A gastric hernia is one of the types of hiatal hernia, in which complete or partial penetration of the stomach into the chest cavity occurs.
Forms of gastric hernia
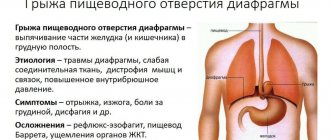
The chest and abdominal cavity are separated by a muscular septum - the diaphragm. The diaphragm dome is directed upward. There are openings in several places in the diaphragm through which the esophagus, blood vessels, and nerves pass. The esophagus connects to the stomach, passing from the chest cavity to the abdominal cavity through the esophageal opening, which is located at the back of the diaphragm and consists of the digestive tube as well as the anterior vagus nerves. Normally, the esophagus is securely held in the esophageal opening, and the muscles and connective tissue fibers of the diaphragm do not allow the abdominal organs to penetrate into the chest. With the development of a gastric hernia, the ligaments in the area of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm are weakened. For this reason, the esophagus and then the stomach penetrate into the chest cavity when intra-abdominal pressure increases.
Gastric hernias in children are diagnosed in approximately 9% of cases; with age, the risk of the disease increases. Women suffer from this pathology more often than men.
Causes and risk factors
Gastric hernias occur more often in elderly and senile people, which is associated with the natural aging process. Over time, connective tissues lose their elasticity and atrophy, and connective tissue structures weaken.
The main factors that can provoke the occurrence of a gastric hernia are conditions in which intra-abdominal pressure increases. Such conditions include chronic diseases of the respiratory and digestive systems, excess weight, excessive physical activity, sudden bending, blunt abdominal trauma, and multiple births. In children, the cause of the disease is often anomalies in the development of the esophagus in the prenatal period.
Gastric hernia is more often diagnosed in old age, which is associated with natural aging of the body.
Hereditary predisposition is of no small importance in the development of the pathological process.
In addition, risk factors for developing a gastric hernia include:
- previous surgical interventions;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- binge eating.
General classification
In medical practice, three types of this pathology have been identified, each of which has certain distinctive features.
Classification of gastric hernias
You can learn about the types of hernia from the video.
Video - Gastric hernia
Complications
When the patient does not receive proper therapy, then when a hiatal hernia is diagnosed, the development of secondary ailments, such as peptic ulcer, erosion, malignant tumor-like neoplasms, and anemia, may occur.
Forms of the disease
Depending on location:
- external hernia of the stomach - the organ enters from the abdominal cavity into the chest through weak areas of the muscle wall;
- internal - the stomach enters the chest from the abdominal cavity through an opening in the diaphragm.
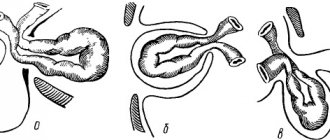
Depending on the anatomical features, the following forms of gastric hernia are distinguished:
- sliding;
- paraesophageal;
- mixed.
Types of gastric hernia
Sliding hernias can be fixed or non-fixed, and depending on the displaced area they are divided into cardiac, cardiofundal, subtotal and total gastric. Paraesophageal hernias, in turn, are classified into antral and fundal.
General description of the pathology
To begin with, to recreate a complete understanding of the disease, we should consider the anatomical details. The diaphragm is a special muscular plate designed to separate the abdominal cavity and the thoracic cavity. If the muscles weaken in the diaphragm, then there is a high probability of penetration of the esophagus through the hole into the adjacent cavity. Weakened muscles, supported by intrauterine pressure, contribute to the protrusion of the stomach with a section of the esophagus into the chest cavity, thus developing a hiatal hernia.
Attention! It is necessary to consult a specialist in a timely manner to confirm the diagnosis in order to avoid surgical intervention.
Combination of hiatal hernia with other gastrointestinal diseases
Symptoms of a gastric hernia
A gastric hernia is often asymptomatic; in this case, it is discovered by chance during an examination for another reason.
With the development of a gastric hernia, the ligaments in the area of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm are weakened. For this reason, the esophagus and then the stomach penetrate into the chest cavity when intra-abdominal pressure increases.
The most characteristic symptoms of a gastric hernia are belching of gastric contents or bile, a burning sensation in the chest, difficulty swallowing, and irregular heart rhythm. A common sign of a gastric hernia is heartburn, which usually appears during physical exertion, in a horizontal position of the body, when bending over, overeating and after drinking alcohol. Patients may experience eating-related aching or burning pain in the upper abdomen and chest cavity, as well as a feeling of a lump in the throat. Pain also occurs during physical activity, bending the body forward, coughing, and flatulence; in this case, the pain decreases or disappears after vomiting, taking a deep breath, or changing body position. The pain can radiate to the back, shoulder and the area between the shoulder blades, and can become encircling.
A burning sensation in the chest may indicate a gastric hernia.
When gastric contents reflux into the esophagus, the patient experiences irritation of the esophageal mucosa, which leads to pathological changes of an erosive or ulcerative nature. If bleeding occurs from ulcers or erosions of the esophagus, as well as gastric bleeding, patients develop signs of anemia and may experience bloody vomiting or vomiting of contents resembling coffee grounds and dark-colored feces. As the disease progresses, it becomes difficult for the food bolus to move through the esophagus. If stomach contents enter the respiratory tract, patients may develop tracheobronchitis, aspiration pneumonia, and bronchial asthma.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of a gastric hernia, it is recommended:
- avoid overeating;
- maintain normal weight, and, if necessary, correct excess body weight;
- avoid excessive physical activity;
- strengthen the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall;
- to refuse from bad habits.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Education: 2004-2007 “First Kiev Medical College”, specialty “Laboratory diagnostics”.
The information is generalized and is provided for informational purposes. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous to health!
In order to say even the shortest and simplest words, we use 72 muscles.
Dentists appeared relatively recently. Back in the 19th century, pulling out diseased teeth was the responsibility of an ordinary hairdresser.
When we sneeze, our body stops working completely. Even the heart stops.
An educated person is less susceptible to brain diseases. Intellectual activity promotes the formation of additional tissue that compensates for the disease.
Even if a person's heart does not beat, he can still live for a long period of time, as the Norwegian fisherman Jan Revsdal demonstrated to us. His “engine” stopped for 4 hours after a fisherman got lost and fell asleep in the snow.
Scientists from Oxford University conducted a series of studies in which they came to the conclusion that vegetarianism can be harmful to the human brain, as it leads to a decrease in its mass. Therefore, scientists recommend not completely excluding fish and meat from your diet.
The highest body temperature was recorded in Willie Jones (USA), who was admitted to the hospital with a temperature of 46.5°C.
There are very interesting medical syndromes, for example, compulsive swallowing of objects. One patient suffering from this mania had 2,500 foreign objects in her stomach.
The average life expectancy of left-handers is shorter than that of right-handers.
You are more likely to break your neck if you fall off a donkey than if you fall off a horse. Just don't try to refute this statement.
American scientists conducted experiments on mice and came to the conclusion that watermelon juice prevents the development of vascular atherosclerosis. One group of mice drank plain water, and the second group drank watermelon juice. As a result, the vessels of the second group were free of cholesterol plaques.
Each person has not only unique fingerprints, but also tongue prints.
Tooth decay is the most common infectious disease in the world, which even the flu cannot compete with.
The rarest disease is Kuru disease. Only members of the For tribe in New Guinea suffer from it. The patient dies of laughter. The disease is believed to be caused by eating human brains.
Four pieces of dark chocolate contain about two hundred calories. So if you don’t want to gain weight, it’s better not to eat more than two slices a day.
Fish oil has been known for many decades, and during this time it has been proven that it helps relieve inflammation, relieves joint pain, and improves sucking.
✓ Article checked by doctor
One of the types of damage to the esophageal opening of the diaphragm is defined in medical terminology as a hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. The pathological condition is characterized by partial or complete prolapse of the stomach from the abdominal cavity into the chest cavity. The danger of the pathology lies in its asymptomatic course, so the patient can detect it quite by accident during a routine examination. Classic manifestations of a hernia are characterized by heartburn and frequent belching, a burning sensation behind the sternum, and impaired swallowing function. The patient's general health deteriorates significantly.
In most cases, gastric hernia can be treated conservatively. By following an individually selected diet, as well as with the help of drug therapy, it is possible to completely block the manifestations of a hernia. The specialist prescribes surgical intervention only in case of complications of the clinical picture. After the operation, the patient has no relapses of pathology.
Gastric hernia: symptoms, treatment
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of a gastric hernia, complaints and medical history are collected, as well as an instrumental examination, including esophagoscopy, gastroscopy and x-ray diagnostics of the chest cavity and gastrointestinal tract organs.
To clarify the diagnosis, they resort to laboratory testing of stool for occult blood, determining the pH and atmospheric pressure in the stomach and esophagus. In some cases, a biopsy of the wall of the esophagus and/or stomach is performed.
To clarify the diagnosis of a gastric hernia, a biopsy of the stomach or esophagus may be required.
Differential diagnosis with polycystic pulmonary disease, relaxation of the diaphragm, cholelithiasis, and gastric ulcer is required.
Symptoms
It is not difficult to suspect a hernia and seek qualified help; the main thing is to be attentive to all atypical signs:
- There is a pain syndrome in the chest area that is aching and sometimes burning in nature, which is aggravated by eating.
- Frequent uncharacteristic belching and heartburn.
- Regurgitation.
- Feeling of a lump in the throat.
- Heart rhythm failure.
- Retrothoracic pain syndrome.
It is important! When diagnosing a gastric hernia, the diagnosis may be incorrect, since one of the patient’s complaints will be heart pain and heart rhythm disturbances, so patients are often referred to cardiology.
Complaints with hiatal hernia
Treatment of gastric hernia
In most cases (about 95%), gastric hernia is treated using conservative methods.
A diet is recommended for patients with gastric hernia. Alcohol, carbonated drinks, coffee, cocoa, chocolate, spices, ketchup, mayonnaise, mushrooms, legumes, cabbage, fatty and fried foods should be excluded from the diet. Food should be taken in small portions 4-6 times a day, chewing thoroughly, the last meal should occur no later than three hours before going to bed. It is recommended to sleep with the head of the bed elevated, avoid those types of physical activity that increase intra-abdominal pressure, and do not wear clothes that compress the chest and/or abdomen.
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of gastric hernia
In order to protect the mucous membrane of the esophagus from the action of gastric contents, antacids are used. In addition, proton pump inhibitors, H2-histamine receptor blockers, and antispasmodics are prescribed.
Indications for surgical treatment of a gastric hernia are developing complications, such as strangulation of the hernia, narrowing of the esophagus, malignant degeneration of cells in the mucous membrane of the esophagus and/or stomach, as well as the lack of a positive effect from several courses of drug therapy for severe digestive disorders. As a surgical treatment for a gastric hernia, operations are performed that consist of suturing the hernial orifice and strengthening the esophageal-diaphragmatic ligament, as well as surgical interventions during which the stomach is fixed.
After surgical treatment of a gastric hernia, relapses are very rare.
The Nissen fundoplication method is popular. The method refers to anti-reflux operations and involves wrapping the fundus of the stomach around the esophagus to form a cuff, which prevents the stomach contents from refluxing into the esophagus. During surgery, the anatomically correct location of the lower esophageal sphincter is restored, which, when intra-abdominal pressure increases, should be below the diaphragm, which allows for the restoration of its functions. Typically, the operation is performed laparoscopically, the advantage of which is minimal tissue trauma and a shorter rehabilitation period. If there are contraindications to laparoscopy, open surgery is used.
Nissen fundoplication
Patients with a gastric hernia are advised to undergo clinical observation by a gastroenterologist.
Treatment methods
In rare cases, surgery is required. It is carried out in ten percent of all cases. This type of treatment is indicated if the hernia is large and complications are observed that threaten the health and life of the patient.
Consequences of gastric protrusion:
- the esophagus noticeably narrows, scarring progresses in a narrow section;
- the presence of ulcerative processes;
- bleeding in the stomach, esophagus;
- cancer;
- perforation;
- organ shortening.
As a rule, conservative treatment, adherence to a special diet, and the use of folk remedies are needed. Among the medications, prokinetics, antacids and antisecretory agents are indicated.
Folk remedies
For treatment with folk remedies, you can use the following methods:
Flax seeds, coltsfoot, mint and marshmallow root
Mix flax seeds, coltsfoot, peppermint and marshmallow root in equal proportions. Stir thoroughly, take 2 tbsp. spoons of the resulting mixture and pour three glasses of boiling water. Place the mixture in an enamel pan, boil and simmer for five minutes. Application: ½ glass every 3-4 hours.
Bought and milk
Pour 50 grams of dry kupena into 450 ml of cold milk. Bring the mixture to a boil, simmer for 4 minutes. Cool, drink a tablespoon 2 times a day.
Gooseberry
Gooseberry infusion helps a lot. You will need one tablespoon of dry leaves, which is placed in a thermos and filled with 500 ml of boiling water. Leave for at least seven hours, take 125 ml three times a day.
Diet and nutrition
The diet for gastric hernia should be fractional, gentle and balanced. It is advisable that nutritional recommendations be prescribed by a doctor. All dishes must be heat treated before use.
You need to remove from your diet:
- fatty, spicy and sour, fried foods;
- confectionery, fresh baked goods and sweets;
- spices, marinades and canned food;
- milk;
- grapes, cabbage;
- soda.
It is imperative to introduce into the diet products that prevent constipation: prunes, beets, vegetable salads, seaweed. The disease is easily treatable if you visit a doctor and follow all his instructions. In the presence of such a pathology, self-medication is unacceptable.
Diagnosis of pathology
Thanks to the collection of anamnesis, clinical symptoms and detailed diagnostics, namely gastroscopy and x-rays. The chest and digestive system are examined directly. To confirm the extent of the disease and exclude the development of a tumor-like process, additional studies are required, which include:
- biopsy (a detailed study of organs, namely their walls, is carried out);
- stool analysis for the presence of blood spots;
- identifying the level of atmospheric pressure directly in the esophagus and stomach.
Types of gastric hernia
Reference! One of the methods of general examination, which provides a visual characteristic of the organ, is gastroscopy. Using an endoscope, a detailed image is displayed on the monitor, confirming the condition of the digestive system.
Rehabilitation period
After surgery to treat a gastric hernia, recovery lasts from 3 to 8 weeks . During this period, subject to proper diet and vital activity, a dense scar is formed, strengthening the esophageal opening.
During the rehabilitation period, you should stick to a light diet in the form of low-fat soups, broths, boiled or stewed meat and vegetables, and purees.
It is advisable to continue taking medications that reduce gastric acidity and antiemetics.
Note! In the first 2 to 3 months, you should avoid any physical activity, stop coughing attacks and eliminate any digestive disorders or constipation.