Pain in the left side of the lower abdomen - main symptoms: Abdominal pain Pain in the abdomen on the left Pain in the abdomen on the right Pain in the navel Pain in the esophagus Pain in the spleen Pain in the upper abdomen Pain in the lower abdomen Pain behind the sternum Acute pain in the abdomen
In the lower abdomen, women experience so-called pelvic pain, usually caused by chronic or acute diseases of various internal organs, bones, blood vessels, and joints of the pelvic girdle. If the left side of the lower abdomen hurts in women, this may be due to both gynecological problems and diseases of other organs located on the left side of the peritoneum.
Pelvic pain in women can be caused more often by chronic or acute diseases of various internal organs
Abdominal pain due to STDs
With STDs, pain is felt above the pubis and in the groin areas, in the lower back. Usually they are constant, pulling, radiating to the inner thighs. The increase in pain intensity depends on the stage and extent of inflammation and is associated with a change in color and an increase in the amount of discharge from the urethra and/or vagina. With specific urethritis and cystitis, a burning sensation is felt in the urethra and bladder, especially at the beginning and end of urination.
As the area of infection increases, inflammation spreads to the ureters, kidneys and internal genital organs. With ascending genital infection, the process involves first the endometrium, and then the muscular and serous layers of the uterus. Pain receptors are located in a thin ring only inside the cervical canal and in the area of the internal openings of the fallopian tubes; the cervix and body of the uterus itself are completely insensitive to pain. At the stage of endo- and myometritis, the pain is mainly referred, often aching, felt in the lower back and inner thighs. Local pain in the lower abdomen increases significantly if the tissue around the uterus (perimetritis) and the pelvic nerve plexus (plexitis) become inflamed.
Cystitis and pyelonephritis are consequences of an ascending urogenital infection. Drawing pains appear above the pubis and in the groin, aching pains appear in the lower back; necessarily combined with urination disorders. During purulent processes, the temperature rises above 38-39 degrees, and intoxication increases sharply. The main burden falls on the liver and kidneys; the development of functional failure of these organs and death are possible.
Pathologies of the genitourinary system
Pain in women that worsens during menstruation may indicate the presence of endometriosis. With acute inflammation of the uterine appendages, there is also colitis in the left side of the lower abdomen. However, pain can also spread to the right side. In such cases, an increase in temperature is often observed. Similar symptoms occur as a result of an ectopic pregnancy. During movement, the pain may intensify and be acute and even cramping in nature. In this situation, you should consult a doctor immediately. Quite often, men face the problem of pain in the left side in the lower abdomen. Typically, this kind of sensation appears with pathologies of the genital organs, such as epididymitis, orchitis, varicocele, funiculitis, and testicular torsion. We should not forget about sexually transmitted infections. If you experience any discomfort in the lower abdomen, you should visit a doctor and get tested for chlamydia, tricimoniasis or gonorrhea.
Pain around the navel
Umbilical hernia : expansion of the umbilical ring and the formation of a hernial sac, which usually contains fatty tissue, sometimes intestinal loops. Pain in the navel area appears after eating or during physical activity (mainly after lifting weights). A hernia often occurs in women who have given birth as a result of stretching of the anterior abdominal wall. An umbilical hernia is clearly visible upon examination and is a rounded protrusion; upon palpation (feeling) it is determined as a soft formation, the local temperature is not increased. When a hernia is strangulated, the pain increases: the contents of the hernial sac are compressed, blood circulation is disrupted and necrosis occurs - tissue death. If there was part of the intestine in the hernial contents, then intestinal obstruction (ileus) occurs and a picture of an acute abdomen occurs. Treatment in this case is only emergency surgery.
Colitis and enteritis - inflammation of the large or small intestine. In addition to sharp pain at the level and below the navel, it is always accompanied by diarrhea. With colitis, the volume of stool is small, there may be an admixture of blood and thick mucus, and the urge is frequent. With enteritis, the amount of stool is large, the masses are liquid or semi-liquid. Normally, the reabsorption of water occurs in the small intestine, and when it becomes inflamed, increased excretion of fluid occurs. The danger of such diarrhea is that the patient loses a lot of water and potassium ions, which can be fatal. A classic example of enteritis is cholera.
Megacolon , an increase in the length and width of the colon, thickening of its walls. It is often a congenital disease; characteristic symptoms are chronic constipation and the need for “mental preparation” for defecation. The patient requires special conditions; on the road or in public places he is physically unable to defecate. The consequences of long-term constipation are primarily intoxication, which is manifested by problems with the skin (pustules, irritation, dull color, premature wrinkles), hair (poor growth, split ends and loss). Then allergic reactions and the development of neuroses are possible. When stool hardens, bedsores form in the wall of the colon; they can later become infected and lead to adhesions or intestinal perforation.
Appendicitis , inflammation of the appendix. First, the pain is localized in the navel area, then moves below the navel and to the right. One-time vomiting and an increase in temperature to 37.3-38 degrees are possible. The clinical picture of appendicitis is very diverse; it can imitate any disease of the abdominal cavity. The level of abdominal pain varies depending on the stage of inflammation (acute or chronic) and the location of the appendix relative to the cecum. With an atypical – retrocecal – position of the process, the pain may radiate to the lower back or even be felt only in the hip joint.
Ileus, intestinal obstruction: sudden and sharp onset - an attack of intestinal colic. Initially, the pain is felt in the navel area, then it becomes diffuse. It is always combined with stool retention and impaired gas discharge, with nausea and repeated vomiting.
Parasites as one of the causes of movement
Many helminthic infestations occur without additional symptoms, but some types of worms can cause noticeable movement in the intestines, especially in the left part.
Even if a person observes the rules of personal hygiene, he is not immune from infection. Parasites enter through soil, meat products, poorly washed vegetables and fruits, as well as water. It is especially easy to become infected when climate zones regularly change - in hot countries the risk is much higher.
Parasitic infestations often manifest themselves with additional signs:
- constant constipation alternating with diarrhea;
- severe nausea and frequent vomiting;
- unexplained pain, heaviness in the abdomen;
- excessive or lack of appetite.
Infestations are disguised as symptoms of completely different diseases. With a large number of parasites, cough, dermatological problems, and fever may occur. With prolonged activity of worms, symptoms of intoxication are observed: weakness, dizziness, fever and temperature.
Small worms, such as pinworms or roundworms, can multiply quickly, causing gas and other digestive problems. In this case, the patient feels a stirring associated with the movement of gases.
A sense of movement, associated specifically with the activity of parasites, is observed when infected with broad tapeworm, bovine and pork tapeworm. Worms live in the intestines and cause extremely severe intoxication. They are often capable of mechanically injuring the intestines and causing obstruction.
Pain in the lumbar region
Lower back pain is a possible sign of many pathological processes and can be different in nature (dull and aching, sharp and shooting, pulling or burning) and intensity. The causes leading to the development of lumbar pain are divided into those associated and not associated with urological diseases.
Urological diseases:
- Glomerulonephritis, systemic damage to the glomeruli. Lower back pain is constant, the process occurs simultaneously in both kidneys and is accompanied by swelling, increased blood pressure, and the appearance of protein and blood in the urine.
- Pyelonephritis, purulent inflammation of the renal pelvis. The pain is combined with dysuria and fever, with a high level of intoxication (headaches, weakness, disturbances of consciousness). Urine is dark brown, many leukocytes, pus.
- Renal cysts are usually diagnosed by ultrasound; the intensity of pain and renal dysfunction are directly dependent on the size of the cysts. Small ones, up to 0.5-1 cm, often become an accidental discovery and do not manifest themselves in any way. Large ones can reach a diameter of 2 cm or more; they put pressure on the kidney and lead to its atrophy, subsequently leading to the development of renal failure. Treatment is surgical.
- Kidney stones : round and smooth stones up to 5 mm in size can pass on their own; larger ones with uneven and sharp edges are removed during surgery. When stones pass through the ureters, renal colic occurs, the pain of which is comparable in strength to late labor pains. The pain is so severe that the patient is literally “thrown” from side to side; he tries to take a position in which the pain will be less, but he fails. In case of renal colic, even if it has been managed, an ultrasound or x-ray examination of the kidneys and ureters is required: if the stone has stopped, the pain may decrease. However, there is a danger of hydronephrosis - accumulation of urine in the renal pelvis due to obstruction of its outflow and subsequent atrophy of the kidney.
- Kidney injuries and tumor disintegration are accompanied by bleeding, which can be detected by blood in the urine or by the formation of perinephric hematomas. In the latter case, blood accumulates in the renal capsule and stretches it, leading to severe lower back pain on the affected side. With massive blood loss, blood pressure drops sharply and a life-threatening state of shock develops.
- Paranephritis, inflammation of the perinephric tissue . Pain in the lower back is combined with pain during flexion and extension in the hip joint, which is associated with tension in the m. psoas major - a large lumbar muscle located on the posterior abdominal wall.
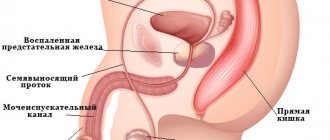
- Prostatitis, prostate tumors (adenoma, cancer) are characterized by referred lumbar pain.
Lumbar pain not associated with urological problems:
- Inflammation of the back muscles (myositis), pathologies of the spine - injuries, herniated discs, radiculitis, mechanical injuries, tumors. The pain is sharp, and when the roots are pinched, lumbago occurs, radiating to the leg, groin, and perineum. A segmental decrease in skin sensitivity is possible, and after injuries - flaccid paralysis of the lower extremities.
- Problems with the hip joint - congenital (dysplasia) and acquired (coxarthrosis) anatomical disorders, inflammation (arthritis), intra-articular fractures.
- Diseases of the digestive system : with pancreatitis, severe pain in the lower back and abdomen, with gastritis - in the lower back and epigastrium (upper abdomen), with a stomach ulcer, the pain intensifies after eating; With a duodenal ulcer, “hunger” pains that begin on an empty stomach are typical.
- Women's diseases : lower back pain due to endometriosis, tumors of the uterus and ovaries. Pain in the lower abdomen and lower back is possible in the first trimester of pregnancy; they are associated with stretching of the abdominal muscles and are considered a normal variant.
Treatment
When a person’s stomach throbs on the left or right side, this is a reason for consultation at a medical institution. If the symptom appears once, then there is no reason to worry. If you experience frequent throbbing pains that are accompanied by other symptoms, an urgent medical diagnosis is needed.
In the treatment of such an indicator, the patient must be provided with first aid:
- calm down;
- identify the nature and strength of manifestations;
- determine whether symptoms depend on changes in body position;
- find out the presence of other pathologies;
- Having determined the cause, you can relieve the pain if it bothers you.
If a patient is diagnosed with unpleasant discomfort due to an aortic aneurysm, treatment is performed surgically.
If a pulsating sensation appears in the abdomen due to a violation of the diet, diet, or the formation of pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract, diet therapy will play a major role. The prescription of medications will depend on the affected organ.
An important role in relieving this symptom is the normalization of the vegetative-vascular system, for which sedatives, vitamin and mineral complexes are used, and psychotherapy sessions are conducted.
If a woman’s abdomen often throbs during pregnancy, then she should definitely visit her doctor to make sure her health is normal. Most often, doctors advise expectant mothers to simply calm down, and also:
- change your posture while in a horizontal position to sitting or standing. After a certain activity, the mother’s blood circulation improves and the discomfort in the abdomen will go away;
- if the cause is a child’s hiccups, then you just need to wait it out. If the symptom manifests itself frequently and intensely, a more detailed examination should be performed;
- If bleeding and throbbing pain in the uterine area are detected, the patient needs urgent hospitalization.
Pain in the groin area
Anatomically, the groin is limited from the outside - by the inguinal folds, from above - by imaginary lines drawn from the anterior-superior convexities of the iliac bones to the edge of the rectus abdominis muscle; the outer edge of the same muscle serves as the medial (inner) border. The main formations are the inguinal canal, through which the round ligament of the uterus passes in women, and the spermatic cord in men, as well as lymph nodes, large arterial and venous vessels, and nerves. Pain in the groin area is often associated with inflammation localized in the lower extremities or pelvic organs, or with the formation of inguinal hernias, with the development of lymphadenitis of various etiologies (inflammation, tumors).
Inguinal hernias can be congenital or acquired; the causes are underdevelopment or weakness of the abdominal muscle wall. Due to anatomical features, the risk of developing an inguinal hernia in men is about 30%, in women – up to 3%. An acquired hernia is diagnosed by a visible protrusion in the groin, which first appears after lifting weights; in the initial stages it is small and easily reduced (reducible inguinal hernia). An irreducible hernia poses a more serious health risk: the hernial sac may be strangulated and its contents may become dead. Considering that there may be intestinal loops in the hernial sac, one can expect the formation of obstruction (ileus) and the development of peritonitis.
Symptoms of inguinal hernia strangulation:
- The hernial protrusion cannot be reduced, is tense and painful when palpated;
- The pain is sharp, constantly intensifying;
- No stool, no gas;
- Nausea, repeated vomiting, hiccups;
- The general condition of the patient is serious.
Treatment of any inguinal hernia is only surgical!
Lymphadenitis : inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes is possible with inflammation of the muscles and/or joints of the leg, external genitalia, STDs, cystitis, adnexitis. Also, malignant tumors of the pelvic organs, bones and muscles of the legs metastasize to the inguinal lymph nodes. With inflammation, the lymph nodes are enlarged, mobile, and sharply painful on palpation. In the presence of metastases, they are often “fused” with surrounding tissues or with each other, the pain is not so pronounced.
Inflammation of the hip joint (coxitis): local temperature is increased, there is swelling and redness; pain during palpation or at rest, intensifies with movement. Localization of pain is the upper outer part of the thigh and groin, right or left.
Pain in the groin in men : occurs with inflammation of the seminal vesicles (vesiculitis) and epididymis (epididymitis), with genital herpes, with lipoma of the spermatic cord (funiculocele). A common cause of pain is cryptorchidism, a congenital defect in which the testicles do not descend into the scrotum, but remain in the inguinal canals. Cryptorchidism can be unilateral or bilateral. At an early age, corrective surgery is possible; in adults, only removal of a defective testicle is possible. With unilateral cryptorchidism, the fertilization function does not suffer; with a bilateral process, the man is infertile.
Pain in the lower left groin can occur with a hematoma - an accumulation of blood after a local injury or puncture, with purulent leaks from the lumbar region (abscess of the lumbar muscle, tuberculosis of the lumbar vertebrae). Varicose nodes of the great saphenous vein and aneurysm (enlargement) of the femoral artery often form on the left, manifesting as pain in the groin area.
Gynecological pain in the lower abdomen
Aching pain is characteristic of tumors and chronic inflammatory diseases of the female genital area, sharp pain is evidence of acute inflammation or a serious surgical condition of the patient. Gynecological pain radiates to the perineum, inner thighs, and rectum.
Severe pain in the lower abdomen due to a delay in menstruation can be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy: if a fertilized egg is implanted into the fallopian tube and the embryo begins to develop, then at about 8-10 weeks the tube ruptures. At this moment, the woman feels a very strong and sharp (“dagger”) pain in the lower abdomen, then internal bleeding begins. Some blood may be released through the vagina. Many women endure literally until the last moment, until they lose consciousness from blood loss. Treatment is exclusively emergency surgery. The damaged fallopian tube is removed, the bleeding is stopped, and a blood transfusion is given if necessary. When one tube is removed, but the other is patent and the ovaries are healthy, the woman is 100% fertile.
Torsion of an ovarian cyst, myomatous node or tumor stalk is also expressed by acute pain, as a complication - peritonitis.
During ovulation, the lower abdomen hurts on one side, the pain is not severe and correlates with the middle of the cycle. During ovulation, rectal temperature is increased compared to normal levels, but only for a short time - up to a day. With inflammation of the abdominal or pelvic organs, pain is combined with a prolonged temperature rise.
Aching pain in the lower back and lower abdomen occurs during menstruation. The origin of the discomfort is associated with the expansion of the cervical canal. The treatment is simple - a couple of No-shpa tablets, warm socks and peace of mind.
Table: possible pain during pregnancy
Nature of pain
To correctly diagnose the disease, the pain symptom must be correctly described and classified.
In order to independently accurately determine the nature of the pain, you need to renounce the painful state as much as possible and remember:
- have similar sensations occurred before;
- whether the type and location of pain have changed since then;
- what events usually precede the onset of illness (for example, physical activity or exposure to rain, etc.);
- what additional symptoms accompany the pain?
This will help to more accurately determine their origin and type.
The pain is dull, closer to aching
If the pain is tolerable, and the lower abdomen aches rather than tugs, then most often such sensations signal problems with the stomach or pancreas.
In this case, the malaise will be accompanied by additional symptoms:
- nausea and sometimes vomiting;
- subfibrile temperature (from 37 to 37.5).
What to do if there are sharp pains in the lower abdomen?
The algorithm for treating acute pain is simple, but requires immediate medical intervention:
- Lie on your back, bend your knees. This will help relax your abdominal muscles and reduce some pain.
- Put cold on your stomach. A plastic bottle with ice wrapped in a towel will do. Cold will help reduce bleeding (if any) and slow down necrosis.
- Without taking any medications, call an ambulance . If you use painkillers or antispasmodics before the doctor arrives, the signs of the disease may become blurred and make diagnosis difficult.
- If you feel dizzy even when lying down, feel nauseated or very weak, have a dry mouth or cold sweat on your skin, be sure to place a cushion under your feet to improve blood flow in the area of the heart and head.
https://youtu.be/jqAnGgCmclI
Let's summarize
- Based on the information received, make only the right decisions.
- Escort the person to the hospital if necessary.
- Do not follow the advice of all-knowing friends. Do not treat your stomach with folk remedies. They may not be safe.
- Never use heat or hot baths for abdominal pain. If there is internal bleeding, it may get worse.
- Make friends with doctors, trust your life and health only in professional hands.
Share with your friends: