Menstrual pain is normal for most women. The first day is usually especially difficult. Women who are accustomed to this condition do not even wonder why their stomach hurts on the first day of their period. But you should know that severe pain may not be the norm, but a symptom of a pathological process. Let's consider possible causes and ways to alleviate acute conditions during menstruation.
Abdominal pain during menstruation is very common
Main reasons
Pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation is not necessarily caused by a disease.
They are considered a physiological norm. Such pain is temporary, but can greatly reduce the quality of life during critical days. It is important to differentiate pain syndrome as a manifestation of a natural process and a disease. Pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation can be a symptom of pathology.
If the pain is severe and is accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms, there may be a pathology of the reproductive organs:
- Inflammation of the appendages. Causes dull pain during chronic adnexitis, cutting pain during exacerbation. Outside of menstruation, inflammation of the appendages is manifested by constant tension in the lower abdomen, yellowish discharge from the vagina.
- Myoma or cyst. Formations in the reproductive organs often provoke pain during menstruation. Particularly severe pain can occur with polycystic ovary syndrome. The severity of pain is influenced by the location and size of the tumor. Irradiation also depends on the last factor - the pain will radiate to the right or left side.
- Formation of adhesions. The pain occurs in waves and radiates to the anus and lower back. This disease causes menstrual irregularities, weakness and fatigue.
- Endometriosis. In the chronic course, the painful sensations are nagging and of moderate intensity. During an exacerbation, the stomach stings or cuts. Outside of menstruation, the disease can manifest itself as a cycle disorder, the appearance of bloody smears after sexual intercourse or physical activity. And during menstruation, dark red or brown clots are noticeable in the discharge.
Painful sensations during menstruation are not necessarily associated with pathologies of the reproductive organs. Cystitis causes severe discomfort. Unpleasant feelings are accompanied by a frequent urge to urinate and pain in the ureter.
Excessive activity of the thyroid gland leads to pain during menstruation. Hyperthyroidism is characterized by profuse and prolonged discharge.
Also, pain in the lower abdomen, including during menstruation, occurs due to:
- with problems of the gastrointestinal tract;
- with exacerbation of appendicitis;
- with polypous growths.
Most gastrointestinal diseases are characterized by nagging pain accompanied by nausea, cramps, and stool disturbances. When the appendix is inflamed, the right side hurts, the lower abdomen is tense, and radiates to the lower back and pubic area. Symptoms are accompanied by an upset stomach and a rise in temperature. If peritonitis is close, it becomes impossible to endure the pain, the woman may lose consciousness. Urgent surgical intervention is required.
Paroxysmal stabbing pain in the lower abdomen on the right in diseases of the upper urinary tract
Drawing, aching or stabbing pain in the lower abdomen on the right is characteristic of lesions in the final section of the small intestine (ileum) and the initial sections of the large intestine (cecum and ascending colon).
Diverticula are sac-like formations of the intestinal wall that communicate with its lumen. Due to their structural features, intestinal contents often stagnate in diverticula, which contributes to the development of inflammation.
Repeated stabbing pain in the lower abdomen on the right occurs with inflammation of the diverticula of the final section of the small intestine (Meckel's diverticulum), as well as with diverticulitis of the cecum and ascending colon. Diverticula in these sections, as a rule, are single, and the clinical picture of their inflammation largely coincides with the clinical picture of acute appendicitis.
A characteristic feature of diverticulitis is a chronically relapsing course. Exacerbations often begin with constipation, which is followed by diarrhea.
If acute or chronic diverticulitis is suspected, careful examination and conservative treatment are indicated.
If left untreated, diverticulitis can lead to serious complications, such as suppuration and perforation with the development of peritonitis, and the formation of fistulas.
Therefore, if an attack of severe pain in the lower abdomen on the right is accompanied by symptoms of local peritonitis, such as muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall, pain on percussion (tapping), a positive Shchetkin-Blumberg sign (increased pain when removing the hand after light pressure), emergency hospitalization is recommended to resolve the issue of surgical treatment.
Chronic inflammatory bowel disease - Crohn's disease - is detected in 20% of cases during surgery for acute appendicitis. The reason for frequent errors in diagnosis is the similarity of the clinical picture of these diseases.
The fact is that the inflammatory process in Crohn's disease is most often localized in the terminal ileum, and is manifested by sharp pain in the lower abdomen on the right, similar in nature to the pain syndrome in appendicitis.
Taking a medical history can help in diagnosis. As a rule, the first sign of Crohn's disease is diarrhea with a tendency to become chronic. So an attack of severe pain in the lower abdomen on the right in this case is preceded by a fairly long (from several weeks to several months, and even years) period of unstable stool with a tendency to diarrhea.
In addition, Crohn's disease is not characterized by such signs of appendicitis as vomiting and migration of pain from the central areas of the abdomen to the right iliac region.
Without adequate treatment, Crohn's disease leads to serious complications, including perforation of the intestine, so symptoms of peritonitis are an indication for emergency surgical treatment of this pathology.
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen on the right can occur with both benign and malignant tumors of the final part of the small intestine and the initial parts of the large intestine.
The mechanism of pain is most often associated with the pressure of a growing tumor on surrounding tissues. The intestinal mesentery, rich in nerve endings, is especially sensitive to such pressure.
With predominantly endophytic growth (growth into the intestinal lumen), pain occurs with the development of inflammation, destruction of the tumor, or its growth through the intestinal wall into the surrounding tissue (observed in the late stages of malignant growth).
In addition to pain, tumors on the right side of the intestine are prone to bleeding, and over time lead to the development of chronic anemia.
Malignant growth is often accompanied by symptoms of cancer intoxication (exhaustion, increasing weakness, disturbances in mood, sleep and appetite).
If you suspect an intestinal tumor, a thorough examination in a hospital is necessary. Both malignant and benign tumors are subject to surgical removal.
Paroxysmal stabbing pain in the lower abdomen on the right is often found in diseases of the upper urinary tract. They are especially characteristic of the so-called renal colic, which most often accompanies urolithiasis.
Even experienced surgeons often have difficulty differentiating between renal colic and appendicitis.
The fact is that in some cases the pain with appendicitis is paroxysmal in nature, and with renal colic it often radiates along the ureters to the right iliac region.
Irradiation of pain to the groin can help in diagnosing diseases of the urinary system. Another characteristic feature of the pain syndrome in renal colic is the constant anxiety of the patient, who cannot find a gentle position in which the pain would be felt the least.
It seems that changing the position of the body brings some relief to a patient with renal colic, while in the case of acute appendicitis the patient tries to lie motionless on the painful side, since unnecessary movements bring additional suffering.
In addition, the pain syndrome in renal colic is accompanied by various urination disorders (increased frequency and/or painful urination, sometimes visible blood in the urine).
And finally, an attack of renal colic is treated with antispasmodics and analgesics, which are practically useless in the case of acute appendicitis.
Suspicion of renal colic is an indication for hospitalization in a urological hospital for additional examination, the results of which will determine the medical tactics. In most cases, conservative treatment is indicated.
https://youtu.be/b5f9iRHdPgk
What to do if the pain does not go away
If the pain is not expressed, you can take an antispasmodic. But severe pain requires medical attention. Before the patient can get to the doctor or the ambulance arrives, you can take some measures that will slightly make you feel better. For example, to reduce pain, apply an ice bottle wrapped several times with a thin cloth to your lower abdomen.
Warming procedures can worsen the condition if the cause of pain is inflammation. It's better to fill the heating pad with ice.
The fetal position helps you endure the pain. During attacks, you should take it and lie down, turning off the lights and TV, that is, removing all irritants to the maximum. Warming procedures are contraindicated in this case. After all, if the pain is caused by inflammation, heat will contribute to its development and worsening of the condition.
Even if there is no inflammatory process, bleeding may increase due to warming procedures.
Pain of unknown etiology requires a visit to the doctor. Until the reasons are found out, it is better not to self-medicate, so as not to make it worse. Strenuous physical activity should also be avoided. Unbearable pain combined with rising temperature, weakness and confusion is a reason to immediately call an ambulance.
What is strictly forbidden to do if you have abdominal pain?
If sudden pain occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor for help. Under no circumstances should you take the following actions:
- take any antispasmodic or painkillers orally without knowing the cause of the pain. This will blur the clinical picture of the disease;
- apply a warm heating pad to the abdomen, which can increase pain and aggravate the patient’s condition. To relieve suffering, a heating pad with ice is recommended;
- eat or drink any liquids;
- do an enema or take laxatives.
If you follow simple rules, you can alleviate the patient’s condition or even save his life
Remember! The body, through pain, makes it clear that it has some problems. The sooner the cause of the disease and the pathology itself are diagnosed, the sooner treatment will begin and serious complications will be avoided.
Diagnostic measures
To determine exactly why the unpleasant sensations occurred, laboratory and hardware diagnostics will be required. It will be necessary to take blood and urine tests, check hormone levels and find out if there are any sexually transmitted infections.
Medicines to reduce pain should be prescribed by a doctor after diagnosis.
Ultrasound can detect changes in the shape and size of the uterine body, endometrial hyperplasia, cystic lesions or fibroids.
Additionally, the gynecologist may prescribe:
- hysteroscopy;
- colposcopy and biopsy;
- hysterosalpingography with the introduction of a contrast agent;
In difficult cases, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, as well as laparoscopy, are prescribed. Sometimes laparoscopy allows for gentle surgical treatment.
If the problem does not lie in the field of gynecology, the doctor will give a referral to another specialist - an endocrinologist, urologist, gastroenterologist.
Drug and surgical treatment
The doctor draws up a treatment route depending on the diagnosis. He can prescribe antispasmodic drugs, if the sensations are unbearable - in the form of injections. In this case, pain relief occurs almost immediately. But this is not enough. It is necessary to treat the primary disease that caused the discomfort.
For endometriosis or polycystic disease, the gynecologist will prescribe hormonal medications. If an inflammatory process is detected, medications are selected depending on the infectious agent that caused it. These can be antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal agents. The doctor may also prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications and douching.
Physiotherapy speeds up the treatment of gynecological diseases.
For most diseases, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed:
- For inflammation of the appendages, electrophoresis with drugs, magnetic therapy, phonophoresis, hydrotherapy, mud and light therapy are used.
- For polycystic disease, galvanophoresis with drugs, mud and paraffin therapy, and magnetic therapy are indicated.
- For endometriosis, exposure to pulsed currents, laser and magnetic therapy, and balneotherapy are useful.
Among folk recipes for gynecological ailments, infusions based on boron uterus give good results.
The growth of the endometrium and the occurrence of neoplasms may require hardware manipulations, for example, the destruction of pathological foci with laser beams, radio and microwaves, liquid nitrogen, as well as cauterization with electric current.
For cystitis, antibiotics are prescribed. You will also need a diet that excludes foods that can irritate the walls of the bladder. These are spicy and fatty foods, fast food, caffeine-containing and alcoholic drinks. For intestinal problems, a diet is also necessary. And first of all, you should avoid foods that cause gas: legumes, cabbage, yeast products, radishes, whole milk. However, they should not be eaten at all during menstruation, even for healthy women.
Gases accumulating in the stomach put pressure on the reproductive organs, which are already weakened during this period.
The need for immediate surgical intervention arises with exacerbation of appendicitis, detection of large formations that continue to grow, or severe growth of the endometrium. If the pathological changes are serious, it may be necessary to remove the diseased organ - the ovary or uterus.
Preventive measures
To reduce your risk of painful periods:
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Avoid cigarettes as nicotine causes vascular spasms.
- Avoid heavy lifting, especially before or during your period.
- Make the right diet, rich in vitamins and healthy minerals.
- Avoid hypothermia, so as not to provoke or intensify the inflammatory process.
Gentle physical activity is beneficial. When the reproductive system is weakened, yoga and other eastern practices are recommended that train the pelvic floor muscles and at the same time relax the nervous system.
Regularly undergo preventive gynecological examinations. This will allow you to identify a disease of the genital organs at an early stage, quickly cure it and get rid of the painful sensations caused by the pathology.
Some women experience the period of menstruation with great difficulties - due to pain and decreased performance. Debilitating discomfort indicates a health condition and requires the attention of specialists. Only on the basis of answers from laboratory and hardware diagnostic methods do they find out why the lower abdomen hurts during menstruation, and how to eliminate the symptom. It is possible that the detected underlying pathology will not be related to the field of gynecology. But even in this case, the therapeutic course should be completed completely without interruption.
Why pain occurs and what to do
With varying degrees of intensity, pain in the lower abdomen accompanies the period immediately before menstruation and all days of physiological bleeding. Only 5 out of 100 women do not experience discomfort before and during menstruation. The range of potential causes of discomfort varies. This includes inflammation, tumor process, tissue destruction. Measures that can potentially make you feel better these days can only be recommended by a gynecologist. A doctor of this profile focuses on the main cause of deterioration in health. If for some women it is enough to take an analgesic tablet and relieve spasms, then for others it is necessary to undergo the full course of treatment.
Types of pain syndromes
The following types of pain syndromes exist:
- Acute pain is pronounced and usually occurs with appendicitis or ulcerative colitis.
- Aching and dull pain appears with sluggish chronic inflammation, which can occur in any part of the intestine.
- Pain of a cramping nature appears as a result of spasms of the mucous walls of the intestines or can occur completely reflexively under the influence of harmful toxins.
- Also, pain in the left side can be caused by such serious gastrointestinal diseases as: colon cancer, diverticulosis, intestinal obstruction. In this case, urgent medical intervention, including surgery, is required.
Since pain can be very different, it is impossible to identify the cause of its occurrence without examination.
Lower abdominal pain is painful sensations of varying intensity in the abdomen below the navel. Pain can be a symptom of inflammation of the genitourinary organs, poisoning, appendicitis, strangulated hernia, injury, pregnancy and some other conditions and diseases. Pain in the lower abdomen occurs more often in women than in men.
Causes of menstrual pain
It should immediately be noted that the localization of the underlying disease that causes painful periods is not always associated with the pelvic organs. The main causes of discomfort during menstruation:
- Diseases of the digestive system (inflammatory, destructive) – colitis, enteritis, peptic ulcer
- Problems in the musculoskeletal system (osteochondrosis)
- Infectious and inflammatory lesions of the urogenital tract (urethritis, cystitis, endometritis, chlamydia)
- Anatomical features of the uterus (bicornuate, saddle-shaped, with a bend)
- Endocrine disorders (increased estrogen concentration in the blood)
- Formation of neoplasms of benign or malignant origin (fibroids, cysts, carcinoma)
Predisposing factors are irregular sex life, previous abortions, and a history of problematic childbirth. Even a disorder in the blood clotting ability leads to additional pain during menstruation. If blood clots form from the secreted masses, it is more difficult for the uterus to move them into the vagina. Increased contractility of the reproductive organ is characterized by spasms. This is what a woman feels during her period and experiences severe pain, which is accompanied by dizziness, weakness, and irritability.
Should I take pills?
If you have dysmenorrhea (painful periods), you can and should take pills to relieve discomfort in the lower abdomen and back. If the pain is severe, you should not endure it, since the level of pressure and performance decrease; general health worsens, dizziness. Antispasmodics are allowed to be taken before visiting a doctor. A woman needs to administer 1 ampoule (2 ml) of No-shpa intramuscularly. When the discomfort is relieved, you can take the same medication, but in the form of tablets (no more than 3 tons per day). Papaverine has antispasmodic activity (it should be administered intramuscularly).
The analgesic effect will be provided by Spazmalgon, Ketanov, Dexalgin. The listed medications belong to the group of analgesics. They relieve pain faster after intramuscular injection. In all cases, the prescription of a medicine should come from a doctor; an intradermal test should first be carried out to determine the body’s sensitivity to the drug.
Pain on the right or left when pressing
2016-06-04 00:13:38
Good afternoon. Half a year ago I had an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. There were no pathologies on the ultrasound. Only torsion of the gallbladder and gall bladder. But I didn't have any complaints. 3 months later I woke up with pain in my left hypochondrium.
The pain was not severe and I fell asleep further. But during the day the pain also continued. Worsened by breathing and sneezing. A day later, the pain in the left hypochondrium passed and moved to the right hypochondrium as well as to the area of appendicitis.
I contacted the surgeon. He said you can dance on my stomach. Which seemed strange to me because there was pain. The gastroenterologist looked at the old ultrasound and said that it was a gastrointestinal tract. But why was there no pain before even though there was already a diagnosis??
She also felt my stomach and said that I had colitis. By the way, on an ultrasound from a gynecologist, they wrote to me that I had fluid in the retrouterine space. I took choleretic drugs. The pain in the hypochondrium went away, but in the lower abdomen when pressed, the pain remained.
Two and a half months have passed already. It didn't bother me. Only when pressed. But about two weeks ago, a periodically aching pain in the lower back appeared, radiating forward. pressing on the lower back was not pleasant.
Aching pain in the right hypochondrium also began to appear again. And three days ago I woke up at night from cold sweat and a slight fever. Nausea. Dizziness. The temperature dropped. Didn't get up again.
My rib hurts almost all the time. Very rarely the left side also shimmers. Diarrhea appeared. About 4-5 times a day. There are also false calls. My stomach hurts and growls, but in the end nothing happens in the toilet.
Nausea is mild and not always present. On the right, the edge sometimes seems like something is in the way. It hurts to press almost the entire right side of the abdomen and gurgles. Also sometimes there is not much itching on the skin. The worst thing is that I’m now in a foreign country and I don’t have much money even for an examination, and I’m only going home in two weeks.
Very scary. What could this be and can you recommend something? I’ve been drinking Allahol and charcoal for the second day. I read a lot about stones and death. about stomach cancer and so on. I also have enlarged lymph nodes in my neck and groin for 5 years.
Hello Olga! You need to undergo a medical examination to determine the degree of urgency. And so, from a distance and without seeing the patient, I can say that despite the predominance of complaints of a gastrointestinal nature, I consider it necessary to be treated mainly by a gynecologist, who will definitely pay attention to the connection (or not) with your lymph nodes.
2015-10-13 14:37:56
Hello. Skills almost 3 months ago was miscarried at 32 weeks. The autopsy showed nothing. My period should come in 4 days, but for almost 2 weeks I have already felt pain in my chest; today, when I pressed my nipples, a white liquid came out.
Hello Maria! These symptoms are nonspecific and do not allow for an accurate diagnosis, but are definitely an indication for a visit to the doctor. Take a pregnancy test, go to an appointment with a gynecologist and get examined.
In addition, be sure to ask your doctor to choose an adequate method of contraception for you. Given your medical history, you should not become pregnant for at least six months. Another topic for discussion should be an examination that should show the cause of premature birth and fetal death. Take care of your health!
2014-06-15 11:00:34
The gynecologist discovered inflammation. Upon examination, it was very painful when pressing on the abdomen. and suffer from pain in the lower abdomen. She advised me to take a course of Rath injections. 5 injections in the stomach, which she will do herself. I couldn’t find any information about the composition or reviews about this on the Internet. Tell me, should I agree? What kind of injections are these?
2013-02-12 19:43:57
Hello! For two days I have periodically experienced pain in the lower abdomen on the right (just below the navel). The pain is acute, but passes quickly. It hurts a little when pressed. With what it can be connected? And in general, is this closer to the symptoms of appendicitis or gynecological inflammation?
Abdominal pain can have different causes: from intestinal spasms (colic) to serious illnesses. A doctor's examination and some tests will help figure this out.
2011-07-10 13:08:19
Hello, I have this problem: burning and pain when urinating, and sometimes there is just a burning sensation in the urethra, especially often after working out in the gym (I assume after running);
and also below the navel, pain when pressed, after I went to the toilet once in a small way - during urination, everything contracted so tightly in the lower abdomen and only released after I had to finish urinating and after that the pain in the lower abdomen began!
In the “Live Healthy” program on June 10, they looked at pain in the lower abdomen in women, but I don’t think there are many differences in men! At the end of the program they said that pain in the lower abdomen can be accompanied by problems with urination and therefore I really hope that you will help me find out the reason!
I’ve been undergoing many tests for half a year now and still haven’t found anything: 1) In the CVD, all infections are negative! Passed by PCR method 2) Ultrasound of the bladder: size 68.9 * 43.4 * 65.1, volume 101.9 ml, wall 2.8 mm, homogeneous content 3) Ultrasound of the prostate: Not enlarged;
erythrocytosis, monocytosis, basophilia 9) Biochemical blood test conclusion: hyperglycemia, hyperbilirubinemia, decreased HDL 10) The surgeon said that there are no hernias. The program talked about kidney stones, nonspecific ulcerative colitis, teleokia and various genecological (urological) diseases!
Dear Alexander. You described an inflammatory lesion of the prostate gland; indeed, the prostate is only a male organ, so prostatitis can only develop in men. It is known that bacterial infection of prostate tissue is the cause of chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
The development of prostatitis is facilitated by irregular sexual life, hypothermia, trauma, decreased immune activity, impaired blood and lymph circulation in the pelvic organs, various hormonal disorders (androgen deficiency), and STDs.
Prostatitis is often combined with urethritis, vesiculitis and prostate adenoma. We are impressed, Alexander, by your systematic approach to examination, but most often chronic prostatitis has an asymptomatic course and the main method of diagnosing the disease is the identification of microorganisms in the tissues of the prostate gland.
To detect bacteria, a culture of prostate secretions is performed. In addition, microscopy of prostate secretions is performed. One of the criteria for diagnosing prostatitis is an increase (more than 10 in the field of view) in the number of leukocytes in the secretion.
2011-05-08 23:57:09
Hello! During the medical abortion process, a fertilized egg and a lot of blood clots were released! Within 5 days I had heavy periods without much discomfort! BUT! On days 6, 7 and 8, nagging pain in the lower abdomen began (without painkillers.
I can’t get by with medications) accompanied by scant discharge. I went for an ultrasound, the doctor said that everything went well, but a small number of clots still remained in the uterus. During the examination, the doctor checked the uterus and ovaries for pain when pressed. No pain.
He recommended Movalis or Olfen suppositories. He also said that these clots will definitely come out with the next menstruation. But I’m worried that the nagging pain does not stop, is this a normal situation? Thank you in advance for your answer!
2008-05-31 23:54:47
Hello, I'm 20 years old. The delay in menstruation was 3-4 months, before that there was a delay last year for 3 months, but then the menstruation started again, everything was fine for 3 months, but now there is a delay again. Lately I have been feeling pain in the lower abdomen on the right side, strong white, sourish discharge, and in the vagina on the right side I feel like some kind of growth in the form of a ball, it does not grow, it is always the same size, I already noticed it 2-3 years ago, it was earlier didn’t bother me and nothing hurt, it appears and disappears from time to time, it doesn’t hurt when pressed, but after sexual intercourse for the last week, after 15-30 minutes the pain begins, 3-4 days ago I had sexual intercourse with my husband and after that the pain lasted almost 2 days. What could it be?
2014-03-27 17:51:33
Hello! A few days ago I asked a question, doctor Roksolana Yosipovna Purpura answered me, thank you for your prompt help! I answer your questions: all the tests are in order, the gynecologist said that nothing was found, the smear was good, cystitis is not yet clear, because
My tests were lost in the laboratory, and now it’s impossible to find out. Now my chest has started to hurt (not too much, but there is discomfort when pressing), and the lower abdomen still feels tight, along the sides, where the ovaries are. The discharge is scanty, creamy, transparent white, after urination it is mucous, but there is not much of it.
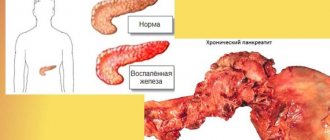
Pancreatitis
How to reduce pain
Through observation and research, gynecologists have identified methods that help alleviate a woman’s well-being, regardless of the root cause of its deterioration:
- Drinking herbal tea. Chamomile, mint, lemon balm, thyme - these medicinal herbs have calming and anti-inflammatory properties. It can be taken outside of menstruation - to strengthen immune properties and stop pathogenic processes that have a hidden course. Drinking warms you up and provides a distracting effect.
- Relieves the intestines naturally, through a laxative or using a microenema. An overloaded intestine puts pressure on the uterus. As a result, pain, spasms, and bleeding increase. To reduce menstrual pain, you need to empty your bowels in a timely manner. If this presents difficulties, you can use a laxative rectal suppository or microenema (its volume is 30-150 ml).
- Applying a heating pad to your stomach. This is not acceptable in all cases, so the technique can be implemented only after approval by a doctor. Relieves pain, stiffness, allows you to relax and get ready for sleep.
During dysmenorrhea, it is not recommended to wear clothes with a tight elastic band at the waist (tight trousers, skirts, belts, corsets). Compression of the uterus increases discomfort and bleeding, hinders movement, and prevents convenient changing of pads.
What you can do on your own
Before taking any measures, you need to find out the reasons for painful periods on one day. If the pain is not pathological, then you can take a warm shower, drink valerian or herbal tea and lie down. Minor cramps can be relieved by applying a heating pad to your stomach.
In case of severe pain, with the permission of a doctor, you can take medications of the non-steroidal group of analgesics and antispasmodics:
- Spasmalgon;
- Nosh-Pa;
You can relieve pain with Ibuprofen
- Ibuprofen;
- Dratoverine;
- Paracitamol.
Folk remedies also have a positive effect:
- berry compote;
- a decoction of parsley or dill seeds;
- camomile tea.
Strong drugs should not be taken. It should be remembered that a number of medications can change hormonal levels, which will affect the process of menstruation, and also have a thinning effect on the state of the blood, which will provoke uterine bleeding.
Ways to feel better
Non-drug methods during dysmenorrhea can partially normalize well-being. They are based on the use of heat sources, performing massage and changing the attitude towards the condition. In addition to the psychological aspect, the remaining 2 factors require prior approval by a gynecologist.
Warming treatments
A warm shower is not only allowed during dysmenorrhea, but also useful. It provides a full level of hygiene, relieves pain, relaxes and warms. The use of hot water is contraindicated. During the procedure, it is advisable to massage the abdominal area.
Physical activity
With dysmenorrhea, many exercises are contraindicated. Especially if they involve impact on the abdominal muscles. Fiber tension contributes to increased discomfort and increased blood loss. It is recommended to limit physical activity aimed at the uterus and genitals to massage. It can be done with or without special oil. Stroking circular movements in the lower abdomen (in the umbilical area) relieve pain, tension, and help reduce spasms. The duration of the procedure is up to half an hour.
Diet during menstruation
To reduce pain, you should avoid foods that irritate the walls of the urogenital tract. It is recommended to refrain from eating sour, spicy, salty foods. Drinking alcohol is strictly contraindicated (alcohol increases bleeding and spasms). Although caffeine is a substance that irritates organ tissue, its use during menstruation is acceptable. The reason is that due to blood loss, the woman’s blood pressure level decreases. Coffee supports its indicators, preventing weakening of the body, dizziness and other symptoms.
How to determine the cause?
To establish the cause of pain in the lower abdomen, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gastroenterologist.
His actions will be like this:
- Collecting anamnesis about symptoms and time of onset of the disease.
- Finger diagnostics.
- X-ray or ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Colonoscopy.
The first three points are usually carried out without fail, and the fourth is prescribed if up to this point in the diagnosis the cause has not been established. Also, colonoscopy can be indicated simultaneously as a diagnostic and therapeutic measure. During the procedure, you can take pieces of tissue for examination, remove a polyp or small tumor, cauterize the bleeding site, etc.
Along the way, other examinations of nearby organs may be needed for diagnosis, if along the way it turns out that the problem is not in the intestines at all.
Diseases that cause pain
Gynecologists have established a relationship between dysmenorrhea and diseases that a woman has. The main pathologies that contribute to the development of painful menstruation are shown in the table.
| Diseases that aggravate health during menstruation | Reasons for development | Treatment of the disease |
| Cystitis | Entry of pathogenic microflora into the bladder. Predisposing factors: |
- hypothermia
- poor personal hygiene
- the presence of inflammation of the urethra or genital organs
- lack of water procedures before and after intimacy
The development of cystitis is promoted by drinking alcohol and coffee, excessive consumption of spicy, sour and salty foods.
Cystitis
Classified into acute and chronic forms. It is an inflammation of the bladder, accompanied by a wide range of symptoms:
- dysuria (sharpness and irritation inside the urethra when urinating)
- pain in the lumbosacral back (of a girdling nature)
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels
- general weakness caused by intoxication of the body
During menstruation, the uterine os is opened enough to facilitate the complete evacuation of blood masses. But this physiological phenomenon injures the reproductive organ before the penetration of pathogenic microflora. The movement of cystitis pathogens from the bladder to the uterus leads to inflammation of the uterus. The reverse process may also occur - cystitis due to menstruation. Inflammation occurs due to the entry of pathological microorganisms present in menstrual blood into the bladder. In both cases, this aggravates the woman’s condition, since the pain comes simultaneously from two sources: the uterus and the bladder.
Endometriosis
A severe gynecological disease always manifests itself with violent symptoms. It is characterized by the discharge of large fragments of the uterine mucosa during menstruation. Outwardly they resemble a liver. Discomfort increases as tissue detaches from the reproductive organ. When these clots are rejected, bleeding increases and pain in the lower abdomen increases. Hyperthermia is not typical for endometriosis. Additional symptoms of the pathology are pain during sexual intercourse, aches in the lumbosacral back, weakness.
Inflammation of the appendages
Adnexitis is a lesion of the fallopian tubes and ovaries (it is these organs that are combined into the term “appendages”). Characteristic symptoms are pain in the lower abdomen, but at a certain point (at the site of inflammation) at rest and during menstruation. Other signs:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Discharge of viscous purulent masses from the vagina during the period between menstruation
- Pain during sexual intercourse (with chronic adnexitis)
- Refusal from intimacy due to discomfort and decreased libido (with acute inflammation of the appendages)
Since pathogenic microflora is present in the blood, body temperature rises to high levels. This contributes to the development of weakness, dizziness, and hypotension. Chronic adnexitis is the leading cause of ectopic pregnancy. The fallopian tubes are glued together by pathological secretion, which prevents the full movement of the fertilized egg into the uterus. As a result, it remains inside the tube and pregnancy develops there. However, menstruation may continue. The phenomenon reduces a woman’s vigilance - she does not suspect that she has an ectopic pregnancy.
In this case, the sources of pain during menstruation are inflamed appendages and the fallopian tube, which stretches under the influence of the growing fetus and creates debilitating discomfort.
Cyst
Benign neoplasm of the ovaries. In rare clinical cases, it has a tendency to degenerate into a malignant tumor. Clinical manifestations are pain during menstruation, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, pale face, darkening before the eyes. During menstruation, a woman is almost completely destabilized - on the first day of bleeding, she is forced to adhere to bed rest. The cyst may rupture under the influence of physical activity. In this case, an urgent call for an ambulance is indicated.
Why does my stomach hurt during menstruation?
Algodismenorrhea is divided into two types - primary and secondary.
Primary algodismenorrhea
The primary type includes painful menstruation in girls, starting from puberty, and for 3-4 years after the start of menstruation. Most often, primary algodismenorrhea is diagnosed in girls of asthenic physique, who are thin. Also, the development of pain during menstruation is influenced by the psychological state; sensitive, easily excitable, emotionally unstable girls are susceptible to it.
Anatomically painful menstruation in young nulliparous women is often caused by the following pathologies:
- Hormonal disorders of the andrenergic or parasympathetic type. In the first case, there is an increased secretion of adrenaline, norepinephrine, and dopharmine, which leads to hormonal imbalance. The peculiarity of this type of algodismenorrhea is headache, constipation, increased heart rate, insomnia, cyanosis of the extremities, paleness of the face. With the parasympathetic type of algodismenorrhea, the serotonin content increases, which leads to digestive upset (nausea, diarrhea), a decrease in heart rate and body temperature, swelling of the limbs and face is often manifested, excess weight gain and allergic reactions are possible.
- Congenital abnormalities of connective tissue - often the cause of painful periods in young girls are genetically determined growths of the connective tissue of the uterus (dysplasia). This disease is characterized by such disorders as scoliosis, flat feet, varicose veins, pathologies of the digestive system, and myopia. These diseases are often triggered by a lack of magnesium during the growth of the body, in most cases they occur in girls of fragile physique.
- Congenital anomalies of the uterus - kinks, malformations (bicornuate, two-cavity uterus) lead to difficulties with the outflow of blood from the uterine cavity during menstruation. This provokes pain caused by excessive contractions of the uterus.
- Diseases of the nervous system - pain in this case is caused by increased sensitivity to pain and emotional instability.
Whatever the causes of painful menstruation in young girls and nulliparous women, if the pain is of moderate or high intensity, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist and undergo a comprehensive examination. Identifying the cause of primary algodismenorrhea makes it possible to get rid of many serious problems that may arise in later life.
Secondary algomenorrhea
The diagnosis of secondary algodysmenorrhea is made when the stomach hurts during menstruation in women who already have children or have crossed the threshold of their 30th birthday. Moderate and severe painful periods occur in a third of women who give birth. This negatively affects the general condition and performance. In addition to pain, secondary algodismenorrhea is additionally accompanied by other pathological symptoms. Most women are diagnosed with excessively heavy menstrual flow, as well as the following disorders:
- digestive disorders - flatulence, nausea, vomiting;
- vegetative-vascular disorders - dizziness, loss of consciousness, headaches, migraines, numbness of the limbs, increased heart rate, arrhythmia;
- psycho-emotional disorders - increased irritability, sudden changes in mood, excessive sensitivity to smells, changes in taste buds;
- endocrine and metabolic disorders - severe causeless weakness, aches and pain in the joints, itching of the skin.
The cause of secondary algodismenorrhea can be inflammatory pathologies of the pelvic organs, non-inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive organs, damage to the uterus after childbirth, surgical interventions or curettage. A common cause of pain during menstruation is pathological changes in the uterine mucosa - the growth of the endometrium into muscle tissue (adenomyosis) or beyond the internal cavity (endometriosis). In addition, secondary algodismenorrhea in adults and women who have given birth is often a symptom of tumor diseases - fibroids, uterine fibroids.
Painful periods in women who have given birth can be a sign of a number of serious pathologies of the reproductive (genital) or endocrine system, as well as a tumor development mechanism. If even a mild degree of algodismenorrhea occurs, it is necessary to consult a doctor, undergo a series of diagnostic procedures and studies to find out its cause and carry out treatment. In addition, during early pregnancy, the stomach hurts like during menstruation, which is caused by swelling and stretching of the uterine ligaments, and a rush of blood to the body of the uterus. In this case, consultation with a gynecologist is also necessary.
Video: Pain during menstruation. What to do? Health. (01/22/2017)
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 1069 Date of publication: 11/15/2017
Gynecologists - search service and appointment with gynecologists in Moscow
When is it necessary to consult a doctor?
Indications for contacting a specialist:
- During menstruation, the degree of pain predisposes to loss of consciousness.
- In addition to pain in the lower abdomen and back, large fragments of mucous membranes are released.
- The discomfort is so severe that analgesics are ineffective.
If a woman’s well-being is aggravated by a decrease in blood pressure and associated symptoms, this is a good reason to make an appointment with a gynecologist. This phenomenon can lead to the development of anemia, which is unfavorable for well-being. You should also visit a gynecologist if the aggravated condition occurs every month, if there is a history of problematic childbirth and previous curettage. An important reason for visiting a specialist is maternity planning.
Other causes of pain
With cholecystitis, pain also occurs in the lower abdomen. Cholecystitis is a condition caused by an exacerbation of cholelithiasis. It is an inflammation that affects the gallbladder and disrupts the flow of bile. In this case, the pain is localized at the bottom and right of the lower part of the peritoneum. Cholecystitis is not difficult to distinguish from other causes of pain, since it manifests itself exclusively in people suffering from the formation of stones in the gall bladder. In addition to pain, this inflammation is accompanied by such characteristic symptoms as:
- incessant itching in the area of inflammation;
- yellow coloration of the skin and sclera of the eye;
- general signs of intoxication with excess bile;
- increased pain after eating.
Experts use this term to refer to a local defect affecting the mucous membrane. Gastric ulcers are formed due to pepsin, hydrochloric acid and bile, the concentration of which increases with poor nutrition. This disease is characterized by accompanying symptoms such as:
- sour belching;
- sudden weight loss;
- feeling of nausea or vomiting after eating;
- increased pain after eating.
The onset of inflammation is signaled by the appearance of a dull pain in the abdominal area. After 12 hours, the painful sensations shift towards the location of the appendix - the lower right region. Their intensity increases, and the pain itself becomes pressing and throbbing. In addition, symptoms of general intoxication appear.
If abdominal pain is accompanied by such symptoms, then you should immediately consult a specialist and undergo a full examination. Since only a qualified doctor can prescribe competent treatment.
When appendicitis develops, it is very important to call an ambulance in time to hospitalize the patient. This inflammation progresses very quickly and can develop into peritonitis, which can be fatal. In addition, the sooner the patient is hospitalized, the easier it will be for doctors to perform surgery to remove the inflamed appendix.
Diagnostics
To identify the root cause of dysmenorrhea, the patient will have to undergo the following types of diagnostics:
- Questioning and inspection. The doctor reproduces the clinical picture of the patient’s condition, plans further interventions, and makes a preliminary diagnosis.
- Laboratory testing of blood and urine. Depending on the factor that contributed to dysmenorrhea, inflammation, anemia, and an infectious process are identified. Laboratory methods determine the state of hormonal balance.
- Ultrasound of the uterus, appendages, bladder, gastrointestinal tract. Allows you to detect almost all pathogenic processes of the urogenital and digestive tract.
Other diagnostic techniques are prescribed taking into account the suspected diagnosis that led to the development of dysmenorrhea. Complex methods of radiation imaging (CT, MRI) are necessary to clarify the characteristics of the tumor, the degree of blood supply to the tissues, and the spectrum of inflammation. When dysmenorrhea is associated with osteoarticular pathologies, the patient is referred for an X-ray examination. Even if such a diagnosis is only assumed.
When pain is normal
70% of women experience stomach pain on the 1st day of their period. However, depending on the severity of symptoms, pathological abnormalities can be suspected.
Many girls experience pain on the first day.
Painful sensations on the first menstrual day are considered normal if:
- pain intensity is low;
- no sharp spasms;
- The pain is intermittent and quickly subsides.
During normal menstruation, a woman should not experience accompanying symptoms of deterioration in her general condition.
Already on the second day, the state of health improves significantly, and on the third or fourth day it is completely restored.
Treatment
During painful periods, it is recommended to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Voltaren). Rectal administration of any of the listed drugs in the form of a suppository relieves pain and relieves tension inside the genital canals.
The following prescriptions help eliminate the main pathologies that cause dysmenorrhea:
- Antibiotic therapy. Stops inflammatory and infectious processes.
- Hormonal drugs. Corticosteroids are administered; substances produced by the pituitary gland.
- Vitamin therapy. Whole complexes or individual vitamins are prescribed.
- Analgesics. They relieve pain and normalize general well-being.
- Drugs are administered aimed at normalizing blood pressure levels (if their levels decrease).
- Dyspeptic disorders are treated with antiemetic medications.
Additionally, the patient is prescribed a course of physiotherapeutic treatment (enterofuresis, magnetic therapy, UHF). To eliminate pathological discharge from the surface of the genitals, it is necessary to treat the tissues with antiseptic solutions. If a woman is diagnosed with anemia (caused by massive blood loss), injection of iron supplements is indicated. When sexually transmitted diseases are detected, not only the woman, but also her sexual partner undergoes treatment.
Prevention
In order not to subsequently encounter the problem of severe pain during menstruation, it is recommended:
- Refuse to perform abortions
- If you don’t want to get pregnant, choose the optimal method of contraception and stick to it
- Don't get too cold
- Timely relief of inflammation of the urogenital and digestive tract. Prevent the pathology from becoming protracted
- Don't abuse alcohol
Other preventive measures are the use of an intrauterine device strictly within the established time limits (do not exceed the period of operation). It is important for a woman to lead an orderly sex life - to avoid casual intimacy. Attention should be paid to the issue of strengthening the immune system, since 90% of diseases are a consequence of weakening the body’s protective properties. It is preferable to refrain from lifting heavy objects at home and not to associate professional activities with exhausting physical labor.
How to prevent pain in the lower abdomen: what you can do and what you should avoid
Remember the basic rules, and then your chances of forgetting about cramps will increase significantly.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene (regular showers, daily change of underwear).
- Sleep at least 6-8 hours.
- Strengthen your immune system (strengthen your body, play sports, eat more fortified foods).
- Do yoga (this will help you begin to understand your body, feel it and the changes occurring in it).
- Limit sex during your period.
- Remember that promiscuity almost always leads to diseases, including incurable ones.
- Do exercises while sitting at work (so as not to disrupt the blood circulation of the pelvic organs).
If you approach your own health wisely, change a number of habits and learn to understand your body, then you can not encounter severe abdominal cramps for a very long time.
Video: Painful menstruation - causes
For some women, severe cramping pain during menstruation is almost the norm of existence, to which they try to get used. However, medical experts do not consider it correct to be patient with the negative symptoms that accompany the natural cyclical process. The physical condition during menstruation should be satisfactory, the inconvenience should be subtle and not interfere with everyday activities. But in 10% of women, the cycle begins with the development of cramping pain in the lower abdomen. The symptom can vary in intensity and duration, accompanies only critical days or makes itself felt long before them. Often, pain such as cramps during menstruation is described by women with a low pain threshold, individual physiological characteristics and hidden pathologies.
Localization and time of pain
The concept of “lower abdomen” already reduces the range of searches for a specialist in the causes of pain, but it can be further narrowed:
- There is pain below the navel due to inflammation of the small intestine.
- On the left side of the abdomen it hurts with dysentery and other infectious diseases. Also, pain on the left side is characterized by inflammation of the sigmoid and colon.
- At the bottom right, the intestines can hurt due to appendicitis and other diseases of the cecum.
- If the entire lower abdomen hurts (usually a dull pain), then it looks like a general inflammation of the intestinal tract or a peptic ulcer.
In addition to the location of the pain, the time of its manifestation will also help to make a diagnosis. She can:
- Appear after bowel movements (typical of hemorrhoids).
- Worse when walking (appendicitis).
- Occur or intensify before defecation (inflammation of the intestinal walls).
- Appear in the morning or evening, depending on the schedule of the intestines (the stronger the peristalsis, the more pain, if the cause is spasms).
- Occur after eating immediately or after 30 minutes (gastritis, gastroenterocolitis, peptic ulcer).
- It does not appear immediately after eating, but after a couple of hours, especially if a person has consumed large amounts of roughage (intestinal tumor).
Constant pain in the lower abdomen can drive anyone crazy. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible and mention the nature, location and time of pain, what this may be associated with, so that the specialist can quickly establish a diagnosis and begin treatment.
One of the main causes of constipation or diarrhea is poor diet.
.
Therefore, to improve bowel function, you need to drink a simple drink
.
Causes of cramping pain
Contractions of the uterus during menstruation can cause physical discomfort or cause mild short-term pain due to microspasms in the smooth muscle fibers. Similar phenomena occur in most representatives of the fair sex and are explained by excessive activity of the muscular walls of the uterus, which gets rid of the contents.
As is normal, symptoms such as heaviness and slight compression in the lower peritoneum may be felt, without disturbing the general well-being. Severe cramping pain is considered a sign of menstrual dysfunction - algomenorrhea. The condition may be accompanied by other negative signs:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels;
- aches in muscles and joints;
- irritability and other emotional disturbances.
The nature of cramping pain in the lower abdomen is different: they can periodically subside and intensify, radiating to the bladder, lower back, and anus. Sometimes spasmodic symptoms develop not at the beginning, but at the end of menstruation.
Natural causes
In a conventional sense, physiological factors that cause severe pain during menstruation are considered natural. Primary algomenorrhea develops during the first years after menarche, can accompany a woman throughout her reproductive period, and disappear spontaneously or after childbirth. The mechanism of formation of painful periods is not fully understood. Among the reasons causing spasms are the following:
- excess prostaglandins - hormone-like substances that increase the sensitivity of pain receptors;
- deficiency of natural endorphins;
- violation of the luteal phase of the cycle, provoking increased contractions of the uterus;
- structural features of the endometrium that make its separation difficult;
- congenital anomalies of the structure or location of the internal genital organs: the presence of pronounced displacement, bends, bicornuity of the uterus.
The above reasons include premenstrual syndrome, which is caused by significant fluctuations in a woman’s hormonal levels. The course and severity of PMS is determined by the level of dopamine and norepinephrine. The higher it is, the more severe the subsequent painful sensations. Signs of illness appear as early as a week before menstruation: sudden mood swings, nervousness, severe irritability, nervous tics, and hysterical attacks are observed. Sharp, severe pain in such cases periodically occurs before bleeding and reaches a peak in the first days of menstruation.
Pathological
Cramping pain during menstruation may indicate a dangerous condition of the body or disease. Common pathologies in which similar symptoms develop:
- Inappropriate contraception - arbitrarily used oral hormonal drugs cause a sharp imbalance in the endocrine systems; an incorrectly selected IUD puts mechanical pressure on the walls or cervix.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs: adnexitis, adenomyosis often worsen during menstruation, provoking painful attacks.
- Neoplasms of the internal genital organs: fibroids, polyps, cysts. With uterine fibroids, severe cramps during menstruation are a hallmark. The larger the nodule, the more painful the symptoms. The so-called birth of a node is the exit of a tumor growing on a thin stalk from the cervical canal to the outside, accompanied by real labor pains.
- Scar formations, adhesions, strictures and other violations of the integrity of the genital organs as a result of injuries, abortions, and surgical treatment.
- Ectopic pregnancy. In some patients with menstrual pain who consult a gynecologist about severe symptoms, a fertilized egg is found in the lumen of the fallopian tube. Its detachment and release causes severe cramps in the lower abdomen and spotting, which can be confused with menstruation.
- Early miscarriages can also be misleading. Bleeding as a result of spontaneous abortion is taken as the beginning of the next cycle, in most cases accompanied by sharp twitching pain caused by the contracting uterus.
- Pathologies of internal organs. Severe renal or intestinal colic, strangulated hernia, coinciding with the onset of menstruation, manifest as painful spasms and are perceived as algomenorrhea.
Reasons why pain occurs
Abdominal pain when pressed may appear in the following cases:
- acute appendicitis;
- gastritis in the acute stage;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- Crohn's disease;
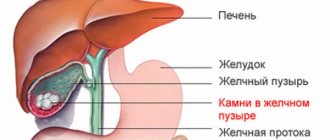
- cholelithiasis;
- hernia;
- poisoning with poor quality food products;
- pathology of organs located in the pelvis (uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, etc.);
- urinary system infections.
Looking at the table, you can briefly learn about the cause of the pain and its location.
| Pathology | The cause of abdominal pain and its location |
| Appendicitis - acute inflammation of the appendix of the cecum | The pain when pressing on the abdomen appears sharp and intensifies with positive Shchetkin-Blumberg syndrome in the supine position. Additional signs of appendicitis are nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief, upset stool, and high body temperature. Most often the pain is localized to the right below the navel |
| Gastritis – acute inflammation of the gastric mucosa | The main symptoms of the disease are loss of appetite, belching, nausea and vomiting, increased gas production, and weight loss. In addition, the stomach hurts when pressed in the epigastric region, there is heartburn and a burning sensation in the chest |
| Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum is a disease in which ulcers form in the mucous membrane of the digestive organs | Pain on the left side of varying intensity, stabbing in nature, most often occurring on an empty stomach. Other accompanying symptoms of gastrointestinal tract and duodenum include heartburn, sour belching, a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen after eating, nausea, weight loss. |
| Gastroesophageal reflux is a condition in which gastrointestinal contents back into the lumen of the esophagus. | Most often, pain occurs in the upper abdomen or behind the sternum, mainly on the left, a burning sensation along the esophagus, difficult and painful swallowing, prolonged cough and hoarseness, destruction of tooth enamel |
| Crohn's disease is a chronic granulomatous disease that affects the entire gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. | Patients with a serious illness develop diarrhea mixed with blood in the stool, increased body temperature and general weakness, decreased or loss of appetite, ulcers from the mouth and throughout the gastrointestinal tract, anal fistulas, and cramping abdominal pain that worsens with palpation. In addition, Crohn's disease can manifest itself as inflammation of the skin, eyes and joints. |
| Gallstone disease is a pathology in which stones form in the gallbladder and ducts | The disease is diagnosed by the following signs: aching pain in the right part of the hypochondrium, belching, bloating, increased irritability, upset bowel movements with proper nutrition, colic on the right side. In addition, it is worth noting that patients complain of sleep disturbances and loss of appetite |
| Strangulated hernia is a condition characterized by compression of the abdominal organ by the hernial orifice, leading to circulatory disorders | If a hernia is strangulated, patients experience sudden sharp pain, an increase in the size of the abdomen, redness and swelling of the skin surrounding the hernial sac, nausea and vomiting, impaired bowel movements, streaks of blood in the feces, fluctuations in blood pressure, general weakness and malaise. |
| Food poisoning is a condition in which the body is poisoned by toxins that appear in food due to the massive proliferation of pathogenic microbes in it. | Poisoning with spoiled foods most often results in body temperature, nausea and vomiting, stool upset and cramping abdominal pain, flatulence, low blood pressure, and cold sticky sweat. On palpation, the patient complains of increased pain in the navel area |
| Urinary tract infection is a group of diseases associated with inflammation of one or more organs that form, store, and excrete urine. | For different diseases, the clinical picture and location of pain will differ. When pressed, the lower abdomen hurts, urinary incontinence, painful urination in small portions is noted with cystitis. The left side may hurt if the kidney is damaged on this side and vice versa. With bilateral kidney damage, for example, pyelonephritis, the pain is localized in the lumbar region |
| Pathology of the female genital organs is a type of disease that includes inflammation of the uterus and appendages, ectopic pregnancy, painful periods, etc. | Due to its location in the pelvis, all pain is noted in the lower abdomen in women with any gynecological pathology. If bacteria are attached, itching and burning of the genitals, unpleasant odor and consistency of discharge, dry mucous membranes, pain during and after sex may occur. |