When a child has a stomach ache, many experienced mothers, even before the doctor arrives, begin to assume - indigestion, poisoning, eating new, unfamiliar foods. Diagnosis is complicated if the child is small and cannot show exactly where it hurts and cannot tell about the nature of the pain. In such cases, some mothers fearfully begin to suspect appendicitis. Of course, only a doctor can confirm or refute the diagnosis, but parents should be able to distinguish some of the primary signs of appendicitis and, if necessary, urgently take the child to the hospital. Today we’ll talk about the peculiarities of appendicitis in children, the symptoms and causes of the disease, as well as the surgical treatment of inflammation.
What is appendicitis
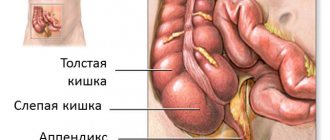
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix (the vermiform appendix of the cecum), which can have varying degrees of severity and be acute or chronic . Inflammation of the appendix is considered the most common inflammatory disease of the abdominal cavity requiring surgical treatment and is the most common cause of peritonitis. Occurs in approximately 5 people per 1000 cases.
Causes
The exact causes of appendicitis in children still remain unknown. Scientists identify 4 main theories:
- Mechanical – explains the occurrence of inflammation by blockage of its lumen, leading to hyperproduction of mucus, its accumulation and active reproduction of opportunistic intestinal microflora. The cause of obstruction may be fecal stones, foreign bodies, helminthic infestations or chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Infectious – suggests that infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, typhoid fever, and yersiniosis can lead to the development of inflammation.
- Vascular – the presence of systemic vasculitis is considered fundamental.
- Endocrine - is caused by the presence in the mucous membrane of the appendix of a large number of cells secreting the inflammatory mediator serotonin.
Modern researchers agree that this disease may have a polyetiological nature, i.e. have several reasons. The following probable causes can be identified that can cause appendicitis in children:
- narrowing of the lumen or blockage of the appendix with fecal stones, parasites;
- congenital anomalies and anatomical and physiological features of the structure and location of the appendix;
- infections;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- hyperplasia of lymphoid follicles of the appendix.
In addition to the direct causes of appendicitis, there are circumstances that contribute to and predispose to its development. Factors that increase the risk of its development include:
- thinness of the wall and poor development of the muscular layer of the appendix;
- a small amount of lymphatic tissue in the appendix;
- anastomoses between the lymphatic vessels of the appendix and other organs;
- anatomical and physiological immaturity of the nerve plexuses and endings of the appendix;
- underdevelopment of the greater omentum;
- abundant blood supply to the peritoneum;
- irregular bowel movements;
- dysbacteriosis;
- poor nutrition.
In addition, the described features of the child’s body are the direct reason that the rate at which appendicitis develops in children is 2 times greater than in adults. Serious complications, including peritonitis and sepsis, can develop in children within a day from the onset of the disease. Regardless of the causes, the mechanism of development of the disease remains unchanged:
- Swelling of all tissues occurs, thickening of the walls of the appendix.
- Due to blood flow, the size of the appendix increases.
- Toxins from the appendix penetrate into the peritoneum.
- Symptoms of peritoneal irritation develop.
- Toxins penetrate into the bloodstream.
- Symptoms of intoxication appear, such as fever.
- Within 2 or 3 days from the onset of the disease, tissue necrosis and perforation of the wall of the appendix occurs with the leakage of its contents into the abdominal cavity.
- Development of sepsis.
- How to connect a subwoofer to a computer
- Classic crab salad: delicious recipes
- What to do if bitten by a wasp. How to provide first aid for a wasp sting at home
Classification
In the classification of childhood appendicitis, there are 2 main directions, depending on the approach - clinical-anatomical and morphological. Clinical and anatomical classification distinguishes 2 forms of appendicitis:
- Acute – acute surgical inflammatory-necrotic disease of the appendix.
- Chronic is a rare form that develops after an acute process. The main characteristic of this form is the presence of atrophic and sclerotic changes in the wall of the process.
The pathological structure of the affected tissues is taken as the basis for the morphological classification of inflammation of the appendix in children. This classification directly reflects the phases of the course of appendicitis in childhood:
- Catarrhal - characterized by impaired blood circulation and lymphatic drainage, venous stagnation and swelling of the appendix wall.
- Destructive - characterized by the spread of edema to the entire thickness of the wall of the appendix, the addition of purulent-necrotic changes. Divided into 2 types:
- phlegmonous - characterized by widespread thickening and swelling of the walls of the appendix;
- gangrenous - manifested by the presence of areas of necrosis of the wall of the process due to vascular thrombosis.
- Empyema is a special variant of destructive phlegmonous appendicitis. Occurs when the lumen of the appendix is blocked with the formation of a closed cavity filled with pus. With this variant of the course, the inflammatory process rarely spreads to the peritoneum, but is accompanied by a sterile serous effusion.
About the signs
Inflammation of appendicitis in children usually occurs at the age of 9-12 years, and in infants this problem occurs quite rarely. If a patient’s appendix becomes inflamed, his condition immediately worsens, he becomes more lethargic, does not want to do anything, and even refuses to play. This indicates discomfort in the child, while the signs of appendicitis in children depend on their age, in particular in children under 3 years of age the signs are somewhat different from adults. Usually the baby will cover the place in the abdomen on the right with his hands, that is, where it hurts. Also, a baby with appendicitis will most likely lie on his tummy, covering the area of pain with his legs and arms, but the true problem can be identified with the help of an ultrasound.
If the child is under 3 years old, then the pain due to inflammation is rather of a general wandering nature, that is, there is no one specific place for the localization of painful sensations, and he will complain of pain in the center of the abdomen and on the right. Symptoms may also include vomiting, diarrhea and an increase in general temperature, which indicate appendicitis. If the baby is under 3 years old, then another sign may be dehydration of the whole body. The oral cavity becomes drier. As soon as the listed symptoms appear, you should immediately go to an ambulance, where they will do an ultrasound and conduct other necessary examinations.
If a preschooler is between 3 and 7 years old, the signs of a problem will vary greatly. At this age, pain is localized primarily in the navel and then moves to the place of the right ilium of the small one. It is at this age that the signs of the problem will be mostly permanent and of a certain nature. Here, children often experience vomiting and severe nausea, and the body temperature will usually be up to 37.5 degrees. There are also cases when the appendix becomes inflamed due to other diseases, such as measles or hepatitis. If these are several diseases at once, then the temperature of the sick person can rise above 39 degrees. In this case, urgent hospitalization and ultrasound are required.
Main clinical forms:
- Simple;
- Phlegmonous;
- Gangrenous;
- Complicated.
Symptoms of appendicitis in children
The symptoms of appendicitis in young patients are directly dependent on age, the anatomical location of the appendix and the phase of the disease. The location of the appendix in relation to other organs determines the rate of onset of symptoms, localization, intensity and nature of the pain syndrome, and age predisposes to changes in the rate of spread of the inflammatory process.
First signs
The first signs of appendicitis in children are characterized by great diversity. They can masquerade as diseases such as cholecystitis, intestinal infections, yersiniosis or food poisoning. Pain may have different characteristics depending on the location of the appendix:
| Location of the appendix | Localization | Characteristics of pain syndrome |
| Medial | Parallel to the ileum | The option with the most pronounced symptoms. Initially, the pain is diffuse throughout the abdomen, and then localized in the umbilical area |
| Lateral | In the right lateral paracolic canal | Pain in the right iliac region |
| Subhepatic | Directed upward to the subhepatic recess | Pain in the epigastric region or in the right hypochondrium radiating to the right shoulder girdle |
| Pelvic | Directed to the pelvic cavity | Pain in the lower abdomen, suprapubic area, stabbing or aching in nature |
| Intramural | Inside the wall of the cecum | Aching in the right side of the abdomen |
| Front | On the anterior surface of the cecum | Acute, in the right iliac region |
| Retrocecal | Posterior to the cecum, includes retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal variants | Dull, aching character in the lower back on the right with radiation to the right thigh |
| Left-handed | In the left iliac region with a mirror arrangement of organs | In the left half of the abdomen of varying intensity |
From an anatomical point of view, medial, lateral, subhepatic and pelvic variants are considered classic. Retrocecal location of the appendix is the most common type of atypical localization of the appendix. In addition to pain, there are other signs of appendicitis in a child:
- refusal to eat;
- nausea and vomiting;
- temperature increase;
- anxiety.
Expanded stage
In each age group, the advanced stage of appendicitis has different characteristics. Symptoms of appendicitis in adolescents are almost identical to the clinical picture in adults.
| Symptom | Children under 3 years old | Children from 3 to 12 years old | Children over 12 years old |
| Onset of the disease | Acute | Gradual | Gradual |
| General condition disorders | Sharply expressed | Gradually increasing | Gradually increasing |
| Temperature increase | Up to 40o C* | 38-39o C | Up to 38o C |
| Vomit | Repeated, without relief | Double, less often multiple | Single or double |
| Pulse | Increased speed | Increased speed | Does not correspond to body temperature, very rapid |
| Pain | They get worse when walking and bending to the right. | Increases in intensity with movement | Increases in intensity when leaning forward |
| Chair | Loose stools mixed with mucus | Retention of stool | Constipation |
| Urination | Painful | Normal | Normal or increased frequency (pollakiuria) |
| Behavior | Anxiety, crying, irritability | Anxiety | Weakness |
*The temperature during appendicitis in children who are breastfed may not rise above 37.5o C.
Features of the course of the disease in newborns
Appendicitis in young children manifests itself with symptoms that can mislead adults. Similar symptoms may occur with colic and bloating, but with appendicitis they have their own characteristics:
- abdominal pain occurs suddenly: the child may scream in his sleep, when changing position, or immediately after waking up;
- the baby often curls up, lying on the right side, often lingers in one comfortable position, without moving;
- the baby may point to the lower abdomen on the right and at the same time push away the hands of adults who want to feel it; vomiting can be repeated and profuse;
- the area of the baby's abdomen, where the appendix is located, may be tense;
- streaks of blood in liquid stool may be evidence of incipient peritonitis.
Complications
With appendicitis, complications can arise both before and after surgical treatment. Acute appendicitis can lead to the appearance of such pathological conditions as:
- appendicular infiltrate;
- abscess;
- perforation;
- peritonitis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- sepsis.
- Zucchini soup - recipes with photos
- Ammonia-anise cough drops. Instructions for the use of ammonia-anise drops for adults and children
- How to open an intercom without a key
Complications can also be caused directly by surgery. Early postoperative complications include pathological conditions that arose in the first 6 days after surgery:
- delayed healing of the surgical wound;
- seam divergence;
- wound infection and suppuration of sutures;
- bleeding from the wound.
Late postoperative complications are those that occur on the 6th to 9th day after the operation. These include the following conditions:
- infiltration or abscess of a postoperative wound;
- infiltrate or abscess in the abdominal cavity;
- inflammation of the stump of the appendix;
- postoperative hernia;
- ligature fistula;
- keloid scar;
- scar neuroma;
- adhesions;
- mechanical intestinal obstruction.
What complications does appendicitis cause?
Delayed surgical intervention, medical errors and unforeseen situations during surgery lead to various complications. Within 48 hours from the onset of inflammation, the body still controls the situation, and no complications arise. The consequences appear between 3 and 5 days, and they are expressed by the following changes:
- Perforation of the appendix.
- Local peritonitis.
- Thrombophlebitis of the mesentery of the cecum.
- Appendicular infiltration.
From the 6th day the situation worsens. The teenager develops diffuse peritonitis, portal vein thrombophlebitis, liver abscess, and sepsis.
Diagnosis of appendicitis in children
The first step when appendicitis is suspected in children is an examination, which includes palpation of the abdomen, identification of specific symptoms, and rectal examination. The greatest difficulty is in diagnosing the disease in children under 3 years of age, since they are not able to describe the symptoms that bother them and almost always react negatively to examination by a doctor . For this reason, children are examined while asleep. Signs of acute appendicitis in children are confirmed by laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Blood tests - to determine the inflammatory process in the body, characterized by a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left.
- Urinalysis - to exclude inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.
- X-ray – to exclude intestinal obstruction.
- Ultrasound - provides an opportunity to detect inflammation of the appendix and the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- Electromyography of the anterior abdominal wall - determines the increase in electrical activity in the affected area caused by the destructive process.
- CT scan – verification of diagnosis when the clinical picture is unclear.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy - used to clarify the diagnosis, in most cases it is extended to appendectomy.
Main causes of the disease
There is no clear and unambiguous theory yet about what appendicitis is in children, that is, the main cause has not yet been established. Today it is generally accepted that inflammation develops due to blockage of the area between the cecum and the appendix itself. Another cause may be inflammation of the common appendages in females, and this disease can also occur when an antigen occurs. Modern doctors suggest that the cause may also be bacterial or infectious infection. Also, the reason may be features in human anatomy, that is, the bend of this area or its large length, which can be easily detected by ultrasound. Another cause of childhood appendicitis may be fecal stones, excessive consumption of meat, atherosclerosis, immune problems and even heart disease.
Treatment of appendicitis in children
If a child develops symptoms of appendicitis, you should immediately seek medical help, since the child needs emergency hospitalization, surgical treatment and medical supervision. If you have symptoms of this disease, you should never use:
- Painkillers, as they may make diagnosis difficult.
- Enemas or laxatives.
- Cold or hot heating pads on the stomach, as they can accelerate the development of the inflammatory process.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
Treatment of appendicitis, with rare exceptions, is surgical. Depending on the severity of the condition and the phase of the disease, different surgical methods are used. The following surgical treatment methods exist:
- Laparoscopic appendectomy – removal of the appendix through punctures in the anterior abdominal wall. The technique is applicable in patients with early stage appendicitis without the risk of appendix rupture and the development of peritonitis.
- Open cavitary appendectomy - removal of the appendix through an incision in the right iliac region. It is used in patients with a high risk of appendix rupture or appendicitis complicated by peritonitis.
After surgery, the patient is required to be prescribed a preventive course of antibiotic therapy. For this purpose, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used, such as Amoxiclav, Ceftiaxone, Cefuroxime, Flemoxin, Azithromycin and others. Self-use of antibacterial drugs is unacceptable, as this can lead to undesirable consequences.
How to protect your child from appendicitis
As noted, appendicitis in children can occur for various reasons. To protect your child from inflammation of the appendix, you need to follow several rules of prevention.
- Nutrition should be correct, balanced, according to the age of the child.
- It is necessary to prevent the development of constipation, especially chronic ones. To do this, you need to eat more fiber, consume fermented milk products, limit the consumption of simple carbohydrates, and drink more clean water. After all, fecal stones, which form during long-term constipation, most often cause blockage and inflammation of the appendix.
- Monitor the health of the gastrointestinal tract - do not overeat, treat diseases of the stomach and intestines in a timely manner, regularly do fasting days, cleanse the intestines with laxative foods.
- Supervise your child so that he does not put foreign objects in his mouth. Remove all small parts of toys from accessibility. Be careful not to swallow fruit pits or other objects that should be spat out.
These rules do not guarantee you 100% protection from appendicitis, but they are quite capable of reducing the risk of its development.
Appendicitis is a complex and easy disease at the same time. On the one hand, the surgical operation to remove appendicitis is quite simple, the postoperative period is short - the person recovers quickly. On the other hand, diagnosing appendicitis is quite difficult, especially if parents associate abdominal pain with food poisoning and do not take their child to the hospital until the last minute. Delay can cost the baby his life. Therefore, do not be shy or lazy to seek medical help once again. Take care of your child, because he has no one else to rely on.
Prevention
In order to avoid the development of appendicitis, the child should be protected from factors that contribute to the occurrence of this disease. Preventive measures that reduce the risk of developing inflammation of the appendix include:
- proper nutrition rich in fiber;
- drinking regime;
- regular bowel movements;
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases;
- prevention of dysbacteriosis.
Highlights
To diagnose appendicitis in children, you need to turn the patient on his left side. Now you should ask him about the sensations; if something is pulling down inside him, then it is most likely appendicitis. Even if there are only suspicions of this disease, then in any case it is better to quickly call an ambulance, otherwise the situation can be fatal. To establish the cause of the problem, a diagnosis is made in medical institutions, that is, the blood and secretions of the sick baby are taken for analysis. So that the analysis of such secretions can be done immediately, it is better to save the diapers from the baby, since an analysis of the secreted liquids will be required in any case for diagnosis. The baby is usually hospitalized, he will have an ultrasound, and then he will be under observation for 6-12 hours or more. And when the treatment is over, an appropriate diet will be mandatory after appendicitis in children.