Let's try to figure out what appendicitis is, where it is located and how it hurts - this is important, since the signs of the disease are very similar to various internal pathologies. And an undetected disease in time is fraught with various unpleasant consequences, including death.
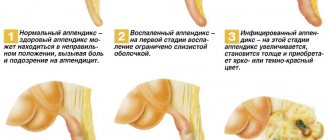
The development of the disease is caused by inflammation reactions in the internal structure of the appendix (vermiform appendix). They can manifest acutely or have a chronic course. Appendicitis in humans is the most common pathology among surgical diseases, which is diagnosed in every 5 out of 1000 people under the age of 35 years.
The first description of the vermiform appendix was found in the works of Leonardo da Vinci, although its official recognition by scientists occurred many years later. For a long time, the organ was considered completely useless for the human body, and was declared rudimentary - underdeveloped and useless, having lost its functions over the course of evolutionary processes. Although this is not entirely true.
Where is appendicitis located?
In the human body, the appendix performs a protective function against pathogens, as it contains a huge number of beneficial bacteria.
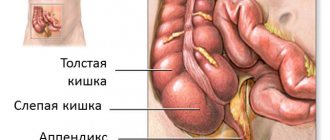
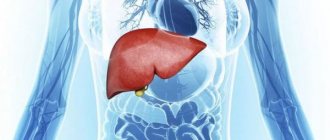
Normally, intestinal contents do not enter it. Sometimes the appendix is even called an incubator, where beneficial microorganisms are stored and developed. Appendicitis in humans (where this pathology is located will be described below) is a disease that is expressed in the inflammatory process in the appendix. This is a vermiform appendage extending from the cecum. It is located in the iliac fossa on the right.
The appendix is located on the periphery of the small and large intestines, that is, between these two sections. Its length can be minimal - 5 cm, or can reach 15 cm. However, its diameter usually does not exceed 1 cm. It is generally accepted that the appendage is necessary to protect the small intestine from the penetration of bacteria living within the cecum.
There are the following options for the location of the appendix:
- pelvic, which is characterized by a descending position of the appendix (most common);
- lateral (observed in approximately 26% of patients);
- medial (at least 20% of cases);
- retrocecal. Expressed by the location of the organ in the abdominal cavity or retroperitoneal space.
Causes of the disease
The appendix is a vermiform appendix of the cecum that is part of the immune system because it contains immune cells. Every person should know which side appendicitis is on, so as not to miss the acute stage of the disease.
So, on which side is the appendix located in the stomach? The vermiform appendix is located closer to the right side of the lower abdomen, in the iliac region, smoothly descending to the pelvis. In some cases, it may be located behind the cecum and reach the liver with its upper part. The length of the appendix can vary from 0.5 to 23 cm. The standard value is 7-8 cm. The width, as a rule, does not exceed 1 cm.
Inflammation in this area develops due to a number of factors:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- infectious processes in the area of the digestive system;
- blockage with undigested food particles or feces;
- strong mobility of the process (most often observed in children).
Experts cannot give a definite answer as to what exactly leads to inflammation of the appendix. Among the most striking hypotheses, predisposing factors such as disturbances in intestinal microflora, overeating or eating large amounts of protein foods should be highlighted. Doctors believe that appendicitis can also become inflamed due to an inactive or sedentary lifestyle.
https://youtu.be/kg1mINGa008
Where in the body is the appendix located?
The human gastrointestinal tract begins with the oral cavity and ends with the rectum. The oral cavity passes into the larynx, and then into the esophagus. It connects the larynx to the stomach, which passes into the small intestine. Behind it begins the large intestine. It is located in the shape of the letter “P” and consists of several sections: the cecum, ascending, colon, sigmoid and rectum.
The sigmoid colon is located in the left lower quadrant of the abdomen. It is in it that the final digestion of food occurs, and the functions of the rectum are mainly evacuation. The cecum is located on the lower right side of the abdomen, and it is it that contains a peculiar appendage in the form of a ventricular appendage, which is called the appendix.
The condition when it becomes inflamed is called appendicitis. Now it becomes clear that to say that a person’s appendicitis was “cut out” is incorrect, because this definition means an inflamed condition of the appendix. Therefore, the question of where the appendicitis is, on the right or on the left, is not correct.
General information about the appendix
For a long time it was considered an ancient remnant of evolution and a mistake of nature. Scientists for many years could not unravel the mystery of its purpose. However, science does not stand still and it has become known that this small process contains lymphoid tissue and is a part of the body’s immune system.
- digestive;
- protective;
- hormonal;
- endocrine.
Beneficial microorganisms, which multiply in the appendix, restore the intestinal microflora after poisoning in a short period. When it becomes inflamed, a disease called appendicitis develops. Everyone needs information about where the appendix is in order to recognize the first signs of pathology in time.
What kind of pain occurs with appendicitis?
In acute appendicitis, the main symptom is pain. Most often it is preceded by loss of appetite. In diagnosis, it is very important to clarify the nature of the pain: when it occurs (immediately after eating or a little later, on an empty stomach, etc.). It is necessary to find out from the patient where the pain initially appeared.
Regardless of the fact that the appendix is located in the right iliac region, one of the most common variants of appendicitis is that in which a person has pain around the navel or in the epigastric region. This localization makes it possible to exclude a perforated gastric ulcer, as well as rupture of an ovarian cyst (in a woman). The above pathological conditions are characterized by more intense and rapidly increasing symptoms.
When asking a patient where it hurts, with appendicitis, a fairly wide area is most often indicated, roughly defined as the middle part of the abdomen. In this case, painful sensations spread from the center to the periphery.
The pain may occur sporadically or may be constant. The intensity depends on the stage of the inflammatory process. Catarrhal appendicitis is most often accompanied by unexpressed painful sensations. When inflammation penetrates into the deep layers of the appendix, the pain becomes prolonged and more intense.
Then the pain migrates and occurs in the side on which the appendicitis is located: in the iliac region on the right. They are already permanent, becoming dull and more intense. Typically, it is these symptoms that make a person realize that something is wrong and seek qualified medical help.
In some cases, in which side appendicitis progresses, pain occurs there. Moreover, they may be the only clear symptom of inflammation of the appendix.
If the appendix is located with the apex upward or is displaced higher than in the classic location, the patient may feel pain in the back, in the side, just below the ribs. Moreover, the stomach remains painless.
Painful sensations in the groin, above the pubis and in the iliac region on the left can occur with the pelvic location of the appendix. Therefore, if appendicitis occurs, on which side and in which zone it hurts is not yet an indication that it is there that the vermiform appendix is located. However, most often they help determine where appendicitis is located, symptoms: pain and symptoms according to the authors.
What diseases can be confused with
Acute inflammation of the appendix is differentiated from renal colic, exacerbation of pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, ulceration or perforation of the small intestine, stomach. Be sure to exclude intestinal obstruction, acute heart attack, diverticulitis, food poisoning and other toxic reactions.
In women, pathologies of the internal genital organs (ectopic pregnancy, ovarian pathologies, inflammation of the fallopian tubes) are excluded.
In men, appendicitis is differentiated from inflammation of the prostate, malignant tumors, and acute venereal diseases. In children, pneumonia, acute respiratory viral infections, coprostasis, pathologies of the urinary tract and gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys are excluded.
If the clinical picture is questionable, an urgent ultrasound of the abdominal organs, biochemical analysis of blood, stool, urine, X-ray with contrast, ECG or therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy is indicated. In rare cases, colonoscopy and MRI are indicated.
Symptoms of appendicitis by author
There are many specific symptoms of such an acute pathology, which bear the names of the doctors who described them.
Sitkovsky's symptom
The patient is placed on his left side. The pain occurs on the side on which the appendicitis is located - on the right, in the iliac region.
Rovsing's symptom
With jerky movements of the fingers, the doctor presses on the area of projection of appendicitis. Painful sensations become more intense.
Obraztsov's symptom
The patient is placed on his back and asked to raise his right leg without bending it upward. In the place where the appendicitis is, the pain becomes stronger.
The doctor pulls on the patient's shirt, holding it with his hand at the bottom edge. After this, the patient is asked to take a breath. At the same time, the doctor uses his fingertips to make quick superficial movements from the upper abdomen down and to the right. The sliding of the hand is ensured by a stretched shirt. The moment the movements stop, the pain becomes more intense.
Knowing how to identify appendicitis, you should not self-medicate. You still can't do it without surgery. And the sooner the inflamed organ is removed, the less likely it is to develop complications.
How to recognize appendicitis? Doctors recommend calling a doctor immediately if a person experiences the following symptoms:
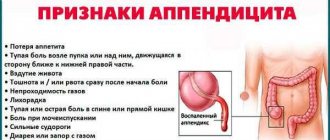
- Pain. This is the very first and main symptom of inflammation of the appendix. At first, the pain may be concentrated in the upper abdomen, reminiscent of an attack of pancreatitis, or around the navel, simulating symptoms of abdominal pain. After 5-10 hours, the pain “sinks” into the right iliac region - the location of the cecal appendage. Depending on the individual characteristics of the structure and location of the appendix, the pain may be located in the area of the femur, liver, or the right edge of the pubis. In this case, any movements cause increased pain in the lower abdomen. Their character is wavy.
- Nausea. It usually appears after abdominal pain occurs. Nausea may be followed by vomiting 1-2 times.
- State of the language. With appendicitis, it becomes covered with a thick layer of white plaque, and salivation is difficult.
- Fever. The patient's body temperature is often above 37 degrees C, but below 38.
- There may also be: diarrhea, frequent urination, cold sweat, increased heart rate.
With inflammation, pain develops on the side in which appendicitis is localized. When the following clinical picture appears, you should immediately call an ambulance.
- The key symptom is pain that appears on the side on which appendicitis develops in a person, that is, on the right, at the bottom of the peritoneum. Discomfort is clearly felt when pressing on the abdomen, especially on the side where the inflammation is located. The abdomen becomes hard to the touch and bloated. It becomes difficult for the patient to walk and stand. He feels relief only in a lying position, with his legs pulled up to his stomach.
- Additional signs. Pain in the abdominal area may be accompanied by symptoms such as an increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees, periodic vomiting and constipation, nausea and back pain. You may experience diarrhea and a painful urge to have a bowel movement, which are often false.
It is not enough to just know which side a person has appendicitis on. It is important to remember additional symptoms, which allows you to consult a doctor in a timely manner, eliminating the likelihood of complications.
It should be noted that a characteristic feature of appendicitis is sharp pain when pressure on the abdomen is relieved. The patient has a white coating on his tongue.
In adults
Men often confuse inflammation of the appendix with inflammation in the bladder or kidney problems. Women mistake the symptoms that arise for inflammation of the appendages.
Appendicitis is a serious danger for people with diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and cancer. Serious consequences can also occur in pregnant women. In order to avoid complications, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
In children
In childhood, the symptoms of appendicitis differ from the manifestations of the inflammatory process in adults. This is due to the fact that in the child’s body the lymphoid tissue of the appendix is poorly developed.
In young children, the location of the appendix is retrocercal (behind the rectum) or subhepatic. This is also the reason why the symptoms differ from the manifestations of the disease in an adult.
In which side does appendicitis hurt in a child? Also on the right side of the lower abdomen. This sign is accompanied by a number of signs characteristic of a child’s body:
- increase in low-grade fever;
- disturbance of urination processes and vomiting;
- bloating, diarrhea, or constipation;
- tachycardia (increased heart rate);
- signs of severe anxiety (sleep disturbances, refusal to eat, crying).
In childhood, the development of the inflammatory process in the area of the appendix occurs rapidly. First, pain occurs in the epigastric region. Discomfort gradually descends to a characteristic location.
If the appendix is in an atypical area, then the pain will be localized in the liver, lower abdomen above the pubis or in the lumbar region, radiating to the groin. In some cases, discomfort may radiate to the back, perineum or groin. In this case, difficulties may arise during the diagnostic process; only an experienced doctor should recognize the disease.
Spanish scientists found that in 40% of cases of acute appendicitis, children under 14 years of age had consumed chips or sunflower seeds the day before.
Appendicitis in humans (where the source of inflammation is located, the patient recognizes by the localization of pain) is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Abdominal pain is the primary sign of inflammation. She manifests herself on the right side. It may start in the upper abdomen and then change to the lower abdomen. The pain can radiate to the back, right hypochondrium, or rectum.
- Pain in the abdomen when palpated.
- Tight abdominal muscles.
- The desire to bend your legs under you.
- Nausea and vomiting and fever may occur.
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Dilated pupil of the right eye.
Differences between appendicitis and other diseases with similar symptoms:
- Acute gastritis. Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea are its main symptoms. There are no local symptoms. Abdominal pain has a cramping appearance. The abdomen, in between pain sensations, is soft.
- Toxic infection of the gastrointestinal tract caused by staphylococcus. Accompanied by fever and chills.
- Stomach or duodenal ulcer. It is characterized by pain in the epigastric region, which may appear or increase after eating.
- Cholecystitis. The pain spreads as inflammation develops. It radiates to the back, right shoulder blade, right shoulder. It intensifies if you shake the patient's bed and take a deep breath. Fever and chills appear, and jaundice may develop.
- Pancreatitis. The painful focus is in the epigastric and umbilical region. The pain subsides when sitting with legs bent.
Differentiating appendicitis from other conditions
Every person should know in which side appendicitis hurts, since there are a number of diseases in which the symptoms are similar to the inflammatory process in the area of the appendix.
Acute gastritis
Accompanied by nausea and vomiting, as well as discomfort in the iliac region.
The difference is that with appendicitis there is a reflex tension of the muscle structures in the peritoneum. With inflammation, pain in the epigastric region is present only at the beginning (Kocher's symptom).
Symptoms of acute gastritis usually occur in response to a dietary disorder.
Toxic infections of the gastrointestinal tract (caused by staphylococcus)
They develop mainly when eating low-quality food products. Accompanied by exacerbation of enteritis or gastritis. Patients experience vomiting, pain in the pancreas or other parts of the abdomen. Distinctive features are the defeat of all family members at the same time. With appendicitis, there is no repeated painful vomiting, and there are signs of peritoneal irritation.
Stomach and duodenal ulcers
In the preperforated state, symptoms similar to appendicitis appear. Persistent pain occurs in the upper region of the peritoneum, followed by nausea accompanied by vomiting.
The upper abdomen becomes painful and the peritoneum may become irritated. The pain syndrome is aching in both cases, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Distinctive features: with an ulcer, the pain is localized in the upper abdomen, with appendicitis - in the iliac region.
Cholecystitis
Both diseases have a sudden onset - pain appears. Body temperature rises, signs of peritoneal irritation appear. Differential diagnosis is based on the difference in the nature of the pain syndrome. With cholecystitis, discomfort is localized in the right hypochondrium and radiates to the right shoulder or scapula. With appendicitis, the pain is concentrated only in the lower abdomen on the right.
Pancreatitis
It has a confused clinical picture, so specialists often make mistakes in recognition. The symptoms are similar to various diseases of the internal organs, which are located in the peritoneum.
It begins with sudden pain in the abdominal area and may be accompanied by persistent vomiting. The blood picture in this case is also changeable.
As a rule, the abdomen is painful in the upper part, and with appendicitis in the lower part.
Types of illness
How to recognize appendicitis? Some doctors believe that it can be acute, requiring emergency medical attention, and chronic - when the organ is in a vulnerable position, but continues to perform its functions, preventing inflammation. Many people come to doctors who complain of pain and suspect that they have appendicitis. Where it is, on the left or on the right, is a question that often baffles them. Experts assure that this organ is located on the right side.
How does appendicitis manifest in children?
When the appendix is inflamed, the child becomes lethargic, eats poorly, is capricious, and refuses to play. He lies down on his side, presses his legs to his stomach and does not allow the “sore spot” to be examined. Which side of the child’s appendicitis hurts is determined by the location of the appendix.
It is very important to know how to identify appendicitis in a child so as not to start the process and prevent the development of peritonitis. After all, young children most often cannot understand what is happening to them. Therefore, they cannot explain their condition to their parents. Adults should pay close attention to all the symptoms of appendicitis and on which side the pain appears in order to promptly seek qualified medical help.
Difficulties
The nature of the pain has been clarified. However, there are several prerequisites for its occurrence. In the female population, signs of appendicitis can be veiled by a ruptured cyst (ovarian apoplexy) or ectopic pregnancy. In males, symptoms of inflammation of the appendix are easier to identify, since the prostate and vas deferens are located in the center of the abdomen, unlike the female genital organs.
And the question immediately arises: where is the appendix? In women and men, the location of the appendix is the same; gender does not play a role in this case. However, in the emergency department of a medical institution, when a patient is admitted with the above symptoms, she will first be examined by a gynecologist to exclude the corresponding pathology.
The many faces of appendicitis
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis are usually very painful. In most people, the disease progresses in a similar way, but often this inflammation can resemble other diseases. A person does not even have the notorious question: “Where is appendicitis located: on the left or on the right?” - because the patient is absolutely sure that he has this particular illness.
A person may experience various types of discomfort. However, no matter what the disturbing manifestations may be, you should never engage in self-diagnosis, because the symptoms of appendicitis in adults, the first signs, and causes can be completely different. For example, women may confuse appendicitis with acute inflammation of the right ovary.
This must be kept in mind and be sure to call an ambulance if some symptoms of inflammation of the appendix are detected.
Risk group
Appendicitis in humans (you can find out where it is located from the anatomy atlas) is one of the most common pathologies. Anyone can get appendicitis. The patient may not even suspect why the inflammatory process occurred.
The following categories of people are most susceptible to appendicitis:
- Those with an appendix with excessive mobility, which leads to kinks (a common cause of inflammation in children).
- Young patients under 33 years of age.
- Eating little plant fiber, which increases the efficiency of intestinal function.
- Residents of developed countries (in Africa and Asia, cases of appendicitis are very rare).
- Patients with a blocked appendix. This is facilitated by the accumulation of feces during constipation (often found among the elderly), and an excess of undigested food particles (especially grains and seeds).
- Suffering from circulatory disorders, which provokes the development of blood clots that block the arteries. Namely, they supply blood to the appendix. Because of this, the organ is no longer supplied with oxygen and nutrients, and subsequently an inflammatory process develops.
- Patients who have developed an allergic reaction against the background of increased immune activity. This is due to the fact that the appendix is an organ that belongs to the human immune system.
- Patients with infectious diseases of any nature.
- People with inflammatory bowel pathologies.
- Patients with abdominal injuries.
Leukocytosis
Leukocytosis is a laboratory sign indicating an increase in the number of white blood cells in the blood. White blood cells are one of the most important protective cells in our immune system. When an infection enters the body or an extensive inflammatory process begins, there is an increase in the production of white blood cells.
More than 80% of patients with acute appendicitis have leukocytosis on blood tests. The more intense the leukocytosis, the more intense the inflammatory process.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
If pain occurs in the abdominal area, a person can try to verify the presence of appendicitis. To do this, you should use one of the following methods.
- Obraztsov's symptom - the patient lies horizontally and straightens his legs. Next, you need to raise your unbent right leg up. With appendicitis, the pain syndrome will increase at the moment. In advanced cases, the patient will not be able to perform this action.
- Rovsing's test - when palpating the abdomen, you need to press on the area on which side the appendix is located. Movements should be jerky. When pressed, the patient does not experience discomfort. Pain appears when the hand is released.
- Sitkovsky test - the patient lies on the right side, and then on the left. On the right side the pain subsides or stops completely. When turning to the left side, the discomfort increases and is concentrated in the area where the appendix is located.
If you suspect appendicitis, you should call an ambulance. Before the doctor arrives, do not give the patient food, drink, or painkillers. It is unacceptable to use a hot heating pad or put pressure on the stomach.
Appendicitis can only be treated surgically. The sooner treatment measures are taken, the less likely it is to develop complications.
The location of the source of inflammation, if appendicitis is suspected in a person, can be determined using the following methods:
- Questioning the patient about the localization of pain and the presence of other signs of the inflammatory process.
- Palpation of the abdomen, which begins with a left-sided examination.
- Pressure on the anterior part of the peritoneum with further sharp weakening of the pressure after a few seconds. The manipulation results in severe pain within the supposed location of the pathological process (according to Shchetkin-Blumberg).
- Palpation of the cecum with the patient lying on his left side. An indicator of pathology is an increase in pain in the right iliac region (according to Bartomier).
- The doctor runs his hand from the xiphoid process along the abdominal wall through the patient’s clothing. From this, the pain begins to intensify (according to Voskresensky).
- Tapping the anterior abdominal wall. Appendicitis is indicated by sharp pain on the right side in the lower abdomen (according to Khedry-Razdolsky).
- The patient is asked to raise his right leg in a straightened position from a sitting position. Acute appendicitis is indicated by pain in the ileocecal region (according to Zattler).
- Palpation of the right side of the abdomen, when the patient lies on his back, raising his right straight leg, causes a sharp increase in pain (according to Obraztsov).
- Turning the patient to the left side increases pain on the right side. This happens because the cecum and appendix change position due to the tension of the peritoneum (according to Ortner-Sitkovsky-Ott).
- Implementation of jerking movements in the ileal region on the left within the descending colon with simultaneous pressing of the sigmoid colon to the posterior wall of the abdomen. This provokes pain in the abdomen on the right (according to Rovzing).
- The patient is asked to cough. As a result of this action, the diseased tissue will make itself felt (according to Kushnirenko).
- Pressing movements on the femoral artery provoke pain in the abdomen on the right (according to Ikramov).
- Examination of the rectum with a finger helps to determine inflammation of the appendix with a pelvic location (according to Wachenheim-Reder).
- The patient lies on his back with his legs pulled up to his stomach. Extension of the right leg in combination with simultaneous palpation of the right iliac region of the abdomen provokes an increase in pain (according to Donnelly).
- Palpation of the ileocecal area provokes contractile activity of the right testicle in men (according to Britten).
- A pregnant woman is placed on her right side. Due to the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the inflamed area, pain on the right increases (according to Michelson).
- A tense right spermatic cord increases pain at the site of the pathological process (according to Horn).
- While lying down, the patient tilts the thigh of the leg bent at the knee to the side. When the appendix is inflamed, pain will appear on the right side inside the pelvis (according to Cope).
- The woman's fingers are inserted into the vagina or rectum, then the uterus is pushed upward. With appendicitis there will be no pain. Pain rather indicates inflammation of the uterus or its appendages (according to Promptov).
- The patient is positioned on her back. The doctor applies a finger to a point located below the navel about 2 cm and to the right. In this position, the woman sits down. With pathology of the appendix, the pain increases. If the pain is provoked by adnexitis, then it will subside (according to Zhendrinsky).
- Pressure on the right lumbar triangle provokes pain (according to Yaura - Rozanov).
- Pressing on the right triangle on the lower back and sharply releasing the tissue causes painful sensations (according to Gabai).
- Pressing on the border between the anterior superior iliac spine and the navel. As a result of this effect, pain appears, a feeling of stretching within the epigastrium (according to Aaron).
- As a result of palpation, the muscle tissue of the peritoneum tenses (according to Krasnobaev).
- Ultrasound.
- Radiography.
- Computed tomography (connected in case of probable complications).
- General blood and urine tests. An increase in the level of certain indicators (leukocytes and red blood cells) indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Laparoscopy is the most reliable way to determine appendicitis.
Picture of malrotation
Malformations of the intestinal tube appear during the first month of life in approximately 60% of patients, in 20% between the 1st and 12th months. The classic symptom is bilious vomiting caused by duodenal obstruction. Incomplete intestinal rotation occurs in 1 in 500 live births (0.2%) [3, 4]. Data are derived from autopsy series, retrospective reviews [5], and prospective barium enema studies [6]. The true incidence of adults with asymptomatic malrotation remains difficult to estimate accurately.
Typically, in adults, intestinal malrotation manifests itself as acute ischemia of a section of the intestine, obstruction due to volvulus, or chronic abdominal pain. The need for surgical intervention for incidentally discovered malrotations in asymptomatic patients older than 1–2 years remains controversial [5, 7]. Even in patients who undergo Ladd's procedure, the cecum and appendix still end up in an unusual location, so they usually undergo an appendectomy afterwards.
The Ledd operation is named after the American surgeon William Ledd. He introduced into practice an effective method for correcting malrotation in the 30s of the last century.
In the case described above, malrotation was accidentally discovered in an adult patient with an “acute abdomen,” which caused difficulties in making a diagnosis. Other cases of appendicitis in adults or adolescents with intestinal malrotation have been described previously [4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]. Preliminary diagnosis was often made incorrectly or delayed. In some of the described cases, doctors diagnosed acute appendicitis on the basis of a CT scan of the abdominal cavity, but then they had to conduct additional studies of the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract to confirm the diagnosis and clarify the nature of the malrotation before surgery.
Based on materials: Left-sided appendicitis in a patient with congenital gastrointestinal malrotation: a case report. Frank J. Welte, Mario Grosso. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2007 1:92 https://doi.org/10.1186/1752‑1947‑1‑92
Sources
- Zaidi E, Daly B: CT and clinical features of acute diverticulitis in an urban US population: rising frequency in young, obese adults. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006, 187: 689–694. 10.2214/AJR. 05.0033.
- Lahat A, Menachem Y, Avidan B, Yanai H, Sakhnini E, Bardan E, Bar-Meir S: Diverticulitis in the young patient - is it different? World J Gastroenterol. 2006, 12: 2932–2935.
- Anjali P, Hatley R: Intestinal Malrotation. WebMD. Accessed: February 25, 2007, https://www.emedicine.com/ped/topic1200.htm
- Keith JCTJ, Buday SJ, Price PD, Smear J: Asymptomatic Midgut Rotational Anomalies in Adults: 2 Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Contemporary Surgery. 2003, 59: 322–325.
- Malek MM, Burd RS: Surgical treatment of malrotation after infancy: a population-based study. J Pediatr Surg. 2005, 40: 285–289. 10.1016/j. jpedsurg. 2004.09.028.
- Kantor JL: Anomalies of the colon. Radiology. 1934, 23: 651–662.
- Dilley AV, Pereira J, Shi EC, Adams S, Kern IB, Currie B, Henry GM: The radiologist says malrotation: does the surgeon operate?. Pediatr Surg Int. 2000, 16:45–49. 10.1007/s003830050012.
- Hollander SC, Springer SA: The diagnosis of acute left-sided appendicitis with computed tomography. Pediatr Radiol. 2003, 33: 70–71. 10.1007/s00247‑002‑0829‑x.
- Kamiyama T, Fujiyoshi F, Hamada H, Nakajo M, Harada O, Haraguchi Y: Left-sided acute appendicitis with intestinal malrotation. Radiat Med. 2005, 23: 125–127.
- Lin CJ, Tiu CM, Chou YH, Chen JD, Liang WY, Chang CY: CT presentation of ruptured appendicitis in an adult with incomplete intestinal malrotation. Emerg Radiol. 2004, 10: 210–212. 10.1007/s10140‑003‑0316‑1.
- Lee MR, Kim JH, Hwang Y, Kim YK: A left-sided periappendiceal abscess in an adult with intestinal malrotation. World J Gastroenterol. 2006, 12:5399–5400.
- Hou SK, Chern CH, How CK, Kao WF, Chen JD, Wang LM, Huang CI: Diagnosis of appendicitis with left lower quadrant pain. J Chin Med Assoc. 2005, 68: 599–603.
- Tsumura H, Ichikawa T, Kagawa T, Nishihara M: Successful laparoscopic Ladd's procedure and appendectomy for intestinal malrotation with appendicitis. Surg Endosc. 2003, 17: 657–658. 10.1007/s00464‑002‑4516‑7.
- Pinto A, Di Raimondo D, Tuttolomondo A, Fernandez P, Caronia A, Lagalla R, Arnao V, Law RL, Licata G: An atypical clinical presentation of acute appendicitis in a young man with midgut malrotation. Radiography. 2007, 13: 164–168. 10.1016/j. radi. 2005.10.010.
- de Roo RA, van Breda Vriesman AC, Steenvoorde P: [Diagnostic image (186) A man with abdominal pain in the left upper quadrant. Acute appendicitis with malrotation of the colon]. Ned Tijdschr Gen
Types of appendicitis
| Spicy | Chronic |
|
|
How many reasons influence the development of appendicitis?
- The reasons for the development of appendicitis have not been specifically established. However, experts have concluded that there is no common universal cause that causes the appearance of such a disease.
- Most often, the disease appears when the entrance to the rectum is blocked in the appendix. Blockage, in turn, also occurs when there are separate reasons. For example, sometimes foreign bodies or stones from stool get inside the appendix. The blockage appears from adhesions. They occur if there is enteritis or cholecystitis. Therefore, the process at the top is compressed.
- Bacteria influence the development of the disease. These are Escherichia coli, enterococci, streptococci, staphylococci. More often there is a combination of two factors.
- When the contents in the appendix become stagnant, its local immunity begins to weaken. Therefore, pathogenic bacteria appear in the mucous membrane.
Treatment
There is only 1 possible treatment option for the inflammatory process in the appendix of the cecum - surgery (appendectomy).
It comes in different types:
- Laparoscopy (endoscopic surgery).
It is performed under general or local anesthesia. A camera and instruments are inserted through punctures in the abdominal wall. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the diseased organ is immediately removed. After the operation, the patient is left with 3 small scars on his abdomen. This is the safest option for removing an inflamed appendix. This manipulation takes no more than 30 minutes. After the operation, the patient is under the supervision of doctors in the hospital for no more than 2 days. The stitches are removed a week later. 14-30 days after the operation, the person’s performance is fully restored.
- A surgical intervention that involves an incision (from 3 to 8 cm) in the right side of the abdomen (iliac region), through which the diseased organ is removed. It is also performed under general or local anesthesia. The operation lasts from 40 to 60 minutes. The atypical location of the process of the cecum, as well as the soldering of tissues as a result of previous diseases, can complicate the operation. With appendicitis complicated by peritonitis, the procedure time can increase to several hours. The age of the person being operated on also matters – children under 3 years of age are more complex patients. The patient is discharged after 5-7 days.
- Transgastric technique. Its main difference is the absence of any incisions on the skin. A needle and gastroscope are inserted into the patient through the navel. This option of appendectomy is used extremely rarely and is rather experimental in nature. The advantages of this method are the absence of complications in the form of hernias and infections.
- Removal of the appendix via the transvaginal route. It is used only when operating on women. The endoscope is inserted through a small opening in the vagina. This method can be combined with laparoscopy. The main advantage of the method is the absence of traces of surgery in the form of scars.
Unfortunately, today there are no methods of conservative treatment of inflammation of the appendix. The only way to save a person's life is to remove the appendix.
It is very important not to endure discomfort and pain, not to guess where appendicitis is located - on the left or on the right - but to immediately seek help from specialists. Doctors do not recommend taking painkillers in such cases, since they do not solve the problem, but only “drown out” it. A person may decide that the discomfort has disappeared and not attach due importance to the current situation.
First actions upon detection of a disease
As a rule, abdominal pain increases within a couple of hours, but no matter how much appendicitis hurts, you should consult a doctor immediately, at least to confirm or refute the presence of inflammatory processes in the body.
Actions that should not be carried out before the doctor arrives:
- Try to wait without painkillers until the doctor arrives, as this may complicate the diagnosis.
- Avoid food and liquid intake.
- Avoid applying warm objects to your stomach, this can only worsen the situation. You can use a cold compress to relieve pain.
If severe pain has subsided, this may indicate that the disease has progressed to a more serious condition, so do not relax and do not let things take their course.
How does the stomach hurt with appendicitis?
Abdominal pain varies depending on gender, age and the state in which the body is.
Features of the course of the disease in women:
- They are more susceptible to inflammation of the appendix. This is due to a monthly increase in the intensity of blood circulation in the pelvic area. This process irritates the intestines as a whole and the appendix as well.
- The pain is similar to the sensations caused by an ectopic pregnancy.
- It is difficult to differentiate appendicitis in women from pathological processes in the uterus and appendages and ovulatory pain. To distinguish appendicitis from diseases of the internal female organs with similar symptoms, the patient is referred to a gynecologist for examination.
- In pregnant women, it is difficult to diagnose inflammation of the appendix. When the stomach has already acquired an impressive size, it is impossible to palpate it. An enlarged uterus displaces all organs, and the pain can be completely different from the typical sensations of appendicitis. Inflammation can appear at any stage of pregnancy.
For men the situation is as follows:
- They are less likely to get appendicitis.
- During diagnosis, when pressing on the scrotum, sharp pain appears (Horn's symptom).
- The presence of inflammation is indicated by the right testicle, pulled up (Larocque's symptom).
- When exposed to a point in the iliac region on the right, a tightening of the right testicle and muscle tension appear. The testicle descends as the intensity of finger pressure decreases.
- The pain may shift to the pubic area and penis (with the pelvic position of the appendix).
Manifestations of the inflammatory process in older people are vague. Therefore, the disease can be diagnosed much later.
Features of the manifestation of pathology in children:
- They cannot pinpoint the exact location where they feel pain. The location of the appendix in childhood differs from its location in the body in an adult.
- The following may indicate a problem: refusal to eat, low physical activity, tendency to cry, desire to lie on the right side in the fetal position.
- In children under 3 years of age, pain may be concentrated in the umbilical region.
- Children over 3 years old experience pain just like adults. At this age, the child can pull his right leg towards his stomach, bending it at the knee.
What is the appendix?
This is the name of the vermiform appendix of the rectum. Not every mammal has this formation. Cats, for example, do not have it. But, it is inside the body of people, monkeys, and rabbits. It is intended to perform protective functions. It is contained in the immune system. With its help, the microflora in the intestines is restored.
The appendix looks like a kind of nursery in which there are beneficial bacteria. They take part in the digestion process. Its role in the intestines is similar to that performed by the tonsils in the respiratory system. Those who have had an appendectomy, if the appendix has been removed, find it more difficult to restore the normal state of the microflora after the infectious disease has passed, compared to those who have such an organ.
There are photographs on the Internet that allow you to determine the approximate location of the organ with the localization of pain during its inflammation.
Where is the appendix located?
Without a doubt, many people once wondered where the appendix is located inside the body? It is contained by the smooth iliac region. Then it gradually descends to the small pelvis. Sometimes, if it is located behind the cecum, and its upper part will reach the liver. The process does not have a constant length. She is changing for him. Sometimes it reaches up to twenty-three centimeters. The standard length of the process is approximately seven to eight centimeters. Its width is no more than one centimeter.
First aid
Appendicitis in humans (where the affected area is located, described above) requires immediate medical attention.
Algorithm of action when the above symptoms are detected:
- call an ambulance (even if the pain subsides);
- lie down and take a comfortable position;
- It is permissible to use a cold compress on the abdominal area.
Postoperative period
Features of the recovery period after appendectomy:
- you should not get up immediately after waking up from anesthesia;
- It is not recommended to walk a lot for the first 3 days after surgery;
- the patient cannot lie on his left side due to acute pain;
- It is necessary to treat the scar daily with brilliant green (before and after removing the sutures) until the tissues have completely fused and a scar has formed;
- the patient is given painkillers and antibiotics as needed;
- with local anesthesia, drinking fluids is allowed 2 hours after surgery (you can drink water, unsweetened tea, rosehip infusion, fruit jelly);
- The basis of the diet on the first day after surgery should be broths, pureed soups, and rice water;
- on the 2nd and 3rd days you can eat vegetable puree, yogurt, fruit jellies;
- It is necessary to eat food in small portions at least 5 times a day;
- It is important to observe the temperature of the food you eat. It should not be colder than 20 degrees and hotter than 50 degrees.