Reasons and factors
The reasons why purulent appendicitis develops are conventionally divided into several groups.
Mechanical
Mechanical causes of purulent lesions of the appendix include blockage of its lumen with fecal stones, helminths, tumor formations or food particles. Obstruction of the appendix leads to disruption of its blood supply and to the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Due to this, an intense inflammatory process develops, the untimely relief of which can lead to serious complications.
Infectious
Among the infectious causes of the disease, the most common are: typhoid fever, tuberculosis, amoebiasis and yersiniosis. But as to whether these pathologies can lead to purulent lesions of the appendix, scientific discussions are still ongoing among scientists.
Endocrine and vascular
The causes of the development of the pathological process, which are less often taken into account by surgeons, are vascular and endocrine. Thus, inflammation of the appendix, according to the vascular hypothesis, develops against the background of vasculitis. More often this deviation is observed in older people.
According to the endocrine theory, the appendix is a place where there is an accumulation of cells that promote the secretion of serotonin, a hormone under the influence of which inflammatory processes develop.
Note. The initial stage of development of the pathological process is called acute appendicitis. As it progresses, leukocyte infiltrates begin to form in the tissues of the appendix. They are the ones who form foci of suppuration.
What antibiotics are prescribed after appendicitis removal?
The use of antibacterial drugs during surgery for both complicated and uncomplicated appendicitis significantly reduced the likelihood of complications, primarily in the early postoperative period.
In order to prevent septic complications in the first days of the postoperative period, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents are used, since it is not known in advance which type of microorganism poses the greatest danger in each specific case.
https://youtu.be/x1Tv37kqXns
Features of the manifestation of pathology
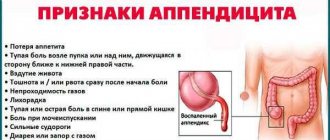
Painful sensations in the epigastric region are one of the harbingers of purulent appendicitis. Gradually, the pain syndrome changes localization, moving to the area of the right ilium.
As the pathological process progresses, other symptoms join the pain:
- increase in body temperature to febrile values;
- general intoxication of the body;
- diarrhea;
- nausea.
But these symptoms are characteristic of all types of acute appendicitis. Purulent appendicitis can be diagnosed only during diagnostic laparoscopy or when examining the appendix during surgery. In this case, the surgeon may note the following abnormalities:
- the formation of fibrinous layers on the surface of the diseased organ;
- pronounced swelling and friability of the appendix;
- thickening of the walls of the organ and their tension;
- purulent contents in the lumen.
Important! If you do not seek help in a timely manner or if surgical intervention is delayed for a long time, the course of the disease worsens. The patient experiences the development of concomitant complications in the form of further purulent tissue melting or the formation of an appendiceal abscess.
Diagnostic manipulations
To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital, where changes in his condition are first monitored for 2-3 hours. Consultation with a gastroenterologist plays an important role, since the symptoms of purulent appendicitis are in many ways similar to the manifestations of other pathologies of the abdominal cavity.
To identify the disease it is necessary to:
- physical examination of the patient;
- palpation of the abdomen;
- clinical tests of urine and blood;
- Ultrasound diagnostics;
- diagnostic laparoscopy;
- plain radiography (according to indications).
It is important to differentiate appendicitis from myocardial infarction, so an ECG is additionally necessary.
Women are additionally referred to a gynecologist, since often purulent inflammation of the appendix can be confused with the development of diseases in the right ovary or with an ectopic pregnancy with subsequent rupture of the right fallopian tube.
Treatment
Purulent appendicitis is treated exclusively through surgical intervention - appendectomy. It is performed under general anesthesia. And only if there are serious contraindications, local anesthesia can be used.
During the operation, an oblique incision of 5 to 10 cm in length is made at McBurney's point. Next, layer-by-layer dissection of the subcutaneous tissue begins. It is performed until the surgeon gains access to the patient's abdominal cavity.
Next, manipulations are performed to ligate the appendix and mesentery, which is subsequently removed first. Next, the appendix is cut off, and the stump that remains after its removal is “reduced” into the lumen of the cecum. After this, the surgeon places 2 stitches necessary to prevent the stump from falling out.
The incisions are sutured in the reverse order: first the muscles and soft tissues, then the skin.
How many days is sick leave given after appendicitis?
The period for which sick leave can be issued directly depends on the legislation of the country in which it was issued, the characteristics of the surgical intervention, the presence or absence of complications, as well as the general condition of the body.
In some cases, primarily with laparoscopic removal, without abdominal surgery, a certificate of incapacity for work may be issued for three days. In the absence of complications, the patient’s good condition and his desire, sick leave can be so short.
In the case of uncomplicated appendicitis and laparoscopic surgery (also without complications), sick leave can be issued for a period of five to ten days - with this type of intervention, trauma is minimal and recovery is as fast as possible.
Postoperative period
The postoperative period proceeds completely depending on what surgical method was used to treat purulent appendicitis, whether there were any complications during the intervention, how quickly the wound heals (if a cavity appendectomy was performed), etc. During the first day after removal of the appendix, :
- careful monitoring of the patient to detect postoperative bleeding (if any occurs);
- monitoring the patient’s general condition with regular measurement of blood pressure and body temperature, inspection of the suture;
- monitoring the restoration of physiological functions of the body.
If necessary, detoxification measures can be carried out.
Drainage and antibiotic therapy
If during the operation a large accumulation of effusion was detected, the patient is given a drainage for subsequent washing of the abdominal cavity with antiseptics and for the administration of antibacterial solutions.
After removal of the appendix, a course of antibiotic therapy is required. It is necessary in order to destroy bacteria remaining in the abdominal cavity and prevent their further reproduction.
To begin with, antibiotics are administered intravenously (for the first few days), after which systemic medications are prescribed. Zinacef, Dalatsin, Metrogyl, etc. are the antimicrobial agents that are most often prescribed to patients who have undergone surgery to remove the appendix.
Some questions
Rehabilitation after removal of appendicitis lasts from one to several months. This is a lot of work on the part of the patient. The patient should know how to behave during this period, whether there are contraindications, what recommendations make recovery easier and faster. It is important to know about the rules of hygiene, nutrition, physical activity and other procedures that the patient encounters daily.
Swimming, pool, sauna
Before the stitch is removed, doctors prohibit showering and swimming. Hygiene can be maintained by washing specific areas. It is better to wipe the abdomen with a wet sponge to prevent water from entering the wound. You should not take a bath or swim for 2 weeks after surgery. After the stitches are removed, you are allowed to shower. The swimming pool after appendicitis is allowed only after the wounds have completely healed, as you need to swim there. Such premature activity can cause wound dehiscence. It is recommended to visit the bathhouse no earlier than every month.
Tanning and solarium
For the first time after an appendectomy, it is not recommended to expose the wound to sunlight and ultraviolet radiation; therefore, it is forbidden to go to a solarium or to places where the scar will be exposed to the sun (for example, the beach). Later, you are allowed to sunbathe, but it should be taken into account that the tan will not be uniform, since the incision site must be covered.
Exercise therapy after appendix surgery will have a beneficial effect on overall health and postoperative recovery.
Physical activity
Prevention of most complications includes breathing exercises. Exercise therapy includes simple exercises that are first performed while lying on your back. It is recommended to do the exercises while still in the hospital and continue at home. Wearing a bandage is mandatory only for children and overweight people. This will help prevent the wound from spreading. Several weeks after discharge, if your condition allows, you should start walking. Walking is done at a slow pace. You should avoid playing sports until the scar is completely healed (hardening at the incision site). This requires more than one week. Usually, sports are allowed after one decade, but you can pump up your abs and lift weights no earlier than six months later.
Smoking after surgery
Cigarette lovers almost immediately after surgery are interested in the question of whether it is possible to smoke after appendicitis. Smoking has an extremely bad effect on the human body, especially on the respiratory system. After an appendectomy, smoking a cigarette can trigger laryngospasm. Based on this, it is strictly forbidden to smoke for 3 days after surgery. If the patient experiences peritonitis, smoking is not recommended for 7 days after surgery.
Intimate life
If the surgical intervention went well with uncomplicated appendicitis, it is recommended to observe sexual rest for 7 days. Sometimes it is allowed to have sex earlier, but subject to a passive position on the part of the patient, avoiding abdominal tension. A return to normal intimate life is allowed seven days after the threads are removed.
Diet food
Diet after leaving the hospital is extremely important. The symptoms that accompany recovery depend on what kind of nutrition you eat. Breaking your diet can cause negative consequences. Sometimes errors cause death. You are allowed to eat low-fat chicken or beef broths, rice, and drink fresh juices diluted with water. Rosehip decoction or herbal tea without sugar are useful. Later, porridge, slimy soups, sour milk, and lean meat are introduced into the diet. All harmful products are completely prohibited. Parents should ensure that children are not given sweets, as they irritate the intestines.
Possible consequences
Delay in surgical intervention or complete lack of treatment for this pathology can result in the formation of an abdominal abscess, the development of peritonitis or a destructive form of acute appendicitis.
Abscess
This pathological process is accompanied by abscess formation (suppuration) in the abdominal cavity. Symptoms depend on how extensive the purulent lesion of the PD is.
Features of the clinical picture of this pathology include:
- presence of symptoms of body intoxication;
- intermittent fever accompanied by hectic temperature;
- development of tachycardia.
An abscess that develops after appendicitis is often accompanied by nausea, loss of appetite, and vomiting. If these symptoms occur, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Peritonitis
Appendicitis and peritonitis are closely related pathological processes. If purulent appendicitis is left untreated for a long time, a large amount of exudate accumulates, which sooner or later leads to rupture of the diseased organ.
Secondary peritonitis in appendicitis develops against the background of a breakthrough of the abscess and is accompanied by a powerful inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity. It is characterized by the appearance of intense abdominal pain, nausea, bloating against the background of gas retention, constipation, tachycardia, increased body temperature, and dry tongue.
These symptoms of peritonitis appear at the reactive, initial stage of pathology. With its further development, the patient's condition will only worsen.
Destructive appendicitis
Ignoring the signs of the disease leads to the spread of infiltrate throughout the entire thickness of the wall of the diseased organ, as a result of which phlegmonous appendicitis develops. Further development of destructive processes ultimately leads to a gangrenous form of pathology. The tissue surrounding the appendix, as well as its mesentery, may be involved in this process.
Rehabilitation after surgery
After diagnosis, the appendix is removed. This is a simple and common surgical procedure. Recovery time depends on the degree of advanced disease, the extent of surgery and postoperative complications.
In the postoperative period, a course of antibiotics is prescribed to suppress bacterial infections. Eight hours after the operation, the patient is allowed to move, but with the condition of constant monitoring of the condition of the sutures. To activate regeneration processes, therapeutic exercises are prescribed. It is aimed at preventing increased gas formation and constipation. After the operation, the patient is prohibited from physical and sexual activity and is prescribed a special diet. You should not eat foods that irritate the intestines - salty, spicy, sour or smoked. Drinking alcohol and smoking is prohibited. Food is received warm; overheating is not allowed for the same purpose. The duration of the diet is at least two months. Rehabilitation takes place under the supervision of the attending physician. With full compliance with medical recommendations, the patient’s health is completely restored.
https://youtu.be/2xOcaFoyA-o
Definition of the concept
According to medical terminology, purulent peritonitis means an infectious disease of the peritoneum.
Peritonitis develops as a result of untimely medical attention, which helps to rupture the appendix, during or after surgery, or as a result of trauma to the peritoneum.
The disease is characterized by a high degree of danger, since any delay can cost a person his life. The disease can provoke hemorrhage, infect the internal cavity of the peritoneum and form stagnation of biological fluid.
Root causes of the disease:
- Ascites associated with liver diseases and the development of microflora unfavorable for the body in it;
- Kidney disease requiring dialysis.
In addition to these reasons, there are also circumstances that contribute to the occurrence of purulent peritonitis.
These include:
- Burst appendix;
- Diverticulosis in perforated form;
- Diseases of the pancreas;
- Surgery on the abdominal organs;
- Gastrointestinal diseases - perforation of an ulcer;
- Inflammation in the genitourinary system;
- Complications associated with the postpartum period;
- Infection by other means.
Infection of the body with one type of harmful microorganism is almost impossible. This is helped by the simultaneous spread of a large number of bacteria, viruses and fungi.
Non-infectious causes of infection: bile, blood.
Forecasts, recommendations
Timely treatment of acute purulent appendicitis, not complicated by an abscess or peritonitis, has a favorable prognosis. As complications develop, they worsen significantly.
In the postoperative period, in the absence of complications, the patient is allowed to walk short distances, and after scarring of the wound, visit the pool and do light exercise.
There are no specific recommendations regarding the prevention of the disease. The only thing that can be advised in this case is to consume more fluids and foods containing plant fiber. This will help prevent the formation of coprolites, which often cause inflammation of the appendix.
The appendix is a very small organ. It is located in the cecum and has the shape of a worm. When unfavorable factors appear in the organ cavity, an inflammatory process forms. There are several types of disease, which manifests itself not only in adults, but also in children. Let's talk today about what purulent appendicitis is? What are the symptoms, how does the treatment proceed, and what are the possible consequences.
Main characteristics of the disease
The appendix is a protruding oblong part of the cecum located in the abdominal cavity on the right. The organ acts as a general filter, accumulating microorganisms found in the digestive system and responsible for the state of the immune system. Most people consider the organ unnecessary and useless, but this is not true.
The peculiar shape and small size indicate that feces do not enter the organ. Thanks to this property, it contains the maximum amount of lymphoid tissue, which feeds the positive intestinal microflora. In its absence, the human body experiences stress, which often leads to the development of third-party unpleasant factors:
- decreased immunity;
- the risk of developing infectious and viral diseases increases;
- the balance of beneficial intestinal microflora is disrupted.
Prevention
To burst appendicitis, you still need to try. If you ignore all the body’s signals, do not pay attention to pain and unexpected temperature fluctuations, complications will not keep you waiting. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to regularly conduct medical examinations, and if your condition and well-being worsen, consult a doctor.
It is also necessary to monitor the condition of blood vessels and the circulatory system as a whole, to increase immunity through exercise, proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
If there is a congenital problem, it is recommended to regularly examine the child and take the necessary tests.
Of course, it is impossible to prevent all diseases. But paying attention to your body and taking care of it will significantly reduce all the risks of many problems. And quality prevention will help prevent many diseases.
https://youtu.be/NB9uNdUVD6M
Fecal subtype of the disease
The cause is a bacterial infection located in the gastrointestinal tract. The disease develops unnoticed by the patient.
Marked by an increased degree of speed. It is treated by surgery.
Symptoms of fecal peritonitis:
- Pain in the abdomen for no apparent reason.
- Changes in human skin. The epidermis takes on a pale tint.
- High degree of sweating.
- Low blood pressure.
- Relief occurs in a supine position.
- There is severe fluid loss, up to 5 kg per day.
- The blood is affected by toxins.
- Possible heart attack.
These symptoms should alert the patient and the doctor, since all manifestations indicate the possibility of developing appendicitis.
Only a doctor is able to correctly diagnose the disease and distinguish it from ordinary poisoning or gastric upset.
Diagnosis of fecal peritonitis is carried out through a comprehensive examination. The patient is required to donate blood for biochemistry, which can confirm the presence of fecal peritonitis. A more detailed picture can be seen by performing an ultrasound or x-ray examination.
Treatment of fecal peritonitis is long-term, so the patient needs patience and endurance. This is the only way to achieve a favorable prognosis and speed up the recovery process.
Fecal peritonitis is a secondary symptom of the underlying disease. The first are appendicitis, cholecystitis, ulcers and pancreatic diseases.
Complications of peritonitis
Peritonitis is a fairly serious disease. Its outcome depends on many factors. Particularly important is the stage at which medical care was provided. The nature of the course of peritonitis and the patient’s health status are also important.
Doctors' forecasts for recovery in this case may vary. With a good set of circumstances and the provision of competent and timely assistance, the patient can expect a full recovery. If assistance is provided untimely and unqualified, even death is possible.
Complications of peritonitis include:
- sepsis
- abscess
- hepatic encephalopathy
- intestinal gangrene
- intra-abdominal adhesions
- septic shock
Despite the achievement of very great heights by modern medicine, the treatment of acute peritonitis is today a big problem. The mortality rate for this disease is about 20%.