Structure (anatomy) of the organ
Anatomically, the duodenum is divided into 4 sections: upper, descending, lower and ascending.
The first upper part or pars superior is from 5 to 6 cm long. It is directed obliquely, from front to back, from left to right, then forms an arched bend (superior curvature), and passes into the descending part.
The next part is the descending part or pars descendens, located to the right of the spine at the level of the lumbar region, at the point of transition to the lower part it forms the lower curvature. The length of this part is from 7 to 12 cm. On the medial wall of this part of the intestine there is a longitudinal fold of the mucous membrane. This fold has a papilla on its surface with ducts opening on it.
The horizontal part of the duodenum, pars inferior, 6 to 8 cm long, is directed from right to left, transverse to the spine, then bends upward, where it becomes the ascending part.
The ascending part or pars ascendens, relatively short (4-5 cm), this part forms a curvature called the duodenum-jejunum. This anatomical formation is located to the left of the spinal column at the level of the lumbar region. Sometimes this part of the intestine is not expressed. The initial section of the upper part is called the duodenal bulb.
The duodenum has a variable shape: the most common is a horseshoe shape, less often ring-shaped and angular.
The location of the duodenum is also variable, depending on weight, age and many other factors. In overweight people and young people, the intestine lies slightly higher than in thin and elderly people.
In relation to the spine, the sections of the intestine are also not always located in the same way. The following options for the location of parts of the intestine are more common: the upper part is located at the level of the first lumbar vertebra, the descending part is located to the right of the spine at the level of the second and third vertebrae. The lower part of the duodenum corresponds to the space from the third to the fifth lumbar vertebrae. Less often it descends to the pelvis.
The duodenum is covered by peritoneum unevenly, over a small area. The upper part of the intestine is in contact with the pancreas, common bile duct, portal vein, and gastroduodenal artery. In this place the intestine is devoid of cover. Therefore, this section is located mesoperitoneally. The ascending intestine is approximately similarly covered with peritoneum.
The descending and lower sections of the intestine are located retroperitoneally; they have peritoneal cover only in the front.
From the walls of the duodenum to the organs of the retroperitoneal space there are connective tissue fibers that fix it. The main function of fixing the intestine is performed by the peritoneum, which covers it in front. The second role is played by the root of the mesentery of the transverse colon. The pancreas has a certain role in fixation.
The least fixed part of the intestine is the upper one, therefore it is the most mobile. She can easily move in different directions.
Diagnostics
A gastroenterologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the duodenum . In rural areas, primary (rather approximate) diagnosis can be carried out by a general practitioner or family doctor, but with a mandatory, at least one-time, consultation with a gastroenterologist.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
FGDS or gastroscopy is the most informative method in which the internal surface is examined using an endoscope inserted through the mouth. The fibrogastroscope is equipped with a video camera that allows you to take pictures, a biopsy instrument and a probe through which you can inject medicine directly into the lesion. The device also allows you to apply hemostatic clips.
The procedure is unpleasant, but harmless, and in many cases allows one to avoid surgery.
Biopsy
Excision of a tiny piece of living tissue for further histological examination. The cellular composition, tissue fluid, and pathological formations are examined. Allows you to reliably distinguish between acute inflammation and chronic inflammation, a benign tumor from a malignant one, and a developmental anomaly from a scar.
Analysis for Helicobacter
Helicobacter is considered the main etiological factor of peptic ulcers and gastric cancer. This is the only bacterium that can live in the hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach. The test is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or ELISA for antibodies to Helicobacter; venous blood sampling is required.
Some laboratories examine stool or exhaled breath.
General blood analysis
The severity of inflammation, the presence of anemia and other general clinical indicators reflecting the general level of health are determined.
Occult blood test
The stool is examined, in which altered red blood cells can be detected. Allows you to detect hidden bleeding from the digestive canal. The pharmacy has express tests for detecting occult blood in the stool on your own.
Sonography of the duodenum reveals thickening of the intestinal walls or an ulcerative defect found in the form of a crater. The boundaries of inflammation and the place of transition into healthy tissue, as well as tumors, if any, are clearly visible.
MRI and CT
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography detect lipomas (tumors from adipose tissue) and leiomyomas (from muscle tissue). These tumors are benign. Duodenal cancer or adenocarcinoma is a rare case, but they are also visible in these studies.
https://youtu.be/zMS9jB4fF9E
What systems surround the duodenum?
In front and above the upper part of the intestine are the following organs: the quadrate lobe of the liver, the neck and the body of the gallbladder. The hepatoduodenal ligament is located between the upper part of the intestine and the left lobe of the liver (lower surface). At the base of this ligament lies the common bile duct. The upper part of the duodenum, not covered by peritoneum, is in contact with the portal vein, common bile duct, and arteries (gastroduodenal and pancreatic-duodenal).
The posterior surface of the descending part of the intestine is in contact with the pelvis of the right kidney, ureter, and renal vessels. The hilum of the kidney is slightly covered by the duodenum. The descending part of the duodenum is in contact with: the right curvature of the colon, the ascending colon, and the head of the pancreas.
The common bile duct is often located in the parenchyma of the head of the pancreas, then it connects with the pancreatic duct and flows into the duodenum. On the surface of the intestinal mucosa there is a small longitudinal fold (up to 1 cm long), on the surface of which there is a large duodenal papilla, on which the pancreatic duct opens. Sometimes there is an accessory pancreatic duct that opens higher than the main one.
Between the descending part of the duodenum and the head of the pancreas, a groove is formed in which the common bile duct lies. The superior mesenteric vein and artery are adjacent to the lower part of the duodenum. These vessels are located at the root of the mesentery. Further along this section the transverse colon and loops of the small intestine are adjacent.
Sometimes the duodenum can be compressed by the superior mesenteric arteries, leading to obstruction. In the clinic, such cases are called arterio-mesenteric obstruction, which often occurs with prolapse of the small intestine and some other diseases of the abdominal organs. Retroperitoneal tissue and loops of the small intestine surround the ascending part of the duodenum. The lower part of the intestine crosses the aorta at different levels: above or below the bifurcation.
The intestinal walls are constructed as follows:
- serous membrane;
- muscle layer;
- mucous membrane.
Between the mucosa and the muscle layer is the submucosa. The mucous membrane is covered with many villi. The villi are lined with prismatic bordered epithelium, which significantly increases the absorption capacity of this part of the gastrointestinal tract. Between these epithelial cells are goblet enterocytes that produce glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans. The hormones enteroglucagon, gastrin and secretin are produced by other cells - Paneth or intestinal enterocytes. The duodenal bulb has longitudinal folds, the rest of the small intestine has circular folds. Due to the common bile and pancreatic ducts, a longitudinal fold of the mucous membrane is formed.
The mucosa contains lymphatic follicles, lymphocytes and plasma cells. The submucosa contains duodenal or Brunner's glands, the ducts of which open on the surface of the intestinal crypts.
The muscular layer of the intestine consists of non-striated muscle fibers arranged in two layers. The outer layer is longitudinal, the inner layer is circular. Serosa covers the duodenum partially, for a short distance. The remaining parts of the intestine are covered with adventitia, which is loose connective tissue. Numerous vessels and nerves pass through it.
Which environment predominates in the lumen of the duodenum depends on the stage of digestion. Before digestion begins, the environment is slightly alkaline (pH from 7.2 to 8.0). When the acidic contents of the stomach enter the intestine, the reaction changes towards acidic, but is then quickly neutralized and restored to its previous levels. The acidic environment is neutralized by pancreatic juice and other digestive juices.
FGDS
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a technique that allows you to visually examine the mucous membrane of the digestive organs of the upper abdominal cavity from the inside. This study is extremely important for making a diagnosis. Thanks to FGDS, the doctor can determine the extent of the area covered with ulcers, take material for analysis for helicobacteriosis and biopsy. In addition, in the presence of bleeding, endoscopy can actually be transferred to the category of therapeutic manipulations (instillation of drugs, coagulation).
Important! Endoscopic diagnosis of gastric ulcers is strictly required if malignant cell degeneration is suspected. If malignancy is detected, the patient is examined and subsequently treated by an oncologist. If it is impossible to perform an FGDS, the patient is prescribed alternative diagnostic methods.
Features of digestion and organ functions
From the stomach, food in a liquid or semi-liquid state enters the duodenum. The pyloric part of the stomach performs peristaltic contractions and pushes the bolus of food towards the sphincter. The latter's receptors send a signal along the vagus nerve, and the sphincter opens. The opposite happens when the food bolus irritates the organ's receptors. The muscle sphincter remains closed until the chyme moves further through the intestines. The main functions of the duodenum: participation in the process of digestion and absorption of nutrients. The next stage of digestion begins in this section of the intestine. The common bile and pancreatic ducts open on the surface of the nipple of Vater. The process of digestion of food is carried out by pancreatic juice, intestinal juice and bile. All these components have a pronounced alkaline reaction, so the acidic environment of food coming from the stomach is quickly neutralized. Pancreatic juice contains organic and inorganic substances. The first include proteolytic, lipolytic, aminolytic enzymes. Proteins are broken down by trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase and carboxypetidase. Inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes protect the pancreas from self-digestion. Lactase, maltase and amylase break down carbohydrates into monosaccharides. Phospholipase and lipase break down fats into simpler components (glycerol and fatty acids). Liver cells secrete bile into the intestinal lumen. Externally, it is a liquid with an alkaline reaction, golden yellow. Dry residue contains up to 2.5%. Main components: pigments, bile acids, cholesterol. From 0.5 to 1.2 liters are produced per day. This process is continuous, however, bile enters the intestines only during meals. The rest of the time, bile is in the gallbladder. Bile is necessary to activate pancreatic enzymes. In particular, lipases. Emulsification of neutral fats is carried out by fatty acids. In addition, bile enhances the peristalsis of the intestinal walls, increases the production of pancreatic juice, and acts as a bacteriostatic substance, preventing the development of putrefactive bacteria.
Laboratory methods
If a peptic ulcer is suspected or detected, the patient is prescribed blood tests (clinical, biochemical and antibody), urine, and stool tests. The presence of anemia indirectly confirms the fact of bleeding. A positive Gregersen reaction indicates the presence of a bleeding vessel in the gastrointestinal tract.
To make a complete diagnosis, it is possible to use various tests for Helicobacter pylori. The most famous is the breath test. The patient is given a special solution with urea to drink. Then, using an indicator, the concentration of substances metabolized by Hp is assessed in the exhaled air.
How it hurts: symptoms
Diseases of this part of the digestive tract can be of inflammatory and non-inflammatory nature.
The most common inflammatory disease is duodenitis. The following bacterial and fungal infections are less common: tuberculosis, actinomycosis. Typically these infections are acquired from other organs. Duodenitis can simulate the symptoms of a peptic ulcer.
The second most common diseases are erosive and ulcerative diseases. Often these diseases are combined with liver pathology, intestinal neoplasms, diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and kidneys. Therefore, all patients who have been found to have erosions of the stomach or duodenum are subject to careful examination.
Approximately 10% of the world's population suffers from peptic ulcer disease. Peptic ulcer disease is mainly provoked by stressful situations, bacterial infection, smoking, the use of certain drugs and poor diet. In approximately half of patients, this disease is hereditary. The disease worsens in the spring. Often the duodenal bulb has scar changes after the healing of the ulcer.
Diseases of a tumor nature are relatively rare. These can be both malignant and benign neoplasms. The risk of developing the disease increases with age. Among malignant tumors, the first place belongs to sarcoma. The predominant localization is the descending part of the organ. The main factors in the development of the disease are diffuse polyposis, adenomas, hereditary intestinal diseases and Crohn's disease. Benign tumors can be multiple or solitary. Often, when large in size, they can contribute to the development of complications of the disease: intestinal obstruction and bleeding. Specific examination methods will help confirm or refute the presence of the disease.
Main symptoms of diseases.
- All diseases of this organ are accompanied by pain. With ulcers and erosions, the patient is bothered by “hunger pains” and frequent night attacks. The peak of pain occurs after eating (after 2 hours). The patient will note that the pain subsides after eating. With an ulcer of the intestinal bulb, the pain subsides after vomiting. Localization of pain: right hypochondrium, epigastrium, radiates to the back and right arm. With peptic ulcer disease, pain is the main clinical concern.
- Bleeding. This symptom occurs in approximately 20% of patients. It manifests itself as melena (black stool), bloody vomit, and vomit the color of coffee grounds. The blood test shows low hemoglobin, the patient is weak and prone to developing collapsing conditions.
- Dyspeptic disorders. The patient is concerned about the following symptoms: heartburn, loose stools, or, conversely, constipation.
- Increased appetite. More often, this symptom is due to the patient’s desire to drown out “hunger pains.”
- Intestinal diseases are accompanied by irritability, poor health, and general symptoms.
The diseases may have the following complications: bleeding, organ perforation, cicatricial deformities, narrowing of the lumen, precancerous conditions, malignancy of benign tumors, reactive pancreatitis, liver and gallbladder diseases.
How a common disease manifests itself: duodenitis (video)
In general, the diseases have a favorable prognosis, with the exception of some complicated situations. Patients are able to work, but the type of activity should be changed if it is associated with stressful situations, poor diet, or heavy physical exertion.
Prevention of diseases of this part of the intestine is not difficult. The main thing for the patient is to follow a diet, exclude certain foods from the menu, and give up bad habits. Diseases of the duodenum of inflammatory and infectious origin have a relapsing course.
Patients with diseases of the duodenum are under constant medical supervision and undergo an anti-relapse course of treatment in the spring and autumn. In the absence of a proper regimen and full treatment, all symptoms of the disease recur. A preventive course of treatment should be taken every 3-5 years, even if there are no obvious symptoms of the disease.
Pathologies of the duodenum
The work of the duodenum is designed for a certain diet and its quality. In case of violations of this regime, she is the first to react to changes, and often this results in certain diseases. There are several factors that lead to them:
- Eating foods that increase stomach acidity. Excess acidity cannot be compensated for by enzymes coming from the pancreas.
- Disturbance of the liver and pancreas. Because of this, the nature of the secretion of enzymes may change, which again leads to a change in the environment in the lumen of the organ. A special role here is played by the phenomenon of biliary dyskinesia.
- Insufficient stomach activity or difficulty chewing food. Undigested lumps injure the mucous membrane of the duodenum.
- Close proximity to other organs leads to metastasis of tumors from them to the duodenum. Primary oncological lesions occur much less frequently here.
Symptoms of common diseases
There are three types of duodenal diseases , the symptoms of which may have similar features or may differ. Moreover, the nature of these differences determines not only the disease itself, but also its exact location, as well as the cause. The most common diseases of the duodenum are:
Common symptoms of duodenal pathologies are indigestion, from constipation and bloating to diarrhea, belching, heartburn, pain just below the solar plexus, which can radiate to both the right hypochondrium and the spine.
Sometimes, especially in old age, diseases may not manifest themselves at all, that is, they may be asymptomatic. In this regard, it is better for people over 60 years of age to regularly check the condition of the gastrointestinal tract instrumentally and laboratory, since this is how oncological diseases of the gastrointestinal tract often begin. Many of them are diagnosed already in the 4th stage, when the tumor has given extensive metastases and become a source of obstruction.
Duodenitis: causes, diagnosis, treatment
Duodenitis is an inflammation of the duodenum. Sometimes this disease can be widespread and involve the stomach - in this case they speak of gastroduodenitis. In other cases, the process can be localized in one section, for example, in the bulb - then a diagnosis of bulbitis is made.
The causes of duodenitis are:
- intestinal infections;
- poisoning;
- eating spicy foods and alcohol;
- mechanical damage.
There are acute and chronic duodenitis. The second occurs when the first is not treated or if the causes that led to the disease have not been eliminated. Pathologies of the biliary tract or pylorus play a significant role in the development of the chronic form.
The acute phase of the disease is characterized by nausea, vomiting and pain in the epigastric region. Sometimes they may be accompanied by increased temperature.
In the ulcer-like form of the disease, pain may intensify at night and on an empty stomach. If the bile ducts are involved in the process, the pain shifts to the right hypochondrium and a characteristic bitter taste appears in the mouth.
Chronic duodenitis is rarely an independent disease. Most often it is secondary, and its symptoms may not be expressed against the background of pathologies of the liver, stomach, pancreas and other neighboring organs. Therefore, special attention is paid to diagnostics, especially instrumental ones.
Treatment of duodenitis should be carried out together with treatment of the underlying disease. At the same time, to eliminate the inflammatory process, antibiotics are used aimed at suppressing the activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, as well as antacids (Almagel) and inhibitors (omeprazole).
Untreated duodenitis can lead to complications. They can be acute - for example, the development of periduodenitis, if the outer wall is involved in the process, and chronic, which include the ulcerative process and the development of secondary lymphangiectasia, when the pancreatic-duodenal lymph nodes expand and their walls become permeable. This leads to loss of lymph, and, as a result, exhaustion, decreased immunity and disruption of water-salt balance.
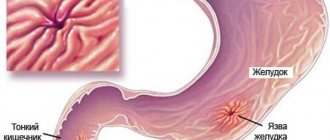
Peptic ulcer
This is a common disease of the duodenum . The symptoms of the disease are familiar to many - pain and dyspepsia, and they are periodic. Duodenal ulcers occur four times more often than in the stomach; men are affected more often than women. Exacerbations of the process occur on average twice a year, although if you follow a diet, remission can last up to several years and even lead to recovery with scar formation. The scar distinguishes an ulcer from the erosions that occur with duodenitis. They affect only the mucous membrane, while an ulcer affects the entire wall of the duodenum.
Surgery for peptic ulcer disease
- with perforation of the ulcer or heavy bleeding;
- frequent exacerbations of the disease that occur despite drug treatment;
- narrowing of the outlet of the stomach, which arose due to scar deformation of the duodenum;
- chronic inflammation that does not respond to drug therapy.
The essence of surgical treatment is to remove part of the stomach. During the operation, the part of the internal organ that is responsible for the secretion of gastrin in the body is excised. This substance stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that if suspicious symptoms characteristic of diseases of the duodenum occur, you should seek help from specialists at the clinic. Self-medication for ailments is inappropriate, because incorrect drug therapy, its absence or unnecessary folk remedies can cause serious harm to your body and worsen your well-being.
Best answers
fatal, but first there will be a perforated ulcer
perforation, hemorrhage. peritonitis and death. Don't joke with your health, go to the doctor!
perforation of the ulcer - the hole will be eaten right through. you will begin to rot from the inside. blood poisoning. lethal outcome - this is promising, isn’t it cool?))) Run to the doctor.
Complications of ulcers can be fatal
Hundreds of thousands of people suffer from stomach ulcers. This serious illness is widespread, and it is much more common among residents of economically developed regions. First of all, peptic ulcer disease is dangerous due to its complications, many of which can be fatal.
Often, bleeding begins suddenly, for no apparent reason. However, there are also provoking factors, for example, addiction to cigarettes and, above all, smoking on an empty stomach, strong coffee in the morning, and frequent stress. The complication has obvious symptoms: a sudden feeling of weakness, cold sweat, dizziness, a feeling of fear, drowsiness, increased heart rate. If a lot of blood accumulates in the stomach, the patient may vomit. This is the so-called vomiting of coffee grounds, since due to interaction with hydrochloric acid, the blood changes color from bright red to dark brown. However, bleeding can also develop in a slow scenario, when a sick person, without knowing it, can absorb and digest a sufficient amount of his blood. In this case, he should be alerted by the fact that the stool turns black. This is a sign of bleeding in the intestines and stomach.
The most dangerous type of bleeding, as experts emphasize, is profuse bleeding, that is, from large vessels. In this case, the patient can lose several liters of blood in just 15-20 minutes. Treatment of bleeding is the task of emergency physicians. Treatment is carried out using modern endoscopic technology. Its use has made it possible to reduce the number of operations for bleeding due to peptic ulcer disease. It should be remembered that bleeding that occurs once can happen again.
pain, severe pain, then intraintestinal bleeding, if you don’t stop it, it’s over. Another scenario: When it hurts very much - consent to surgery, removal of part of the intestines and a strict diet for the rest of your life. In short, if you don’t treat now, you may not see a bright future....
Dedicated to supporters of separate nutrition
The fundamental principle of pancreatic secretion is that the pancreatic juice of the pancreas always contains three main groups of enzymes:
Amylase is necessary for the processing of carbohydrates, only thanks to it they are destroyed and absorbed into the blood. Different types of sugars have their own specific type of this enzyme.
Lipase is an enzyme produced in the pancreas, without which the breakdown and absorption of fats is impossible.
Proteases are enzymes also produced by the pancreas. They are necessary for the breakdown of protein compounds.
Although pancreatic digestive enzymes do not replace each other, they have a lot in common.
“Three fellows, identical in appearance” are classified as proteins and act only within a certain temperature range, without access to light and oxygen.
Metabolism of fats, carbohydrates and proteins in the body occurs only in the presence of these enzymes, and all three at once.
Pavlov, the founder of physiology, conducted experiments during which dogs were fed isolated food for some time.
After some time, the animals died, but the composition of the pancreatic juice secreted in their body throughout the entire time remained unchanged in three components - amylases, proteases and lipases.
The ratio in which the pancreas produces enzymes depends on what types of food a person eats.
It has been established that if a person eats only protein foods for a long time, then after 2 weeks the enzyme composition will show 70% proteases and 15% each of lipases and amylases; if a person eats only fats for a long time, then lipase will predominate in the structure - 70-80%
And if you are on a carbohydrate diet, the percentage will shift towards amylase - 60-70%, respectively, the share of proteases and lipases will remain at 15-20%.
That is, the law of the producing pancreas is as follows: whatever the chemical composition of the food entering the duodenum, the enzymatic composition of pancreatic juice always contains 3 unchanged essential components.
In other words, when food passes, all three enzymes that need to work are dripped onto it from the sphincter of Oddi.
Nature, as it were, takes care and helps us in any case to play it safe and digest all the mountains of food that we throw into our stomachs.
Let’s say someone doesn’t eat fat on principle, then the lipase enzyme will grind not on a fatty piece of food, but directly on the wall of the duodenum. Or a person refuses proteins and the protease enzyme begins to eat away not a piece of meat, but the same long-suffering wall
Hence the wide distribution (up to 30%) of ulcerative processes of the duodenum in those who are obsessed with various dietary restrictions - vegetarians, fans of separate meals, etc.
The method of better and more reasonable nutrition is dictated to us by the very organization of our physiology and looks simple and convincing - we need to eat everything, and the duodenum itself will determine what and how to digest it all and send the precious substrate further.
Further - this means into the sphere of activity of the small intestine, the length of which in an adult with a height of 1.7 m reaches 7 m, in a person of 2 m - 10 m, in a small child - 1 m.
Diagnostic procedures for peptic ulcer disease
A suitable and reliable method for diagnosing peptic ulcer disease is fibrogastroduodenoscopy. During this test, a special instrument with a light source and camera is inserted through the mouth into the stomach to examine the lining of the digestive system. The image is formed on the monitor. The doctor evaluates the stomach and duodenum. Diseases are diagnosed by noticeable pathological changes. If necessary, the specialist takes a sample of the mucous membrane to examine for the presence of microorganisms that provoke the occurrence of peptic ulcers.
What is meant by peptic ulcer?
When considering diseases of the duodenum, special attention should be paid to peptic ulcers. This term refers to a serious disease that occurs in a chronic form with alternating periods of remission and exacerbation. The etiology of this disease is not well understood. Previously, it was believed that peptic ulcers were caused by substances such as pepsin and hydrochloric acid, which were produced in the digestive system. However, studies have shown that the microorganisms Helicobacter pylori play an important role.
Statistics show that the prevalence of duodenal ulcer ranges from 6 to 15%. It cannot be said that a representative of a particular gender gets sick less often or more often. Men and women are equally susceptible to this disease.
Prevention measures
Paying attention to your diet will help protect the duodenum from damage.
- You should not eat food that is too hot or too cold.
- Chew food thoroughly so that the pulp enters the duodenum, because the stomach and intestines do not have teeth.
- You should not wash down food with cold drinks, as this opens the sphincter, and all food enters the duodenum undigested by gastric juice.
- Eat food in a good mood and without rushing.
- Monitor normal stomach acidity.
- Follow the rules of hygiene - wash your hands and food.
https://youtu.be/VQua_8pjJPA
data-matched-content-rows-num=”4.2″ data-matched-content-columns-num=”1.2″ data-matched-content-ui-type=”image_stacked” data-ad-format=” autorelaxed">
https://youtu.be/ziU3RkTHR0c