When receiving the results of a biochemical analysis, some patients may learn that the direct fraction of bilirubin in their body is increased. Not everyone knows about the presence of this substance and its role, and the phrase “high level” immediately makes one think about the presence of some kind of disease. What does it mean if direct bilirubin is elevated, what are the causes of this condition and how to deal with it, is discussed in the article.
How is bilirubin formed in the body?
Bilirubin is an extremely important indicator of the coordinated functioning of various components of the body. The source of this substance is hematopoiesis - the process of formation and breakdown of red blood cells (erythrocytes). The red component of blood is produced in large quantities in the bone marrow. Red blood cells are disc-shaped cells containing the protein hemoglobin inside. It is with its help that red blood performs its main job in the body - transporting oxygen from the lungs to all other tissues and organs. Hemoglobin, although it is a protein in its chemical nature, is a complex structure. In addition to the protein part itself, it contains a functional part - heme. It is in its center that the iron ion that carries oxygen is contained.
Hemoglobin is a complex protein that transports oxygen
A large number of red blood cells are produced per day. However, the lifespan of a red blood cell is relatively short - only 120 days. After this time, the red blood cell dies. However, nothing is lost in the body. After the death of the red cell, it is disassembled into its component parts in the spleen. The protein portion of hemoglobin is detached from the heme and used to build other necessary proteins. The body carefully transports heme iron back to the bone marrow to build new red blood cells.
Read more about bilirubin in the blood here:
The hemoglobin residue heme undergoes the most complex transformations. It is he who, through several intermediate stages, is converted into bilirubin. This chemical compound is extremely toxic and must be removed from the body. At this stage, three synonyms are often added to the term bilirubin:
- indirect;
- unconjugated;
- toxic.
Before bilirubin can leave the body without harm to organs and tissues, it enters the most powerful cleansing station - the liver cells. It is here that it becomes a harmless conjugate substance, that is, combined with neutralizing components. This type of bilirubin is called direct, it is non-toxic and is able to penetrate the kidney filter and be excreted in the urine, causing its yellowish color. However, most of it leaves the body along with bile. In the intestines, bilirubin is converted into stercobilin, which gives stool its characteristic brown color.
Bilirubin is neutralized in the liver and excreted in bile
What is bilirubin
Bilirubin is the pigment responsible for the yellow-brown hue.
Contained in human bile and blood. Formed during the breakdown of red blood cells when hemoglobin cells change. All healthy people have bilirubin. It is not dangerous if its level does not exceed the maximum value. Normal bilirubin is also called free (indirect, unbound). Indirect or bound pigment is formed as a result of the interaction of direct bilirubin with glucuronic acid in the liver.
Thus, bilirubin is divided into two types:
- direct (dissolves in water and is naturally excreted from the body);
- indirect (dissolves only in fats, poses a danger due to its toxicity, elimination is real only after conversion to a bound form).
Normal levels of bilirubin in the blood
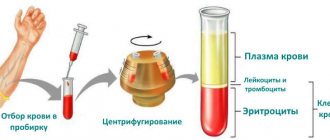
The level of bilirubin is one of the main indicators of the body’s activity, determined using a biochemical blood test. Currently, in the vast majority of cases, this process is automated; the result is issued by the machine in the form of a paper printout. When preparing for the test, remember that blood is donated on an empty stomach. On the eve of the study, it is advisable to limit fatty and fried foods.
Determination of the level of bilirubin in the blood is currently carried out using a special apparatus
As a result, the level of direct and indirect bilirubin and their total amount must be indicated. Their ratio is shifted towards the latter, which accounts for four-fifths of the total content in the blood. However, it must be remembered that standards vary depending on the age of the patient. This circumstance especially applies to newborns and children of the first year of life.
What is the reason for high levels of bilirubin in the blood and how to reduce it:
Normal levels of bilirubin in the blood - table
| Gender/age | Total µmol/l | Indirect µmol/l | Direct µmol/l |
| Newborn 1–3 days of life | 23,1–190 | 23,5–179,8 | 0,5–10,2 |
| Newborn 3–6 days | 28–210 | 27–197,6 | 1–12,4 |
| 1 month - 14 years | 3,5–20,4 | Up to 16.5 | up to 5.1 |
| Men | 3,4–17,1 | 3,4–16,5 | 1,7–5,1 |
| Women |
Symptoms
The signs of unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinemia, as well as conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, may vary somewhat, depending on the cause of these pathologies. Thus, with cirrhosis of the liver, patients complain of pain in the right side, nausea, bitter taste in the mouth, gagging, and bloating. With liver steatosis, vomiting with bile and pain in the right side after eating are observed. With severe hemolysis, patients may experience dizziness, loss of consciousness, convulsions, weakness, shortness of breath, and heart murmurs. With Gilbert's syndrome, patients complain of insomnia, fatigue, and lack of appetite. But in all cases, regardless of the reasons that caused the increase in indirect bilirubin, hyperbilirubinemia has the following symptoms:
- Yellowing of the sclera.
- Jaundice color of the skin.
- Fatigue.
- Decreased performance.
- Skin itching.
- Uncomfortable sensation (even pain) in the right hypochondrium.
- Nausea, worsening after eating certain foods (fatty, fried, spicy).
In addition, some patients complain of insomnia and depression.
It should be said that the degree of change in skin color in different patients can vary greatly and vary from a pale yellow, barely noticeable shade, to deep yellow. Changes in skin color can be observed without hyperbilirubinemia, for example, when eating large amounts of fresh carrots, pumpkin, oranges and certain medications (for example, Mepacrine). In this case, the sclera, as a rule, does not change its color. This yellowing of the skin is not associated with bilirubin and is caused only by the accumulation of another coloring pigment in the cells - carotene.
Why does the level of bilirubin in the blood increase?
A high level of bilirubin in the blood makes a specialist think about its possible cause. There are a lot of similar situations, and not all of them affect liver function.
Liver diseases
The liver is a unique organ that performs many roles in the body, including neutralizing and removing all toxic substances from the bloodstream. Liver diseases, especially inflammatory ones, often lead to increased levels of bilirubin in the blood.
Hepatitis is inflammation of liver cells. Most often, this disease is viral in nature. However, each type of infection can cause the death of liver cells. Those who remain are often unable to cope with the large amount of waste material from destroyed red blood cells, as a result of which the level of indirect and direct bilirubin in the blood increases.
Cirrhosis is a condition that often occurs against the background of long-term inflammation in the liver. In the foci of the infectious process, connective tissue grows and multiple scars are formed. The liver loses its unique architecture at the microscopic level. The result is also an increased level of bilirubin of both types in the blood.
Liver cirrhosis is the growth of scar tissue with a total change in the structure of the organ
Liver inflammation is not always an infectious process. Quite often this organ becomes a target of aggression from its own immunity. Immune cells destroy the liver over a long period of time, which also leads to a deficiency of structures that neutralize bilirubin. The consequence, again, is an increase in the level of all its types.
In addition, the liver may suffer due to the presence of secondary foci of tumor formations - metastases. They are prone to uncontrolled destructive growth, changing the normal functioning of the organ.
The liver is a favorite site for metastases of many types of tumors
There are a number of hereditary diseases that are based on the functioning of the bilirubin neutralization process. In this case, the level of direct and indirect types also increases. Examples of such pathologies are Gilbert and Crigler-Najjar syndrome. Most often these deviations are detected in childhood and adolescence.
Hepatic vascular diseases
Normal liver function largely depends on adequate blood flow in the vascular system. Stagnation of blood, increased pressure inside the arteries and veins is the cause of high levels of bilirubin in the blood. A common cause of inadequate blood flow to the liver is congestive heart failure . In this case, the root of the problem is a severe heart disease, leading to stagnation of blood in the vessels. A special condition is constrictive pericarditis. Inflammation of the heart sac (pericardium) can transform it from a highly extensible structure into a rough, tight shell. In this case, the heart also becomes unable to adequately pump blood throughout the body.
Badi-Chiari syndrome is one of the causes of increased bilirubin levels in the blood
Blockage of bile flow from the liver
The gallbladder is a favorite place for the formation of various types of stones. However, the mere existence of stones in the lumen of the bladder is not a reason for an increase in bilirubin levels in the blood. Problems are created by those stones that have grown to a certain size and blocked the normal path of bile outflow into the intestines. In this case, the level of direct bilirubin in the blood increases sharply. In addition, tumors - neoplasms of the intestines, gallbladder, pancreas, and bile ducts - can create an obstruction to the outflow of bile.
Stones can be localized in any part of the biliary tract
Destruction of red blood cells
Normally, the creation and destruction of red blood cells is subject to strict laws. Any imbalance in this process instantly affects the functioning of the body. High levels of indirect bilirubin may result from massive destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis). As a rule, this pathological process is accompanied by anemia (anemia). In this case, so much indirect bilirubin is sent to the liver that even a completely healthy organ is unable to cope with it.
Massive death of red blood cells is often observed in hematopoietic diseases. Cells that are non-standard in shape or degree of maturity are destroyed in the first rows in the spleen. Similar pathologies include hereditary diseases: sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, porphyria.
Sickle cell anemia is a hereditary hematopoietic disease
The death of red blood cells can be caused by an infectious disease - malaria. Its causative agent, Plasmodium malaria, is a special type of parasite that lives inside red blood cells.
Transfusion of incompatible blood is another reason for the development of hemolysis of red blood cells. In this case, the immediate cause is immune mechanisms. In addition, certain medications, such as antibiotics, can cause red cell death.
Diseases of the newborn period
A special type of red blood cell circulates in the vessels of the fetus, containing so-called fetal hemoglobin. It is very different in structure from that of adults. During intrauterine development, this feature plays an important role: fetal hemoglobin has a much greater affinity for oxygen. By the time of birth, the newborn’s body contains the vast majority of red blood cells containing hemoglobin of this particular type.
After the onset of pulmonary respiration, the need for fetal hemoglobin disappears. It is gradually being replaced by the adult type. However, this process is inevitably accompanied by the death of red blood cells and the formation of large amounts of indirect bilirubin. This condition is not a deviation from the norm and is called neonatal jaundice. However, the level of bilirubin never reaches extremely high values.
An absolute pathology is hemolytic disease of the newborn. In this case, the cause is an immunological conflict between the mother’s immunity and fetal blood cells. Indirect bilirubin in this situation can reach extremely high values, leading to irreversible brain damage. In severe cases of hemolytic disease, the fetus may die in utero.
Immunological conflict is the cause of high levels of bilirubin in the blood of a newborn
In addition, infectious hepatitis can cause high bilirubin levels in a newborn. The pathogen enters the fetal blood through the placenta. Most often it is the hepatitis B and C virus.
Why is high bilirubin dangerous?
Provoking factors for high bilirubin are associated with impaired formation of the water-soluble fraction of bile pigment in the liver, hemolysis, or malfunction of the biliary tract. Most often, the problem is a malfunction of the gallbladder. Common predisposing factors to this are cholelithiasis, intoxication, helminthic infestations, and infections.
With an increased pigment content, a change occurs in the number of red blood cells that are destroyed. Because of this, protein metabolism indicators are disrupted. Bilirubin is a toxic substance. As a result of its increase in the blood, it penetrates into the cells of various organs, preventing them from “breathing” normally, which leads to death.
But hyperbilirubinemia is especially dangerous for the brain. There is a risk of encephalopathy and coma.
The sooner you start taking medications, the faster you can reduce the levels of the substance and the more undesirable consequences you can avoid.
Symptoms of high bilirubin levels in the blood
Symptoms of high bilirubin levels in the blood depend greatly on the specific values of the indicator. The total amount of the compound, which does not exceed 30 µmol/l, does not bother the patient in any way and is most often discovered by chance during laboratory tests for another reason.
A bilirubin content in the blood above this figure will cause two characteristic symptoms - yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes (jaundice) and itchy skin. Color changes will primarily affect the sclera and mucous membrane of the lower surface of the tongue. Itching is due to the fact that bilirubin is very toxic, especially when it is found in large quantities in small vessels of the skin. With hemolytic jaundice, the skin has a greenish tint; with liver damage, it is yellow-orange. An earthy gray-green color indicates a problem with the flow of bile.
Jaundice is the main sign of high bilirubin levels in the blood.
In addition, increased bilirubin levels will inevitably affect the color of stool and urine. Large amounts of direct bilirubin will cause noticeable darkening of the urine and stool. When the outflow of bile is blocked, the latter may become discolored.
Extremely high levels of bilirubin in the blood have a direct negative effect on brain activity. In such a state, a person may begin to behave inappropriately, consciousness may be impaired, and the patient may fall into a coma. The same signs are observed in hemolytic disease of the newborn. However, it must be remembered that the brain of a child at this age is much less sensitive to high levels of bilirubin in the blood than that of an adult.
Jaundice - video
Reasons for increased indirect bilirubin
This pathology is called “unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia syndrome.” This condition may occur for the following reasons:
- Increased hemolysis (red blood cells break down quickly and in large quantities, and hemoglobin is released into the blood).
- Hemolytic anemia (thalassemia, hereditary microspherocidosis).
- Mechanical damage to red blood cells (for example, when large amounts of toxic substances enter the body).
- Vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Hypersplenism.
- Gilbert's syndrome.
- Chronic hepatitis (persistent).
- Reactive hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Liver steatosis (fat accumulations in the parenchyma).
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosing the level of bilirubin in the blood itself most often does not cause difficulties. A biochemical blood test is a routine laboratory test. The main difficulties accompany the search for the causes of such changes. To establish the correct diagnosis, the close attention of specialists is necessary - a gastroenterologist, hematologist, cardiologist, neonatologist, pediatrician, therapist, infectious disease specialist. The following types of studies are prescribed:
- a general examination will allow you to suspect a specific type of jaundice, damage to the liver, gallbladder, heart;
- A general blood test can reveal signs of anemia and other hematopoietic disorders;
- a biochemical blood test allows you to evaluate the functioning of the liver and kidneys;
- a blood test for the content of antibodies or genes of the pathogen will determine the infectious nature of the disease;
A blood test can detect hepatitis B and C virus
- urine analysis reveals high levels of urobilin (a successor to bilirubin);
- stool analysis allows you to assess the level of stercobilin and suspect the level of jaundice;
- ultrasound examination is carried out to assess the structure and size of the liver, gall bladder, biliary tract, pancreas, heart, blood vessels;
Ultrasound is the main method for diagnosing liver diseases
- Computer (magnetic resonance) tomographic examination will allow us to accurately assess the anatomical structure of any organ of interest.
Reasons for increased direct bilirubin
This pathology is called conjugated hyperbilirubinemia syndrome. The causes of this pathology are as follows:
- Impaired excretion of bilirubin from the body.
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
- Acute viral hepatitis.
- Chronic hepatitis in the active phase.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Blockage or compression of the biliary tract (tumors, stones).
- Long-term use of anabolic steroids.
- Taking hormonal drugs (for example, birth control).
Treatment methods
High bilirubin levels in themselves are not a target for specific treatments. You must first correct the problem that caused this situation.
Treatment of high levels of bilirubin in the blood - table
| Cause | Infectious liver disease | Autoimmune hepatitis | Blockage of bile flow | Systemic circulatory disorder | Tumor lesion of the liver, red bone marrow | Hemolytic anemia | HDN |
| Treatment methods | Prescribing antibiotics and antiviral drugs to eliminate the infectious agent | Prescription of steroid hormones and cytostatics to suppress immune aggression | Dissolution of stones using drugs, surgical removal of stones and tumors | Prescription of diuretics, surgical treatment for arrhythmias, heart valve defects | Chemotherapy, surgery, radiation treatment, bone marrow transplant | Blood transfusions, iron supplements, antimalarial drugs | Blood transfusion, phototherapy with a light source (conversion of indirect bilirubin into direct) |
Treatment
Which doctors should I contact?
First of all, you need to contact a general practitioner, who, if necessary, can refer the patient to more specialized specialists: a gastroenterologist and hepatologist.
Drugs
To treat hepatitis, choleretic drugs are used: Ursofalk, Chofitol, Gepabene, as well as vitamins. To reduce bilirubin levels, the drugs Zixorin and Phenobarbital are used, but they are prescribed very rarely.
Thermal and electrical physiotherapeutic procedures in the liver area cannot be performed for this disease. To exclude the acute form of the disease, it is worth reducing nervous and physical stress.
Newborns are treated using a modern method - phototherapy. Bilirubin can be removed from the body using fluorescent light. Newborns with mild forms of the disease are prescribed treatment with a fiber-optic blanket. It can also be done at home.
Sorbovit-K is also prescribed to ensure the normal functioning of the body. To reduce the level of bilirubin in the blood, various choleretic drugs may be recommended.
In the acute period of the disease, the main goal is to reduce the toxic effect of high concentrations of bilirubin. For this purpose, medications with antioxidant properties are prescribed, for example, ionol and tocopherol. To treat severe hyperbilirubinemia, glucose is injected into the blood and insulin is given subcutaneously.
Surgery
If there is a risk of developing kernicterus in newborns, a blood transfusion is performed. This operation is performed in an operating room or treatment room where there is a heated radiant heat source. The blood transfusion operation is performed by a doctor with the help of an assistant.
Treatment with traditional medicine
Folk remedies can be used to treat hyperbilirubinemia. This is allowed during the recovery stage. They are also often prescribed for congenital pathologies. Traditional medicine offers herbal teas and individual herbs that have a choleretic effect. Among them, mint, corn silk, and calendula can be especially noted, which are taken for about a month .
Diet
For benign hyperbilirubinemia, a special diet is prescribed, for example, No. 15 . But it can be used only in the absence of disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. In the presence of gallbladder diseases, diet No. 5 No. 5 is prescribed.
Prevention
Prevention of increased bilirubin levels in the blood includes the following measures:
- annual medical examination with a biochemical blood test;
- timely treatment of diseases of the liver, heart, and hematopoietic system;
- examination after an abortion if there is a threat of an immunological conflict;
- planning pregnancy with the threat of an immunological conflict.
A high level of bilirubin in the blood is a reason to consult a specialist and undergo a full examination. Only after establishing the correct diagnosis will the doctor prescribe treatment that can solve the problem.
- Author: Elena Timofeeva
I have a higher medical education and work experience. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(6 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Benign hyperbilirubinemia
With this pathology, the amount of bilirubin increases, but the functions of the liver, as well as its structure, are not impaired, hemolysis and cholestasis are absent. Causes of the disease:
- Hereditary changes in the liver.
- Complication of acute viral hepatitis.
- Impaired transport of bilirubin from plasma to blood cells (microsomes are not able to capture bilirubin).
- Impaired binding of glucuronic acid and bilirubin.
Benign hyperbilirubinemia manifests itself as yellowing of the sclera. The skin color of some patients may not change, while in others it may acquire a jaundiced tint. This pathology is characterized by the periodicity of symptoms. Only in some patients they are constantly present. In addition, the following signs of illness may be observed:
- Fatigue.
- Irritability.
- Depression.
- Weakness.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Lack of appetite.
- Nausea.
- Flatulence.
- Dark colored urine.
- Pain in the right side.
However, all or some of these symptoms may be completely absent.
Causes of hyperbilirubinemia
An increase in total bilirubin occurs for several reasons:
- increased pigment formation (red blood cell breakdown) due to hemolysis;
- the problem with its elimination is Gilbert's syndrome;
- the combined option is a rarer occurrence.
These conditions usually occur due to hemolytic anemia, hepatogenic diseases or diseases of the biliary tract (gallbladder disease, gallstones). Causes of elevated levels also include:
- atherosclerosis;
- cancer;
- inflammation;
- autoimmune diseases;
- neurodegenerative diseases;
- hepatitis A, B, C, E;
- Wilson's disease;
- alcohol poisoning;
- drug abuse;
- malaria;
- mononucleosis;
- heart failure;
- liver infections;
- artificial heart valves.
Factors provoking an increase in overall indicators
Small numbers are normal for bilirubin. If bile pigment increases in men or women, there are always serious reasons for this.
Especially in cases where bilirubin is elevated to critical levels:
- diseases and pathological disorders affecting the gallbladder-duct link;
- red blood cells disintegrate several times faster than acceptable values;
- liver diseases affecting its structural state and functions (cirrhosis, cholestasis, cholelithiasis and other malfunctions);
- autoimmune liver diseases, toxic damage or infections of the organ;
- jaundice, especially in pregnant women;
- disruption in the process of generating enzymes responsible for bile pigment;
- tumor formations in the organ (benign and malignant).
However, the reasons for increased direct or indirect bilirubin in an adult may differ.
Causes of high direct bilirubin
If direct bilirubin is increased in the blood, this indicates disorders associated with the outflow of bile. When such malfunctions occur, the fluid does not enter the gastrointestinal tract, as it should, but is released directly into the blood. A similar condition is associated with some diseases:
- cholelithiasis of the bladder;
- bacterial, viral and toxic forms of hepatitis in chronic or acute course;
- drug-induced hepatitis, formed due to the use of hormonal or anti-inflammatory drugs, sometimes the disease develops due to the use of heavy drugs of other groups;
- biliary cirrhosis of the liver caused by gallbladder disease;
- cancer of the liver, gallbladder or pancreas;
- Dubin-Johnson and Rotor syndrome;
- Holdocholithiasis is a disease that provokes cholelithiasis;
- primary sclerosing cholangitis - pathology is formed due to inflammation and proliferation of the bile ducts, after this disorder biliary cirrhosis and immunological disorders occur;
- malignant tumors in the pancreas also provoke pathology;
- Dabin-Johnson syndrome, in which the processes of producing fractions in liver cells are disrupted (bilirubin flows from the bile ducts back into the organ);
- alcoholic liver damage – alcohol intoxication for 10 years or more.
All these factors cause high levels of direct bilirubin in an adult.
Reasons for increased indirect bilirubin
If increased bilirubin in the blood of the indirect fraction is diagnosed, then as a result of a more detailed study of the patient’s body, the following pathologies are discovered:
- Jlbert syndrome, or Crigler-Nayyar disease, as well as Lucy-Driscoll syndrome;
- anemia of an autoimmune or acquired type resulting from arthritis, systemic lupus, lymphocytic leukemia and other serious diseases;
- acute infectious diseases: sepsis, typhoid fever, malaria;
- congenital hemolytic anemia;
- toxic hemolytic anemia after poisoning with poisons or chemicals.
If the levels of indirect bile pigment are increased by more than 2 times, this indicates the rapid destruction of red blood cells.
Reasons for increasing fractions in equal shares
An increase in fractions in equal parts is an indicator of high total bilirubin, which is usually associated with common liver diseases: hepatitis, cirrhosis, viral hepatitis type 4, tapeworm infection, abscess.
Gilbert's syndrome as one of the causes
Gilbert's syndrome is a little-known but fairly common benign hereditary disease. It is quite difficult to detect due to the lack of specific symptoms. If doctors have made the correct diagnosis, the treatment process is characterized by a favorable prognosis.
Fact! Gilbert's disease appears due to a mutation in the genes of the second chromosome and occurs mainly in people with dark skin color, in the Negroid race.
The syndrome has virtually no signs of illness. Only some patients develop jaundice due to physical exertion, emotional stress, and alcoholism. This pathology does not require treatment - only the elimination of provoking factors.
Are there differences for women and men?
In men and women, total and specific bilirubin fractions do not differ. The reasons are also similar in most cases. The only thing that distinguishes the causes of increased total bilirubin in the blood is the prevalence of Gilbert's syndrome. In men it occurs 10 times more often.
However, women have one specific provoking factor - pregnancy. While carrying a child, a girl may encounter the following diseases and disorders that increase total bilirubin:
- fatty liver;
- intrahepatic cholestasis occurring in pregnant women;
- the appearance of gallstones;
- severe early toxicosis;
- preexlampsia and eclampsia.
Total bilirubin may increase due to the Epstein-Barr virus, which can be carried by a pregnant woman. Cytomegalovirus also provokes an increase in bilirubin in a pregnant woman.
Fact! If there are no diseases, then a high level of bile pigment may appear due to severe stress.
An increasing size of the fetus provokes an increase in total bilirubin, which may mean: organs are compressed, the gallbladder ducts are reduced, and bile stagnation appears.
Signs of elevated bilirubin
As is known, the primary role in the metabolism of bilirubin belongs to the liver, and jaundice is a characteristic syndrome that reflects its damage and also manifests itself in cases where the amount of bilirubin exceeds the functional ability of the liver to bind its excess, or there are obstacles to the outflow of bile and, accordingly, the excretion of conjugated bilirubin from the body.
Sometimes it happens that the severity of jaundice does not correspond to the levels of bilirubin in the serum. For example, with obesity and edema, jaundice is less noticeable, while in thin and muscular people it is more pronounced.
The reasons for high bilirubin in the blood are very diverse and are associated either with its increased formation in the cells of the reticuloendothelial system, or with a disturbance in one or several metabolic links in the hepatobiliary system.
From a clinical point of view, it is important to note that the degree of hyperbilirubinemia affects the staining pattern of various tissues:
- So, most often the sclera is the first to acquire a jaundiced tint.
- Oral mucosa
- Then the face, palms, soles and finally the entire skin turn yellow
It must be remembered that yellow discoloration of the skin is not always a consequence of hyperbilirubinemia. For example, when eating food containing a large amount of carotene (carrots, tomatoes), diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function), the skin may acquire a yellow tint, but in these cases the sclera will be of normal color (intact).
Increased bilirubin in babies
Hyperbilirubinemia in children over one year of age is regarded as the same pathology as in adults. In newborns, this condition is in most cases caused by immature liver function, as well as an imbalance in the body's metabolic reactions, and is therefore classified as benign. As a rule, with the development of all the child’s systems, the amount of bilirubin in the blood is restored to normal. This type of jaundice is called physiological. The reasons for its appearance include fetal asphyxia and some maternal diseases during pregnancy.
However, in some newborns, the increase in bilirubin is caused by pathological reasons:
- Rhesus conflict.
- Spherocytosis (disturbance of red blood cell membranes).
- Infections.
- Thelassemia.
- Antigenic mismatches.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Cholestasis.
- Thickening of bile.
- Gilbert's syndrome.
- Infectious hepatitis.
- Intestinal akinesia.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Biliary tract anomalies.
Pathology during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the immune system works in slow mode. Therefore, infectious and viral diseases often develop during this period. Benign hyperbilirubinemia is no exception.
The disease can be triggered by an infection or virus, or appear as a result of changes that occur in a woman’s body during a given period. In the first case, the disease is accompanied by pain in the abdomen, increased body temperature, and yellowing of the skin. Often the disease can lead to the development of negative consequences, and therefore requires drug therapy. In the second case, the disease is not dangerous and develops against the background of toxicosis.
Normal for men
A laboratory blood test for bilirubin provides information about the level of total bile pigment, direct and indirect. The relationship between the last two varieties is very important. This indicator makes it possible to make a correct diagnosis if there are deviations from normal values. The content of bile pigment should be as follows: 20% for bound and 78% for free.
As for the quantitative content, the norm of bilirubin is as follows:
- general: 8.40−19.80;
- straight: 0.10−8.10;
- indirect: up to 20.0.
These indicators are measured in µmol/l. Standards are provided for representatives of the fair sex. However, men have one characteristic feature. They can act as carriers of Gilbert's syndrome. This pathology occurs 10 times more often in them than in women. This is the designation for a hereditary variant of hepatosis. Unconjugated bilirubin increases with this disease, causing the sclera and the surface of the epidermis to become jaundiced. The disease is found in 5% of the world's population, 90% of whom are men.
A number of experts are of the opinion that Gilbert's syndrome is not a pathological condition, but a physiological feature. It was not possible to establish why he targets men more often. Many carriers of the syndrome do not know that they have it. TO
Clinical manifestations sometimes do not make themselves felt until the age of 19. The disease is often discovered by chance: during a standard doctor’s examination or after laboratory tests.
Therapy methods
For physiological jaundice, all treatment consists of breastfeeding. The sooner the baby is put to the breast, the more active the release of excess bilirubin occurs in the baby’s feces. Walking in the fresh air also has a good effect, especially in sunny weather. Hyperbilirubinemia in newborns with high bilirubin levels requires more serious treatment methods. If values on the first day are more than 100 µmol/l, children are prescribed phototherapy. For this, the child is placed in a special box under a blue lamp with a wavelength of 425-428 nm. According to the rules, monitoring is required every 4 hours of such exposure.
In special cases, when bilirubin values remain at high levels for a long time, Phenobarbital and parenteral (drip) administration of electrolytes are additionally prescribed. If pigment levels are very high, a blood transfusion may be prescribed in the first 12 hours from birth. If therapy is carried out in a timely manner, as a rule, there are no deviations in the further development of the child.
Reasons for the low level
If a biochemical analysis revealed that a man has a low level of bilirubin, this also has important clinical significance. This phenomenon is quite rare, but no less dangerous to health.
- Pigment levels may drop due to chronic renal failure. First of all, you need to find out what condition the kidneys and adrenal glands are in.
- This is often caused by serious diseases such as acute leukemia or tuberculosis intoxication.
- Occasionally, an underestimated rate is a consequence of aplastic anemia. This disease is quite rare and far from simple; its treatment requires complex and timely therapy.
- If the patient is over 60 years old, then it is very likely that he has coronary heart disease.
The amount of bilirubin in the blood is a fairly serious indicator that should not be ignored. If you have even the slightest doubt or suspicion, you should immediately take a biochemical blood test.
Did you like the article? Share it with your friends on social networks:
Blood contains many different substances. Each of them has its own content standards. Exceeding the established indicators indicates the presence of certain pathologies or disorders. One of these substances is bilirubin. It performs an important function and if its level in the blood is exceeded, therapeutic measures are required.
Prognosis and prevention
The pathological prognosis is good. But unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia often causes the death of a child.
For preventive purposes, you need to avoid alcoholic beverages, spicy and fatty foods. Stressful situations and heavy loads of force are unacceptable. You need to monitor your health and the well-being of your children.
Thus, hyperbilirubinemia is a disease in which the concentration of bilirubin in the body increases. Usually the disease is not life-threatening, but sometimes cholecystitis can develop due to it, and in the most severe cases, brain damage. But with a timely response to the problem, this can be avoided. Therefore, in maternity hospitals, doctors closely monitor the condition of children, especially those who have developed jaundice.
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of adults. In case of congenital defects, it must be observed at all times. This way it is possible to normalize the level of bile pigment in the body for a long time.
© 2019 — 2019, . All rights reserved.
How can you reduce bilirubin levels?
Bilirubin can be reduced only after receiving a diagnosis. If this is a serious illness, then you must first undergo a course of treatment. As the provoking factor is eliminated, the total bilirubin level in an adult will also decrease.
So, if a symptom occurs against the background of liver disease, it is necessary to treat it. If it is caused by stagnation of bile, it is necessary to find out what is preventing the movement of fluid through the ducts. In newborns, high bilirubin levels are usually treated by pediatricians; they prescribe special substances that activate the production of liver enzymes.
Recommended Diet
Regardless of what reason provoked the increase in total bilirubin, the patient is prescribed a special diet. It reduces the load on the liver and helps reduce pigment production:
- it is necessary to limit salt to 10 g per day;
- Any refined foods, preparations and marinades are removed from the diet;
- a ban is imposed on fatty meat and canned food, as well as smoked products;
- you cannot eat sour fruits and vegetables, baked goods and foods with soda are prohibited;
- Mushrooms, seafood, spices and alcohol are strictly prohibited.
The basis of the diet is lean meats, non-acidic juices and unrefined oils used in the preparation of salads and stewed vegetables. In the morning or for dinner, the patient eats watery porridge. Low-fat fermented milk products help keep the body healthy. You can eat honey and sugar in small quantities, as well as chicken proteins. Sweet fruits, salt-free bread and marmalade can be included in the diet.
Reducing bilirubin with folk remedies
You can combat high levels of total bilirubin in an adult using folk remedies. Their preparation takes a minimum of time:
- Decoctions of mint and chamomile. The products are combined in equal parts, evaporated, and poured with boiling water. After 2 hours you can start taking them 65 ml before meals. You need to take it 3 times a day for 2 weeks, then take a break.
- Boiled beet juice. You can use chopped boiled product without squeezing out the juice. Every day they eat 50-100 g of beets. It cleanses the liver well and reduces bilirubin levels.
- Corn silk. The herb is used to treat the liver and gallbladder. It is brewed according to the instructions and taken 50-100 ml several times a day for 10-12 days.
- Milk thistle. A decoction is prepared from the grass seeds in a water bath, using 40 seeds steamed with 0.4 liters of water. You need to take 1 tbsp after filtering. l. up to 8 times a day. The course of treatment lasts no more than 2 weeks.
- Dog-rose fruit. A decoction is prepared from dried berries. Requires 20-30 g of dry raw materials per 1 glass of boiled water. Boil for 2-3 minutes, filter and take 0.5-1 glass per day before meals.
Other herbs, such as calendula or St. John's wort, can also be used for treatment.
How to achieve a reduction?
How to lower bilirubin in the blood?
How to lower bilirubin in the blood? First of all, it is necessary to find out the reason for its increase.
If the increase in bilirubin is associated with liver disease, then after the disease is eliminated, the bilirubin itself will return to normal.
If bilirubin has increased due to stagnation of bile, you will need to remove the obstruction to the outflow of bile.
If there is a decrease in bilirubin caused by Gilbert's syndrome, phenobarbital and zixorine are prescribed for two weeks.
To reduce bilirubin in newborns, medications are used - inducers, that is, activators of liver enzymes.
What can you do to lower bilirubin levels?
- To lower the level of bilirubin, decoctions of medicinal herbs are used. In pharmacies you can buy a mixture of dried mint, chamomile, motherwort and St. John's wort. A mixture of these herbs is brewed in boiling water, infused and filtered, and then taken before meals in the morning and evening;
- You will need to cleanse your intestines. To relieve constipation and diarrhea, you should take medications prescribed by your doctor. To eliminate the problem of increased gas exchange, you can take activated carbon;
- You should pay attention to a healthy diet. You will need to avoid fatty and fried foods. You will also need to abstain from sweets and starchy foods. It is recommended to bake the dishes in the oven and steam them. You cannot drink alcohol;
- It is necessary to get rid of parasites;
- Try to avoid stressful situations, as stress can have a negative impact on the development of diseases that lead to increased bilirubin levels;
- The patient needs to undergo infusion therapy. Droppers with special medications will cleanse the blood and normalize bilirubin levels.
Video. Increased bilirubin is a sign of liver problems.
What does indirect, direct and general mean?
Focusing on metabolism, several types of bilirubin can be distinguished: direct and indirect. Unconjugated bilirubin (indirect) appears during the breakdown of toxic substances. Able to penetrate cell membranes. The main task is the penetration of bilirubin into the liver, where it is neutralized. Brain cells are susceptible to high bilirubin. The normal component of the indirect indicator is 15.4-17.1 µmol/l.
Direct is considered non-toxic. It begins to form in cells:
- liver;
- spleen.
Takes part in the formation of liver cells. In the absence of the above functions, the level of the total enzyme is determined; it increases with the growth of at least one of the components.
Prognosis and consequences of the disease
In the blood of adults, about 1% of blood cells are destroyed every day. The normal level of total bilirubin in the blood is from 8 to 20 µmol/l. The borderline indicator, which requires additional thorough examination of the body, is considered to be a level from 20 to 27 µmol/l.
Timely consultation with a doctor will help prevent the development of diseases of the liver and biliary system. Hyperbilirubinemia is a disease that does not require treatment at the initial stage, but it can develop rapidly in the complete absence of therapeutic and preventive measures.
The hereditary type of the disease will not allow for a complete recovery, but complications that may arise as a result of increased bilirubin in the blood with another type of pathology can significantly undermine a person’s health. Most diseases that occur against the background of hyperbilirubinemia (liver failure, cholecystitis, cirrhosis, cholelithiasis, hepatitis) require long-term treatment.
Diagnostics
The amount of bilirubin is determined mainly using a blood test. Diagnosis of hyperbilirubinemia is carried out if the patient has yellowing of the sclera and/or skin, as well as in the presence of an underlying disease (acute or chronic hepatitis, hemolysis, cirrhosis or steatosis of the liver, and others). Blood sampling is performed in the morning. Three days before the test, the patient should exclude fatty foods, fried foods, alcohol, coffee, and some medications (Aspirin, choleretic drugs, Heparin, Warfarin) from the diet. Donate blood on an empty stomach.
The presence of bilirubin is determined colorimetrically (by color) using the Van den Berg reaction. For this purpose, Ehrlich's deazoreagent is added to the blood serum. As a result, azobilirubin is formed, which gives the liquid a pink color. The presence of bilirubin in the blood serum is determined by its intensity.
Sometimes a test for bilirubin is performed not in blood, but in urine. Normally there should be no coloring pigment there. When examining urine, a Harrison test is performed, which is based on the use of Fouche's reagent. This method is very accurate and is considered unified. If bilirubin is present in the urine, it turns green or blue when the reagent is added.
Forms of the disease
When the patient does not have any pathologies of internal organs and there are no morphological changes in the liver, then when symptoms of the syndrome occur, benign hyperbilirubinemia (functional) is diagnosed.
No special treatment is prescribed in this situation. Manifestations of jaundice in the benign form of the disease are congenital in nature and have a chronic course. An increase in the level of bilirubin and the associated icteric staining of the sclera or skin can occur as a result of severe mental stress, infection during pregnancy (such jaundice does not pose a threat to the fetus) and after surgery.
Indirect hyperbilirubinemia (unconjugated) occurs with liver cirrhosis, chronic and acute hepatitis. It is established when an increased breakdown of erythrocyte blood cells occurs in the patient’s body, accompanied by increased synthesis of the indirect fraction of bilirubin. Increased hemolysis, which occurs with this form of hyperbilirubinemia, is often observed in newborns with hemolytic disease, with hemolytic disease having a hereditary form.
Increased decay can occur when red blood cells are damaged (due to mechanical stress). The level of indirect bilirubin increases as a result of poisoning with toxic substances and heavy metals and is associated with glucuronidation processes.
Conjugative hyperbilirubinemia indicates an increased concentration of the direct bilirubin fraction. In adults, it is caused by health problems that make it difficult to remove bilirubin from the body (toxic liver damage, blockage of the bile ducts, liver stones, hepatitis, etc.).
Physiological jaundice in young children also manifests itself for these reasons. The enzyme system of the liver of premature infants is immature, so they are more likely than other infants to be susceptible to the pathological process. Jaundice appears a day or two after the baby is born and can last up to a month.
Transient hyperbilirubinemia is recorded in 70% of newborns in the first 2–3 days of life. Increased hemolysis of red blood cells is caused by a weak reduction of bile pigments due to the immaturity of internal organs. The color of feces and urine in newborns does not change; only increased drowsiness may be observed. Signs of the pathological condition persist for no longer than a week. Cases of neonatal jaundice developing into a stable pathology are extremely rare. Treatment is prescribed by a pediatrician.