Women have long been accustomed to the fact that their well-being, mood and appearance change throughout the entire calendar month, depending on the days of the cycle. If no one is surprised by headaches and lower back pain on the eve of menstruation, then some women of childbearing age are sometimes bothered by frequent urination before menstruation.
Normally, the number of urinations per day should be no more than 10 times , as doctors say. But if there are more of them, then this is not necessarily a pathology. Since it may be due to the individual characteristics of the body of each individual person.
What is the connection between menstruation and the urge to urinate?
Diarrhea, increased frequency of urination, and delayed menstruation are common disorders and are not dangerous in themselves. However, these symptoms sometimes indicate infections and pathologies.
If you are worried about frequent urination before your period, perhaps the reason lies simply in the characteristics of the reproductive cycle. Often the symptom is caused by irritation of the tissues of the bladder or intestines, relaxation and swelling of the vaginal muscles, an imbalance of hormones with an increase or increase in the production of estrogens or androgens.
Even if urination remains frequent and diarrhea persists after your period, this in itself should not be a cause for concern. On the contrary, this behavior of the body indicates the elimination of excess fluid and waste, which are formed due to undigested food residues. As a result, a couple of extra kilos are lost and the swelling that is characteristic of each cycle subsides.
Frequent urination without pain during menstruation, frequent urination during menstruation, causes
Even if, after the end of your monthly discharge, frequent urination or diarrhea continues, there is no serious cause for concern.
In this case, the body’s behavior should be perceived as a positive phenomenon: cleansing of excess fluid, as well as toxins in the intestines formed due to stagnation of food residues.
Thus, without the use of diets and physical activity, you can lose some excess weight, get rid of swelling and fluid retained in the tissues - characteristic signs of any menstrual period.
Of course, diarrhea and the constant desire to urinate are not the most comfortable ways to improve well-being, however, after the end of the critical days, the woman feels relief and renewal of the body. The positive effect persists only if these symptoms stop along with menstruation.
If diarrhea and frequent urination continue after menstruation, you should immediately go to the hospital to diagnose possible diseases, since the previously assumed cause of disorders in some cases turns out to be false and hides the manifestations of serious diseases.
The main reasons why frequent urination without pain appeared before menstruation could be problems such as bladder irritation or bowel irritation.
If your stomach does not hurt, but you often want to go to the toilet a little before your period, then this may be a consequence of increased gas formation, which, in turn, contributes to pressure on the bladder area.
If there is no pain in the lower abdomen, and frequent urge to go to the toilet, frequent urination before menstruation does not give rest, then such symptoms may be due to the fact that the vaginal muscles may swell due to severe relaxation.
Such symptoms appear due to the fact that the level of androgens and estrogens can significantly increase. The problem that often makes you want to go to the toilet before your period can also be caused by a lack of certain hormones.
The reasons for frequent urination before menstruation most often do not carry any hidden painful overtones. But this does not mean that a woman should not pay attention to the fact that she has frequent urination for no reason, without pain, before her period.
A woman also needs to remember that there are a number of different reasons for frequent urination without pain, reasons that provoke frequent urination.
So, if a woman often goes to the toilet a little before menstruation, before her period, then this may be one of the symptoms of PMS (premenstrual syndrome). As you know, for a number of women, this premenstrual syndrome can be very painful.
For some women, PMS is a headache (even a migraine), frequent urge to urinate, pain in the lower abdomen, when the lower abdomen hurts and pulls, chest pain and pain in the nipples, mood swings, drowsiness, increased fatigue and other painful symptoms.
While for others, the symptoms and signs of premenstrual syndrome may consist of mild discomfort in the lower abdomen.
If urination is frequent, but there is no abdominal pain, then these may be the first signs of a disease of the urinary system. Such a problem, with the progression of the inflammatory process and other causes of diseases of the urinary system, can lead to the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen, when the lower abdomen hurts and pulls in the area of the bladder.
Endocrine diseases, some physiological processes, frequent stress and long-term depressive states, all this can lead to the appearance of such a symptom as a very frequent urge to go to the toilet before menstruation. Another reason for these symptoms is pregnancy.
Frequent urination without pain that begins before menstruation (menstruation) may be one of the first signs of pregnancy.
The causes of this problem can be such as the use of drugs, drugs with a pronounced diuretic effect, a consequence of menopause, the consequences of hypothermia, an unbalanced diet.
Among the pathological problems that can lead to frequent urge to go to the toilet and other painful symptoms, there may be such serious diseases as cystitis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, urethritis, overactive bladder, and weakness of the bladder wall.
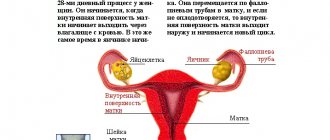
Nowadays, a fairly common problem has become increased frequency of urination in women, in particular in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, during which blood discharge from the vagina occurs.
Going to the restroom may be accompanied by pain in the urinary canal.
At the first manifestation of symptoms such as pain and involuntary urinary retention, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Each body is individual, so it is difficult to define the exact number of trips to the toilet acceptable for an adult.
The frequency of visits to the ladies' room depends on individual characteristics, the amount of liquid drunk during knocking and other factors that directly or indirectly affect trips to the toilet. You can definitely declare the development of pathology if the number of visits to the toilet exceeds 10 times per knock.
Frequent visits to the restroom can be explained if a woman is used to drinking a lot of liquid (especially before bed), takes diuretics or medications for which frequent urination is a side effect.
The reason for frequent visits to the toilet is often the diuretic properties of herbal teas and weight loss products, coffee and coffee drinks, and alcohol. The urge to have a small need can be caused by strong emotions, as well as a natural factor - low air temperature. When freezing, the female body reacts to the cold by urinating more often. This is not considered a pathology.
It is also considered normal for women going through menopause to frequently visit the restroom. This behavior of the body is a reaction to disruptions in the menstrual cycle and significant changes in the usual hormonal background. In case of urination accompanied by painful sensations, it is necessary to seek advice from a specialist.
The need to consult a doctor if the described symptoms appear is clearly necessary. First of all, you should contact a gynecologist. Increased urination before menstruation often indicates a hormonal imbalance that requires urgent treatment. Lack of medical intervention can lead to the development of serious diseases.
Frequent urination can also be a symptom of tumor formations in the bladder, diseases of the uterus, diabetes and neuroses. Most often, urination occurs more times due to cystitis - an inflammatory process in the urinary system.
Unpleasant sensations accompany the patient from the very beginning of the disease during the process and immediately after completion of bowel movement. There may be blood in the urine, causing an unpleasant odor. Possible burning and itching before and during urination. At the same time, the amount of urine is very small, in some cases just a few drops.
At the first symptoms of cystitis, you should consult a doctor for examination and prescribe a course of antibiotic treatment. Without timely treatment, cystitis easily becomes chronic and recurs many times throughout life.
It is very important for women to remember that if you often want to go to the toilet for a little while before menstruation, you should definitely seek help from a doctor if you experience pain and burning during urine output, if you suddenly lose your appetite, if you have severe pain in the lower abdomen , if the lower abdomen aches, then weakly, then strongly, if there is urinary retention, after which incontinence appears.
The appearance of bloody discharge from the genital area before menstruation, which is accompanied by frequent urination, can also be considered dangerous. You should also go to the hospital if you notice changes in the usual course of menstruation: if their abundance has changed, the color of the blood secreted has changed, the duration of the actual bleeding has become shorter or longer, a deterioration in well-being has become noticeable with the onset of critical days, expressed through nausea, weakness, headaches and dizziness .
Also a serious factor is a change in pain, namely, increased pain in the lower abdomen, if before they were insignificant or absent altogether.
You should also consult a doctor if pain during menstruation interferes with a woman’s usual activities and ability to work: if nausea, vomiting or diarrhea occurs, if clots are released with the blood, painkillers cannot cope with the pain.
To prevent painful sensations during menstruation, it is necessary to take warm baths with sea salt added to the water every day (except premenstrual and menstrual periods).
Algomenorrhea is less common in women who take hormonal contraceptives. It must be remembered that taking any medications, in particular hormonal ones, should only be started as prescribed by a doctor, after studying the individual characteristics of your body.
Very dangerous symptoms are when frequent or too frequent urination with pain in the abdomen, when there is strong pulling or aching in the lower abdomen, when there is severe pain in the bladder area.
You should definitely seek help from a doctor if urination is painful, if there is discharge of an unpleasant odor and unhealthy color.
What is normal and what is pathology?
Frequent urination is normal during or after menstruation if a woman:
- drank a lot of fluids at night or takes diuretics;
- drinks a lot of coffee, alcohol (especially beer), herbs or diet pills;
- got overexcited or was in the cold for a long time, which caused hypothermia;
- has reached menopause (hormonal changes occur that cause cycle disruption and other changes in the body).
Painful urination and frequent urges that persist a week after your period ends are reasons to go to the clinic. There may be hormonal disorders, endocrine, gynecological and other pathologies.
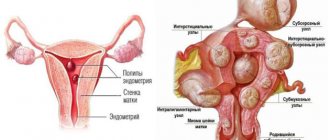
Menstruation only when urinating can also be both normal and abnormal. This is usually the end of menstruation, when the endometrium has almost been renewed, and the remains are released. In other cases, we are talking about an anomaly that can be caused either by pregnancy or by low tone of the uterus or stenosis of its cervix.
Cystitis during menstruation
If measures to prevent inflammation have not been followed, then cystitis during menstruation becomes common. Inflammatory processes occurring in the pelvis provoke the manifestation of cystitis during menstrual periods. If cystitis is chronic, it will constantly return with each cycle. If such a pattern already exists, then it’s time to think about the root cause of this phenomenon.
The most common reasons why cystitis and menstruation occur simultaneously include:
- Severe hypothermia;
- Violation of personal hygiene;
- Existing fungal infections;
- Changes in hormonal levels;
- Physiological characteristics;
- Weakening of the immune system;
Cystitis during menstruation can be caused by inflammatory processes that occur in the appendages and uterus. They progress during critical days, bacteria begin to actively multiply and enter other organs. The effect of cystitis on menstruation occurs in disruption of the cycle itself. There may be a delay and the nature of the discharge may change. Cystitis affects menstruation, increasing pain and its duration.
The chronic form of cystitis often becomes the reason due to which pathogenic microorganisms disrupt the functioning of the pelvic organs, in particular the reproductive organs. Cystitis during menstruation is most dangerous for the ovaries. If menstruation and cystitis occur together more than once, then treatment should be done by two specialists: a urologist and a gynecologist.
Physiology
Menstruation makes many women want to eat salty or sweet foods, and such food increases thirst. As fluid consumption increases, its excretion in the form of urine also increases - this causes frequent urge to go to the toilet. Hormonal changes also occur: estrogen production increases sharply. It is their influence that becomes the main reason for increased urination.
Passion for diets
Weight loss diets sometimes include large amounts of fluids and foods that stimulate urination. For example, mono-diets based on kefir, melons, and watermelons are popular. Cucumbers and cranberries also have a diuretic effect.
When drinking tea, coffee, soda, liquid is retained in the body. This provokes frequent urination. Alcohol also changes fluid balance.
To prevent fluid retention in the body, it is better to minimize the consumption of alcohol and coffee.
PMS
Quite often, the cause of frequent urination a week before your period is PMS. During this period, the female body begins to prepare for pregnancy, so changes occur in it. PMS manifests itself in different ways - it depends on the psyche and the endocrine system.
Usually, along with more frequent trips to the toilet, the following appear:
- changes in mood and well-being;
- thickening of the mammary glands;
- headache;
- swelling of the face, arms and legs;
- high blood pressure.
Urine with blood in women: possible causes
Hematuria is a pathology in which the physiological norm of blood in the urine is disrupted. In most cases, such symptoms signal the development of serious diseases affecting the genitourinary system. What can cause blood when urinating in women?
Possible reasons
According to medical statistics, approximately 60% of cases of blood appearing in the urine are due to urological pathology of the kidneys, urinary tract or bladder.
The causes of another 40% of hematuria are blood diseases and gynecological diseases.
Common reasons include:
- urethritis;
- cystitis;
- long-term use of anticoagulants;
- kidney injuries;
- endometriosis;
- polyps or tumors in the urinary tract;
- genitourinary infections;
- stones in the kidneys;
- urethral injuries.
In rare cases, panic may be premature if the causes of dark urine are side effects of certain medications or the result of eating colored foods. Also, blood in the urine may be mild. There are no visible color changes; with microhematuria, pathology can only be detected during laboratory tests.
Blood appears in the urine after severe mechanical injuries to the abdominal cavity, in which the kidneys or bladder were affected.
Such a symptom cannot be ignored: it is possible that the injury could cause abdominal bleeding, after which the patient needs urgent medical attention.
A few days before your period or during the first days after it, menstrual blood may be detected in the urine. Therefore, if hematuria is suspected, the duration of the cycle must be taken into account.
If other alarming symptoms (pain or pain when urinating) are not observed, you can “wait” and monitor the condition. In addition, a small amount of blood may be observed when the cycle fails.
Features of diseases
The most likely cause of blood when urinating in women is cystitis: acute or chronic inflammation of the bladder. It is accompanied by a false urge to go to the toilet, and during the process itself pain and burning occur.
Cystitis can be provoked by almost any reason, from hypothermia and inflammatory processes to insufficient adherence to personal hygiene rules. If you try to treat this disease on your own, if you choose the wrong medication, the acute form can become chronic. A urine test for cystitis is mandatory, even if blood does not seem to be visible.
Urethritis is a consequence of inflammation of the walls of the urethra. Associated symptoms are sharp pain when going to the toilet, obvious blood in the urine and mucopurulent discharge from the urethra. Possible causes of inflammation are injuries after medical procedures, narrowing of the urethra or urolithiasis.
Endometriosis is a secondary pathology that in most cases affects the urinary tract. As the disease progresses, a formation similar to a tumor appears in the walls of the bladder; morphologically it resembles endometrial tissue - cells that are excreted from the body during menstruation.
If blood clots appear in the urine, this may indicate a malignant tumor in the urinary tract. Women who are approaching menopause should pay particular attention to such symptoms.
Hematuria during pregnancy
Blood in the urine during pregnancy is of particular concern. If your urine darkens, you should immediately consult a doctor and get tested. The presence of blood can only be confirmed by analysis; the color change can be caused by other reasons, many of which are absolutely harmless.
The causes of hematuria can be chronic or acquired diseases. But in some cases, the pathology is physiological in nature and does not pose a danger. Thus, blood in the urine during pregnancy is often caused by the pressure that the enlarged uterus puts on the bladder.
https://youtu.be/cpGhXIAEiUI
In the later stages, intra-abdominal pressure increases significantly, which leads to rupture of blood vessels in the bladder. Hormones are also important: due to such changes, “unreasonable” hematuria may occur. After childbirth, the pathology goes away without medical intervention.
As a rule, “causeless” hematuria is not accompanied by pain.
During pregnancy, it is important to listen to the state of your body to help the doctor make the correct diagnosis during the examination. The sooner the disease is noticed, the easier it will be to get rid of it.
Necessary diagnostics
After any of the alarming symptoms occur, you should immediately contact a therapist, urologist or gynecologist.
The patient will have to undergo a series of studies, which include:
- collection of complaints;
- gynecological examination;
- urine cytology;
- general urine analysis;
- microscopy and culture;
- intravenous urography;
- Ultrasound;
- computed tomography;
- cystoscopy.
The presence of blood must be confirmed by microscopic examination of urine. To exclude the possibility of infection, a culture is performed - a bacteriological study; cytology evaluates the cells found in the liquid.
When taking tests, it is important to carefully follow all the rules for collecting urine. So, the container for urine must be sterile: you can purchase a suitable container at the pharmacy. Before collection, you must wash yourself thoroughly and insert a tampon into the vagina to eliminate the possibility of excess discharge.
Only the first morning urine is suitable for analysis. The container with the material is hermetically sealed, and it is advisable to deliver it to the laboratory within an hour and a half after collection.
Treatment
Hematuria itself is not a disease - it is just a symptom, so it is necessary to fight the root cause of the pathology. Therapy is selected individually, based on examination data, tests and other studies.
So, for cystitis, antibiotics are needed (Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime, Norfloxacin), in parallel with which there is anti-inflammatory therapy (Nimesil or Paracetamol).
If it is necessary to improve the flow of urine, diuretics (Furosemide) or antispasmodics (Drotaverine) are used.
You should take such medications only on the recommendation of a doctor, without interrupting the course even if there are obvious improvements and the disappearance of all unpleasant symptoms.
A similar treatment regimen is used for urethritis, with the additional use of antiseptics for rinsing the urethra. In case of urolithiasis or tumors, surgical intervention may be required, which is performed in a hospital setting.
To prevent such pathologies, it is necessary to take care of your health, avoid hypothermia and injuries, and carefully observe intimate hygiene. Even if nothing bothers the body, it is worth visiting a urologist and gynecologist at least once every six months to assess the current state of health of the genitourinary area.
With timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, the cause of hematuria can be eliminated in a short time and without consequences. Preventive examinations even help prevent the disease by destroying its cause at the earliest stage.
Source: https://vseprivivki.com/zabolevaniya/mocha-s-krovyu-u-zhenshhin-vozmozhnye-prichiny
Gynecological pathology
Frequent urge to urinate is an alarming signal indicating gynecological diseases. The following features are added:
- pain when urinating before the onset of menstruation;
- dryness, burning in the genital tract;
- non-menstrual vaginal discharge;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
With gynecological diseases, urination becomes more frequent not only before menstruation, but also at other times. Your temperature may rise.
Diagnostics
To dispel all doubts regarding the causes of frequent urination, the results of a clinical and gynecological examination should be confirmed by additional methods. This will allow us to make a final conclusion about the presence or absence of pathological changes in the woman’s body. Depending on the situation, the following diagnostic tools are used:
- Blood tests (general, biochemical, carbohydrate tolerance test).
- Urine tests (general, according to Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky, for sugar, for microbial flora).
- Bacteriological analysis of vaginal discharge.
- Ultrasonography.
- Colposcopy.
In most cases, these studies are sufficient to make a diagnosis or exclude the described pathology. Thus, it is necessary to consider frequent urination as one of the symptoms, which may not have any connection with the menstrual cycle. But in the absence of other factors, a conclusion should be made about the physiological nature of this phenomenon.
Frequent urination in women is a fairly common phenomenon that more than 40 percent of all women experience in their lifetime. This problem can have a different etymology, ranging from a minor inflammatory process to anatomical changes in the walls of the uterus, vagina, bladder and intestines. The problem described is quite delicate, however, if you do not pay due attention to the phenomenon, the situation can worsen and lead to permanent consequences.
Endocrine disorders
The reasons for frequent urination before menstruation are sometimes caused by pathologies of the endocrine system. Diabetes mellitus must be excluded. Its symptoms:
- dry mouth;
- strong thirst;
- excretion of a large volume of urine;
- weight loss or weight gain.
In diabetes mellitus, the danger is high levels of glucose in the blood, which negatively affects many systems of the body. Against this background, angio- and neuropathies develop, and the risk of purulent infections increases. Possible diabetic foot.
Diseases of the urinary system
Frequent urge and menstrual cramps sometimes indicate an infection in the urethra. Possible cystitis, urethritis or pyelonephritis. The following symptoms are added:
- change in the amount of urine excreted;
- pain in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- heat;
- urine is cloudy and bloody.
If you experience pain when urinating during your period, it is especially important to go to the doctor and get treatment. Otherwise the disease will become chronic.
Effective methods and rules of treatment
Doctors develop a treatment regimen depending on the cause of discomfort during urination. Self-medication provokes a chronic course of the pathology; the use of inappropriate antibiotics leads to bacterial resistance to the effects of drugs. It is important to strictly follow the recommendations of specialists, take a more careful approach to hygiene procedures, and abstain from sexual intercourse during treatment.
Medications
Main groups of medicines:
- antibiotics. For inflammation of the kidneys and bladder, Monural, Palin, Nolitsin, Nevigramon, Nitroxoline are prescribed. For each patient, the doctor selects the most effective medicine. To determine the appropriate remedy, bacterial culture of urine and vaginal contents is prescribed. Based on the results of an antibiotic sensitivity test, the doctor selects a medicine whose components destroy harmful microorganisms. The best option is the bactericidal rather than bacteriostatic effect of the drugs;
- general strengthening compounds to support the immune system, vitamin and mineral complexes, echinacea tincture;
- antispasmodics. The drugs reduce pain when urinating and relieve spasms of smooth muscles. No-shpa, Baralgin, Drotaverin, Riabal;
- drugs from the NSAID group with active anti-inflammatory effects. Ibuprofen, Nimesil, Movalis, Diclofenac. Medicines also reduce pain;
- compositions for improving the outflow of urine, stopping the inflammatory process in the bladder and kidneys. Effective names: Cyston, Urolesan, Nephrosten, Uronephron, renal collection. The best option is formulations with a complex of plant extracts;
- antifungal agents for candidiasis (thrush). Local (ointments, suspensions, suppositories) and systemic drugs (tablets) are recommended. Effective medications: Pimafucin, Nystatin, Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Zalain, Polygynax, Micogal, Candibene, Livarol and others. The drugs are selected by the gynecologist on an individual basis;
- potent compounds for the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases. The optimal type of drug is selected by a venereologist, taking into account the identified pathogen.
Folk remedies and recipes
Proven formulations based on fruits, medicinal herbs and roots are used only as prescribed by a urologist. During treatment, it is recommended to drink plenty of warm fluids to flush out the infection from the urinary tract. When selecting traditional medicines, it is important to take into account contraindications. Important: not all herbal decoctions and berries are allowed for pregnant women.
Proven means:
- cranberry juice;
- medicinal tea is half gone;
- decoction of rosehip, bearberry;
- douching with a decoction of chamomile, sage, oak bark, calendula.
When to see a doctor?
In itself, frequent urination during menstruation is not a pathology and can be caused by physiology. A woman should be concerned about a significant deterioration in her health during menstruation - severe pain in the abdomen and back, nausea, dizziness.
The presence of pathology is also indicated by:
- change in the color of menstrual fluid;
- too much discharge or lack thereof;
- change in the duration of menstruation;
- pain with every urination during menstruation, as well as before and after it.
Such signs may indicate a gynecological disease, metabolic-endocrine pathologies, or problems of the urinary system. Only a medical examination will allow you to establish the correct diagnosis and carry out effective treatment.
Possible causes of burning and stinging
Experts identify a number of factors that can provoke the appearance of pain during bladder emptying:
- Genital infectious diseases. Accompanied by burning, itching and painful urination. Symptoms appear against the background of an STD after urine enters the vagina. The mucous membrane is irritated, resulting in pain.
- Gynecological pathologies. They develop due to hormonal disorders, allergies, weak immunity and digestive disorders, diabetes, and mucosal damage. They occur as inflammatory processes in the vagina. There is often a desire to urinate, dysuria is characterized by pain, burning, redness, a strong odor and pus in the urine, and hyperthermia.
- Pregnancy and childbirth. Incorrect catheterization after childbirth can lead to pain when urinating. However, the condition should return to normal after a few days. During a caesarean section, discomfort is most likely caused by inflammation. In this case, the urine becomes cloudy, there is an unpleasant odor, back pain and fever.
Chlamydia
This is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacteria chlamydia. Transmitted through unprotected sexual contact.
Chlamydia may not make itself felt for a long time. The only obvious symptoms are:
- itching and burning;
- stomach ache;
- pain when urinating.
The surest way to find out about the disease is to regularly check with a gynecologist.
Gonorrhea
Another disease that is sexually transmitted. The causative agent is the harmful bacterium gonococcus. The infection affects the urinary system, vagina, and uterus.
- frequent urge to urinate, even to the point of incontinence;
- pain at the end of urination or when trying to pass a little;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- the presence of pus impurities in urine;
- redness, swelling, irritation of the genitals;
- dryness in the vagina.
Urolithiasis disease
The disease occurs when stones and sand form in the bladder, ureter or kidneys. When moving, these stones injure the mucous membranes of organs, which causes inflammation.
- sharp and cutting pain in the lower abdomen;
- burning and itching in the vagina;
- constant desire to relieve need;
- incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- swelling of the genitals.
In addition, mucus, blood and small stones (dense rocky formations) are observed in the urine.
Urethritis
The disease consists of inflammation of the urethral canal. The pathological process is caused by microorganisms that can cause infection, including during sexual intercourse.
Symptoms of urethritis are as follows:
- sharp pain at the final stage of urination;
- blood, mucus and pus in urine (in advanced cases);
- dysuria (impaired urinary function);
- general malaise.