Appendicitis is a disease that can affect absolutely anyone.
It cannot be protected from by preventive measures and it cannot be cured with pills. But it can be recognized at a very early stage and seek medical help, and for this you need to know the causes and symptoms of the disease. The signs of appendicitis in women will be the same as in men, but it is more difficult to diagnose for women, and we will now figure out why.
What kind of disease is this
The development of inflammatory reactions in the appendix is called appendicitis in medicine. This is the most common pathology of the peritoneal cavity. More than 85% of the total number of hospitalized patients are patients with inflammation of the appendix.
The disease affects people of any age, regardless of gender. Peak development is from 10 to 35 years. According to statistics, every year 5 out of 1000 people are diagnosed with an inflammatory lesion of the appendix.
How does appendicitis manifest in children?
When the appendix is inflamed, the child becomes lethargic, eats poorly, is capricious, and refuses to play. He lies down on his side, presses his legs to his stomach and does not allow the “sore spot” to be examined. Which side of the child’s appendicitis hurts is determined by the location of the appendix.
It is very important to know how to identify appendicitis in a child so as not to start the process and prevent the development of peritonitis. After all, young children most often cannot understand what is happening to them. Therefore, they cannot explain their condition to their parents. Adults should pay close attention to all the symptoms of appendicitis and on which side the pain appears in order to promptly seek qualified medical help.
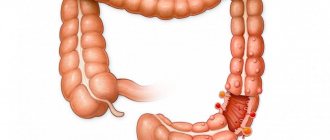
Where is appendicitis located in humans (on which side)
It is not easy for an ignorant person to immediately recognize the disease, since the clinical picture of appendicitis is in many ways similar to other pathologies of internal organs.
Therefore, it is important to know where exactly appendicitis is located - on the right or on the left, and whether it is possible to recognize the disease on your own.
According to the anatomical norm, the appendix, together with the cecum, is located in the ileum on the right side of the abdomen . However, there are also atypical locations that make diagnosis difficult.
Without taking into account the “mirror anomaly” of location, this is explained by the fact that the process itself can have several options for location to the cecum itself - lateral (medial), pelvic (descending), anterior (ascending), or behind the intestine (retrocecal) with various localization options - intramural, intraperitoneal or retroperitoneal.
This “scatter” of possible positions of the appendix is reflected by an ambiguous picture of clinical symptoms.
The pain syndrome can manifest itself in the right side, radiate to the middle part of the abdomen and hypochondrium to the liver, lower back, pelvic and genital areas, and radiate to the leg and groin.
By nature, the pain can be intense, intensifying, subsiding or cramping. Manifest in short-term episodes and long-term ones.
Location
As a rule, the classic location of the appendix is on the right in the lower corner of the abdomen in the iliac region. But depending on the structure of the human body, the object is located slightly differently:
- The appendage may hide behind the cecum;
- Rises towards the liver;
- Located on the side of the intestine;
- Located between the loops of intestine;
- On the left side, with mirror placement of organs. Rarely seen.
The location of the appendix in a pregnant woman is also slightly different. During fetal growth, internal organs shift relative to their original position. Therefore, the vermiform appendix is located slightly higher than in the normal state.
Is it possible to determine appendicitis on your own?
In some publications you can find recommendations for self-diagnosis of appendicitis by palpation.
This is a dangerous method and is strictly not recommended . It is impossible to know for sure at what stage of inflammation the appendage is.
By palpating, you can aggravate the inflammatory process, cause organ rupture and provoke peritonitis .
You should focus on abdominal discomfort and pain:
- Localization of pain in the area of the umbilical ring, moving over time to the lower abdomen on the right side.
- If the disease is suspected during pregnancy, the feeling of discomfort and pain will be on the side of the central area of the abdomen, and not in its lower area.
- Progressive inflammation manifests itself as diffuse pain - constant or episodic. At the beginning of inflammation, there may not be intense pain. Constant pain appears after 1–2 days and is localized in the lower abdomen on the right .
- Appendicitis can be suspected by reflected pain, localized in the navel area and radiating from it to the sides.
In order not to miss the development of the disease, it would be good to familiarize yourself with its clinical signs.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the doctor prescribes antibiotic therapy. Medicines and their regimen are selected on an individual basis. If there is a predisposition to thromboembolism, anticoagulants are prescribed.
A scar measuring up to 10 cm is formed at the site of the operation. It heals for about six months. Immediately after the operation, it has a burgundy tint, and over time it turns white. To resolve it, specialized ointments and creams are prescribed. Following your doctor's recommendations ensures a quick recovery. With proper care, the likelihood of wound suppuration is significantly reduced.
Diagnosis is simplified by specific symptoms of appendicitis in women; how to determine the disease at home becomes clear after studying physiology. The main difference is the location and nature of the pain. But only a specialist can make a final diagnosis.
Symptoms and signs of appendicitis
First signs
The first signs of appendicitis are characterized by a sharp manifestation of pain in the lower abdomen .
Unpleasant discomfort often occurs in the evening or at night, accompanied by pressing and pulling pain that migrates to any area of the abdomen. The localization of the pain syndrome can be in the navel area, radiating to the lumbar region and legs.
Characteristic early signs of appendicitis appear:
- disorders of digestive functions - retention of gases and bowel movements, diarrhea;
- signs of intoxication (nausea and vomiting) most pronounced in the destructive form of the disease;
- the presence of low-grade fever.
Signs of an acute clinic
Common signs of acute appendicitis for men and women include:
- pain symptoms in the abdomen;
- development of a feverish state;
- signs of asthenia (what is this?) and intoxication;
- lack of appetite;
- dyspeptic disorders (diarrhea, constipation, uncontrollable movements);
- signs of xerostomia (dry mouth) and white coating on the tongue;
- rapid heartbeat;
- accepting a forced body position;
- increased pain symptoms when laughing, hiccups, coughing.
The severity of symptoms depends on the patient’s age, the presence of underlying gastrointestinal diseases and the stage of appendicitis.
As for appendicular signs according to the symptoms of various luminaries (Zhendrinsky, Promptov, Grube, Taranenko, Michelson, Britten, Laroque or Horn), these are diagnostic tests intended for a specialist who can correctly conduct the test and identify or refute pathology in men and women.
You should focus on obvious symptoms. Test diagnostics is the prerogative (how is that?) of the doctor.
The clinical manifestations of acute appendicitis in childhood and adolescence are unique.
In young children and adolescents with an acute clinical picture of the disease, signs characteristic of many childhood infections predominate, manifesting themselves:
- febrile temperature;
- diarrhea;
- repeated vomiting;
- decreased activity;
- lethargy and restlessness;
- increased nervous excitability.
Signs of chronic appendicitis
The chronic clinical picture of the disease is characterized by dull aching pain in the right iliac region . The pain periodically intensifies, especially during physical activity.
The disease is accompanied by impaired digestive functions, which causes frequent constipation or diarrhea. There is discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region.
The patient's temperature usually does not exceed normal. Clinical monitoring of blood and urine within acceptable standards. Only deep palpation causes pain in the right peritoneum.
Recovery after appendix removal
The postoperative period depends on the type and form of the operation performed; with laparoscopy it lasts several days, after open surgery it can last for 2-4 weeks with a special diet. If the patient’s parameters return to normal and he does not experience discomfort, he is transferred to outpatient treatment 4-5 days after the operation.
After surgery, the patient should lie on his left side for 8 hours, during which time antibiotics and antispasmodics may be administered to relieve pain. If during this period the patient does not experience any deviations, then careful movements with the help of medical personnel are recommended.
Diet after surgery
Symptoms of appendicitis in a woman should provoke her to refuse to eat any food or drink until she consults a doctor. After surgery, nutrition should be of high quality, maintaining the normal amount of calories for age, but you should not overload the intestines or overeat.
Portions need to be small but frequent, excluding foods that affect the formation of gases. To do this, the patient is prescribed menu table No. 5, after 2-3 days table No. 2, gradually adding one product every 2-3 days.
| Day | Products |
| 1-3 after surgery. |
|
| 3-5. |
|
| 5-10. | Add boiled vegetables and grated fruits:
|
More about the appendix
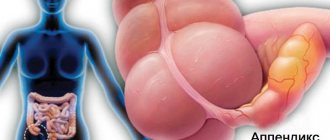
Appendix, according to translation, from Latin - appendage . This is the name doctors gave to a small vermiform appendix attached through a leaf-shaped movable mesentery in the area of the first section of the large intestine (cecum).
Since the process does not lead anywhere, no one really knew what it was needed for . There were different versions.
Some argued that the appendix is a container for collecting garbage that the body could not digest. Others believed that the purpose of the appendage was to neutralize negative energy accumulated in the intestinal chyme (digested food).
According to the Italian celebrity Da Vinci, the intestinal appendage is nothing more than a natural “depot” that protects the intestines from possible damage by flatulence (accumulation of gases).
Naturalist C.R. Darwin considered the appendage to be a dying organ (rudiment) that had lost its main functions in the process of ontogenetic transformation. The famous immunologist I. Mechnikov adhered to the same version.
The Germans went even further. Considering the appendix completely useless, in the 30s of the last century in Germany they decided to remove the appendage immediately after the birth of the child in order to protect against further problems.
As time has shown, the appendix is not useless . If he is healthy, people can more easily endure illnesses, various stresses and the effects of radioactive radiation. Under the mucous layer covering the appendix there is a large accumulation of lymphoid tissues, which form the basis of all immune organs.
It is this feature that allows it to perform protective functions (like tonsils), preventing the penetration of pathogenic flora from the large intestine into the small intestine.
In fact, this process “stands guard” over the so-called dirty and clean zones of the body, protecting the clean zone from the introduction of pathogenic organisms. If the protective function of the nasopharynx is performed by the adenoids, and the larynx is performed by the tonsils, then the function of the appendix is to ensure the cleanliness of the small intestine .
In medical practice, surgeons sometimes call inflammation of the appendix abdominal tonsillitis . But, unlike the pharyngeal tonsils, inflammation of the appendix occurs only once.
Therefore, it is impossible to treat it otherwise except by surgery. This is facilitated by the peculiarity of the terminal type of artery that provides blood circulation in the appendix.
The slightest inflammation leads to the development of thrombosis and blockage. With the cessation of blood supply, the appendix dies, its walls become thinner, and gaps appear through which the accumulated purulent substrate flows into the peritoneal cavity.
`Therefore, delay in surgical treatment of appendicitis often ends in the patient's mortality .
What contributes to the development of appendicitis
An active part in the development of the disease is taken by a special Focus virus , discovered by US researchers, which acts on the principle of influenza viruses that cause inflammatory outbreaks of the appendix in the spring and summer, as well as representatives of the polymicrobial flora - coccal associations, rod-shaped intestinal and anaerobic flora.
It penetrates the walls of the appendix in an enterogenous way - through its lumen. Create conditions for inflammatory reactions:
- bending of the appendix, which provokes stagnation of intestinal contents in the appendix;
- blockage of the lumen with appendicular stones and other foreign bodies;
- excessive new formation of lymph tissue (hyperplasia).
The processes of mechanical blockade of the lumen of the appendage cause an increase in pressure inside the lumen and disrupt blood circulation in its walls.
Such “anomalies” reduce local immunity, activate pyogenic microflora and promote their penetration into the mucous lining of the organ.
Predisposing factors that cause the development of inflammation in the cavity of the appendix include the nature of the nutritional diet and the peculiarities of the localization of the appendix.
It has been proven that with a rich meat diet and a tendency to difficult bowel movements, excess protein breakdown accumulates in the intestines, which creates favorable conditions for the replication (reproduction) of pathogenic microorganisms.
In addition to mechanical causes, parasitic and infectious diseases such as typhoid fever, amebiasis, yersiniosis, intestinal tuberculosis and other infections can become a prerequisite for the development of inflammatory reactions in the appendix.
are at higher risk of developing the disease during pregnancy , which is due to changes in the immune system, the presence of constipation, and migration of the appendix along with the cecum caused by an increase in the size of the uterus and changes in blood supply to the pelvic organs.
Causes of inflammation of the appendix
The appendicular process, which is located at the end of the cecum, can become inflamed even in a completely healthy representative of the fair sex. The fact that a woman has more organs in her abdominal area often makes it difficult to diagnose the correct disease.
Reasons affecting the inflammatory process in the appendix:
- Microorganisms of a pathogenic nature. Inside the appendix there are bacteria and viruses that cause inflammation.
Bacteria and viruses in the body
- Blockage of the appendicular orifice. Occurs due to the accumulation of solid masses (husks, seeds, helminths, hardened feces).
- Inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes or the appearance of neoplasms near the passage of the appendicular process.
- Inflammatory processes in organs and tissues (tonsils, sinuses, dental diseases).
- HIV infections. Weakened immunity is at risk of developing appendicitis due to cytomegalovirus infection, tuberculosis, etc.
In addition to physical reasons, a psychological reason can provoke inflammation. Stressful situations negatively affect the female body as a whole, and not just neurological health.
Forms of appendicitis
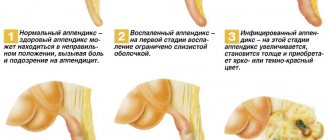
The appendicitis clinic is characterized by two main forms - acute and chronic . Each of them manifests itself in a variety of clinical and morphological variants.
The acute form of the disease can manifest itself as catarrhal (simple) and several destructive forms - phlegmonous, phlegmonous-ulcerative, apostematous and gangrenous .
- In the catarrhal form of appendicitis, there are disturbances in blood circulation and lymph retention (lymphostasis) in the tissue structure of the appendix. Purulent foci of inflammation form in the mucous membrane of the organ. There are processes of swelling of the appendage and hyperemia of the serous membrane.
- The basis for the development of the purulent form of the disease is the progression of inflammatory reactions. A day after the onset of the inflammatory process, the leukocyte infiltrate fills the walls of the appendix to their entire depth, forming a form of phlegmonous appendicitis - with thickened walls, a hyperemic and edematous mesentery, with processes of purulent discharge from the lumen of the appendix.
- The apostematous form of the disease is characterized by the presence of diffuse (spread) inflammation with multiple formation of microabscesses.
- The phlegmatic-ulcerative process is preceded by numerous ulcerations of the mucous lining of the organ.
- Gangrenous appendicitis develops as a result of the progression of destructive processes in the tissues of the appendix.
Involvement of the tissues surrounding the appendix in the purulent-inflammatory process provokes the formation of adhesions, inflammatory damage to the peritoneum (pereappendicitis) and mesenteric tissue (mesenteriolitis).
The stages of progression of appendicitis , in the absence of treatment, can be viewed in the table.
Among the chronic forms of the disease, there are residual (residual form), primary chronic (weakly expressed) and recurrent appendicitis.
In a chronic clinic, the development in the appendix is characterized by:
- sclerotic and atrophic processes;
- the presence of inflammatory-destructive changes in the form of proliferation of granulations (connective tissue);
- the formation of adhesions between the organ shell and adjacent tissues;
- accumulation of serous exudate in the lumen of the appendix, promoting the formation of cysts.
Diagnosis and treatment
The basis for diagnosing appendicitis is a thorough collection of anamnesis (what is this?) and patient complaints.
This takes into account the nature of the abdominal pain and the forced position that the patient takes.
A palpation examination is carried out using various diagnostic tests (Shchetkin-Blumberg, Rovsing, and Sitkovsky, etc.), which make it possible to confirm the development of acute appendicitis with a 90% probability.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following is prescribed:
- A biochemical blood test to detect the severity of leukocytosis, which can confirm or refute the presence of inflammatory processes.
- Ultrasound or CT - in unclear cases.
- Irrigoscopy or colonoscopy - to exclude intestinal pathologies.