Almost 75% of all emergency operations in the department of pure surgery are appendectomies. How to make a diagnosis without error? Is a blood test important for appendicitis?
This diagnosis is made very often, in 10% of people throughout their lives. Most often, the risk of getting sick exists in people aged 20 to 25 years. The diagnosis of appendicitis is the most common after acute inflammation of the gallbladder, cholecystitis, which leads to sudden hospitalization. A quarter of all emergency hospitalizations are suspected of acute inflammation of the appendix, and at the same time appendicitis is the first diagnosis in terms of the number of surgical interventions performed for emergency indications.
Clinical picture of biochemical studies in inflammation of internal organs
With appendicitis, discomfort is localized in the lower right part of the abdominal cavity.
But pain in the right side during physical activity is not the main sign of the disease. Most often this is a consequence of muscle spasm or neuralgia. If painful sensations are accompanied by a thickening of the abdomen, which is located below and to the right of the navel, an increase in body temperature, and vomiting, this is a sure sign of a serious intestinal disease. Doctors consider a chemical study of blood composition to be the main indicator of the general condition of the body.
A blood test for appendicitis is the main indicator of the presence or absence of this disease.
The chemical composition of human blood is a constant value. They donate blood for analysis in order to find out the quantitative relationships of its components. If the levels of white and red blood cells are increased, the composition of the plasma has changed, then you need to start treatment without delay.
A mandatory laboratory test for the presence of leukocytes in the blood is prescribed if inflammation of the appendix is suspected. During acute inflammatory processes, the composition of human blood changes due to the ingress of bacterial metabolic products into it. Leukocytes with appendicitis increase in size and number.
They are the main tool of immunity, but at the first stage of inflammation this increase is imperceptible. The state of red blood cells also changes. Their number is not subject to strong fluctuations, but inflammation shortens the lifespan of the red blood cell.
Urine also changes its composition, which correlates with the type of disease. The amount of dead leukocytes and red blood cells in it increases, the alkaline reaction changes, and the most severe cases are accompanied by the appearance of protein. To determine appendicitis using a blood test, it must be taken early in the morning on an empty stomach.
Blood tests for children are highly dependent on the individual condition of each child. The metabolic rate of a child's body is much higher than that of an adult. The leukocyte is actively involved in metabolism. Their amount in the blood of children significantly exceeds the proportions for older people.
The correct indicators for a mature person in relative values of leukocytes are from 4 to 8 units. In children they can reach 17. During pregnancy – 12-18.
If leukocytes exceed 20, then there is a suspicion of peritonitis - a severe form of appendicitis that requires urgent surgical intervention. The decision about the severity of the disease should be made by specialized specialists - a pediatrician and a gastroenterologist.
Other signs of appendicitis:
- Physiological signs. An increase in temperature, painful lumps in the lower abdomen, vomiting, and loose stools are the first external signs. If the disease has progressed, bloody discharge may appear in the stool and urine. In particularly difficult cases, a fistula develops with access to the skin.
- Changes in the composition of urine. The vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms is reflected in all body secretions. The kidneys separate metabolic products, signaling the onset of the disease by the changed chemical composition of the filtrate. If proteins appear in the general urine analysis, the bacterial background is increased, and its color takes on an unhealthy, cloudy appearance, this is a sure sign of internal inflammation.
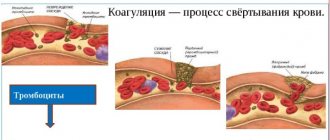
- ESR. An ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) analysis is designed to show what stage the disease is at. The activity of red blood cells varies depending on the state of the body. The inflammatory process provokes red blood cells to increase the consumption of their resources. ESR shows how long these cells live. Expressed in the height of the plasma layer and measured in millimeters per unit of time. In a healthy man it is 1-10 millimeters per hour, in a woman 3-15, in a child 12-17, in a newborn 0-2.
- However, only the results of a comprehensive examination, taking into account the total number of leukocytes and erythrocytes, will help to draw a conclusion about the nature of the disease.
Children are more susceptible to changes in blood composition. This makes it difficult to diagnose appendicitis in a timely manner. A child's blood contains a much larger number of leukocytes. Because of this, in children the disease at an early stage is easy to miss. It is accompanied by a relatively unnoticeable change in laboratory test results or is not diagnosed at all.
Pain syndrome is attributed to physical activity, general malaise to a cold, digestive problems to stress, and so on. If these signs are present, it is necessary to submit samples of discharge for testing for general composition. Sampling should only be done in the absence of stimuli. A comprehensive blood and urine test is designed to help identify the disease at this stage.
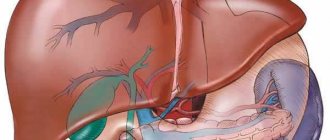
The cecum performs the function of storing enzymes necessary for digestion and immune function. It is isolated from the intestines, and this causes suppuration when the immune system is weakened.
Diagnosis based on a high white blood cell count clearly indicates inflammation. This condition is called leukocytosis. It is necessary to determine whether an acute inflammatory process has begun in cases of suspected appendicitis as quickly as possible! This disease is dangerous with complications.
Strict adherence to the recommendations guarantees complete recovery, and failure to comply will lead the disease to the chronic stage.
The transition to this stage will show that the permissible level of leukocytes is many times exceeded (by 2 or more times). The beginning of tissue breakdown threatens general blood poisoning. The accumulating liquid containing the remains of dead leukocytes in the form of suppuration becomes a source of intoxication.
It can cause severe anaphylactic shock and coma. The proximity of the appendix to the lymph nodes poses a particular danger. Only urgent surgery will save a patient with this form of the disease. Drug treatment cannot help in this case.
People often die from medical errors when treating peritonitis.
At a time when human internal organs remained poorly understood, doctors were not able to localize inflammation. Dissection of corpses was prohibited by medieval religion.
Diseases of the cecum were studied by ancient scientists. Hippocrates wrote about severe intestinal suppuration, but did not know its causes. Cases of cure were rare. The cause of appendicitis was discovered only in the 16th century. The treatment methods offered were wild by modern standards. For example, doctors advised swallowing small lead balls to clear the cecal valve.
Until the beginning of the 20th century, the causative agents of appendicitis were considered to be foreign bodies that had no way out of it, since there is no through passage through the cecum. Popular superstitions still contain advice on prohibiting the consumption of small, difficult-to-digest foods, for example, sunflower cake.
In the 20th century, medicine achieved great development and refuted such misconceptions.
Intestinal diseases are affected by the following reasons:
- Poor nutrition;
- Bad habits such as smoking and alcohol;
- Harmful working conditions associated with toxins;
- Lack of food hygiene.
Once these factors are eliminated, the risk of appendicitis will decrease.
Appendicitis is an inflammatory process in the adnexal part of the cecum. The disease poses a danger not only to human health, but also to human life. Therefore, timely diagnosis is the main measure to prevent possible complications. A blood test for appendicitis helps determine how quickly the inflammatory process is progressing.
Goals of testing
If appendicitis is suspected, there is severe pain in the right side of the abdomen. Discomfort in the peritoneum may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature, loss of consciousness and vomiting. The intensity of symptoms depends on the stage of neglect of the pathological condition. The main complication of inflammation of the appendix is its rupture. In this case, there is a risk of developing peritonitis.
Due to the vagueness of symptoms, appendicitis can be mistaken for other pathologies in the abdominal cavity and genitourinary system. Losing time can cost a person his life. Early diagnosis allows you to take timely measures. Therefore, it is important to study the characteristic features of appendicitis and what tests need to be taken to make a diagnosis.
First of all, palpation and visual examination of the patient is performed. The following tests are also additionally performed:
- Women are required to donate blood for the hCG hormone. This will eliminate the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy.
- Urinalysis helps distinguish appendicitis from urological diseases.
- The leukocyte formula is involved in identifying the source of the inflammatory process in the body. It shows the percentage of white blood cells.
- A test that determines the amount of C-reactive protein allows you to identify the origin of the inflammatory process in the body.
- A complete blood count is performed to identify leukocytes and other blood parameters.
The appendix is located on the right side of the abdominal cavity. Its upper part touches the liver, and the lower part is localized in the pelvis. The focus of pain depends on where the source of inflammation is located.
If pain occurs in women, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of gynecological diseases.
For this purpose, an analysis is done for hCG, an ultrasound of the genital organs is performed, and the regularity of the menstrual cycle is analyzed.
Sometimes appendicitis is confused with urological diseases. Their distinctive feature is burning and discomfort during urination. With appendicitis, the urge to urinate may become more frequent. Other symptoms characteristic of urological diseases do not appear.
One of the most important indicators in diagnosing appendicitis is C-reactive protein. It is a blood plasma substance produced by the liver.
In a healthy person, the level of this indicator does not rise above 10 mg/l. An increase in the amount of protein in the body indicates an inflammatory process in the peritoneum. It is not always concentrated specifically in the appendix.
Leukocytes in the body
Laboratory analysis – for what?
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendix:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- temperature increase;
- attacks of nausea.
Sometimes the symptoms are vague, which is why inflammation of appendicitis is mistaken for other pathologies of the abdominal cavity or diseases of the genitourinary system. A blood test for appendicitis in adults and children is a method that will allow you to make a correct diagnosis in time for latent symptoms or atypical forms of the disease.
A blood test for appendicitis will help make an accurate diagnosis if the symptoms are vague.
In older people, it is more difficult to detect inflammation of appendicitis using a blood test, since their leukocyte levels are slightly elevated. Your doctor will tell you in detail how to determine appendicitis using a blood test.
https://youtu.be/qe75kcAhKEo
Leukocytosis depending on age
If a patient is diagnosed with symptoms characteristic of inflammation of the appendix of the vermiform cecum, a standard blood test records an excess of the norm in the content of leukocytes in the blood, then the previous diagnosis is made: “appendicitis”. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor has the right to prescribe additional studies.
The child has
When deciphering the results of a blood test for leukocytes in a child, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s age. Thus, leukocytes in the blood of a child with appendicitis are two or more times higher than the norm for adults. So, if the content of leukocytes in dm3 of blood of a mature person is 11 * 109, appendicitis can be suspected, then for a five-year-old child it is necessary to exceed the value of 15.5 * 109.
In a teenager
Thus, the upper limit of normal leukocytes in young people under 16 years of age is 13.0 * 109, and in adults over 16 years old it is 9.0 * 109 cells per liter of heme
Each person is individual and his physiological age is not always identical to the calendar age, therefore, in adolescence it is necessary to pay attention to the clinical symptoms of the disease
In pregnant women
You need to know that in case of appendicitis, blood tests will not necessarily detect leukocytosis. The blood cell protection system in old age begins to collapse and may not respond to inflammation of the appendix with leukocytosis. Moreover, clinical symptoms may be erased.
Sources
- https://SostavKrovi.ru/analizy/obshchiy/skolko-lejkocitov-v-krovi-pri-appendicite.html
- https://MyAnaliz.ru/blood/analiz-krovi-pri-appenditsite/
- https://diametod.ru/krov/analiz-krovi-appendicite
- https://GastroTract.ru/appenditsit/analiz-krovi-pri-appenditsite.html
- https://jktguru.ru/diagnostika/analiz-krovi-appendicite
- https://appendicit.net/obshhee/kakie-analizy-nuzhno-sdat-dlya-opredeleniya-appendicita.html
- https://gastrot.ru/kishechnik/analiz-krovi-pri-appenditsite
- https://1diagnos.ru/laboratornye-issledovaniya/analiz-krovi-pri-appenditsite.html
- https://gastritam.net/bolezni/appenditsit/lechenie-2/analiz-krovi.html
Signs of inflammation in a blood test
After a blood test, the doctor pays attention to the content of formed elements in the composition. The number of leukocytes in appendicitis is 18 units.
Leukocytes in appendicitis in a child and an adult, exceeding the normal level by 2 or more times, indicate the stage of tissue breakdown, which is dangerous due to general blood infection. The remains of dead leukocytes in the form of purulent masses become a source of intoxication.
In addition to the level of formed elements, the specialist also pays attention to the percentage of leukocytes. They are divided into 5 types:
- neutrophils;
- lymphocytes;
- eosinophils;
- monocytes;
- basophils.
Neutrophils are divided into band, young and segmented. The predominance of band leukocytes indicates the development of acute appendicitis.
With appendicitis in an adult, the level of not only leukocytes changes. The presence of appendicitis can be determined by markers such as:
- The level of red blood cells - blood cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- CRP (C-reactive protein). The element is synthesized by the liver after the appearance of inflammation in the body. The purpose of the protein is to suppress latent infection.
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). The indicator determines the intensity of the inflammatory process. The faster the red blood cells settle, the more widespread the inflammation. If this indicator increases along with an increase in the proportion of leukocytes in the blood, then this indicates an aggravated inflammatory process.
The normal values for the listed markers depend on the age of the patient. After donating blood for appendicitis, the doctor examines it, guided by the data from the table.
All ways to determine the disease
Appendicitis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the appendix of the cecum. This diagnosis is more often given to women, mostly young. There are 0.2 - 0.4% of deaths per year due to untimely visits, when complications of appendicitis already appear.
Purulent peritonitis is by far the most common complication, when an inflamed appendix with all the pus inside breaks into the free abdominal cavity. To prevent these complications, you need to quickly collect anamnesis and take a blood test to determine the number of white blood cells. First of all, you need to clarify what complaints the patient has.
If appendicitis is suspected, the following complaints are typical:
- Pain in the right side;
- Nausea;
- There may be constipation or diarrhea;
- Weakness, malaise;
- Fever, chills;
- Coated tongue.
In addition to determining symptoms, the patient is examined, the abdomen is palpated and some tests are performed. When palpating the abdomen, the most important sign of appendicitis is the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom.
It is checked as follows: first, press the hand on the sore spot and sharply remove it; if the pain intensifies, then this symptom can be considered positive.
In addition, the disease is determined by other symptoms (Razdolsky, Rovzing, Voskresensky, Sitkovsky), and a detailed blood test is required.
In case of appendicitis, a general blood test is a very significant diagnostic method, since its results can be used to draw a conclusion about the condition of the appendix - whether there is inflammation or not. In adults, it is easier to determine the diagnosis than in children, because the latter cannot show the exact location of pain due to appendicitis.
Many people remember very well how they took a blood test from a finger, and are more afraid of it than others who take it from a vein. Is it possible to establish a diagnosis of acute appendicitis without a blood test? No. Only from a blood test can we draw a conclusion and say for sure that this is acute appendicitis.
This study determines the number, volume of red blood cells, white blood cells, their percentage, platelet count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). In case of appendicitis, attention is mainly paid to blood leukocytes. Leukocytes are blood elements that protect the body from pathogenic bacteria, viruses and microbes. Their norm is 4.0 – 10.0x109/l.
With appendicitis, these indicators can increase to 15.0x109/l and higher. Leukocytes are divided into 5 types:
- Neutrophils.
- Eosinophils.
- Basophils.
- Lymphocytes.
- Monocytes.
The white blood cell count can sometimes increase or decrease, depending on the underlying disease.
An increase in leukocytes is observed in infectious diseases, inflammatory processes in any organ, cancer, operations, bleeding, etc.
A decrease in white blood cells can be found with influenza, rubella, typhoid fever, measles, malaria and AIDS. Since appendicitis is an inflammatory disease, white blood cells are elevated in blood tests.
In case of appendicitis, the patient undergoes a detailed blood test, during which the leukocyte formula is determined. A leukogram is the percentage of all leukocytes. Only neutrophils determine the state of inflammation in the diseased organ.
In medicine, the term “leukocyte shift to the left” is used when a large number of band neutrophils are found in the blood. This indicates that an inflammatory process is developing in the body. There are 3 types of neutrophils: young, band and segmented.
It is during acute appendicitis that band neutrophils increase, and this indicator is used to clarify the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. If segmented neutrophils increase in the blood, this is called a “shift of leukocytes to the right.”
If the diagnosis is made correctly and in a timely manner, then the patient’s treatment goes smoothly, he quickly begins to recover, and various complications of the disease do not arise. In the case of appendicitis, the same rules apply. If the patient consults a doctor on time, and after examination, surgery is performed without delay, then there will be no perforations or peritonitis.
If the patient presents late, the appendix is filled with pus, the patient’s general condition worsens every minute, symptoms of intoxication arise, and this can lead to death. If a person suddenly experiences acute abdominal pain against the background of well-being, this is an alarm signal.
If you experience abdominal pain, especially on the right side, it is recommended:
- Do not use painkillers, antipyretics and antibacterial drugs;
- Urgently contact a medical facility;
- Get examined and take a detailed blood test.
If a patient is suspected of having appendicitis and the test results show elevated white blood cells, after the tests have been carried out, an operation is urgently prescribed - appendectomy, during which the appendix is completely removed.
Loading…
Blood test for appendicitis: interpretation, indicators in adults and children
| Age | Red blood cells | Leukocytes | ESR | S-RB | Neutrophils |
| 6-12 months | 3,4-5,2 | 7-32 | 3-10 mm/h | 0-5 mg/l | 2-7 |
| 2-5 years | 3,7-5 | 5-15,5 | 5-11 | 0-5 | 1-6 |
| 6-14 years | 3,5-5,5 | 4,5-13,5 | 4-12 | 0-5 | 1-5 |
| 15-17 years old | 3-5.5 (girls), 3.9-5.6 (boys) | 4,5-11 | 2-15 (girls), 1-10 (boys) | 0-5 | 1-6 (girls), 1-7 (boys) |
| 18-30 years old | 3-5.5 (women), 4.2-5.6 (men) | 4-10.5 (women), 4.2-9 (men) | 8-15 (women), 2-10 (men) | 0-5 | 1-6 (women), 1-7 (men) |
| 30-60 years | 3.5-5.1 (w), 4-5.6 (m) | 4-10.5 (w), 4.2-9 (m) | 8-20 (w), 2-10 (m) | 0-5 | 1-6 (w), 1-7 (m) |
| 60 years and older | 3.4-5.2 (w), 3.1-5.7 (m) | 3.7-9 (w), 3.9-8.5 (m) | 8-20 (w), 2-15 (m) | 0-5 | 1-6 (w), 1-7 (m) |
If it was found that the number of red blood cells has reached a minimum level, while the content of CRP, leukocytes and neutrophils is increased, as is ESR, then this indicates progressive appendicitis.
Some symptoms of inflammation of the appendix resemble the clinical picture of an ectopic pregnancy, so women are sometimes prescribed a blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone secreted by the placenta during pregnancy).
If the blood test for hCG for appendicitis in adult women does not exceed 0-5.3 mIU/ml, then pregnancy is excluded.
Blood test indicators for appendicitis in children depend on the individual condition of the body. The metabolic rate of a child is much higher than that of an adult. Since leukocytes actively participate in metabolic processes, their content in the blood significantly exceeds the number of these formed elements in the body of an adult.
A blood test for appendicitis in children is not the only diagnostic measure. To confirm inflammation, a urine test is additionally prescribed. This eliminates inflammation of the urinary tract or excrement in the kidneys.
In addition to blood and urine tests, to detect appendicitis the following are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the appendix.
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
- Laparoscopy.
The laparoscopic method is the most informative. Allows you to accurately determine the type of inflammation in the abdominal cavity. If necessary, proceeds to surgery to remove appendicitis.
Diagnostic methods
For inflammation of the appendix, the main diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- primary examination - palpation;
- lab tests:
- blood;
- urine;
- instrumental research:
- computer, magnetic resonance imaging;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- medical thermography;
- laparoscopy;
- radiography.
Diagnostics allows you to detect the disease in a timely manner, prescribe effective treatment, and eliminate the pathology.
Initial examination
The first diagnostic method is an initial examination with palpation of the abdominal area. If the blood supply to the appendix is disrupted, strong, sharp pain is observed when pressing on the iliac region on the right side. In some clinical cases, the doctor may feel the inflamed appendix. The basic rule of palpation is to sharply release the hands after pressing on the abdomen. A description of associated symptomatic signs is an important part of the purpose of additional studies.
Submitting biological material for laboratory testing is important to determine further treatment for appendicitis. The exception is clinical cases when there is a serious complication that requires immediate surgical intervention to avoid the death of the patient. Based on the results of laboratory tests of blood and urine, it is possible to determine the cause of inflammation and eliminate possible problems with urination.
Biological material is collected to carry out the necessary tests:
- general blood and urine analysis if appendicitis is suspected;
- measuring the level of red blood cells, leukocytes;
- establishing the reactive protein indicator;
- determination of hCG level.
Establishing the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes contained in the blood allows us to identify the internal inflammatory process. Urine examination makes it possible to exclude diseases of the urinary system and determine the presence of pathogenic bacteria, infections, and viruses.
Beginning of the acute phase of inflammation
Diagnosis based on a high white blood cell count clearly indicates inflammation. This condition is called leukocytosis. It is necessary to determine whether an acute inflammatory process has begun in cases of suspected appendicitis as quickly as possible! This disease is dangerous with complications. Prompt treatment with modern antibiotics and close clinical supervision can completely stop the disease at this stage. Strict adherence to the recommendations guarantees complete recovery, and failure to comply will lead the disease to the chronic stage.
Treatment regimen
Appendicitis can only be treated surgically. Appendectomy is performed under local or general anesthesia. In case of peritonitis, drains are left in the abdominal cavity to drain the inflammatory exudate and administer antibiotics.
If chronic appendicitis is diagnosed, it is possible to delay the operation to remove the appendix in order to carry out preliminary antibiotic therapy . In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of purulent complications, hormone therapy and plasmapheresis are added.
The sooner the patient seeks help, the lower the risk of complications of the disease and the shorter the postoperative period.
Acute appendicitis is dangerous because it takes the form of many diseases, but requires immediate surgical intervention. Therefore, early contact with a surgeon at the slightest suspicion of this disease will help to avoid many complications.
Source: monrb.ru
Leukocyte formula shift
When assessing blood test results, the doctor examines not only the number of formed elements, but also estimates the proportion of each type of cell. The percentage of leukocytes is called the leukocyte formula, or leukogram.
A microscope is used to count the number of white blood cells. With its help, 100-200 blood cells are counted and their numbers are arranged in a special table. Then the percentage is calculated for each type. This is a leukogram. Under the influence of certain factors, it changes, moving left or right.
A shift in the leukocyte formula to the left is changes associated with an increase in the number of immature (young) neutrophils. This clinical picture indicates a severe degree of intoxication, as well as infectious processes.
A shift of the leukogram to the right occurs with an increase in the number of mature neutrophils, in other words, due to blood aging. Such a change indicates chronic pathologies of internal organs.
No surgery is performed until the results of the blood test are received. After receiving the necessary information, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition and, if the diagnosis is confirmed, prescribes surgery.
Be healthy!
What does leukocyte level mean?
Leukocytes (WBC, white blood cells) are small cells (up to 20 microns) that respond to negative changes occurring in the body. When a threat arises, the bone marrow produces an increased amount of WBC to create a protective barrier against viruses, bacteria and other foreign cells.
It is worth highlighting 2 main types of leukocytes, namely:
- Granulocytes are either band-nuclear or segmented. This type includes eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils.
- Agranulocytes – these include lymphocytes and monocytes.
The level of white blood cells can be determined using a general and detailed blood test (for a complete study of the leukocyte group).
In addition, white blood cells come in 3 levels, namely:
- Normal – set depending on the individual characteristics of the patient (gender, age).
- Increased (leukocytosis) - leads to negative processes that require consultation with a doctor.
- Decreased (leukopenia) – associated with the development of serious diseases.
Prevention of appendicitis
Diseases of the cecum were studied by ancient scientists. Hippocrates wrote about severe intestinal suppuration, but did not know its causes. Cases of cure were rare. The cause of appendicitis was discovered only in the 16th century. The treatment methods offered were wild by modern standards. For example, doctors advised swallowing small lead balls to clear the cecal valve.
Until the beginning of the 20th century, the causative agents of appendicitis were considered to be foreign bodies that had no way out of it, since there is no through passage through the cecum. Popular superstitions still contain advice on prohibiting the consumption of small, difficult-to-digest foods, for example, sunflower cake. In the 20th century, medicine achieved great development and refuted such misconceptions.