most clinical cases of bulimia in the psychological plane of the individual’s state. That is, the disease is caused not by objective, but by subjective reasons.
- Low self-esteem.
- Schizophrenia.
- Nervous-obsessive states.
- Hysteria and psychopathy.
All these, as well as many other mental disorders, lead to illness. It was only in the early twentieth century that bulimia and anorexia began to be considered signs of eating disorders. More often it develops in rich people who are prone to ambition. The desire to conform, low assessment of achievements, successes, fear of not living up to someone’s hopes, disgrace, and letting loved ones down leads to disastrous consequences.
It is worth mentioning individuals with a tendency to frequent depression, lonely and unsociable. They try to replace everything that is lacking in communication and healthy interaction with other people with food and its excessive consumption. As a result, complete self-isolation sets in, which aggravates the problem.
Who should worry?
Bulimia is considered a certain form of obsession (addiction) regarding food. Many scientists suggest that the disease has distinct socio-ethnic forms. The main risk group is women and girls starting from the age of thirteen. Moreover, the main peak groups most often appear at sixteen or eighteen, twenty-two - twenty-five, and also at twenty-seven - twenty-eight years.
However, mild forms can occur with equal frequency in both sexes. The male share of cases is only fifteen percent of the total. Symptoms that are noticeable to others appear less frequently and weaker in them, and they tend to react more aggressively to attempts to provide psychological help. This makes treatment much more difficult.
Symptoms often develop in people following strict dietary restrictions. Bulimics themselves generally support the stereotype that there is no disease, but only a lack of willpower to refuse overeating. Their loved ones may support their misconceptions. You will have to fight it seriously and thoroughly. After all, it is akin to drug addiction, only instead of psychotropic substances it is food.
Classification and forms of bulimia
In medicine, there are two types of bulimia: bulimia nervosa and pubertal bulimia.
Bulimia nervosa
This type of bulimia is typical for patients 25-35 years old. The occurrence of the disease is facilitated by prolonged depression, emotional shocks, worries, and unbearable psychological stress. In this case, food becomes a kind of cure for stress, and a person begins to “eat away” his failures and disappointments.
Risk factors for bulimia nervosa include a lack of or dissatisfaction with a personal life, low self-esteem and dissatisfaction with one's appearance.
Bulimia of puberty
Bulimia is characteristic of adolescence. Against the background of hormonal changes, teenagers are too emotional and sensitive. The slightest discrepancy with the beauty standards imposed by society can cause extreme dissatisfaction with one’s appearance. To achieve a satisfying result, teenagers, especially girls, may even refuse to eat. Bulimia during puberty is characterized by alternating prolonged fasting with bouts of uncontrolled overeating.
In adolescence, in addition, so-called autotonic anemia is distinguished, which is not associated with the desire for an ideal figure and is characterized by frequent bouts of overeating, uncontrolled cravings for food and a lack of satiety.
Classification of bulimia
Structural-psychopathological analysis implies a different classification of bulimia, in which the following types are distinguished:
- Obsessive. The patient understands that overeating is undesirable, and tries to fight with himself, constantly feeling the desire to eat and trying to resist overeating.
- Dysthymic type. Attacks of overeating are more episodic in nature and appear only during nervous shock and stress.
- Impulsive type. The patient does not resist overeating in any way. Flashes often disappear from memory.
In addition, bulimia can be classified according to the presence or absence of procedures performed by the patient to remove the food eaten from the body. When a patient takes any measures to, in his opinion, neutralize the harm of ingested food, there are several methods of cleansing:
- Medication. Involves uncontrolled use of laxatives and diuretics.
- Physiological. The patient induces vomiting. Moreover, vomiting may be a kind of ritual that reduces guilt for overeating, or the patient may feel a sense of satisfaction or euphoria after vomiting.
- Physical (grueling workouts).
Forms of bulimia
Depending on whether bulimia is a consequence of another disease, there are the following forms:
- Primary bulimia is a self-occurring disease with an uncontrolled desire to consume various foods.
- Bulimia caused by anorexia. In some cases, patients with anorexia may experience uncontrollable bouts of eating, which later cause a feeling of guilt. To get rid of it, the patient provokes vomiting or attempts to cleanse the body by other methods.
Symptoms and warning signs of bulimia nervosa
People who experience bulimia nervosa may exhibit some of the following symptoms and/or warning signs of the disease. Sometimes, after diagnosis, family members and friends comment that they are surprised that they did not notice the eating disorder or did not realize that certain behaviors or physical complaints were associated with the eating disorder.
However, people who struggle with bulimia nervosa often feel shame and guilt about their behavior. This means that many people with bulimia nervosa will go to great lengths to hide their behavior so that no one finds out they have an eating disorder.
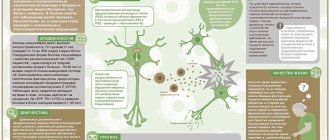
Diagnostics
Diagnosing bulimia is not easy. Bulimics rarely admit that they have symptoms of bulimia and can hide the disorder from others for quite a long time. The anamnesis is collected based on a survey of the patient and possibly his relatives.
Various psychological tests are also conducted, the most famous of which is the Eating Attitudes Test. This method was created in 1979 by scientists at the Canadian Clark Psychiatric Institute in Toronto. The test consists of 26 questions that the subject is asked to answer. This method cannot establish a diagnosis with absolute certainty, but it helps to detect behavioral characteristics that manifest themselves in bulimia, anorexia and other eating disorders. You can take this test yourself, online, but you should know that only a specialist can correctly evaluate the results of the test and make a diagnosis by comparing all the complaints, signs and symptoms of bulimia.
To make a correct diagnosis, an examination by a gastroenterologist, nutritionist, or therapist is necessary.
To assess the condition of the body and identify possible pathologies caused by bulimia, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and some organs, and an ECG. The necessary blood and urine tests are taken.
All about bulimia
What is bulimia, and what are the features of this disease?
As already mentioned, the disorder is more typical for the fair sex, especially for those who carefully monitor their weight. Often the disease develops as a result of an irresistible desire to lose weight. Unfortunately, artificially inducing vomiting after eating does not help to lose extra pounds, and some time after the onset of the pathology, the patient gains weight even faster. The problem with bulimia is that this disease can go unnoticed for quite a long time both for the patient himself (after all, he believes that watching his figure is a normal desire) and for others (who do not notice changes in the patient’s behavior). In addition, getting rid of the disease is quite difficult, because it depends on the patient’s self-esteem, on his attitude towards his appearance, nutrition, etc. Stopping overeating and starting to control the amount of food you eat is becoming increasingly difficult.
The risk group includes girls from 13 to 35 – 37 years old. The greatest peaks of symptoms are observed at 15–16, 21–24 and 26–28 years.
Treatment for bulimia
Treatment for bulimia is usually carried out by a psychotherapist. As a rule, treatment is outpatient, but hospitalization with further treatment in a hospital setting is also possible. Reasons for hospitalization:
- suicidal thoughts;
- severe depression;
- dangerous degrees of exhaustion;
- concomitant disorders requiring hospital treatment;
- bulimia in pregnant women, when the health and life of the fetus is threatened.
Effective treatment of bulimia involves an integrated approach and combines therapy with a psychologist and the use of appropriate medications. Of course, treatment of concomitant diseases is necessary.
Psychotherapy
Tactics and methods of treatment are selected individually for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease. The psychotherapist determines the frequency of therapy sessions and the duration of treatment, which in severe cases can take up to 9 months.
At the initial stage, the specialist conducts a psychoanalysis of the disease, identifying its causes and features of its course. At this stage, the specialist’s goal is to help the patient understand the disease, the causes of its occurrence and the need for treatment.
The psychotherapist analyzes significant events in the patient’s life, his dreams, dreams, interests and selects appropriate therapy tactics. Treating bulimia with psychotherapy along with controlling food intake is a very important aspect to achieve a positive result.
Cognitive behavioral therapy
During sessions, a specialist helps a person change his view of the disease, adjust behavior, recognize the onset of a breakdown and resist obsessive thoughts about food and reduce other unpleasant symptoms. This treatment method is very effective for suspicious and anxious individuals for whom bulimia causes moral suffering.
Interpersonal therapy
The treatment method is used for people whose disease is caused by depression and difficulties in communicating with people. The patient learns how to properly resolve conflicts and interact with others.
Group classes
The specialist recruits a circle of people with bulimia and other types of pathological changes in eating behavior, conducting collective treatment. During the sessions, they share their experiences, tell how their illness progresses, what symptoms bother them, and how they fight it. This allows the patient to feel that he is not alone in his experiences and improves self-esteem.
Analysis and control of food consumption
This is a very important aspect, without which it is impossible to treat bulimia. The specialist helps the patient create a balanced menu that will contain all the necessary vitamins and microelements. To change the attitude towards food, foods that the patient previously considered forbidden are gradually allowed into the diet.
The patient is asked to keep a diary, where he will indicate what, when and in what quantities he consumed food, whether there was a urge to vomit or a desire to eat something else. To relieve depression, sports games are also recommended, which will help a person learn to receive positive emotions not only from food.
Remote therapy for bulimia is also possible, during which the patient will receive consultations via Skype or email.
Drug therapy
Antidepressants are most often prescribed for bulimia. It should be remembered that most drugs in this group slow down the speed of psychomotor reactions; therefore, during the treatment period, patients are not recommended to drive a car or carry out potentially dangerous work that requires increased attention.
One of the groups of drugs prescribed for the treatment of bulimia are third-generation drugs - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter also called the “happy hormone.” By acting on serotonin receptors, SSRIs prevent the reuptake of serotonin released by neurons, thereby increasing its concentration and helping to relieve depressive and anxiety states, which are symptoms of bulimia. The drugs in this group are generally well tolerated by patients and rarely cause side effects. Despite this, the use of SSRIs is recommended after consultation with a specialist.
The group of drugs is extensive, but the most prescribed of them are:
- Prozac;
- Fluvoxamine;
- Sertraline;
- Paroxetine;
- Cipramil.
Treatment of bulimia is often accompanied by the prescription of tricyclic antidepressants; these drugs are combined into a group due to the similarity in their chemical structure. Compound molecules have three connected rings in their structure. The mechanism of action is based on inhibition of neurotransmitter reuptake. They increase the speed of impulse transmission between neurons, increase the concentration of serotonin and norepinephrine, reduce the number of bouts of overeating, relieve depression and reduce other symptoms. These antidepressants belong to the last, third generation. SSRIs are prescribed much less frequently because they can have a cardiotoxic effect, increasing the risk of heart disease. The most famous tricyclic antidepressants include:
- Amitriptyline;
- Imipramine;
- Desipramine;
- Doxepin.
In cases where the patient has induced vomiting, at the beginning of treatment for bulimia, an increase in the gag reflex may be observed during meals in general or when consuming certain foods. Antiemetics are used to treat this condition. The mechanism of action is based on blocking the transmission of impulses from the vomiting center of the medulla oblongata to the stomach, suppressing the gag reflex. The most famous and accessible drugs are Zofran and Cerucal, which not only suppress the gag reflex, but also normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which is especially important in the treatment of complications of the digestive system due to bulimia.
Drugs from other pharmaceutical groups may also be prescribed to treat pathologies of various body systems caused by bulimia.
Characteristics
A constant feeling of hunger can be considered an alarm bell that should hint at the presence of a problem. It should not be confused with appetite, which comes during or before a meal, but ends as you are full.
Patients with bulimia do not enjoy a tasty dish; their goal is to quickly satisfy their hunger. Almost without chewing, they don’t really feel the taste of the dish. They do not think about the compatibility of products, their freshness and the degree of digestibility by the body.
Once the task of satiation is completed, an acute feeling of regret comes. Particularly strong emotional tossing is typical for young girls who are prone to worrying about being overweight.
If we try to specify the possible symptoms of bulimia, they include:
- hasty eating and swallowing large pieces of food;
- eating large portions of food;
- interrupting food intake to go to the toilet (where you can secretly induce artificial vomiting);
- the appearance of scratches on the fingers as a result of attempts to induce vomiting;
- the presence of diuretics, laxatives and diet pills in the home medicine cabinet.
Most often, people suffering from bulimia try to hide their eating habits. For them, a meal is to some extent a ritual that requires serious preparation. If someone disturbs them while they are eating, they stop eating, feeling ashamed.
Bulimics worry about their weight and almost always follow a variety of diets. Frankly, their lives resemble the eternal struggle with dieting, alternating with periods of loss of control. Sometimes they “break down” into yet another binge, after which the feeling of guilt and shame overtakes them with even greater force, and they plunge headlong into yet another diet. Patients with bulimia rarely suffer from obesity; their weight most often varies within the normal range.
The most dangerous aspect of bulimia nervosa can be considered the attitude of patients to what exactly they eat. They practically do not think about the quality of food and its benefits, because their main goal is to satisfy their hunger. They prioritize quantity over quality. Such an attitude can have negative consequences for a person’s physical health and can be expressed in:
- gum damage, tooth enamel destruction, throat irritation;
- increased salivation;
- ruptures of capillaries on the whites of the eyeball;
- brittle nails and hair;
- unhealthy skin color and dehydration;
- pain in the stomach;
- muscle cramps and tremors;
- menstrual irregularities;
- change in stool;
- problems with the kidneys and liver.
Important
Patients with bulimia nervosa are characterized by increased fatigue, jerky movements and bouts of irritability.
Complications of bulimia
Bulimia is a disorder that can affect many systems in the body. Let's look at the complications that this disease can cause.
Chronic dehydration
Due to the uncontrolled use of diuretics and laxatives, artificially induced vomiting, the water-electrolyte balance in the patient’s body is disrupted, ensuring the maintenance of water and acid-base balances, osmotic pressure in tissues, and ionic composition. Potassium and magnesium ions, which are required for normal muscle function, including the myocardium, are excreted in the urine in significant quantities. As a result, convulsions, tachycardia, and weakness may occur. The possibility of developing dangerous heart pathologies increases. There is a high probability of pathology of the kidneys, resulting in swelling.
Endocrine system disorders
As a result of a lack of microelements, the synthesis of thyroid and parathyroid hormones is disrupted, the level of cortisol (stress hormone) increases, and the production of sex hormones decreases. In women, the menstrual cycle changes pathologically, and menstruation may disappear altogether. Men have problems with potency.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Stomatitis and other inflammations of the oral cavity occur due to irritation of the mucous membrane, frequent vomiting and a deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body. For the same reason, tooth enamel deteriorates and turns yellow. With further development of the disease, complete destruction of teeth and their loss is possible.
May develop:
- Inflammation of the parotid salivary gland. Short-term but frequent episodes of increased blood pressure caused by vomiting interfere with the normal flow of saliva, causing pathology of the gland.
- As a result of gross violations of the diet, hunger and vomiting, gastritis and ulcers of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum develop, and heartburn occurs.
- Stool disorders. Overeating and unnecessary use of laxatives cause diarrhea and constipation.
Deterioration in appearance
The structure and appearance of the skin, hair and nail plates deteriorate. As a result of dehydration, hormonal changes and lack of nutrition, vitamins and minerals, hair falls out, becomes dry and dull, nail growth slows down, and their fragility increases. The skin becomes dry.
Disorders of the central nervous system
Patients experience sleep disturbances, depression, and feelings of anxiety and restlessness. Bulimics often look lethargic and sleepy. Concentration and memory functions are impaired.
Signs
- Increased salivation;
- Loss of color of tooth enamel, the appearance of wounds on the gums, irritation on the oral mucosa and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes and in the ear area;
- The appearance of red dots in the eye area;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- The appearance of fragility of the nail plates and tarnishing of the hair;
- Dry skin and change in its natural color;
- Abnormal bowel movements (constipation, diarrhea or flatulence);
- The appearance of seizures;
- Liver and kidney disease.
These health features lead to changes in a person’s appearance. He feels constantly tired, and his weight can decrease or increase in the range of 5 to 10 kg.
Forecast
The prognosis for this disease primarily depends on the patient’s state of mind and his desire to overcome the disease. With stable therapy, correction of mental disorders and consent to treatment, the prognosis is favorable and in most patients bulimia is successfully treated. Sudden self-healing as a result of significant positive moral shocks is also possible.
If treatment is inadequate and the patient refuses therapy, the complications of the disease progress, and in this case the prognosis is unfavorable. Especially with bulimia, the cardiovascular, digestive and nervous systems are affected. Death can occur as a result of heart failure, gastric rupture, and bleeding. Mental disorders and long-term depression can push a bulimic to commit suicide.
Iloreflexotherapy
Acupuncture is a treatment technique that came from the ancient East. It is not used as an independent method of treatment, but only as a complement to traditional medicine. Acupuncture points are stimulated with needles. For effective therapy it is necessary to know the exact location of these points. Acupuncture in the treatment of bulimia is a new direction.
Effects of therapy: normalizes the patient’s appetite and energy metabolism. In addition, acupuncture relaxes and helps relieve stress.
How to overcome bulimia
To treat the disease, a set of procedures is used, which consists of psychological assistance and the use of medications. To get rid of the underlying causes, individual or group psychotherapy is used, because only a psychologist can accurately determine the true cause of this disorder.
Unfortunately, without your own desire to overcome the disease, it will be quite problematic to treat it.
Therefore, if you suspect yourself or your loved ones of having symptoms of the disease, then the most important thing to do is to immediately contact a doctor.
During a conversation with a doctor, it is important to honestly and in detail talk about your own lifestyle, about your diet, down to how much food you eat per day, and it is also necessary to mention how strong and at what frequency the feeling of hunger occurs. At this point, the doctor will analyze and try to identify the main cause of bulimia, after which he will prescribe a specific course of treatment.
After a detailed examination and test results, the doctor will also be able to determine whether the patient needs hospitalization or not. Typically, inpatient treatment options for bulimia sufferers include:
- restoration and treatment of all organs that may have been damaged as a result of the disease,
- psychotherapy sessions,
- preparation of a special diet,
- prescription of certain antidepressants,
- physiotherapy.
Treatment of the disease
To successfully treat a disease, it is necessary to remove the causes of its occurrence, so patients undergo psychodynamic therapy and drug treatment simultaneously. Treatment can take the form of group therapy sessions, but for severe depression, patients first receive antidepressants and only then join a rehabilitation group. The most famous pills for bulimia are Phenibut and Fluoxetine.
To treat metabolic disorders, gastrointestinal diseases and other consequences of the disease, specific therapy is used. During this entire time, the patient is monitored by psychotherapists in order to exclude relapses of the disease and cure bulimia completely.
Usually the prognosis for treating the disease is encouraging, but much depends on the mental state of the patient himself. If the patient makes contact with the doctor and wants to get rid of the disease, then in most such cases the treatment is successful. Treatment of bulimia at home is possible if the degree of the disease is not severe. If treatment is refused, patients may die from heart disease, gastric rupture, mental instability and prolonged depression often provoke suicide.
Watch the video:
Getting rid of the problem
Many relatives of bulimics wonder whether bulimia can be treated without consulting a specialist. As practice shows, independent treatment is impossible. All patients, even with strict control, still have breakdowns; they literally attack food. It is impossible to achieve progress without treating a nervous disorder. Today, a variety of types and approaches are used in the treatment of bulimia.
Treatment for bulimia involves proper nutrition and adherence to a routine. Patients are contraindicated from overeating or fasting. The correct option would be to consult a doctor. Patients with bulimia not only diet, but also exercise without losing weight. Your doctor will help you choose the right diet. The best results are obtained from complex treatment of bulimia through a combination of the following activities:
- drug treatment;
- psychological and therapeutic treatment;
- herbal medicine;
- bioenergy therapy;
- acupuncture.
Drug treatment
The priority in the treatment of bulimia is drug therapy. As many studies have shown, patients often have impaired serotonin production. This is a hormone that is responsible for mood. As a result of its constant changes, the diet is disrupted. Antidepressants are considered the most effective drugs in the treatment of bulimia. New generation products have fewer side effects. These include the following drugs: Prozac, Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, Sertraline, Velafax, Ephelon.
To give a feeling of fullness and eliminate spontaneous vomiting, antiemetic drugs are used. The most effective of this series is Ondansetron.
"Sertraline" - a modern antidepressant
Psychotherapy
To understand how to get rid of bulimia, the patient must realize that he has a problem and admit it. Treatment of bulimia nervosa through psychotherapeutic techniques is based on transforming incorrect behavior into correct behavior and rethinking one’s own attitudes. In other words, the patient must first love himself and understand that he is killing his body with his own hands. Cognitive behavioral therapy is about eradicating all negativity directed towards your own body. A person must find the positives in himself and focus on them.
Over the course of six months, patients learn to eat properly and follow a routine. All this time, the patient keeps a diary in which he describes what he ate and in what quantity, his feelings. They are encouraged to make notes about their failures and successes.
To get rid of severe bulimia, they practice not only cognitive behavioral therapy, but also interpersonal therapy. It is aimed at reducing anxiety and eliminating depression. The goal of therapy is to adapt the patient to changes in his life and motivate him to move on. With the help of interpersonal therapy, patients are able to fully understand the reasons that contributed to the appearance of a nervous disorder. People learn to feel their individuality, uniqueness, and try to find themselves.
Phytotherapy
An experienced doctor can advise you on how to properly treat bulimia through herbal medicine. Herbal remedies are often prescribed. Medicinal herbs contain many vitamins that humans cannot get from food. In addition, natural antidepressants do not cause side effects and stimulate brain function. Plants that have a nootropic effect are also used. They help improve blood circulation in the brain, clarify consciousness and enrich the body with vitamins.
The most effective among sedatives are: mint, oregano, hawthorn, lemon balm, angelica, St. John's wort. Nootropics include rosehip, yarrow, and lemon balm.
Bioenergy therapy
It is partly a psychotherapeutic method. Bioenergy therapy is considered one of the most effective methods of treatment using non-traditional methods. Most of the diseases in our body begin to progress when a person thinks about them.
In the case of bulimia, it turns out that a person who is always dissatisfied with his proportions himself causes attacks of gluttony because he constantly thinks about food. Treatment is based on eliminating unnecessary thoughts and developing a positive attitude towards your own body. This is one of the options for independent psychotherapy.
Acupuncture
The technique came to us from the Ancient East. It cannot be used as an independent treatment. The human body consists of points through which energy circulates. By influencing them, the patient’s physical and moral condition can be improved. For example, eliminate problems with metabolism.
Acupuncture should be performed by a specialist
How to treat bulimia
Since it is impossible to “get sick” from bulimia in the usual sense of the word for a common person, treatment will not be easy. It must necessarily combine psychotherapeutic sessions, taking a certain number of medications, support from loved ones and, of course, the desire of the patient himself to overcome the disease.
How to fight? You need to start with a consultation with a psychotherapist. Experience shows that patients with bulimia are most often treated on an outpatient basis, although hospitalization in a neuropsychiatric hospital is more effective. 24-hour monitoring of bulimics and their support by qualified medical personnel contribute to a speedy recovery. According to the rules, only patients with a significant deterioration in health, concomitant diseases, a combination of anorexia and bulimia, or weight loss of more than 20% of the original weight are subject to hospitalization.
The patient must be prescribed courses of psychotherapy. The doctor helps the patient understand himself, the causes of the eating disorder, and also forms in him normal ideas about a person’s weight and appearance, ways to achieve success, etc. The psychotherapist supports the client, helps him understand the features of a balanced diet.
Support from loved ones will also be an important component of treatment. Typically, relatives and friends of the patient, before visiting him in the clinic, consult with the doctor about “what can and cannot be said,” what topics can and cannot be discussed, and how best to set up the bulimic for recovery.
As for the drug treatment method, this also has its own characteristics. The patient is prescribed drugs not only to get rid of the disorder itself, but also vitamin complexes, immunomodulators and other drugs to maintain health.
Interestingly, the previously mentioned drug Fluoxetine is often used in the treatment of bulimia. If we consider this fact from a psychological point of view, then taking the medicine is not advisable. The patient may develop a craving for taking the drug for the sake of losing weight, reducing appetite, etc. For the same reason, Fluoxetine is not prescribed for patients who have received two diagnoses: anorexia and bulimia.
Prognosis for bulimia
You need to know not only how to deal with bulimia, but also what the prognosis for your health is. Complete recovery is rarely achieved. There are many cases where people have suffered from bulimia nervosa for years. In most cases, after 30-40 years, the symptoms of the disease gradually weaken.
Timely and correct treatment can improve the quality of life and prevent dangerous consequences. In stressful situations and an unhealthy lifestyle, relapse and reappearance of hunger attacks are possible. Without treatment, complications develop. There may be a decrease in performance up to the point of disability. The prognosis for bulimia is relatively favorable.
External manifestations of the disorder
The appearance of bulimics becomes a kind of indicator of the “ugliness” going on in their bodies. They are revealed by dry, dull skin that loses moisture due to dehydration. The dermis loses turgor and provokes the appearance of wrinkles.
Swelling disfigures the face. The girl, who is barely 20 years old but has been suffering from bulimic disorder for four years, says that her face has somehow inexplicably widened. The face is swollen, and the cheeks stick out shapelessly.
The hair of people with this disorder loses its beauty, becomes dull, lifeless, and falls out immensely. The nails soften and crumble, and on those fingers that the patient places in the mouth, they are destroyed and deformed to an even greater extent.
But the most interesting thing is: no matter how hard a bulimic tries to get rid of what he eats, he does not lose weight. And there are logical explanations for this. Firstly, such ruthless interference with the body’s physiology slows down metabolism and reduces the rate of calorie burning. Secondly, from the moment the process of food absorption begins until vomiting is provoked, more than 50% of calories are absorbed and then turn into fat.
Obviously, vomiting does not save you from extra pounds. Slow metabolism and poor diet are taking their toll.
Consequences of bulimia
Being a serious disease of the nervous system, bulimia leads to serious complications, including:
- decreased blood pressure, causing fainting;
- arrhythmias and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- renal failure developing due to a deficiency of potassium salts;
- problems in the reproductive sphere: early miscarriages, fetal development disorders, infertility;
- diseases of the oropharynx and the entire digestive system as a whole;
- chronic pneumonia;
- sleep disorders;
- decreased performance;
- irritability;
- obesity;
- severe depression, suicide attempts.
In an effort to hide the disease from others, bulimics often lose social connections and move away from relatives and friends, which only worsens their emotional state.
Classification of bulimia
There are 3 forms of this pathology:
- Paroxysmal. Characterized by periodic attacks of bulimia, which occur spontaneously after bowel movement. The intervals between uncontrolled meals range from 6 hours to several days.
- Constant. Episodes of binge eating occur constantly and with minimal intervals. Such people feel hungry almost immediately after vomiting, taking a laxative or cleansing the intestines.
- Night. Gluttony occurs mainly at night. During the day and morning, appetite is normal or reduced.
They also distinguish between non-purifying (overeating is compensated by exercise, sports or diet) and purifying (sick people independently induce vomiting and cleanse the intestines).
Psychotherapy
The most effective psychotherapy is cognitive-behavioral: often it alone is enough to get rid of the disease. In addition to this, psychologists use the following types of therapy:
- behavioral - eliminates unwanted forms of behavior (overeating), forming new habits;
- psychodynamic - psychoanalysis to determine the unconscious that pushes the patient towards bulimia;
- family - resolving family conflicts to eliminate powerful stressors;
- interpersonal - resolving the patient’s interpersonal conflicts;
- “twelve steps” - used in the treatment of addictions.
Psychotherapy continues for more than one month - this is a prerequisite for its effectiveness: interruption of work before the war with eating disorder is completed in victory is fraught with the return of bulimia.
Diet changes
The main change regarding the diet is the transition to fractional meals: 5-7 meals a day in small portions, which will eliminate the risk of overeating. A bulimic should have on his plate:
- seafood, green vegetables, legumes, dairy products, vegetable oils are sources of Omega-3 and Omega-6, good for the heart, skin, and a stable emotional state;
- porridges and dried fruits are high-calorie, but nutrient-rich foods to satisfy hunger;
- orange and yellow fruits, vegetables, berries - stabilize the emotional state.
During recovery, it is better to give up meat - a difficult product for a stomach exhausted by illness. It is recommended to avoid sucrose: it stimulates the appetite, which can cause overeating.
Some nutritionists recommend consuming sports nutrition: it contains a large amount of nutrients.
Medications to treat symptoms of bulimia
Treatment for bulimia is based on mandatory medication. First of all, antidepressants allow one to cope with a psycho-emotional problem; fluoxetine is one of the effective drugs in this group. The antidepressant effect of Fluoxetine is combined with a stimulating effect. When taking this antidepressant, the patient experiences an improvement in mood, nervous tension is relieved, anxiety, panic, apathy and feelings of fear disappear. The therapeutic effect is achieved four weeks from the start of treatment.
In the most serious and severe forms of bulimia, which threatens the patient’s life mentally, you should seek help from a psychotherapist. Sometimes it is necessary to immediately hospitalize the patient in a medical facility, where he remains until his condition improves.
Description of the problem
A disease such as bulimia begins to develop as a result of a neuropsychiatric disorder, which manifests itself in a lack of control over the absorption of food with the individual’s full concentration on the calories consumed, one’s own weight and the food itself.
Psychopathology is combined with paroxysmal appearances of severe hunger, the use of laxatives and drugs for weight loss, and provoking vomiting.
The main feature of the psychological portrait of patients with this problem is low self-esteem. Patients often criticize themselves greatly, do not like their body, and feel guilty before everyone for their ugly body.
The severe stage of the disease is characterized by sudden changes in the patient’s weight. Constant hunger is often accompanied by stomach pain and muscle weakness. Patients do not feel satisfied with their hunger, which leads to gluttony. In this particular case it is called polyphagia.
Self-treatment
Many people try to treat bulimia on their own, but coping with the disease without medical help is difficult: the problem lies not so much in the physical plane as in the mental one. Getting rid of eating disorder without outside help is possible, but it takes longer than professional treatment.
The following stages are involved in fighting the disease on your own:
- Correction of eating behavior. A detailed nutritional schedule is required, including at least 5 meals in small portions.
- Refusal of medications. At first, the body, accustomed to the effects of laxatives and diuretics, will refuse to perform its functions of removing waste products without pills, but soon the problem will disappear.
- Psychotherapy. The task of psychological correction is to show the patient that his body is beautiful without the grueling alternation of eating and vomiting. Auto-training, meditation, acupressure (impact on the points of the body responsible for appetite, metabolism, gastrointestinal tract, and other vulnerable “spots” of bulimics) relieve the psychosomatics of the disease and restore mental balance.
Self-treatment of the disease is in most cases less effective: the likelihood of failure is much higher.