One of the most common types of scoliosis is lumbar scoliosis. The main risk group is office workers or long-distance drivers. Many people who have worked for more than 3 years in these industries are diagnosed with stage 1 scoliosis. Without proper attention, the disease will only develop further.
Scoliosis is often caused by incorrectly selected furniture and a sedentary lifestyle. Other causes of scoliosis include:
- Large body mass, large excess weight.
- Sedentary and sedentary lifestyle.
- Work involving constant sitting.
- Having flat feet.
- Improper development of tendons, muscles and bones from birth.
- Diseases like tuberculosis or rheumatism.
If you have any suspicions, you should immediately contact a medical facility. Since such a disease can bring many problems in the future.
There are several types of lumbar scoliosis: left-sided, right-sided, S-shaped and lumbosacral.
Left-sided scoliosis can be diagnosed for several reasons:
- Congenital anomalies of the spine (rare).
- Oncological diseases of the spine.
- Marfan syndrome.
But there are also frequent cases when doctors are unable to identify the root cause of the disease.
During puberty, adolescents often experience poor posture and, as a result, a diagnosis of scoliosis. At the initial stage of the onset of the disease, there are no symptoms, and only a specialist is able to notice the curvature of the spinal column.
There are 4 known degrees of left-sided scoliosis:
- 1st degree – deviation from the norm no more than 10 degrees. There are no complaints, as the patient does not notice any changes.
- 2nd degree – deviation no more than 25 degrees. Complaints of aching pain in the back after physical activity.
- 3rd degree – deviations no more than 50 degrees. The patient complains of constant aching and nagging pain. The asymmetry is noticeable to the naked eye.
- 4th degree – deviations more than 50 degrees. Complaints of pain when moving. Formation of the chest hump.
Right-sided scoliosis is much less common than left-sided scoliosis. It is extremely difficult to diagnose it yourself, since the deviation angle is very small. The disease strikes many people between the ages of 20 and 30. It is characterized by short-term pain in the lumbar region, mainly after physical activity. At this age, the disease cannot be treated, but it is possible to prevent its spread.
S-shaped scoliosis is complicated because it appears as two curves, which complicates its treatment. This type of scoliosis is more common in school-age children; this is due to incorrect body position during classes.
4 degrees of development of S-shaped scoliosis:
- 1st degree – there is only one curvature of the spine, the deviation does not exceed 10 degrees.
- 2nd degree - the deviation of the first arc is approximately 10-25 degrees, the second arc is formed. This degree of development of scoliosis is characterized by a shift of the shoulder blades relative to the spine.
- 3rd degree - the primary arc has reached an angle of more than 25 degrees, the deviation of the second increases to 25 degrees. In this position of the spine, most body systems fail. The cardiovascular system is most susceptible to changes.
- 4th degree – the most severe changes in the spine, subsequently leading to disability. The primary arc is curved by more than 50 degrees, the angle of deviation of the second arc is within 25-50 degrees. All actions of a specialist in such a situation are aimed at preventing further development of the pathology.
A less common type of scoliosis is lumbosacral scoliosis. The curvature occurs in the area of the lower lumbar vertebrae. The main cause of this type of scoliosis is the weakness of the elements of the supporting complex of the spine.
What is scoliosis - definition
Spinal scoliosis is a persistent deformity of the human axial skeleton, which is characterized by lateral curvature in relation to the normal position of the spinal column. What is this in simple terms? Pathology causes a change in the location of part of the vertebrae due to a displacement to the side, to the right or left side. All parts of the spine can be involved in the pathological process of scoliosis; moreover, if there is a problem in one part, anomalies arise in all other segments and other organs:
- curvature in the anterior or posterior direction;
- twisting of the spinal column;
- secondary deformation of the chest;
- violation of the position of the pelvic bones.
In addition to troubles with the musculoskeletal system, advanced cases of the disease lead to damage to the lungs and heart. Most often, pathology develops during active skeletal growth - at 4-7 years, at 10-15 years. Often, a sharp progression of the disease occurs precisely at this age, especially if the child has even minimal postural disorders. If the latter can be cured with simple exercises and exercise therapy, then when suffering from different types of scoliosis, a combined approach will have to be used.
Prevention of scoliosis in adults
Prevention of scoliosis includes:
- Maintaining an active lifestyle . If you have scoliosis or prerequisites for its development, you need to keep yourself in good physical shape, because with weakened muscles, the curvature can progress. At the same time, it is better to avoid excessive loads.
- Change of professional activity . There are professions that more often than others lead to the development of scoliosis. Thus, people with poor posture should avoid professional sports, as well as work as builders, drivers and loaders. Sedentary work can also aggravate the curvature, so office workers should walk more and take breaks every 30 minutes.
- Proper nutrition . Overeating negatively affects the functioning of internal organs and puts stress on the spinal column. In addition, it leads to the development of obesity, which can aggravate the existing curvature. As for the diet itself, it should be balanced in carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Vegetarians, whose diet contains insufficient proteins, which are responsible for the development of muscle mass and bone strength, should review their menu first of all.
Video: “Manual therapy for scoliosis”
Types of scoliosis
Since the spine consists of three sections, scoliosis can develop in any of them, depending on which it is classified into the following types:
- Cervicothoracic. Rarely observed. The apex of the curvature occurs at 3-4 vertebrae in the chest area.
- Thoracic or thoracolumbar. A common, yet severe form - in this case, scoliosis can disrupt the functioning of vital organs, cause the appearance of a hump, and severe back pain.
- Lumbar. It does not cause severe symptoms, is relatively mild, progresses slowly, but can cause the development of osteochondrosis.
- Lumbosacral. It is rarely registered, provokes a distortion of the pelvis, sacrum, and leads to asymmetry of the legs.
Types of scoliosis are also divided according to the specific shape of the curvature of the spine:
- S-shaped - a complex curvature with the formation of two arches (scoliotic, compensatory), while the back resembles the letter of the same name;
- C-shaped – the most “popular”, it causes the appearance of one arc, which is clearly visible when tilted;
- Z-shaped - a severe form with 3 lateral bends, is rare, can be treated surgically.
Vertebrologists and orthopedists divide scoliosis into progressive and non-progressive. Also, all types of this pathology are conditionally divided into two large groups:
- Structural scoliosis. Causes a permanent change in the position of the vertebrae themselves. For reasons, structural scoliosis is divided into traumatic, cicatricial, metabolic, osteopathic, and myopathic.
- Non-structural scoliosis. Leads to normal lateral curvature of the spinal column without rotation of the vertebrae. Depending on the cause, non-structural scoliosis can be postural, compensatory, reflexive, or hysterical.
What is scoliosis and when does it occur? Usually the disease develops in childhood, therefore it is divided into the following forms: infantile (1-2 years), juvenile (4-6 years), teenage (10-14 years).
Methods for measuring scoliotic angle
There are several methods for measuring the scoliotic angle.
Measuring the scoliotic angle using the Cobb method
This method is the most common type of measuring the angle of the spine, which is formed due to scoliosis.
On an X-ray of the spine of a person with scoliosis, the vertebra most deviated to the left or right (the vertebra that is located at the top of the scoliotic arch) is determined and its center is marked with a dot. Then the vertebrae that are least deviated to the right or left (the vertebrae that are at the base of the scoliotic arch) are found above and below and are also marked with dots.
Next, draw a straight line using a ruler from the upper vertebra along its upper edge and from the lower vertebra along its lower edge.
The angle between these two lines or between perpendiculars dropped from these lines is the desired Cobb angle.
The disadvantage of measuring the angle of deviation of scoliosis using the Cobb method is that it displays the degrees of displacement in only one plane, i.e. if the spine is curvated simultaneously to the side and anteriorly or posteriorly (rotation), the true degree of deviation will be increased.
Measuring the scoliotic angle using the Chaklin method
In the post-Soviet space, the degree of scoliosis is often determined using the Chaklin method. With this measurement method, not only the magnitude of the scoliotic angle is taken into account, but also the magnitude of the scoliotic arc, which, like the angle, is measured in degrees:
- First degree of scoliosis: scoliosis angle – 50 – 100, scoliotic curve angle – 1750 – 1700;
- Second degree of scoliosis: scoliosis angle – 110 – 300, scoliotic curve angle – 1690 – 1500;
- Third degree of scoliosis: scoliosis angle – 310 – 600, scoliotic curve angle – 1490 – 1200;
- Fourth degree of scoliosis: scoliosis angle – more than 600, scoliotic curve angle – less than 1200.
To determine the angle of scoliosis using the Chaklin method, an x-ray of the spine taken in the anteroposterior projection is used, this allows a more accurate determination of the degree of scoliosis compared to the Cobb method.
On the x-ray, 2 spines are found (above and below from the curvature), which are not changed, are parallel to the upper and lower vertebrae, respectively, and have a smooth, horizontal intervertebral gap.
Two lines are drawn through the top of the upper vertebra and the base of the lower vertebra. A perpendicular is lowered from the middle of the upper line in the center of the neutral vertebra, and a perpendicular is drawn upward from the middle of the lower line. The intersection of perpendiculars on the inside forms the Chaklin angle.
Measuring the scoliotic angle using the Ferguson method
On the x-ray, the most protruding vertebra is found, which forms the top of the scoliotic arch. The center of this vertebra is marked with a dot. Then the vertebrae that protrude least to the side are found and form the basis of the scoliotic arch. The centers of these vertebral bodies are also marked with dots.
Thus, three points are obtained on the radiograph: the first is the base of the scoliotic arch, the second is the apex of the scoliotic arch, and the third is the base of the scoliotic arch.
Next, a straight line is drawn through the center of the first and second points, and a straight line is drawn through the center of the second and third points, the angle between the resulting lines is the Ferguson angle.
The disadvantage of this method is the impossibility of using measurements of the scoliotic angle, which has a value of more than 500.
Measuring the scoliotic angle using the Ishalov method
This method of determining the degree of scoliosis is the most accurate, since it reflects not only the angle of spinal deformation, but also the angle of inclination of each vertebra in the scoliotic arch.
First, it is necessary to determine the size of the scoliotic arch, which is based on the unchanged (neutral) vertebrae above and below. Then, through the base of the upper most neutral vertebra and the top of the lower one, we draw a straight line, in the figure (a - a1). Next, parallel to the first line, through the upper point of the adjacent vertebra, we draw a line in - in1, which indicates the height of the vertebra on the concave side of the curvature. After this, we draw a third line – c – c1, which runs along the upper surface of the adjacent vertebra.
The intersection of line a - a1 with line c - c1 forms an angle, the magnitude of which expresses the degree of inclination of the vertebra, and the transfer of lines b - b1 and c - c1 forms the angle of deformation of the spine.
The sum of these angles is the desired value using the Ishal method.
Measuring the scoliotic angle using the Lekum method
This method is used when it is difficult to determine the neutral vertebrae (the base of the scoliotic arch).
On the radiograph, the centers of the two vertebral bodies, which are located above and below the most convex part of the spinal column (the apex of the scoliotic arch), are marked with scoliosis. Then two straight lines are drawn through the obtained points, the angle obtained between them is the angle of the scoliotic arch.
Scoliosis degrees
There are different degrees of scoliotic disease, depending on which treatment is selected. Symptoms will vary greatly, as will the objective data obtained during diagnosis. Here are the four degrees of scoliosis:
- First. It is not visually noticeable if a person is dressed, and during examination it can only be noted by a specialist by the lowered head and different heights of the shoulder girdles. Changes in the spinal column are minimal. X-ray examination establishes a deviation from the natural axis of 10 degrees or less.
- Second. The deflection angle increases to 11-25 degrees. The curvature of the spine does not disappear when lying down. The shape of the pelvis changes, the waist is also asymmetrical, as are the contours of the neck. There is a slight protrusion on the chest, and a roll of muscles on the back.
- Third. This disease is almost impossible to treat with conservative therapy, because the angle of deviation is 26-50 degrees. The rib hump becomes obvious, the abdominal muscles are weak, and some ribs may sink. The symptoms are severe, the pain reaches a high frequency.
- Fourth. Due to the sharp curvature of the spinal column (above 50 degrees), a person necessarily requires surgery. There is a pronounced hump and concavity, the muscles are weakened and stretched.
Exercise therapy for lumbar scoliosis
Therapeutic physical education (PT) is widely used at home for the first degree of spinal curvature, and only in rehabilitation centers for the second degree. This is due to the fact that with a large degree of curvature there is a risk of pinching the spinal nerves. The main goal of exercise therapy is to strengthen the muscles that support the spine and correct posture. There are a number of exercises for this.
Performed while lying on your back:
- Alternately pull your knees towards your chest. As you exhale, we lift, as you inhale, we stretch. We repeat the same thing with straightened legs.
- We press the lower back to the floor, then raise it by 5-7 centimeters.
- We move the arm on the side of scoliosis to the side, and pull the other up.
Performed while lying on your stomach:
- We take our hands behind the belt and put them in a lock. Hold this position for 10 seconds.
- We try to lean on our arms extended forward, lifting our torso above the floor.
- We place the hand on the scoliotic side under the chest, the other on the back of the head. We try to straighten our back.
- We move the leg on the side of scoliosis to the side.
Each exercise should be performed up to 5 times, depending on how you feel. After performing the exercises, be sure to give your muscles a rest for 10-15 minutes.
Reasons for the development of the disease
What is scoliosis, and why does it develop? There are a huge number of causes of the disease, but they are found out only for 20% of all cases of scoliosis. The remaining 80% is made up of spinal curvature of unknown etiology, and it occurs in childhood, more often in girls. Presumably, the reason is low tone of the spinal muscles, when, with active growth, the muscle corset is not able to hold the vertebrae in an anatomically correct state. Risk factors in these situations are:
- sleeping on a mattress that is too soft;
- carrying a school bag in your hand rather than on your back;
- incorrect posture in class, when sitting at home;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- other forms of violation of the orthopedic regime.
Scoliosis is a disease that can even be congenital. Typically, sick babies have other skeletal structural abnormalities. The traumatic form occurs after bruises, vertebral fractures or unsuccessful operations. When one leg is shortened, the spinal column adjusts compensatoryly, and without wearing special heel pads or shoes, it begins to bend.
In adults, and less often in children, scoliosis can also be caused by serious diseases:
- osteochondrosis;
- osteoporosis;
- hernias;
- polio;
- spondylitis;
- metabolic diseases;
- myopathies;
- muscular dystrophy.
What methods are used?
Diagnosis of diseases is not difficult, since visual signs of pathology are clearly visible. Before prescribing treatment for spinal curvature, doctors determine the type of deformity, the stage of the process and the cause of its occurrence. Based on this, the optimal comprehensive treatment regimen is selected.
Congenital curvatures can be a consequence of birth trauma or disturbances in the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Acquired curvatures are in most cases traumatic, hereditary in nature, or are the result of disorders of physical development. The most difficult to treat are untimely diagnosed, severe deformities due to scoliosis in adulthood.
To treat spinal curvatures, doctors at our clinic use the following methods:
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- cryosauna;
- production of orthopedic insoles.
The best results can be achieved using kinesitherapy, since this technique is aimed at correcting and eliminating factors that provoke spinal deformities.
Symptoms of scoliosis
Initially, it is almost impossible to independently determine scoliotic deformation and identify the disease. That is why it is worth regularly showing the child to an orthopedist so that the first stage of the pathology can be identified in time at a scheduled appointment. Later, scoliosis begins to cause unpleasant signs:
- visually noticeable asymmetry of the shoulders, shoulder blades, hips;
- strong protrusion of the scapular angle on one side of the spine;
- feeling of stiffness, presence of a foreign body in the back;
- general decrease in performance, faster fatigue;
- pain in the chest, back, lower back;
- increased pain after prolonged sitting or physical activity;
- in the cervical form of the pathology - headaches, aching in the neck, shoulders, arm on one side;
- resting the body more on one side than the other.
Then the pathology begins to cause even more severe symptoms. The chest becomes deformed, a characteristic depression appears on the bone, and a “hump” grows on the back. Torsion (twisting) of the vertebrae may occur. As the chest is compressed, the heart and respiratory system work less well. There is a risk of developing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, and reduction in limb size due to insufficient blood supply.
Diagnostics
The disease manifests itself with a number of unpleasant symptoms, and in most cases it can be identified by a visual examination of the patient. But it is possible to check its availability without even leaving home. To do this, just stand near a flat wall and try to stick your hand into the lumbar region. Ideally, it should barely move in space. Any deviations are grounds for contacting a doctor. To clarify the condition, the following types of studies are prescribed:
- X-ray.
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
If respiratory function is impaired, adult patients are additionally prescribed fluorography. Usually there are no problems with making a diagnosis, since there is no difficulty in separating pathology from any other.
Diagnosis of pathology
Most often, the initial stages of the disease are detected at a routine appointment with a doctor. After an examination and a series of physical tests, the curvature can be identified. Afterwards, the orthopedist or vertebrologist will assess the condition of the body based on the following signs:
- length of both legs;
- symmetry of large joints;
- presence of kyphosis;
- degree of mobility of the spine;
- symmetry of the shoulder blades, shoulder girdles, muscles at the waist;
- correct structure of the chest;
- muscle tone;
- total length of the spinal column;
- location of the pelvis, internal organs.
Next, the patient must be referred for instrumental studies. To make an accurate diagnosis, a simple method is enough - radiography of the back (standing and lying down, including stretching). Pictures will need to be taken regularly in order to notice any changes in the body’s condition in time. To measure the exact angle of lateral scoliosis, drawing the image with special lines will help, using which you can make all the necessary calculations. Also, from the image you can conclude that there is one or more altered vertebrae:
- beveled;
- deformed;
- turned to the side;
- hemivertebrae.
If it is necessary to more frequently monitor the condition of the spine to avoid harm from radiography, other techniques are performed - ultrasound and MRI, as well as scoliometry. MRI is additionally performed to clarify the cause of back disease and in complex cases of scoliosis.
Sure signs of lumbosacral scoliosis are:
- Displacement of the sacrum and pelvis.
- Displacement of the pelvic girdle. One leg becomes longer relative to the other.
- Frequent pain in the lower back and sacrum.
Each type of scoliosis has its own symptoms, which vary depending on the degree of development of the pathology:
External symptoms:
- With grade 1 scoliosis, the shoulder blades are asymmetrical, the pelvis is skewed, the shoulders are at different levels and lowered, and the symmetry of the waist triangles is disturbed.
- With scoliosis of the 2nd degree, the formation of a vertebral hump, obvious asymmetry of the whole body.
- With scoliosis grades 3 and 4, there is divergence of the shoulder blades, changes in the structure of the chest.
Neurological symptoms:
- Hypermobility of the spinal joints in arthrosis against the background of functional disorders.
- Organic hypermobility syndrome.
- Hypermobility syndrome with disruption of intervertebral joints.
With the hypermobile variety with damage to the intervertebral joints, pain in the spine is inherent, even when the patient is at rest. Pain in the spine appears in the morning, mainly after waking up. The distinctive features of these pains are:
- The appearance of pain at the beginning of exercise.
- Increases when a constant load appears.
- Decreased when walking.
Treatment of scoliosis - basics of therapy and special devices
Any child or adult with scoliosis should visit a doctor regularly in order to notice the rapid progression of the pathology in time. If there is a chest deformity, the patient must be simultaneously registered with a pulmonologist and a cardiologist. Treatment of the disease is conservative; scoliosis is also treated surgically. If the cause of the disease is found, all measures are taken to eliminate it:
- wear special insoles to compensate for the difference in leg length;
- carry out correction of metabolic disorders;
- eliminate muscular dystrophy.
At the initial stage of curvature, wearing corsets, correctors and reclinators during the day helps a lot, and in more advanced situations they are not removed even at night. Corsets help straighten the spinal column during its growth and form beautiful posture, but in adults they are less effective. The corset is selected depending on the problem; most often a thoracolumbar model is required. The course of orthopedic treatment is 6-12 months and must be combined with exercise therapy.
Treatment options
Treatment methods for scoliosis are selected depending on the cause of the disease, the age of the patient and the degree of curvature. Some patients are prescribed conservative therapy, while others undergo immediate surgery to relieve internal organs of compression. Main methods of therapy:
- Taking medications. The patient is prescribed painkillers to eliminate pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins to strengthen bones and chondroprotectors if damage to cartilage tissue has been identified. Drugs are selected depending on the presence or absence of contraindications in the patient.
- Massage. The gentle impact allows you to increase blood circulation, improve back muscles, correct posture, and saturate tissues with oxygen. All manipulations must be carried out exclusively by a specialist with a sufficient level of qualifications.
- Manual therapy. A slight deviation of the vertebrae from the correct shape can be restored using techniques used by chiropractors. They will return the bone segments to their places and reduce the manifestations of deformity.
- Wearing a corset. A special device designed specifically for posture correction allows you to relieve tension from the spinal column, improve its condition, and return it to its normal shape.
- Physiotherapy. Many modern techniques are used: electrophoresis, ultrasound, hydromassage, electrical stimulation, thermal therapy and others. Their main task is to strengthen muscle tissue, improve blood circulation, and eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
The main part of conservative treatment is performing the exercises included in the exercise therapy complex. Only regular training, visiting a physiotherapy room and swimming can eliminate stoop, stretch the spinal column, and relieve the patient of chronic back pain.
Massage, exercise therapy, manual therapy
Stages 1-2 of spinal scoliosis can be corrected with the help of manual therapy and massage. When performing special manipulations, the methods have the following effects:
- increased muscle tone;
- alignment of the vertebrae;
- normalization of the location of intervertebral discs and ribs;
- improved blood circulation;
- removing muscle tension;
- elimination of pain - aching, shooting.
The achieved results in straightening the curvature should be consolidated with the help of exercise therapy. If you do not strengthen the muscle corset, scoliosis will quickly make itself felt again. Therapeutic classes will correct posture, relieve stress on the vertebrae, and improve metabolic processes. The complex should be selected individually, depending on the severity of the disease. First, they do warm-up and stretching, then the main block of exercises.
Most often, one course of exercise therapy lasts 3-4 months, then other classes are selected, including supportive ones. At the same time, it is recommended to swim, since this type of physical activity affects all muscles at once. Until the age of 14, most often the listed treatment methods are enough to completely eliminate the problem, of course, if the degree of the disease does not exceed 2.
The principle of treatment of scoliosis in adults
The formation of the skeleton in men is completed at 25 years of age, and in women at 20. It is not surprising that scoliosis found in patients 30-40 years of age cannot be cured . All that can be done at this stage is to get rid of the manifestations of the disease.
To eliminate scoliosis after the completion of the formation of the scoliotic arch, measures are taken aimed at:
- reduction of spinal curvature;
- normalization of bone structure;
- restoration of vertebral mobility;
- improved blood circulation;
- eliminating pain in the back area;
- strengthening the muscle corset.
Physiotherapy and medications
Physiotherapy for a disease such as scoliosis is a necessary step. Treatment helps strengthen muscles, improve blood supply to the spine, and eliminate pain, spasms, and stiffness. Most often, muscle myostimulation is prescribed - “lazy gymnastics”, which is carried out to enhance the effectiveness of exercise therapy. Courses are also offered:
- ultrasound;
- magnetic therapy;
- ozokerite;
- paraffin;
- electrophoresis;
- baths – salt, pine.
Drug therapy is not the main thing, because it is not able to straighten the curvature. But the medications have a strong symptomatic effect and make the patient’s life easier. Most often, NSAIDs are prescribed (Meloxicam, Arcoxia, Ketanov) to relieve pain and eliminate inflammation in the muscles. In case of severe pain, local administration of anesthetic drugs (Novocaine, Procaine) is possible. To improve the functioning of nerve trunks, B vitamins are introduced into the course in the form of complex preparations (Milgamma, Neuromultivit). At the same time, children are given products with vitamin D, calcium, and fish oil.
Scoliosis of the spine - description
Scoliosis of the spine
Scoliosis is a curvature of the spine to the right or left relative to its axis. Most often, the disease occurs when spinal curvature was not treated in childhood. The initial stages of scoliosis are effectively treated with conservative methods.
Scoliosis is an asymmetry of the body, not only the curvature of the spine, but also protruding shoulder blade or ribs on one side (right or left). This asymmetry is especially noticeable when a person leans forward with his arms hanging freely.
In no case should you confuse scoliosis with kyphosis (stooping) - these are completely different postural disorders. Although in fairness it must be said that sometimes kyphosis (stoop) is aggravated by scoliosis.
This combination is called kyphoscoliosis. But in general, kyphosis and scoliosis are different conditions and should be considered separately. Scoliosis is a complex deformation of the spine, in which there is a lateral curvature in the plane of the back and twisting (torsion) rotation of the spine around its axis.
Scoliosis is a disease of the spine, which is a persistent lateral deviation from the normal axis with mandatory rotation of the vertebral bodies. In the absence of rotation, we are talking about a violation of posture, that is, the presence of a prescoliotic condition.
Scoliosis is characterized by rotation of the vertebrae, which is usually detected using x-rays. The designation “scoliosis” (from the Greek “scolios”) was first used by Galen back in the 2nd century. That is, the disease has been known for quite a long time and attempts to treat it have been made since ancient times.
Scoliosis, or curvature of the spinal column, is a disease that affects about 2% of the world's population. The disease was first described by Hippocrates 2,400 years ago, but since then both the explanation of the causes and the basic principles of treatment have remained virtually unchanged.
Currently, based on our published research, we believe that the disease scoliosis is related to the tension on the spinal cord by a ligament called the filum terminale. In an adult, this ligament does not perform any function.
Lateral curvature of the spine occurs in childhood and persists for life if left untreated. Scoliosis leads to a misalignment of the pelvis, which places uneven load on the hip joints.
Scoliosis also has a negative impact on the lungs and heart, gastrointestinal tract and other internal organs. Scoliosis most often begins and rapidly progresses in adolescence, especially during the period when a teenager quickly grows taller. That is, from the ages of 10 to 17 years.
Other types of scoliosis treatment
The operation is prescribed if the angle of curvature of the spine is more than 40 degrees. Also, surgical treatment may be required in milder cases, but for certain reasons for the development of the disease (myodystrophy, trauma, abnormal vertebral structure, etc.). The position of the spinal column is straightened to a physiologically correct angle using metal rods and plates, followed by complete immobilization of the patient. Often it is necessary to insert bone inserts between the vertebrae, for example, in the presence of hemivertebrae. Patients are indicated for treatment in sanatoriums as an additional measure to improve blood circulation and symptomatic effects. Baths, mud, therapeutic showers, massages, and exercise equipment are prescribed. Taking courses of therapy in sanatoriums helps speed up and consolidate results, including after surgery.
Therapy with folk remedies is a symptomatic part of general treatment. Traditional methods will help relieve pain and muscle stiffness due to scoliosis. You can take baths with pine needles, a decoction of aspen bark, as well as make compresses, rub your back with ointments - all this will help quickly eliminate muscle spasms. They also take infusions of medicinal herbs internally (cinquefoil, comfrey, St. John's wort) for a course of 1-2 months.
Varieties
Scoliosis is a disease that is classified into several types. First of all, the nature of the occurrence of the pathology is taken into account. If this beginning of the process is observed during intrauterine development, then they speak of the congenital type. This can be affected by the pregnant woman’s drug therapy or viral diseases she has suffered. When the curvature of the spine is caused by a number of negative external factors, acquired scoliosis is diagnosed. It, in turn, is divided into the following types:
- Neuromuscular. It is also called paralytic, as it appears after a history of polio. Why is this type of scoliosis dangerous? It progresses quickly, and the curvature is pronounced. A hump appears in the chest area, severe muscle weakness and excessive mobility of the vertebrae occur.
- Rachitic. It appears against the background of acute vitamin D deficiency, so it is diagnosed mainly in childhood. It can be easily prevented by including foods rich in this component in your diet. This is much easier than trying to eliminate the consequences of the pathological process later.
- Primary. Appears mainly in schoolchildren who prefer to wear backpacks on one shoulder. This can be aggravated by incorrect back position during exercise. As in the previous case, preventing a pathological process is much easier than treating it later.
- Idiopathic. They talk about it if the exact cause of the curvature has not been identified. This type develops mainly during the period of active growth of bone tissue, which the muscle corset cannot keep up with.
- Static. This disease manifests itself in the lumbar region. The appearance of this type is provoked by a disruption of the normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system. And first, this problem is corrected, after which scoliosis is eliminated.
- Functional. Appears as a result of the negative impact on the back of a number of factors. These could be inflammatory processes of internal organs, colds, uneven distribution of the load on the spine.
- Thoracogenic. Develops when a severe back injury or chest deformation occurs.
There are also rarer types of pathology that appear as a result of vertebral fusion or infantile paralysis. Each of them poses a certain danger to the body, as it leads to unpleasant consequences.
Disease prevention
There are preventive measures to prevent the disease - scoliosis can be prevented. Need to:
- sit correctly and walk with a straight back;
- sleep only on an orthopedic mattress;
- eliminate excess weight, sedentary lifestyle;
- organize a diet according to the principles of healthy eating, eat more vitamin-rich foods;
- swim, ski;
- When working sedentarily, use comfortable tables and chairs, if necessary, buy special devices for your back and legs.
Scoliosis often develops during pregnancy, therefore, if there is a tendency to curvature of the back, you should wear special corsets and do exercise therapy as prescribed by your doctor.
Prevention
The appearance of scoliosis can only be avoided by practicing prevention from an early age. Only the right approach to maintaining the health of the spine can provide support for the ridge during periods of intense growth. The main measures that can protect the musculoskeletal system from curvature include:
- Swimming or athletics classes, yoga. They will gently strengthen the muscle frame, ensure the correct position of the vertebrae, improve blood circulation in the back, which will strengthen the bone tissue as a whole.
- Ensuring the correct position while sleeping, waking, and working at the computer. To do this, you need to choose the right orthopedic mattress, choose a table and chair of a suitable height, and regularly perform simple exercises during breaks.
- Developing correct posture. From an early age, it is necessary to constantly teach the child to keep his back straight, to wear a backpack on only two shoulders at a time, and not to lean his head and shoulders forward when working at the table.
- Proper nutrition is also important in maintaining a healthy spine. The body should always receive sufficient amounts of protein, calcium, phosphorus and other beneficial components to ensure healthy skeletal development.
- Refusal to carry heavy bags and packages. For shopping in the store, you can always buy a roomy backpack, which will also be easier to carry.
All preventive measures often come down to general rules and recommendations, since to prevent scoliosis, it is important to maintain overall health, paying attention to the harmonious development of the whole organism.
Scoliosis is an insidious disease, since it is easiest to notice its progression at the final stage. But it is better to start treatment at the first signs of a change in the position of the spine. Simple self-testing methods will help with this. If there is a suspicion of a pathological process in the body, it is dangerous to delay visiting a specialist, since the lack of correct therapy often leads to unpleasant complications.
How to determine scoliosis at home
Everyone knows that a person’s health can be determined by their posture. However, many people, even apparently healthy ones, suffer from spinal curvature - scoliosis.
Scoliosis develops in children under 18 years of age while the spine is growing and forming. If the disease is not prevented in time, then serious back problems may arise in the future. Scoliosis in the initial stages occurs almost asymptomatically, but it can still be identified even without the help of a doctor.
To determine whether a person has scoliosis, he needs to undress to the waist. The person being examined should put his heels together and his hands at his sides. Let him look straight ahead at head level. He should stand relaxed, as comfortable as possible.
So, we determine whether he has the following signs:
One ear is higher than the other - cervical scoliosis.
Locate the 7th vertebra, which protrudes the most, at the base of the neck. Take any weight suspended on a thread and apply it to this protruding place. If the plumb line passes exactly along the spine and then between the gluteal folds, everything is in order. When there is a curvature of the spine, the plumb line usually passes past the gluteal fold. This is a sign of unbalanced scoliosis, which can progress. In this case, S-shaped scoliosis is formed.
Let the person being examined bend over and look to see if one of the shoulder blades is protruding and if a rib hump is forming. These defects are more effectively viewed through a mirror.
Assess the height of the shoulder girdles and the angles of the shoulder blades, whether the waist lines are symmetrical, whether both iliums are at the same height
To do this, place your hands, palms down, on the pelvis, while paying attention to whether the intergluteal fold is tilted to the side, whether the subgluteal and popliteal folds are symmetrical. Pay special attention to the neck - whether its axis coincides with the axis of the rest of the spine
Get tested for hidden scoliosis. To do this, use the pads of your index fingers to feel the area of the back of the neck at the border with the head, stepping back 1 cm from the midline of the neck. The sensation of tissues of unequal density indicates the presence of a hidden curvature. If a person walks or sits crookedly, then you will definitely detect the presence of tissues of unequal density.
By identifying scoliosis in a timely manner, you can avoid serious consequences that will affect a person’s quality of life. This is why prevention and treatment
scoliosis.
The essence of pathology
Scoliosis is a persistent deformity of the spinal column, which is characterized by lateral curvature in a certain direction. Another feature of the disease is the twisting rotation of the spine around its own axis. This leads to serious dysfunction of various organs.
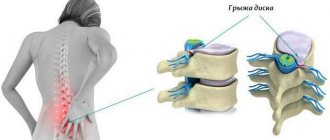
In addition, scoliosis can cause the formation of osteochondrosis, radiculitis, hernias and other back diseases.
Typically, scoliosis is acquired and occurs as a result of traumatic injuries to the back, incorrect body position during study, and abnormalities in the structure of the spine. That is why the disease is usually diagnosed in childhood - at 6-15 years.
Causes of scoliosis
Factors that can provoke spinal curvature:
- a sedentary lifestyle, which results in poor posture;
- rickets, poliomyelitis, metabolic disorders and connective tissue diseases;
- lack of calcium, leading to osteoporosis;
- spinal injuries and tumors;
- dystrophy of the muscles of the lumbar, thoracic and cervical regions;
- injuries of the pelvic bones and congenital defects;
- different leg lengths
- inflammatory processes in muscles.
Types of surgical treatment
There are 3 methods: operations with anterior access, with posterior and combined. The essence of the operations is to introduce metal structures into the spine, which can be static or movable. The advantages of a dynamic implant: it can be adjusted, ensuring the correct growth of the child, and allows you to play sports. The design is not externally visible and can be used in the treatment of severe spinal deformities in adults. It allows you to fix the curvature and stop its progress.
Treatment of children and adolescents
In children and adolescents, scoliosis is more common than others; treatment should begin as soon as signs are detected:
Scoliosis in an infant
- Children and adolescents are prescribed physical therapy and massages that strengthen the back muscles.
- Manual therapy is also used . First, the back muscles are relaxed, and then they are moved to their correct location. It is indicated for scoliosis 1-2 in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
- Hydrotherapy methods are effective . These are sodium chloride baths, 10 procedures 2-3 times a year. It is recommended to wear corsets that fix the muscles in the correct position.
- Physiotherapy and mud . Heat therapy with paraffin and ozokeritin, electrophoresis and electrical muscle stimulation are indicated. They are prescribed 10-20 procedures with an interval of 3 months. Ultrasound removes pain syndromes.
To prevent scoliosis, a child needs a special orthopedic mattress.
Possible consequences
Why is scoliosis of the spine dangerous? This question interests many people. The main consequences of scoliosis include the following:
- Chronic back pain syndrome;
- High probability of spondyloarthrosis;
- Deterioration in appearance and associated psychological discomfort;
- Damage to internal organs - severe forms of pathology can lead to diseases of the lungs and heart;
- Deterioration of potency in men;
- Weakness of labor in women;
- Weakening of the immune system;
- Allergic reactions;
- Poor blood circulation in the brain.
Physiological curves of the spinal column
- Cervical and lumbar lordosis. They are formed during the physical development of the child, when his motor capabilities expand (he begins to hold his head and sit). They are a convexity of the spine anteriorly.
- Thoracic and sacral kyphosis are formed in utero, the baby is already born with them. Represented by a convexity at the back.
In the frontal plane, the line of the spine runs along the middle axis of the body. Active and correct holding of the body in space is posture. Spinal deformation leads to the development of pathological posture and vice versa.
How to determine spinal curvature
Correct diagnosis of this disease requires proper diagnosis. The patient himself can identify a curved spine based on personal feelings and external signs, but only a doctor can correctly determine the type of curvature. At home, you can find out the approximate type of deformation. To do this, you need to stand straight in front of the mirror, straighten your shoulders and see which one is higher or lower. If they are the same, there is no curvature; if there is a noticeable asymmetry, then this is scoliosis. Often a person carries a bag on the lower shoulder.
Kyphosis can also be recognized using a mirror. You need to stand sideways and see if there is a so-called “hump” behind you; if so, then this is kyphosis. Lordosis is more difficult to detect; radiography can give an accurate result. As a rule, externally, a patient with this diagnosis has a sunken chest, protruding stomach and head. The musculoskeletal system does not function correctly. If there are any early signs of a problem, you should get tested immediately.
Which doctor should I contact?
For proper diagnosis and treatment, spinal curvature must be constantly monitored by a specialist. Statistics show that in most cases, patients come to the doctor when the deformity is advanced and the person begins to feel severe pain and discomfort. Doctors of different specializations can help in the fight for a healthy spine:
- neurologist;
- surgeon;
- orthopedist-traumatologist;
- therapist;
- vertebrologist
Such a wide choice of doctors is explained by the fact that treatment of spinal curvature can begin with solving problems of the central nervous system (neurologist), the therapist will do a preliminary examination and, based on the patient’s complaints, refer him to the appropriate doctor. The final decision is made after an x-ray will show the exact problem. With the result, the patient will be referred to a surgeon, orthopedist-traumatologist or vertebrologist, depending on the pathology.
- What does a manual therapy doctor treat - methods and techniques of massage of the musculoskeletal system
- Complex of physical therapy - exercises, benefits for diseases of the spine and joints
- Back massage for osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions - benefits for treatment and prevention
Kinds
| By etiology (origin) |
|
| By localization of curvature |
|
| By the nature of the curvature |
|
Scoliosis in adults and children can be suspected if a person has one hip or shoulder visually located higher, one shoulder blade protrudes more clearly than the other, and the head is not located in the center of the shoulders. If a person with scoliosis leans forward, the ribs on one side are higher than on the other. The left or right side will be higher, depending on whether the patient has developed left- or right-sided scoliosis.
Right-sided scoliosis
Right-sided scoliosis - what is it? This curvature of the spine is a more severe pathology. Clinical manifestations in this case increase rapidly, and diagnosis does not present any particular difficulties, especially for grades 3-4 of the disease. In this case, the asymmetry of the body is pronounced, general asthenia and fatigue are observed. Ultimately, the disease may result in the patient's disability.
Left-sided scoliosis of the spine
Left-sided scoliosis is statistically more common than right-sided scoliosis. In general, its manifestations are characteristic of right-sided, the arch has the opposite nature of curvature. There is also a distinction between lumbar and thoracic scoliosis.
How to treat scoliosis?
Patients with scoliosis should be seen by an experienced orthopedist or vertebrologist who is well acquainted with this pathology. The possible rapid progression and impact of the curvature on the condition of the internal organs requires adequate treatment, as well as, if necessary, referral to other specialists: pulmonologists, cardiologists, etc. Treatment of scoliosis can be either conservative or surgical, depending on the cause and severity pathology, presence or absence of progression. In any case, it is important that it be comprehensive, constant, and timely.
Treatment of scoliosis includes the following therapy methods:
- Manual therapy;
- Therapeutic gymnastics (therapeutic exercises);
- Wearing posture correcting devices;
- Physiotherapy;
- Symptomatic treatment;
- Surgical treatment (operation);
- Spa treatment.
The doctor selects the treatment:
- In the first stage, massage and gymnastics allow you to achieve good results, and everything happens quite quickly.
- The second degree of scoliosis is treated a little longer and using almost the same methods, only supplemented by wearing a corset and manual therapy.
- With grades 3 and 4 of the disease in adults and children, surgery is most often prescribed, but before it is performed, they try to reduce the angle of curvature with the help of physiotherapy, exercise therapy, and a corset. If the degree of curvature reaches grade 4, then surgical intervention is required.
Wearing a corset for people with scoliosis
There are 2 types of corsets: supporting and correcting. Supportive corsets remove excessive loads from the spine, while corrective corsets are designed to reduce the angle of deformation of the spinal column.
The principle of operation of the corset:
- creates pressure on curved areas of the spine, stopping the deformation;
- fixes the spine in an anatomically correct position;
- reduces the load on the affected part of the back;
- reduces pathological mobility of the spine;
- “reminds” you to keep your back in the correct position (for patients with stage 1 scoliosis).
Disadvantages of a corset:
- restricts movement;
- the muscles lose the habit of holding the spine independently and weaken;
- an incorrectly selected corset can provoke the progression of scoliosis;
- Possible skin damage at pressure points.
Therapeutic gymnastics (therapeutic exercises)
Physical therapy exercises have a good effect. But here, with inadequate physical activity, spinal instability increases and scoliosis progresses. Therefore, a set of exercises is developed for each patient individually, taking into account the location and severity of the curvature. With a high degree of scoliosis, running, strength exercises, jumping, and outdoor games are contraindicated.
Objectives of physical therapy for scoliosis:
- strengthen the back muscles and thereby stabilize the spinal column
- correct deformation of the spine and chest, ensure normal functioning of the heart and lungs
- correct your posture
- strengthen all organs and systems of the patient.
When performing therapeutic gymnastics complexes, sports equipment can be used: gymnastic benches and walls, inclined planes, dumbbells, rollers, bands, cuffs, frames, sticks, weights, medicine balls, etc.
Massage
Therapeutic massage is indicated at any stage of development of spinal scoliosis in both adults and children. Massage relieves pain, normalizes blood circulation, strengthens muscles. The main goal of massage sessions for the muscles of the back and chest is to restore the strength lost during the disease. At the same time, concave areas are relaxed using various techniques, and convex areas are toned.
Massage courses are carried out up to 3 times a year and are combined with other types of treatment, for example, such as physiotherapeutic procedures.
Physiotherapy for scoliosis
Physiotherapeutic procedures play an important role in the fight against spinal curvature. They are especially effective in combination with physical therapy and massage.
The list of the most effective physiotherapeutic procedures includes the following types:
- Electrical stimulation of weakened muscles. Thanks to the influence of electric current, it is possible to effectively influence muscle tissue.
- Heat therapy. It is usually prescribed if there is no intensive progression of the pathology. Includes ozokerite applications, hot wraps and some other procedures.
- Electrophoresis. There is an effect of “weak” currents on a certain area of muscle tissue using phosphorus and calcium.
- Ultrasound. Prescribed to suppress pain in the back and in cases of osteochondrosis.
Surgery
In most cases, scoliosis does not require surgery. However, severe pain or progressive deformity is an indication for surgery.
An angle of more than 45° requires surgical correction due to the formation of persistent deformities of the chest, pelvis and limbs. The surgical technique is chosen individually, based on age and concomitant disorders in the spine.
The essence of the operation is the use of special metal structures to straighten and fix the spine at the desired angle.
Scoliosis surgery allows you to solve three main problems:
- straighten the spine as safely as possible;
- create balance in the torso and pelvic area;
- support the correction long-term.
Achieving these goals is carried out in two stages:
- the vertebrae along the curve are united;
- these fused bones are supported by appliances—steel rods, hooks, and other devices—attached to the spine.
There are several ways to surgically treat spinal curvature in adults. Among them are such methods as:
- Implantation of special metal structures to correct posture and fix the spinal column in the correct position.
- Restoration of damaged vertebrae and spinal discs.
- Fixation of the spine in a certain position using a surgical method.
- Correction of a violation of the structure of the chest using a surgical method.
- Surgical treatment of the ligamentous apparatus of the spine and spinal muscular system.
After the age of 18, when most growth is complete, scoliosis is much more difficult to eliminate. At this age, efforts are directed toward preventing further development of the curvature.
Treatment of scoliosis in Europe, Israel and Korea
Treatment in foreign centers is prescribed after diagnosis. Based on conservative treatment for patients with grade 1-2. They are also prescribed special exercises and the use of corsets. From grade 3, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Surgical treatment is carried out by neurosurgeons. The range of prices for treatment in Europe , in particular in Germany ranges from 10 thousand dollars to 37 thousand dollars. An important process after surgery is rehabilitation. Its duration is at least 3 weeks. It is paid and costs from $300 to $2500.
In Israel, the cost of laboratory tests ranges from $320 to $910. Conservative treatment can range from $5,000.
Treatment in Korea will cost more; for 12-14 days of hospitalization you will need to pay 12,000 - 18,000 dollars.
Symptoms
Symptoms of spinal curvature vary markedly and depend on the location of the pathological deformity.
Thus, disorders in the cervical spine manifest themselves as follows:
- pain when turning or tilting the head;
- numbness in the shoulder girdle, goosebumps, burning and tingling;
- loss of consciousness;
- blood pressure changes;
- migraine;
- deterioration of hearing and vision.
When the lumbar segment is curvature, the following signs appear:
- protrusion of one of the shoulder blades;
- shoulder asymmetry;
- slouch;
- uncertainty in movements, gait disturbance;
- different lengths of the upper limbs.
General signs of spinal curvature include rapid fatigue, constant back pain, discomfort when sitting for a long time, changes in the chest skeleton, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, heart, and lungs. The patient complains of fatigue from walking, pain in the legs, and shortness of breath.
How to fix
The treatment process for spinal deformity is always complex. It is worth remembering that the older the patient, the more difficult it is to correct the deformity; sometimes doctors recommend sticking to maintenance therapy (massages, exercises, ointments). Basically, the treatment focuses on strengthening the back muscles and maintaining an even posture. In rare, advanced cases, surgery may be necessary.
For patients with scoliosis and other types of curvatures, regular physical therapy exercises, a course of massages, and daily exercises aimed at strengthening the back and maintaining muscle tone and vertebrae are recommended. For example, with scoliosis, swimming has a good effect on the back, during which the muscles of the neck and back actively work and strengthen.
Exercises
Exercises are highly effective in the treatment of scoliosis, lordosis and kyphosis. You can easily perform them at home. They help not only patients who have crooked posture, but also those who want to perform them as a preventive measure. One of the most effective exercises is done like this:
- take a sitting position;
- place your palms behind your head;
- twist your back to the right, then to the left, movements are smooth.
A very useful exercise that can be done at home several times a day, for example, after waking up and before going to bed. You need to sit on your knees, bend your head towards your shins, stretch your arms forward and stretch your back as much as possible. This will help relax the back muscles and vertebrae; this exercise also helps with pinched spine or sciatic nerve.
Massage
Many patients like this method of therapy. Even for people without back problems, massage is very useful - it relaxes the body, helps relieve stress, and improves blood circulation. Therapeutic massage for patients with spinal curvature is best done by a competent specialist. The massage relaxes the back muscles and may have a warming effect.
Before undergoing a massage, you need to make sure that the patient has no contraindications, such as:
- diseases of the circulatory system;
- inflammation on the skin of the back;
- nausea;
- hypertensive crisis;
- allergic reactions (Quincke's edema);
- open form of tuberculosis;
- cerebral vascular sclerosis;
- inflamed lymph nodes;
- skin diseases.
Auxiliary treatment
Therapy prescribed by a doctor always includes several points. This is a treatment that includes main and auxiliary methods. Additional recommendations may include: gels, ointments, creams with a cooling effect (they are especially useful in acute stages of the disease), massage, physical therapy, and a corset. Drug therapy as a fast-acting remedy comes in the form of vitamins, food additives, minerals, and immunostimulants. During inflammation, the temperature may even rise to 39 degrees, then the doctor will prescribe antipyretics.
What is spinal curvature
A healthy person has slight curves in the back. This is considered normal for the spine. However, when these bends are very strong, a curvature of the spinal column is diagnosed. This pathological condition can be congenital, it can occur due to abnormal development of the fetus, when pathologies of skeletal development, rickets, poliomyelitis and other diseases are present.
Deformation of the spine negatively affects the functions of internal organs, because pressure on the vertebrae impairs blood circulation. Pathology can appear over the years, for example, such a deviation from the norm can occur due to injury or surgical interventions. Even sedentary work can cause curvature of the spine, and with age this condition only worsens, because a person is in a hunched position for a long time.
How to identify scoliosis at an early stage
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine with twisting around its axis. The disease occurs during difficult childbirth, or appears in children of preschool age, because it is difficult for them to monitor their posture
Scoliosis in the early stages and at a young age of the patient can be treated, so it is important to identify this disease in a child in a timely manner
How to determine spinal curvature at home? There are several methods, but the extent of the disease and treatment options can only be prescribed by a qualified doctor. Below are ways to recognize scoliosis.
Treatment of torticollis
Conservative methods:
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- treatment by position;
- physical therapy;
- water procedures in the pool using a circle for newborns;
- wearing a collar that fixes the cervical spine in the correct position.
Surgical treatment is performed if there is no effect from conservative:
- myotomy - dissection of the neck muscle;
- plastic surgery (muscle lengthening).
Kyphosis and lordosis are treated with conservative methods (physical therapy, massage, drug pain relief, muscle spasm relief).
Causes
There are some prerequisites for the development of this pathology. There are congenital and acquired changes in the spine. Each type has its own reasons. Congenital physiological curvature of the spine is caused by pathologies of intrauterine development such as, for example, the development of extra or underdeveloped vertebrae, insufficient development of the ridge. This deformity can only be corrected through surgery.
The acquired form of the disease is characterized by gradual development over the years. The reasons for this curvature may be:
- sedentary work;
- complications after rickets, polio, pulmonary tuberculosis, radiculitis;
- serious spinal injuries;
- pathologies associated with abnormal gait - flat feet, amputation of one of the lower limbs, different size of limbs;
- nearsightedness, farsightedness or strabismus - with such diseases a person is forced to take an incorrect sitting position.
In children
Age category has virtually no effect on the number of patients with spinal deformity. However, in children the situation is aggravated by the fact that constant growth of the body can become an obstacle to effective treatment of the disease. From five to fifteen years of age, the curvature of the back is most noticeable in children. At this age, the treatment of such a disease is very effective, since the final stage of skeletal formation has not yet occurred.
The classification of the disease in children is the same as in adults - curvature can be congenital or acquired. However, in the second case of this type of scoliosis is explained not by a sedentary profession, but by the formation of incorrect posture at school. You can often find classrooms where the height of desks and chairs does not meet the standards, and the constant work of children at such tables causes crooked posture and various spinal deformities.
- Vertebral artery syndrome with cervical osteochondrosis - symptoms. How to treat vertebral artery syndrome at home
- Flat feet in adults: symptoms and treatment
- Posture corrector - review of models and contraindications
Cervical spine deformity
- Torticollis is a pathology in which there is simultaneously a tilt of the head to one side and a turn of the neck to the other.
- Kyphosis is a backward curvature of the neck. This is a rare occurrence.
- Lordosis is an increase in physiological bending. The neck stretches forward, the shoulders round, and a stoop develops.
Causes of congenital torticollis:
- incorrect intrauterine position of the fetus;
- birth injuries;
- spasm or shortening of the neck muscles;
- congenital pathology of the cervical vertebrae (Klippel-Feil disease);
- rotational subluxation of the 1st cervical vertebra.
Causes of acquired deformity of the cervical spine:
- installation torticollis - when a child takes an incorrect position in the crib for a long time;
- compensatory - for inflammatory diseases of the ear, purulent processes in the neck (the child spares the sore side and tilts his head to the healthy side);
- fracture, dislocation or subluxation of the first cervical vertebra;
- osteomyelitis, tuberculosis, tertiary syphilis - the vertebrae are destroyed, axial deformation of the skeleton occurs.
Thoracic disorders
Kyphosis is accompanied by deformation in the form of increased physiological bending. There is a pathological bending backwards with the formation of a round back. Acquired kyphotic deformity of the spine is more common.
Causes of thoracic kyphosis:
- Weakness of the muscle corset, which does not have time to form following the accelerated growth of the child.
- Early rickets (up to 1 year) - the thoracic and lumbar regions are affected. The deformity disappears in the supine position (unfixed curvature). The severity of the pathological bend is aggravated when the child sits and stands on his legs.
- Late rickets (5-6 years) - fixed kyphosis and kyphoscoliosis develop.
- Osteochondropathy is observed at the age of 12-17 years. Boys suffer more often. In the medical world it is called Scheuermann-Mau disease. Dystrophic changes develop in the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs. A fixed wedge-shaped deformity of the spine is formed.
Causes and signs of S-shaped curvature
The main provoking factor of scoliosis (regardless of the form of curvature) is poor posture in childhood. If a child often slouches, spends a long time in the same position, and pays little attention to physical activity, the risk of developing scoliosis increases sharply. But it is impossible to say in advance what exact form the deformation will take, since it depends on the physiological characteristics of the body.
Poor posture in childhood can lead to the development of scoliosis
Common causes of S-shaped scoliosis include:
- congenital pathologies of the vertebrae;
- back injuries, including birth injuries;
- spinal infections;
- muscle diseases;
- obesity.
At the initial stage, when changes occur in the vertebrae themselves and the tissues surrounding them, pathology can only be determined using hardware examination, for example, radiography. External manifestations are either completely absent or expressed so weakly that they are not given importance. You can notice the first characteristic signs after the bend of the main arc reaches 7-10 degrees.
Scoliosis can be detected at the earliest stage of development using radiography.
Early symptoms of scoliosis are manifested primarily by a hunched back. The patient hunches excessively, stretches his neck forward, and walks with his head down. When examining the back, you may notice that one shoulder blade is slightly higher than the other, and upon palpation, a slight muscle thickening may be felt on one side of the back at the level of the ribs. As the disease progresses, new signs are added:
- asymmetry increases in the shoulder blades and shoulders;
- there is a gradual distortion of the pelvis, the gait changes;
- when the body tilts, a hump appears in the area of the ribs, shifted to one side;
- the muscle roll on the back thickens and becomes larger;
- rapid fatigue appears after physical activity;
- A dull aching pain and muscle spasms often occur in the side.
Main signs of S-shaped scoliosis
When the bending angle exceeds 40 degrees, negative changes occur in the chest organs and circulatory system. Due to skeletal deformation, blood vessels are compressed, which causes disruption of microcirculation of fluids and metabolic processes in tissues. A reduction in the chest leads to displacement of the lungs and heart, resulting in shortness of breath and irregular heart rhythm. Over time, disorders of the digestive tract and excretory system may occur.