Main reasons for changes
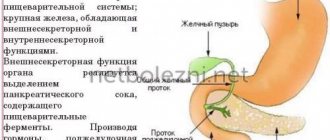
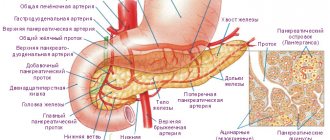
The main parts of the organ include:
- Head.
- Tail.
- Corpuscle.
The pathological process can cover both the entire organ and its individual zones. The most dangerous is considered to be an enlargement of the pancreas zones. If the size of the organ is much larger than normal, this indicates progressive pancreatitis.
Sometimes an ultrasound examination shows an increase in the size of only the head or tail. If the patient has never complained of symptoms characteristic of inflammation of the gland, then after an ultrasound he needs to be examined for oncology.
How is pathology detected?
Read about how to check your pancreas here.
Before prescribing any therapy, a correct diagnosis should be made that led to the formation of pathological processes. Ultrasound echo signs are the initial stage of examining the patient.
In such cases, specialists do additional examinations and tests:
- X-ray of the abdominal organs;
- Blood tests: clinical and biochemical;
- Analysis of urine;
- If necessary, CT scan and biopsy.
Symptoms and factors voiced by patients are of great importance. It happens that an ultrasound reveals hepatomegaly of the pancreas, but the patient has no complaints or characteristic signs of the organ’s functioning and the tests are within normal limits. Therapy in such a situation is not approved; they are only advised to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
https://youtu.be/JXPuL_Bhnjo
Enlargement of parts of the pancreas
The size of the head of the pancreas may be increased due to the presence of:
- stone;
- scar of the lesser duodenum;
- duodenitis;
- neoplasms on the minor duodenal papilla;
- metastatic tumor;
- cystic adenoma;
- own cancer;
- abscess;
- pseudocysts.
For the same reasons, the size of the tail increases. Another factor in changing its parameters is a calculus in the Wirsung duct of the organ body zone.
What causes the disease
The most common causes of this disease, which account for up to 80% of all cases of inflammation of the pancreas:
- Alcohol abuse. Alcoholic pancreatitis is primary and is more common in men. Alcoholic pancreatitis is more characterized by an acute course.
- Cholelithiasis. This is secondary pancreatitis (i.e., the root cause lies in another organ, in this case, the gallbladder), it is also called reactive. This type is more common in women. In most cases, such pancreatitis is chronic.
Pancreatitis can be primary or secondary, when the original problem lies in a nearby organ (for example, the gallbladder).
Other, less common reasons are:
- disease of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- long-term use of medications such as steroids, azathioprine, furosemide, valproic acid, enalapril, carbamazepine and others;
- metabolic causes: hypercalcemia (increased calcium concentration in the blood), increased triglycerides type 1 and 5 in the blood;
- ingestion of toxins into the body (organophosphates, scorpion venom after its bite);
- infectious diseases: Coxsackie viruses, Epstein-Barr viruses, cytomegalovirus, viral hepatitis, mycoplasma and other pathogens;
- injuries, including those received during operations;
- neoplastic processes, that is, the occurrence of tumors;
- hereditary predisposition;
- autoimmune processes.
It is worth noting that depending on the form of the disease, the mechanism of its development will have its own characteristics, which is why the symptoms will be different in each case.
Change in liver size
Next to the pancreas is the liver. Both organs are connected by ducts. Enlargement of the liver and pancreas is due to improper metabolism. Sometimes the cause is the presence of vascular or infectious pathologies.
When the inflammatory process in the acute form of pancreatitis is very severe, the liver, which performs a compensatory function in neutralizing excess toxic substances, also begins to enlarge.
This symptom signals the depletion of an organ that cannot cope with its job. In the absence of timely treatment, pathological changes are observed in the liver parenchyma and affect its circulatory system. This contributes to the deterioration of human health.
The cause of diffuse changes in the liver is associated with prolonged use of antibiotic drugs. This symptom is also justified by smoking and alcohol abuse. Organ tissue changes due to viruses, cirrhosis, sudden weight gain, and autoimmune hepatitis.
Sometimes a doctor diagnoses hepatomegaly. The cause of this pathology is considered to be poisoning by toxins. It is characterized by complete damage to all tissues of the organ. During the examination, the liver can be easily felt under the ribs.
In children, organ enlargement is often explained by the progression of jaundice.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, with a moderate degree of diffuse changes, there are no signs of hepatomegaly and diffuse changes in the pancreas. Often they can only be detected by ultrasound.
If hepatomegaly is severe, the patient experiences the following manifestations:
- Feeling of heaviness in the side.
- Pain on palpation.
- Nausea, worse after eating.
- Frequent heartburn.
- Yellow tint to the skin.
- Decreased appetite.
- Skin rashes.
- Decreased performance, lethargy, fatigue.
Acute pancreatitis manifests itself more clearly , the patient experiences severe pain in the left side, constant nausea, vomiting, decreased blood pressure, and tachycardia. In case of cirrhosis, hepatitis, other symptoms are added to the existing ones:
- Bitter taste in the mouth.
- Change in color of urine and feces.
- Yellowness of the sclera, mucous membranes, skin.
- Increased abdominal volume.
Another article on this topic: How do problems with the pancreas manifest themselves?
Features of treatment
Therapeutic tactics depend on what kind of disease the doctor diagnosed. If the pancreas and liver are enlarged due to an abscess or acute pancreatitis, the person is immediately hospitalized. After this, the patient is prescribed surgical or conservative treatment.
When the cause of the enlarged gland is a pseudocyst, the patient is examined by a surgeon. He makes a decision regarding removal of the pathological area. The tumor process is cured by an oncologist. Chronic pancreatitis is treated by a gastroenterologist. When diabetes is diagnosed, the patient is registered with an endocrinologist.
When treating the liver, if the root cause is a viral pathology, antiviral medications are used. To restore organ cells, the patient is prescribed hypoprotectors. Folk remedies can be used as additional therapy under the supervision of a specialist.
Hepatomegaly
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LIB {amp}gt;{amp}lt;iframe{amp}gt;{amp}lt;p{amp}gt; {amp}lt;p{amp}gt;{amp}lt;span class=
Liver diseases are characterized by an increase in its size, when even without palpation the outlines of the organ become noticeable upon examination. One of these diseases is hepatitis. It occurs when infected with hapatitis viruses (there are currently 7 different types), as well as during prolonged exposure to alcohol, drugs, and even infection with parasites.
At first, hepatitis does not show any symptoms, but as the disease progresses more severely, a clinical picture begins that is similar to simple flu. Subsequently, the tissues are destroyed, become inflamed and become completely dysfunctional. If the disease is recognized in time and treatment is started, it is possible to achieve a complete recovery without serious consequences.
Another disease in which the liver significantly increases in size is cirrhosis. It occurs due to poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and long-term viral infections. The increase is due to the fact that healthy tissue is gradually replaced by fibrous tissue.
Diet as a method of treatment
The patient undertakes to follow diet No. 5 prescribed by the doctor. Its main goal is to restore the functioning of both organs. The diet has a gentle effect on the digestive system. It limits fats and provides a certain amount of carbohydrates and proteins. To normalize the functioning of the liver, glands, and stomach, you need to eat only warm food.
Medical nutrition includes:
- lean vegetable soups;
- lean turkey, rabbit or pork;
- low-fat milk;
- boiled eggs;
- mashed boiled vegetables;
- jelly from non-acidic berries;
- stale bread;
- Bee Honey;
- apple jam.
You can eat non-acidic fruits. It is better to drink tea and coffee with milk. Gastroenterologists advise replacing these drinks with rosehip decoction.
What products need to be excluded?
When diagnosing diffuse changes in the liver, it is recommended to exclude from the diet:
- sausage;
- sorrel;
- store-bought confectionery;
- chocolate;
- spicy foods;
- fatty milk;
- okroshka;
- smoked meats, canned products;
- fresh bread;
- rich sweet pastries;
- scrambled eggs;
- fat meat;
- offal;
- fatty broths.
It is not advisable to drink whole milk. It is recommended to avoid cheeses, sour cream, mayonnaise, and margarine. You should temporarily refrain from sorrel and radishes.
Major liver diseases: classification and symptoms
The liver destroys and filters toxic substances that enter the body; without this organ, life is impossible. There are no nerve endings in it, which means that a person does not experience pain when liver diseases develop. This leads to the disease being diagnosed at a later stage.
The liver and its role in the human body
A characteristic symptom of liver damage is the development of yellowness of the skin, sclera of the eyes and mucous membranes. At the same time, the level of bilirubin in the blood increases. The patient's general condition worsens, and the organ itself increases significantly in size (this can be detected even by palpation).
The most common liver diseases include hepatitis (viral, chronic, etc.) and hepatosis, cirrhosis, benign or malignant neoplasms, parasite damage, and stenosis.
Important! In almost all diseases, the patient experiences discomfort or pain on the right under the ribs (sometimes it can be very strong and cramping). Body temperature rises to 38-39 degrees, profuse vomiting, digestive disorders (uncontrolled diarrhea), and severe sweating are observed.
Types of hepatitis
Hepatitis is divided into acute (usually develops from poisoning, but can be a complication of viral diseases), chronic (typical for people who abuse alcohol and drugs). There are also viral, secondary, bacterial, and toxic varieties of the disease.
Development of the disease that begins with hepatitis B
Table. Symptoms of several types of hepatitis.
| Name of the disease | Symptoms |
| Hepatitis C | This type is characterized by a long asymptomatic period, while liver cells are actively degenerating, which leads to the development of organ pathologies. |
| Hepatitis A and E | The patient experiences weakness, body temperature rises, severe headache, and the liver increases in size. As the disease progresses, jaundice develops, urine darkens, and stool becomes lighter. |
| Hepatitis B (chronic form) | The patient feels depressed and experiences aching pain under the ribs on the right. The sclera and skin turn slightly yellow, and bleeding may come from the nose. The liver and spleen increase in size. |
Cirrhosis of the liver
With a disease such as cirrhosis, liver cells are destroyed. Over time, they are replaced by fibrous tissue, but this leads to a gradual decrease in the functions of the affected organ. Metabolism is disrupted, toxins accumulate in the body, and as a result the person dies.
Course of alcoholic liver disease
This life-threatening disease occurs without any symptoms in almost half of the cases (up to 40%).
Early symptoms include the appearance of aching pain in the right side, which intensifies after consuming fatty foods and alcohol-containing drinks. The mucous membrane in the mouth dries out in the morning, and a feeling of bitterness appears. The patient complains of bloating and upset bowel movements, loses weight, gets tired quickly, and is more nervous.
Complications of liver cirrhosis
There are four stages of cirrhosis:
- During the first stage, the patient does not feel unwell, but may notice periodic aching pain in the right side. A blood test shows a slight increase in bilirubin.
Structural formula of bilirubin
Spatial image of serum albumin
Pain in right side
On a note! With cirrhosis, patients also experience other symptoms, for example: itching of the skin, the appearance of spots on the eyelids, thickening of the fingers, swollen joints, the appearance of spider veins on the chest and back, swelling of the tongue, and nosebleeds.
Hepatosis: what kind of disease is it?
The disease hepatosis develops against the background of severe poisoning. It can occur in chronic or acute form. In the first case, aching pain is observed in the right side, the liver increases in size, and the patient feels depressed.
In the acute form, jaundice rapidly develops, and the body suffers from intoxication. The diseased organ may increase slightly, but later the size returns to normal. With cholestatic hepatosis, skin itching appears, urine darkens, feces become gray, and body temperature may rise.
Neoplasms in the liver
Tumors or neoplasms are divided into benign and malignant. The first include liver adenoma, which is formed from hepatocytes. It may present with pain in the right side and anemia.
Neoplasm in the liver
Also classified as benign neoplasms is hemangioma, which is formed from the vascular elements of the liver. This tumor rarely causes symptoms.
Malignant neoplasms include angiosarcoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatoblastoma (develops in children) and cholangiocarcinoma. The appearance of such tumors is accompanied by pain in the right side, nausea and vomiting, enlarged liver, and deterioration of the patient’s general condition.
Liver damage by parasites
Parasites can live and multiply in the liver.
Table. Liver parasites.
| Parasite name | Effects on the liver |
Common symptoms of infection with liver parasites include the appearance of acne on the skin, peeling of the nail plate, the formation of papillomas and pigment spots, hair loss, roughening and cracking of the skin on the heels. The patient loses weight, sleeps poorly, and becomes nervous.
Video - Symptoms of liver disease
Dietary recommendations for a child
Having answered the question why the child’s liver and pancreas are enlarged, the doctor also prescribes diet No. 5. Fat components are replaced with protein components that improve the condition of both organs.
The following products contain substances harmful to the pancreas and liver:
- meat broths;
- cream;
- sour cream;
- fruits and vegetables that have not undergone heat treatment;
- ice cream;
- chocolate;
- jam;
- fruit juices.
During treatment of a child, it is recommended to boil, bake or steam food. Children can be given black tea. The amount of sugar should be small. It is better to cook porridge in water. You can add some apples or dried fruits there. Vegetable stew is steamed, fruits are baked. Children can be given biscuits or crackers. The bread should be slightly dry.
When neoplastic processes occur, the use of diet as the main method of treatment is excluded. Pancreatic tumors can only be eliminated surgically. It is advisable to adhere to a diet after surgery, when the organ needs a reduced load.
Prevention and prognosis
It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, sleep at least 7 hours a day, follow a proper diet, and give up bad habits. If after treatment the patient changes his lifestyle, the prognosis is often favorable.
In case of further consumption of alcohol and poor diet, uncontrolled use of medications without a doctor’s prescription, the condition of the liver and pancreas can greatly worsen. The prognosis of another complication can be fatal for a person.
The patient is recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations and lead a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary to spend more time in the fresh air. Sports activity must be agreed upon with a specialist. Excessive exercise can be harmful. The diet should be complete and healthy. The patient must adhere to a diet throughout his life. It is very important to scrupulously follow all medical recommendations and stop drinking alcohol.
In many cases the prognosis is favorable.
Enlarged pancreas: causes, symptoms and treatment
Causes of enlarged pancreas
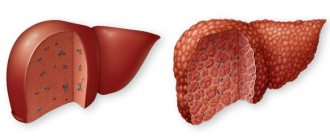
It is important to understand: an enlarged gland is not a diagnosis or a specific disease.
Healthy and enlarged gland
This problem may be a congenital feature; it can be caused by internal infection, inflammation or dysfunction of the endocrine gland itself. When for some reason she does not cope with the work, she noticeably swells up in attempts to compensate for this.
An enlarged pancreas can manifest itself in different ways. It can be total (the gland expands evenly) or diffuse (one part swells). The causes of pancreatic enlargement can vary significantly depending on the type of pathology.
Reasons for the total increase
Acute inflammation of the pancreas
This phenomenon usually occurs with acute pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) or exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis. When the gland is diseased, neighboring organs often suffer: the liver, spleen, etc. The following can provoke a total enlargement of the organ:
Causes of local enlargement of the pancreas
Causes of enlargement of the tail of the pancreas
Tumor in the tail of the gland
- pseudocyst in acute pancreatitis;
- abscess (accumulation of pus in the capsule);
- cystic adenoma (benign tumor);
- large malignant tumors;
- stone in the main duct of the gland.
- pseudocyst (small cavity with fluid formed by the tissues of the head);
- abscess;
- adenoma or cancerous tumor;
- duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenal mucosa) with damage to the intestinal papilla;
- tumor or scar of the duodenal papilla;
- stone in the duct.