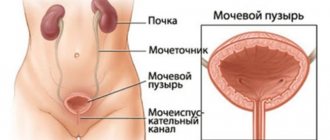
Normally, women should not have discharge from the urethra outside of urination. But anatomical features lead to the fact that a woman’s urethra is often subject to infectious attacks. The appearance of discharge with an unpleasant odor, varying consistency and intensity, indicates the development of an inflammatory process - urethritis. The causes of the disease are different, as are their manifestations.
Pathologies are accompanied by other unpleasant sensations: itching, hyperemia, swelling, burning sensation when urinating. The symptoms manifest themselves most clearly at the beginning of the disease, in the acute period. In the absence of adequate treatment, the disease enters the chronic stage, the amount of discharge decreases, the symptoms disappear, and a false sense of recovery arises.
What does discharge from a woman's urethra mean?
The female body at any age is susceptible to various infections and inflammatory processes. Due to anatomical features, women, more often than men, experience such phenomena in the form of the appearance of a secretory substance from the urethra - the urethra. This is the main symptom that determines disturbances in the functioning of the genitourinary system and the presence of infections in it.
During the menstrual cycle, discharge from the uterus changes. Since the urethra is close to the vaginal wall, it is difficult to distinguish secretions from the urethra from those from the vagina. The secreted secretion can be of different colors, transparency and have a different smell. The reasons for its appearance can also be completely different.
Treatment
Treatment of cystitis consists of eliminating the cause, relieving symptoms and restoring damaged bladder walls. There is no single drug for all types of cystitis.
Only complex therapy can be effective:
- The bacterial flora is affected by cephalosporin antibiotics.
- For viral etiology, Viferon and Gelon are used.
- Fungal infections are suppressed with Nystatin and Fucis.
- Painful symptoms are relieved with Papaverine and No-shpa.
- The bladder is strengthened with uroseptics “Furagin”, “Palin”, “Nitroxoline”.
- Rinse the bladder cavity regularly with plenty of water and berry juices.
- Herbal medicine with kidney tea, bearberry and horsetail extracts, chamomile, and calendula is useful.
If inflammation occurs due to sexually transmitted diseases, the pathogen must first be eliminated.
What color is the discharge?
The secretion secreted by the urethra contains various components, due to the differences of which there are different colors of the substance secreted by the body:
- Yellow-green discharge . They are always formed due to infectious lesions of the urethra due to the abundance of pus. The stronger the infection, the more purulent the discharge. If an unpleasant smell of rot is added to this color, then this is an infection with gonorrhea. With gonorrhea, the discharge is very profuse, accompanied by itching and pain when urinating, in the kidneys.
- White cheesy discharge . Accompanied by candidiasis or thrush (fungal infection). Abundant and thick discharge is formed both in the vagina and in the urethra, accompanied by a sour milk smell.
- Yellow discharge with a reddish or brown tint . Characterized by the accumulation of pus and blood, they appear with urolithiasis and inflammatory processes in the kidneys, bladder and urethra.
- Transparent and mucous discharge is normal; it appears during the period of ovulation, after sexual intercourse, and it is also possible that such a secretion may appear with minor inflammation in the mucous membrane of the urethra.
Often, inflammation of the urethra and, as a consequence, the occurrence of discharge, occurs in women without any special symptoms, but sometimes the following is observed:
- frequent urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain when urinating;
- burning and itching in the urethral area;
- pain in the kidney area;
- vaginal discharge;
- blood in urine.
All these are signs of various diseases in the genitourinary area, as a result of which discharge from the urethra occurs in women.
Symptoms
There are often no pronounced manifestations of pathology, as evidenced by discharge from the urethra in women. However, if a woman has a frequent urge to go to the toilet and discomfort appears when she urinates, then we can judge the development of an infectious or inflammatory process.
Additional signs:
- Burning and/or pain when urinating and white, yellow or purulent discharge;
- There are streaks of blood in the urine;
- Drawing sensations in the ovarian region.
Even if there are no additional symptoms (which is a reason to make an appointment with a gynecologist or urologist), the appearance of discharge from the urethra requires close attention from the woman.
Causes of discharge and unpleasant odor
The appearance of excretory secretion from the urethra occurs for various reasons. When it is transparent and does not have an unpleasant odor, a woman may often not notice their occurrence. But with infectious diseases there is always a change in color, an unpleasant odor and an abundance of secretory substance. The reasons can be both physiological and pathological.
Physiological features
The normal physiological state is a transparent, colorless and odorless secretion secreted from the urethra. In such cases, you should not worry and carry out any therapeutic actions.
This happens in the following cases:
- during ovulation, when the egg descends into the fallopian tube, clear, thick substances appear from the urethra and may appear within several days;
- after sexual intercourse, as a result of excitement and the release of large amounts of hormones;
- poor nutrition.
After a certain period of time, the secreted secretion, which arose due to the listed physiological reasons, ceases to appear and resumes when these circumstances are repeated. But when it acquires an unpleasant odor and changes color and transparency, this indicates pathological processes.
Pathological diseases
The main cause of discharge from a woman’s urethra is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra (urethritis).
There are several reasons for the occurrence of urethritis and the appearance of various secretory substances:
- Infections . The most dangerous are sexually transmitted infections, as well as all other sexually transmitted infections (gonorrhea, syphilis, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, herpes virus and others). There are nonspecific bacterial infections caused by E. coli, fungi, streptococcus and staphylococcus. The course of the disease in the first days is usually asymptomatic, which is very dangerous. The disease becomes chronic. Exacerbations of the disease occur after sexual intercourse or hypothermia. The color and smell of secretion from the urethra is specific to a certain type of infection. A woman feels a burning sensation when urinating and a frequent urge to go to the toilet. Basically, infectious urethritis occurs after contact with a sexual partner, that is, it is transmitted sexually.
- Non-infectious urethritis . The causes of this type of disease can be: injuries to the urethra during urological, gynecological manipulations, as well as rough sex using special devices; as a result of an allergy to synthetic underwear, pads or when taking contraceptives.
- Urolithiasis disease . When sand or small stones move, the mucous membrane of the urethra is injured, it swells and infection penetrates into the wounds. Discharge from the urethra includes blood, and after a while - pus, if you do not take antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
In case of weakened immunity and the presence of provoking factors (hypothermia, mechanical damage), non-infectious urethritis can become infectious.
Causes
Discharge from the urethra of women has different causes - we list the main ones:
- Cystitis. Kidney stones descend down the urethra, injuring it - this contributes to the development of inflammation;
- A number of sexually transmitted diseases. Increased secretion in women, if accompanied by frequent urination, may be a consequence of the proliferation of trichomonas, chlamydia and a number of other microorganisms. For example, gonococcus, the causative agent of gonorrhea, also causes discharge;
- Decreased immunity;
- Mechanical damage to the urinary canal. Occurs after accidents or disruption of the integrity of the mucous membrane during medical procedures;
- Spending a long time in the cold. This affects the activity of bacteria in the body in women;
- Poor nutrition – when a woman eats sour, fatty or bitter foods in excessive quantities.
- Cancerous formations in the urethra also contribute to the appearance of inflammation in it.
The main causes of discharge are various sexually transmitted diseases. A woman becomes infected through unprotected sexual intercourse. In addition, the disease is affected by personal hygiene rules, non-compliance with which leads to infection of the urethral canal.
We must remember: prolonged emotional stress in itself can cause frequent urination. But if discharge is added to it, then this, as a rule, is already a sign of an infectious disease.
Causes of urethral discharge during pregnancy
When a woman is expecting the birth of a child, her body works under load: hormonal levels change, the load on the organs of the excretory system increases. All this leads to an increase in the appearance of secretions from the urethra and vagina, which have a characteristic color: yellow or brown. As the period increases, the fetus also increases. As a result, pressure on the pelvic organs increases, the bladder becomes deformed, urine is retained in it and becomes dark in color when urinating. This is not a pathology.
But in the case when a pregnant woman experiences all the symptoms of infectious urethritis: itching, burning, frequent urination, purulent discharge mixed with blood and an unpleasant odor, doctors take urgent measures to determine the cause and treat such pathologies.
The fact is that these types of urethritis can lead to pathologies and even death of the unborn child in the womb or cause premature birth, so it is very important to diagnose the cause of inflammation of the urethra in time.
Other causes of discharge
Discharge from the urethra in a woman can be caused by the following factors:
- A common reason for the occurrence of female urethritis can be a low degree of general defense of the body - a weakened immune system. In this case, for the appearance of discharge, a slight hypothermia will be enough, which will contribute to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
- One of the most dangerous causes of bleeding can be neoplasms in the kidneys. They can cause damage to organ tissue, which will be the reason for their appearance. In such circumstances, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Neoplasm in the kidney
- Pathologies of intestinal microflora. Streptococcus and other pathogenic bacteria can contribute to their occurrence.
- The presence of discharge in a woman during pregnancy requires special consideration. Pregnancy has a combination of determining factors, the main one of which is the same low threshold of the body’s general defense. You can also include normal physiological processes here: the enlarged uterus, under its weight, presses on the urethra. This leads to another type of urethritis - non-infectious. Ignoring this disease can lead to fetal developmental abnormalities.
- Also, reduced immunity is indicated by the presence of white discharge with a cheesy consistency. This symptom is characteristic of thrush or candidiasis. Another factor influencing the appearance of this fungus is poor diet.
There are many reasons for the appearance of discharge from the urethra. Among the most common:
- Inflammation caused by the movement of stones in urolithiasis.
- Caused by sexually transmitted infections.
- The urinary system often becomes inflamed after severe hypothermia.
- Violation of the principles of healthy eating by including fatty, salty or excessively spicy foods in the daily diet.
- Decreased immunity.
- Malignant neoplasms of the urethra and others that provoke inflammatory processes.
It is necessary to determine the cause when contacting a doctor. The type of treatment depends on clearly identifying the appearance of the discharge. This includes a visual inspection that determines the characteristics of the substance:
- Mucus without an unpleasant odor and without color may be a manifestation of the normal functioning of the excretory systems. In this case, the patient should not complain of burning and pain.
- Normally, liquid urea discharge may occur.
- A white cheesy substance becomes the basis to assume an inflammatory process. Diagnostics are required to identify the cause of the inflammatory process.
- In women, yellow discharge from the urethra occurs with gonorrheal urethritis.
- When the substance has a greenish color, has purulent and blood streaks, a check for the presence of a sexually transmitted diagnosis is required.
- White discharge from the urethra in women is observed with thrush. The substance has a cheesy structure and no odor.
- Foamy whitish or grayish variants occur with bacterial vaginosis. They are distinguished by an unpleasant “fishy” smell. The substance may look like snot in appearance.
- The foamy gray-green discharge that appears with trichomoniasis has a similar odor.
- With urolithiasis, the appearance of sand and flakes with solid particles is noted.
- Normally, increased secretion without itching and discomfort is observed during pregnancy.
Diagnostic methods
A woman, even with mild symptoms of discomfort and the appearance of substances from the urinary canal, should definitely consult a doctor. First, see a gynecologist, since often the cause may be a gynecological disease or infection. If necessary, the women's doctor will give a referral to a urologist.
Most often, a specialist prescribes the following types of studies:
- general urine analysis;
- general blood analysis;
- bacteriological analysis for the presence of a certain infection (scraping from the walls of the urethra);
- urine analysis using the “three-glass” test method (according to Nechiporenko);
- bacteriological analysis for the presence of infection;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder.
After passing all the prescribed tests and examination methods, the specialist, having studied the results, as well as all the woman’s symptoms and complaints, establishes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes therapy.
Diagnostics
First, the doctor interviews the patient. He learns from her about accompanying symptoms, complaints, and the duration of signs of the disease. After this, diagnostics is carried out: smear microscopy is performed. Sometimes the urethra is examined using a special cystoscope apparatus.
Additional methods of examining the genitourinary system are also used to confirm the diagnosis:
- Bacterial culture,
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs,
- Urine and blood tests.
Based on all examinations, the doctor can make a diagnosis.
Many diseases of the genitourinary system manifest themselves insignificantly in the initial stages. You should contact a competent specialist as soon as possible: he will help relieve the symptoms of the disease.
Recommended Treatment
In most cases, a course of antibiotics is prescribed depending on the specific nature of the bacterial infection. It is selected individually. Previously, the doctor may prescribe a test for a certain antibacterial drug for a more effective effect on the infection.
It is also important to simultaneously take immunomodulatory drugs, follow a diet, and give up sex life. Additionally, it will be useful to take baths or soaks in the urethral area with herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect. The use of tampons and suppositories with therapeutic and anti-inflammatory effects, which are prescribed by a doctor, is used comprehensively.
So, if a woman notices transparent discharge from the urethra during the period of maturation and release of the egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube, then this is a normal, physiological process that will end in two to three days.
But in the event that discharge of any color with an unpleasant, specific odor appears, you should definitely consult a doctor, undergo an examination and find out the cause. Because urethritis that is not completely cured, especially caused by a bacterial infection of any kind, will lead to chronic inflammatory processes in the kidneys and other organs of the female body.
Methods and principles of treatment
If the cause and the pathogenic organism that forms the basis of the discharge are detected, the doctor prescribes adequate medical treatment, which depends on the patient’s condition, as well as on the presence of a particular disease.
An important principle of therapy is to immediately begin to influence the cause of the disease.
So, if the departments are bacterial in nature, adequate antibiotic therapy to destroy pathogenic bacteria in the girl’s body. The most common drugs prescribed today for diseases of the genitourinary system are Amoxiclav , Azithromycin , Clarithromycin and others. In addition, sulfonamides, which are more effective and have a wider range of effects, are excellent in fighting bacteria.
Also among the prescribed drugs for the patient, in order to influence the infection, is an antimicrobial complex - for example, Metronidazole , Trichopolum .