Natural causes
If the pain syndrome occurred once and was not too intense, there is no cause for concern. Discomfort can be caused by natural reasons:
- overeating;
- eating excessively fatty or spicy foods;
- drinking alcoholic beverages.
This phenomenon often occurs in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. Due to lack of physical activity, blood supply to the abdominal cavity and lower extremities deteriorates. Staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time leads to stagnation of blood, which causes pain.
Pain in the right side under the ribs after eating is often observed in late pregnancy. In the third trimester, the uterus grows to such a size that it interferes with the passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract. The pain syndrome is aching or pulling in nature.
https://youtu.be/Vk-5a7Pqd84
Nature of the symptom
Any pain indicates health problems, and ignoring the symptom is dangerous. Whether a person requires emergency hospitalization or should undergo medical diagnostics on an outpatient basis depends on the nature of the pain manifestations.
Aching
When the right side ache, this is a sign of sluggish chronic inflammation. Depending on the location, aching pain will indicate the following diseases:
- Cholecystitis. With chronic inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder, the right hypochondrium aches, and the discomfort intensifies when a person eats fatty, spicy or spicy foods.
- Colitis. The inflammatory process of the colon mucosa provokes aching painful sensations in the lower abdomen on the right.
- Chronic adnexitis. In women with ovarian pathology, pain occurs in the groin on the right. The resulting painful sensations radiate to the coccyx or lumbar spine.
- Kidney diseases. Chronic renal inflammation is characterized by a dull aching pain in the right back.
In terms of intensity, aching pain in the right side can be either pronounced or barely noticeable, causing moderate discomfort.
Pulling
A feeling of pulling on the right side most often appears when the functioning of the digestive organs is disrupted. The reason may be:
- Chronic cholecystitis. Constant inflammation of the walls of the organ reduces the contractile function of the gallbladder and leads to stagnation of bile. People complain that there is a pulling on the right side under the ribs. Patients often complain of morning sickness and stool upset (diarrhea, constipation).
- Liver diseases. In the subacute course of liver pathologies, it pulls under the costal arch in front. The patient develops an unpleasant bitterness in the mouth and stools are disturbed. In severe functional disorders, the skin becomes dry, jaundice and/or rashes appear.
In women, nagging pain in the lower right occurs with an ovarian cyst.
Often, during unusual physical exertion (running, fast walking) or after eating a large amount of heavy food, a person experiences an unpleasant pulling sensation on the right side. The appearance of the sensation is associated with increased load on the liver.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Pain in the right side is characteristic of the following diseases of the digestive tract:
- Cholecystitis is an inflammatory process in the gallbladder. The disease develops due to the formation of stones, stagnation of bile and activation of intestinal microflora. In chronic cholecystitis, the pain is dull, accompanied by nausea and discomfort. The acute form of the disease manifests itself more clearly: after eating, the right side under the rib hurts quite strongly, the stomach swells, repeated vomiting begins, the heart rate rises to 110-120 beats per minute. In this condition, emergency hospitalization is required.
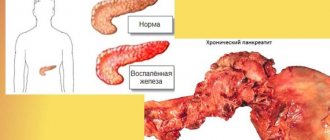
- Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. It may be a consequence of regular alcohol abuse (70% of cases), previous infections, viral diseases, poisoning and injuries. The acute form of the pathology is accompanied by uncontrollable vomiting mixed with bile. A sharp pain radiates (“gives”) to the left side of the body.
- Duodenitis is damage to the mucous membrane of the duodenum. It can be triggered by excessively spicy foods and drinking alcohol. The disease is manifested by nausea and vomiting, general malaise, and fever. Pain increases with palpation of the epigastric region.
- Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease characterized by the replacement of healthy organ tissue with connective tissue (stroma). Develops with prolonged alcohol intoxication, hereditary predisposition, as a result of previous infections. The disease manifests itself gradually: it begins with decreased ability to work, weakness, and dyspeptic disorders. In later stages, jaundice, swelling and ascites appear.
- Hepatitis is a series of inflammatory liver diseases that have a predominantly viral etiology. Characteristic symptoms include a yellowish tint to the skin and general malaise. Pain under the rib can be both intense and nagging.
- Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma. A malignant tumor can manifest itself as dull and aching pain, fever and weakness. Due to mild symptoms, it is often diagnosed in late stages, which significantly complicates treatment.
- Appendicitis. At an early stage, inflammation of the appendix manifests itself as sharp pain in the solar plexus area. Then the pain spreads further, including the area of the right hypochondrium. Appendicitis can be recognized by nausea, vomiting, heartburn, and fever. In addition, the disease is manifested by stool disorders and changes in the color of stool. Inflammation of the appendix is a dangerous disease that requires immediate hospitalization.
It is quite difficult to independently diagnose gastrointestinal pathologies. If you notice several characteristic symptoms, call a doctor.
Etiology
The pathogenesis of abdominal pain after a meal is that food passes through the esophagus and reaches the stomach, which increases in size and begins to secrete gastric juice. Active contractions begin, and food enters the duodenum.
If at any stage a digestive disorder occurs, a person experiences pain in the area of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. Unpleasant sensations are formed against the background of the influence of digested food and digestive juices on the damaged membrane.
The most common abdominal pain after eating is the consequences of poor nutrition:
- eating food immediately before bedtime;
- dry food;
- eating “on the run”;
- lack of a meal plan - it is better to eat every day at the same time;
- eating spicy, sour and overly seasoned foods;
- prolonged refusal to eat followed by overeating;
- insufficient amount of food consumed;
- ingestion of excessively dry food;
- eating high protein foods.
Lactose intolerance can cause severe abdominal pain. Allergies to the following foods can cause illness:
- eggs;
- milk products;
- cocoa and chocolate;
- nuts;
- Fish and seafood;
- citrus;
- honey;
- strawberries and wild strawberries;
- flour and pasta;
- soybeans, beans and other legumes.
It is worth noting that food allergies are the most common cause of abdominal pain after eating in a child.
The causes of abdominal pain after eating can be pathological. The underlying disease may be:
- narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus;
- peptic ulcer;
- gastritis;
- esophagitis;
- gastric obstruction;
- colitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- hiatal hernia;
- urolithiasis disease;
- intestinal or stomach polyps;
- cholecystitis;
- intestinal flu;
- pylorospasm;
- mesenteric ischemia;
- pancreatitis;
- chronic constipation;
- pathologies of the spleen;
- cholelithiasis.
Cholelithiasis
The anomaly may appear due to a disease that is not associated with the digestive system:
- fractures of the lower ribs;
- sternum injury;
- pleurisy;
- myocardial infarction;
- purulent form of sore throat or pneumonia;
- inflammation of the reproductive organs in women;
- rupture of aortic aneurysm;
- ketoacidosis.
The reason why your stomach hurts after a meal may be indicated by the nature of the pain. For example, long-term nagging pain occurs as a result of such pathologies:
- chronic gastritis;
- binge eating;
- gastric oncology;
- excessively fast food consumption;
- stomach ulcer.
Burning pain can be caused by ingestion of sour or salty foods, the development of gastritis or pancreatitis.
Sharp abdominal pain immediately after eating appears in the following situations:
- consumption of low-quality products;
- inflammation of the appendix;
- open stomach ulcer;
- acute food poisoning;
- the course of infectious processes;
- exacerbation of gastritis;
- pancreatitis.
The etiological factor can be indicated by the localization of pain:
- pain in the upper abdomen or in the navel area occurs due to inflammatory damage to the stomach or duodenum;
- in the iliac zone with irradiation to the right hypochondrium they speak of cholelithiasis, inflammation of the bile ducts or gallbladder;
- “in the pit of the stomach” and under the ribs is a sign of an ulcer of the duodenum or stomach.
It is noteworthy that if the pain appears immediately after a meal or after about an hour, the problem lies in the esophagus or stomach, and if the pain occurs after 2 hours or more, the cause of the abnormality is in the intestines.
Abdominal pain after eating while carrying a child is most often associated with displacement of organs located in the abdominal cavity. Filling the stomach causes them to compress, causing aching pain.
Other pathologies
Urinary tract diseases are also accompanied by pain in the right side. This pain is stabbing in nature and is present constantly, not only after eating. The most common cause is urolithiasis: the passage of a stone injures the mucous membranes and causes severe discomfort.
The main causes of pain in the right hypochondrium in the front after eating are problems with the digestive tract. This area contains the gallbladder, pancreas, liver, and part of the duodenum. Pathologies of these organs cause pain. They can have an acute or chronic development.
Treatment
The nature of treatment depends on the identified pathologies and accompanying symptoms. In diseases of the colon, accompanied by excessive gas formation, the nature of a person's stool is very important.
But even constipation can have a dual nature that needs to be clarified. The therapeutic regimen for spasmodic intestinal phenomena is fundamentally different from the treatment for weakened motility, intestinal sluggishness, or intestinal polyps identified during colonoscopy, although all these pathologies may have the same symptom in the form of flatulence.
In case of pathologies of the biliary system, the timely outflow of bile and the condition of the liver tissue are important.
Drug treatment
As a rule, gastritis and duodenal ulcers are of an infectious nature; their diagnosis involves examination for the presence of Helicobacter pylori and its specific treatment with penicillin antibiotics.
Note! The unclear nature of pain anywhere in the abdomen makes thermal procedures an absolute contraindication. An exception can be made if the patient is firmly convinced that the pain was caused by a spasm of the biliary tract: a hot bath will help remove it and alleviate the condition.
Diet
The secretion of all digestive enzymes has the character of conditioned reflexes, which has a time dependence and binding. Strict adherence to the food intake helps to consolidate this binding: the maximum intensity of enzyme secretion occurs at a certain time of the day.
Therefore, it is very important to eat fractionally and at the same time, so that the food mass has time to undergo adequate processing by the digestive enzymes of the stomach and the complex complex of digestive juices formed in the duodenum. Deficiency or untimely intake of any component disrupts the complex digestive chain.
If there are problems with the biliary system, the diet should contain a minimum amount of fat so as not to overload it.
The diet should contain the optimal amount of fiber, mainly plant fiber. Plant fiber stimulates intestinal motility, acting as a powerful cleansing factor that relieves flatulence.
Traditional medicine
For persistent dull pain in the right side, a mixture of dried St. John's wort, dandelion root, anise and coriander fruits, and corn silk taken in equal parts is quite effective. Pour 1 tbsp with a glass of boiling water. mixture with top and leave for at least 30 minutes. This infusion is drunk in a glass 3 times a day before meals. Due to the essential oils contained in spicy fruits, excess gas formation in the intestines is suppressed.
The protective properties of the liver are increased by milk thistle, immortelle, rose hips, and plantain. A mixture of these herbs in an amount of 1 tsp. Infuse in a glass of boiling water for 20 minutes and take 100 g before each meal. The course of treatment is at least 15 days. After 3 months it should be repeated.
Note! Any choleretic drugs, including herbs, are taken only after consultation with a doctor. A stone with sharp edges that suddenly moves can seriously injure the bile ducts and cause an emergency. Oil-based dosage forms should also be taken with caution.
Causes of pain in the right hypochondrium after eating
Doctors identify several diseases that are the most common causes of pain in the right hypochondrium.
Cholecystitis
The disease is accompanied by inflammation of the gallbladder, which can be chronic or acute. It is characterized by a violation of the release of bile and its stagnation. Cholecystitis is caused by consumption of fatty foods, alcohol, spicy foods, and a sedentary lifestyle. Quite often, inflammation of the gallbladder is diagnosed during pregnancy. Main symptoms of the disease:
- cramping acute pain that radiates to the shoulder blade and back;
- nausea and vomiting;
- signs of heart rhythm disturbances;
- belching with a bitter taste.
If cholecystitis is accompanied by the presence of stones, there is a high probability of blockage of the ducts, which can lead to infection of the organ. Patients complain of dull pain in the right front, increased body temperature and a sharp deterioration in health. Signs of intoxication are clearly visible.
Cholangitis
Inflammation of the bile ducts is provoked by conditionally pathogenic microflora that gets there from the intestines. The disease often occurs together with cholecystitis. The infection quickly spreads to the gallbladder tissue, causing inflammation. Characteristic symptoms of cholangitis:
- the stomach on the right side begins to hurt immediately after eating fatty foods;
- jaundice develops, severe itching of the skin is observed;
- body temperature rises.
In the absence of adequate treatment, the disease leads to the development of cirrhosis. The most dangerous complications of cholangitis include renal and hepatic failure.
Cholelithiasis
The pathology is closely related to cholecystitis. Inflammation in the gallbladder creates optimal conditions for the formation of stones. The condition is accompanied by the appearance of acute pain and discomfort in the right hypochondrium after drinking alcohol or fatty foods.
Symptoms of gallstone disease include chills and vomiting, which leaves a bitter taste in the mouth. After the acute pain subsides, the patient experiences weakness and weakness, and the discomfort in the abdomen becomes aching.
Liver pathologies
You may experience a tingling sensation in your stomach after eating fatty or fried foods, alcohol, carbonated drinks, or spicy seasonings. In this case, pain in the right side is usually caused by hepatitis. The diseases are accompanied by inflammation of the liver due to damage by viruses, against the background of the negative effects of toxins and autoimmune processes in the body. Many hepatitis can be hidden for some time, only the following symptoms are observed:
- slight nausea;
- decreased appetite;
- intolerance to certain odors.
As the disease progresses, the pain in the right hypochondrium becomes stronger. Against the background of a violation of the outflow of bile, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes appears. Urine becomes dark in color, stool becomes grayish. With the development of fatty degeneration, the liver is gradually excluded from the digestive process. At the same time, its increase and pain on palpation are observed.
Peptic ulcer
Pain and tingling on the right side can be caused by a duodenal ulcer. The development of this pathology begins with bulbitis. Pain usually appears 2 hours after eating or at night. Patients also indicate other complaints - nausea, vomiting, increased sweating, weakness.
Character of abdominal pain after eating
The pain may be:
- piercing;
- intense;
- blunt;
- cutting;
- weak;
- drilling;
- aching;
- moderate;
- cramping.
Often, abdominal pain after eating is also accompanied by the following symptoms:
- nausea, may turn into vomiting;
- flatulence, feeling of abdominal distension;
- constipation;
- lack or decreased appetite;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- diarrhea;
- belching of air or stomach contents.
They can be triggered by the following factors:
- late meals (just before bedtime);
- poor nutrition;
- alcohol;
- smoking;
- too dry food;
- dishes with a lot of hot spices;
- eating disorder;
- food “on the run”;
- congenital lactose intolerance, when the patient is contraindicated to consume milk and milk-containing products;
- binge eating;
- violation of the drinking regime, when an adult consumes less than 2 liters of fluid per day;
- a lot of protein foods of animal origin (especially if it is fatty meat, pork).
Diagnostics
Pain in the right hypochondrium after eating is explained by problems with the digestive system, so the patient should consult a gastroenterologist. The doctor studies the medical history, examines the patient, and then prescribes a number of tests:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- urine examination for diastase, glucose level, bilirubin, protein presence;
- immunological tests to detect hepatitis and determine its type;
- stool analysis for the presence of helminthic infestations.
Additionally, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is prescribed. The contents of the duodenum are obtained by probing and the qualitative composition of bile is determined. In some cases, contrast radiography of the gallbladder, stomach and other organs is prescribed. Using fibrogastroscopy, the condition of the stomach and duodenum is determined.
What can cause pain in the right side?
Pathological causes can be divided into two types: therapeutic and emergency.
Therapeutic, usually do not manifest themselves too acutely and do not pose a threat to life, so there is no need for urgent intervention. Urgent, speaks for itself. In such cases, emergency medical care should be provided.
Therapeutic causes of pain in the right side include:
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Duodenitis
- Chronic cholecystitis, especially if stones are found in its cavity
- Presence of biliary dyskinesia
- Bulbit and cholangitis
- Gastritis
Emergency causes include the same diseases, but with an acute course. They have very clear symptoms and are accompanied by severe pain.
Pain in the right side after eating food can be caused by pathological processes in the liver, gall bladder, stomach and pancreas.
Therapy methods
The list of methods used to treat pain in the right hypochondrium after eating depends on the underlying disease and the general condition of the patient. Doctors recommend that patients completely change their lifestyle:
- give up intense physical activity, but maintain daily physical activity;
- normalize weight;
- prevent stress;
- follow a special diet: give up alcohol, heavy food, spicy seasonings.
Additionally, patients are prescribed a number of medications to relieve symptoms of diseases and prevent exacerbations. For peptic ulcers, enveloping agents (Gastal) are used, and if Helicobacter pylori is detected, antibiotics are used. If there are problems with the pancreas, enzymes, vitamins, and drugs are prescribed to restore absorption processes in the intestines.
If hepatitis is diagnosed, antiviral and immunomodulatory agents are used for treatment. Additionally, vitamins, choleretic drugs, hepatoprotectors, and corticosteroids are prescribed. With the development of liver failure, detoxification is performed in the form of hemodialysis and plasmapheresis. If cholecystitis is detected, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. If stones are present, treatment is used to soften and remove them. To improve the outflow of bile, choleretics and cholekinetics are used.
If complications develop, a decision is made to perform surgical intervention. Doctors may remove the gallbladder if there are signs of cellulitis or gangrene. The ulcer is excised and the stomach and intestines are sutured. If malignant tumors are detected, they are removed followed by chemotherapy.
Preventive measures
To prevent pain in the right hypochondrium, a person needs to be careful about his diet. Heavy, spicy foods should be excluded from the diet, and an optimal drinking regime should be adhered to. You need to try to stabilize your weight, give up alcohol and smoking. If complaints from the gastrointestinal tract are detected, you need to visit a doctor and undergo an examination. Diseases in the early stages of development are easier to treat and do not lead to life-threatening complications.
On the right side of a person there is one of the most important organs - the liver. Therefore, if the right side hurts under the rib after eating, then the doctor may initially suspect the presence of hepatological diseases. However, there are no less serious reasons for this manifestation.
In addition, discomfort may occur during diseases of the internal organs. The psychological factor plays a major role in the occurrence of pain. To determine the main cause of this manifestation, patients need to undergo a comprehensive examination. You can get rid of painful sensations using conservative techniques. However, it is not always possible to eliminate the provoking factor in this way.
Classification
If your right side hurts after eating, this can be caused by a variety of factors. To determine the provoking factor, in addition to the main symptoms, one must also take into account the classification of such a disorder. Depending on the duration of the pain, it is divided into constant and periodic. Depending on the nature of the pain syndrome, it can be:
In addition, painful manifestations also differ depending on the area of localization of discomfort. If the pain is at the top, this may indicate damage to the diaphragm. Discomfort in the lower part indicates acute appendicitis.
In case of pain in the back, there is a risk of pathology occurring in the area of the kidneys or pancreas. If such manifestations of pathology are noted in the front, then this may indicate the occurrence of diseases of the stomach, intestines, liver, lungs, and gall bladder.
Causes of pain in the lower abdomen on the right
If you have pain in the lower right area of your abdomen, it may indicate appendicitis, irritable bowel syndrome, an intestinal infection, or a urinary tract infection.
How does your stomach hurt with appendicitis?
In most cases, appendicitis manifests itself at the initial stage as pain in the abdomen on the right side near the navel, then it spreads to the right lower abdomen. Sometimes the pain is first felt around the navel and can spread to both the left and right lower abdomen. With acute inflammation, bloating, fever, and nausea appear. Inflammation of appendicitis can be mistaken for an intestinal infection. Therefore, if you have such symptoms, it is better to call a doctor.
In some cases, inflammation of appendicitis can be caused by infection with worms.
Pain in the right lower abdomen due to irritable bowel disease
Cramping, cramping, or throbbing pain in the right lower abdomen can be caused by irritable bowel disease, the medical name is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). This disease also manifests itself with symptoms such as bloating, constipation or diarrhea. Irritable bowel syndrome can be caused by a number of reasons. The most common include stress, the consequences of intestinal infections, or disruption of the composition of bacteria in the intestinal microflora. Symptoms of IBS can be uncomfortable, but the disease is not dangerous. However, it is necessary to ensure that there are no other causes of this discomfort by conducting an examination.
Causes of discomfort
In some cases, after a fatty meal, the right side hurts, especially when overeating, as well as in the presence of problems with the liver and stomach. In addition, discomfort is felt after consuming very cold or hot food.
If your right side hurts under the rib after eating, this may be a sign of inflammation in the area of the cecum. Also, this kind of pain can indicate inflammation in the gallbladder area, as a result of which fatty foods are poorly tolerated, and hepatitis, in which there is an intolerance to protein foods.
If your right side starts to hurt immediately after eating, this may be a sign of irritable bowel disease. In this case, additional signs such as:
- rumbling;
- bloating;
- problems with bowel movements.
In this case, the right side hurts after eating, and the discomfort goes away after passing gas or defecation. The pain does not bother the person until the next meal, and is not accompanied by anemia, fever, or sudden weight loss. If discomfort occurs after eating spicy or salty food, we can talk about the presence of pathologies of the right kidney.
If there are problems with the intestines, pain will appear 1-1.5 hours after eating food. Inflammation of the small intestine and enteritis, in addition to painful manifestations, is accompanied by stool disturbances, and intestinal diseases occur with constant constipation and bloating. The right side often hurts under the rib after eating due to inflammation of the stomach.
How to determine the cause of pain?
The abdominal cavity contains many internal organs that can lead to right abdominal pain. Sometimes these pains have no serious cause. They can occur due to disruption of the usual diet or overeating. If the pain is prolonged, then it is necessary to understand its cause and consult a doctor.
To understand the cause of the pain and more accurately describe it to the doctor, it is necessary to pay attention to where exactly the pain occurs, what its nature is and under what circumstances it appears.
Answering the following questions for yourself can help clarify the situation.
- How bad is the pain?
- Does the right side of the navel hurt?
- What kind of pain - stabbing, sharp, dull, aching?
- Does the pain occur mainly after eating?
- Does the pain get worse with pressure?
- Is the stool discolored?
- Has your facial skin turned yellow?
- Are there any associated symptoms such as nausea, vomiting or diarrhea?
- Does the pain radiate to other parts of the body, such as the back or shoulders?
1- liver
2- gallbladder
7 - ileum
8.9- ovary, uterus
Diseases of the stomach, pancreas
If after eating the right side of the lower abdomen hurts, this may be a sign of inflammation of the duodenum or the formation of an ulcer. There are also signs such as nausea, belching, a feeling of fullness, flatulence, increased sweating, and weakness. If you complain of severe cutting pain and dizziness, urgent medical attention is required.
A stomach ulcer is characterized by pain in the middle of the right side after eating, and additional nausea and weakness. With this disease, it is also necessary to take into account the frequency, strength and localization of painful manifestations.
The cause of inflammation of the pancreas can be acute cholecystitis, stones, gallbladder disease, consumption of fatty foods, alcoholic beverages, as well as taking certain medications. With pancreatitis, the discomfort can be very strong with nausea, fever, decreased blood pressure and rapid heartbeat. The most important thing is to undergo a comprehensive examination, since if your right side hurts after eating, the reason for this may even be hidden in food poisoning.
Liver pathologies
Many people are concerned about the question of why the right side hurts under the ribs and what diseases such a disorder may be associated with. Pain can occur with hepatitis. This disease is an inflammation of the liver with the formation of tissue necrosis. It can be triggered by a number of different reasons, in particular such as alcohol abuse, viruses, prolonged use of medications, as well as a violation of the outflow of bile.
In addition to the fact that with hepatitis it hurts in the right side after eating, there are also a number of other signs of the presence of the disease, in particular such as itching, jaundiced skin, nausea, dark urine and light-colored feces. The person has a fever and there are signs of intoxication in the body.
The chronic form of hepatitis is characterized by the absence of symptoms for a long time. However, during exacerbation, nagging pain is observed. In this case, the liver tissue is completely replaced with connective tissue. This ultimately leads to cirrhosis.
Pain in the right side can also occur with hepatosis. This is a chronic liver disease that develops due to alcohol abuse or poisoning with toxic substances. In this case, disorders of fat metabolism in liver cells are often promoted by diseases such as thyrotoxicosis and diabetes.
Among the main symptoms, one should also highlight digestive system disorder, headache, weakness, increased fatigue, soreness and enlargement of the liver, pain in the right side after eating.
Another liver disease that causes side pain is liver dysfunction. This disease is congenital and hereditary. It is characterized by an increased level of bilirubin in the blood. It is often asymptomatic or there are minor signs, such as yellow discoloration of the skin and sclera of the eyes. Often a person complains that after eating, the lower right side hurts, especially when consuming spicy or fatty foods. Treatment must be comprehensive so that the existing problem can be eliminated.
Prevention
Surely everyone knows that preventing any disease is much easier than treating it later. To prevent pain in the side after meals, you should follow simple rules:
- Don't overeat and stick to a healthy diet.
- Monitor and control weight gain.
- If you are prone to obesity, stick to a low-calorie diet.
- Drink enough mineral water – up to 2 liters per day.
- Do not give up moderate physical activity, do not forget about morning exercises.
- Stop drinking alcohol altogether.
- Control blood cholesterol levels.
By following these simple rules, there is a high probability that a person will never experience pain in the side after eating.
When pain appears in the right side after eating, a person needs to think about his health, especially if it recurs regularly. This pathological condition may indicate the presence of quite serious diseases.
In most cases, pain in the right side indicates a malfunction of the digestive tract.
Gallbladder diseases
If your right side hurts under the rib after eating, this may be a sign of cholecystitis. This is an acute or chronic disease that affects the gallbladder. It is characterized by the presence of acute cramping pain after eating food. In this case, painful manifestations radiate to the shoulder and shoulder blade area. In addition to such unpleasant sensations, a person is bothered by nausea, and an abnormal heart rate may also be observed. A painful attack can even cause loss of consciousness.
With chronic cholecystitis, the right side hurts after eating. However, the sensations are not as intense as during the acute form of the disease. Doctors recommend following a diet and taking medications to eliminate spasms.
When parasites and bacteria penetrate the bile ducts, tissue inflammation occurs - cholangitis. This disease is characterized by severe pain in the right side after eating and reminiscent of hepatic colic. In addition, the skin turns yellow and itches, the temperature rises, and palpation can reveal an enlarged liver.
If there is an excessive intake of cholesterol into the bile, stones can form due to changes in its qualitative composition or stagnation of bile. The main symptom is the appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth. Pain in the right side after eating food occurs a little later and mainly occurs when consuming alcoholic beverages. The attack lasts several minutes or hours.
If your right side hurts immediately after eating, this may indicate a functional disorder of the biliary system. This pathology is also characterized by the presence of bitterness in the mouth, decreased appetite, bad mood, and constant fatigue.
Self-diagnosis for stomach pain after a meal
Stomach pain can be of different nature and have different localization. Therefore, when visiting a doctor, the patient will have to try to describe his feelings as accurately as possible. Based on the medical history and description of symptoms, the doctor will make assumptions and develop examination tactics.
The nature of pain after eating
Severe and sharp pain in the stomach after eating
It can be caused by eating low-quality foods, food poisoning, infection, appendicitis, pancreatitis, open stomach ulcer, gastritis in the acute stage and many other reasons.
Burning pain
After eating spicy, sour or salty foods, such pain is typical for exacerbation of gastritis with high or normal acidity, pancreatitis.
Constant nagging pain
It can occur against the background of chronic gastritis and stomach ulcers, cancer of the stomach and adjacent parts of the gastrointestinal tract, overeating, eating food too quickly, as a reaction to certain foods. When a stomach ulcer worsens, the pain is constant and goes away after eating light food.
Psychosomatics of pain
Mental disorders can manifest themselves in the form of various disorders and painful sensations. Very often, when there is a mental disorder and stress after eating, the right side in the lower abdomen hurts. However, it is worth noting that discomfort in this case may occur even when inhaling.
These symptoms are also accompanied by fear of terminal illness or death. In addition, they may be accompanied by aversion to food and constant nausea. You may lose your appetite completely. In some cases, the pain is unclear and localized in different areas of the abdominal region.
A person with various mental disorders may not have any physical illnesses. Pain is a response to prolonged subconscious stress. Food consumption then becomes a real problem. In such people, immediately after eating food, pain in the abdomen begins and the urge to defecate arises. The only method of therapy in this case is psychotherapy, as well as correction of the patient’s behavior. When conducting a diagnostic study, generally the patient does not notice any pathologies in the organs and systems.
Main symptoms
Since pain in the right hypochondrium after eating often occurs in the presence of various diseases, this symptom will not be the only one in the clinical picture. If the cause of discomfort is physiological, then there will be no additional signs. In some cases, there is a strong increase in this unpleasant sensation. For example, aching pain in the side can become acute when:
- consumption of fatty foods;
- movement;
- excessive physical activity;
- coughing or sneezing;
- sudden change in body position;
- pressing on the problem area.
If pain after eating occurs due to the presence of diseases of the stomach or intestines, then among the main signs it is necessary to highlight the following:
- excessive gas formation;
- bloating;
- nausea;
- violation of the act of defecation;
- heartburn and burning in the chest area;
- weakness and malaise;
- belching air;
- heavy sweating;
- decreased performance;
- slight increase in temperature.
If pain appears on the right side under the ribs when coughing, this indicates the presence of problems with the heart or lungs. If liver disorders occur, severe pain in this area after eating is also additionally accompanied by such symptoms as:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- yellowness of the skin;
- nausea and vomiting;
- darkening of urine color;
- white coating on the tongue;
- depression.
It is worth noting that these are only external manifestations of pathology, so it is not always possible to determine the presence of the disease only by the existing signs. It must be taken into account that in children the disease progresses much faster than in adults. Therefore, if even minor pain occurs in a child, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Which doctor should I contact?
Why the right side hurts after eating can only be determined by a qualified doctor, since this is only one of the signs of the presence of disorders in the body. Very important organs are localized in this area and pathological changes in this area can lead to human death. Doctors say that you should not engage in self-diagnosis, since improper treatment can only significantly aggravate the problem. Severe pain in this area can result from:
- rupture of the gallbladder and ducts;
- renal paraphimosis;
- organ injuries;
- prolapse or rupture of the kidney.
All these pathologies require very urgent surgical intervention. Initially, you need to visit a therapist or pediatrician who will conduct an examination and diagnosis. In addition, consultation and examination by an endocrinologist, surgeon, neurologist, and cardiologist is required.
Nature of pain
Acute pain in the right side: sometimes surgical intervention is unavoidable.
The nature of pain in the right side can be varied.
If the patient experiences acute pain in the right side, this indicates the need for urgent surgical intervention.
Most often, this pathological condition is diagnosed with damage to internal organs, intestinal obstruction, intestinal perforation, thrombosis of the veins and arteries of internal organs.
The cause of pain can be pancreatitis, appendicitis. Acute pain can also be observed with the development of blockage of the bile ducts, hematomas, and intestinal obstruction.
A dull pain may also occur in the right side after eating, which is explained by chronic cholecystitis during remission, hepatitis and adrenal tumors. Pathology can appear with cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Some patients complain of dull pain due to apostematous nephritis, intestinal diverticulosis, and pyelonephritis. The cause of the pathological condition may be cholangitis or a tumor in the kidneys.
Some people confuse soreness with a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium. This pathological condition is observed in fatty hepatosis and hepatitis. The cause of its appearance may be an edematous liver or hypomotor dysnesia of the biliary tract. A feeling of heaviness can be a symptom of diseases such as chronic cholecystitis or congestive heart failure.
Meals are characterized by accelerated secretion and movement of bile. At the same time, there is an increase in blood supply to the liver, as well as stimulation of intestinal peristalsis.
That is why, if a patient has pathologies of organs such as the gallbladder, intestines or liver, then eating will lead to pain.
Stitching pain occurs with biliary dysnesia or cholelithiasis. With dull pain, cholecystitis is diagnosed in most cases.
Soreness in the right side can have different characters. They are used to determine the disease and make a preliminary diagnosis.
Carrying out diagnostics
If pain occurs in the right hypochondrium, even if it is periodic, you should definitely contact a pediatrician or therapist, who will then refer you to specialized specialists. Diagnostics must be comprehensive so that it is possible to correctly determine which disease provoked the disorder. Diagnostics includes:
- familiarization with the medical history to determine the provoking factor;
- collection and analysis of anamnesis;
- a thorough physical examination of the patient;
- abdominal percussion and palpation;
- assessment of skin condition;
- measurement of pressure, temperature;
- detailed survey of the patient.
A survey of the patient is required for the doctor to obtain the required information regarding the existing symptoms, which may indicate the cause of the pain. After an initial diagnosis aimed at determining the condition that provoked the onset of pain, studies such as:
- urine and blood analysis;
- study of feces;
- liver tests;
- serological tests and PCR;
- ultrasonography of the peritoneum;
- radiography;
- endoscopic examination;
- tomography.
Only after carefully studying the results of diagnostic measures, the doctor selects a treatment method.
Features of treatment
To get rid of pain under the ribs on the right side, you need to treat the underlying disease. The tactics of therapy are selected individually for each patient. Despite this, almost all patients are prescribed:
- physiotherapy;
- oral or intravenous administration of drugs;
- diet therapy;
- completing a therapeutic massage course;
- doing exercises;
- use of folk remedies and techniques.
It is worth noting that all therapy methods are selected only by the doctor on an individual basis. Drug therapy is aimed at treating the disease and alleviating symptoms. Vitamin therapy and diet correction are also required.
Surgical intervention is resorted to only in the most extreme cases. Surgery is required if the patient’s condition is serious or if therapeutic measures are unsuccessful. In any case, therapy should be strictly supervised by the attending physician.
Preventive measures and prognosis
To prevent pain in the right side under the ribs, there are no specific preventive measures. However, the likelihood of developing complex pathological conditions can be reduced by following a number of simple measures. The main preventive measures are:
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- healthy and balanced diet;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- taking only those medications prescribed by the doctor;
- avoiding any bruises, wounds, injuries;
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- early identification and rapid elimination of provoking pathological factors.
In addition, you must periodically undergo a full laboratory and instrumental examination in the hospital, which is accompanied by mandatory visits to all specialists.
The prognosis for the course of the pain syndrome is quite favorable, therefore, it usually responds to therapeutic methods without problems. However, it is worth remembering that treatment will not be complete without eliminating provoking factors, both diseases and physiological causes.
But it must be remembered that the lack of comprehensive treatment of the underlying disease can lead to various kinds of complications, which do not even exclude the possibility of death.