Bad breath due to a diseased liver
Clean breathing indicates the adjusted mechanism of the body. However, the cloying smell of raw meat almost always indicates a diseased liver. Confirmation is the presence of the following symptoms:
- skin rash on the body;
- itching;
- liver odor from the skin;
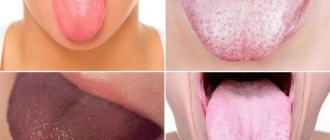
- icteric color of the skin, sclera of the eyes, tongue;
- pain in the right hypochondrium.
Excess toxins damage the liver.
Reactive changes in the body are accompanied by a sweet smell from the mouth due to the liver and are the cause of intoxication of the body with medications, organic compounds or food. The body may be covered with pale pink spots, which do not cause concern. A cloying, slightly rotten smell occurs with excess bilirubin. The skin and organs covered with mucous membranes change pigmentation, acquiring yellowish tints. A pungent, bitter odor can be caused by stagnation of bile or malfunction of the biliary tract. The tongue turns yellow-brown and there is a bitter taste in the mouth. Pain appears behind the right rib. When liver disease is in a severe stage, there is an unpleasant smell of rotten meat from the body and from the mouth, bright red or white pimples appear, which cause severe itching, including scratching and bruising.
What is halitosis
Halitosis is a condition characterized by a person having an unpleasant odor from the mouth that brushing or rinsing does not help. This is due to the fact that the reason is much deeper. To determine what caused the development of halitosis, you need to consult a doctor for timely detection or prevention of a serious illness.
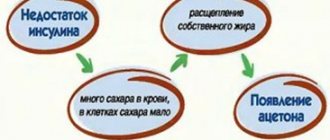
Children can also have bad breath. The initial diagnosis of childhood halitosis is carried out by a pediatrician, who will then, if necessary, refer the child to a specialist. One of the reasons for bad odor in childhood is the presence of acetone in the body. You can even check this at home: to determine glucose levels, there are test strips that are sold in pharmacies. This is a good method of early diagnosis, allowing you to quickly make a decision about which specialist to take your baby to. An adult can first contact a therapist or dentist.
Halitosis can be physiological or pathological, which is more dangerous. The first does not require special treatment - the stench can be avoided if you do not eat a number of certain foods, including garlic and onions. The second type of disease is associated with certain disorders, dysfunction of organs, and the presence of infection. Pathological halitosis can be recognized if, in addition to the unpleasant “aroma” from the mouth, a number of other symptoms are present.
Causes of unpleasant odor
The liver plays the role of a filter in the body and passes through itself all compounds and substances that come with food, water, and medications. Liver lesions that are characterized by an unpleasant odor are as follows:
- poisoning by alcohol, chemicals, poisons;
- reaction to taking medications;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis.
General intoxication of the body
The disease destroys the organ at the cellular level.
Toxins entering the body disintegrate, leading to the death of liver cells. The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. But in any form, the disease without proper treatment leads to serious consequences. The action of the allergic reaction affects the hepatoprotector, and the symptoms spread to different organs depending on the type of toxic substance. The main ones include:
- increase in liver size;
- nausea with vomiting;
- weakness;
- body temperature from 37 to 38 degrees;
- pain under the rib;
- photophobia;
- change in color of stool and urine.
In this case, the tongue acquires a bright red tint, bad breath appears, and nodular bruises on the legs are possible, which turn into trophic ulcers or weeping wounds. Their treatment is unproductive, since the released toxins act poisonously and support allergic manifestations in the active phase.
Drug allergies
Often, therapeutic agents cause an anti-effect, i.e., instead of therapeutic effects, toxicosis occurs. Antibiotics, anticonvulsants, antipyretics and analgesics should be taken with caution. For liver diseases, drugs of such groups are contraindicated or are taken according to a reduced dosage regimen, taking into account the type and degree of liver disease, as well as the inability of the diseased organ to perform its functions fully.
Hepatic hepatitis
Symptoms vary depending on the type of virus.
Acute or chronic liver disease of viral etiology is called hepatitis. The main routes of transmission: through blood transfusion, from mother to fetus, fecal-oral and sexual contact. Viral hepatitis is divided into 6 groups:
- A - resembles the flu and is accompanied by a high temperature with the presence of aches, headaches, and no bad breath. With this type, it is necessary to observe bed rest, adhere to a diet and carry out detoxification therapy.
- B - low-grade fever, joint pain, and rarely skin rashes. Recovery occurs in 80% of cases and often develops into a chronic form, which is fraught with the development of cirrhosis or oncology. If the process is chronic, there is practically no cure. A daily routine and diet are followed, which is supplemented with drugs that act to improve metabolism in liver cells.
- C - characterized by decreased appetite, weakness, nausea, vomiting, pain in the right rib. An increase in the size of the liver and spleen, an increase in bilirubin and liver tests by 8-10 times is recorded. The treatment uses interferon-alpha, which prevents infection of hepatocytes.
- D - occurs against the background of hepatitis B, with the same symptoms. Antiviral treatment in hospital.
- E - nausea, headache present. This type is treated symptomatically, since the body's immune system is able to destroy the virus on its own. The recovery period is achieved after 1-1.5 months.
- G - similar to hepatitis C, but less dangerous. The route of transmission is mainly through non-sterile needles. Diet and immunomodulatory therapy quickly relieve all painful manifestations.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Symptoms worsen after eating.
A disease characterized by the death of hepatoprotective cells of the body’s main “filter” with the replacement of its structure. In place of the voids, fibrous tissues and nodes form, reducing the functioning of the organ. The causes of cirrhosis can be: hepatitis, heredity, pathologies of the biliary tract, alcohol, poisoning, and disruptions in the immune system. Symptoms of the disease:
- bitterness in the mouth;
- rib pain;
- dystrophy;
- nausea and vomiting;
- amyotrophy;
- redness of the face and palms.
Diagnosis
The treatment of hepatic bad breath is carried out by a hepatologist. But not all clinics have such specialists, so you can contact a gastroenterologist. When visiting a medical facility, a specialist examines the medical history and asks questions to the patient. Then he prescribes the following procedures:
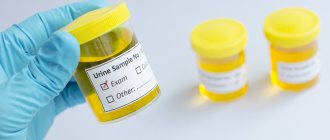
- biochemical analysis of blood and urine. With liver diseases, a change in characteristics occurs because the composition of the blood depends on the cleansing by the organ. If the functionality of the liver is impaired, this will be visible in the results of a blood test;
- examination of stool for the presence of incompletely digested food. An unpleasant odor may indicate a disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, and sometimes the liver;
- gastroscopy (if necessary). Fibragastroduodenoscopy is necessary for examining the gastrointestinal tract;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity.
Other symptoms
In the chronic course of the disease, reactive changes occur in the liver, followed by its destruction. There are 4 stages of the disease, which have the following symptoms:
The onset of the disease is accompanied by a feeling of muscle weakness and fatigue.
- With grade 1 disease, signs may be absent or insignificant.
- At stage 2 there is: decreased ability to work;
- weakness throughout the body;
- dyspepsia;
- yellowness of the integument, swelling;
- ascites;
- bleeding.
- metabolic imbalance;
- reduction in liver size;
Features of the pathology
Liver diseases can be judged when the following symptoms appear in a child or an adult:
- yellow color of the skin and mucous membranes;
- a garlicky odor emanates from the skin;
- the color of the tongue changes and a coating forms on it;
- rashes appear on the skin that bring discomfort to a person;
- veins dilate;
- dyspepsia;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- rapid fatigue in the absence of physical activity;
- pain in the right side of the abdomen.
Diagnostics
Hardware diagnostics will help diagnose pathology in a timely manner.
When initial symptoms of the disease appear, a medical examination by a hepatologist is necessary, who will prescribe a series of studies to determine the type and degree of liver failure. These include methods such as:
- Ultrasound of the peritoneum;
- liver tests;
- blood biochemistry.
Treatment
During the treatment process, it is necessary to achieve the appearance of feces without a sour odor and restore the consistency of feces. Therapy is prescribed only after diagnosis.
Smelly diarrhea is often the result of an infection. It is necessary to identify the causative agent of the disease. Elimination of foul-smelling stool is possible with the use of absorbent medications. These drugs bind toxic substances and carefully remove them from the body.
The drug Imodium is also prescribed. It improves gastrointestinal motility and digestive functions. As a result of the action of the medicine, food is easily and completely digested, and feces of the desired consistency are formed.
When treating foul-smelling diarrhea, it is necessary to normalize the microflora of all parts of the intestine. For this purpose, probiotics and prebiotics are taken. They eliminate pathogenic flora and saturate the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines with bacteria beneficial for digestion. Probiotics contain beneficial microorganisms that, when entering the gastrointestinal tract, actively populate its mucosa.
To combat dehydration, it is necessary to replace lost fluid and saturate the body with water. To achieve this, drink plenty of fluids frequently. Solutions of Regidron and Polysorb are also used. The medicinal powder is diluted with water and taken for diarrhea according to the instructions. You need to drink the product in small sips every 20 minutes.
Important! A small amount of incoming liquid will be better absorbed into the gastric mucosa and will not cause vomiting.
To restore the intestinal mucosa, the following are used:
- Smecta;
- Activated carbon;
- Enterosgel.
These drugs remove harmful toxins from the body and help restore intestinal microflora. In some cases, the doctor prescribes an intestinal antiseptic - Sumetrolim, Stopdiar, Enterofuril.
Timely contact with specialists
According to statistics, people who seek qualified medical help have diseases that are already in advanced stages. Therefore, if prevention, oral care and diet do not give the desired results, then you should definitely go to the doctor and the sooner the better - the early stages of illnesses are much easier to identify and cure.
The health of the internal organs, and, in particular, the main filter of the body - the liver, affects the appearance of a person, that is, the color and condition of the skin, hair, nails, tongue, as well as the smell emanating from the oral cavity. With changes, the body clearly “signals” about problems that have arisen, in some cases requiring immediate medical attention.
Often, attempts to combat allergic or purulent rashes, itching, unhealthy complexion, brittle nails, bitter taste and bad breath using various medical and cosmetic methods do not give the slightest result. The combination of such manifestations with other characteristic symptoms of liver disease requires paying close attention to the condition of the “main culprit”.
Diagnostic methods
What you should do first when one or more signs appear is, of course, consult a doctor. This problem is solved by both therapists, dentists, otolaryngologists, and gastroenterologists.
To find out the causes and make the correct diagnosis, the doctor must carefully study the medical history, collect an anamnesis to establish or exclude factors that allow the pathology to develop. The specialist examines the mouth, tongue, skin, palpates the abdomen, and measures the temperature.
Since bad breath often appears when the liver is damaged due to the presence of inflammatory processes in it, it is important to undergo all the necessary diagnostic procedures.
To confirm the diagnosis it is necessary:
Preventing breathing problems
To avoid unpleasant symptoms, you should carefully monitor your condition. Considering that the most common cause of bad breath is the growth of pyogenic bacteria, paying sufficient attention to oral hygiene and the prevention of gastrointestinal diseases solves most of the problems.
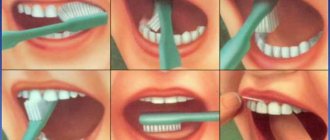
Important. When brushing your teeth, the gums, tongue and cheeks must be cleaned (especially if the smell has already developed). In addition to brushing, you need to use dental floss to clean the space between your teeth and mouthwash throughout the day. To quickly eliminate the aftertaste, you can use mints or chewing gum.
An important step in preventing pathology, in addition to hygiene, is visiting the dentist to eliminate minor violations and hygienic treatment of the oral cavity. identified inflammatory processes should be immediately treated.
Source: zhktok.ru
Why liver failure may develop
Fulminant (fulminant) liver damage can occur against the background of autoimmune and viral hepatitis, exposure to toxic substances, taking medications and some chronic diseases. The mortality rate reaches 80%, but this is a fairly rare occurrence. According to statistics, about 2,000 people worldwide die from fulminant liver failure per year.
Causes of acute forms of the disease:
- Poisoning with poisons (for example, phosphorus, arsenic, inedible mushrooms).
- Viral hepatitis (severe forms).
- Side effect when taking certain medications.
- The appearance of chronic liver failure is affected by diseases such as oncology, cirrhosis and others.
Stages of development of liver diseases
Symptoms may differ depending on the stage and severity of the process and the nature of the disease. The chronic form develops over several weeks or even months. Its main danger is the risk of coma, especially in the presence of additional provoking factors (infections, fatigue, gastrointestinal bleeding, alcohol intake, etc.). The acute form develops over several days, and in some cases hours.
Timely diagnosis and effective therapy will help reverse this process!
With this disease, there is a decrease in appetite, fatigue, nausea, aversion to tobacco, alcoholic drinks, food, and emotional disorders. If the cause of liver problems is poisoning, a crimson color of the tongue is observed.
In the chronic course of the disease, the skin of the face becomes jaundiced or sallow. The white of the eye can also turn yellow. Endocrine disorders, redness of the palms, the appearance of spider veins and pimples, swelling, and hemorrhages are observed. Multiple changes in biochemical parameters are observed in the blood serum.
The chronic course of the disease is divided into 3 stages: initial, severe and terminal (in the absence of necessary treatment it ends in coma).
At the initial stage of the disease, symptoms may be mild and do not cause alarm in the patient. Moreover, the characteristic smell of the oral cavity is the most obvious and widespread. Then dyspeptic disorders, weakness, jaundice of the sclera of the eyes and skin, swelling, etc. appear. The terminal stage is characterized by degenerative phenomena in the liver and other internal organs, deep, irreversible metabolic disorders.
The body, due to an excess of decay products, can malfunction the internal organs. A sweetish liver odor from the mouth is a signal of illness. Positive dynamics of the disease are observed when metabolism is normalized and the body is cleansed of toxic compounds.
Preventive measures
It is easier to prevent any disease than to have to deal with its consequences for a long time. Therefore, there are a number of preventive measures that will prevent the development of halitosis.
Changing your diet
Garlic, onions, and spices should be excluded first. Products containing carbohydrates cause fermentation in the intestines and, accordingly, an unpleasant odor. Therefore, it is better to avoid excessive consumption of flour, sweets, and carbonated drinks. Excessive gas formation can be caused by vegetables and fruits (cabbage, apples). To find out how diet affects bad breath, you can avoid eating certain types of foods for a while and see if the condition improves.
Additional measures
The treatment process can be lengthy, so during its course patients resort to auxiliary means:
- It is possible to temporarily reduce unpleasant symptoms with the help of rinses. In addition to store-bought drugs, you can resort to decoctions of chamomile, sage or eucalyptus.
- When brushing your teeth, do not forget about your tongue and gums, because the accumulated plaque on them does not add freshness.
- A small amount of mint helps mask unpleasant notes and stimulates the liver.
If an alarming symptom appears, you should not hope for its disappearance. Timely consultation with a doctor, compliance with recommendations and an integrated approach to the issue can help you defeat halitosis!
The air exhaled by the patient has a sweetish odor, slightly reminiscent of the smell of feces; it can be compared to the smell of a recently opened corpse or the smell of a mouse. It develops in severe hepatocellular disease, especially with pronounced collateral circulation. Liver odor (fetor hepaticus)
is predominantly of intestinal origin, since it weakens after defecation or after changes in the intestinal flora with broad-spectrum antibiotics. In patients with hepatic coma and hepatic odor, methyl mercaptan is detected in the urine. This substance is formed from methionine when normal demethylation is suppressed by a damaged liver and can be excreted in exhaled air.
In case of acute liver damage, a liver smell, especially spreading throughout the entire room, is an unfavorable sign; after its appearance, coma often develops. It very often occurs with pronounced portocollateral circulation and does not indicate such an unfavorable prognosis. If the cause of the coma is unclear, detecting a liver odor may aid diagnosis.
(495) 50-253-50 — information on diseases of the liver and biliary tract
| Liver function test |
| Liver biopsy |
| Hematological aspects of liver diseases |
| Ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging |
| Hepatocellular failure |
| Ascites |
| Portal vein system and portal hypertension |
| Hepatic arteries and veins. Liver with circulatory failure. |
| Jaundice |
| Cholestasis |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis |
| Sclerosing cholangitis |
| Viral hepatitis |
| Chronic hepatitis |
| Medicines and liver |
| Cirrhosis of the liver |
| Alcohol and the liver |
| Conditions associated with excess iron accumulation |
| Wilson's disease |
| Liver diseases caused by nutritional and metabolic disorders |
| Liver in children |
| Liver during pregnancy |
| Liver in systemic diseases. Liver injuries. |
| Liver damage due to infectious diseases |
| Liver tumors |
| Methods of visualization of the biliary tract: X-ray and endoscopic surgery |
| Cysts and congenital anomalies of the biliary tract |
| Gallstone disease and cholecystitis |
| Benign bile duct strictures |
| Diseases of the ampulla of Vater and pancreas |
| Tumors of the gallbladder and bile ducts |
| Liver transplantation |
| Hepatology in Germany |
| Liver treatment in Germany |
| Hepatology in Israel |
| Liver treatment in Israel |
| SIRT therapy in Israel |