Neuralgia refers to severe shooting pain that occurs due to a damaged or irritated nerve. Neuralgia can affect any part of the body, causing mild to severe pain. Certain medications and surgical procedures can effectively treat neuralgia.
Severe neuralgia can affect a person's ability to perform everyday tasks and can affect their quality of life.
Neuralgia has many possible causes, including:
- infections such as shingles, Lyme disease, or HIV
- pressure on bone nerves, blood vessels or tumors
- other medical conditions such as kidney disease or diabetes
- aging
This article examines the different types of neuralgia, their symptoms, and available treatment options.
The main causes of neuralgia
The most common causes of neuralgia are identified. Among them:
- Nerve compression. This condition develops as a result of an increase in the lumen of a nearby vessel, tumor growth, or disruption of the integrity of the bone or ligamentous apparatus.
- Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes. Elevated sugar levels lead to destruction of the myelin sheath. The disease develops as a result of prolonged absence of therapy or lack of effect from therapy.
- Infectious process. The development of symptoms is provoked by the herpes simplex virus, chickenpox, human immunodeficiency, as well as treponema pallidum.
- Multiple sclerosis. Myelin destruction occurs as a result of autoimmune disorders. As the disease progresses, the patient's condition worsens.
More rare causes
A more rare cause of neuralgia may be:
- Porphyria. Hereditary pathology is accompanied by changes in the skin, circulatory and digestive systems.
- Chronic pathology of the urinary system.
- Use of medications such as cisplatin or vincristine.
- Chemical poisoning.
- Traumatic impact.
Surgery
Certain surgical procedures can help relieve neuralgia pain when the condition does not respond to treatment.
Examples of surgical procedures that may help treat neuralgia include:
Microvascular decompression : Helps remove an enlarged blood vessel affecting a nerve. The procedure involves placing a soft pad between the blood vessel and the affected nerve.
Stereotactic surgery : This is a non-invasive procedure that directs highly concentrated beams into the root of the damaged nerve. The radiation disrupts the transmission of pain signals to the brain.
Percutaneous balloon compression : This involves inserting a small balloon into the affected nerve. The balloon is inflated, causing controlled, deliberate nerve damage. This procedure prevents the affected nerve from sending pain signals to the brain. However, the effects of the procedure usually wear off after 1-2 years.
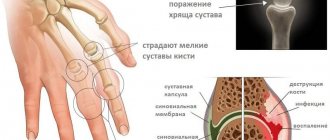
Types and symptoms of neuralgia
In clinical practice, there are several types of neuralgia, which are divided depending on which peripheral nerve is affected. Among them are:
- Trigeminal neuralgia. This nerve is most often affected, which is associated with providing tactile sensitivity on the face. The disease can be manifested by the development of pain and vegetative reactions. The pain is acute and piercing in nature, causing severe discomfort in the patient and worsening the quality of life. It occurs only on the side of the face where the nerve is affected. Autonomic reactions are manifested by lacrimation, salivation and the production of excess contents from the nasal cavity. Symptoms worsen when moving or talking. If the lower branch of the trigeminal nerve is damaged, difficulty opening the jaw may occur, followed by atrophy, spasms and twitching of individual muscle fibers. The disease is characterized by a long course with periods of exacerbation and remission.
- Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve. Due to this branch, sensitivity is provided in the tonsils, ears, tympanic cavity and tongue. In addition, the functioning of the parotid glands and the motor activity of the muscles in the pharynx are monitored. Acute piercing or paroxysmal pain can be localized behind the ears, the back of the tongue, and also in the tonsil area. The patient experiences pronounced disturbances in sensitivity, for example, its complete loss or a change in taste. All food becomes very monotonous, but may also be bitter or sour. Disruption of the salivary glands leads to dry mouth. The development of a pathological clinic is provoked by talking, swallowing or yawning. The first signs of the disease can be noted when eating hot food or drinks.
- Damage to the pterygopalatine ganglion. Its development is accompanied by inflammation in the ENT organs. The pain is localized in the orbit, root of the tongue and teeth of the upper jaw. Irradiation occurs in the temporal and cervical region. Most often, its exacerbation develops at night. Its duration is several minutes or hours. Following an exacerbation, remission occurs, which can reach several months. An exacerbation can be triggered by overwork, a cold or excessive emotionality.
- Herpetic neuralgia. This type is a complication of herpetic infection. Most often it can be detected in elderly patients, as well as in people with weakened immune systems. The risk group includes patients with human immunodeficiency virus. The pain is localized along the affected area. It can have different characteristics, most often it is dull, burning or shooting. Symptoms continue for a long time, in some cases they bother patients for several months.
- Roth's disease. Discomfort or burning occurs on the outer thigh. In rare cases, the duration persists until the cause is eliminated.
- Intercostal neuralgia. The pain, which sharply increases during rotation of the torso, is localized in the chest area. The development of intercostal neuralgia is provoked by sneezing, coughing, and talking. Severe discomfort occurs when trying to touch the ribs.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Neuralgia develops in both adults and children as a result of various causative factors. They vary depending on the location of the lesion. The main reasons are the following: benign and malignant neoplasms arising in the cervical spine; osteochondrosis and degenerative changes in intervertebral discs; gout and cervical vertebrae injuries.
Nerve lesions are often infectious. The causative agents can be both viruses and bacteria. For example, in most cases, intercostal lesions are represented by herpetic neuralgia.
Predisposing factors to the development of the disease:
- physical inactivity leading to disturbances in muscle tone;
- obesity and overweight;
- chronic infectious foci in the body: sinusitis, caries, pulpitis, etc.;
- diabetes mellitus and other metabolic disorders;
- chronic alcoholism;
- in women - pregnancy;
- chronic stress or acute stressful situations (the psychosomatics of neuralgia is still being studied by specialists).
A given patient may simultaneously have several risk factors for the disease. In this case, treatment should be aimed at eliminating each of them.
Diagnostics
Confirmation of the diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia is often carried out without the use of additional diagnostic methods. Its use is necessary to exclude other pathologies, as well as to exclude various complications. An important step in making a diagnosis is to clarify the patient’s complaints. The doctor clarifies the time of onset of symptoms, provoking factors, nature and duration. The response to taking medications or other manipulations that can reduce the severity of the disease is assessed. These include heating, massage or applying a tight bandage.
Important information
A neurological examination is necessary to determine the location of the pathological focus, as well as the sensitivity of the skin, the strength and tone of muscle fibers. The severity of the main reflexes is assessed.
If necessary, consultation with related specialists is required. Additional research methods can be used:
- Complete blood test with sugar level measurement.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Its implementation is indicated to exclude tumors or multiple sclerosis in the brain.
- Electromyography. The method is necessary to test the conduction of nerve impulses and muscle reactions.
Diagnostic measures
Only a doctor can determine neuralgia. To select therapy, it is necessary to establish the cause of the disease. Diagnostic measures are carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Collection of complaints and medical history.
- Clinical examination using questionnaires to determine the nature of pain.
- Laboratory and instrumental research methods.
During the collection of anamnesis, the neurologist learns the characteristics of the occurrence of pain, their nature, as well as the factors that provoke the appearance of pain. It is important to identify its location, prevalence and duration. During the survey, existing disorders are identified: muscle weakness, the appearance of paresthesia, etc., as well as concomitant diseases.
During a clinical examination, the doctor determines the nature of the pain. In case of damage to nerve structures, it is neuropathic, i.e. it is localized in the anatomical area of innervation of a particular nerve. This makes it possible to distinguish it from psychogenic or muscular neuralgia. A neurological examination reveals sensory disturbances, decreased muscle strength and reflexes. To determine the intensity of pain, special scales and a diagnostic questionnaire for neuropathic pain are used.
Changes in laboratory tests are typical for neuralgia that occurs due to infection. A clinical blood test determines an increase in the number of lymphocytes and an acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. In biochemical analysis, the level of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen increases. The identified deviations indicate an inflammatory process in the body.
Instrumental examination methods are used to identify the cause of nerve damage. If osteochondrosis, benign or malignant tumors, as well as traumatic changes are suspected, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is performed. Electrodiagnostic evoked potential studies are used to assess the structural integrity of nerves.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with pain syndromes of a muscular or psychogenic nature. In the case of neuropathic pain, the localization of unpleasant sensations corresponds to the area of innervation of the affected nerve. Psychogenic disorders are manifested by the transient nature of the clinic, as well as their occurrence in the presence of “observers”. Muscle pain is accompanied by impaired tone of the back muscles. An ECG can be used to distinguish neuralgia from heart pain.
Drug treatment
In order to determine how to treat neuralgia, you need to seek help from a specialist. The doctor, based on the cause, severity and main symptoms, determines the complex of therapy. Drug therapy is used in systemic and local form.
Pills
Neuralgia, the symptoms of which are not clearly expressed, can be eliminated using the tablet form. Among them are:
- Muscle relaxants.
- Analgesics.
- Neuroprotectors.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- B vitamins.
- Sedatives.
Injections
The injection form is indicated for quickly eliminating the clinic and making the patient feel better. Therapy is carried out for severe pain or autonomic disorders. Among the most effective injection forms are:
- Painkillers. Injections eliminate pain in a short period of time.
- Anti-inflammatory. After administration, the swelling and inflammatory reaction in the pathological focus are removed, due to which the processes of blood circulation and trophism are improved.
- Muscle relaxants. The mechanism of their action is to relieve muscle tone, which facilitates motor activity.
- B vitamins. With regular use, a neuroprotective effect develops with the protection of the myelin sheath.
Classification of pathology
Depending on the type of occurrence, the disease is divided into idiopathic and secondary. Idiopathic is assigned to patients if it is not possible to establish a specific cause for the development of symptoms. Secondary disorders occur against the background of any disease: herpetic infection, malignant tumor, etc.
In neurology, pathology is divided according to the type of course:
- acute – occurs with severe pain of a constant or paroxysmal nature;
- chronic – manifested by periodic relapses of symptoms.
In most patients, acute neuralgia becomes chronic due to late consultation with a doctor.
Treatment of neuralgia at home
Neuralgia symptoms that bother the patient can be treated at home only after the cause has been established. For this purpose, medications and non-drug methods are used, which include physical therapy, physiotherapy and folk remedies. To achieve maximum therapeutic effect, it is recommended to combine them.
It must be remembered that non-drug methods do not completely eliminate the cause of the disease, but only make it easier to feel better, moving the process into remission.
Prevention
Specific prevention of neuralgia of the intercostal nerves has not been developed; general strengthening measures will help prevent the development of pathology. Recommended:
- a healthy lifestyle, including regular moderate physical activity and a rational, balanced diet;
- hardening of the body;
- timely treatment of spinal diseases, chest injuries, pathologies of internal organs;
- measures to help prevent spinal curvature or treat an existing curvature;
- avoiding hypothermia;
- work in comfortable conditions, with prolonged forced body positions, take breaks for a short warm-up.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
https://youtu.be/ufhTBj1wE80
Treatment of neuralgia with folk remedies
The use of traditional methods to eliminate the pathological symptoms of this disease is widespread.
Helpful information
Most often they are prescribed to patients for whom medications are contraindicated; in addition, folk remedies can be part of an integrated approach.
They are recommended to be used during remission in order to prevent exacerbation. The most popular recipes include:
- Chamomile decoction. To prepare it, you need to pour chamomile with hot water in the ratio of one tablespoon per 200 ml of water. The infusion time is 15 minutes, after which the mixture is filtered. To achieve a therapeutic effect, it is necessary to rinse, holding water in the mouth for 5-7 minutes. The plant helps eliminate inflammatory reactions.
- Althea root decoction. To prepare the solution, finely chopped root is poured with hot water and infused for 8-9 hours. After cooling, the mixture is filtered and used to apply compresses to the affected area. It is recommended to apply the compress at night for longer contact.
- Egg. A heated boiled chicken egg applied to the site of pain helps eliminate it by relieving inflammation and tissue swelling.
Independent attempts to eliminate pathological symptoms can lead to a deterioration in health and progression of the disease. Therefore, in the early stages after the appearance of complaints, it is necessary to seek help from a doctor.
Why is neuralgia dangerous?
Long-lasting pain syndrome leads to the fact that a person becomes irritable, he has mood lability and an anxiety disorder. Negative emotions can provoke somatic pathology - angina pectoris, arterial hypertension, etc. This causes a decrease in performance and social maladjustment.
Untreated pathology leads to persistent depression. The patient may not seek medical help for a long time, trying to independently cope with pain with the help of non-steroidal analgesics. Depressive disorder tends to progress, affecting personal and professional life.
https://youtu.be/fUloSy0VUKg
Traditional methods
In addition to the treatment options listed above, acoustic neuritis can be treated with folk remedies. Naturally, before applying these recommendations, it is imperative to consult a doctor in order to avoid complications.
https://youtu.be/-tyxu8TzdlE
Golden mustache
One large and two small leaves of this herb are finely crumbled and poured with boiling water. After which it is boiled for 4–5 minutes and infused in a thermos for up to 2 hours. It is necessary to consume 1 tsp four times a day. This tincture should be given to the patient for at least 3 weeks.
Juniper tincture
A 100 ml bottle is filled exactly halfway with juniper berries. The second half is filled with boiled water. The resulting substance is infused in a dark place for three weeks.
There is no need to drink the tincture; 3-4 drops are dripped into the snakes every day. The positive effect appears after 2 weeks of use.
Onion drops
You need to squeeze the juice out of one onion and mix it with vodka in a ratio of one to four (1 part onion juice to 4 parts vodka). Drop this solution into the ear no more than 2 drops per day. It is advisable to consult a doctor before use.
Garlic pouch
Three drops of camphor oil are mixed with a crushed clove of garlic and the resulting substance is wrapped in gauze. This bag is placed in the sore ear and is not removed until a burning sensation occurs. It's important not to overdo it. You can use this bag until the painful symptoms disappear completely.
At home, you can also use mumiyo tincture. A compress is made from 10% of the tincture, which is inserted into the sore ear, and you can additionally take 20 grams of mumiyo before meals in the morning. The course of treatment is no more than 10 days, after a break for 10 days and repeat. This can be done 3-4 times.
Soy tincture
Soybeans are soaked for up to seven hours in boiled water, after which the beans are cleaned and crushed. Pour boiling water over a third of the glass and bring to a boil. After straining, you can drink the decoction with honey before bed until the symptoms stop.
There is a recipe for instilling a solution based on chloramphenicol into the ears, but we will not describe it; if your doctor deems it necessary, he will tell you this recipe.
And probably the most exotic type of therapy is treatment with leeches.
Acoustic neuritis can be treated with hirudotherapy.
The procedure is as follows: the patient is applied 4-5 leeches to the area behind the ears. It is necessary to carry out up to 7–9 sessions until complete recovery.
So, wherever the disease finds you, at home or at work, remember to consult a doctor and do not self-medicate. This disease is insidious, since hearing loss can occur due to banal inflammation.
- Treatment with garlic. Before going to bed, you need to finely chop the garlic and mix it with three drops of any oil. The resulting mixture should be carefully folded into gauze, wrapped and inserted into the ear. After a burning sensation appears, you can remove the garlic.
- Help from the golden mustache. You will need one large or several small leaves of this plant. They should be finely chopped and cooked for just a few minutes. Let it brew in a thermos. The resulting decoction is recommended to be consumed three times a day, one teaspoon.
You should resort to alternative medicine only after consulting your doctor. Otherwise, the disease will progress, which can lead to complete hearing loss.
It is not possible to completely get rid of acoustic neuritis using folk remedies, but you can alleviate the condition and improve the effect of the main course of therapy. The use of such methods is allowed only after consulting a doctor.
The following traditional methods can be used as a supplement to the course of ear treatment:
- The auditory nerve can be treated with a compress. It is based on garlic ground into a pulp and 2-3 drops of camphor oil. The finished mixture should be placed on gauze and then applied to the ear. It is better to do this at night, and if a burning sensation occurs, you need to urgently remove the compress and rinse the auricle;
- A decoction made from golden mustache can help relieve inflammation. To prepare, you need to take 3 leaves of this plant and pour 1 liter of them. water and then boil for 5 minutes. Next, the medicine should be allowed to brew for 24 hours, and then you can drink this remedy 3 times a day, 1 tsp.
Treatment of acoustic neuritis with traditional methods is an addition to traditional therapy. It is used as an auxiliary tool, usually to relieve hidden inflammatory processes and improve immunity.
- Pour boiling water over thyme herb (4 tablespoons) and wrap in gauze. While hot, apply to the ear for 10 minutes. Duration – 10 days.
- Mumiyo (0.2 g tablets) should be taken on an empty stomach for 10 days. In parallel with this, compresses are made from a 10% mummy solution. There are 3 courses with 10-day breaks.
- Calendula officinalis flowers, hawthorn fruits (1 part each), rosehip, Rhodiola rosea root, string and safflower leuzea (2 parts each), brown rose hips (3 parts) are mixed. One tablespoon of the mixture is poured with boiling water. The infusion is taken three times a day, 70 ml.
What it is?
Ear ganglion neuralgia is irritation of the nerve roots of the ear ganglion , which is formed from autonomic and sensory neurons.
This system is responsible for the proper functioning of the salivary glands and regulates the sensitivity of the ear canal.
In addition, the ear ganglion is responsible for the sensitivity of the skin between the temple and lower jaw. Therefore, when it is damaged, sharp pain, increased salivation and ear congestion occur.
The pathological process goes by several names: ganglionitis of the nerve ganglion or neuralgia of the ear . The auricular node belongs to the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve, so if it is damaged, there is a risk of developing trigeminal neuralgia.
The child has
Not only adults, but also children can damage the auditory nerve. There are no significant differences in causes, symptoms and diagnostic methods between neuritis in children and adults. Any reason typical for an adult (with the exception of age-related changes) can provoke inflammation of the auditory nerve in a baby.
The main symptom for a child, the same as for an adult, is hearing impairment, which is aggravated by accompanying symptoms.
https://youtu.be/y1Mj6o91KQw
The main difference is the treatment, or rather, the dosage of the drugs prescribed. After all, a child’s weight and immunity are much smaller than an adult’s, which means he needs much less of the active substance of a particular medicine.
Main signs of the disease in women
There are no specific signs of intercostal neuralgia in women, so it is often confused with a number of other pathologies. But characteristic symptoms help differentiate it from other diseases:
- Aching or paroxysmal pain in the chest area.
- Increased discomfort when sneezing or coughing.
- Skin redness or excessive paleness.
- Pain in the epidermis when pressed.
- Stiffness in the chest area.
Associated symptoms include bouts of sweating, sudden elevation of the body or convulsions, even at rest, and numbness of the affected area. These symptoms of intercostal neuralgia will help to suggest a violation, but the diagnosis can only be confirmed by a doctor based on a visual examination and a series of studies. Usually this is a urine and blood test, x-ray or MRI. Additionally, an ECG is performed to exclude heart pathology.
Symptoms
Symptoms of neuralgia of the back depend on the part of the spine where the pathology is located. It may be located in:
- cervical-occipital;
- chest;
- lumbar region.
Patients experience severe and shooting back pain, which occurs as a result of compression of the nerve endings. They are accompanied by general weakness and increased sweating. Palpation in the area of the affected nerve causes the patient severe discomfort.
Cervical region
Cervical neuralgia is manifested by severe pain that affects the head and eye area. A characteristic sign of the disease is numbness in the fingers.
Thoracic region
Neuralgia of the thoracic spine has the most pronounced symptoms. The pain in the back is so severe that patients mistake it for a heart attack, a manifestation of pneumonia. Unpleasant sensations radiate to the arm, abdominal area, and shoulder blades.
The pain is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- decreased blood pressure;
- pale skin at the site of the lesion;
- increased sweating.
An attack of pain is provoked by coughing, sneezing or emotional speech.
Lumbar
Characteristic symptoms of lumbar neuralgia are pain and muscle spasms. They occur after sharp turns of the body or physical exertion. Provoking factors are hypothermia, stress.
Additional signs of pathology are:
- muscle swelling;
- trembling, weakness;
- increased sweating;
- pain on palpation of the damaged area;
- redness of the skin of the lower back.
Neuralgia of the lumbosacral spine occurs suddenly and in attacks. With an advanced disease, it may not leave the patient in a lying position.
Non-drug therapy
Treatment of muscular neuralgia also involves non-drug therapy, including:
- physical therapy;
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- use of magnet and electrophoresis.
https://youtu.be/WYB3Nw3K1W8
Various types of physical exercises, such as race walking, swimming and yoga, can also be beneficial. Non-drug therapy should be carried out regularly, as it helps reduce the number and intensity of attacks.
Muscular neuralgia is a fairly serious and dangerous disease, which is much easier to prevent than to treat over a long period of time.
General
Nerve branches of the cranial area
The symptoms and treatment of neuralgia are interrelated. If you notice the first signs of the development of such a disease, you should immediately contact a neurologist. Diagnosis of pathology begins with an initial examination of the patient and examination of his complaints.
In order for the diagnosis to be as accurate as possible and the treatment to be effective, you need to undergo additional examination. Most often, doctors prescribe instrumental electroneurography, especially if the cause of neuralgia is injury. In addition, magnetic resonance imaging may be needed to detect intervertebral hernia, tumor, protrusion and other diseases.
Reviews
Most of the patients managed to cure intercostal neuralgia, since they consulted a doctor on time and followed his recommendations. But in some cases, therapy was delayed due to diagnostic difficulties.
Valery, 39 years old: “I had my first attack of neuralgia 2 years ago. I suffered for a week, and then went to the doctor. The pain was due to hypothermia. I was prescribed medications, vitamins, and physical therapy. I completed the course and the pain subsided. Now I am fighting the disease with the help of physical therapy and massage. There was no relapse."
Alina, 45 years old: “I turned to a neurologist at the very height of my illness. To relieve the pain, I was prescribed NSAIDs. Then I found a good manual therapist who helped consolidate the result. In addition, she attended reflexology sessions. At home, she massaged the sore areas with warming ointments and performed a set of exercises. It’s been a year now and the pain doesn’t bother me.”
Elena, 42 years old: “I believe that first of all you need to understand what exactly caused the intercostal neuralgia. If there are problems with the spine, then there is no point in taking a lot of medications, putting blockades, you need to find a good chiropractor. I was given blockades for about 4 weeks to relieve severe pain, but there was no point, it returned very soon.
Anatomy and physiology of the auditory nerve
The ear itself has three sections:
- External.
- Average.
- Internal.
The physiology of human hearing is such that all three sections are involved in its perception and processing, and each of these sections has its own function.
The outer ear picks up sound (acts as a kind of locator), recognizes its source, frequency and conducts it to the eardrum.
The anatomy of the outer ear also involves protecting the entire system from dirt, infections, etc. due to earwax and small hairs growing inside.
The middle ear has the following structure:
- Tympanic cavity.
- Auditory bones (hammer, incus and stapes).
The middle ear plays only a conducting function.
The inner ear has:
- Snail.
- Semicircular canals.
The diagram of the inner ear suggests the presence of not only an organ responsible for sound and its transmission, but also a special department that performs the function of maintaining balance.
The auditory nerve originates from the auricle, or to be precise from its deepest part, the inner ear. It is characterized by the presence of two branches:
- The part responsible for hearing.
- The part responsible for balance.
Acoustic neuritis is often confused with a disease such as sensorineural hearing loss, however, this is completely wrong.
Another common misconception is the comparison of neuritis with eustachitis. Eustachitis is a disease of the middle ear, and it has the same symptoms as neuritis, but not the causes.
In addition, the cause of hearing loss is often damage to the outer, middle or inner ear, which also has nothing to do with the nervous system.
The auditory nerve is the conductive part of the hearing analyzer. It consists of several thousand nerve fibers, each of which receives a specific sound frequency. Fibers from the upper part of the cochlea transform low-frequency waves, and from the base - high-frequency sounds.
The nerve signal is recognized in the temporal regions of the brain, then it is processed and correlated with the person’s sensations. This is a very complex physiological process that provides the ability to hear sounds and determine their origin.
We invite you to read: Features of treatment of urachus cysts in women, men and children
This disease usually affects the subcortical hearing centers, hair cells and nerve endings. Microcirculation is disrupted, hypoxia of the cells of the nerve trunk gradually develops, which becomes inflamed and ceases to function fully.
Consequences
If you have decided that going to the doctor and taking care of your own health is not your thing, then you should find out what awaits you in the event of an advanced case of the disease.
Since neuralgia most often affects the extensor muscles of the spinal region, as well as the muscles located near the shoulder blades and shoulders, therefore, it will spread with great speed throughout the entire lumbar-thoracic region of the back.
The acute pain that arises will intensify, the attacks will begin to radiate from the lumbar region to the thoracic region, and will become stronger when making the slightest movements of the spine and chest. As a result, weakness of the abdominal muscles, respiratory apparatus, and human stiffness will occur.
There is also a high risk of inflammatory processes in the intervertebral tissues. From here, herpes, shingles and other infectious diseases often begin to appear, characterized by the appearance of painful blisters with fluid on the body.
The body temperature will begin to rise, and the biochemical composition of the blood will change. The disease will go away, but then return with a hundredfold complication and worsening of the condition.
If neuralgia is completely neglected, the risk of developing neuritis will increase, which will serve as an impetus for atrophy of the musculoskeletal system and paralysis.