To diagnose appendicitis and treat it, what could be easier? This is what most people who are not involved in medicine think so, but know about this disease only from the words of friends or from various Internet sources. In reality, everything is not quite like that. Appendicitis is perhaps one of the most difficult diagnoses in surgery. And even modern diagnostic methods do not always allow doctors to clearly determine what ailment the patient has within a few minutes. So how is this disease treated? Is surgical removal of appendicitis always necessary or are there alternative treatment methods? What is the role of antibiotics in the treatment of this disease?
How to suspect appendicitis
Absolutely anyone can suspect appendicitis. People always think about this disease when a patient experiences intense abdominal pain that does not go away completely while taking antispasmodics or analgesics. However, in order to be confident in the diagnosis, doctors have to use various diagnostic procedures. These include:
- A general blood test.
- Ultrasonography.
- Laparoscopic examination.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe any other study: x-ray, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, biochemical blood test, urinalysis, etc.
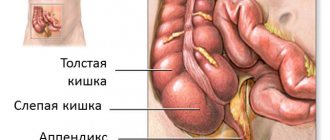
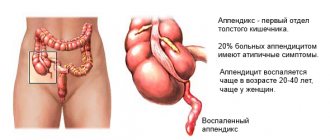
However, no less important is communication with the patient and examination of the abdomen. It is important for the doctor to know when the pain began and what the patient himself associates it with, what helps relieve the pain, and what ways the patient tried to help himself before calling an ambulance. Pain with appendicitis most often begins in the epigastric region (the area immediately under the xiphoid process of the sternum), then increases and gradually “descends” to the right groin area. However, this is very individual, and the localization depends, first of all, on the location of the vermiform appendix itself. When attempting to examine the abdomen, the patient experiences severe pain. In addition to pain, there may be a number of symptoms that will help determine the diagnosis: fever, nausea and vomiting, pale skin, palpitations, etc.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - a
| Treatment of lung abscess |
| Treatment of brain abscess |
| Treatment of liver abscess |
| Treatment of splenic abscess |
| Treatment of overuse headaches |
| Treatment of pituitary adenoma |
| Treatment of adnexitis |
| Treatment of acromegaly |
| Treatment of alcoholism |
| Treatment of alcoholic hepatitis |
| Treatment of alcoholic liver disease |
| Treatment of allergic dermatitis |
| Treatment of alopecia |
| Treatment of alveolitis |
| Treatment of amoebiasis |
| Treatment of liver amyloidosis |
| Treatment of renal amyloidosis |
| Treatment of sore throat |
| Treatment of aneurysm |
| Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis |
| Treatment of anuria |
| Treatment of kidney aplasia |
| Treatment of aplastic anemia |
| Treatment of ovarian apoplexy |
| Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis) |
| Treatment of ascariasis |
| Treatment of ascites |
| Treatment of pulmonary atelectasis |
| Treatment of atherosclerosis |
| Treatment of atypical pneumonia |
| Treatment of autoimmune hepatitis |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.
Is surgical removal of appendicitis necessary?
After the doctor decides on the diagnosis, he is faced with the fundamentally important question of how to treat the patient: surgically or conservatively (that is, with medication). The decision is made individually and depends, first of all, on the form of the disease. However, in our country, the majority of practicing doctors are of the opinion that the leading method of treating this disease is surgical removal of appendicitis. Nevertheless, there are studies that show that the use of certain antibiotics helps reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process and avoid surgery.
There are situations in which surgery is vital and no discussion about its expediency is acceptable. We are talking about conditions when suppuration of the appendix occurs, that is, the patient has signs of phlegmonous or gangrenous appendicitis.
In this case, the appendix becomes a reservoir for infection: given its anatomical features, its spontaneous release from the inflammatory masses is impossible. As appendicitis progresses, its walls become thinner, and the unfortunate outcome is perforation and spillage of its contents into the abdominal cavity with the development of peritonitis. In this case, the patient needs emergency surgery, otherwise his life is at risk. Timely removal of appendicitis allows you to prevent this complication and save the person.
What diseases can it be associated with?
Appendicitis is not one of those diseases that are based on specific primary diseases. At the same time, appendicitis is sometimes associated with other diseases, for example, it is involved in Crohn's disease, or ulcerative colitis, or pancolitis.
The risk of developing appendicitis is higher if the amount of pathogenic intestinal microflora in the body exceeds normal limits. For example, E. coli - normally it is present in a healthy person, but is suppressed due to the beneficial intestinal microflora, strong immunity, and compliance with hygiene standards. When poisoning occurs and the number of E. coli increases, the risk of appendicitis increases against the background of such a disease.
It is important to differentiate the symptoms of an acute abdomen characteristic of appendicitis from other causes.
Complications of untreated appendicitis usually include appendiceal infiltrate (abscess), intra-abdominal abscesses, peritonitis and pylephlebitis. The risk of their development will be practically reduced to zero if the operation to remove appendicitis is performed by a qualified specialist in appropriate conditions in a timely manner - usually the first day after diagnosis.
Appendectomy and its possible complications
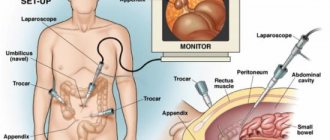
Appendectomy is one of the most common operations in the practice of surgeons. Tens of thousands of them are held every day all over the world. In most cases, doctors choose general anesthesia for pain relief, although local anesthesia is theoretically possible. The incision is made in the right iliac region, but this will depend primarily on the location of the appendix. The laparoscopic method of performing the operation is more gentle, since after it only small incisions remain on the abdomen, and the person himself recovers earlier and can be discharged from the hospital already on the 4-5th day.
Before the operation, the patient is given antibiotics, which protect him from the development of infectious complications in the postoperative period. If after surgical treatment a person does not have severe pain and high fever, then there is no reason to necessarily take antibacterial drugs in the following days.
However, like any operation, appendicitis removal is a surgical procedure that always involves certain risks. We are talking about possible intolerance to the components of anesthesia, painkillers, suppuration of a postoperative wound, and the subsequent development of adhesive disease. Also, one of the possible complications is the formation of an abscess or abscess in the place where the inflamed appendix was previously located. This is possible if, after removal of appendicitis, fragments of inflamed tissue remain. The reason may be the lack of adequate antibiotic prophylaxis, or it depends on the individual characteristics of the patient, namely the shape and location of the appendix.
Folk remedies
It is impossible to cure appendicitis with folk remedies at home. This is a dangerous illness that requires medical attention. Alternative medicine serves as an aid to conservative treatment and during rehabilitation after surgery. It is useful to take infusions from plants, the action of which is aimed at:
- improving the functioning of the intestines and stomach: fennel, centaury, cumin, golden mustache;
- combating parasitic bacteria and relieving inflammation: chamomile, mint, wormwood, tarragon, St. John's wort;
- protecting the liver from the influence of chemical compounds (antibiotics cause serious damage to it): milk thistle, lemongrass;
- bile diversion (increasedly secreted in acute forms): celandine, dandelion roots, birch leaves;
- pain relief: valerian root, calamus, tansy.
You can use any remedy or drug for the prevention or treatment of appendicitis, as after appendectomy, only with the consent of the attending surgeon. The doctor himself prescribes dosages, since self-medication can harm the body and cost a person his life.
Echinacea will strengthen the body's immune system.
Invaluable help in the fight against the disease will also be provided by immunostimulants such as honey, echinacea, cranberry, lemon balm, which supply the body with many vitamins and beneficial microelements that improve the natural protective function and stimulate the renewal of damaged tissues. Low-fat fermented milk products will be indispensable in the daily diet, helping to restore the natural microflora of the gastrointestinal tract and normalize its functioning. A decoction of nettle leaves, hay or dill seeds, acting as a laxative, helps to cope with difficult bowel movements after removal of the appendix, relieve pain and eliminate bloating.
Antibiotics as an alternative to surgery
Is conservative treatment of appendicitis possible with antibiotics? This question worries many people, because any operation is a risk, and no doctor can guarantee unambiguous success.
A study was conducted in which patients with clinical appendicitis were given the antibiotics cefotaxime and tinidazole intravenously for the first two days, and then they continued taking tablet forms of ofloxacin and tinidazole for the next 7 days. As a result, 3 out of 4 people avoided surgical treatment and were subsequently discharged home in satisfactory condition. However, the subsequent fate of these patients was not monitored, because the risk of relapse of the disease cannot be excluded.
In addition to this study, there are other experiments in which antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, etc. were used. After all, it is these antibacterial agents that act on bacteria that cause inflammation of the appendix.
However, the role in deciding how best to treat a patient with appendicitis belongs only to the attending physician. Certain forms of the disease require immediate surgical intervention, and the patient’s life depends on how quickly it is performed.
Doctors Research
In search of alternatives to surgical treatment, which is fraught with many postoperative complications, leading specialists from European medical research institutes studied conservative treatment, which was first tried in practice by E. Coldrey back in 1959. The bottom line: patients are given an antibiotic drip to rid the intestines of pathogens.
Published in 2012 by the British Medical Journal, the results of an experiment conducted by specialists from the Nottingham Royal Medical Center prove the effectiveness of antibacterial therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis: 63% of participants in the experimental group were cured without further relapses during a year of medical observation. In addition, the complication rate among them was 31% lower than among participants in the control group who had their appendix removed. The positive result was confirmed by Swedish and Finnish scientists, who in 2020 managed to increase the recovery rate to almost 73%.
Results
Every person can have a stomach ache from time to time. But if the pain is acute, intensifies with movement or coughing, and is accompanied by fever, this indicates the first signs of inflammation of appendicitis. In this case, the patient feels nauseous, his abdominal muscles tense, and there may be diarrhea or constipation. In this case, you need to quickly consult a doctor and get diagnosed. The earlier the inflammation is detected, the more effective and simpler the treatment will be. This should not be forgotten.
See
Purulent appendicitis symptoms Blood test for appendicitis Temperature after removal of appendicitis how long does it last On which side of appendicitis
Useful decoctions and infusions that help in treatment
- White clover infusion. To prepare, you will need flowering clover grass, which should be poured with boiling water (250 g). The decoction is infused for about half an hour. The drug is taken orally several times a day, after main meals. Please note that the broth must be fresh, that is, it will need to be prepared daily.
- A decoction of yarrow herb. This recipe can be called not so medicinal as more of an anesthetic since the prepared remedy effectively helps with exacerbations of a chronic illness by relieving pain. In order to prepare such an effective antispasmodic at home, you will need nutrients such as raspberry and strawberry leaves, they must be mixed in equal proportions with yarrow herb. The collection of plants is brewed in a liter of water (boil for 15-20 minutes over high heat). Note that the volume of the prepared broth is enough for the whole day. It is necessary to take the product during the day in small quantities.
- Infusion with milk. This remedy has also proven itself to be effective in relieving pain symptoms, and therefore, instead of taking painkillers, you can use this folk remedy for chronic appendicitis. The product is prepared in this way: add cumin in the amount of one tablespoon to boiling milk and cook for five minutes. This remedy is taken hourly.